Effects of Long-Term Sod Culture Management on Soil Fertility, Enzyme Activities, Soil Microorganisms, and Fruit Yield and Quality in “Jiro” Sweet Persimmon Orchard
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Impacts on Soil Chemical Properties
2.2. Impacts on Soil Enzyme Activity
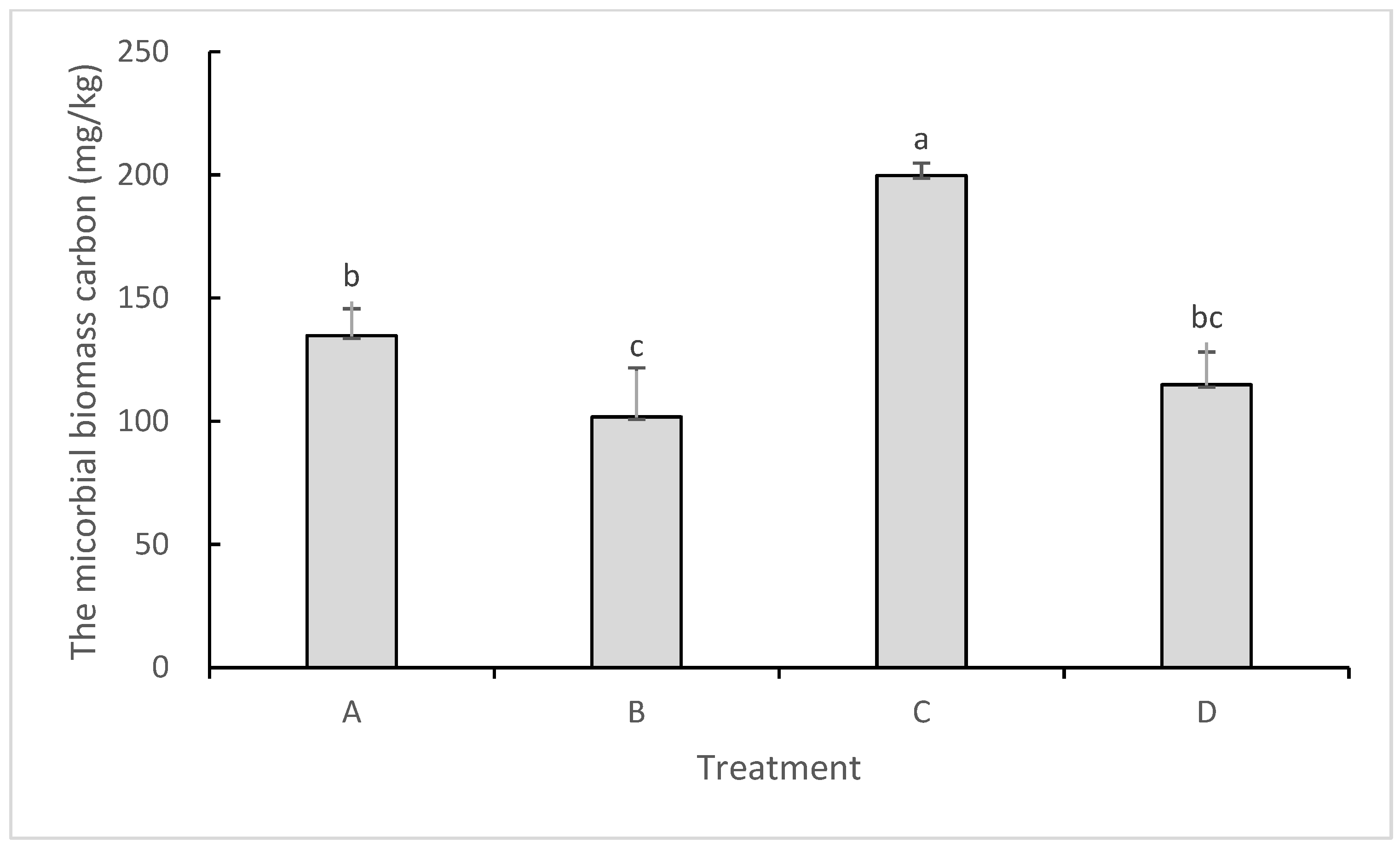
2.3. Impacts on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Microbial Diversity
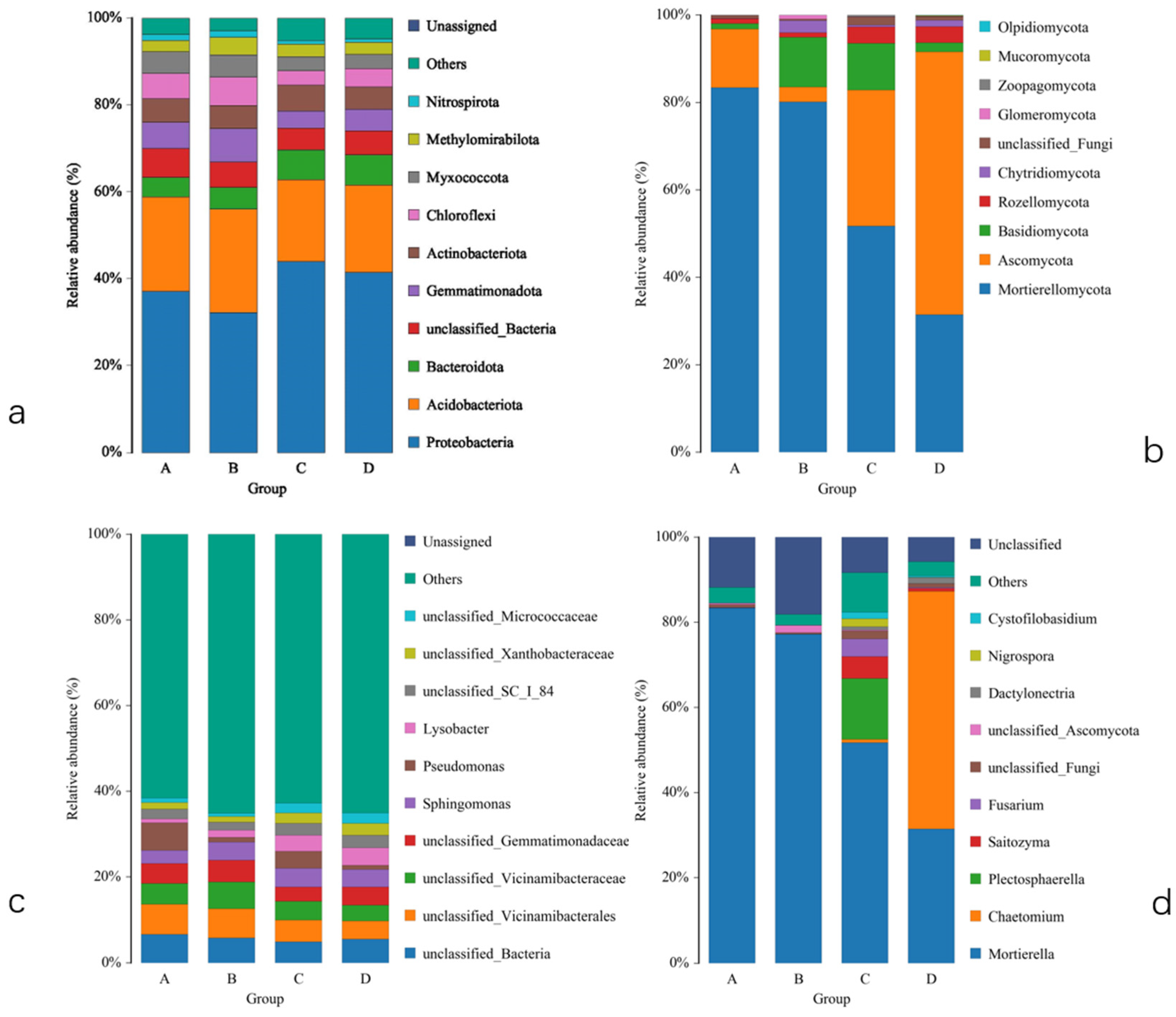
2.4. Impact on the Soil Microbial Community Composition
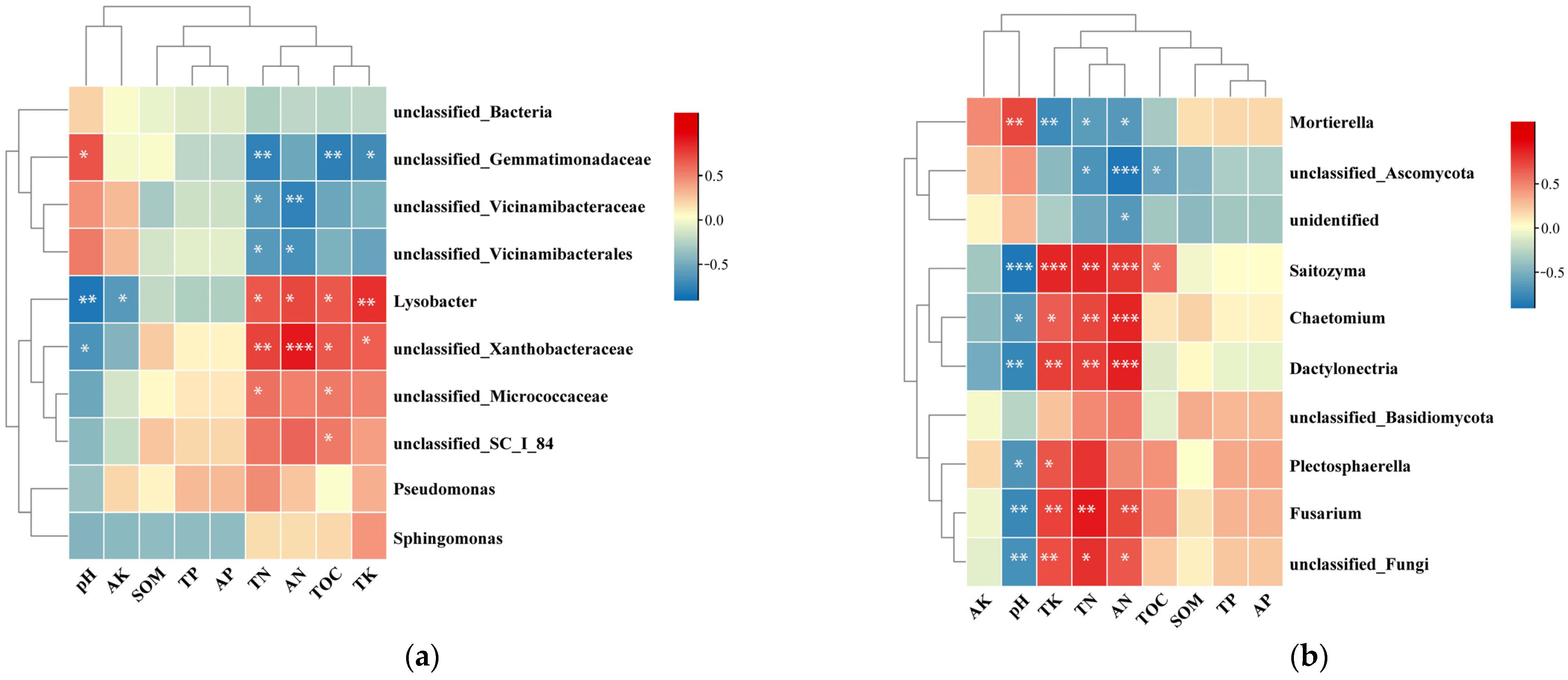
2.5. Correlation between Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure
2.6. Impacts on Persimmon Yield and Fruit Quality
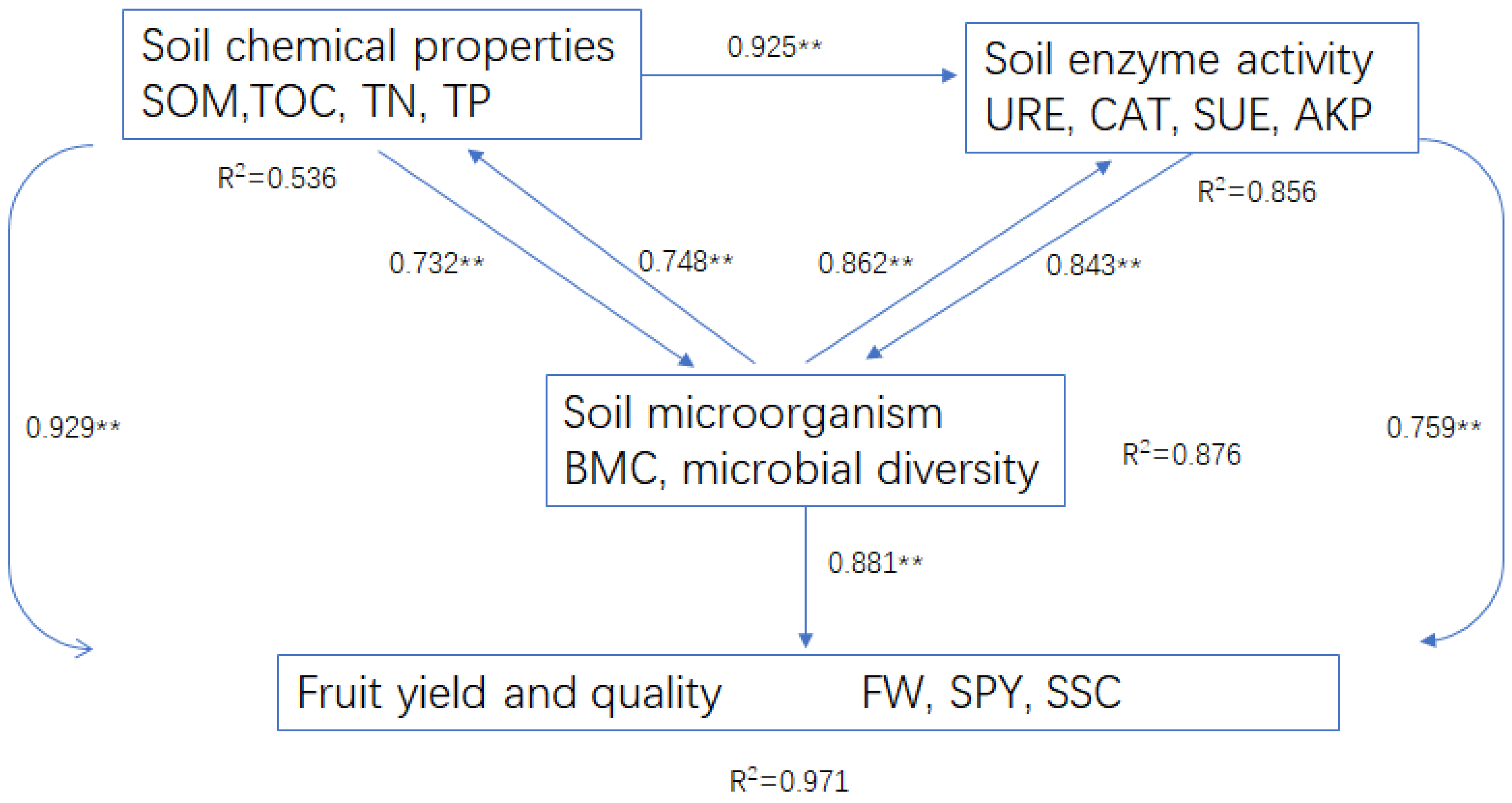
2.7. Plant–Soil–Microbe Interactions
3. Discussion
3.1. Impacts of Sod Culture on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Impacts of Sod Culture on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.3. Impacts of Sod Culture on Soil Microbial Diversity and Population Structure
3.4. Impacts on Sod Culture on Fruit Yield and Quality
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Situation of the Experimental Place
4.2. Test Material
4.3. Soil Sample Collection
4.4. Test Methods
4.4.1. Determination of Soil Chemical Indices
4.4.2. Determination of Soil Enzyme Activities
4.4.3. Determination of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon Content
4.4.4. Soil DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
4.4.5. Fruit Yield and Quality Detected
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, K.Y.; Liu, T.X.; Zhang, J.Z.; Su, R.G.; Gong, B.C. Effect of Fruit Load on Yield and Fruit Auality of ‘Ji-ro’ Persimmon and Its Economic Benefit Analysis. China Fruits 2023, 1, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhao, B.D.; Tao, W.F.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Shao, W.X.; Xiao, Z.X.; Hu, Z.M. Correlation Analysis between Chemical Compositions of Flue-cured Tobacco Leaves and Soil Nutrients in Baoshan. China Soils Fert. 2012, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.X. Analysis for Optimum Parameters of Mineral Nutrient and the Relationship between Mineral Nutrient and Fruit Yield and Quality of Sweet Persimmon Orchards in Baoshan City. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-S.; Um, N.-Y.; Park, S.-M. Selection of Native Ground Cover Plants for Sod Culture in an Organic Apple Orchard. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2015, 28, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of sod cultivation on soil nutrients in orchards across China: A meta -analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Bai, W.X. Effects of Tillage Rotation and Fertilization on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon Content in Corn Field in Weibei Highland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Zeer, L.; Di, X.Y.; Zhang, N.M.; Su, Y.B.