Impact of Prosopis velutina Wooton on the Composition and Diversity of Native Woody Species in a Semi-Arid Zone along the Molopo River, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Species Composition and Density
2.2. Ecological Indices
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
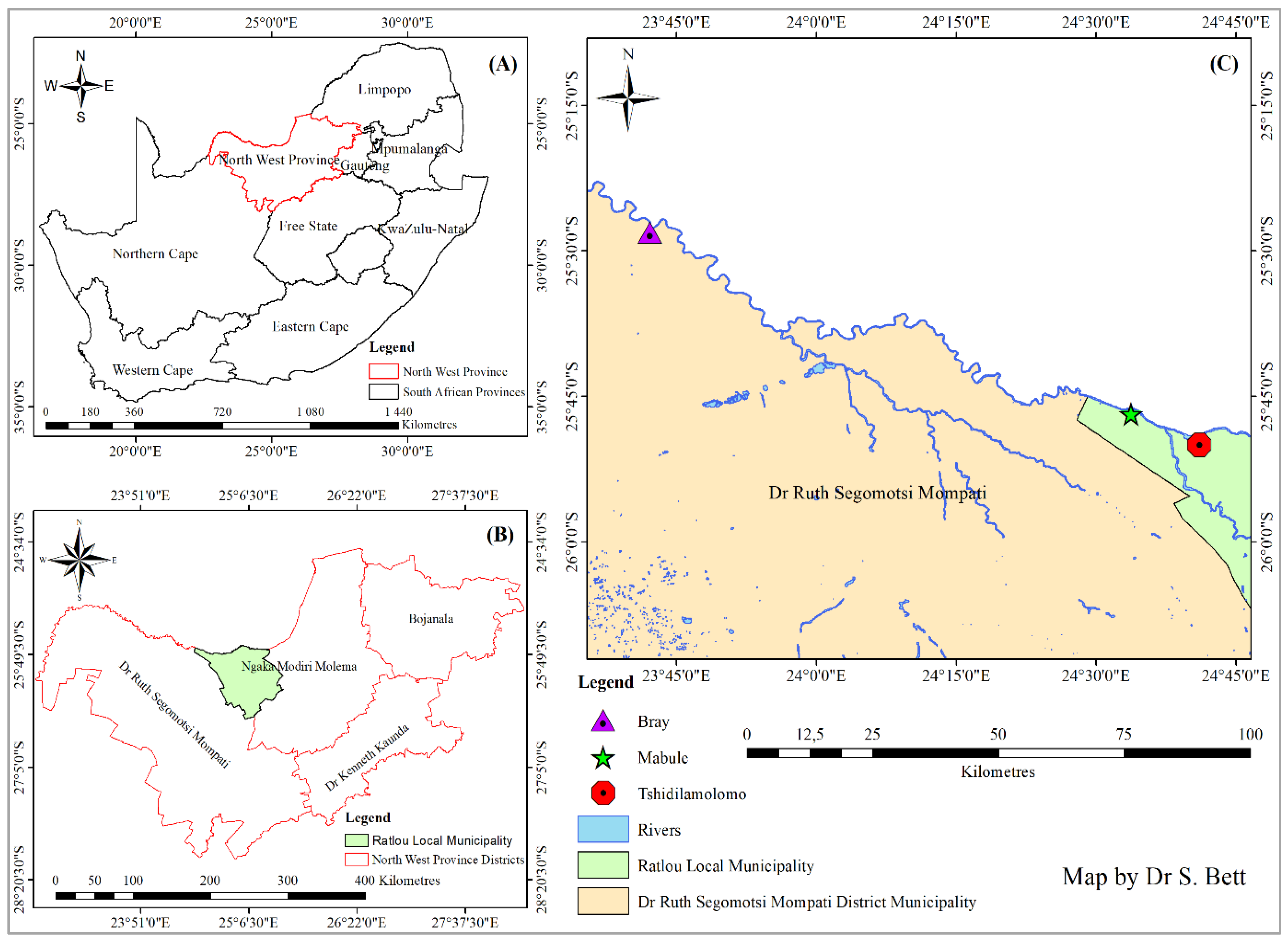
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Data Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catford, J.A.; Vesk, P.A.; Richardson, D.M.; Pyšek, P. Quantifying levels of biological invasion: Towards the objective classification of invaded and invasible ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; Winter, M.; Arianoutsou, M.; et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G. Ecosystem consequences of biological invasions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.I.; Chase, J.M.; Knight, T.M. A synthesis of plant invasion effects on biodiversity across spatial scales. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C.M.; Shackleton, S.E.; Buiten, E.; Bird, N. The importance of dry woodlands and forests in rural livelihoods and poverty alleviation in South Africa. For. Policy. Econ. 2007, 9, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, I.J.; Grice, A.C.; Abbott, B.N.; Nicholas, D.M.; Whiteman, L. Impacts of changed fire regimes on tropical riparian vegetation invaded by an exotic vine. Austral Ecol. 2008, 33, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Peet, R.K. Diversity and invasibility of southern appalachian plant communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lite, S.J.; Bagstad, K.J.; Stromberg, J.C. Riparian plant species richness along lateral and longitudinal gradients of water stress and flood disturbance, San Pedro River, Arizona, USA. J. Arid. Environ. 2005, 63, 785–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.M.; Holmes, P.M.; Esler, K.J.; Galatowitsch, S.M.; Stromberg, J.; Kirkman, S.; Pyšek, P.; Hobbs, R.J. Riparian vegetation: Degradation, alien plant invasions, and restoration prospects. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.M.; Richardson, D.M.; Esler, K.J.; Witkowski, E.T.F.; Fourie, S. A decision-making framework for restoring riparian zones degraded by invasive alien plants in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2005, 101, 553–564. [Google Scholar]
- Pattison, Z.; Minderman, J.; Boon, P.J.; Willby, N. Twenty years of change in riverside vegetation: What role have invasive alien plants played? Appl. Veg. Sci. 2017, 20, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Espinar, J.L.; Hejda, M.; Hulme, P.E.; Jarošík, V.; Maron, J.L.; Pergl, J.; Schaffner, U.; Sun, Y.; Pyšek, P. Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: A meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.G. Biological control of Prosopis, Prosopis spp. (Fabaceae), in South Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 37, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynton, R.J. Tree Planting in Southern Africa: Other Genera; Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries: Pretoria, South Africa, 2009; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariades, C.; Hoffmann, J.H.; Roberts, A.P. Biological