Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
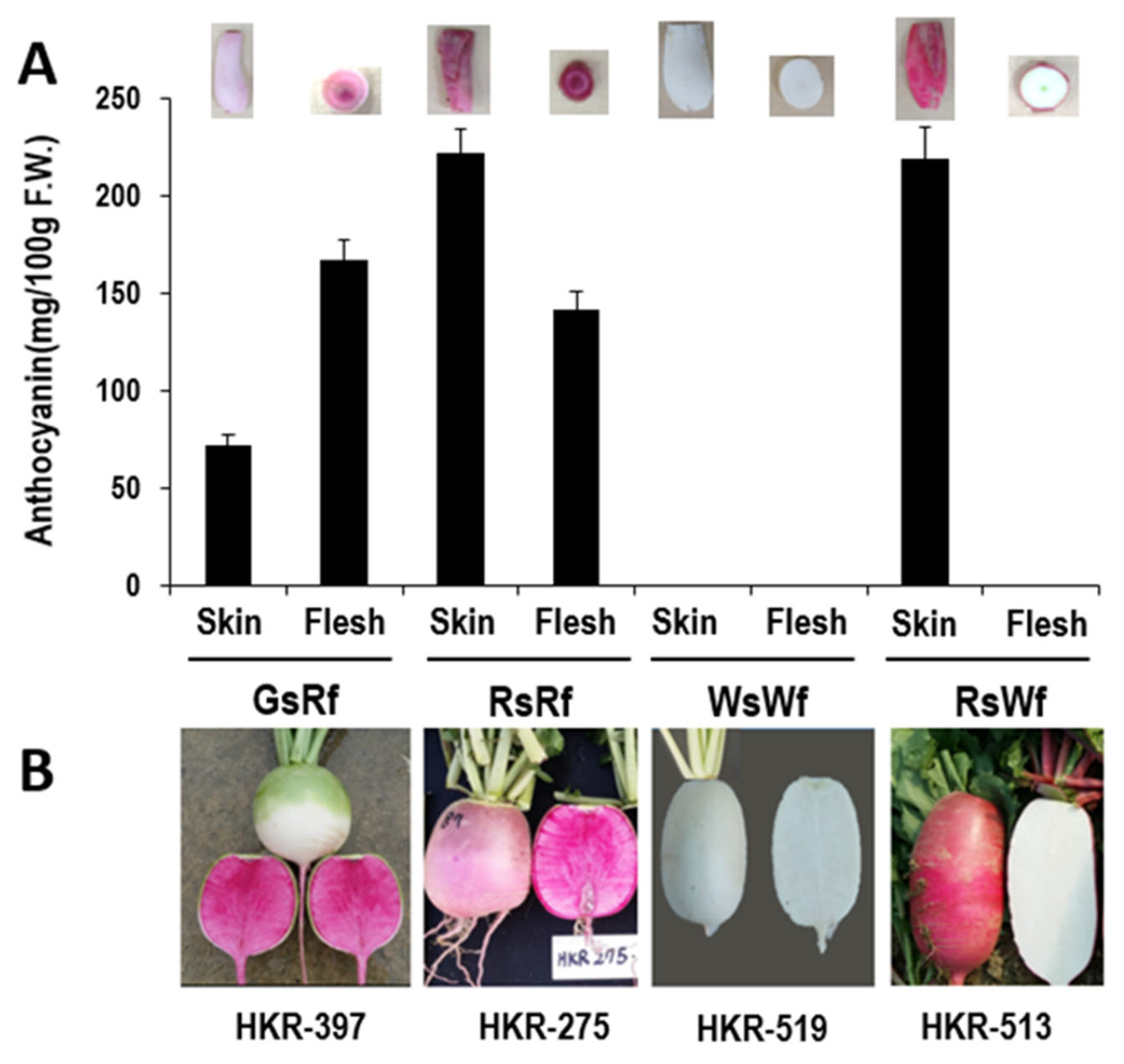
2.1. Selection of Radish Inbred Lines with Different Taproot Coloration
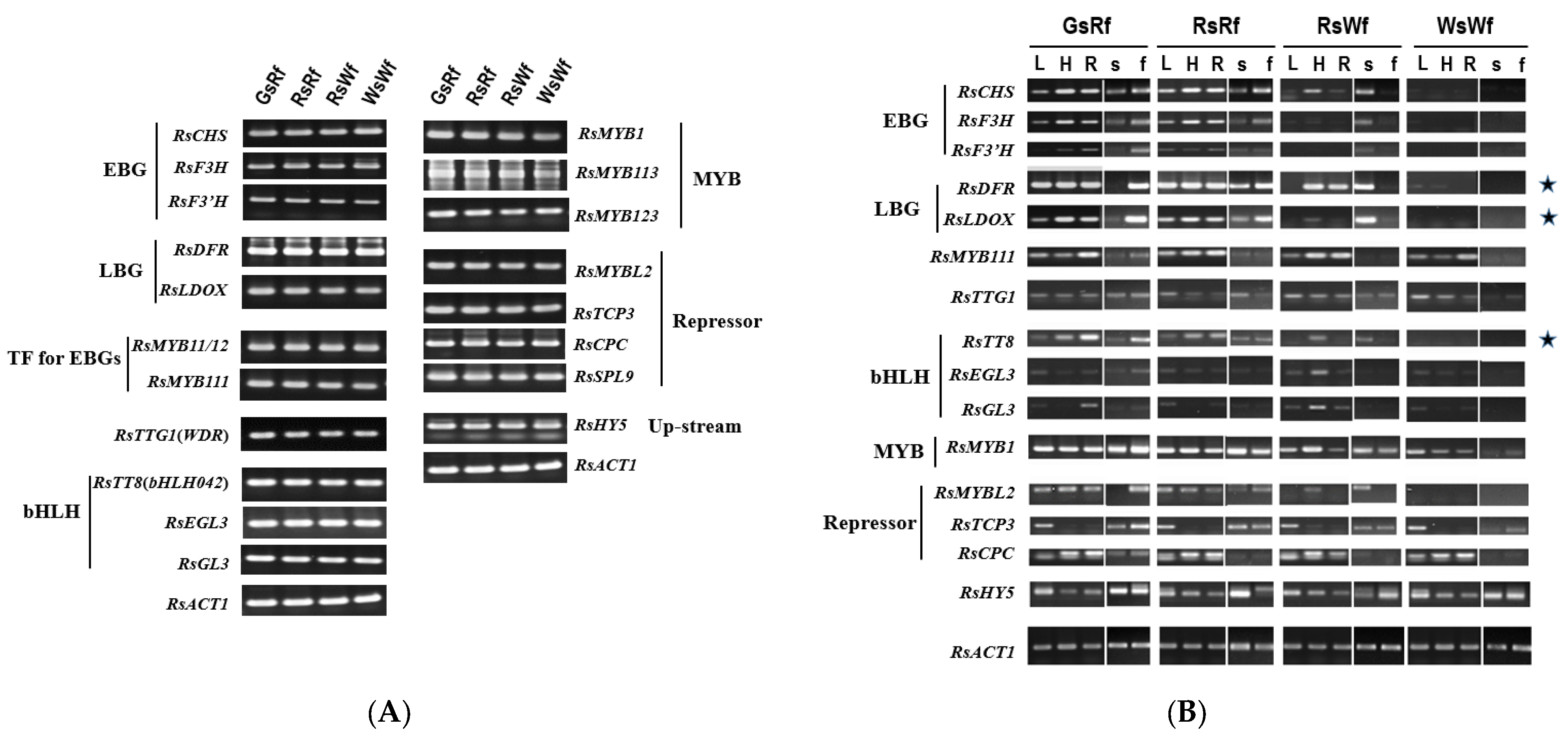
2.2. RsTT8 as a Target Gene for Affecting Anthocyanin Accumulation in Radish
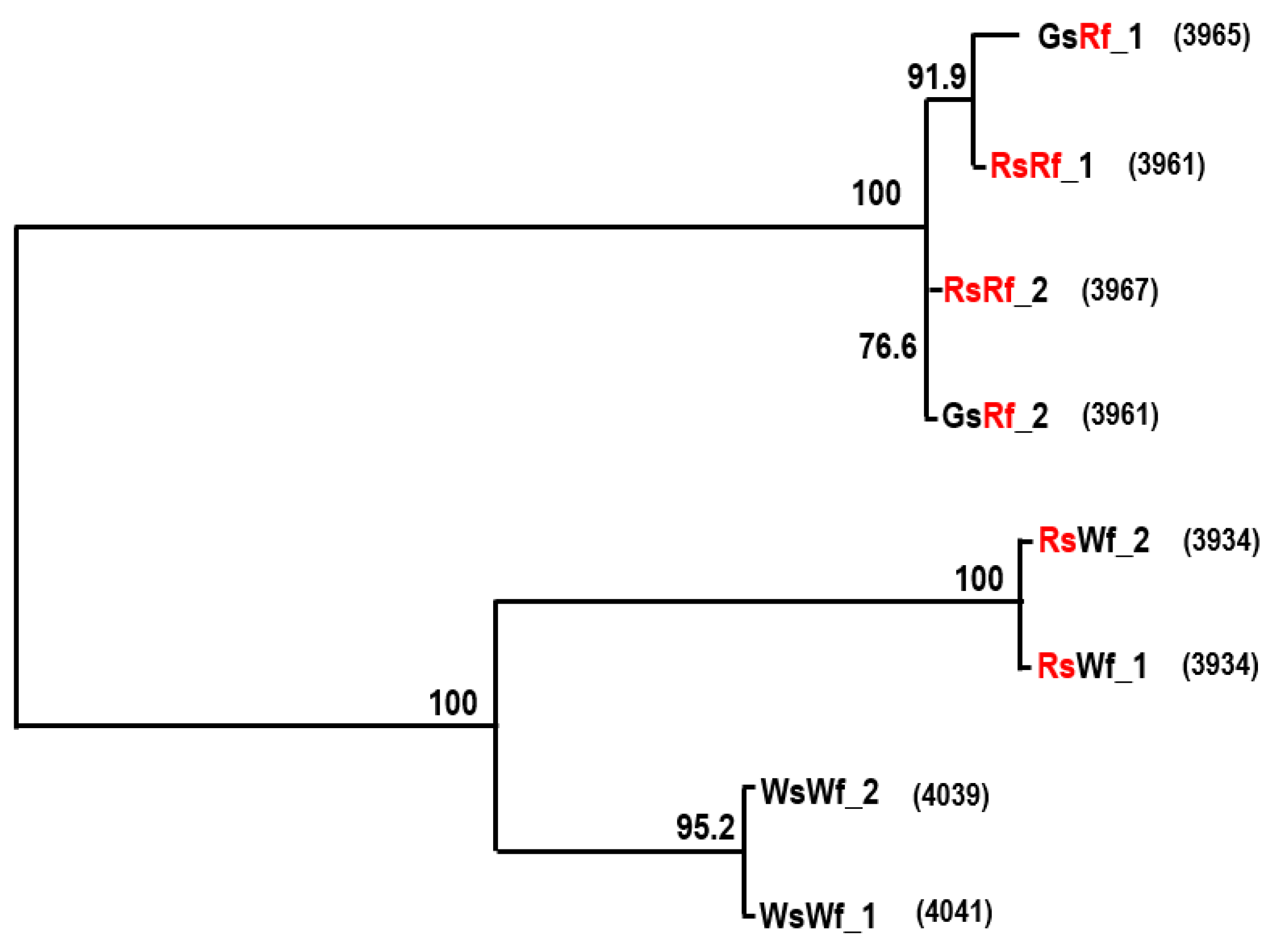
2.3. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of RsTT8
2.4. Promoter Analysis of RsTT8
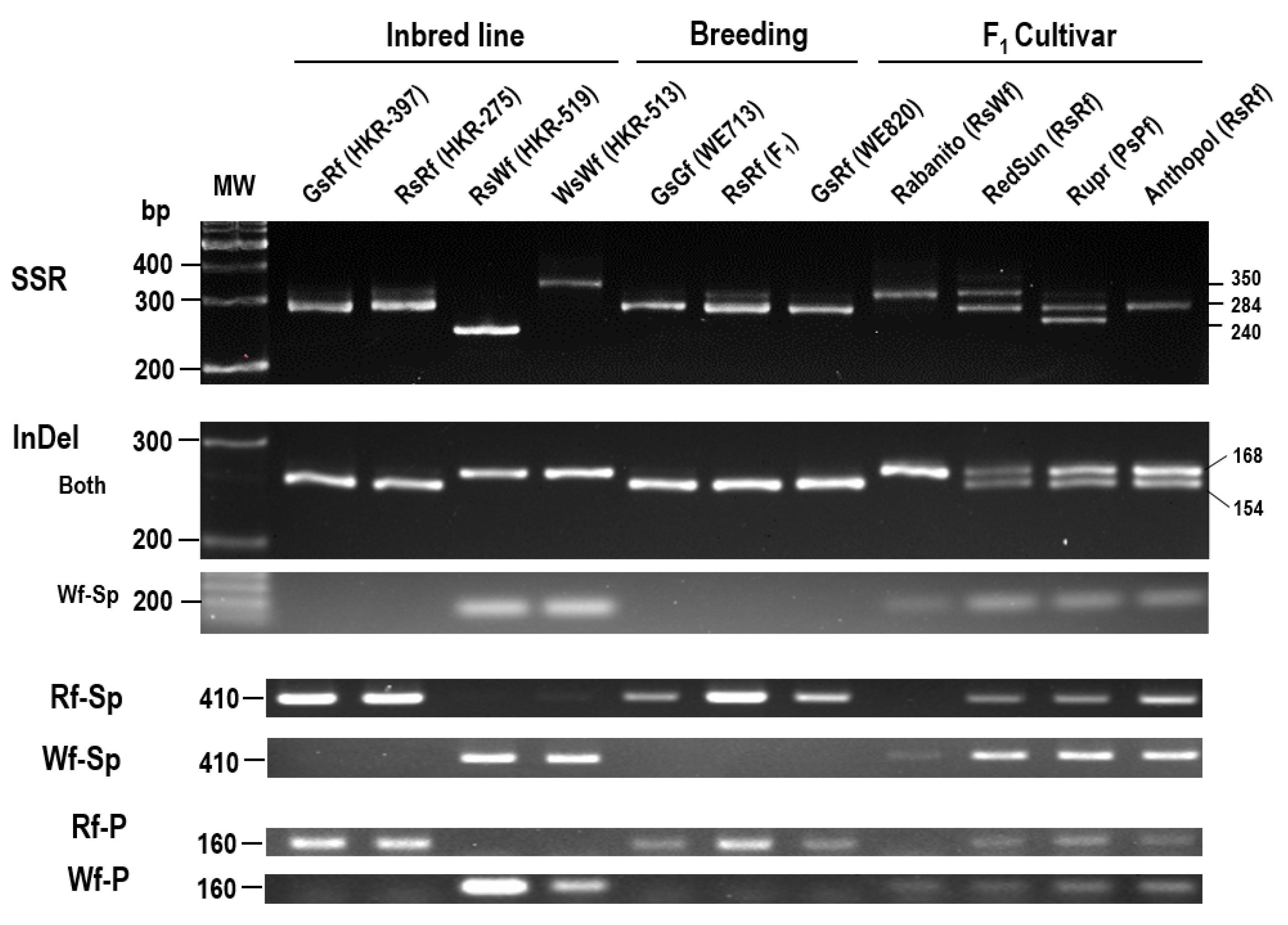
2.5. Development of Molecular Markers Associated with Flesh Color
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Cloning and Sequence Analysis of RsTT8
4.3. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
4.4. Anthocyanin Extraction and Quantification
4.5. Promoter Activity Assay
4.6. Marker Development and Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, C.H.; Baskar, T.B.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Valan Arasu, M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Metabolic profiling and antioxidant assay of metabolites from three radish cultivars (Raphanus sativus). Molecules 2016, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Xing, C.; Huo, S.; Cao, C.; Yao, Q.; Fang, P. Red pigment content and expression of genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in radishes (Raphanus sativus L.) with different colored flesh. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 10.5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, J.; Li, X. Identification of ‘Xinlimei’radish candidate genes associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis based on a transcriptome analysis. Gene 2018, 657, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muminović, J.; Merz, A.; Melchinger, A.E.; Lubberstedt, T. Genetic structure and diversity among radish varieties as inferred from AFLP and ISSR analyses. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2005, 130, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanlon, P.R.; Barnes, D.M. Phytochemical composition and biological activity of 8 varieties of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) sprouts and mature taproots. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C185–C192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Radish anthocyanin extract as a natural red colorant for maraschino cherries. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Rodriguex-Saona, L.E.; Baggett, J.R.; Reer, G.L.; Durst, R.W.; WRolstad, R.E. Anthocyanin pigment composition of red radish cultivars as potential food colorants. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Ghanadan, H.; Wrolstad, R.E. Elucidation of the structure and conformation of red radish (Raphanus sativus) anthocyanins using one-and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4858–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.M.P.; Perez, R.L. Raphanus sativus (Radish): Their chemistry and biology. Sci. World J. 2004, 4, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Prior, R.L. Identification and characterization of anthocyanins by high-performance liquid chromatography− electrospray ionization− tandem mass spectrometry in common foods in the United States: Vegetables, nuts, and grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3101–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.I.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Jang, I.H.; Park, S.; Ahn, G.H.; Lim, Y.P.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.U. Anthocyanin accumulation and expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in radish (Raphanus sativus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6034–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.-M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, C.; Le Gourrierec, J.; Baudry, A.; Huep, G.; Lanet, E.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Alboresi, A.; Weisshaar, B.; Lepiniec, L. MYBL2 is a new regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2008, 55, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, I.M.; Heim, M.A.; Weisshaar, B.; Uhrig, J.F. Comprehensive identification of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB transcription factors interacting with R/B-like BHLH proteins. Plant J. 2004, 40, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrtens, F.; Kranz, H.; Bednarek, P.; Weisshaar, B. The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB12 is a flavonol-specific regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stracke, R.; Ishihara, H.; Huep, G.; Barsch, A.; Mehrtens, F.; Niehaus, K.; Weisshaar, B. Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J. 2007, 50, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: Fine-tuning of the MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) complex. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e27522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaujon, I.; Nesi, N.; Perez, P.; Devic, M.; Grandjean, O.