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, W.H.; Ma, X.; Hu, C.L. Study on Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Nutrients in Fuit and Vegetable Growing Areas of Yunnan. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.X.; Li, G.L.; He, Z.H.; Fu, C.Y. Risk Potential of Secondary Soil Salinization by Repeated Application of Chicken and Pigeon Manure. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2007, 15, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, E.; Grossman, J.; Edgell, J.; Hoyt, G.; Osmond, D.; Hu, S. Soil biological properties, soil losses and corn yield in long-term organic and conventional farming systems. Soil. Tillage Res. 2014, 139, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlbachová, G.; Kusá, H.; Růžek, P. Soil characteristics and crop yields under different tillage techniques. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babujia, L.; Hungria, M.; Franchini, J.; Brookes, P. Microbial biomass and activity at various soil depths in a Brazilian oxisol after two decades of no-tillage and conventional tillage. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Q.; Chen, D.Y.; Yang, X.P.; Gan, Y.Y.; Huang, W.X. Effects of Grass Cover in ‘Nanfeng’ Tangerine Orchard on Nutrients and Microbial Characteristics in Soil Aggregates and Fruit Quality. J. Fruit. Sci. 2020, 37, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.X.; Bai, G.S.; Zou, C.Y.; Shao, F.Q. Effects of Self-sown Grass on Soil Porosity and Soil Infiltration in Apple Orchard in Weibei Dry Plateau. J. Chin. Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 146–156. [Google Scholar]
- Do, V.H.; La, N.; Bergkvist, G.; Dahlin, A.S.; Mulia, R.; Nguyen, V.T.; Oborn, I. Agroforestry with contour planting of grass contributes to terrace formation and conservation of soil and nutrients on sloping land. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 345, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Gou, M.; Yu, B.; Sun, C.; He, J.; Qin, S.; Lyu, D. Effects of mowing dominant grasses on root exudation and soil nitrogen cycling in a natural sod culture apple orchard. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.N.; Chen, X.; Srivastava, A.K.; Wang, P.; Wu, Q.S. Changes in Rhizosphere Properties of Trifoliate Orange in Response to Mycorrhization and Sod Culture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-F.; Zhou, P.; Han, Q.-F.; Li, Z.-H.; Yang, B.-P.; Nie, J.