control of mesquite (Prosopis species) (Fabaceae) in South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2011, 19, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L. Invasive, naturalized and casual alien plants in southern Africa: A summary based on the Southern African Plant Invaders Atlas (SAPIA). Bothalia 2007, 37, 215–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Klinken, R.D.; Graham, J.; Flack, L.K. Population ecology of hybrid mesquite (Prosopis species) in Western Australia: How does it differ from native range invasions and what are the implications for impacts and management. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wilgen, B.W.; Scott, D.F. Managing fires on the Cape Peninsula, South Africa: Dealing with the inevitable. J. Mediterr. Ecol. 2001, 2, 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.M.; van Wilgen, B.W. Invasive alien plants in South Africa; how well do we understand the ecological impacts? S. Afr. J. Sci. 2004, 100, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, T.; van Wilgen, B.W. The impact of invasive alien plants on rangelands in South Africa. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; Van Wilgen, B.W., Measey, J., Richardson, D.M., Wilson, J.R., Zengeya, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 457–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maitre, D.C.; Van Wilgen, B.W.; Gelderblom, C.M.; Bailey, C.; Chapman, R.A.; Nel, J.A. Invasive alien trees and water resources in South Africa: Case studies of costs and benefits of management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 160, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.M.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Latombe, G.; Le Maitre, D.C. The biogeography of South African terrestrial plant invasions. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; Van Wilgen, B.W., Measey, J., Richardson, D.M., Wilson, J.R., Zengeya, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wilgen, N.J.; van Wilgen, B.W.; Midgley, G.F. Biological invasions as a component of South Africa’s global change research effort. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; Van Wilgen, B.W., Measey, J., Richardson, D.M., Wilson, J.R., Zengeya, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 851–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comole, A.A.; Malan, P.W.; Tiawoun, M.A.P. Effects of Prosopis velutina invasion on soil characteristics along the riverine system of the Molopo River in north-west province, South Africa. Int. J. Ecol. 2021, 2021 , 6681577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiawoun, M.A.P.; Malan, P.W.; Comole, A.A. Composition and structural patterns of encroaching woody plant species along riparian zones of the Molopo River, North-West Province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 147, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environmental Affairs. National Environmental Management: Biodiversity Act 2004 (Act No. 10 of 2004) Alien and Invasive Species Lists; Government Gazette of South Africa: Pretoria, South Africa, 2014; pp. 3–80.
