Foliar Application of Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Improves the Growth and Yield of Brown Mustard (Brassica juncea) by Modulating Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Defense, and Osmolyte Production under Lead (Pb) Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
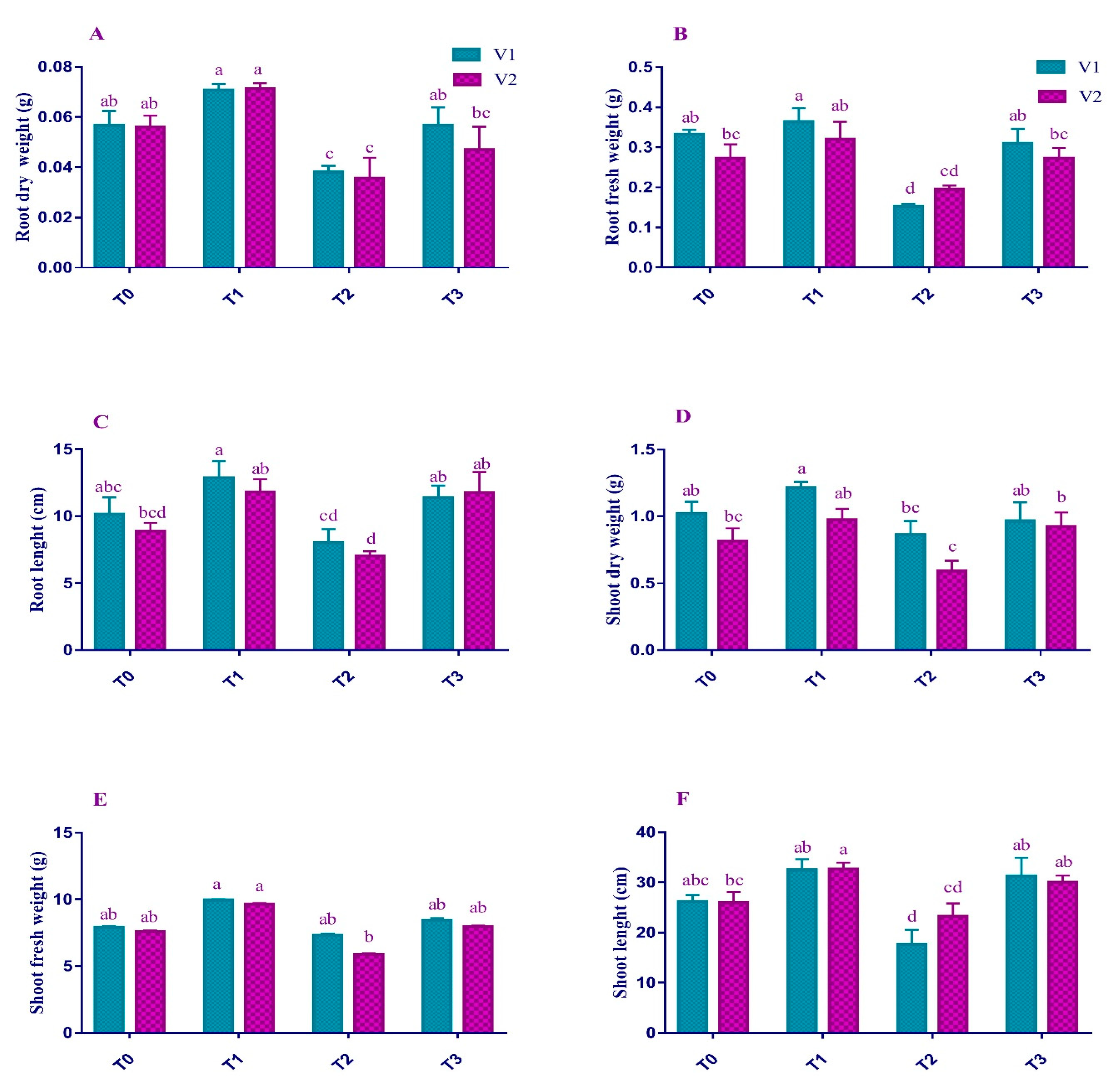
2.1. Morphological Attributes
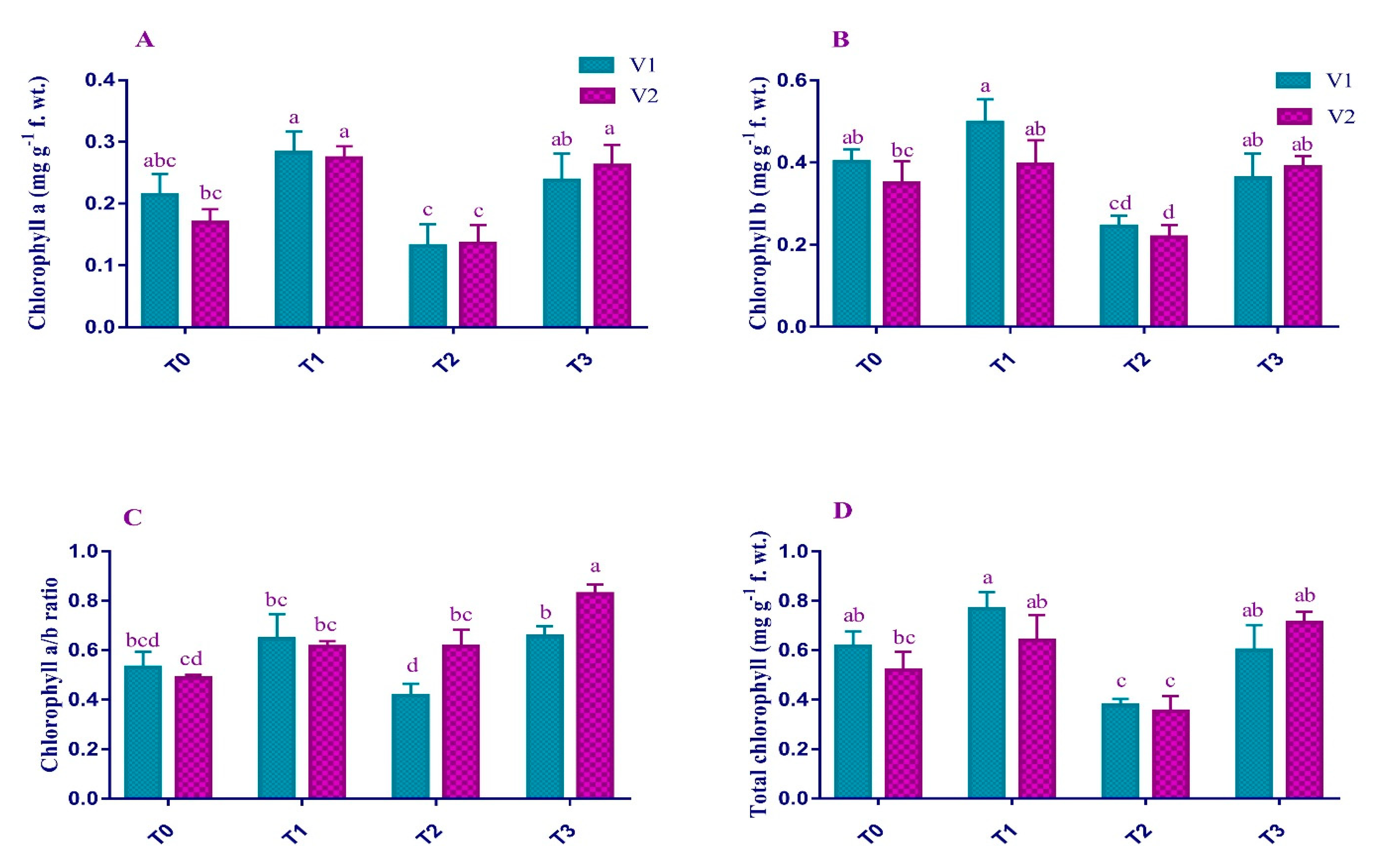
2.2. Photosynthetic Pigments
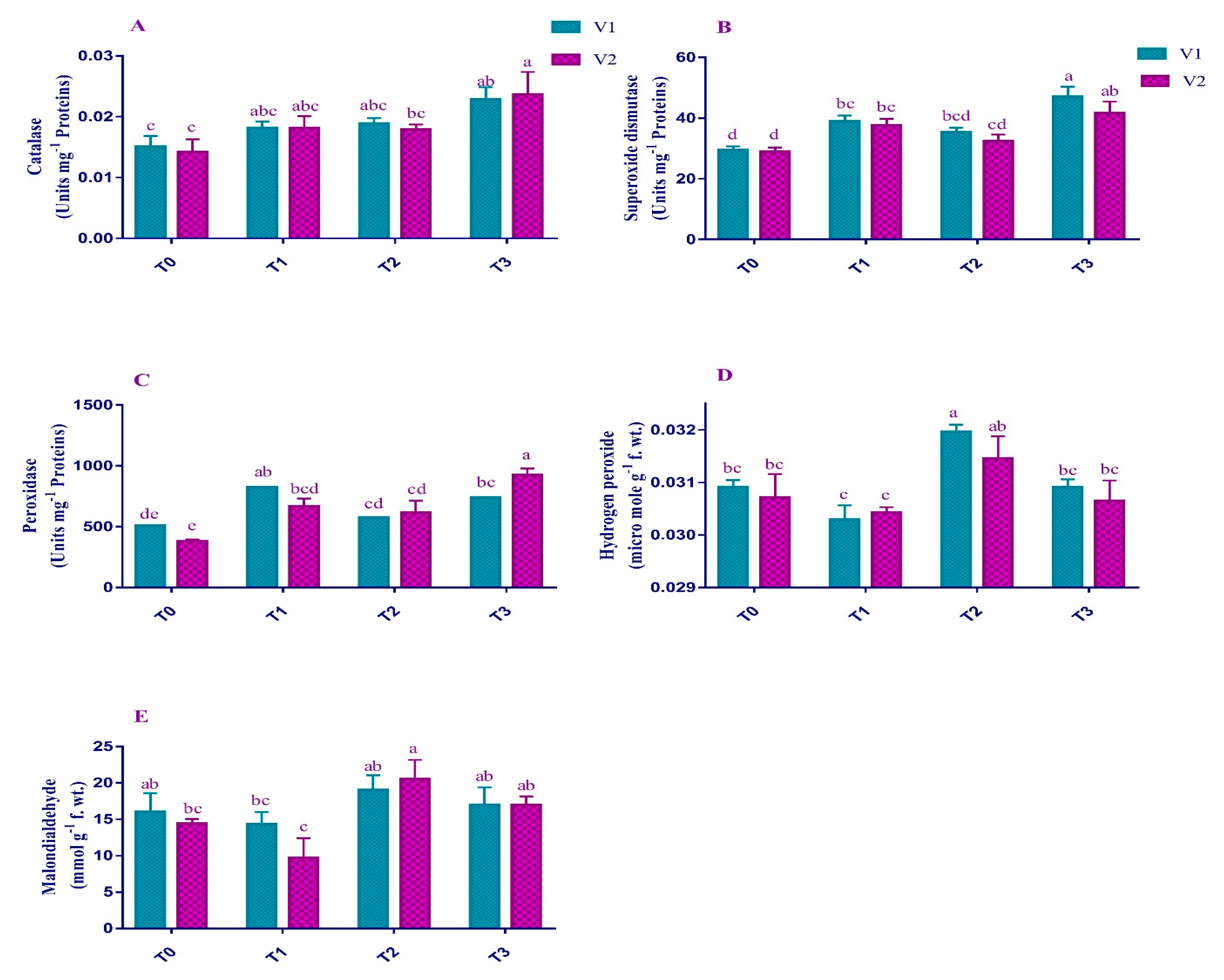
2.3. ROS and Enzymatic Antioxidants
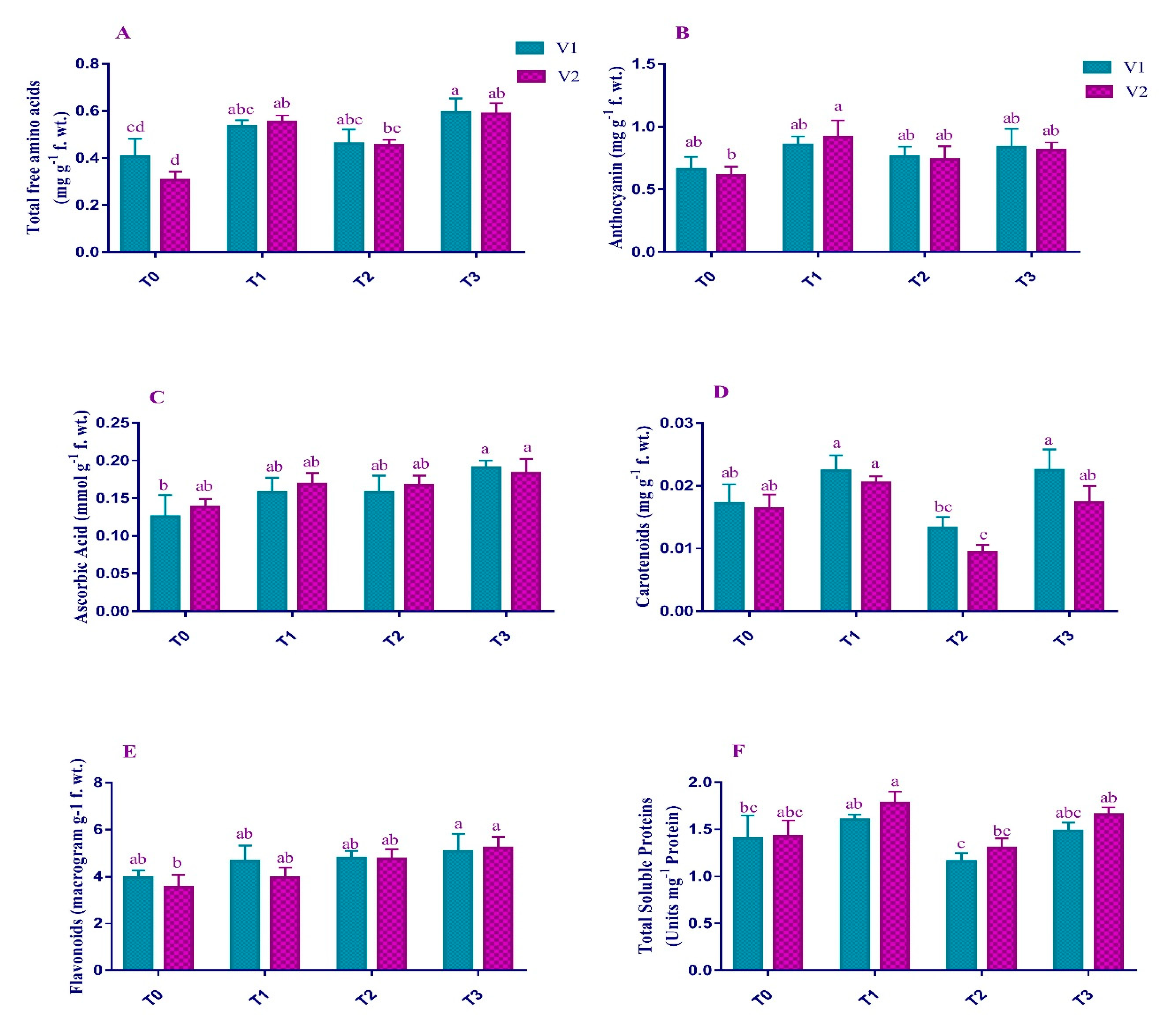
2.4. Non-Enzymatic Antioxidants
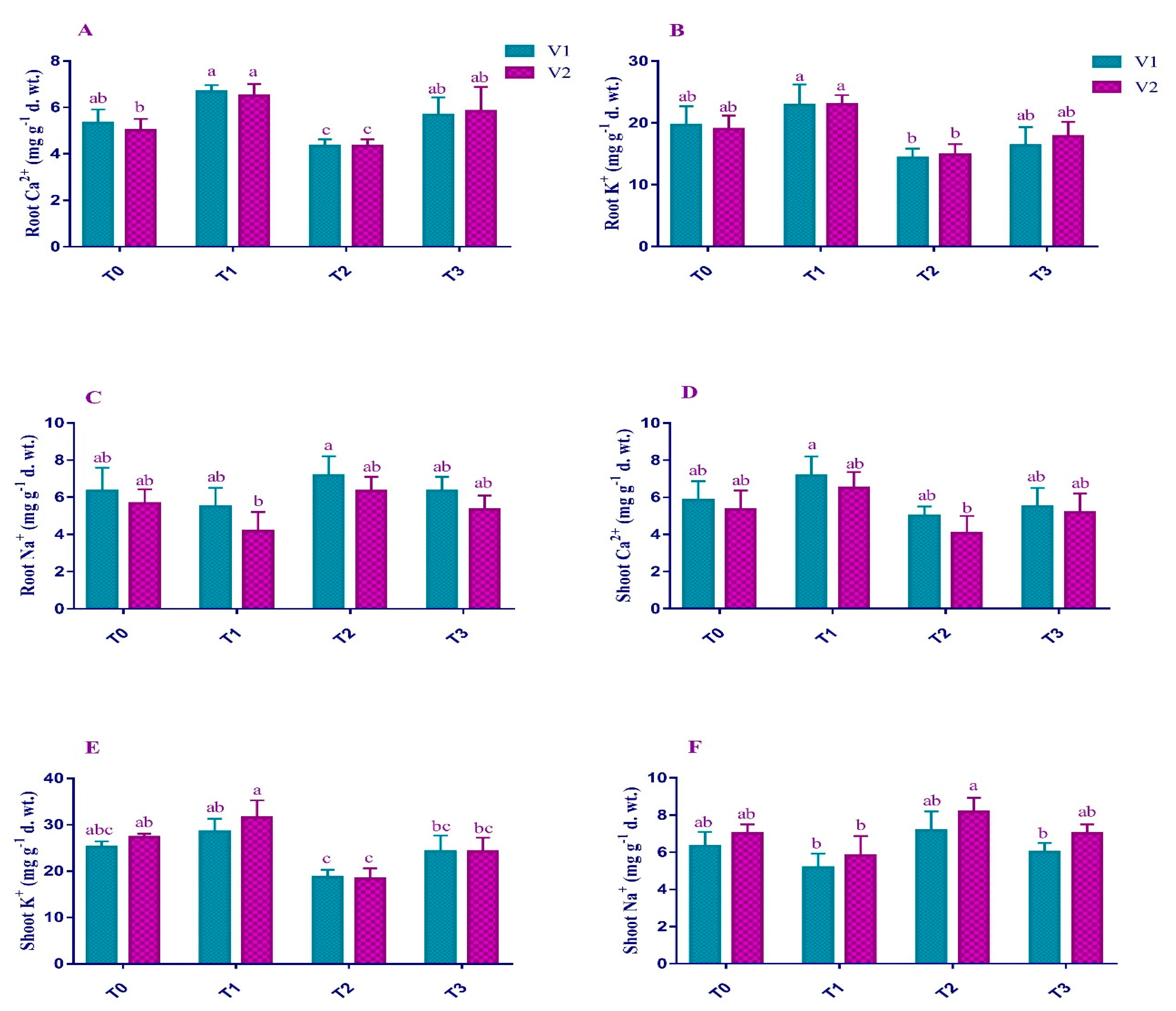
2.5. Mineral Ion Content
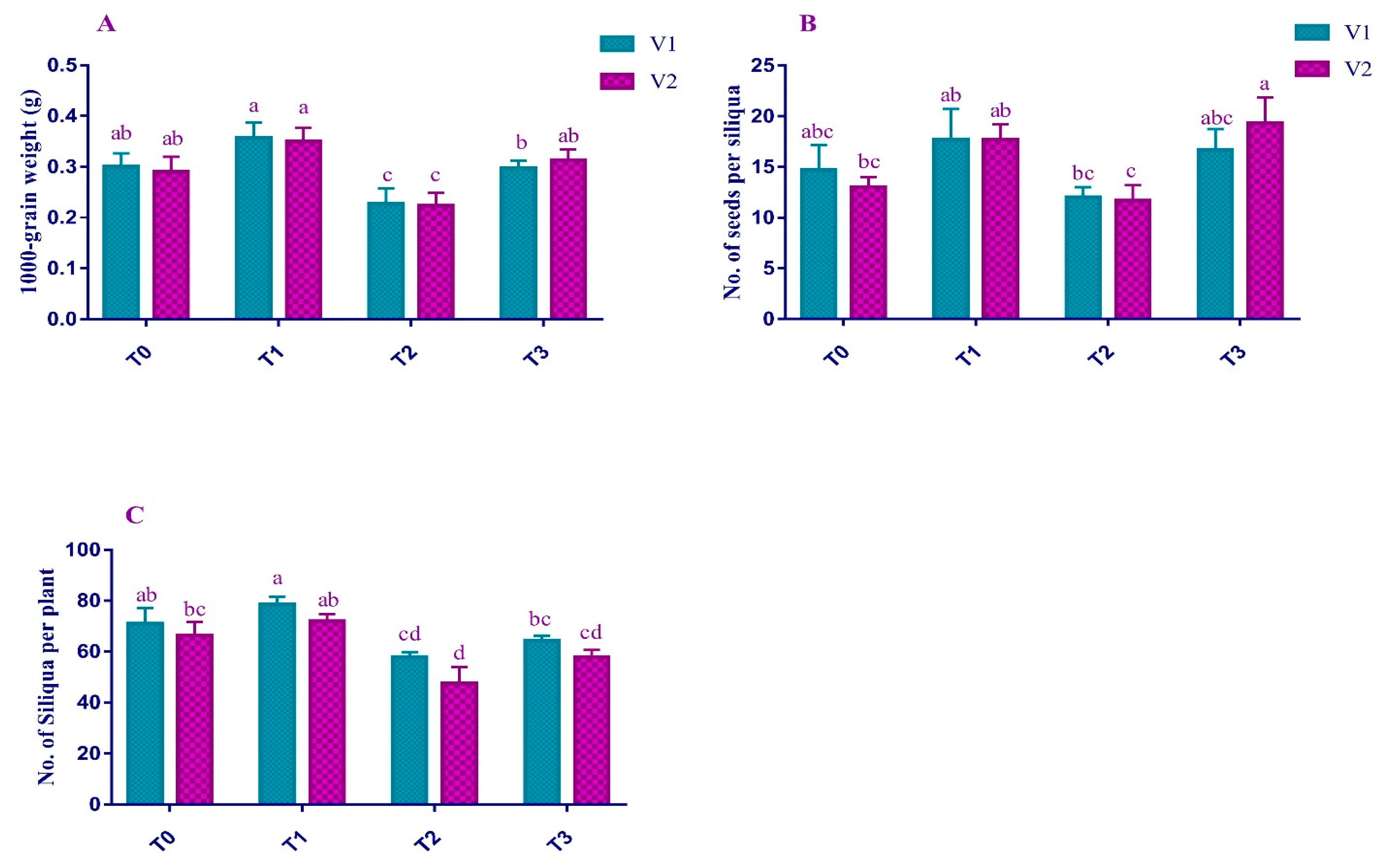
2.6. Yield Attributes
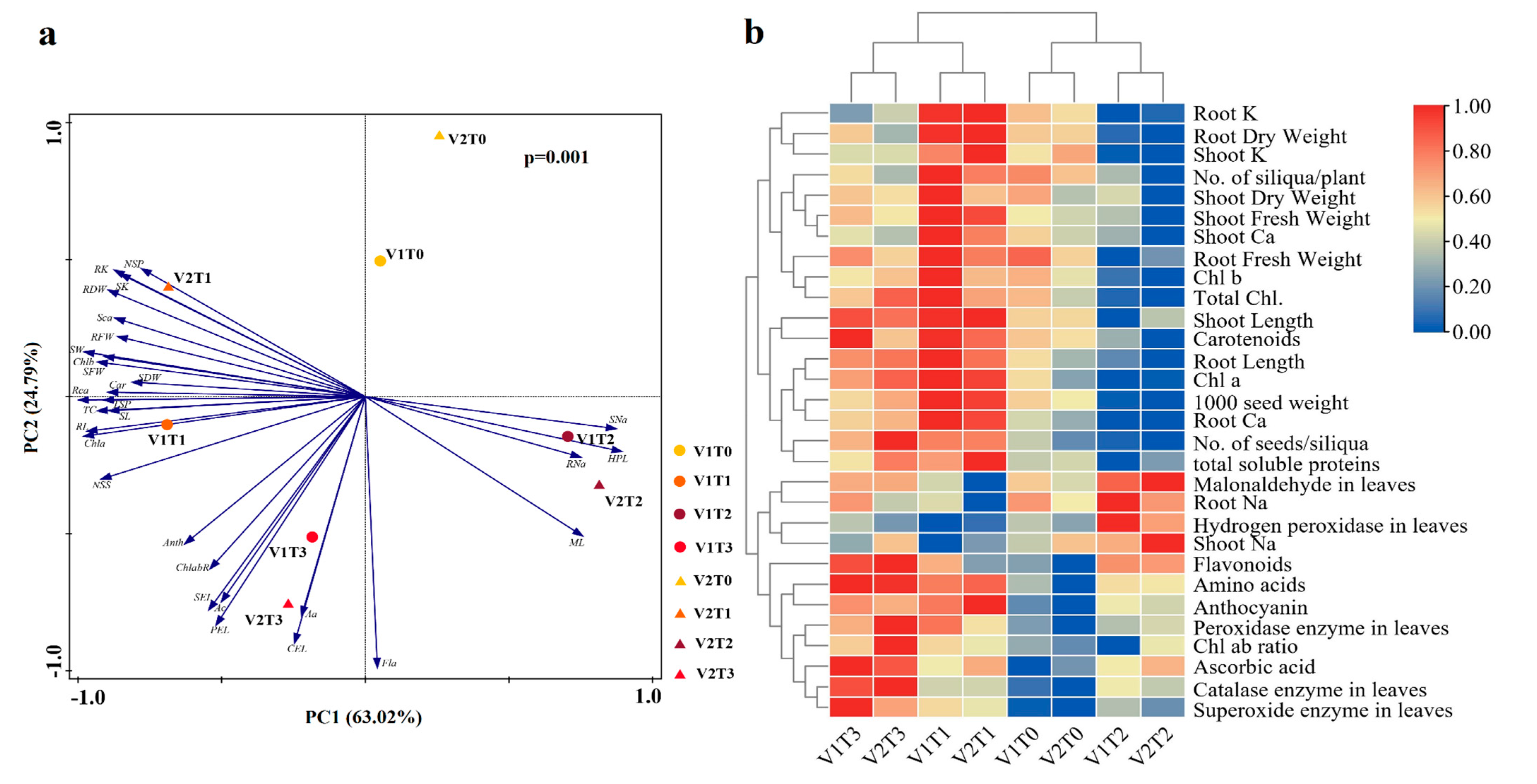
2.7. Principal Components Analysis (PCA) and Heatmap Analysis
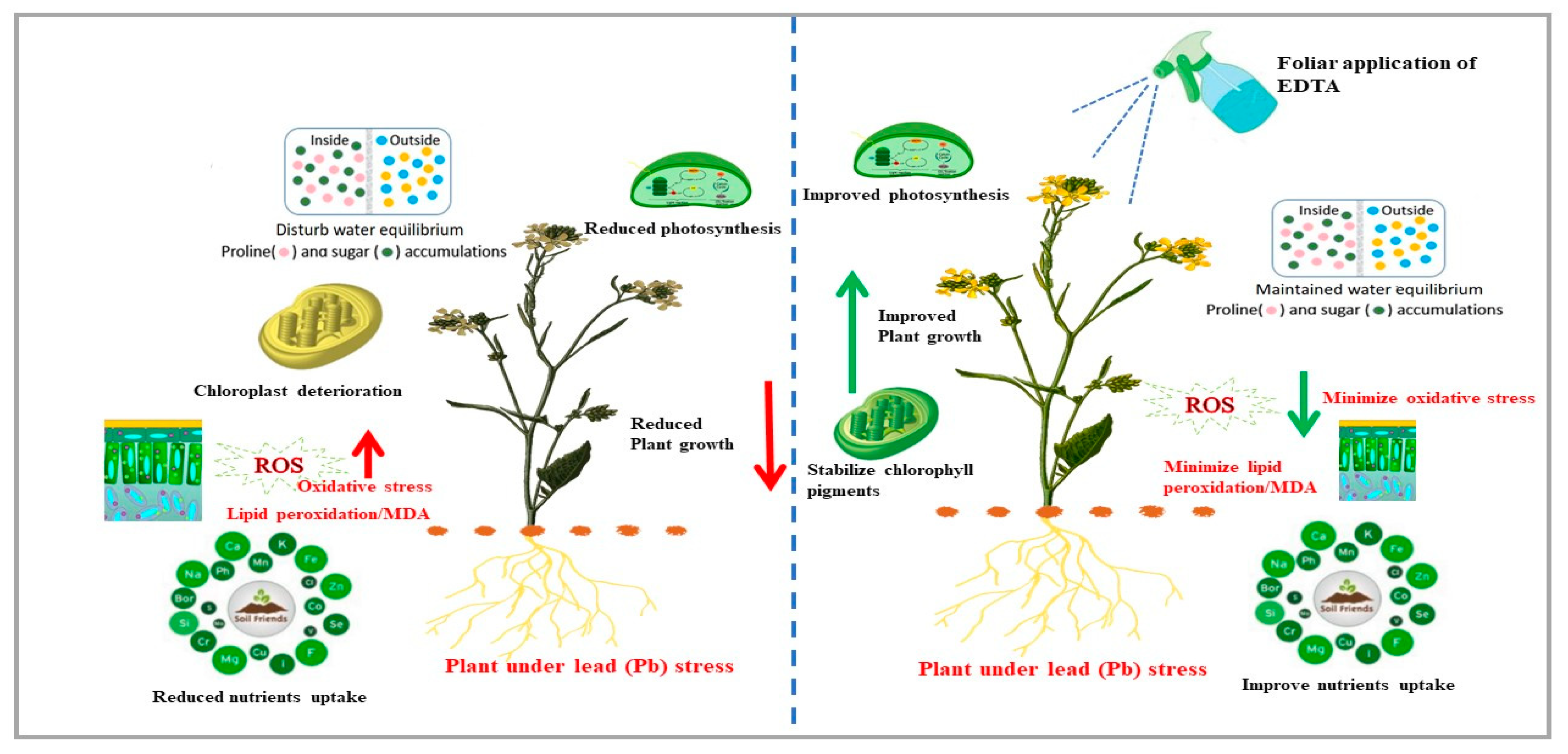
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Experimental Design and Setup
4.3. Morphological Attributes
4.4. Photosynthetic Pigments
4.5. Oxidants Activities in Plant Leaves
4.6. Enzymatic Antioxidants Activities in Plants Leaves
4.7. Non-Enzymatic Antioxidants Activities of Plants
4.8. Ion Analysis (Na+, Ca2+, K+)
4.9. Yield Attributes
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batool, T.; Javied, S.; Ashraf, K.; Sultan, K.; Zaman, Q.U.; Haider, F.U. Alleviation of cadmium stress by silicon supplementation in peas by the modulation of morpho-physio-biochemical variables and health risk assessment. Life 2022, 12, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Jiang, W.; Xiukang, W.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ali, N.; Ishfaq, M.; Kaleem, M.; Haider, F.U. Cadmium phytotoxicity, tolerance, and advanced remediation approaches in agricultural soils; A comprehensive Re-view. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 773815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, W.; Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Junaid, J.; Xu, N.; Rasool, A.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z. Comprehensive review of the basic chemical behaviors, sources, processes, and endpoints of trace element contamination in paddy soil-rice systems in rice-growing countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.U.; Virk, A.L.