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. Proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells in Arabidopsis testa: Regulation of differentiation and role in seed development. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2514–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baudry, A.; Heim, M.A.; Dubreucq, B.; Caboche, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Lepiniec, L. TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2004, 39, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heim, M.A.; Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Martin, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Bailey, P.C. The basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor family in plants: A genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feller, A.; Hernandez, J.M.; Grotewold, E. An ACT-like domain participates in the dimerization of several plant basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28964–28974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hülskamp, M.; Miséra, S.; Jürgens, G. Genetic dissection of trichome cell development in Arabidopsis. Cell 1994, 76, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, C.; Lee, M.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Zhang, F.; Lloyd, A.; Schiefelbein, J. The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) andENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development 2003, 130, 6431–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Payne, C.T.; Lloyd, A. A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis. Development 2003, 130, 4859–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, D.N.; Løvdal, T.; Olsen, K.M.; Slimestad, R.; Lillo, C. The endogenous GL3, but not EGL3, gene is necessary for anthocyanin accumulation as induced by nitrogen depletion in Arabidopsis rosette stage leaves. Planta 2009, 230, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Wen, J.; Mysore, K.S.; Zhao, J. Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by M edicago truncatula b HLH transcription factor M t TT 8. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, V.V.; Hatlestad, G.; Lloyd, A.M. Natural allelic variation defines a role for ATMYC1: Trichome cell fate determination. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruex, A.; Kainkaryam, R.M.; Wieckowski, Y.; Kang, Y.H.; Bernhardt, C.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.Y.; Lee, M.M.; Benfey, P. A gene regulatory network for root epidermis cell differentiation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesi, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Jond, C.; Pelletier, G.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baudry, A.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2006, 46, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ha, S.-H. A radish basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, RsTT8 acts a positive regulator for anthocyanin biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, F.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Ma, C.; Shen, J.; Tu, J. A large insertion in bHLH transcription factor BrTT8 resulting in yellow seed coat in Brassica rapa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmaja, L.K.; Agarwal, P.; Gupta, V.