- Moshobane, M.C.; Mukundamago, M.; Adu-Acheampong, S.; Shackleton, R. Development of alien and invasive taxa lists for regulation of biological invasions in South Africa. Bothalia 2019, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.W. Plant community diversity and native plant abundance decline with increasing abundance of an exotic annual grass. Oecologia. 2011, 167, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, S. Ecological impacts of the non-native macrophyte Crassula helmsii on Freshwater Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in Dartmoor National Park, UK. Plymouth Stud. Sci. 2022, 15, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshete, A.; Treydte, A.C.; Hailemariam, M.; Solomon, N.; Dejene, T.; Yilma, Z.; Birhane, E. Variations in soil properties and native woody plant species abundance under Prosopis juliflora invasion in Afar grazing lands, Ethiopia. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtschneider, K.; February, E.C. Impact of Prosopis invasion on a keystone tree species in the Kalahari Desert. Plant. Ecol. 2013, 214, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Richardson, D.M. Prosopis invasions in South Africa: Population structures and impacts on native tree population stability. J. Arid. Environ. 2015, 114, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ndhlovu, T.; Milton, S.J.; Esler, K.J. Effect of Prosopis (mesquite) invasion and clearing on vegetation cover in semi-arid Nama Karoo rangeland, South Africa. Afr. J. Range. For. Sci. 2016, 33, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.E.; Callaham, M.A.; Stewart, J.E.; Warren, S.D. Invasive species response to natural and anthropogenic disturbance. In Invasive Species in Forests and Rangelands of the United States; Poland, T.M., Patel-Weynand, T., Finch, D.M., Miniat, C.F., Hayes, D.C., Lopez, V.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravhuhali, K.E.; Mudau, H.S.; Moyo, B.; Hawu, O.; Msiza, N.H. Prosopis Species—An Invasive Species and a Potential Source of Browse for Livestock in Semi-Arid Areas of South Africa. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Pasiecznik, N.M.; Richardson, D.M. Prosopis: A global assessment of the biogeography, benefits, impacts and management of one of the world’s worst woody invasive plant taxa. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejda, M.; Pysek, P.; Jarosík, V. Impact of invasive plants on the species richness, diversity and composition of invaded communities. J. Ecol. 2009, 97, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.E., III; Seybold, S.J.; Haag, W.R.; Tracy Johnson, M.; Kerns, B.K.; Kilgo, J.C.; Larkin, D.J.; Lucardi, R.D.; Moltzan, B.D.; Pearson, D.E.; et al. Impacts of Invasive Species in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems in the United States. In Invasive Species in Forests and Rangelands of the United States; Poland, T.M., Patel-Weynand, T., Finch, D.M., Miniat, C.F., Hayes, D.C., Lopez, V.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmida, A.; Wilson, M.V. Biological determinants of species diversity. J. Biogeogr. 