-F. Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Matter and Nutrients in the Pear Orchard Under Clean and Sod Cultivation Models. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.Q.; Xu, J. Preliminary Study on Diurnal Variations of Photosynthesis of Mopan Persimmon Trees with Different Tree Age. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 16, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.B.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, X.F. Effects of Inter-planted Grasses in Persimmon Orchard on Soil Microbes and Enzyme Activities. North. Hortic. 2019, 9, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.J. Effects of Grass Cultivation on Persimmon Yield and Quality and Soil Physicochemical Properties. China Fruits 2008, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Zhao, X.Q.; Shi, Y.; Liang, Y.T.; Shen, R.F. Ammonium and Nitrate Shift the Spatial Distribution of Soil Bacterial Communities and Association Networks Along a Distance from Maize Roots in an Acidic Red Soil. Maize 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.C.; Lal, R.; Che, Y.N.; An, S.S. Soil, Leaf and Root Ecological Stoichiometry of Caragana Korshinskii on the Loess Plateau of China in Relation to Plantation Age. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Yan, W.D.; Xiang, W.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Lei, P.F. Stoichiometry Characterization of Soil C, N, and P of Chinese Fir Plantations at Three Different Ages in Huitong, Hunan Province, China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2015, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, B.R.; Yang, S.K.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, K.J. Soil Physico-chemical Properties of Organic Grapes Farms with Different Culture Facilities and Soil Management Practices. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fertil. 2013, 46, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.C.; Duan, W.B.; Chen, L.X.; Qu, M.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, M.J.; Shi, Y.J.; Pan, L. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen and Phosphorus Deposition and Litter Treatment on Soil Organic Carbon Components in Two types of Pinus Koraiensis Forests. J. Nanjing For. Univ. Natl. Sci. Ed. 2023, 47, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Hu, J.W.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, K.X.; Tian, S.; Zhou, W.X. Alterations in Litter Chemical Traits and Soil Environmental Properties Limit the Litter Decomposition of Near-mature Robinia Pseudoacacia Plantations. Geoderma 2013, 439, 116668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Mao, Y.F.; Hu, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Yin, Y.J.; Pang, H.L.; Su, X.F.; Liu, Y.P.; Shen, X. Effects of Orchard Grass on Soil Fertility and Apple tree Nutrition. J. Plat. Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Duan, Y.M.; Zhang, R.Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, M.; Ding, Y.Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Li, H.K. Connecting Soil Dis-solved Organic Matter to Soil Bacterial Community Structure in a Long-term Grass-mulching Apple Orchard. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 149, 112344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, G.; Qi, X.; Yu, Z.; Abdallah, Y.; Ogunyemi, S.O.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Mohany, M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; et al. The Effects of Accompanying Ryegrass on Bayberry Trees by Change of Soil Property, Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure, and Metabolites. Plants 2023, 12, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.Y.; Saman, B.; Tian, P.; Peng, Z.C.; Hou, F.J.; Li, C.J. Research Developments on the Effects of Grass–endophyte Fungi Symbiosis on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Microbes. Pratac. Sci. 2019, 36, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Loganathan, M.; Rai, A.B.; Grag, R. Role of Microbes in Soil Health Improvement Introduction. Satsa Mukha-patra Annu. Tech. Issue 2016, 20, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, R.A.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, L.C. The Effect of Sod-culture on Orchard Soil Properties and the Floral Physiology of Olives. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2018, 27, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, K.K.; Ji, L.D.; Slaughter, L.C.; Hou, J.F.; Shen, M.C.; Li, J.G.; Dong, Y.H. Synergistic Changes of Rhizosphere Bacte-rial Community and Soil Properties in Greenhouse Soils under Long-term Tomato Monoculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 183, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Neuberger, P.; Daly, E.J.; Gorzelak, M.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi community linkages to soil nutrient availability across contrasting agroecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 176, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfarita, N.; Unisma, I.U.I.M.; Muhibuddin, A.; Imai, T. Exploration of indigenous free nitrogen-fixing bacteria from rhizosphere of Vigna radiata for agricultural land treatment. J. Degraded Min. Lands Manag. 2019, 6, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, A.K.; Ganzert, L.; Rojas-Jimenez, K.; Fonvielle, J.; Hose, G.C.; Grossart, H.