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Skalicky, M.; Ata-ul-Karim, S.T.; Ahmad, N.; Soufan, W.; Brestic, M.; Sabagh, A.E.L.; Liqun, C. Integrated application of thiourea and biochar improves maize growth, antioxidant activity and reduces cadmium bioavailability in cadmium-contaminated soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 809322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhum, S.A.H. Effect of different dosage from lead acetate administrated on the liver enzymes and histopathological of liver in white male rats. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 11, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Issac, U.E. Ameliorative effect of administering avocado (Persea americana) leaf extract on lead acetate toxicity in the brain-cerebellum of albino rats. J. Complment. Altern. Med. Res. 2020, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Bhardwaj, S.; Ishtiaq, H.; Devi, Y.K.; Kapoor, D. Lead uptake, toxicity and mitigation strategies in plants. Plant Arch. 2021, 21, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, B.; Singh, D. Assessment of different multipurpose tree species for phytoextraction of lead from lead-contaminated soils. Bioremediation J. 2020, 24, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Hans, N.; Kumar, S.; Rani, R. A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Farooq, M.; Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.; Hussain, M.; Ishfaq, M.; Ahmad, M.; Anjum, M.Z. Lead toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.Z.; Archana, K.M.; Krishnaswamy, V.G.; Rajagoparl, R. Remediation of heavy metals (Cr, Zn) using physical, chemical and biological methods: A novel approach. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, J.A.; Shivaraj, S.M.; Singh, P.; Navadagi, D.B.; Tripathi, D.K.; Dash, P.K.; Solanke, A.U.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R. Role of silicon in mitigation of heavy metal stresses in crop plants. Plants 2019, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, B.E.; Guerrero, J.M.; Sokolski, S. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in tropical soils an overview. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Gai, X. Bamboo an untapped plant resource for the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 246, 125–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, A.; Khan, A.A.; Ahmad, G. The potential of thermal power plant fly ash to promote the growth of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) in agricultural soils. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.S.B.; Hasan, E.U.; Tariq, M.; Amir, H.; Qurban, H. Enhancing food security in arid areas of Pakistan through newly developed drought tolerant and short duration mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Genetika 2018, 50, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Shekhawat, K.; Dass, A. Phytoremediation mechanism in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) and its enhancement through agronomic interventions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India 2019, 89, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Muedi, K. Environmental contamination by heavy metals. In Heavy Metals; Saleh, H., Aglan, R., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Uddin, M.; Ara-Sharmeen, I.; Alharby, F.; Alzahrani, H.; Hakeem, Y.; Zhang, L. Assisting phytoremediation of heavy metals using chemical amendments. Plants 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, E.; Haneklaus, S.; Haensch, R.; Schnug, E. EDTA application on agricultural soils affects microelement uptake of plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, I.; Maria, M.; Jerome, S.; Rizwan, M.; Kiran, H.; Jean, K.; Muhammad, A. EDTA-assisted phytoextraction of lead and cadmium by Pelargonium cultivars grown on spiked soil. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh-Dahaji, P.; Baniasad-Asgari, A.; Hamidpour, M. The effect of Cu-resistant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and EDTA on phytoremediation efficiency of plants in a Cu-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31822–31833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipu, M.I.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Sarwar, N. Growth and Physiology of Maize (Zea mays L.) in a Nickel-Contaminated Soil and Phytoremediation Efficiency Using EDTA. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Favas, P.; Pratas, J. EDTA-Assisted Metal Uptake in Raphanus sativus L. and Brassica oleracea L.: Assessment of Toxicity and Food Safety. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, J.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Rahman, A.; Fujita, M. EDTA reduces cadmium toxicity in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) by enhancing metal chelation, antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Acta Agrobot. 