1985, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muturi, G.M.; Poorter, L.; Mohren, G.M.J.; Kigomo, B.N. Ecological impacts of Prosopis species invasion in Turkwel riverine forest, Kenya. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 92, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Keblawy, A.; Al-Rawai, A. Impacts of the invasive exotic Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) D.C. on the native flora and soils of the UAE. Plant. Ecol. 2007, 190, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, W.; Demissew, S.; Bekele, T.; Aynekulu, E. Effects of Prosopis juliflora Invasion on Native Species Diversity and Woody Species Regenerations in Rangelands of Afar National Regional State, Northeast Ethiopia. J. Resour. Ecol. 2022, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifian, A.; Niknahad-Gharmakher, H.; Foladizada, M.; Tabe, A.; Shackleton, R.T. Socio-ecological evidence highlights that native Prosopis species are better for arid land restoration than non-native ones. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 31, e13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Keblawy, A.; Abdelfatah, M.A. Impacts of native and invasive exotic Prosopis congeners on soil properties and associated flora in the arid United Arab Emirates. J. Arid. Environ. 2014, 100, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mathur, M. Impact of invasion by Prosopis juliflora on plant communities in arid grazing lands. Trop. Ecol. 2014, 55, 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg, J.C.; Tiller, R.; Richter, B. Effects of ground-water decline on riparian vegetation of semi-arid regions: The San Pedro, Arizona. Ecol. Appl. 1996, 6, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, H.; Teketay, D.; Nemomissa, S.; Assefa, F. Some biological characteristics that foster the invasion of Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC. at Middle Awash Rift Valley Area, north-eastern Ethiopia. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 58, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashe, K.; Donald, L.K.; Demel, T. Invasiveness of biofuel crops: Implications for energy research and policy in Botswana. S Afr Geogr. J. 2021, 103, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standish, R.J.; Robertson, A.W.; Williams, P.A. The impact of an invasive weed Tradescantia fluminensis on native forest regeneration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, K.; Kaufman, S.; Durbin, L.; Lowenstein, F. Impacts of garlic mustard invasion on a forest understory community. Northeast. Nat. 2007, 14, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, G.; Carboni, M.; Mahaut, L.; Violle, C. Functional traits modulate plant community responses to alien plant invasion. Perspect. Plant. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2019, 37, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougill, A.J.; Thomas, A.D. Kalahari sand soils: Spatial heterogeneity, biological soil crusts and land degradation. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucina, L.; Rutherford, M.C. (Eds.) The Vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; Strelitzia 19; South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI): Pretoria, South Africa, 2006; ISBN 1-919976-21-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tiawoun, M.A.P.; Malan, P.W.; Comole, A.A. Effects of Soil Properties on the Distribution of Woody Plants in Communally Managed Rangelands in Ngaka Modiri Molema District, North-West Province, South Africa. Ecologies 2022, 3, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E. Effects of large herbivores and fire on the regeneration of Acacia erioloba woodlands in Chobe National Park, Botswana. Afr. J. Ecol. 2001, 39, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.S.G.; Sporton, D.; Perkins, J. The environment impact of livestock ranches in the Kalahari, Botswana: Natural resource use, ecological change and human response in a dynamic dryland system. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahikeng Local Municipality. Mahikeng Local Municipality Audited Annual Report; City Council of Mahikeng: Mmabatho, South Africa, 2013.
- Bezuidenhout, H. The classification, mapping and description of the vegetation of the Rooipoort Nature Reserve, Northern Cape, South Africa. Koedoe 2009, 51, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.M.; Macdonald, I.A.; Forsyth, G.C. Reduction in plant species richness understands of alien trees and shrubs in fynbos biome. S. Afr. For. J. 1989, 149, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.N. Quantitative description of woody plant communities: Part 1: An approach. J. Grassl. Soc. S. Afr. 1989, 6, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Ecologycal Diversity and Its Mesurement; Pricenton University Press: Pricenton, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

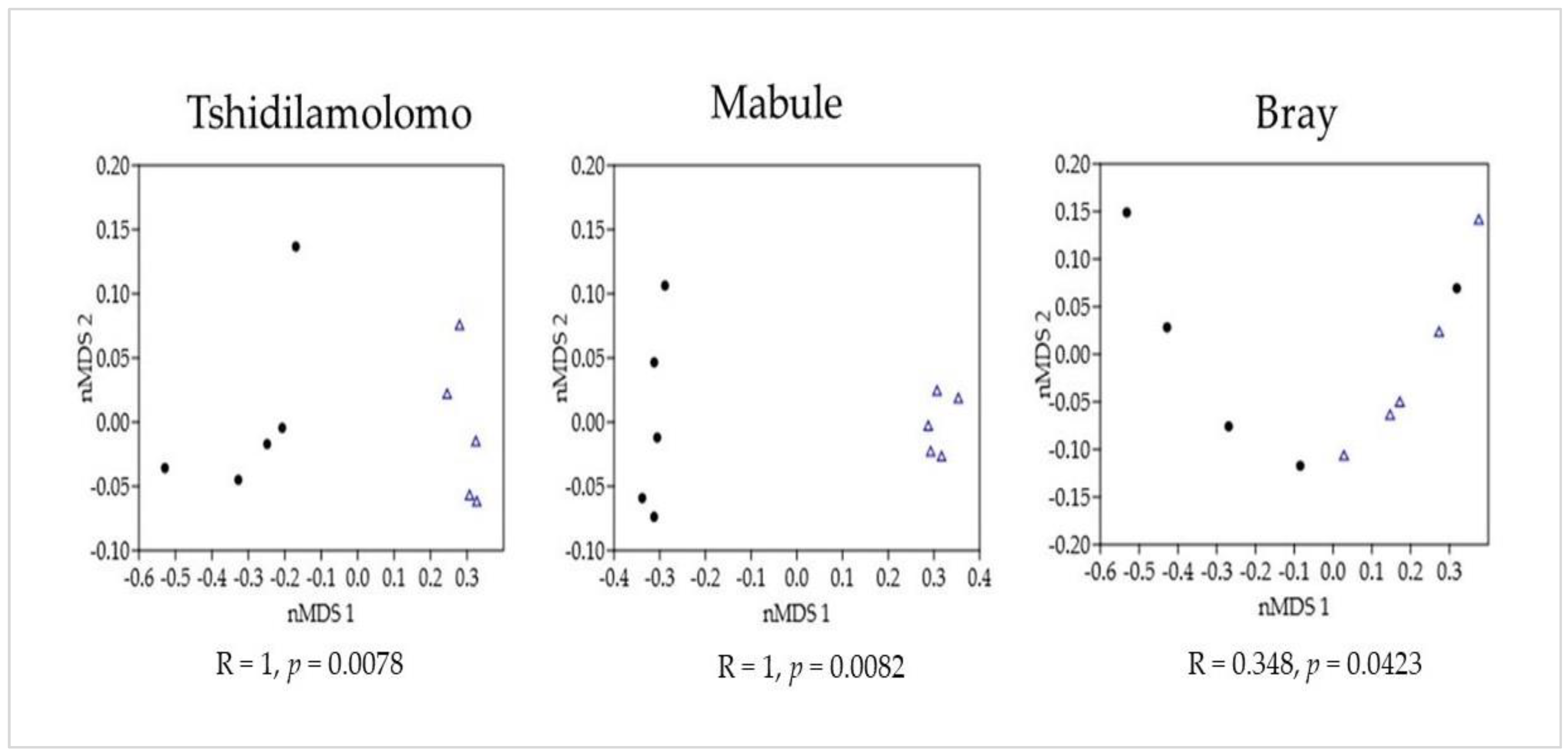

| Woody Species | Family | Tshidilamolomo | Mabule | Bray | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (TE ha−1) | Composition (%) | Density (TE ha−1) | Composition (%) | Density (TE ha−1) | Composition (%) | ||||||||
| In | Un | In | Un | In | Un | In | Un | In | Un | In | Un | ||
| Senegalia mellifera | Fabaceae | 44 | 321 | 51.2 | 28.9 | 131 | 250 | 30.3 | 14.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vachellia hebeclada | Fabaceae | 42 | 273 | 48.8 | 24.6 | 231 | 121 | 53.5 | 7.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vachellia erioloba | Fabaceae | 0 | 367 | 0 | 33.1 | 0 | 444 | 0 | 26.5 | 76 | 132 | 46.3 | 64.7 |
| Vachellia tortilis | Fabaceae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ziziphus mucronata | Rhamnaceae | 0 | 17 | 0 | 1.5 | 70 | 103 | 16.2 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Grewia flava | Malvaceae | 0 | 124 | 0 | 11.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tarchonanthus camphoratus | Asteraceae | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0.7 | 0 | 686 | 0 | 40.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| p-value | p < 0.05 | p < 0.05 | p = 0.6 | ||||||||||
