Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Testing of the Various Nutrient Media for Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration
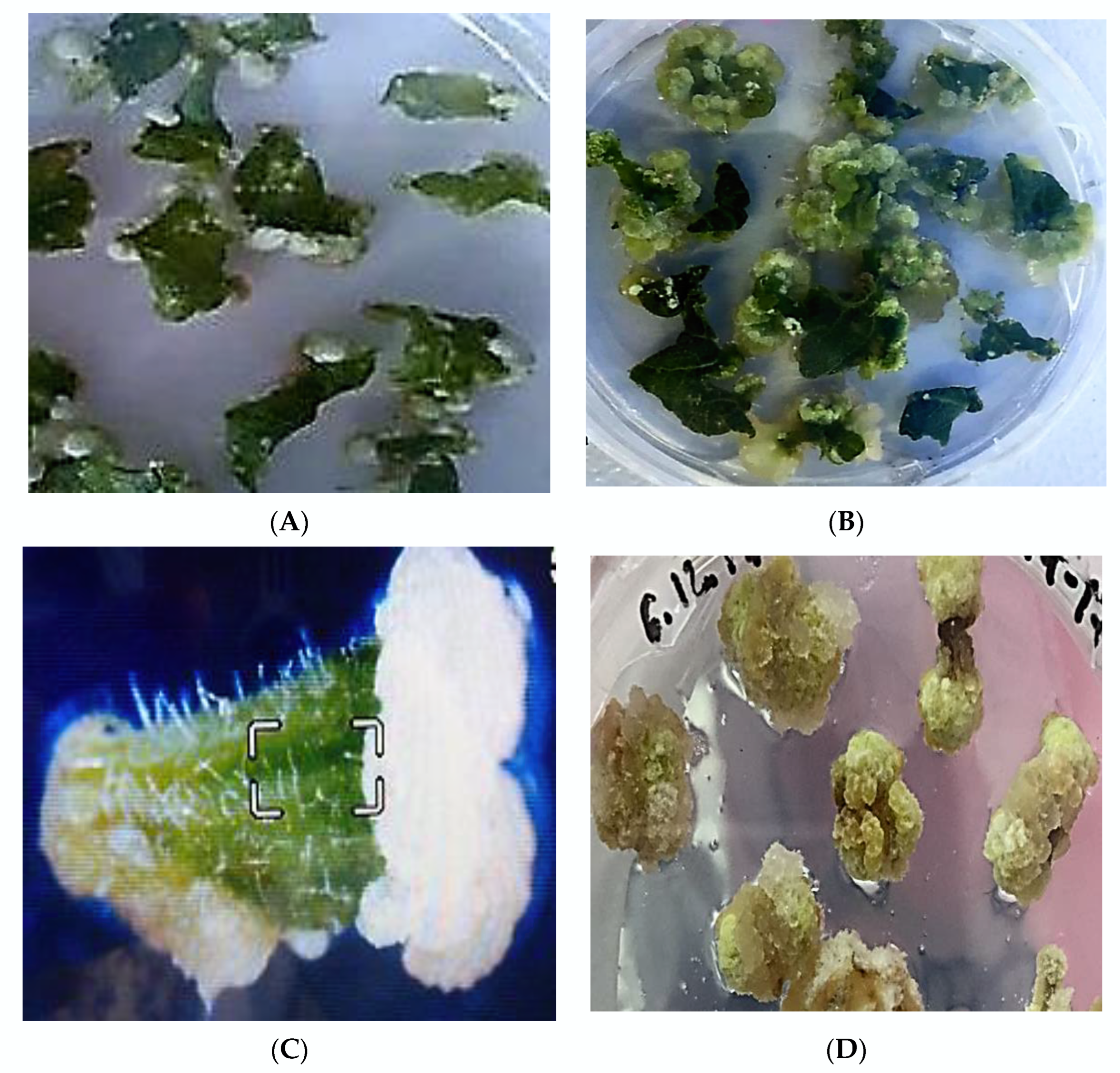
2.2. Study the Callusogenesis and Morphogenesis of Different Types of Explants
2.3. Plant Regeneration In Vitro from Different Types of Explants
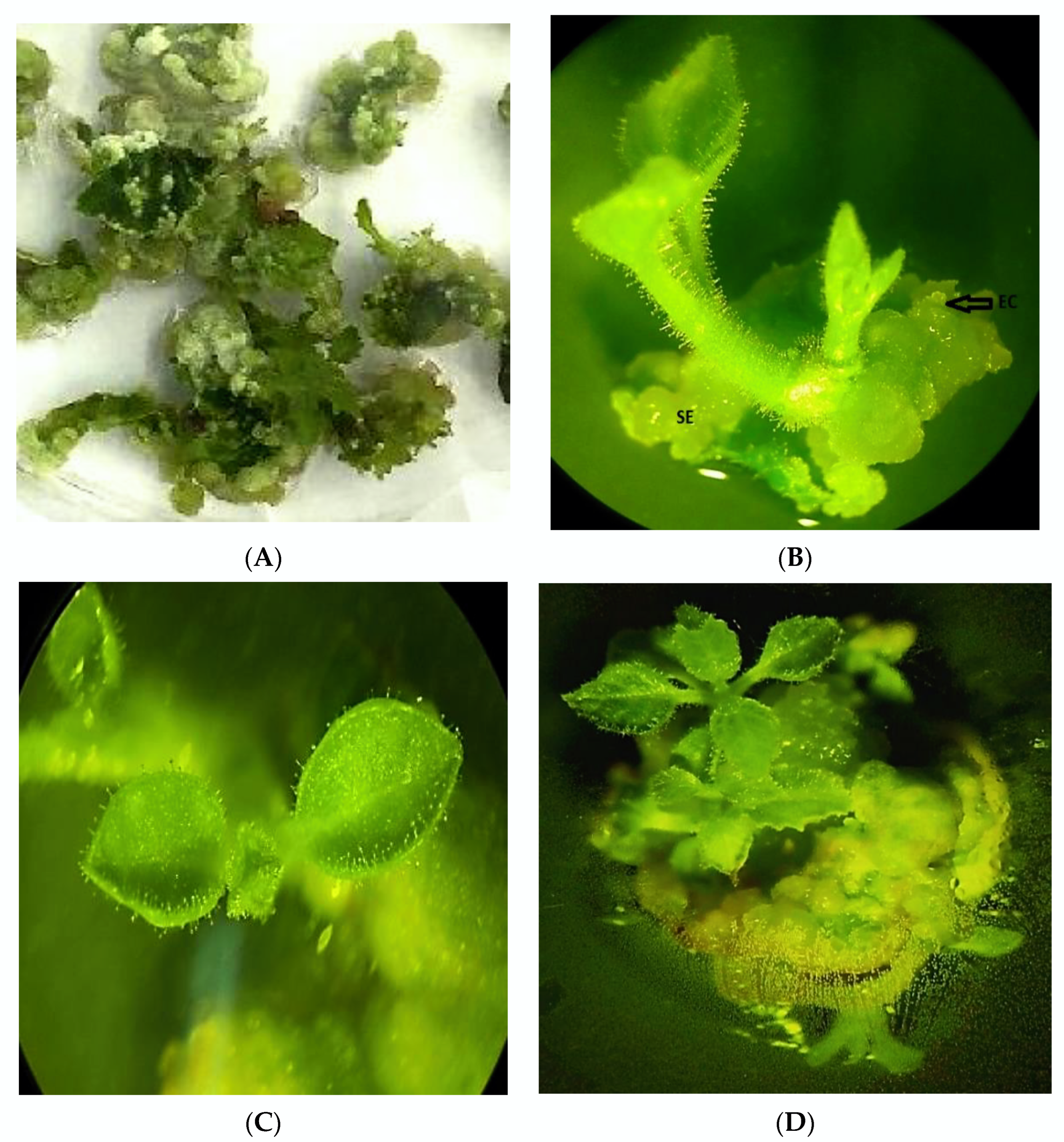
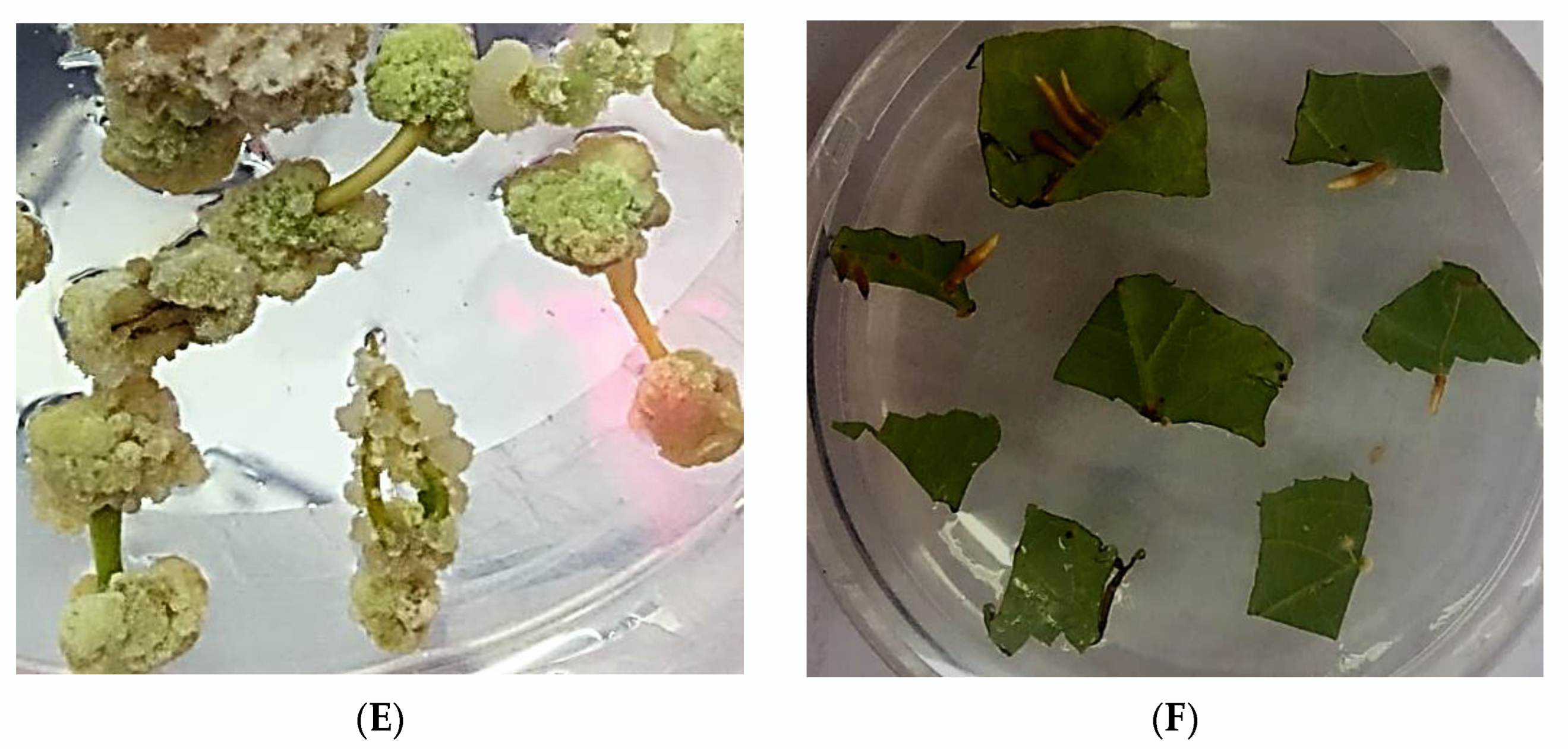
2.4. Selection of Highly Regenerable Embryogenic Calli (EC)
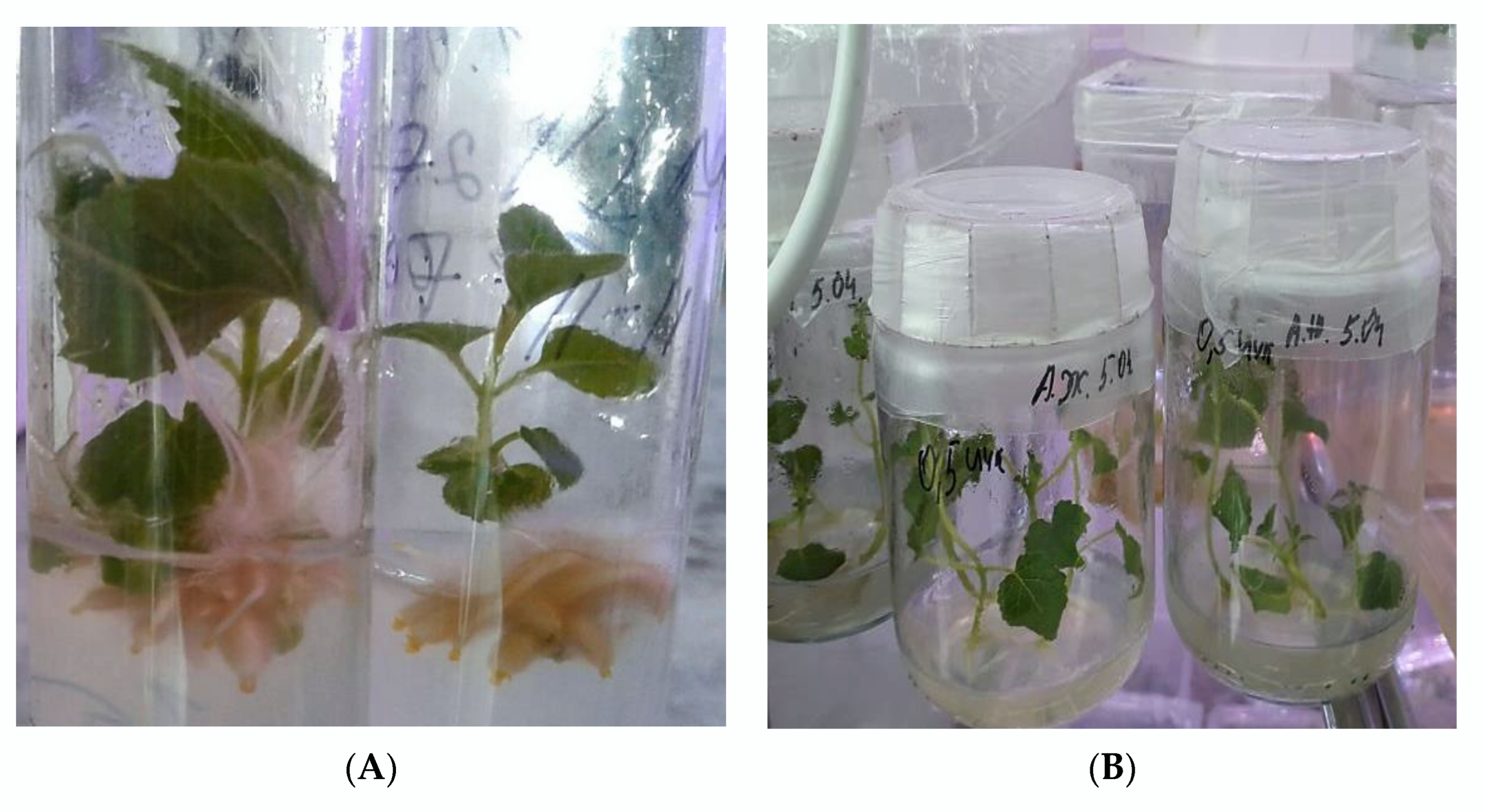
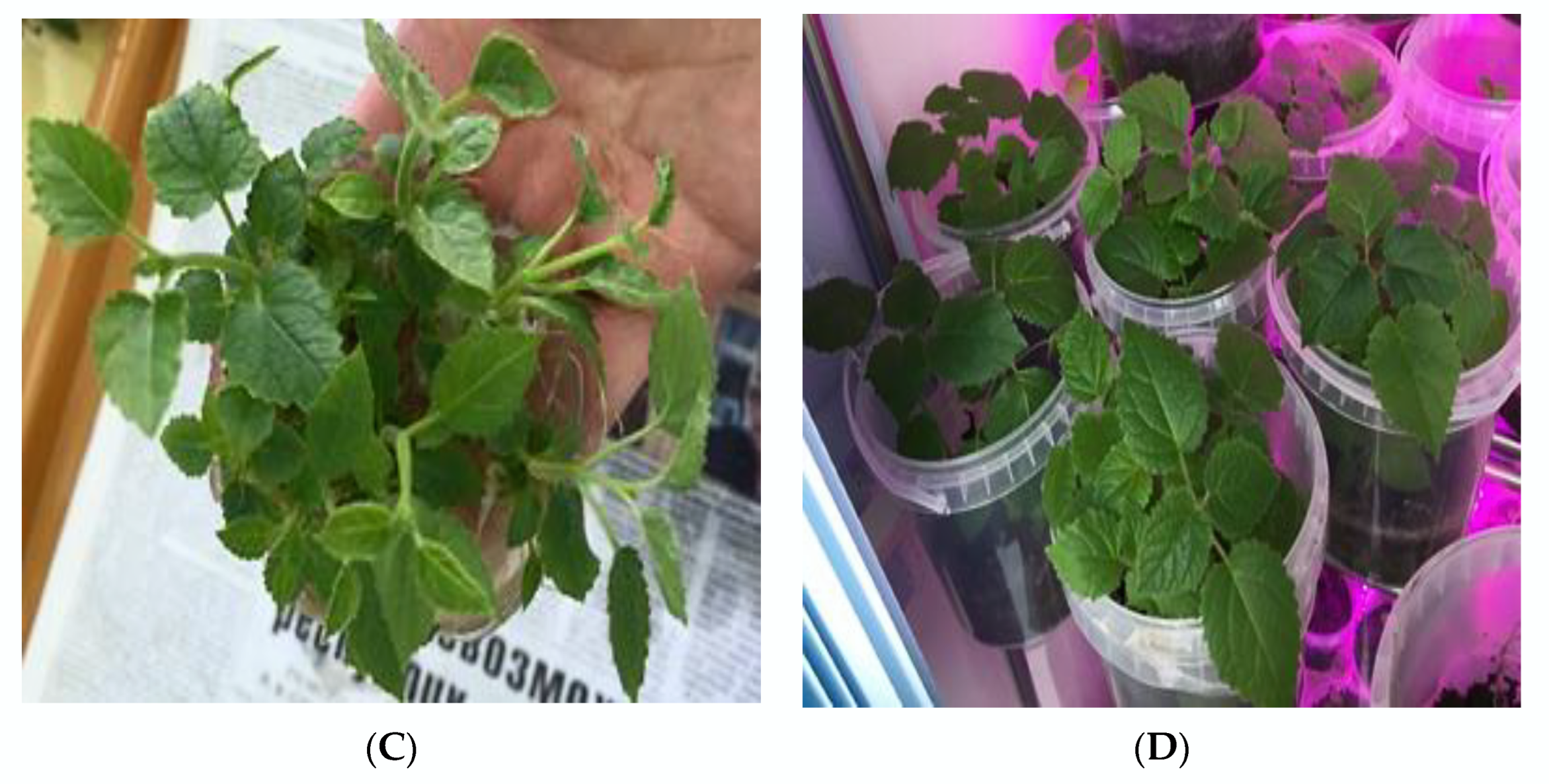
2.5. Rooting and Acclimatization of Regenerated Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. In Vitro Culture Techniques
4.3. Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration
4.4. Testing of the Various Nutrient Media for Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration
4.5. Study the Callusogenesis and Morphogenesis of Different Types of Explants
4.6. Rooting and Acclimatization of Regenerated Plants
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erbar, C.; Gülden, C. Ontogeny of the flowers in Paulownia tomentosa—A contribution to the recognition of the resurrected monogeneric family Paulowniaceae. Flora Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2011, 206, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.K.; Vaidya, B.N.; Henderson, K.; Lee, J.F.; Stewart, W.M.; Dhekney, S.A.; Joshee, N. A Review of Paulownia Biotechnology: A Short Rotation, Fast Growing Multipurpose Bioenergy Tree. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, I.L.; Nicholas, I.D.; Ecroyd, C.E. Paulownia. For. Res. Bull 2007, 231, 5–68. [Google Scholar]
