Two Non-Necrotic Disease Resistance Types Distinctly Affect the Expression of Key Pathogenic Determinants of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria in Pepper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria and Bacterial Treatments of Leaves
2.2. Plants Materials
2.3. In Planta Bacterial Growth Determination
2.4. RNA Processing and Quantitative PCR Assays
3. Results and Discussion
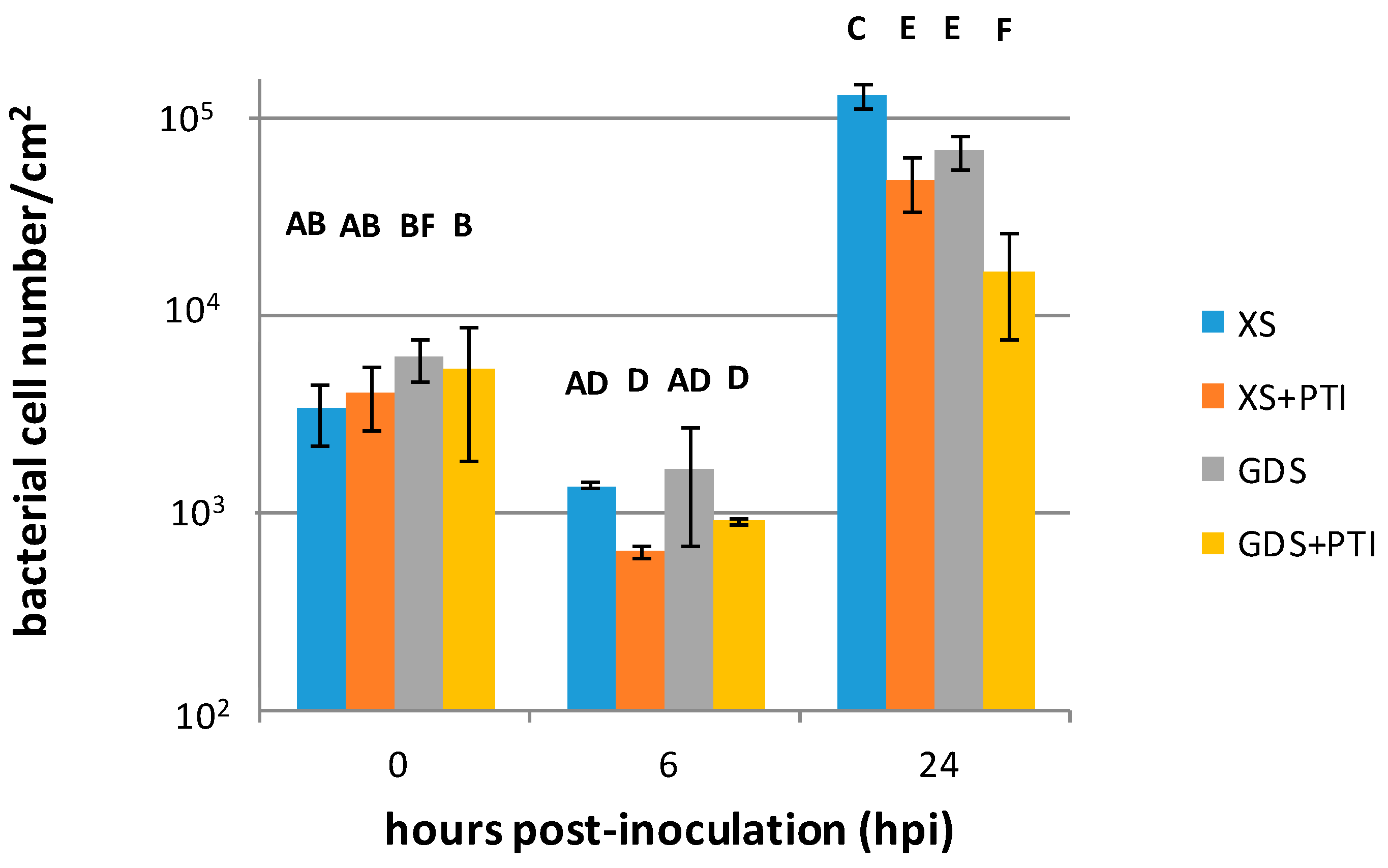
3.1. X. euvesicatoria Multiplies to Varying Degrees in Plants with Different Resistance Responses
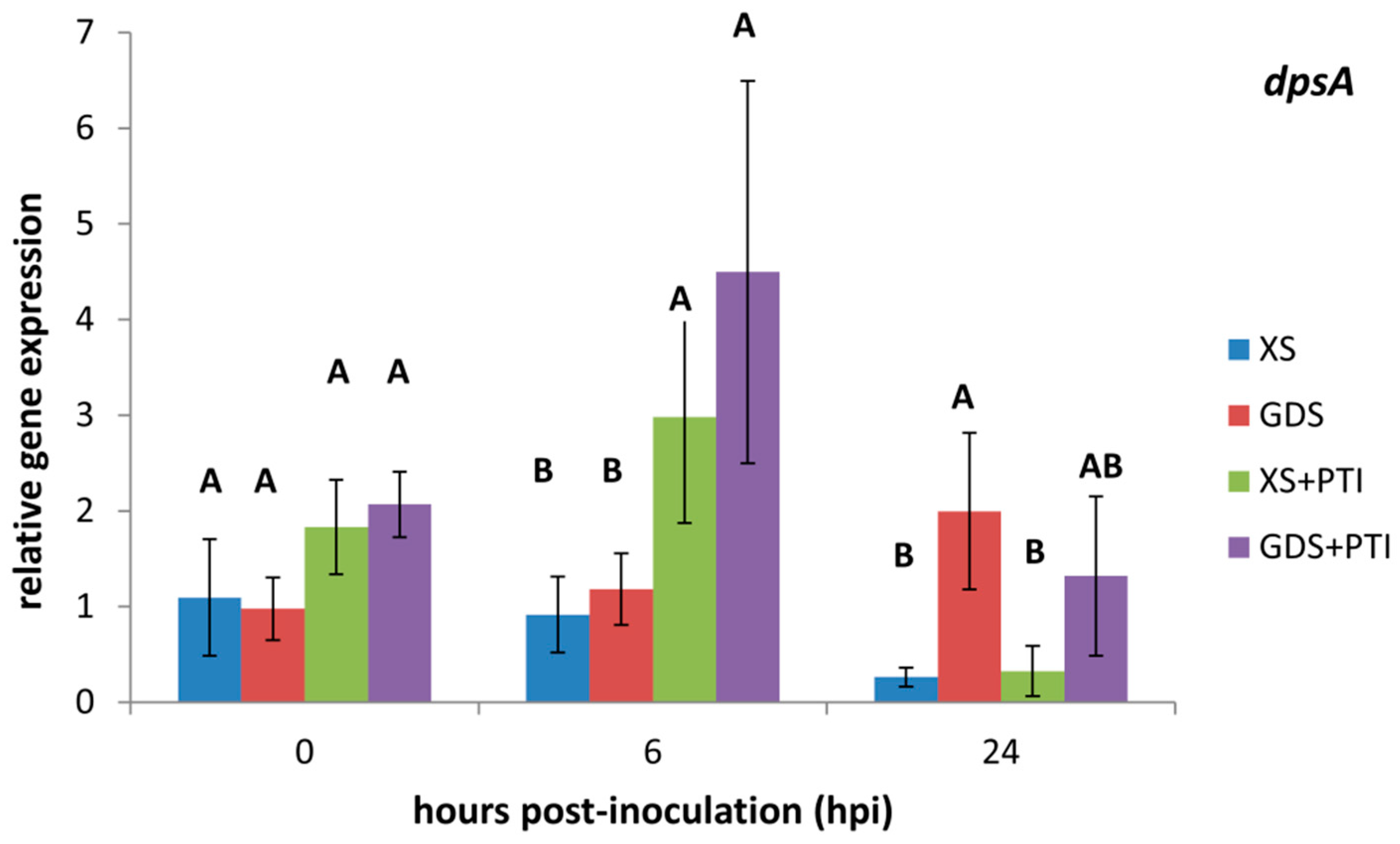
3.2. In Planta Expression of Stress-Related dpsA Gene
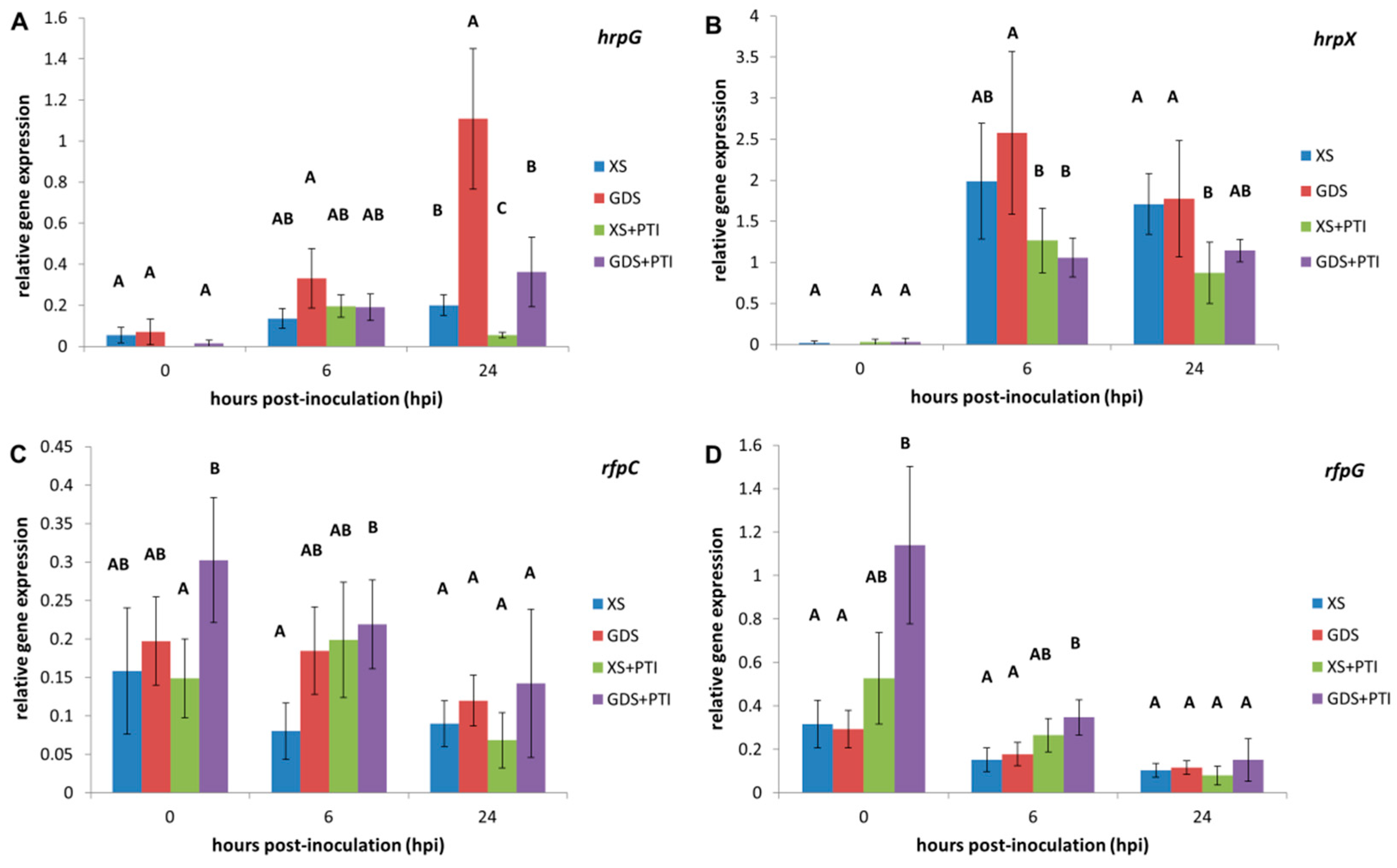
3.3. In Planta Expression of T3SS-Related Regulators
3.4. In Planta Expression of T3SS Structural Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henry, E.; Yadeta, K.A.; Coaker, G. Recognition of Bacterial Plant Pathogens: Local, Systemic and Transgenerational Immunity. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicaise, V.; Roux, M.; Zipfel, C. Recent Advances in PAMP-Triggered Immunity against Bacteria: Pattern Recognition Receptors Watch over and Raise the Alarm. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A Renaissance of Elicitors: Perception of Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns and Danger Signals by Pattern-Recognition Receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.A.; Sundelin, T.; Nielsen, J.T.; Erbs, G. MAMP (Microbe-Associated Molecular Pattern) Triggered Immunity in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, Z.; Bozsó, Z.; Kecskés, M.L.; Besenyei, E.; Arnold, C.; Ott, P.G. Local Early Induced Resistance of Plants as the First Line of Defence against Bacteria. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Eschen-Lippold, L.; Lassowskat, I.; Böttcher, C.; Scheel, D. Cellular Reprogramming through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Saijo, Y.; Nakagami, H.; Takano, Y. Regulation of Sugar Transporter Activity for Antibacterial Defense in Arabidopsis. Science 2016, 354, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shan, L.; He, P. Microbial Signature-Triggered Plant Defense Responses and Early Signaling Mechanisms. Plant Sci. 2014, 228, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.L.S.; Souza, A.A.; Vieira, M.L.C. Molecular Basis for Host Responses to Xanthomonas Infection. Planta 2022, 256, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.S.; Park, D.H.; Collmer, A. Components of the Pseudomonas Syringae Type III Secretion System Can Suppress and May Elicit Plant Innate Immunity. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozsó, Z.; Ott, P.G.; Kecskés, M.L.; Klement, Z. Effect of Heat and Cycloheximide Treatment of Tobacco on the Ability of Pseudomonas Syringae Pv. Syringae 61 Hrp/HrmA Mutants to Cause HR. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1999, 55, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabill, E.; Joe, A.; Block, A.; van Rooyen, J.M.; Alfano, J.R. Plant Immunity Directly or Indirectly Restricts the Injection of Type III Effectors by the Pseudomonas Syringae Type III Secretion System. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, Z. Hypersensitivity. In Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes; Mount, M., Lacy, G.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; Volume 2, pp. 149–177. ISBN 9780323147200. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Tsuda, K.; Parker, J.E. Effector-Triggered Immunity: From Pathogen Perception to Robust Defense. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Gust, A.A.; Nürnberger, T. Plant Immunity Unified. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stall, R.E.; Jones, J.B.; Minsavage, G.V. Durability of Resistance in Tomato and Pepper to Xanthomonads Causing Bacterial Spot. