Advances in ERECTA Family Regulation of Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
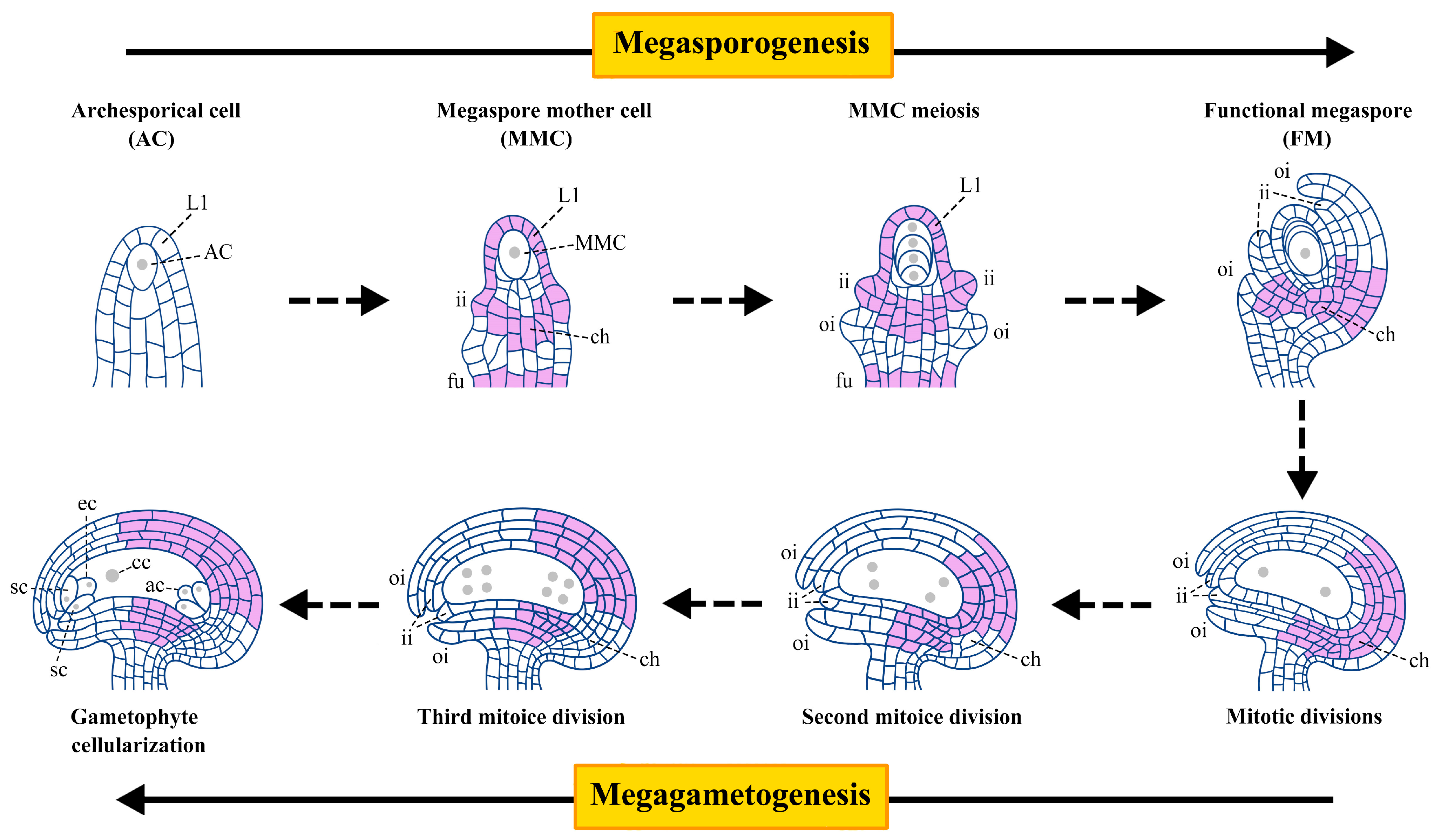
1. Introduction
2. ERf and Its Ligands EPFLs Mediate MMC Specification in Arabidopsis
3. The EPFL-ERf and BR-BRI1 Signaling Modules Maintain the Correct Germline Progression by Activating the BZR1 Transcription Factor Family
3.1. EPFL-ERf and BR-BRI1 Signaling Activate BZR1-WRKY23/NSN1 to Restrict MMC Specialization
3.2. The SWR1-SDG2-ER Module Activates BZR1 to Promote H2A.Z Deposition and Limit Germline Specialization
4. ER Participates in Epigenetic Pathways to Regulate Female Gametophyte Development
5. ERf Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Integument Development
5.1. SDF2-ERdj3-BiP Chaperone Complex Mediates ERf Translocation from Endoplasmic Reticulum to Plasma Membrane to Maintain Normal Integument Growth
5.2. EPFL-ERf-SERK Signaling Regulates Integument Development
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.A.; Bramsiepe, J.; Durme, M.V.; Komaki, S.; Prusicki, M.A.; Maruyama, D.; Forner, J.; Medzihradszky, A.; Wijnker, E.; Harashima, H.; et al. RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED1 mediates germline entry in Arabidopsis. Science 2017, 356, eaaf6532. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.; Schmid, M.W.; Grossniklaus, U. Plant germline formation: Common concepts and developmental flexibility in sexual and asexual reproduction. Development 2015, 142, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, G.; Koltunow, A. The female gametophyte. Arab. Book 2011, 9, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Shi, D.Q.; Chen, Y.H. Female Gametophyte Development in Flowering Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.C.; Mendes, M.A.; Coimbra, S.; Tucker, M.R. Revisiting the Female Germline and Its Expanding Toolbox. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10763–10787. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, K.U.; Mitsukawa, N.; Oosumi, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Yokoyama, R.; Whittier, R.F.; Komeda, Y. The arabidopsis ERECTA gene encodes a putative receptor protein kinase with extracellular leucine-rich repeats. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 735–746. [Google Scholar]
- Kosentka, P.Z.; Zhang, L.; Simon, Y.A.; Satpathy, B.; Maradiaga, R.; Mitoubsi, O.; Shpak, E.D. Identification of critical functional residues of receptor-like kinase ERECTA. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, J.; Sun, X.; Du, J. Multifaceted roles of the ERECTA family in plant organ morphogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 7208–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillitteri, L.J.; Bemis, S.M.; Shpak, E.D.; Torii, K.U. Haploinsufficiency after successive loss of signaling reveals a role for ERECTA-family genes in Arabidopsis ovule development. Development 2007, 134, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Liu, L.; Su, Z.; Cai, H.; Qin, Y. High-throughput single-cell transcriptomics reveals the female germline differentiation trajectory in Arabidopsis thaliana. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lv, M.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.; Yao, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Du, W.; Wang, R.; et al. The EPFL-ERf-SERK signaling controls integument development in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2023, 238, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Shpak, E.D.; Berthiaume, C.T.; Hill, E.J.; Torii, K.U. Synergistic interaction of three ERECTA-family receptor-like kinases controls Arabidopsis organ growth and flower development by promoting cell proliferation. Development 2004, 131, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hord, C.L.H.; Sun, Y.J.; Pillitteri, L.J.; Torii, K.U.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, H. Regulation of Arabidopsis early anther development by the mitogen-activated protein kinases, MPK3 and MPK6, and the ERECTA and related receptor-like kinases. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 645–658. [Google Scholar]
