Transcriptome Sequencing of Agave amaniensis Reveals Shoot-Related Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in Agave
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
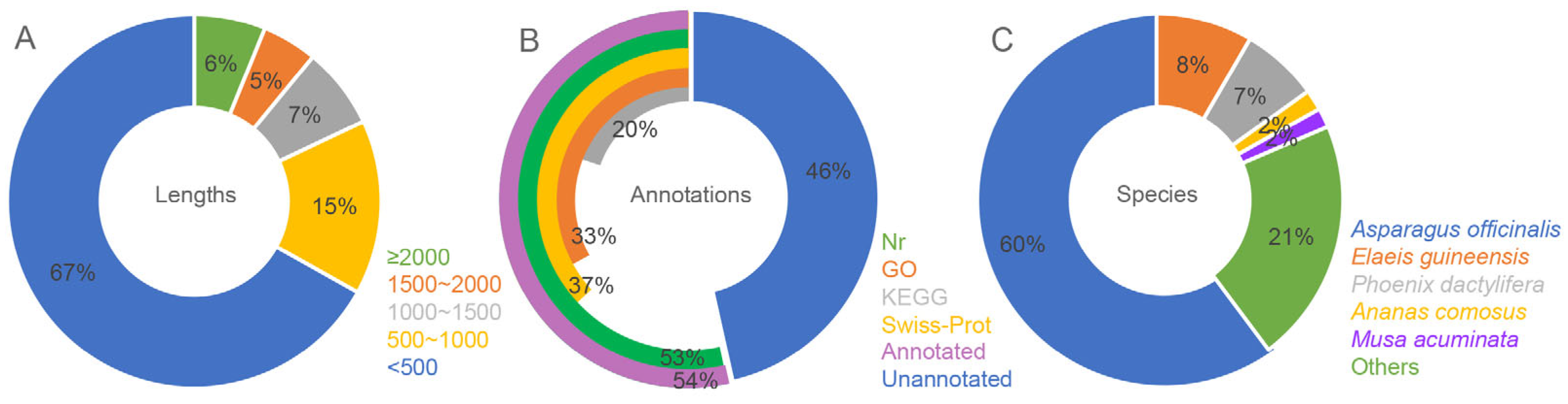
2.1. Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation of A. amaniensis
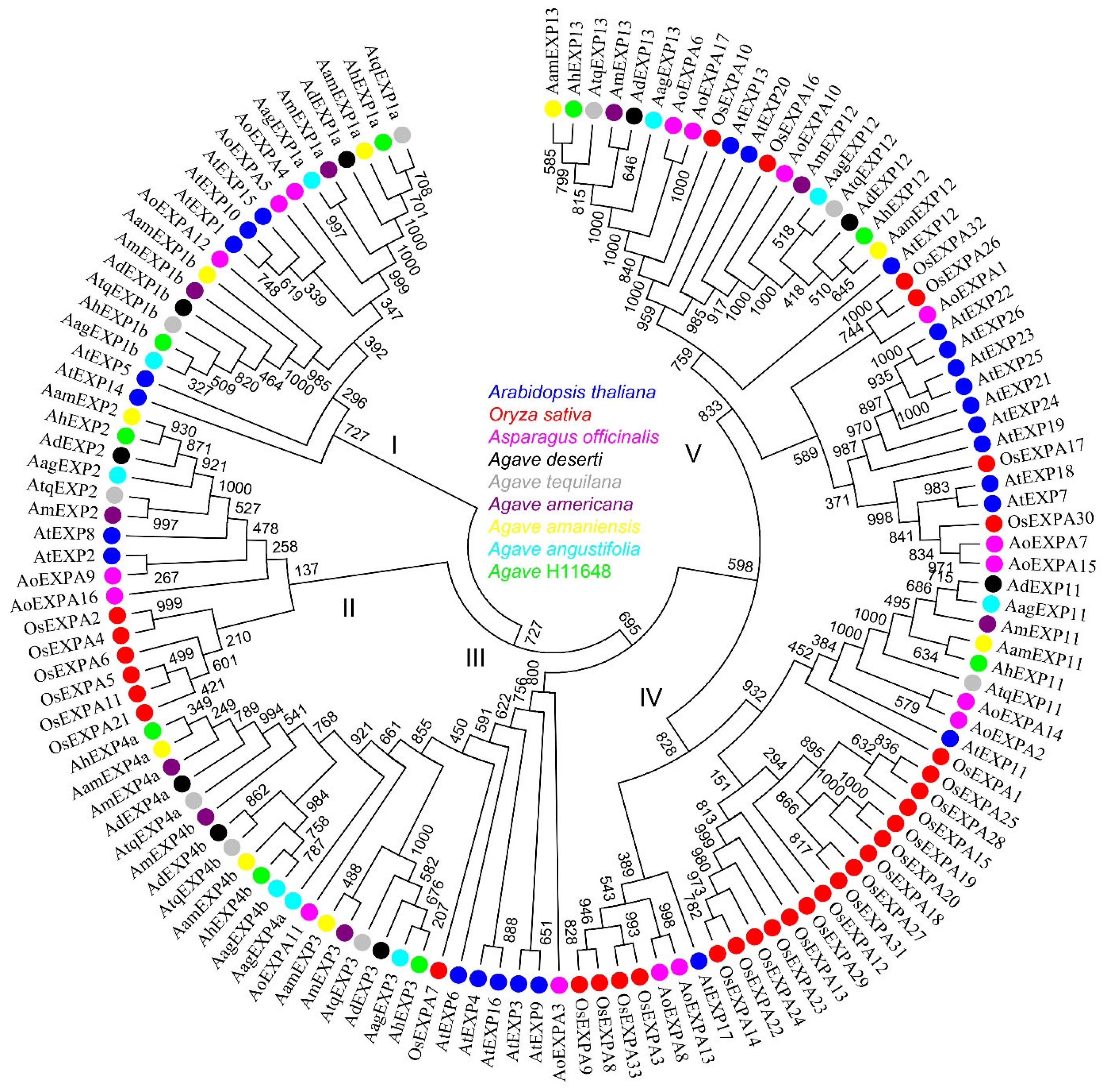
2.2. Identification and Cloning of Expansin A Genes in Agave Species
2.3. Phylogeny of Expansin Genes
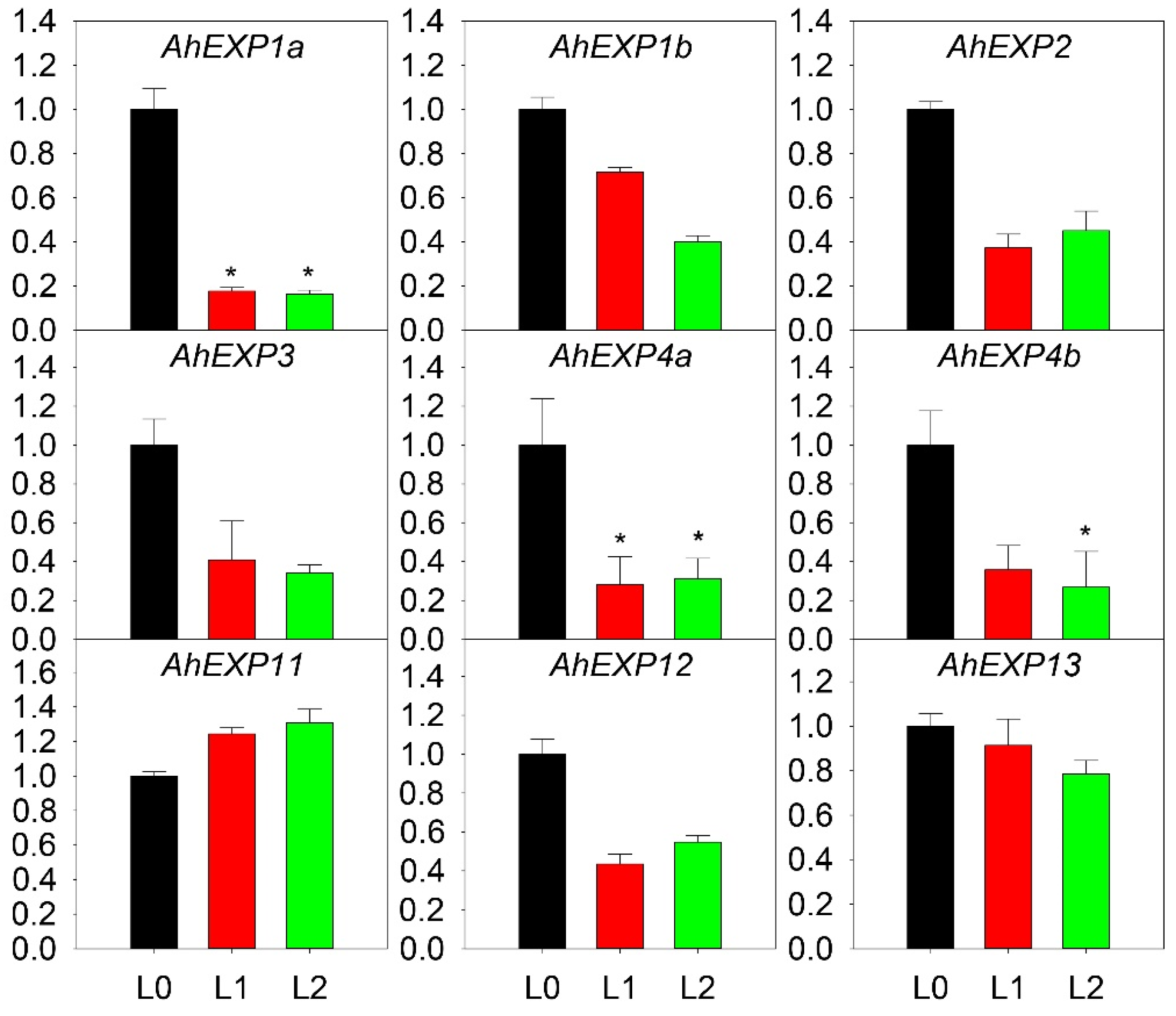
2.4. Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in A. H11648
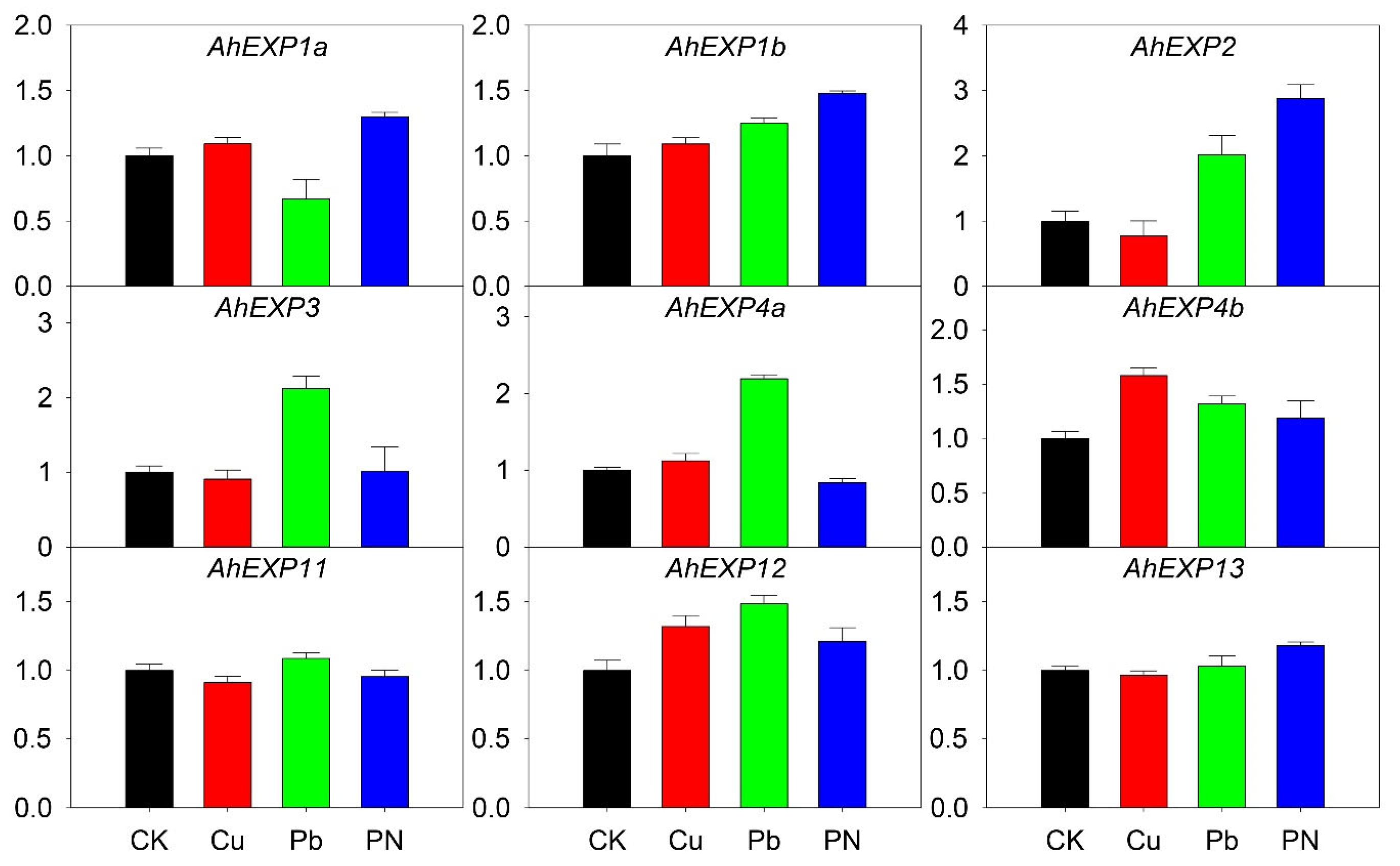
2.5. Expression of Expansin A Genes under Abiotic and Biotic Stresses
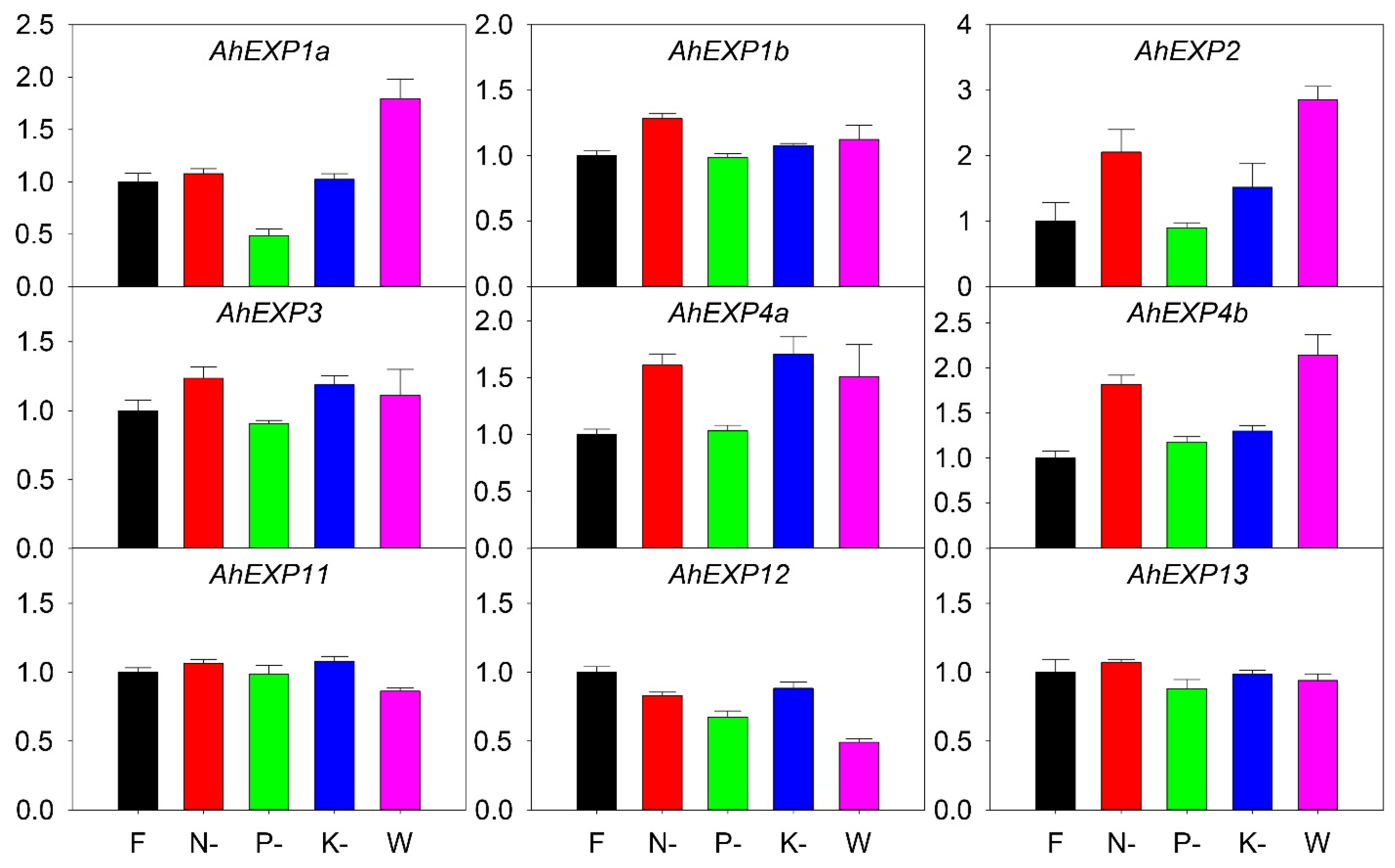
2.6. Expression of Expansin A Genes under Nutrient Deficiency
3. Discussion
3.1. Characterization of A. amaniensis Transcriptome
3.2. Candidate Expansin A Genes in Shoot Development of Agave
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and RNA Extraction
4.2. Transcriptome Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
4.3. Characterization and Phylogeny of Expansin Genes
4.4. Expression Patterns of Agave Expansin Genes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borland, A.M.; Griffiths, H.; Hartwell, J.; Smith, J.A. Exploiting the potential of plants with crassulacean acid metabolism for bioenergy production on marginal lands. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2879–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R. Agave as a model CAM crop system for a warming and drying world. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Romero, J.C.