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Sodhi, Y.S.; Pental, D.; Pradhan, A.K. Natural mutations in two homoeologous TT8 genes control yellow seed coat trait in allotetraploid Brassica juncea (AABB). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Resentini, F.; Dalla Vecchia, F.; Trainotti, L. Effects on plant growth and reproduction of a peach R2R3-MYB transcription factor overexpressed in tobacco. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Hu, C.; Yan, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, H. Identification and differential expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in root-skin color variants of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muleke, E.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y.; Karanja, B.K.; Liu, L. Coordinated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes confers varied phenotypic and spatial-temporal anthocyanin accumulation in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Su, N.; Jia, L.; Tian, J.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Shen, Z.; Cui, J. Transcriptome analysis of radish sprouts hypocotyls reveals the regulatory role of hydrogen-rich water in anthocyanin biosynthesis under UV-A. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Li, W.-B.; Liu, H.-F.; Chen, F.-B. De novo transcriptome sequencing of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) fleshy roots: Analysis of major genes involved in the anthocyanin synthesis pathway. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, F.; Luo, M.; Li, W. Genome-wide analysis of transcription factors related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in carmine radish (Raphanus sativus L.) fleshy roots. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Li, X. Combined QTL-Seq and traditional linkage analysis to identify candidate genes for purple skin of radish fleshy taproots. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Li, X. Transcriptome analyses reveal key genes involved in skin color changes of ‘Xinlimei’radish taproot. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, M.; Liu, L. Genome-and Transcriptome-wide characterization of bZIP gene family identifies potential members involved in abiotic stress response and anthocyanin biosynthesis in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Yao, Q.; Chen, F. Karyotype analysis of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) with different freshy colors. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2011, 40, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, D.; Wang, A.; Li, T.; Jiang, S.; Cong, P.; Li, T. The Methylation of the PcMYB10 Promoter Is Associated with Green-Skinned Sport in Max Red Bartlett Pear. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L. Transposon-induced methylation of the RsMYB1 promoter disturbs anthocyanin accumulation in red-fleshed radish. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2537–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Wicker, L. Anthocyanin pigments in the skin of lychee fruit. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Characterization and measurement of anthocyanins by UV-visible spectroscopy. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, F1.2.1–F1.2.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