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, T.H.; Dahlbeck, D.; Clark, E.T.; Gajiwala, P.; Pasion, R.; Whalen, M.C.; Stall, R.E.; Staskawicz, B.J. Expression of the Bs2 Pepper Gene Confers Resistance to Bacterial Spot Disease in Tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14153–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dahlbeck, D.; Krasileva, K.V.; Fong, R.W.; Staskawicz, B.J. Computational and Biochemical Analysis of the Xanthomonas Effector AvrBs2 and Its Role in the Modulation of Xanthomonas Type Three Effector Delivery. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Minsavage, G.V.; Roberts, P.D.; Johnson, R.R.; Kousik, C.S.; Subramanian, S.; Stall, R.E. A Non-Hypersensitive Resistance in Pepper to the Bacterial Spot Pathogen Is Associated with Two Recessive Genes. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, C.E.; Jones, V.; Stall, R.E.; Jones, J.B.; Minsavage, G.V.; Schultz, D.C.; Rodrigues, R.; Olsen, L.E.; Mazourek, M. Characterization of Two Recessive Genes Controlling Resistance to All Races of Bacterial Spot in Peppers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szarka, J.; Csilléry, G. Defence Systems against Xanghomonas Campestris Pv. Vesicatoria in Pepper. In Proceedings of the IXth Eucarpia Meeting on Genetics and Breeding on Capsicum and Eggplant, Budapest, Hungary, 21–25 August 1995; pp. 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Szarka, J.; Csilléry, G. General Defense System in the Plant Kingdom. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, G.B.; Szabó, Z.E.; Illiescu, C.; Balogh, M. WO2014068346A2-Identification of a Xanthomonas Euvesicatoria Resistance Gene from Pepper (Capsicum Annuum) and Method for Generating Plants with Resistance-Google Patents 2013. WO2014068346A2, 3 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 2Blades Foundation 2Blades Foundation Technology Patent Estate and Development-2Blades Foundation. Available online: https://2blades.org/projects-and-technology/technology-patent-estate-and-development/ (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Timár, Z.; Palotás, G.; Csilléry, G.; Szarka, J. Study of Recessive Bacterial Leaf Spot Resistance Genes in Capsicum Annuum L. In Proceedings of the Innovations in Genetics and Breeding of Capsicum and Eggplant, Avignon, France, 11–13 September 2019; Lefebvre, V., Daunay, M.