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A.; Pena-Ramos, E.A.; Gonzalez-Rios, H. Biological activities of Agave by-products and their possible applications in food and pharmaceuticals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Tan, S.; Qin, X.; Huang, X.; Xi, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, T.; Yi, K. The complete chloroplast genome of Agave amaniensis (Asparagales: Asparagaceae: Agavoideae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2022, 7, 1519–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xiao, M.; Xi, J.; He, C.; Zheng, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Liang, Y.; et al. De Novo transcriptome assembly of Agave H11648 by Illumina Sequencing and identification of cellulose synthase genes in Agave species. Genes 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, B.; Xi, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Zheng, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; et al. Transcriptome comparison reveals distinct selection patterns in domesticated and wild Agave species, the important CAM plants. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 5716518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, B.; Tan, S.; Huang, Y.; Xi, J.; Qin, X.; Chen, T.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Yi, K. Transcriptome sequencing of Agave angustifolia reveals conservation and diversification in the expression of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase genes in Agave species. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.L.; Lim, K.Y.; Hanson, L.; Sanchez-Teyer, F.; Bennett, M.D.; Leitch, A.R.; Leitch, I.J. Wild and agronomically important Agave species (Asparagaceae) show proportional increases in chromosome number, genome size, and genetic markers with increasing ploidy. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 158, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.C. Next-generation sequencing transforms today’s biology. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.S.; Anderson, C.T. Small molecule probes for plant cell wall polysaccharide imaging. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Plant expansins: Diversity and interactions with plant cell walls. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, J.; Cosgrove, D.J. The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kende, H.; Bradford, K.; Brummell, D.; Cho, H.T.; Cosgrove, D.; Fleming, A.; Gehring, C.; Lee, Y.; McQueen-Mason, S.; Rose, J.; et al. Nomenclature for members of the expansin superfamily of genes and proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 55, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Meng, J.; Niu, L.; Pan, L.; Lu, Z.; Cui, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, W. Transcriptomic and metabolic analyses reveal the mechanism of ethylene production in stony hard peach fruit during cold storage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Peng, D. Cloning of expansin genes in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) based on universal fast walking. Gene 2015, 569, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuqamar, S.; Ajeb, S.; Sham, A.; Enan, M.R.; Iratni, R. A mutation in the expansin-like A2 gene enhances resistance to necrotrophic fungi and hypersensitivity to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Quintana, L.; Barrera, A.; Hereme, R.; Jara, K.; Rivera-Mora, C.; Valenzuela-Riffo, F.; Gundel, P.E.; Pollmann, S.; Ramos, P. Molecular and structural characterization of expansins modulated by fungal endophytes in the Antarctic Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. Exposed to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Y. Bulk segregation analysis in the NGS era: A review of its teenage years. Plant J. 2022, 109, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdlickova, R.; Toloue, M.; Tian, B. RNA-Seq methods for transcriptome analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, H.; Togi, S.; Niida, Y. A