Effects of Slow-Release Fertilizer on Lotus Rhizome Yield and Starch Quality under Different Fertilization Periods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Release Characteristics of SCU and RCU
2.2. Effects of SCU and RCU on SPAD Value and Pn
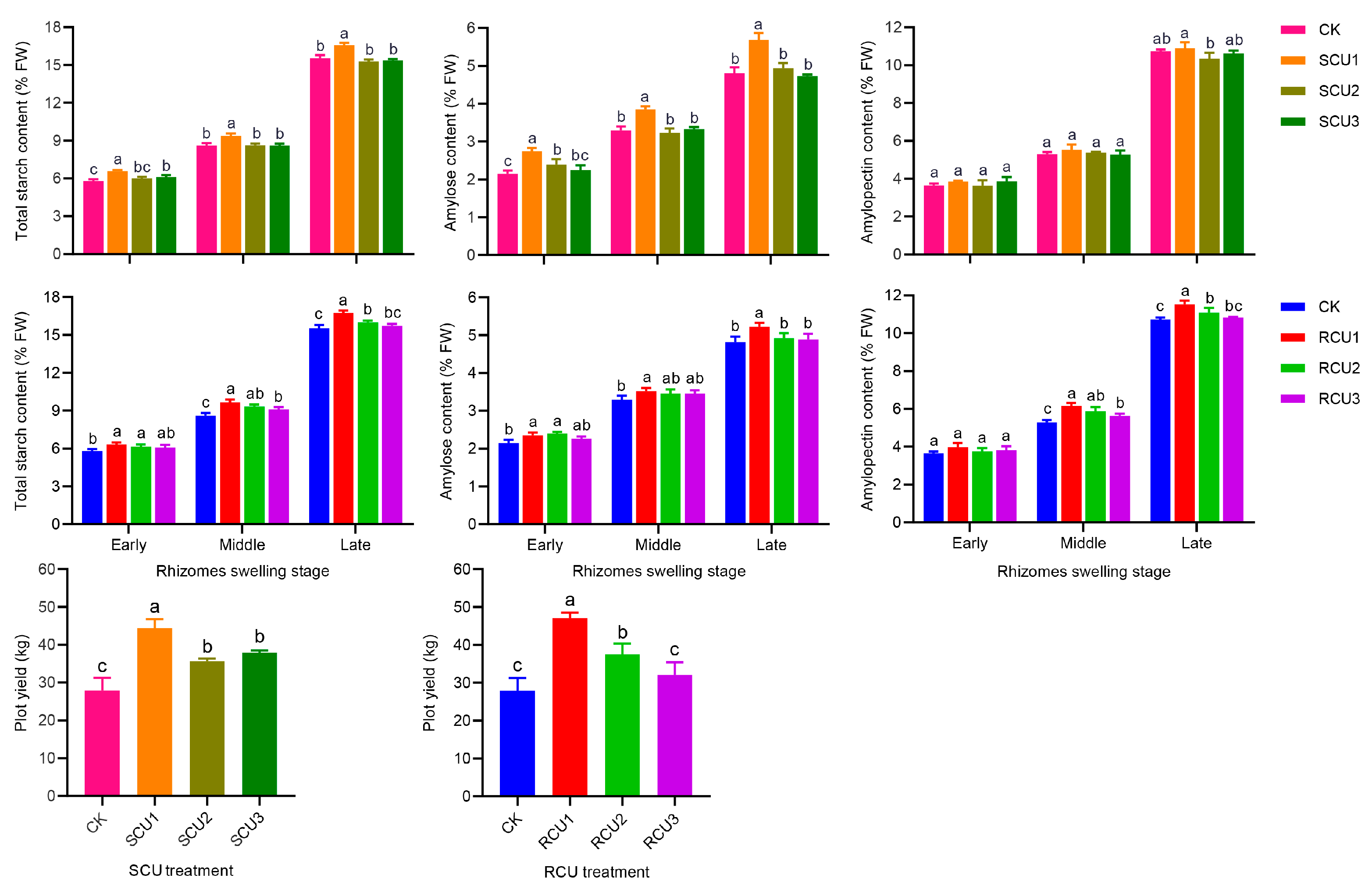
2.3. Effects of SCU and RCU on Starch Content and Yield
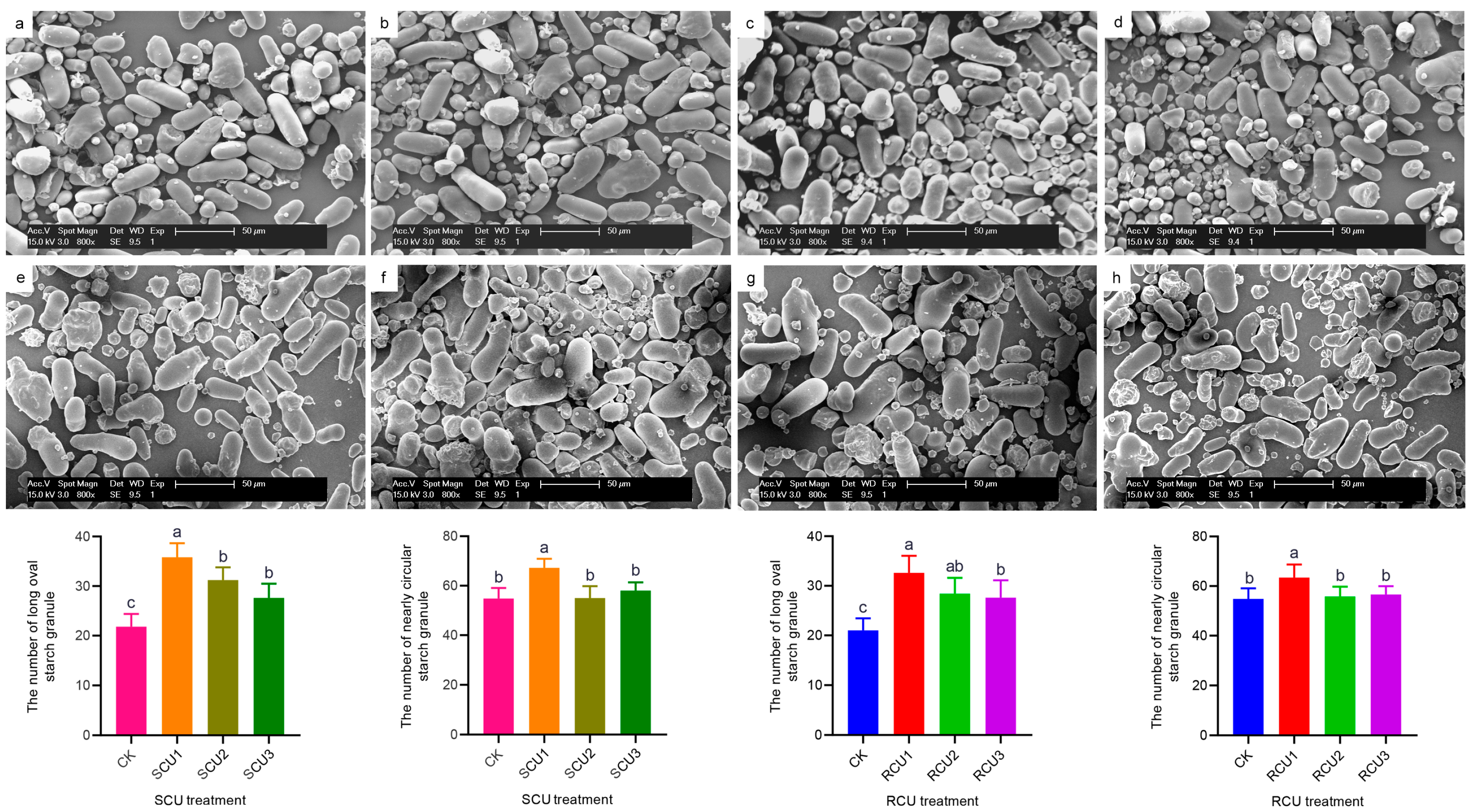
2.4. Effects of SCU and RCU on Starch Granule Morphology
2.5. Effects of SCU and RCU on Starch Pasting Properties
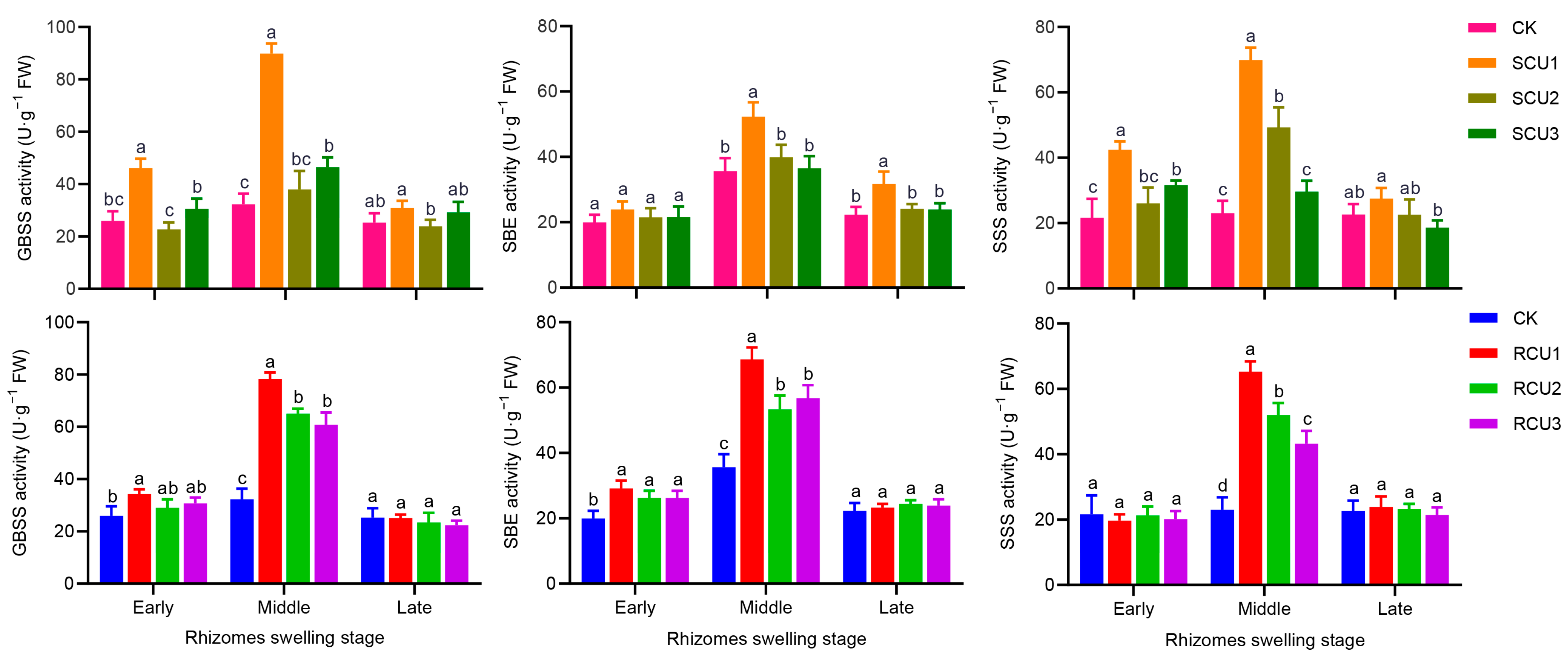
2.6. Effects of SCU and RCU on Starch Synthesis Key Enzyme Activity
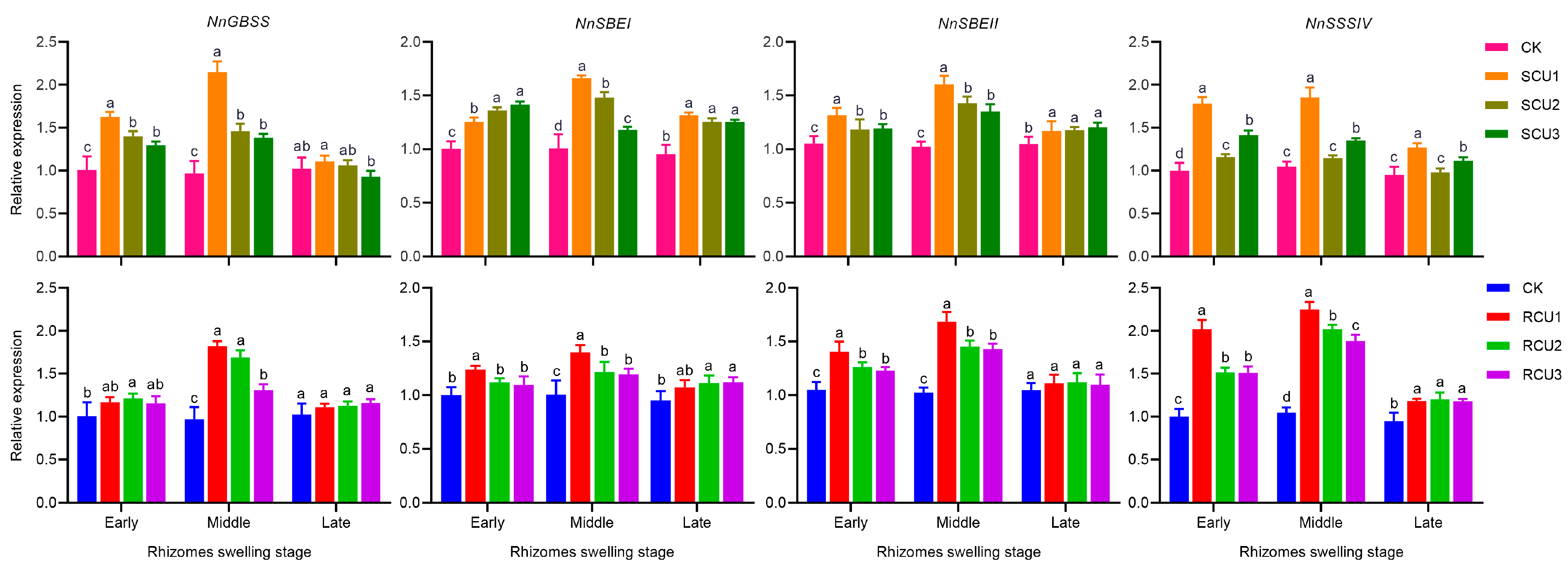
2.7. Effects of SCU and RCU on Relative Expression of Key Enzyme Genes in Starch Synthesis
2.8. Correlation Analysis of Key Enzyme Activities for Starch Synthesis and Starch Accumulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. N Release Characteristics of SCU and RCU
4.4. SPAD Value and Pn
4.5. Plant Sample Harvesting
4.6. Starch Content
4.7. Starch Isolation
4.8. Starch Granule Morphology
4.9. Starch Pasting Properties
4.10. Key Enzyme Activity in Starch Synthesis
4.11. Relative Expression of Key Enzyme Genes in Starch Synthesis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Min, T.; Niu, L.; Feng, X.; Yi, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. The effects of different temperatures on the storage characteristics of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera G.) root. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folina, A.; Tataridas, A.; Mavroeidis, A.; Kousta, A.; Katsenios, N.; Efthimiadou, A.; Travlos, I.; Roussis, I.; Darawsheh, M.; Papastylianou, P.; et al. Evaluation of Various Nitrogen Indices in N-Fertilizers with Inhibitors in Field Crops: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Song, W.; Zhong, N.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X. Improving Crop Nitrogen Use Efficiency toward Sustainable Green Revolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 523–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Deng, K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, P.; Feng, K.; Li, L. Optimization of slow-release fertilizer application improves lotus rhizome quality by affecting physicochemical properties of starch. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Xie, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Yin, S.; Wang, D.; Yan, B. Effects of biological nitrification inhibitors on nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, F. Crop responses to nitrogen overfertilization: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 205, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowski, K. Environmental impact of fertilizer use and slow release of mineral nutrients as a response to this challenge. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2016, 18, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.; Adhikari, R.; Casey, P.; Muster, T.; Gill, H.; Adhikari, B. Enhanced efficiency fertilisers: A review of formulation and nutrient release patterns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Yan, X.; Zhao, W. Effect of Urea-Formaldehyde Resin-Coated Colour-Change Powder Microcapsules on Performance of Waterborne Coatings for Wood Surfaces. Coatings 2022, 12, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Qian, X. Effect of Microcapsule Concentration with Different Core-Shell Ratios on Waterborne Topcoat Film Properties for Tilia europaea. Coatings 2021, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, S.; Razali, R.; KuShaari, K.; Mansor, N.; Azeem, B.; Versypt, A. A review of mathematical modeling and simulation of controlled-release fertilizers. J. Control. Release 2018, 271, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, M.; Hsieh, L.; Cai, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Shen, C.; Hu, B.; Lou, L. Feasibility of bioleaching of heavy metals from sediment with indigenous bacteria using agricultural sulfur soil conditioners. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Thobakgale, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, Q.; Cang, B.; Bai, C.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Wu, M.; et al. Construction of dominant rice population under dry cultivation by seeding rate and nitrogen rate interaction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Ran, C.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, T.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Geng, Y. Effect of straw return with nitrogen fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of rice in soda saline-alkali rice paddy fields. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; He, B.; Cui, Z.; Kusutani, A.; Ito, S.; Matsue, Y. Effect of Amount of Nitrogen Application on Physicochemical Properties, Taste Value and Yield of Chinese Japonica-Type Rice Varieties. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2017, 62, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, J.; Cai, M.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Y. Judge the taste quality of rice by screening the thickness of rice under nitrogen conditions. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Sharma, S.; Singh, D.; Chaudhari, R.; Mahala, R.; Dadarwal, R. Effect of nutrient management on growth and yield of quality protein maize (Zea mays L.). Res. Crops 2013, 14, 743–747. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, A.; Sebetha, E. Data on influence of different nitrogen fertilizer rates and plant density on grain yield and yield components of Water Efficient Maize (WEMA) variety. Data Brief 2020, 30, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Fu, P.