-C., Eds.; Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA): Avignon, France, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 132–133. [Google Scholar]
- Büttner, D.; Bonas, U. Regulation and Secretion of Xanthomonas Virulence Factors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teper, D.; Pandey, S.S.; Wang, N. The HrpG/HrpX Regulon of Xanthomonads-an Insight to the Complexity of Regulation of Virulence Traits in Phytopathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.W.; Zhang, L.H. Quorum Sensing and Virulence Regulation in Xanthomonas Campestris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; An, S.-Q.; Allan, J.H.; McCarthy, Y.; Dow, J.M. The DSF Family of Cell–Cell Signals: An Expanding Class of Bacterial Virulence Regulators. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Yao, X.; Duan, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, B.; Qi, P.; Sun, M.; Ruan, L. Two Overlapping Two-Component Systems in Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae Contribute to Full Fitness in Rice by Regulating Virulence Factors Expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.-L.; Jiang, G.-F.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.-C.; Wang, L.; Hang, X.-H.; Tang, J.-L. RpfC Regulates the Expression of the Key Regulator HrpX of the Hrp/T3SS System in Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Campestris. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.R.; Costa, J.R.; Ferreira, M.A.S.V.; Quezado-Duval, A.M. Simultaneous Detection and Identification of the Xanthomonas Species Complex Associated with Tomato Bacterial Spot Using Species-Specific Primers and Multiplex PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašič, K.; Ivanović, M.M.; Ignjatov, M.; Calić, A.; Obradović, A. Isolation