Trade-Offs of Plant Biomass by Precipitation Regulation Across the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
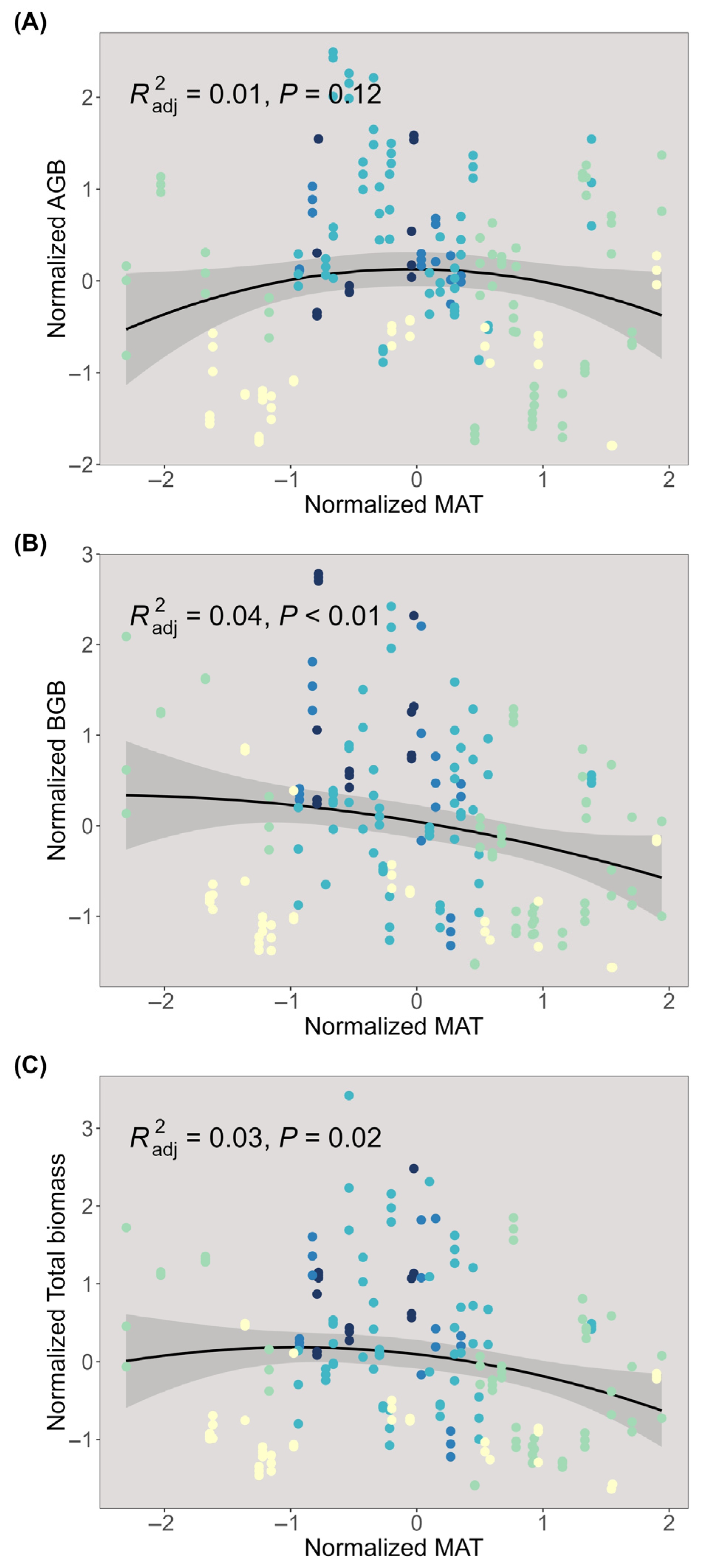
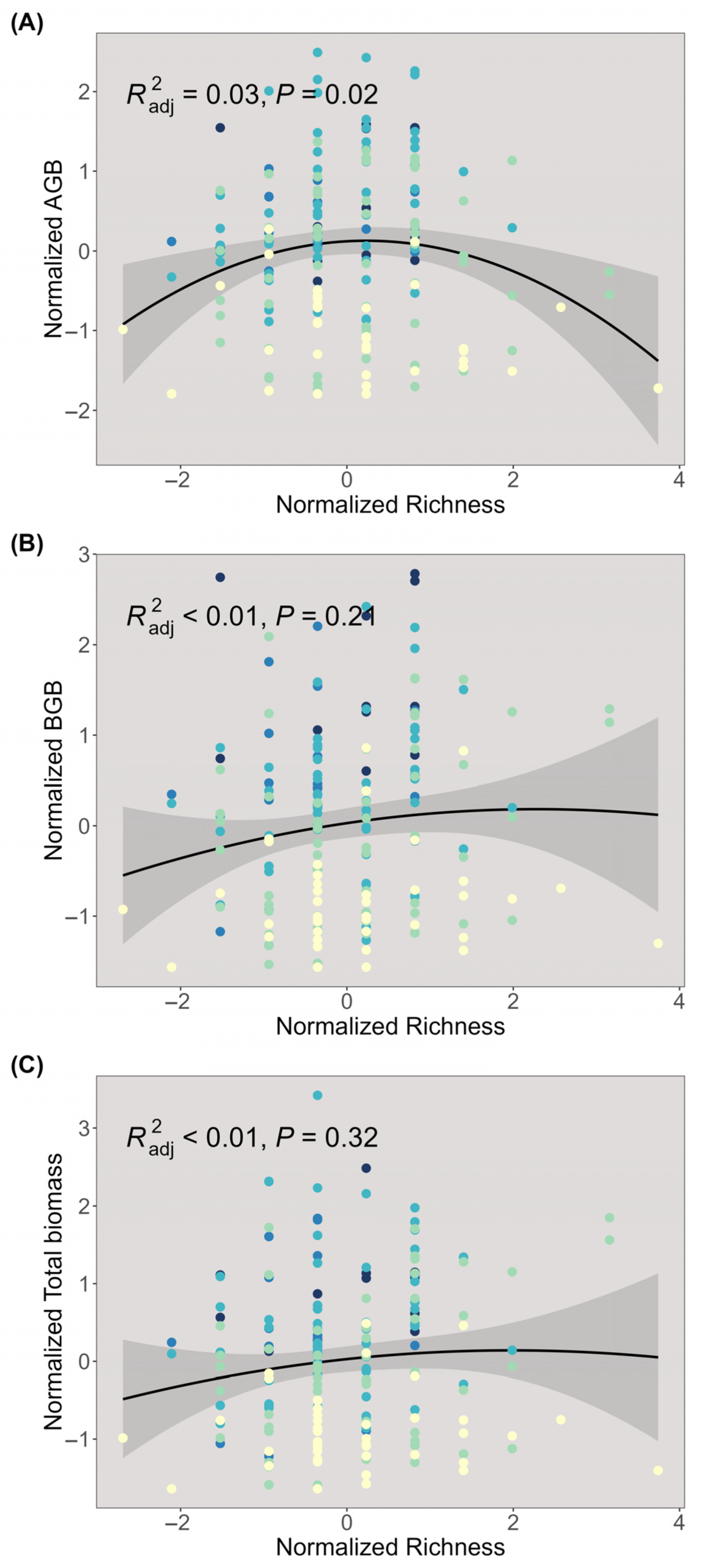
2.1. Distributions of Plant Biomass
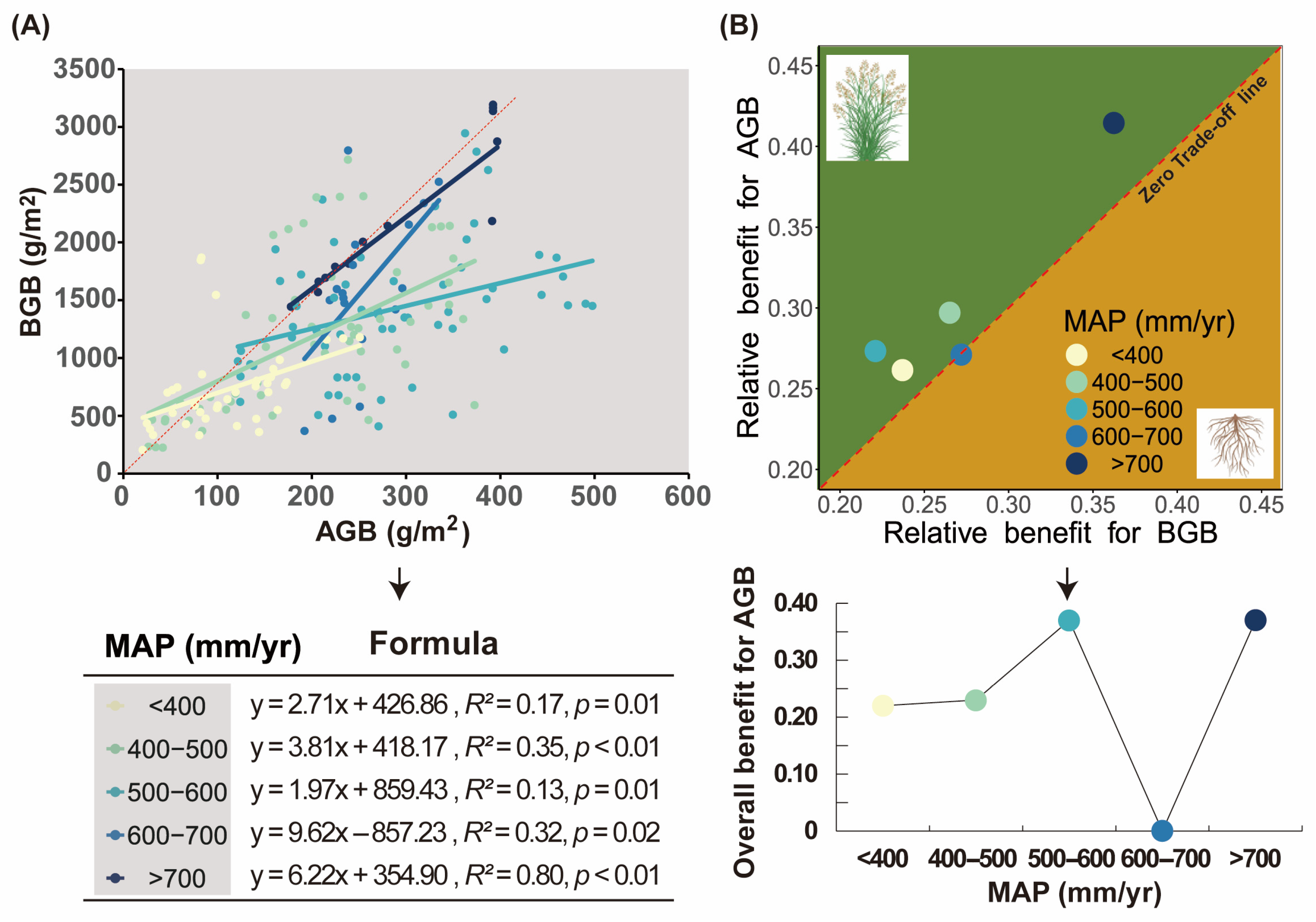
2.2. Trade-Off Between Above- and Belowground Biomass
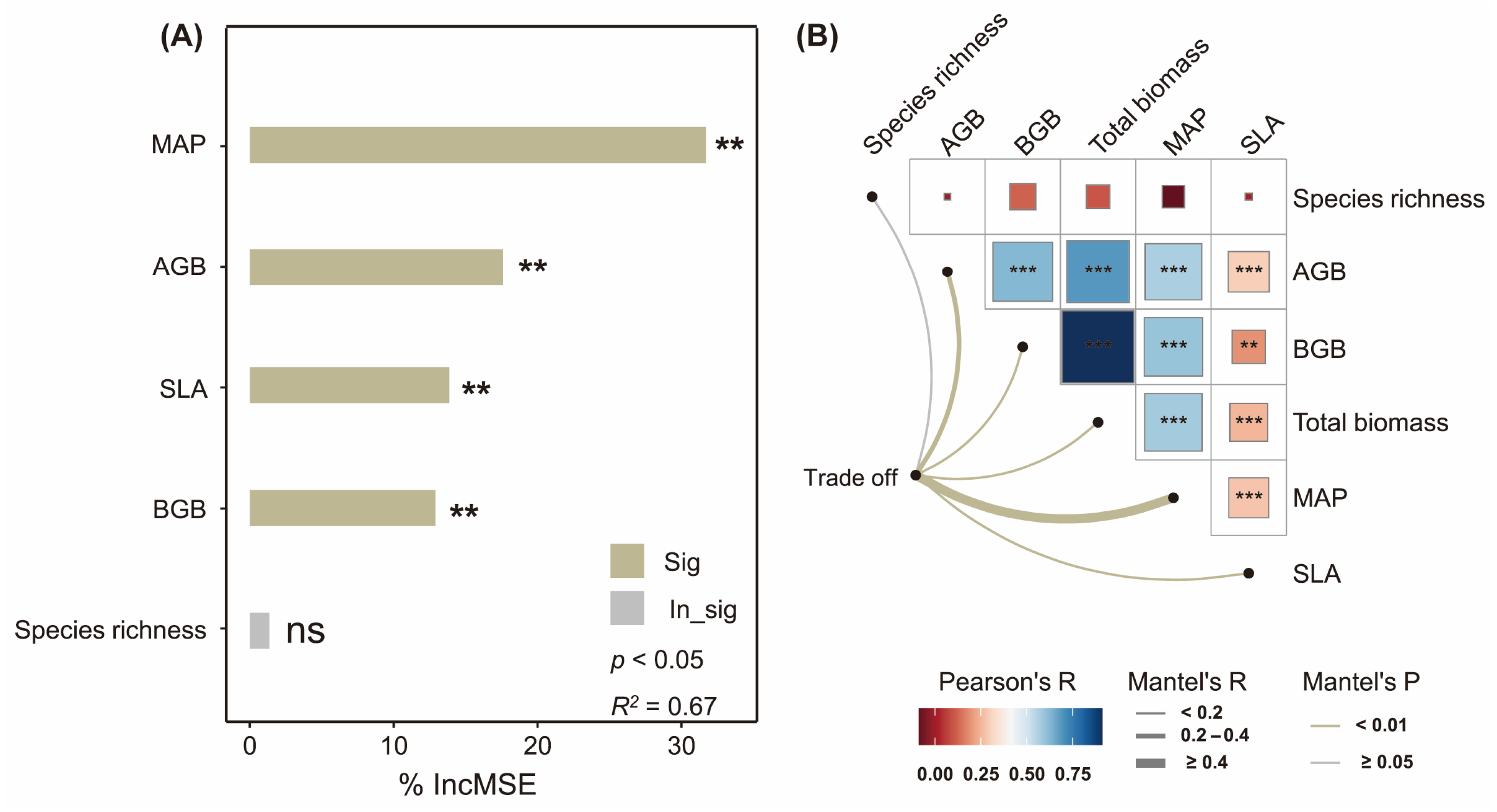
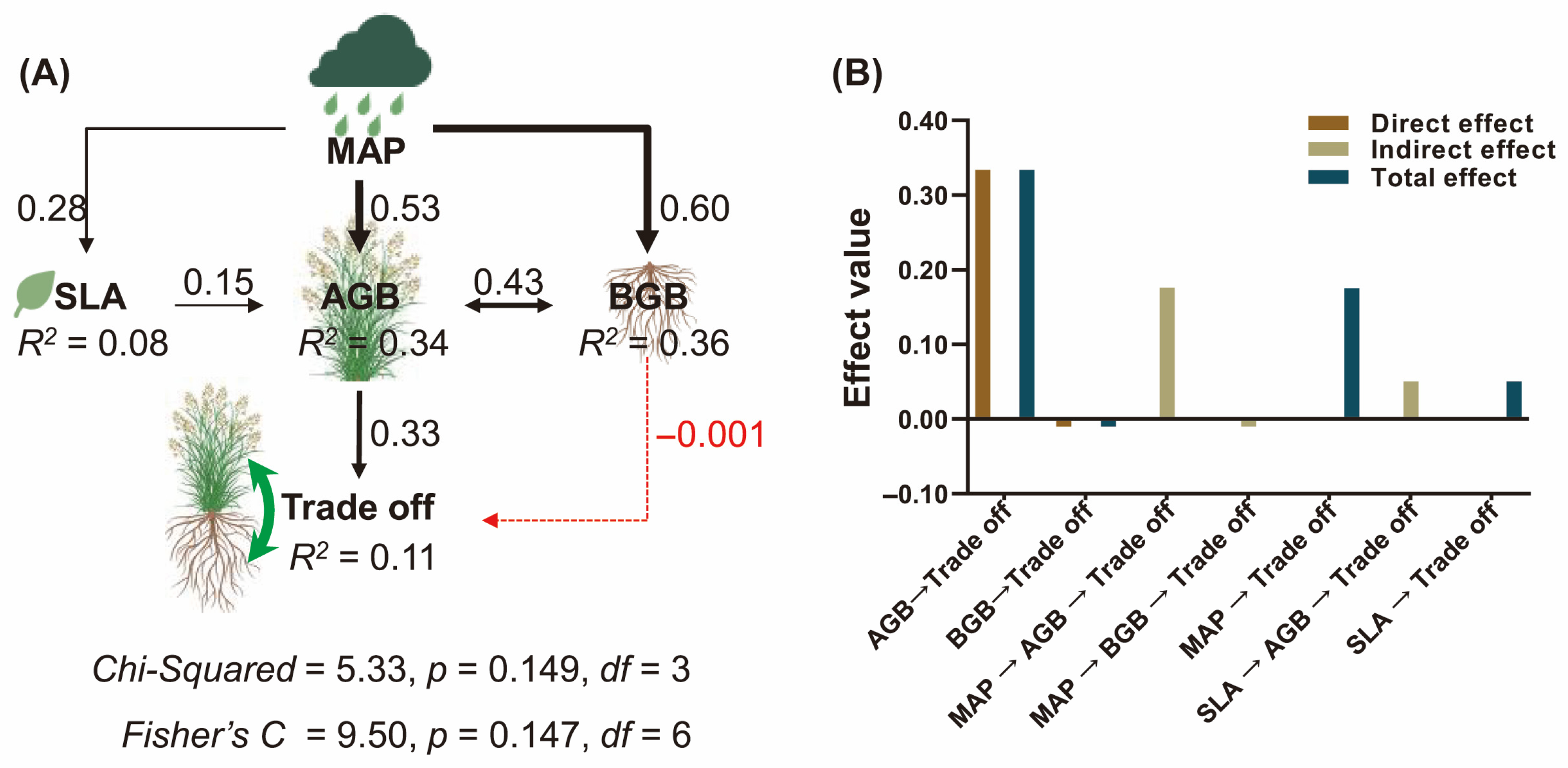
2.3. Influencing Factors of Biomass Trade-Off
3. Discussion
3.1. The Effects of Climate and Plant Characteristics on Above- and Belowground Biomass
3.2. Precipitation-Driven Aboveground Biomass Dominance Mediates Alpine Grassland Allocation Trade-Offs
3.3. Uncertainties in Plant AGB–BGB Trade-Offs
4. Materials and Methods
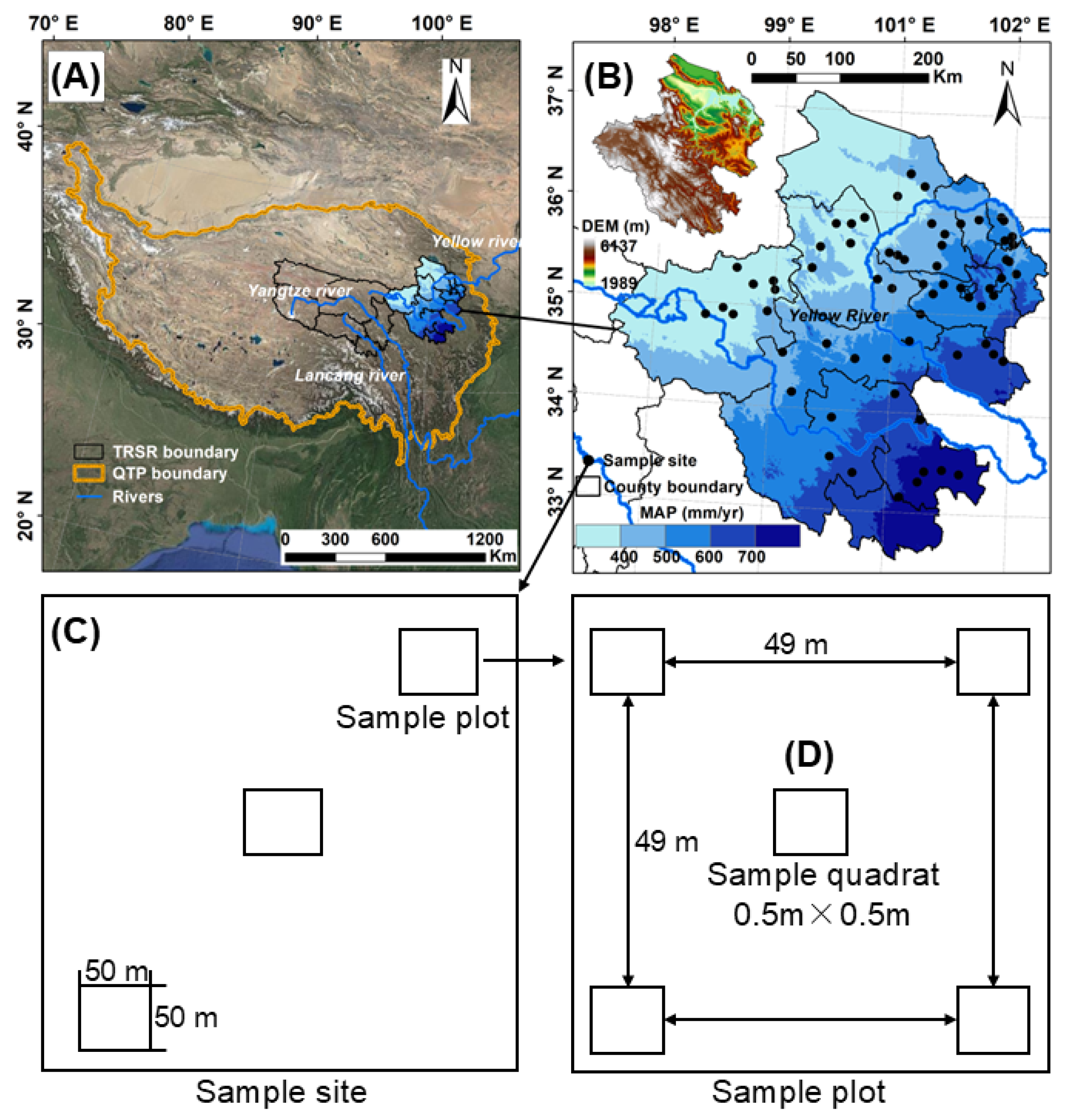
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Climate Data Processing
4.3. Plant Sampling
4.4. Data Calculation
4.4.1. Statistic Analysis of Plant Biomass
4.4.2. Calculation of the Biomass Trade-Off
- xi = observed AGB (g/m2) or BGB (g/m2) in the i-th sampling quadrat;
- xmin and xmax = minimum and maximum observed values of AGB or BGB (g/m2) across all quadrats, respectively.
- is the expected biomass benefit (mean of all AGB or BGB measurements);
- n = total number of quadrats.
- Positive values (RBAGB/RBBGB > 1): AGB allocation dominance;
- Negative values (RBAGB/RBBGB < 1): BGB prioritization;
- Values approaching zero: Balanced allocation.
4.4.3. Mantel Test, Random Forest Analysis, and Structural Equation Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Cheng, D.; Niklas, K.J. Above- and Below-ground Biomass Relationships Across 1534 Forested Communities. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Niu, S.L.; Wang, J.N. Divergent biomass partitioning to aboveground and belowground across forests in China. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 11, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Isometric biomass partitioning pattern in forest ecosystems: Evidence from temporal observations during stand development. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, B.; Meziane, D. The balanced-growth hypothesis and the allometry of leaf and root biomass allocation. Funct. Ecol. 2002, 16, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa-Fuentes, L.L.; Campo, J.; Parra-Tabla, V. Plant Biomass Allocation across a Precipitation Gradient: An Approach to Seasonally Dry Tropical Forest at Yucatán, Mexico. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, A.J.; Chapin, F.S.; Mooney, H.A. Resource limitation in plants-an economic analogy. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1985, 16, 363–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enquist, B.J.; Niklas, K.J. Global allocation rules for patterns of biomass partitioning in seed plants. Science 2002, 295, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Ji, C.; Han, W. Above- and belowground biomass allocation in Tibetan grasslands. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 20, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, B.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, Q. Plant biomass partitioning in alpine meadows under different herbivores as influenced by soil bulk density and available nutrients. Catena 2024, 240, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H. Soil nitrogen and carbon determine the trade-off of the above- and below-ground biomass across alpine grasslands, Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sun, R.; Zhao, G.; Zheng, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Climate shifts biomass allocation by altering plant functional group in alpine vs. temperate grasslands on both Inner Mongolian and Tibetan plateaus. Catena 2024, 238, 107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Dong, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhi, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Resilience of revegetated grassland for restoring severely degraded alpine meadows is driven by plant and soil quality along recovery time: A case study from the Three-river Headwater Area of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 279, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Gao, X.; Qian, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Dai, L. Relationship between Biomass and Biodiversity of Degraded Grassland in the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Diversity 2022, 14, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, J.S.; Li, S.C.; Zhang, B.H.; Zu, J.X.; Zhang, H.M.; Ding, M.J.; Paudel, B. Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.B.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Gang, C.C.; An, R.; Li, J.L. Vegetation dynamics and its driving forces from climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region, China from 1982 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.Q.; Yang, L.C.; Xiong, F.; Li, C.B.; Li, F.; Zhou, G.Y. Aboveground biomass of the alpine shrub ecosystems in Three-River Source Region of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Shen, Q.Y.; Fan, W.D.; Dong, S.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.D.; Ma, T.X.; Cao, Y. Nature-Based Solutions vs. Human-Induced Approaches for Alpine Grassland Ecosystem: “Climate-Help” Overwhelms “Human Act” to Promote Ecological Restoration in the Three-River-Source Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.L.; Tian, Y.C.; Yin, K.; Huang, H.P.; Li, L.P.; Chen, Q. Research on Forage-Livestock Balance in the Three-River-Source Region Based on Improved CASA Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zheng, G.D.; Liang, T. The impact of land use and land cover changes on the landscape pattern and ecosystem service value in Sanjiangyuan region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Li, M.; Fiedler, S.; Ma, W.L.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, X.Z.; Tietjen, B. Impacts of grazing exclusion on productivity partitioning along regional plant diversity and climatic gradients in Tibetan alpine grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, T.X.; Li, R.C.; Tang, Y.H.; Du, M.Y. Causes for the unimodal pattern of biomass and productivity in alpine grasslands along a large altitudinal gradient in semi-arid regions. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Hu, Z.M.; Li, S.G.; Li, X.R.; Sun, X.M.; Yu, G.R. Spatial variations in aboveground net primary productivity along a climate gradient in Eurasian temperate grassland: Effects of mean annual precipitation and its seasonal distribution. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Shen, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Yan, R.; Yan, Y.; Xin, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, M.; et al. Spatial patterns and driving factors of aboveground and belowground biomass over the eastern Eurasian steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Arunachalam, K.; Arunachalam, A.; Alatalo, J.; Pandey, R. Associations of plant functional diversity with carbon accumulation in a temperate forest ecosystem in the Indian Himalayas. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, W.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Elevational variation and driving factors of leaf functional traits in alpine shrubs of Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 59, e03555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Gao, J. Climate factors dominate the elevational variation in grassland plant resource utilization strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1430027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tu, D.; Duan, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Suonan, C.; Ying, J.; et al. Dominant plant functional groups regulate soil respiration response to warming in three types of alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Process. 2025, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, K.R.; Shi, Z.; Gherardi, L.A.; Lemoine, N.P.; Koerner, S.E.; Hoover, D.L.; Bork, E.; Byrne, K.M.; Cahill Jr, J.; Collins, S.L.; et al. Asymmetric responses of primary productivity to precipitation extremes: A synthesis of grassland precipitation manipulation experiments. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4376–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wuda, E.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Xie, L.; Luo, L.; et al. The above- and below-ground biomass of alpine meadow on eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and their relationships with abiotic and biotic factors. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 48, e02701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Song, Z.B.; Cong, P.