comparison of mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) library preparation methods for transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics 2022, 23, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadamoto, H.; Takahashi, H.; Okada, T.; Kenmoku, H.; Toyota, M.; Asakawa, Y. De novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis of the central nervous system of mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis by deep RNA sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tu, L.; Pettolino, F.A.; Ji, S.; Hao, J.; Yuan, D.; Deng, F.; Tan, J.; Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. GbEXPATR, a species-specific expansin, enhances cotton fibre elongation through cell wall restructuring. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, M.J.; Deyholos, M.K. Microarray analysis of developing flax hypocotyls identifies novel transcripts correlated with specific stages of phloem fibre differentiation. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrayanto, G.; Rahayu, L.; Rahman, A.; Noeraeni, P.E. Effect of calcium, strontium, and magnesium ions on the formation of Phytosteroids in callus cultures of Agave amaniensis. Planta Med. 1993, 59, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.; Botura, M.B.; Dos, S.J.; Argolo, D.S.; Da, S.V.; Da, S.G.; de Lima, H.G.; Braz, F.R.; Vieira, I.; Branco, A.; et al. Saponin-rich fraction from Agave sisalana: Effect against malignant astrocytic cells and its chemical characterisation by ESI-MS/MS. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.R.; Byrt, C.S.; Bauer, S.; DeBolt, S.; Chambers, D.; Holtum, J.A.; Karem, G.; Henderson, M.; Lahnstein, J.; Beahan, C.T.; et al. Prospecting for energy-rich renewable raw materials: Agave leaf case