| Woody Species | Average Dissimilarity = 78.2% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invaded | Uninvaded | Av. Dissim. | Contribution (%) | Cumulative (%) | |
| Vachellia erioloba | 25.3 | 214 | 23.18 | 29.64 | 29.64 |
| Senegalia mellifera | 66 | 211 | 16.56 | 21.17 | 50.81 |
| Vachellia hebeclada | 51 | 176 | 13.93 | 17.82 | 68.63 |
| Ziziphus mucronata | 31 | 123 | 8.50 | 10.88 | 79.51 |
| Vachellia tortilis | 24.7 | 96 | 6.76 | 8.64 | 88.15 |
| Tarchonanthus camphoratus | 0 | 98 | 5.33 | 6.81 | 94.96 |
| Grewia flava | 0 | 55 | 3.94 | 5.04 | 100 |
| Site | Invasion Categories | Number of Species (S) | Species Richness (R) | Shannon’s Index of Diversity (H’) | Simpson’s Index of Diversity (D) | Species Evenness (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tshidilamolomo | Invaded | 2 | 0.22 ± 0.0 | 0.70 ± 2.3 | 0.27 ± 0.1 | 0.70 ± 0.0 |
| Uninvaded | 6 | 0.71 ± 0.8 | 1.41 ± 0.1 | 0.50 ± 0.0 | 1.00 ± 0.1 | |
| % Decrease over uninvaded | 67 | 69.0 ± 0.4 | 50.0 ± 1.7 | 31.5 ± 0.0 | 43.0 ± 0.0 | |
| p-value | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Mabule | Invaded | 3 | 0.33 ± 0.4 | 1.00 ± 0.1 | 0.27 ± 0.1 | 0.75 ± 0.1 |
| Uninvaded | 6 | 0.67 ± 0.1 | 1.50 ± 0.1 | 0.40 ± 0.0 | 0.90 ± 0.0 | |
| % Decrease over uninvaded | 50 | 50.7 ± 0.2 | 33.3 ± 0.1 | 17.8 ± 0.0 | 20.0 ± 0.0 | |
| p-value | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Bray | Invaded | 2 | 0.19 ± 0.1 | 0.65 ± 0.0 | 0.54 ± 0.0 | 1.00 ± 0.0 |
| Uninvaded | 2 | 0.20 ± 0.0 | 0.70 ± 0.0 | 0.50 ± 0.1 | 0.96 ± 0.0 | |
| % Decrease over uninvaded | 0 | 5.26 ± 0.1 | 7.70 ± 0.0 | 7.40 ± 0.1 | 4.20± 0.0 | |
| p-value | =0.05 | =0.05 | =0.06 | =0.06 | =0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiawoun, M.A.P.; Malan, P.W.; Comole, A.A.; Moshobane, M.C. Impact of Prosopis velutina Wooton on the Composition and Diversity of Native Woody Species in a Semi-Arid Zone along the Molopo River, South Africa. Plants 2023, 12, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071561
Tiawoun MAP, Malan PW, Comole AA, Moshobane MC. Impact of Prosopis velutina Wooton on the Composition and Diversity of Native Woody Species in a Semi-Arid Zone along the Molopo River, South Africa. Plants. 2023; 12(7):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071561
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiawoun, Makuété A. P., Pieter W. Malan, Alvino A. Comole, and Moleseng C. Moshobane. 2023. "Impact of Prosopis velutina Wooton on the Composition and Diversity of Native Woody Species in a Semi-Arid Zone along the Molopo River, South Africa" Plants 12, no. 7: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071561
APA StyleTiawoun, M. A. P., Malan, P. W., Comole, A. A., & Moshobane, M. C. (2023). Impact of Prosopis velutina Wooton on the Composition and Diversity of Native Woody Species in a Semi-Arid Zone along the Molopo River, South Africa. Plants, 12(7), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071561