and characterization of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria bacteriophages. Journal of Plant Path. 2011, 93, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- King, E.O.; Ward, M.K.; Raney, D.E. Two Simple Media for the Demonstration of Pyocyanin and Fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1954, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Csilléry, G.; Szarka, E.; Sárdi, É.; Mityko, J.; Kapitány, J.; Nagy, B.; Szarka, J. The Unity of Plant Defense: Genetics, Breeding and Physiology. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the XIIth EUCARPIA Meeting on Genetics and Breeding of Capsicum and Eggplant, Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 17–19 May 2004; Voorrips, R., Ed.; European Association for Research on Plant Breeding (EUCARPIA): Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Szarka, J.; Timár, Z.; Hári, R.; Palotás, G.; Péterfi, B. General Defense Response under Biotic Stress and Its Genetics at Pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas De Vaulx, R.; Chambonnet, D.; Pochard, E. Culture in Vitro d’anthères de Piment (Capsicum Annuum L.): Amélioration Des Taux d’obtention de Plantes Chez Différents Génotypes Par Des Traitements à + 35 °C. Agronomie 1981, 1, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, T.R.; Laia, M.L.; Ferro, J.A.; Ferro, M.I.T. Selection and Validation of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Studies by Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR in Xanthomonas Citri Subsp. Citri during Infection of Citrus Sinensis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| GenBank ID a | Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| BJD11_20695 | hrcC | 5’ TCAAAGAAGTGCTGCGTGAT 3’ | 5’ CCAGACAAAGCCGTAGGTG 3’ |
| BJD11_20740 | hrcU | 5’ CCGATTTCATCACCAATAAC 3’ | 5’ AGAAGCCGACCGAGAAGAAACT 3’ |
| BJD11_20785 | hrpE | 5’ CCGATGAACTTGTTGAGTGC 3’ | 5’ GACGAGGCTCAGAAGTCCAT 3’ |
| BJD11_20815 | hrpF | 5’ GCCGATCCAGAACCGAAACA 3’ | 5’ AACTGGGCGGGAAGAACGAC 3’ |
