Identification of Gene Associated with Sweetness in Corn (Zea mays L.) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Development of a Functional SNP Marker for Predicting Sweet Corn
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
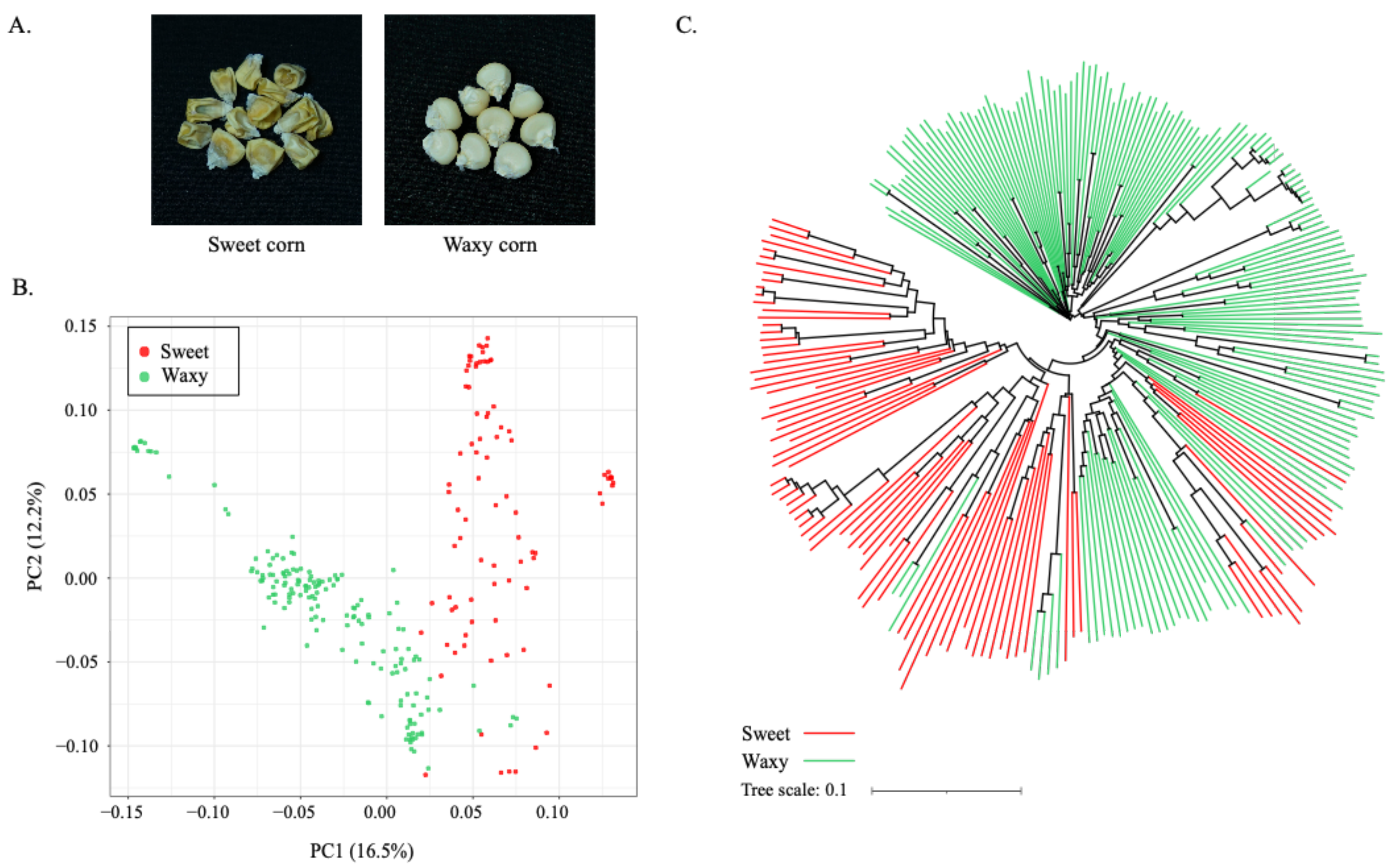
2.1. Trait Evaluation, Genotyping, and Population Study in Panel of 250 Maize Lines
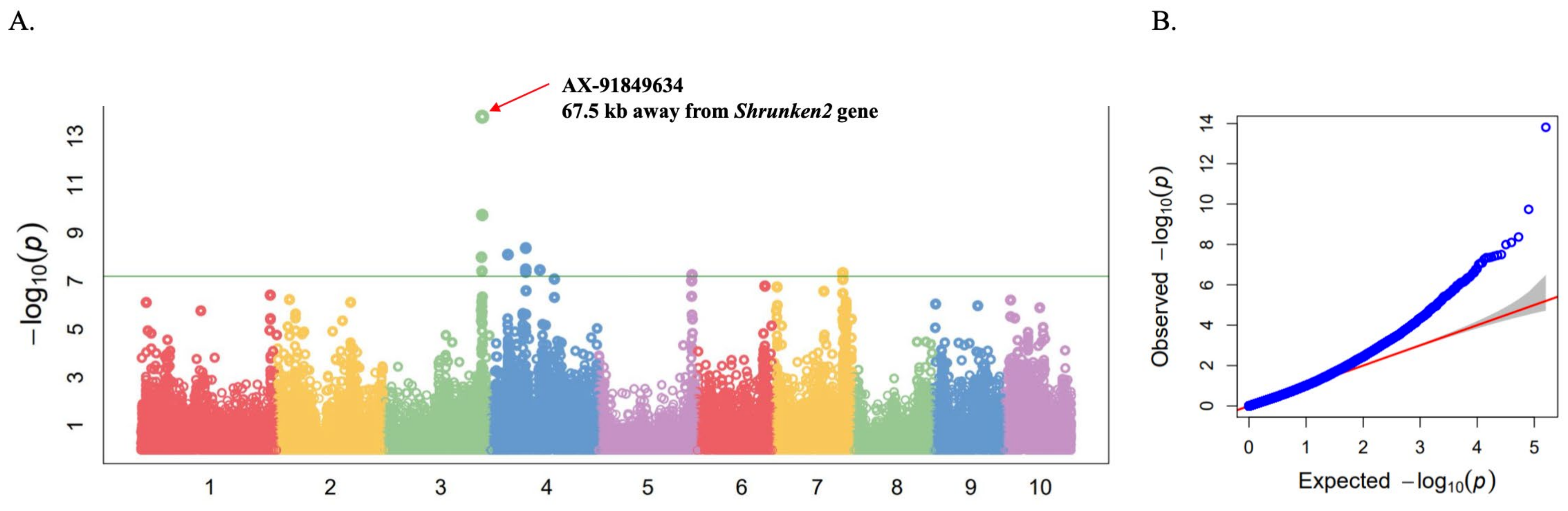
2.2. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) for Sweetness Trait
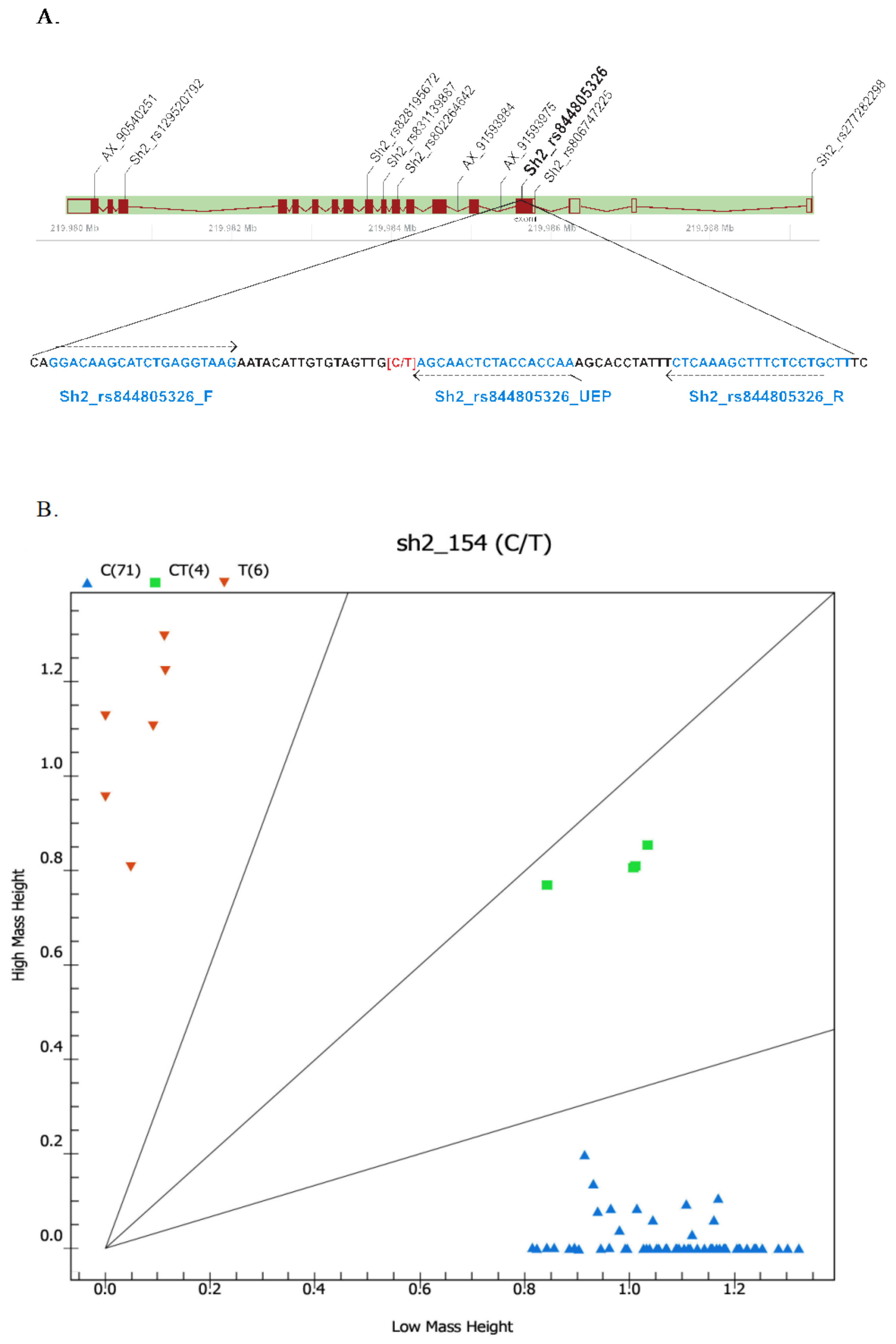
2.3. Development of SNP Markers Associated with Sweetness Trait Based on Sh2 Variants and Validation among Different Maize Types
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Kernel-Trait Evaluation
4.2. SNP Array Genotyping and Data Filtering
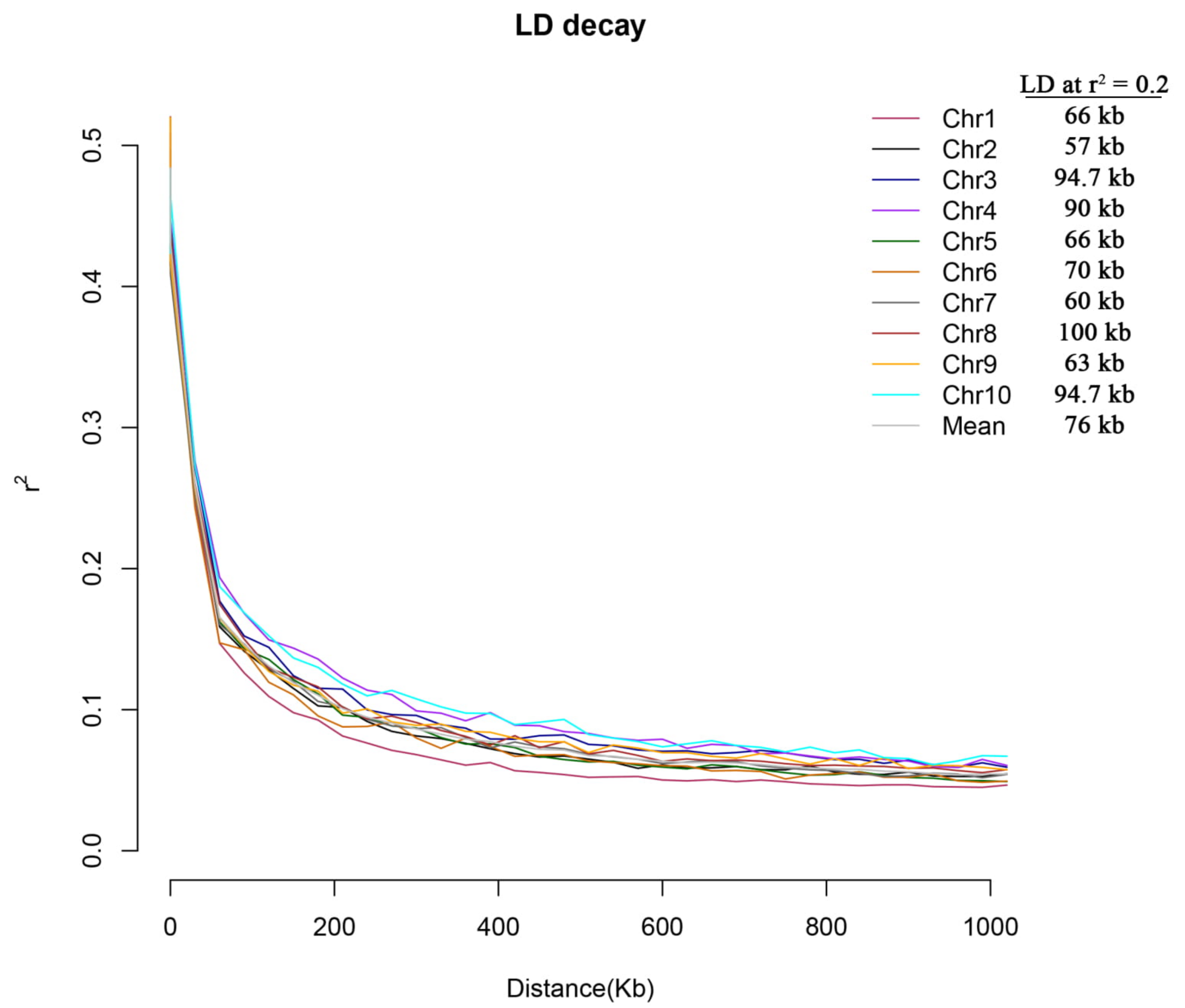
4.3. Population-Structure Analysis and Linkage-Disequilibrium (LD) Decay
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS)
4.5. Candidate-Gene Analysis
4.6. Gene-Based SNP Marker Development and Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tracy, W.F.; Shuler, S.L.; Dodson-Swenson, H. The Use of Endosperm Genes for Sweet Corn Improvement: A Review of Developments in Endosperm Genes in Sweet Corn since the Seminal Publication in Plant Breeding Reviews, Volume 1, by Charles Boyer and Jack Shannon (1984). Plant Breed. Rev. 2019, 43, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, C.D.; Shannon, J.C. The use of endosperm genes for sweet corn improvement. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983; pp. 139–161. ISBN 9780870553974. [Google Scholar]
- Tracy, W.F. History, genetics, and breeding of supersweet (shrunken2) sweet corn. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 189–236. ISBN 9780470650073. [Google Scholar]