2019, 72, 17–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Rifat, R.; Afrin, S. Lead (Pb), Zinc (Zn) and Copper (Cu) uptake by (Brassica juncea) grown in dumpsite soil. Parana J. Sci. Edu. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sofy, M.R.; Seleiman, M.F.; Alhammad, B.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Mohamed, H.I. Minimizing Adverse Effects of Pb on Maize Plants by Combined Treatment with Jasmonic, Salicylic Acids and Proline. Agronomy 2020, 10, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Farooq, M.; Naveed, M.; Cheema, S.A.; Ain, U.-N.; Salim, M.A.; Liqun, C.; Mustafa, A. Influence of biochar and microorganism co-application on the remediation and maize growth in cadmium-contaminated soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 983830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamdi, M.; Galiou, O.; Bakrim, A.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R. Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Austruy, A.; Echevarria, G.; Arshad, M.; Sanaullah, M.; Aslam, M.; Dumat, C. EDTA-Enhanced Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals: A Review. Soil Sediment Contam. 2019, 23, 38–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, U.; Ali, S.; Shakoor, M.B.; Fareed, M.; Hussain, S.; Yasmeen, T.; Adrees, M.; Bharwana, S.A.; Abbas, F. EDTA ameliorates phytoextraction of lead and plant growth by reducing morphological and biochemical injuries in (Brassica napus L.) under lead stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.; Cheng, M.; Hu, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q. Toxic effects of Pb on Spirodela polyrhiza L.: Subcellular distribution, chemical forms, morphological and physiological disorders. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, K.H.; Anwar, S.; Nawaz, K.; Hussain, K.; Siddiqi, E.; Sharif, R.U.; Talat, A.; Khalid, A. Effect of heavy metal lead (Pb) stress of different concentration on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 14, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Nas, F. The effect of lead on plants in terms of growing and biochemical parameters: A review. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 3, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, S.K.; Handa, N.; Sharma, A.; Gautam, V.; Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Ahmad, P. Combined effect of 24-epibrassinolide and salicylic acid mitigates lead (Pb) toxicity by modulating various metabolites in Brassica juncea L. seedlings. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, M.; Lin, Y.; Dash, C.K. Temperature-dependent development of Asian citrus psyllid on various hosts, and mortality by two strains of Isaria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 119, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecka, A.; Konkolewska, A.; Hanć, A.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Ciszewska, L.; Ratajczak, E.; Staszak, A.M.; Kmita, H.; Jarmuszkiewicz, W. Insight into the phytoremediation capability of Brassica juncea (v Malopolska): Metal accumulation and antioxidant enzyme activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.; Singh, M.P.; Kaur, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Zheng, B.; Sharma, A. Modulation of the functional components of growth, potosynthesis, and anti-oxidant stress markers in cadmium exposed (Brassica juncea L.). Plants 2019, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Song, H.; Chen, Q. EDTA-facilitated toxic tolerance, absorption and translocation and phytoremediation of lead by dwarf bamboos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, D.; Lai, A.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Long, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Leaching characteristics of EDTA-enhanced phytoextraction of Cd and Pb by Zea mays L. in different particle-size fractions of soil aggregates exposed to artificial rain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A. Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11679–11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xiang, Q.; Zhiwei, P.; Yunguo, L.; Xiaomin, G.; Guangming, Z.; Chao, H.; Min, C.; Wenjing, X.; Xi, W.; et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron assisted phytoremediation of Pb in sediment: Impacts on metal accumulation and antioxidative system of Lolium perenne. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, A.; Bhardwaj, R. Plant steroidal hormone epibrassinolide regulate—Heavy metal stress tolerance in Oryza sativa L. by modulating antioxidant defense expression. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, V.; D’Amelia, V.; Esposito, M.; Amitrano, C.; Carillo, P.; Carputo, D.; Maggio, A. Anthocyanins are key regulators of drought stress tolerance in tobacco. Biology 2021, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, A.; Latifeh, P.; Sina, S.M.; Jelena, P.D. The effect of the exogenous application of EDTA and maleic acid on tolerance, phenolic compounds, and cadmium phytoremediation by okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) exposed to Cd stress. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirani, M.; Kashani, A.; Koohi-Dehkordi, M. The role of iron nanoparticles on morpho-physiological traits and genes expression (IRT1 and CAT) in rue (Ruta graveolens). Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 110, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, R.; Jamei, R.; Rahmani, F. Role of salicylic acid and hydrogen sulfide in promoting lead stress tolerance and regulating free amino acid composition in Zea mays L. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Fatma, M.; Per, T.S.; Anjum, N.A.; Khan, N.A. Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Min, X.; Zhou, Z.H. Hydrogen sulfide: A signal molecule in plant cross-adaptation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Ali, A.; Saleem, M.H.; Ameer, A.; Hafeez, A.; Jamil, M.; Farid, G. Comparative effectiveness of EDTA and citric acid assisted phytoremediation of Ni contaminated soil by using canola (Brassica napus). Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoula, A.; Therios, I.; Chatzissavvidis, C. Effect of lead and copper on photosynthetic apparatus in Citrus (Citrus aurantium L.) plants. The role of antioxidants in oxidative damage as a response to heavy metal stress. Plants 2021, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Ruiz, A.; Ortiz, J.; Larama, G.; Perez, R.; Santander, C.; Ferreira, P.A.A.; Cornejo, P. Antioxidant responses of phenolic compounds and immobilization of copper in imperata cylindrica, a plant with potential use for bioremediation of cu contaminated environments. Plants 2020, 9, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Siddique, A.; Ashraf, M.A. Does exogenous application of ascorbic acid modulate growth, photosynthetic pigments and oxidative defense in okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) under lead stress? Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammam, A.; Weam, A.; Reda, A.S.; Mahmoud, M. Improved of growth and phytostabilization potential of lead (Pb) in Glebionis coronaria L. under the effect of IAA and GA3 alone and in combination with EDTA by altering biochemical attributes of stressed plants. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.; Xi, X.; Rafaqat, A.; Yang, S.; Shafaqat, A.; Muhammad, T.; Weijun, Z. Promotive role of 5-aminolevulinic acid on mineral nutrients and antioxidative defense system under lead toxicity in Brassica napus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaier, H.; Tahar, G.; Abelbasset, L.; Rawdha, B.; Rim, G.; Majda, M.; Souhir, S.; Stanley, L.; Chedly, A. Comparative study of Pb-phytoextraction potential in Sesuvium portulacastrum and Brassica juncea: Tolerance and accumulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareshkumar, A.; Krishnappa, B.V.; Kirankumar, T.V.; Kiranmai, K.; Lokesh, U.; Sudhakarbabu, O.; Chinta, S. Effect of Pb-stress on growth and mineral status of two groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Matin, M.A.; Fardus, J.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Parvin, K. Foliar application of salicylic acid improves growth and yield attributes by upregulating the antioxidant defense system in Brassica campestris plants grown in lead-amended soils. Acta Agrobot. 2019, 72, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, U.; Tang, X. Yield and quality responses, plant metabolism and metal distribution pattern in aromatic rice under lead (Pb) toxicity. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzyme in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Yordanov, I.; Edreva, A. Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: Protective roles of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Horst, J.H. Effects of aluminum on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Physiol. Plant. 1991, 83, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A. Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 2, 764–817. [Google Scholar]
- Spitz, D.R.; Oberly, L.W. Measurement of MnSOD and CuZnSOD activity in mammalian tissue homogenates. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2001, 8, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Van-Slyke, D.D. Amino acid determination with ninhydrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1943, 150, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.; Wray, V. Anthocyanins. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry; Harborne, J.B., Ed.; Acdemic Press: London, UK, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 325–356. [Google Scholar]