study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e135382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Yu, J.; Huang, B. Identification of expansin genes as promoting or repressing factors for leaf elongation in tall fescue. Physiol. Plant 2023, 175, e13861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Tuteja, N. NPKS uptake, sensing, and signaling and miRNAs in plant nutrient stress. Protoplasma 2016, 253, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xi, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Yi, K. Phylogeny and expression atlas of the nitrate transporter 1/peptide transporter family in Agave. Plants 2022, 11, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.Y.; Guo, B.; Li, X.; Liao, X.; Qi, Z. A primary research on sisal’s uptake property and the accumulation rule to Pb ions. J. Agro Environ. Sci. 2007, 26, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Sisal tolerance of cupreous and its accumulation preliminary explore. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2006, 22, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Luo, P.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, C.; Dai, Z.; et al. AFLP analysis and zebra disease resistance identification of 40 sisal genotypes in China. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 6379–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Bao, Y.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; An, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Peng, D. Transcript profiling reveals auxin and cytokinin signaling pathways and transcription regulation during in vitro organogenesis of Ramie (Boehmeria nivea L. Gaud). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, K.; Shutov, O.; Lapoint, R.; Kimelman, M.; Brister, J.R.; O’Sullivan, C. The sequence read archive: A decade more of explosive growth. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D387–D390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D61–D65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank and its supplement TrEMBL in 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, D.W. Using the basic local alignment search tool (BLAST). CSH Protoc. 2007, 2007, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, S.M.; Martin, J.A.; Simpson, J.; Abraham-Juarez, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Visel, A. De novo transcriptome assembly of drought tolerant CAM plants, Agave deserti and Agave tequilana. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, P.E.; Yin, H.; Borland, A.M.; Weighill, D.; Lim, S.D.; De Paoli, H.C.; Engle, N.; Jones, P.C.; Agh, R.; Weston, D.J.; et al. Transcript, protein and metabolite temporal dynamics in the CAM plant Agave. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkess, A.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C.; Bowers, J.E.; Van der Hulst, R.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Mercati, F.; Riccardi, P.; McKain, M.R.; Kakrana, A.; et al. The asparagus genome sheds light on the origin and evolution of a young Y chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKain, M.R.; Wickett, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ayyampalayam, S.; McCombie, W.R.; Chase, M.W.; Pires, J.C.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J. Phylogenomic analysis of transcriptome data elucidates co-occurrence of a paleopolyploid event and the origin of bimodal karyotypes in Agavoideae (Asparagaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2−ΔΔCT method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]

| Genes | Forward Primers | Reverse Primers | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AhEXP1a | CAGTACAGGGCTGGGATTGT | CTGGCCATTGAGGTAGGTGT | 234 |
| AhEXP1b | AACAATGGGAGGAGCTTGTG | GCATTGTTTGGGAGAGCATT | 216 |