- James, M.G.; Robertson, D.S.; Myers, A.M. Characterization of the Maize Gene Sugary1, a Determinant of Starch Composition in Kernels. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughnan, J.R. The Effect of the Sh(2) Factor on Carbohydrate Reserves in the Mature Endosperm of Maize. Genetics 1953, 38, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Langyan, S.; Yadava, P. Sweet Corn and Corn-Based Sweeteners. Sugar Tech 2014, 16, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, C.; Simond-Côte, E.; Reyss, A.; Manicacci, D.; Trouverie, J.; Le Guilloux, M.; Ginhoux, V.; Sidicina, F.; Prioul, J.-L. QTLs for Enzyme Activities and Soluble Carbohydrates Involved in Starch Accumulation during Grain Filling in Maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada, J. ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase from corn grain. In Complex Carbohydrates; Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1966; Volume 8, pp. 259–262. ISBN 9780121818081. [Google Scholar]
- Smidansky, E.D.; Clancy, M.; Meyer, F.D.; Lanning, S.P.; Blake, N.K.; Talbert, L.E.; Giroux, M.J. Enhanced ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase Activity in Wheat Endosperm Increases Seed Yield. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.L.; Liu, J.; Fu, F.L.; Li, W.C. Molecular Mechanism of Sweet and Waxy in Maize. Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2008, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Creech, R.G. Genetic Control of Carbohydrate Synthesis in Maize Endosperm. Genetics 1965, 52, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanek, M.; Tanaś, W.; Kassar, F.H. Kernel Carbohydrates Concentration in Sugary-1, Sugary Enhanced and Shrunken Sweet Corn Kernels. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 7, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertrat, K.; Pulam, T. Breeding for Increased Sweetness in Sweet Corn. Int. J. Plant Breed. 