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Effects of Nitrogen Rates on the Physicochemical Properties of Waxy Maize Starch. Starch-Starke 2019, 71, 1900146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jing, L.; Wang, D.; Bao, F.; Lu, W.; Wang, G. Grain and starch granule morphology in superior and inferior kernels of maize in response to nitrogen. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, M.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.; Gao, H.; Zhao, C.; Kubar, K.; Korai, P.; Gujar, A.; Sher, A.; Yang, W. Nitrogen application improved nitrogen use efficiency, photosynthetic characteristics and yield components of field grown winter wheat. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, D. Screening of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties with high nitrogen use efficiency under rainfed and irrigated conditions. Turk. J. Field Crops. 2019, 24, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Xia, M.; Bai, W.; Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Feng, B.; Gao, J. Effects of nitrogen level on the physicochemical properties of Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.) starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litke, L.; Gaile, Z.; Ruza, A. Effect of nitrogen rate and forecrop on nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 582–592. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, M.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, W.; Dai, T.; Jiang, D. Nitrogen topdressing timing influences the spatial distribution patterns of protein components and quality traits of flours from different pearling fractions of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Field Crops Res. 2018, 216, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, B.; Niazi, M.; Jahan, Z.; Zia, M.; Shah, G.; Iqbal, Z.; Douna, I. Facile coating of micronutrient zinc for slow release urea and its agronomic effects on field grown wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, C.; Attia, A.; Ulloa, S.; Mainz, M. Use of Five Nitrogen Source and Placement Systems for Improved Nitrogen Management of Irrigated Corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, D. Fertilization time of slow-release fertilizer affects the physicochemical properties of starch from spring-sown waxy maize. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F. Structures, properties, and applications of lotus starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.; Wani, S. Characterization of Lotus Stem (Nelumbo nucifera) Starches Purified from Three Lakes of India. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2013, 22, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cheng, L.; Yin, J.; Yan, S.; Liu, K.; Zhang, F.; Xu, B.; Li, L. Structure and physicochemical properties of starches in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) rhizome. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tan, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H. Regulators of Starch Biosynthesis in Cereal Crops. Molecules 2021, 26, 7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, A.; Guo, H.; Rehman, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Raza, A.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Soluble Starch Synthase Enzymes in Cereals: An Updated Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yi, B.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Chen, X. Activities of Key Enzymes Involved in Starch Accumulation in Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor L. Moench) Grains with Different Starch Contents. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2022, 51, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Xie, H.; He, L.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, I.; Raza, H.; Khan, A.; Wei, S.; Quan, Z.; Wu, K.; et al. Partial substitution of organic nitrogen with synthetic nitrogen enhances rice yield, grain starch metabolism and related genes expression under the dual cropping system. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Z.; Xing, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, P.; et al. Effects of slow or controlled release fertilizer types and fertilization modes on yield and quality of rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2222–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Deng, J.; Pan, J.; Xiong, F. Analysis of development, accumulation and structural characteristics of starch granule in wheat grain under nitrogen application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3739–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Ryoo, N.; Hahn, T.; Walia, H.; Nakamura, Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Subburaj, S.; Zhang, M.; Han, C.; Hao, P.; Li, X.; Yan, Y. Dynamic development of starch granules and the regulation of starch biosynthesis in Brachypodium distachyon: Comparison with common wheat and Aegilops peregrina. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Xi, M.; Kong, L. Split application enhances sweetpotato starch production by regulating the conversion of sucrose to starch under reduced nitrogen supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Li, L.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Anwar, S.; Fudjoe, S. Nitrogen Supply Affects Yield and Grain Filling of Maize by Regulating Starch Metabolizing Enzyme Activities and Endogenous Hormone Contents. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 798119. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Teng, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, H.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Excessive nitrogen in field-grown rice suppresses grain filling of inferior spikelets by reducing the accumulation of cytokinin and auxin. Field Crops Res. 2022, 283, 108542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Hu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. Low Nitrogen Application Enhances Starch-Metabolizing Enzyme Activity and Improves Accumulation and Translocation of Non-Structural Carbohydrates in Rice Stems. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Fan, X.; Dai, T.; Cao, W. Nitrogen fertiliser rate and post-anthesis waterlogging effects on carbohydrate and nitrogen dynamics in wheat. Plant Soil 2008, 304, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Gruissem, W.; Bhullar, N. Facilitated citrate-dependent iron translocation increases rice endosperm iron and zinc concentrations. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; He, L.; Ullah, S.; Quan, Z.; Wei, S.; Igbal, A.; Munsif, F.; Shah, T.; Xuan, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Biochar addition coupled with nitrogen fertilization impacts on soil quality, crop productivity, and nitrogen uptake under double-cropping system. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e208. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, A.; Satake, A. Understanding Circadian Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Arabidopsis Using Mathematical Models. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 586–593. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Chen, G.; Dang, K.; Yang, P.; Wang, M.; Feng, B. Nitrogen deficiency induced a decrease in grain yield related to photosynthetic characteristics, carbon-nitrogen balance and nitrogen use efficiency in proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 398–413. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, X.; Huang, R. Effects of nitrogen application strategy and planting density optimization on sorghum yield and quality. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, K.; Huang, X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer applications on the early senescence and grain filling characteristics of Tartary buckwheat. ScienceAsia 2021, 47, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Ni, X.; Tao, L.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhong, W.; Wu, Y. Rice productivity and profitability with slow-release urea containing organic-inorganic matrix materials. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto, K. Utilization advantages of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on paddy rice cultivation. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2004, 38, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, A.; Singh, P.; Shah, M.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Gul, K.; Wani, I. Rice Starch Diversity: Effects on Structural, Morphological, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties—A Review. Compr Rev Food Sci. F. 2012, 11, 417–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Simi, C.; Abraham, T. Physicochemical Rheological and Thermal Properties of Njavara Rice (Oryza sativa) Starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 12105–12113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tian, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Yu, S.; Feng, B. Nitrogenous Fertilizer Levels Affect the Physicochemical Properties of Sorghum Starch. Foods 2022, 11, 3690. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Wan, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Eeckhout, M.; Gao, J. Relationship between nitrogen fertilizer and structural, pasting and rheological properties on common buckwheat starch. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 132664. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, E.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Gu, J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on structure and physicochemical properties of ‘super’ rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Xia, M.; Wan, C.; Jia, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; et al. Analysis of synthesis, accumulation and physicochemical properties of Tartary buckwheat starches affected by nitrogen fertilizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118570. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K. Conventional Analysis Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ruan, F.; Shen, W.; Deng, K.; Jiang, T.; Wu, P.; Feng, K.; Li, L. The Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Rhizome Quality and Starch Physicochemical Properties in Nelumbo nucifera. Agronomy 2022, 12, 794. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tao, W.; Gao, S.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Effects of different types of slowand controlled-release fertilizers on rice yield. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

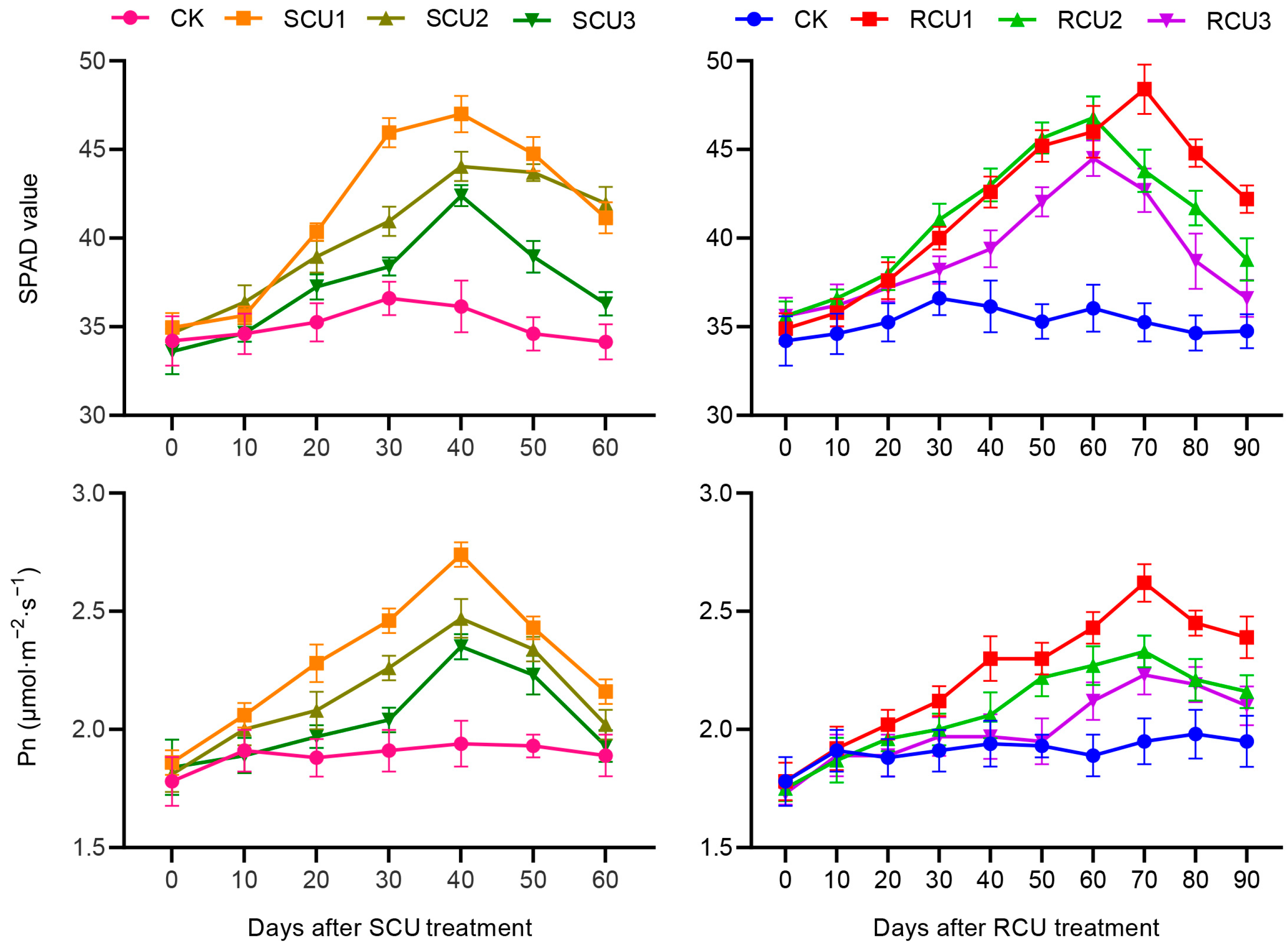
| SPAD/Pn | Treatment | Day after SCU/RCU Treatment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0d | 10d | 20d | 30d | 40d | 50d | 60d | 70d | 80d | 90d | ||
| SPAD | CK | 34.20 ± 1.40 cd | 34.60 ± 1.14 d | 35.25 ± 1.07 e | 36.60 ± 0.94 e | 36.15 ± 1.46 e | 34.60 ± 0.97 f | 34.15 ± 1.32 g | 35.25 ± 1.14 d | 34.65 ± 0.99 d | 34.75 ± 0.97 d |
| SCU1 | 34.95 ± 0.83 ab | 35.65 ± 0.49 c | 40.35 ± 0.49 a | 45.95 ± 0.83 a | 47.00 ± 1.03 a | 44.75 ± 0.97 b | 41.15 ± 0.88 e | - | - | - | |
| SCU2 | 34.65 ± 0.49 bc | 36.40 ± 0.94 a | 38.95 ± 0.89 b | 40.95 ± 0.83 b | 44.05 ± 0.83 b | 43.70 ± 0.47 c | 41.95 ± 0.94 d | - | - | - | |
| SCU3 | 33.60 ± 1.27 d | 34.65 ± 0.49 d | 37.25 ± 0.72 d | 38.40 ± 0.50 d | 42.40 ± 0.60 c | 38.95 ± 0.89 e | 36.30 ± 0.66 f | - | - | - | |
| RCU1 | 34.90 ± 0.85 b | 35.80 ± 0.77 bc | 37.60 ± 1.05 cd | 40.00 ± 0.65 c | 42.60 ± 0.88 c | 45.20 ± 0.89 ab | 46.00 ± 1.45 b | 48.40 ± 1.39 a | 44.80 ± 0.77 a | 42.20 ± 0.77 a | |
| RUC2 | 35.60 ± 0.82 a | 36.60 ± 0.50 a | 38.00 ± 0.92 c | 41.05 ± 0.89 b | 43.00 ± 0.92 c | 45.65 ± 0.88 a | 46.80 ± 1.20 a | 43.80 ± 1.20 b | 41.70 ± 0.98 b | 38.80 ± 1.20 b | |