- Marinova, D.; Ribarova, F.; Atanassova, M. Total phenolics and flavonoids in bulgarian fruits and vegetables. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2005, 40, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Choudhri, M.A. Implications for water stress-induced changes in the level of endogenous ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide in Vigna seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 1983, 58, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saman, R.U.; Shahbaz, M.; Maqsood, M.F.; Lili, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Naz, N.; Shahzad, B. Foliar Application of Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Improves the Growth and Yield of Brown Mustard (Brassica juncea) by Modulating Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Defense, and Osmolyte Production under Lead (Pb) Stress. Plants 2023, 12, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010115
Saman RU, Shahbaz M, Maqsood MF, Lili N, Zulfiqar U, Haider FU, Naz N, Shahzad B. Foliar Application of Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Improves the Growth and Yield of Brown Mustard (Brassica juncea) by Modulating Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Defense, and Osmolyte Production under Lead (Pb) Stress. Plants. 2023; 12(1):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010115
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaman, Rafia Urooj, Muhammad Shahbaz, Muhammad Faisal Maqsood, Nian Lili, Usman Zulfiqar, Fasih Ullah Haider, Nargis Naz, and Babar Shahzad. 2023. "Foliar Application of Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Improves the Growth and Yield of Brown Mustard (Brassica juncea) by Modulating Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Defense, and Osmolyte Production under Lead (Pb) Stress" Plants 12, no. 1: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010115
APA StyleSaman, R. U., Shahbaz, M., Maqsood, M. F., Lili, N., Zulfiqar, U., Haider, F. U., Naz, N., & Shahzad, B. (2023). Foliar Application of Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Improves the Growth and Yield of Brown Mustard (Brassica juncea) by Modulating Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidant Defense, and Osmolyte Production under Lead (Pb) Stress. Plants, 12(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010115