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, X.B.; Song, W.J.; Yue, P.; Wang, S.K.; Zuo, X.A. Precipitation-induced biomass enhancement and differential allocation in Inner Mongolia’s herbaceous and shrub communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Graciano, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.; Hughes, A.C.; Ahmed, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, S.; Gao, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Plant root mechanisms and their effects on carbon and nutrient accumulation in desert ecosystems under changes in land use and climate. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, C.; He, Y.; Shao, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; et al. Responses of biomass allocation to multi-factor global change: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Lin, L.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, G. Response of the plant community and soil water status to alpine Kobresia meadow degradation gradients on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecol. Res. 2015, 30, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Song, B.; Quan, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Niu, S. Light Competition and Biodiversity Loss Cause Saturation Response of Aboveground Net Primary Productivity to Nitrogen Enrichment. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2020, 125, e2019JG005556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Kèorner, C. Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.Q.; Su, Z.X.; Shangguan, Z.P. Trade-off analyses of plant biomass and soil moisture relations on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 197, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Li, S.; Lai, Z.Q. Effects of extreme precipitation intensity and duration on the runoff and nutrient yields. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, M.S.; Schneider, R.L.; Sullivan, P.J.; Walter, M.T. Drought and post-drought rain effect on stream phosphorus and other nutrient losses in the Northeastern USA. J. Hydrol. -Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.Y.; Ding, J.Y.; Zhan, T.Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Pereira, P. Plant biomass allocation is mediated by precipitation use efficiency in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitsuyama, Y. Morphological root responses of soybean to rhizosphere hypoxia reflect waterlogging tolerance. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 95, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.Q.; Gao, J.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Xu, X.L.; Deng, Z.H.; Yu, F.H. Effects of waterlogging on carbon assimilate partitioning in the Zoige alpine wetlands revealed by 13CO2 pulse labeling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, U.N.; Ball, B.A. Impacts of altered precipitation regimes on soil communities and biogeochemistry in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, A.P.; Huntingford, C.; Fu, B.J.; Li, L.Z.X.; Huang, J.P.; Sheffield, J.; Berg, A.M.; Keenan, T.F.; et al. Multifaceted characteristics of dryland aridity changes in a warming world. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eziz, A.; Yan, Z.; Tian, D.; Han, W.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. Drought effect on plant biomass allocation: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 11002–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Di, N.; Xi, B.; Yang, J.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; Feng, J.; Choat, B.; Tissue, D. Herb hydraulics: Variation and correlation for traits governing drought tolerance and efficiency of water transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M.; Ackerly, D.D.; Baruch, Z.; Bongers, F.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Chapin, T.; Cornelissen, J.H.; Diemer, M.; et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 2004, 428, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, K.L.; Hu, S.J. Distinct fine-root responses to precipitation changes in herbaceous and woody plants: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, A.; Pancotto, V.; Mastrantonio, L.; Giordano, C.V. Fine roots of Prosopis flexuosa trees in the field. Plant and soil variables that control their growth and depth distribution. Plant Ecol. 2018, 219, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.E.; Liu, T.X.; Hao, L.A.; He, C.; Duan, L.M.; Wu, R.; Wang, G.L.; Singh, V.P. Variation in water use patterns of three typical plants in a dune-meadow cascade ecosystem of the Horqin Sandy Land: Implications from stable isotope compositions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Nie, Y.Y.; Bai, S.H.; Zhou, L.Y.; Shao, J.J.; Cheng, W.S.