- Shpak, E.D. Diverse Roles of ERECTA Family Genes in Plant Development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Lee, J.S.; Horst, R.J.; Lai, H.H.; Kajita, R.; Kakimoto, T.; Tasaka, M.; Torii, K.U. Regulation of inflorescence architecture by intertissue layer ligand–receptor communication between endodermis and phloem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6337–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kuroha, T.; Hnilova, M. Direct interaction of ligand-receptor pairs specifying stomatal patterning. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.S.; Shimada, T.; Imai, Y.; Okawa, K.; Tamai, A.; Mori, M.; Nishimura, I.H. Stomagen positively regulates stomatal density in Arabidopsis. Nature 2010, 463, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.; Gray, J.E. The Signaling Peptide EPF2 Controls Asymmetric Cell Divisions during Stomatal Development. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Chai, M.; Xi, X.; Aslam, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Su, H.; et al. Signaling by the EPFL-ERECTA family coordinates female germline specification through the BZR1 family in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; Yan, M.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; She, Z.; Lai, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Comparative Expression Profiling Reveals Genes Involved in Megasporogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 2006–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.H.; Vafeados, D.; Tao, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 120, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Qi, J.; Xi, X.; Aslam, M.; Dresselhaus, T.; Qin, Y. Brassinosteroid signaling regulates female germline specification in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 1102–1114.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Shi, C.; Peng, Y.; Tan, H.; Xin, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Brassinosteroid-Activated BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR 1 Inhibits Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Coordinates Growth and UV-B Stress Responses in Plants. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3224–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.A.; Cui, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Gou, X.; Li, J. BES1 is activated by EMS1-TPD1-SERK1/2-mediated signaling to control tapetum development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cai, H.; Su, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Dai, X.; Zhao, H.; Palanivelu, R.; et al. KLU suppresses megasporocyte cell fate through SWR1-mediated activation of WRKY28 expression in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E526–E535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chai, M.; Su, H.; Ma, S.; Liu, K.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xi, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of female germline development through ERECTA signaling pathway. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, A.; Gómez-Zambrano, A.; López-González, L.; Piñeiro, M.; Jarillo, J.A. Mutations in the Arabidopsis SWC6 gene, encoding a component of the SWR1 chromatin remodelling complex, accelerate flowering time and alter leaf and flower development. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Zhao, X.; Kelly, K.A.; Venn, O.; Higgins, J.D.; Yelina, N.E.; Hardcastle, T.J.; Ziolkowski, P.A.; Copenhaver, G.P.; Franklin, F.C.; et al. Arabidopsis meiotic crossover hot spots overlap with H2A.Z nucleosomes at gene promoters. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Harder, M.V.; Cigliano, R.A.; Schlögelhofer, P.; Mittelsten Scheid, O. The Arabidopsis SWR1 Chromatin-Remodeling Complex Is Important for DNA Repair, Somatic Recombination, and Meiosis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Park, C.; Lee, J.; Oh, M.; Noh, B.; Lee, I. Arabidopsis homologs of components of the SWR1 complex regulate flowering and plant development. Development 2007, 134, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, G.; Shen, X.T.; Landry, J.; Wu, W.H.; Sen, S.; Wu, C. ATP-Driven Exchange of Histone H2AZ Variant Catalyzed by SWR1 Chromatin Remodeling Complex. Science 2004, 303, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Laflamme, L.; Gervais, A.L.; Gaudreau, L. Reconciling the positive and negative roles of histone H2A.Z in gene transcription. Epigenetics 2010, 5, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Hui, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. H2A.Z Represses Gene Expression by Modulating Promoter Nucleosome Structure and Enhancer Histone Modifications in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.V.; Wigge, P.A. H2A.Z-Containing Nucleosomes Mediate the Thermosensory Response in Arabidopsis. Cell 2010, 140, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Redon, C.; Pilch, D.; Rogakou, E.; Sedelnikova, O.; Newrock, K.; Bonner, W. Histone H2A variants H2AX and H2AZ. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yu, Y.; Law, J.; Zhang, X. SET DOMAIN GROUP2 is the major histone H3 lysine 4 trimethyltransferase in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18557–18562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, E.T.; Selker, E.U. H3K27 methylation: A promiscuous repressive chromatin mark. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 43, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berr, A.; McCallum, E.J.; Menard, R.; Meyer, D.; Fuchs, J.; Dong, A.; Shen, W.H. Arabidopsis SET DOMAIN GROUP2 Is Required for H3K4 Trimethylation and Is Crucial for Both Sporophyte and Gametophyte Development. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3232–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chai, M.; Huang, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhu, W.; Xi, X.; Chen, F.; Qin, Y.; Cai, H. SDG2 regulates Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture through SWR1-ERECTA signaling pathway. iScience 2021, 24, 103236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosana, M.Z.; Jose, C.R. The Beauty of Being a Variant: H2A.Z and the SWR1 Complex in Plants. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 565–577. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, C.; Tan, L.; Shao, C.; Lin, R.; Su, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; et al. A plant-specific SWR1 chromatin-remodeling complex couples histone H2A.Z deposition with nucleosome sliding. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e102008. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Su, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qin, Y. ERECTA signaling controls Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture through chromatin-mediated activation of PRE1 expression. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Chai, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, F.; Yan, M.; Su, Z.; Henderson, I.; Palanivelu, R.; et al. Spatiotemporal control of miR398 biogenesis via chromatin remodeling and kinase signaling ensures proper ovule development. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1530–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenicová, L.; Folter, S.d.; Kieffer, M.; Horner, D.S.; Favalli, C.; Busscher, J.; Cook, H.E.; Ingram, R.M.; Kater, M.M.; Davies, B.; et al. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: New openings to the MADS world. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ji, L.; Le, B.H.; Zhai, J.; Chen, J.; Luscher, E.; Gao, L.; Liu, C.; Cao, X.; Mo, B.; et al. ARGONAUTE10 promotes the degradation of miR165/6 through the SDN1 and SDN2 exonucleases in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, F.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Sze, S.-H.; Liou, L.W.; Barefoot, A.; Dickman, M.; Zhang, X. Arabidopsis Argonaute10 Specifically Sequesters miR166/165 to Regulate Shoot Apical Meristem Development. Cell 2011, 145, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, W.; Yumul, R.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Thanh, T.D.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Zheng, B.; et al. ARGONAUTE10 and ARGONAUTE1 Regulate the Termination of Floral Stem Cells through Two MicroRNAs in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.; Tofanelli, R.; Strauss, S.; Cerrone, L.; Wolny, A.; Strohmeier, J.; Kreshuk, A.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Smith, R.S.; Schneitz, K. A digital 3D reference atlas reveals cellular growth patterns shaping the Arabidopsis ovule. eLife 2021, 10, e63262. [Google Scholar]