2007, 1, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, J.E.; Dickinson, D.B.; Rhodes, A.M. Analysis of Endosperm Sugars in a Sweet Corn Inbred (Illinois 677a) Which Contains the Sugary Enhancer (Se) Gene and Comparison of Se with Other Corn Genotypes. Plant Physiol. 1979, 63, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, R.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Baveja, A.; Mehta, B.K.; Uttamrao Zunjare, R. Development and Validation of Gene-based Markers for Shrunken2-Reference Allele and Their Utilization in Marker-assisted Sweet Corn (Zea Mays Sachharata) Breeding Programme. Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, X.; Li, H.; Pfeiffer, W.H.; Crouch, J.; Wan, J. Application of Identified QTL-Marker Associations in Rice Quality Improvement through a Design-Breeding Approach. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kulwal, P.L.; Gaur, A.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P.; Khurana, P.; Balyan, H.S.; Gupta, P.K. QTL Analysis for Grain Weight in Common Wheat. Euphytica 2006, 151, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacchi, D.; Beck-Bunn, T.; Eshed, Y.; Lopez, J.; Petiard, V.; Uhlig, J.; Zamir, D.; Tanksley, S. Advanced Backcross QTL Analysis in Tomato. I. Identification of QTLs for Traits of Agronomic Importance from Lycopersicon Hirsutum. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Babka, H.L.; Graef, G.L.; Staswick, P.E.; Lee, D.J.; Cregan, P.B.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Specht, J.E. The Seed Protein, Oil, and Yield QTL on Soybean Linkage Group I. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachi, B.; Morris, G.P.; Borevitz, J.O. Genome-Wide Association Studies in Plants: The Missing Heritability Is in the Field. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnable, P.S.; Ware, D.; Fulton, R.S.; Stein, J.C.; Wei, F.; Pasternak, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fulton, L.; Graves, T.A.; et al. The B73 Maize Genome: Complexity, Diversity, and Dynamics. Science 2009, 326, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiffer, J.A.; Romay, M.C.; Gore, M.A.; Flint-Garcia, S.A.; Zhang, Z.; Millard, M.J.; Gardner, C.A.C.; McMullen, M.D.; Holland, J.B.; Bradbury, P.J.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Maize Height. Genetics 2014, 196, 1337–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Buckler, E.S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T. Joint-Linkage Mapping and GWAS Reveal Extensive Genetic Loci That Regulate Male Inflorescence Size in Maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-M.; Shao, X.-Y.; Pei, Y.-H.; Guo, X.-M.; Li, J.; Song, X.-Y.; Zhao, M.-A. Genetic Diversity and Genome-Wide Association Study of Major Ear Quantitative Traits Using High-Density SNPs in Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseggio, M.; Murray, M.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; Kaczmar, N.; Chamness, J.; Buckler, E.S.; Smith, M.E.; DellaPenna, D.; Tracy, W.F.; Gore, M.A. Genome-Wide Association and Genomic Prediction Models of Tocochromanols in Fresh Sweet Corn Kernels. Plant Genome 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Xie, L.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J. Genome-Wide Association Study of Vitamin E in Sweet Corn Kernels. Crop J. 2020, 8, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandillo, N.B.; Lorenz, A.J.; Graef, G.L.; Jarquin, D.; Hyten, D.L.; Nelson, R.L.; Specht, J.E. Genome-Wide Association Mapping of Qualitatively Inherited Traits in a Germplasm Collection. Plant Genome 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, M.R.; Lawrence, S.; Barton, C.; Hannah, L.C. Identification and Molecular