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, F.Q.; Fu, Y.L. Drought-induced changes in root biomass largely result from altered root morphological traits: Evidence from a synthesis of global field trials. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Hiltbrunner, E. Why Is the Alpine Flora Comparatively Robust against Climatic Warming? Diversity 2021, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, P.; Song, J.X.; Fu, B.J. Interannual precipitation variability dominates the growth of alpine grassland above-ground biomass at high elevations on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, J.L.; Williams, J.W.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Jackson, S.T.; Ferrier, S. Space can substitute for time in predicting climate-change effects on biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9374–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.M.; Bajgain, R.; Starks, P.; Steiner, J.; Doughty, R.B.; Chang, Q. Estimating leaf area index and aboveground biomass of grazing pastures using Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat images. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Mo, L.; Crowther, T.W.; Maynard, D.S.; van den Hoogen, J.; Stocker, B.D.; Terrer, C.; Zohner, C.M. The global distribution and environmental drivers of aboveground versus belowground plant biomass. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, J.; Chondol, T.; Chlumská, Z.; Altman, J.; Capková, K.; Dvorsky, M.; Fibich, P.; Korznikov, K.A.; Ruka, A.T.; Kopecky, M.; et al. Contrasting biomass allocations explain adaptations to cold and drought in the world’s highest-growing angiosperms. Ann. Bot. 2024, 134, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Qin, J.; Hu, Y.H.; Guo, C.B. Asymmetric growth of belowground and aboveground tree organs and their architectural relationships: A review. Can. J. For. Res. 2023, 53, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Field, C.B.; Berry, J.A. Allometric growth and allocation in forests: A perspective from FLUXNET. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, X.; Xia, J. Runoff variation and its response to climate change in the Three Rivers Source Region. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Li, G.; Yin, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of precipitation in the Three-River Headwater Region from 1961 to 2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Harguindeguy, N.; Diaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E.; et al. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Lavorel, S.; Garnier, E.; Díaz, S.; Buchmann, N.; Gurvich, D.E.; Reich, P.B.; ter Steege, H.; Morgan, H.D.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; et al. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 335–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKight, P.E.; Najab, J. Kruskal-Wallis Test. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Kneib, T.; Augustin, T.; Zeileis, A. Conditional variable importance for random forests. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, M.; Fu, G.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y.; Ma, T.; Zheng, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X. Trade-Offs of Plant Biomass by Precipitation Regulation Across the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Plants 2025, 14, 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152325
Xiang M, Fu G, Wu J, Ma Y, Ma T, Zheng K, Wang Z, Zhao X. Trade-Offs of Plant Biomass by Precipitation Regulation Across the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152325
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Mingxue, Gang Fu, Junxi Wu, Yunqiao Ma, Tao Ma, Kai Zheng, Zhaoqi Wang, and Xinquan Zhao. 2025. "Trade-Offs of Plant Biomass by Precipitation Regulation Across the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Plants 14, no. 15: 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152325
APA StyleXiang, M., Fu, G., Wu, J., Ma, Y., Ma, T., Zheng, K., Wang, Z., & Zhao, X. (2025). Trade-Offs of Plant Biomass by Precipitation Regulation Across the Sanjiangyuan Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Plants, 14(15), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152325



.png)