- Stupin, D.Y. Soil Pollution and the Latest Technologies for Their Restoration: Training Manual; Publishing House: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2009; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Merkle, S.A. Engineering Forest Trees with Heavy Metal Resistance Genes. Silvae Genet. 2006, 55–56, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ydyrys, A.; Abdolla, N.; Seilkhan, A.S.; Masimzhan, M.; Karasholakova, L. Importance of the geobotanical studying in agriculture (with the example of the Sugaty region). E3S Web Conf. 2020, 222, 04003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ydyrys, A.; Yeszhanov, B.; Baymurzaev, N.; Sharakhmetov, S.; Mautenbaev, A.; Tynybekov, B.; Baidaulet, T. Technology of landscaping in arid zones by using biohumus from sheep wool. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 169, 02012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.M.; Sameen, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Shahid, M.; Sezen, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Ozdemir, B.; Sevindik, M.; Kaplan, D.N.; Anitha, T.; et al. Citrus Genus and Its Waste Utilization: A Review on Health-Promoting Activities and Industrial Application. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2021, 20, 2488804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painuli, S.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Semwal, P.; Martorell, M.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Rad, J.S.; Alshehri, M.M.; Daştan, S.D.; Taheri, Y.; et al. Nutraceutical Profiling, Bioactive Composition, and Biological Applications of Lepidium sativum L. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 19, 2910411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, Y.