-P. Highly diverse fungal communities in carbon-rich aquifers of two contrasting lakes in Northeast Germany. Fungal Ecol. 2019, 41, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.H.; Man, X.L.; Duan, B.X.; Cai, T.J.; Ge, Z.X.; Li, X.F.; Vesala, T.; Hose, G.C.; Grossart, H.P. Changes in Soil Bacte-rial Communities and Nitrogen Mineralization with Understory Vegetation in Boreal Larch Forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 38–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioli, A.M.D.; Giles, A.L.; Costa, P.B.; Wolfsdorf, G.; Pecoral, L.F.; Verona, L.; Piccolo, F.; Sampaio, A.B.; Schmidt, I.B.; Rowland, L.; et al. Abandoned Pastures and Restored Savannas Have Dis-tinct Patterns of Plant–soil Feedback and Nutrient Cycling Compared with Native Brazilian savannas. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Q.; Zhu, H.J.; Zhou, B.B.; Sheng, J.Y.; Zhang, M. Effects of Sod Culture with Vulpia Myuros on Weed Control, Soil Microbial Biomass and Soil Enzyme Activities in Pear Orchard. J. Fruit Sci. 2010, 27, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Qin, S.-J.; Lyu, D.-G. Responses of soil microorganisms, enzyme activities and nutrient contents to inter-row grass ploughing and returning to the field in a natural sod culture apple orchard. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D. Microbial Allocation to Soil Enzyme Production: A Mechanism for Carbon and Nutrient Cycling. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, California, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, G.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Wright, S.; Li, Y.Z.; Shen, Y.M.; Liu, F.Q.; Du, L.C. Biosynthetic Mechanism for Sunscreens of the Biocontrol Agent Lysobacter enzymogenes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Lang, J.M.; McClung, A.; Wamishe, Y.; Jia, Y.; Leach, J.E. First Report of Rice Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pantoea ananatis in the United States. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkopru, S.; Ozaktan, H. Identification of Rhizobacteria that Increase Yield and Plant Tolerance to Angular Leaf Spot Disease in Cucumber. Plant Prot. Sci. 2018, 54, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Harighi, B.; Mozafari, A.A.; Esmaeel, Q.; Barka, E.A. Screening of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Domes-ticated and Wild Growing Grapevines as Potential Biological Control Agents Against Crown Gall Disease. BioControl J. Int. Organ. Biol. Control 2019, 64, 723–735. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, K.A.; Sajjad, A.; Ahmed, A.R.; In-Jung, L.; Ahmed, A.H. Rhizospheric Microbial Communities Associated with Wild and Cultivated Frankincense Producing Boswellia Sacra Tree. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186939. [Google Scholar]