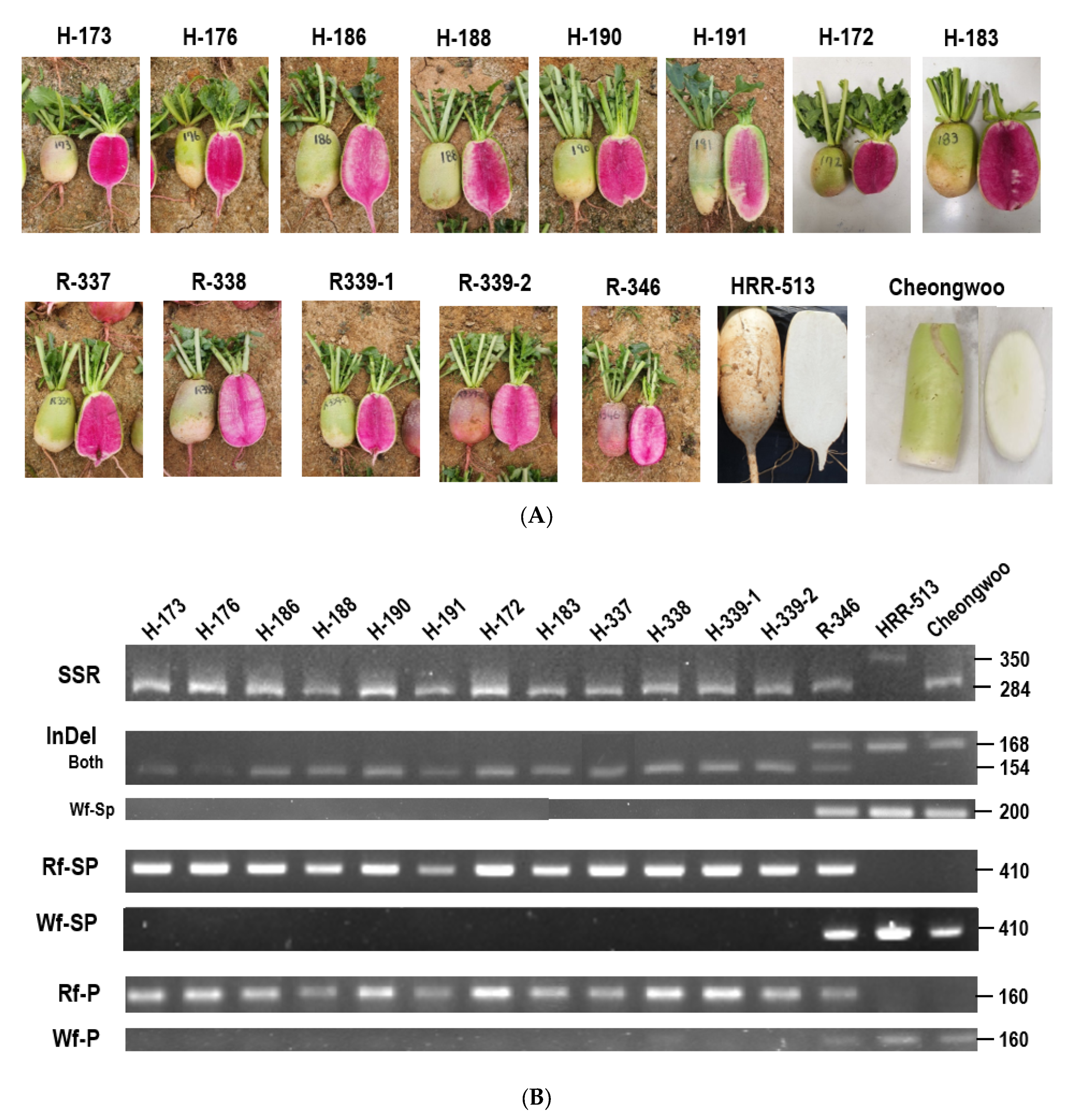
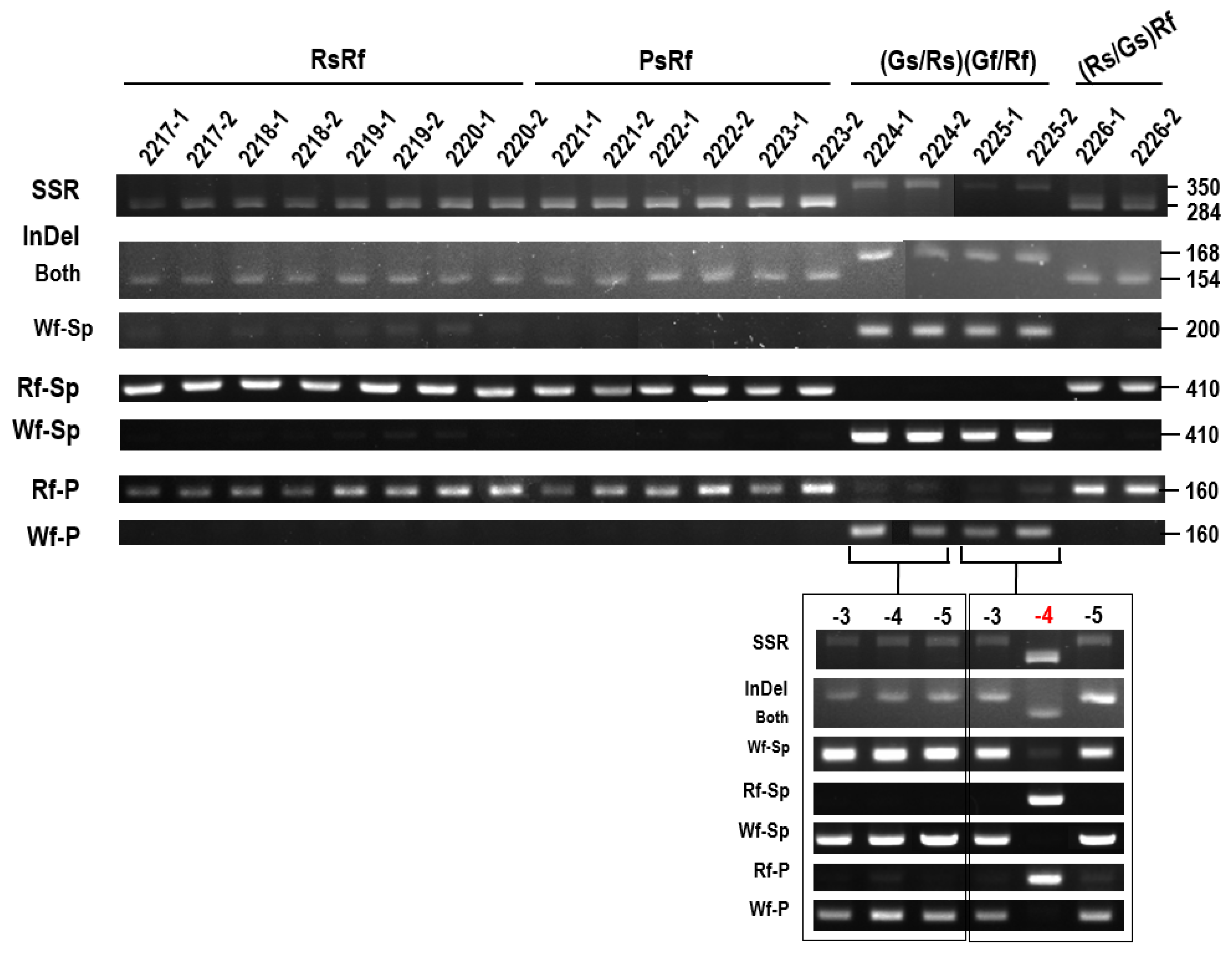
| Region | Between Rf and Wf | WsWf-Specific | RsWf-Specific | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | InDel | SSR | SNP | InDel | SSR | SNP | InDel | SSR | |
| Promoter | 16 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| Exon | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | - |
| Intron | 10 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | - | 1 |
| Total | 28 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Yun, K.; Park, H.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Song, H.; Lee, O.N.; Hur, Y.; Oh, M.-H. Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene. Plants 2021, 10, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071386
Kim S, Yun K, Park HY, Ahn JY, Yang JY, Song H, Lee ON, Hur Y, Oh M-H. Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene. Plants. 2021; 10(7):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071386
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Soyun, Keunho Yun, Han Yong Park, Ju Young Ahn, Ju Yeon Yang, Hayoung Song, O New Lee, Yoonkang Hur, and Man-Ho Oh. 2021. "Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene" Plants 10, no. 7: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071386
APA StyleKim, S., Yun, K., Park, H. Y., Ahn, J. Y., Yang, J. Y., Song, H., Lee, O. N., Hur, Y., & Oh, M.-H. (2021). Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene. Plants, 10(7), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071386