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Merghany, R.M.; Shaheen, S.; Azmi, L.; Mishra, A.P.; Sener, B.; et al. Urtica dioica-Derived Phytochemicals for Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2022, 24, 4024331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ydyrys, Y.; Serbayeva, A.; Dossymbetova, S.; Akhmetova, A.; Zhuystay, A. The effect of anthropogenic factors on rare, endemic plant species in the Ile Alatau. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 222, 05021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ydyrys, A.; Zhaparkulova, N.; Aralbaeva, A.; Mamataeva, A.; Seilkhan, A.; Syraiyl, S.; Murzakhmetova, M. Systematic Analysis of Combined Antioxidant and Membrane-Stabilizing Properties of Several Lamiaceae Family Kazakhstani Plants for Potential Production of Tea Beverages. Plants 2021, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukenova, E.A.; Bassygarayev, Z.M.; Akhmetova, A.B.; Zhunusbayeva, Z.K.; Ydyrys, A. Development of the method of obtaining the endogenic biostimulator from wheat green spike glumes. Res. Crops 2019, 20, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Goh, C.; Kumar, P.P. High frequency adventitious shoot regeneration from excised leaves of Paulownia spp. cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Rep. 1996, 16, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaslan, M.; Can, C.; Aytekin, T. Effect of explant source on in vitro propagation of Paulownia tomentosa Steud. Biotechnol. Biotech. Equipment. 2005, 19, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, B.A.; Moon, H.K. In vitro adventitious shoot production in Paulownia. Plant Cell Rep. 1997, 16, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurganov, B.V.; Mishutkina, Y.V.; Neskorodov, Y.B. Development of an effective regeneration system for Paulownia Shan Tong (P. fortunei × P. tomentosa). Bull. RUDN Univ. Agron. Livest. Series. Sect. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasil, I.K. Developing cell and tissue culture systems for the improvement of cereal and grass crops. J. Plant Physiol. 1987, 128, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.G.; Maheswaran, G. Somatic embryogenesis: Factors influencing coordinated behavior of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 1986, 57, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, V.M. Regulation of in vitro somatic embryogenesis with emphasis on to the role of endogenous hormones. Rev. Bras. Fisiol. Veg. 2001, 13, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishimbayeva, N.; Yertayeva, B.; Amirova, A.; Rakhimbayev, I. Morphogenesis in Tissue Culture of Local Kazakh Cotton Varieties. OnLine J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 17, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ipekci, Z.; Altinkut, A.; Kazan, K.; Bajrovic, K.; Gozukirmizi, N. High Frequency Plant Regeneration from Nodal Explants of Paulownia Elongate. Plant Biol. 2001, 3, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.; Roy, P.K.; Mamun, A.N.K. High frequency shoot regeneration from nodal and shoot tip explants in Holarrhena antidysenterica L. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plantarum. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunchukov, A.; Yancheva, S. Micropropagation of Paulownia species and hybrids. First National Conference of Biotechnology, Sofia. Annu. L’université Sofia “St. Kliment Ohridski” Fac. Biol. 2015, 100, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.K. In vitro plant regeneration of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. from shoot tip and leaf segment. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2015, 44, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtereva, L.; Vassilevska-Ivanova, R.; Karceva, T.; Kraptchev, B. Micropropagation of six Paulownia genotypes through tissue culture. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2014, 15, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredoira, E.; Ballester, A.; Vieitez, A. Thidiazuron-Induced High-Frequency Plant Regeneration from Leaf Explants of Paulownia tomentosa Mature Trees. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 95, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Litwinczuk, W.; Bochnia, E. Development of royal paulownia (Paulownia tomentosa Steud.) in vitro shoot cultures under the influence of different saccharides. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus. 2012, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, L.S.; Soad Ibrahim, M.M.; Farahat, M.M. A micropropagation of Paulownia kowa-kami through in vitro culture technique. Austral. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2008, 2, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ipekci, Z.; Gozukirmizi, N. Direct Somatic Embryo-genesis and Synthetic Seed Production from Paulownia elongate. Cell Biol. Morphog. 2003, 22, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ipekci, Z.; Gozukirmizi, N. Indirect Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Leaf and Inter- node Explants of Paulownia elongate. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2005, 79, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozoga, M.; Olewnicki, D.; Jablonska, L. In vitro propagation protocols and variable cost comparison in commercial production for Paulownia tomentosa × Paulownia fortune hybrid as a renewable energy source. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, F.; Rahmatullah, M. In vitro regeneration of Paulownia tomentosa Steud. plants through the induction of adventitious shoots in explants derived from selected mature trees, by studying the effect of different plant growth regulators. Am. -Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2013, 7, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hussien, E.T. Production of transgenic Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) steud using chitosan nanoparticles to express antimicrobial genes resistant to bacterial infection. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2020, 9, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, F.L.; Sarnatskaya, V.V.; Polishchuk, V.E. Methods of Tissue Culture in Plant Physiology and Biochemistry; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1980; p. 488. [Google Scholar]
- Dehestani-Ardakani, M.; Hejazi, M.; Aliabad, K.K. Indirect somatic embryogenesis of purple conefower (Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench): A medicinal-ornamental plant: Evaluation of antioxidant enzymes activity and histological study. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6621–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, R.; Zare, N.; Asghari-Zakarta, R.; Sheikhzadeh, P. Efficient In Vitro Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Mature and Immature Embryos of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016, 59, e160288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khajuria, A.K.; Hano, C.; Bisht, N.S. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration in Viola canescens Wall. Ex. Roxb.: An Endangered Himalayan Herb. Plants 2021, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Culture Medium | Concentration of Plant Growth Regulators | Callus Induction, % | Plant Regeneration, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS1 | 22.2 µM BAP + 5.4 µM NAA | 87.6 ± 2.6 | 44.4 ± 0.8 |