- Leff, J.W.; Jones, S.E.; Prober, S.M.; Barberán, A.; Borer, E.T.; Firn, J.L.; Harpole, W.S.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hofmokel, K.S.; Knops, J.M.H.; et al. Consistent Responses of Soil Microbial Communi-ties to Elevated Nutrient Inputs in Grasslands Across the Globe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10967–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, E.; Leeflang, P.; Gommans, S.; Van Den Broek, J.; van Mil, S.; Wernars, K. Diversity and Seasonal Fluctuations of the Dominant Members of the Bacterial Soil Community in a Wheat Field as Determined by Cultivation and Molecular Methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J. On the Ecology of Saprotrophic Fungi and Bacteria in Soil: Biotic and Abiotic Control of Growth Rates. Master’s Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Lin, Z.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, W.; Guo, X.P.; Nie, Y.C.; Li, Y.H. Mapping and Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis of Verticillium Wilt Resistance Genes in Cotton. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 2, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado-Salazar, C.; Rossman, A.Y.; Chaverri, P. The genus Thelonectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota) and closely related species with cylindrocarpon-like asexual states. Fungal Divers. 2016, 80, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varssney, E.; Kashyap, A.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, R.; Kashyap, M.K. Prevalence of Penicillium Chrysogenum, Its Qualita-tive, Quantitative Determination and Antibacterial Activity in Indian. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2005, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.Z.; Ma, D.H.; Cai, Z.J.; Zhang, J.B. Effects of Mortierella on Nutrient Availability and Straw Decomposition in Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 55, 206–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.W.; Wang, X.B.; Li, J.C.; Ye, A.H.; Wang, Y.; Che, W.; Zhu, L. Effects of Fertilization and Straw Incorporation on Bacterial Communities in Lime Concretion Black Soil. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.J.; Zeng, F.J.; Lei, J.Q.; Lu, Y.; Guan, J.H. Root Distribution and Growing of Walnut Trees and Medicago sativa Sod-culture Pattern. Arid. Zone Res. 2015, 3, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lyu, D. Natural Grass Cultivation Management Improves Apple Fruit Quality by Regulating Soil Mineral Nitrogen Content and Carbon–Nitrogen Metabolism. Metabolites 2023, 13, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcwhirt, A.L. The Use of Sustainable Soil Management Practices in Fumigated and Non-fumigated Plasticulture Straw-berry Production in the Southeastern United States. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil; China Agricultural Publishing: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 14–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tuo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, M.; Yang, Q. Effect of water and fertilizer regulation on the soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, enzyme activity, and saponin content of Panax notoginseng. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, S.M.; Behnke, G.D.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B. Carbon and Nitrogen Content of Soil Organic Matter and Microbial Biomass under Long-Term Crop Rotation and Tillage in Illinois, USA. Agriculture 2018, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Data2: High Resolution Sample In-ference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | pH Value | TN (g/kg) | TK (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | TOC (g/kg) | |||
| A | 7.48 ± 0.91 a | 1.93 ± 0.18 a | 9.51 ± 0.13 c | 1.09 ± 0.16 a | 11.17 ± 041 c | |||
| B | 7.46 ± 0.35 a | 1.29 ± 0.19 b | 10.42 ± 0.22 b | 0.64 ± 0.15 b | 8.20 ± 0.25 d | |||
| C | 7.41 ± 0.40 a | 1.99 ± 0.16 a | 18.11 ± 0.16 a | 1.09 ± 0.13 a | 27.70 ± 1.05 a | |||
| D | 7.42 ± 0.03 a | 1.77 ± 0.14 a | 18.03 ± 0.17 a | 0.88 ± 0.14 ab | 17.40 ± 0.17 b | |||
| Treatment | HN (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | SOM (g/kg) | ||||
| A | 119.14 ± 2.05 c | 201.95 ± 2.24 a | 96.02 ± 0.25 b | 32.04 ± 1.89 a | ||||
| B | 93.94 ± 0.41 d | 111.17 ± 1.71 c | 46.20 ± 0.18 d | 26.19 ± 0.16 b | ||||
| C | 154.87 ± 2.38 a | 143.97 ± 3.41 b | 126.02 ± 2.14 a | 31.09 ± 0.86 a | ||||
| D | 131.01 ± 0.44 b | 78.73 ± 0.18 d | 51.63 ± 0.23 c | 27.30 ± 0.08 b | ||||
| Treatment | Urease (mg g−1 d−1) | Catalase (mL g−1 d−1) | Sucrase (mg g−1 d−1) | Phosphatase (mg g−1 d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.61 ± 0.03 b | 0.34 ± 0.03 ab | 2.19 ± 0.08 c | 6.73 ± 0.14 c |
| B | 0.44 ± 0.01 d | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 1.74 ± 0.02 d | 4.79 ± 0.19 d |
| C | 0.67 ± 0.03 a | 0.37 ± 0.03 a | 2.55 ± 0.08 a | 13.01 ± 0.41 a |
| D | 0.50 ± 0.10 c | 0.36 ± 0.02 a | 2.05 ± 0.03 b | 9.21 ± 0.30 b |
| Treatment | OTUs | ACE Index | Chao l Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial community | A | 3457.67 ± 133.77 a | 3472.37 ± 133.10 a | 3292.51 ± 256.85 a | 3292.56 ± 259.42 a | 0.99 ± 0.00 a |