- Coen, O.; Magnani, E. Seed coat thickness in the evolution of angiosperms. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneitz, K.; Hülskamp, M.; Pruitt, R.E. Wild-type ovule development in Arabidopsis thaliana: A light microscope study of cleared whole-mount tissue. Plant J. 1995, 7, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, C.S.; Skinner, D.J. Development and evolution of the unique ovules of flowering plants. Plant Dev. Evol. 2019, 131, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, C.S.; Broadhvest, J.; Hauser, B.A. Genetic analysis of ovule development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Sundaresan, V. Genetics of gametophyte biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegari, R.; Drews, G.N. Female gametophyte development. Plant Cell 2005, 16, S133–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Q.; Russell, S.D. Female germ unit-organization, isolation, and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 140, 233–293. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.O.; Zheng, Z.G.; Oppenheimer, D.G.; Hauser, B.A. The PRETTY FEW SEEDS2 gene encodes an Arabidopsis homeodomain protein that regulates ovule development. Development 2005, 132, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.O.; Hwang, S.; Hauser, B.A. The phenotype of Arabidopsis ovule mutants mimics the morphology of primitive seed plants. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, K.; Wu, P.; Xia, Y.; Zuo, C.; Luo, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Arabidopsis ERdj3B coordinates with ERECTA-family receptor kinases to regulate ovule development and the heat stress response. Plant Cell 2022, 34, koac226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, L.; Usherwood, Y.K.; Chung, K.T.; Hendershot, L.M. A subset of chaperones and folding enzymes from multiprotein complexes in endoplasmic reticulum to bind proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4456–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekrasov, V.; Jing, L.; Batoux, M.; Roux, M.; Chu, Z.; Lacombe, S.; Rougon, A.; Bittel, P.; Kiss-Papp, M.; Chinchilla, D.; et al. Control of the pattern-recognition receptor EFR by an ER protein complex in plant immunity. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3428–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Suno, R.; Iemura, S.-I.; Natsume, T.; Wada, I.; Hosokawa, N. Endoplasmic reticulum proteins SDF2 and SDF2L1 act as components of the BiP chaperone cycle to prevent protein aggregation. Genes Cells 2017, 22, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Bruffett, K.; Lee, J.; Hause, G.; Walker, J.C.; Zhang, S. Haplo-insufficiency of MPK3 in MPK6 mutant background uncovers a novel function of these two MAPKs in Arabidopsis ovule development. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tena, G.; Sheen, J.; Henry, Y.; Champion, A.; Kreis, M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Hirt, H.; Wilson, C.; et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: A new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 301–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Klessig, D.F. MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chevalier, D.; Larue, C. The Protein Phosphatases and Protein Kinases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Arab. Book 2007, 5, e106. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, D.C.; Lukowitz, W.; Somerville, C.R. Stomatal Development and Pattern Controlled by a MAPKK Kinase. Science 2004, 304, 1494–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpak, E.D.; McAbee, J.M.; Pillitteri, L.J.; Torii, K.U. Stomatal patterning and differentiation by synergistic interactions of receptor kinases. Science 2005, 309, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zanten, M.; Snoek, L.B.; Proveniers, M.C.G.; Peeters, A.J.M. The many functions of ERECTA. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wang, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Walker, J.C.; Torii, K.U.; Zhang, S. A MAPK cascade downstream of ERECTA receptor-like protein kinase regulates Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture by promoting localized cell proliferation. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4948–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordá, L.; Sopea-Torres, S.; Escudero, V.; Nunez-Corcuera, B.; Delgado-Cerezo, M.; Torii, K.U.; Molina, A. ERECTA and BAK1 Receptor Like Kinases Interact to Regulate Immune Responses in Arabidopsis. PhytoKeys 2016, 7, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kui, H.; Yi, J.; Li, J.; Gou, X. SERKs regulate embryonic cuticle integrity through the TWS1-GSO1/2 signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.Q.; Lease, K.A.; Doke, J.T.; Tax, F.E.; Walker, J.C. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR Receptor-like Protein Kinase, Interacts with BRI1 and Modulates Brassinosteroid Signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.; Chen, L.; Yin, G.; Yang, X.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, W. Brassinosteroids regulate outer ovule integument growth in part via the control of INNER NO OUTER by BRASSINOZOLE-RESISTANT family transcription factors. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.; Sundaresan, V. The SPOROCYTELESS gene of Arabidopsis is required for initiation of sporogenesis and encodes a novel nuclear protein. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, D.; Lora, J.; Schrempp, S.; Lenhard, M.; Laux, T. Arabidopsis WIH1 and WIH2 Genes Act in the Transition from Somatic to Reproductive Cell Fate. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobeta-Hardt, R.; Lenhard, M.; Laux, T. WUSCHEL signaling functions in interregional communication during Arabidopsis ovule development. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnowska, E.; Kubala, S.; Cwiek, P.; Sacharowski, S.; Oksinska, P.; Steciuk, J.; Zaborowska, M.; Szurmak, J.M.; Dubianski, R.; Maassen, A.; et al. A non-canonical function of Arabidopsis ERECTA proteins and a role of the SWI3B subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex in gibberellin signaling. Plant J. 2023, 115, 788–802. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Xia, Q.; Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Shu, J.; Liu, Z.; Chi, Y.; Xu, H.; et al. Dynamic changes in 3D chromatin structure during male gametogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol. 2025, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tong, M.; Zhang, A.; Liu, M.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, R. COPII genes SEC31A/B are essential for gametogenesis and interchangeable in pollen development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2021, 105, 1600–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Qin, Y.; He, Q.; Cai, H. Advances in ERECTA Family Regulation of Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2025, 14, 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131900
Su H, Jiang X, Liu Y, Cao Z, Liu Z, Qin Y, He Q, Cai H. Advances in ERECTA Family Regulation of Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131900
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Han, Xiaohu Jiang, Yanfen Liu, Zhuangyuan Cao, Ziqi Liu, Yuan Qin, Qing He, and Hanyang Cai. 2025. "Advances in ERECTA Family Regulation of Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 14, no. 13: 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131900
APA StyleSu, H., Jiang, X., Liu, Y., Cao, Z., Liu, Z., Qin, Y., He, Q., & Cai, H. (2025). Advances in ERECTA Family Regulation of Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 14(13), 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131900