| AhEXP2 | GCACCTTCAGTGGCTTCTTC | AGAGATTGCCGTACCCACAG | 181 |
| AhEXP3 | ATGGCTCCCCTTGCTATTCT | TGGCTGTACAAATTGCCGTA | 179 |
| AhEXP4a | TTCTCTCTCTCTGGCCCTCA | AAATAACGCCGTGCTTAACG | 226 |
| AhEXP4b | GGGGACATCACGAAGGTCTA | AAGTTTTTCCCGGTGAAGGT | 209 |
| AhEXP11 | GTGCGGTCAGTGCTACAAGA | GCATGGAACCCTTTGGTAGA | 241 |
| AhEXP12 | GCCTGCCTTCATCTCAAAAC | TTCTTACCGTACCCCGACTG | 212 |
| AhEXP13 | CTGGAGATGTGACGGCTGTA | TTGGGTGCAACGTTGTAAGA | 172 |
| PP2A | CCTCCTCCTCCTTCGGTTTG | GCCATGAATGTCACCGCAGA | 235 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, Z.; Tan, S.; Qin, X.; Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Xi, J.; Chen, H.; et al. Transcriptome Sequencing of Agave amaniensis Reveals Shoot-Related Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in Agave. Plants 2023, 12, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12102020
Wang X, Huang X, Chen L, Xie Z, Tan S, Qin X, Chen T, Huang Y, Xi J, Chen H, et al. Transcriptome Sequencing of Agave amaniensis Reveals Shoot-Related Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in Agave. Plants. 2023; 12(10):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12102020
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuxia, Xing Huang, Lisha Chen, Zhouli Xie, Shibei Tan, Xu Qin, Tao Chen, Yanlei Huang, Jingen Xi, Helong Chen, and et al. 2023. "Transcriptome Sequencing of Agave amaniensis Reveals Shoot-Related Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in Agave" Plants 12, no. 10: 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12102020
APA StyleWang, X., Huang, X., Chen, L., Xie, Z., Tan, S., Qin, X., Chen, T., Huang, Y., Xi, J., Chen, H., & Yi, K. (2023). Transcriptome Sequencing of Agave amaniensis Reveals Shoot-Related Expression Patterns of Expansin A Genes in Agave. Plants, 12(10), 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12102020