| B | 3253.00 ± 214.89 a | 3265.20 ± 214.19 a | 3253.97 ± 214.33 a | 3253.98 ± 214.33 a | 0.96 ± 0.00 a | |
| C | 3600.07 ± 295.47 a | 3612.29 ± 290.54 a | 3568.96 ± 496.73 a | 3335.01 ± 491.11 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| D | 3526.00 ± 60.02 a | 3576.01 ± 57.68 a | 3236.06 ± 57.58 a | 3268.28 ± 280.38 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| Fungal community | A | 63.67 ± 17.78 b | 82.84 ± 8.26 c | 73.44 ± 12.16 c | 0.67 ± 0.07 bc | 2.22 ± 0.35 bc |
| B | 48.33 ± 2.52 b | 70.21 ± 12.67 d | 59.75 ± 7.33 d | 0.58 ± 0.04 c | 1.92 ± 0.21 c | |
| C | 119.67 ± 8.51 a | 130.40 ± 18.37 a | 129.37 ± 7.98 a | 0.87 ± 0.04 a | 3.99 ± 0.45 a | |
| D | 113.00 ± 20.66 a | 106.73 ± 9.73 b | 106.10 ± 22.14 b | 0.79 ± 0.10 ab | 2.96 ± 0.59 b |
| Treatment | FW (g) | FTL (mm) | FLL (mm) | SPY (kg) | FF (kg.cm−2) | SSC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 249.82 ± 29.111 a | 54.89 ± 2.91 ab | 81.11 ± 5.04 a | 44.31 ± 3.73 c | 7.04 ± 0.71 a | 14.56 ± 0.87 a |
| B | 228.52 ± 25.13 bc | 54.51 ± 2.37 b | 79.76 ± 4.16 a | 38.82 ± 2.75 d | 7.09 ± 0.49 a | 13.93 ± 0.93 bc |
| C | 239.11 ± 30.60 ab | 56.06 ± 2.25 a | 81.37 ± 4.63 a | 62.01 ± 3.40 a | 7.07 ± 0.90 a | 14.33 ± 1.52 ab |
| D | 219.59 ± 30.53 c | 53.79 ± 3.15 c | 79.90 ± 3.29 a | 56.16 ± 3.20 b | 6.85 ± 0.58 a | 13.56 ± 1.12 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Gong, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Effects of Long-Term Sod Culture Management on Soil Fertility, Enzyme Activities, Soil Microorganisms, and Fruit Yield and Quality in “Jiro” Sweet Persimmon Orchard. Plants 2024, 13, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111573
Yang X, Gong B, Liu C, Wang Y, Xu Y. Effects of Long-Term Sod Culture Management on Soil Fertility, Enzyme Activities, Soil Microorganisms, and Fruit Yield and Quality in “Jiro” Sweet Persimmon Orchard. Plants. 2024; 13(11):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111573
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xu, Bangchu Gong, Cuiyu Liu, Yanpeng Wang, and Yang Xu. 2024. "Effects of Long-Term Sod Culture Management on Soil Fertility, Enzyme Activities, Soil Microorganisms, and Fruit Yield and Quality in “Jiro” Sweet Persimmon Orchard" Plants 13, no. 11: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111573
APA StyleYang, X., Gong, B., Liu, C., Wang, Y., & Xu, Y. (2024). Effects of Long-Term Sod Culture Management on Soil Fertility, Enzyme Activities, Soil Microorganisms, and Fruit Yield and Quality in “Jiro” Sweet Persimmon Orchard. Plants, 13(11), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111573