| MS2 | 35.5 µM BAP + 5.4 µM NAA | 95.5 ± 3.9 | 95.2 ± 1.9 |
| MS3 | 4.5 µM TDZ + 2.8 µM IAA | 82.4 ± 4.3 | 23.9 ± 2.5 |
| MS4 | 13.6 µM TDZ + 2.8 µM IAA | 80.2 ± 3.7 | 12.5 ± 1.8 |
| MS5 | 13.9 µM kinetin + 2.8 µM IAA | 0 | 0 |
| MS6 | 23.2 µM kinetin + 2.8 µM IAA | 0 | 0 |
| Explants Type | Induction of Callus Tissues, % | Plant Regeneration, % |
|---|---|---|
| Leaves | 95.5 ± 3.9 | 95.2 ± 1.9 |
| Apical shoot tip | 83.3 ± 14.5 | 87.2 ± 2.9 |
| Nodes | 78.6 ± 6.1 | 45.3 ± 2.0 |
| Internodes | 87.8 ± 9.0 | 37.6 ± 0.8 |
| Petals | 73.9 ± 7.2 | 34.7 ± 1.5 |
| Culture Media | Embryogenic Callus (EC) Types | Shoot Number Per 1 EC Number of Passages | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | IV | VI | X | ||
| MS2 | EC (from leaves) | 7.4 ± 2.7 | 27.3 ± 2.2 | 36.3 ± 3.4 | 22.8 ± 1.9 |
| EC (apical shoot tips) | 9.1 ± 2.1 | 29.6 ± 4.2 | 38.6 ± 2.3 | 23.6 ± 2.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amirova, A.; Dossymbetova, S.; Rysbayeva, Y.; Usenbekov, B.; Tolegen, A.; Ydyrys, A. Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. Plants 2022, 11, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081020
Amirova A, Dossymbetova S, Rysbayeva Y, Usenbekov B, Tolegen A, Ydyrys A. Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. Plants. 2022; 11(8):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmirova, Aigul, Symbat Dossymbetova, Yeldana Rysbayeva, Bakdaulet Usenbekov, Arman Tolegen, and Alibek Ydyrys. 2022. "Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud" Plants 11, no. 8: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081020
APA StyleAmirova, A., Dossymbetova, S., Rysbayeva, Y., Usenbekov, B., Tolegen, A., & Ydyrys, A. (2022). Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. Plants, 11(8), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081020