| RCU3 | 35.60 ± 1.05 a | 36.20 ± 1.20 ab | 37.20 ± 0.77 d | 38.20 ± 0.77 d | 39.40 ± 1.05 d | 42.05 ± 0.83 d | 44.50 ± 1.00 c | 42.70 ± 1.22 c | 38.70 ± 1.56 c | 36.60 ± 1.05 c | |
| Pn(μmol m−2 s−1) | CK | 1.78 ± 0.10 bcd | 1.91 ± 0.09 b | 1.88 ± 0.08 d | 1.91 ± 0.09 f | 1.94 ± 0.10 e | 1.93 ± 0.05 d | 1.89 ± 0.09 e | 1.95 ± 0.10 d | 1.98 ± 0.10 c | 1.95 ± 0.11 c |
| SCU1 | 1.86 ± 0.05 a | 2.06 ± 0.05 a | 2.28 ± 0.08 a | 2.46 ± 0.05 a | 2.74 ± 0.05 a | 2.43 ± 0.05 a | 2.16 ± 0.05 c | - | - | - | |
| SCU2 | 1.81 ± 0.07 abc | 2.00 ± 0.07 a | 2.08 ± 0.08 b | 2.26 ± 0.05 b | 2.47 ± 0.08 b | 2.34 ± 0.05 b | 2.02 ± 0.06 d | - | - | - | |
| SCU3 | 1.84 ± 0.12 ab | 1.89 ± 0.07 b | 1.97 ± 0.05 c | 2.04 ± 0.05 d | 2.35 ± 0.05 c | 2.23 ± 0.08 c | 1.93 ± 0.07 e | - | - | - | |
| RCU1 | 1.78 ± 0.08 bcd | 1.92 ± 0.09 b | 2.02 ± 0.06 bc | 2.12 ± 0.06 c | 2.30 ± 0.09 c | 2.30 ± 0.07 b | 2.43 ± 0.07 a | 2.62 ± 0.08 a | 2.45 ± 0.05 a | 2.39 ± 0.09 a | |
| RCU2 | 1.75 ± 0.05 cd | 1.87 ± 0.09 b | 1.96 ± 0.05 c | 2.00 ± 0.07 de | 2.06 ± 0.10 d | 2.22 ± 0.08 c | 2.27 ± 0.08 b | 2.33 ± 0.07 b | 2.21 ± 0.09 b | 2.16 ± 0.07 b | |
| RCU3 | 1.73 ± 0.05 d | 1.89 ± 0.09 b | 1.88 ± 0.09 d | 1.97 ± 0.08 e | 1.97 ± 0.09 e | 1.95 ± 0.10 d | 2.12 ± 0.08 c | 2.23 ± 0.08 c | 2.19 ± 0.07 b | 2.10 ± 0.08 b | |
| Treatment | Total Starch Content/% FW | Amylose Content/% FW | Amylopectin Content/% FW | Yield/kg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early | Middle | Late | Early | Middle | Late | Early | Middle | Late | ||
| CK | 5.80 ± 0.16 d | 8.60 ± 0.22 c | 15.54 ± 0.25 cd | 2.15 ± 0.08 c | 3.30 ± 0.10 cd | 4.81 ± 0.15 c | 3.65 ± 0.10 a | 5.30 ± 0.11 cd | 10.73 ± 0.10 bcd | 27.92 ± 3.93 e |
| SCU1 | 6.58 ± 0.08 a | 9.38 ± 0.18 ab | 16.58 ± 0.17 a | 2.74 ± 09 a | 3.85 ± 0.87 a | 5.68 ± 0.19 a | 3.84 ± 0.05 a | 5.54 ± 0.26 bcd | 10.90 ± 0.31 bc | 44.35 ± 1.55 b |
| SCU2 | 6.02 ± 0.13 cd | 8.61 ± 0.16 c | 15.29 ± 0.15 d | 2.39 ± 0.15 b | 3.23 ± 0.11 d | 4.94 ± 0.14 c | 3.63 ± 0.28 a | 5.38 ± 0.06 cd | 10.36 ± 0.29 d | 35.63 ± 1.44 c |
| SCU3 | 6.11 ± 0.16 bc | 8.60 ± 0.17 c | 15.36 ± 0.10 d | 2.25 ± 0.13 bc | 3.33 ± 0.06 cd | 4.73 ± 0.05 c | 3.86 ± 0.24 a | 5.27 ± 0.22 d | 10.64 ± 0.14 cd | 37.92 ± 2.03 c |
| RCU1 | 6.34 ± 0.15 ab | 9.67 ± 0.21 a | 16.75 ± 0.17 a | 2.35 ± 0.07 b | 3.52 ± 0.08 b | 5.22 ± 0.10 b | 3.99 ± 0.22 a | 6.15 ± 0.17 a | 11.53 ± 0.20 a | 47.06 ± 3.56 a |
| RCU2 | 6.15 ± 0.17 bc | 9.32 ± 0.16 b | 16.01 ± 0.13 b | 2.40 ± 0.05 b | 3.46 ± 0.11 bc | 4.92 ± 0.13 c | 3.75 ± 0.18 a | 5.86 ± 0.24 a | 11.09 ± 0.25 b | 37.53 ± 3.52 c |
| RCU3 | 6.09 ± 0.21 bc | 9.10 ± 0.20 b | 15.71 ± 0.17 c | 2.27 ± 0.06 bc | 3.46 ± 0.09 bc | 4.88 ± 0.16 c | 3.82 ± 0.20 a | 5.64 ± 0.11 bc | 10.83 ± 0.04 bc | 32.02 ± 2.24 d |