| BJD11_16105 | hrpX | 5’ GACTGCAACATCTCCAACAG 3’ | 5’ CTGATATTCCAGGATCAGCAAC 3’ |
| BJD11_16110 | hrpG | 5’ CGAAGATCAGCAGCTCGCA 3’ | 5’ GATCGGTGTTCCTGTTGACG 3’ |
| BJD11_12825 | rpfC | 5’ CGATCCTGATTTCGCCTTACT 3’ | 5’ ATCAAGCCCAGCAACAATCC 3’ |
| BJD11_12835 | rpfG | 5’ TCGACTTCCTGGTCAAGCCGATCC 3’ | 5’ GCGCTCTTCGACCTCGTTCATGC 3’ |
| BJD11_06505 | dpsA | 5’ CGTTGACCTCGATCCCGGAAGA 3’ | 5’ CTGACGCACCATTTCACGCCAGTC 3’ |
| BJD11_17780 | rpoB | 5’ GGAACTGATCAATGCCAAGCC 3’ | 5’ TCTGGTCCATGAACTGCGAC 3’ |
| BJD11_03830 | atpD | 5’ TACACCATCGCCACCTTGTC 3’ | 5’ GGCAACGACTTCTACCACGAGA 3’ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bozsó, Z.; Krüzselyi, D.; Szatmári, Á.; Csilléry, G.; Szarka, J.; Ott, P.G. Two Non-Necrotic Disease Resistance Types Distinctly Affect the Expression of Key Pathogenic Determinants of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria in Pepper. Plants 2023, 12, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010089
Bozsó Z, Krüzselyi D, Szatmári Á, Csilléry G, Szarka J, Ott PG. Two Non-Necrotic Disease Resistance Types Distinctly Affect the Expression of Key Pathogenic Determinants of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria in Pepper. Plants. 2023; 12(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleBozsó, Zoltán, Dániel Krüzselyi, Ágnes Szatmári, Gábor Csilléry, János Szarka, and Péter G. Ott. 2023. "Two Non-Necrotic Disease Resistance Types Distinctly Affect the Expression of Key Pathogenic Determinants of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria in Pepper" Plants 12, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010089
APA StyleBozsó, Z., Krüzselyi, D., Szatmári, Á., Csilléry, G., Szarka, J., & Ott, P. G. (2023). Two Non-Necrotic Disease Resistance Types Distinctly Affect the Expression of Key Pathogenic Determinants of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria in Pepper. Plants, 12(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010089






