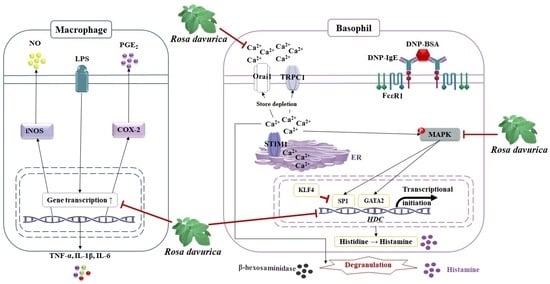
Rosa davurica Inhibited Allergic Mediators by Regulating Calcium and Histamine Signaling Pathways
Abstract
Share and Cite
Lim, S.; Oh, S.; Nguyen, Q.T.N.; Kim, M.; Zheng, S.; Fang, M.; Yi, T.-H. Rosa davurica Inhibited Allergic Mediators by Regulating Calcium and Histamine Signaling Pathways. Plants 2023, 12, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071572
Lim S, Oh S, Nguyen QTN, Kim M, Zheng S, Fang M, Yi T-H. Rosa davurica Inhibited Allergic Mediators by Regulating Calcium and Histamine Signaling Pathways. Plants. 2023; 12(7):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071572
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Seojun, Sarang Oh, Quynh T. N. Nguyen, Myeongju Kim, Shengdao Zheng, Minzhe Fang, and Tae-Hoo Yi. 2023. "Rosa davurica Inhibited Allergic Mediators by Regulating Calcium and Histamine Signaling Pathways" Plants 12, no. 7: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071572
APA StyleLim, S., Oh, S., Nguyen, Q. T. N., Kim, M., Zheng, S., Fang, M., & Yi, T.-H. (2023). Rosa davurica Inhibited Allergic Mediators by Regulating Calcium and Histamine Signaling Pathways. Plants, 12(7), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071572