| Treatment | PV (cP) | HV (cP) | BV (cP) | FV (cP) | SV (cP) | Ptime (min) | Ptemp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6781 ± 28 c | 2112 ± 29 c | 4669 ± 11 de | 2572 ± 33 cd | 460 ± 7 c | 3.52 ± 0.02 cd | 73.83 ± 0.03 c |
| SCU1 | 6545 ± 25 e | 1856 ± 11 e | 4689 ± 61 cd | 2484 ± 13 e | 628 ± 33 a | 3.64 ± 0.07 a | 74.65 ± 0.27 a |
| SCU2 | 6886 ± 12 b | 2164 ± 30 c | 4722 ± 28 bc | 2718 ± 33 b | 554 ± 25 b | 3.53 ± 0.03 c | 74.15 ± 0.10 b |
| SCU3 | 7043 ± 30 a | 2321 ± 11 a | 4822 ± 38 a | 2794 ± 49 a | 473 ± 11 c | 3.47 ± 0.04 d | 73.15 ± 0.07 e |
| RCU1 | 6630 ± 55 d | 1986 ± 59 d | 4644 ± 56 e | 2536 ± 46 de | 550 ± 13 b | 3.59 ± 0.05 b | 74.17 ± 0.11 b |
| RCU2 | 6982 ± 37 a | 2246 ± 34 b | 4736 ± 35 b | 2603 ± 33 c | 357 ± 17 d | 3.47 ± 0.03 d | 73.53 ± 0.13 d |
| RCU3 | 6840 ± 50 bc | 2164 ± 36 c | 4676 ± 14 de | 2613 ± 26 c | 449 ± 12 c | 3.54 ± 0.02 c | 73.65 ± 0.13 cd |
| Starch Content | Key Enzymes | SCU Treatment | RCU Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early | Middle | Late | Early | Middle | Late | ||
| Total starch content | GBSS | 0.92 | 0.97 * | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.89 * | 0.32 |
| SBE | 0.99 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.93 * | 0.99 ** | 0.85 * | 0.21 | |
| SSS | 0.96 * | 0.86 | 0.87 | −0.78 | 0.98 ** | 0.78 * | |
| Amylose content | GBSS | 0.82 | 0.98 ** | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.88 * | 0.32 |
| SBE | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.67 * | 0.84 | 0.78 * | 0.71 * | |
| SSS | 0.88 | 0.77 | 0.62 | −0.37 | 0.76 * | 0.13 | |
| Amylopectin content | GBSS | 0.74 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.99 ** | 0.83 * | 0.31 |
| SBE | 0.64 | 0.98 ** | 0.60 | 0.90 | 0.87 * | 0.25 | |
| SSS | 0.80 | 0.96 * | 0.52 | −0.94 | 0.92 ** | 0.81 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Deng, K.; Wu, P.; Feng, K.; Zhao, S.; Li, L. Effects of Slow-Release Fertilizer on Lotus Rhizome Yield and Starch Quality under Different Fertilization Periods. Plants 2023, 12, 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061311
Zhu Y, Deng K, Wu P, Feng K, Zhao S, Li L. Effects of Slow-Release Fertilizer on Lotus Rhizome Yield and Starch Quality under Different Fertilization Periods. Plants. 2023; 12(6):1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061311
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yamei, Kangming Deng, Peng Wu, Kai Feng, Shuping Zhao, and Liangjun Li. 2023. "Effects of Slow-Release Fertilizer on Lotus Rhizome Yield and Starch Quality under Different Fertilization Periods" Plants 12, no. 6: 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061311
APA StyleZhu, Y., Deng, K., Wu, P., Feng, K., Zhao, S., & Li, L. (2023). Effects of Slow-Release Fertilizer on Lotus Rhizome Yield and Starch Quality under Different Fertilization Periods. Plants, 12(6), 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061311