Characterization of Shrunken-2 CDNA Clones of Maize. Plant Cell 1990, 2, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.C.; Nelson, O.E. Characterization of ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase from Shrunken-2 and Brittle-2 Mutants of Maize. Biochem. Genet. 1976, 14, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.D.; Hannah, L.C. Kernel mutants of corn. In Specialty Corns; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 13–44. ISBN 0429127456. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, F.; Scapim, C.A.; Maldonado, C.; Mora, F. SSR-Based Genetic Analysis of Sweet Corn Inbred Lines Using Artificial Neural Networks. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Ma, X.; Su, C. QTL Analysis and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL Conferring Kernel Size in Maize (Zea mays). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 603920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, C. Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci for Yield-Related Traits and Predicting Candidate Genes for Grain Weight in Maize. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, A.; Shahi, J.P.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, M. Genetic Diversity of Sweet Corn Inbreds Using Agro-Morphological Traits and Microsatellite Markers. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Baveja, A.; Zunjare, R.; Jha, S.K.; Gupta, H.S. Microsatellite-Based Genetic Diversity Analyses of Sugary1-, Shrunken2- and Double Mutant- Sweet Corn Inbreds for Their Utilization in Breeding Programme. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2017, 23, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiani, P.; Saleh, G.; Panandam, J.M.; Abdullah, N.A.P.; Selamat, A. Molecular Characterization of Tropical Sweet Corn Inbred Lines Using Microsatellite Markers. Maydica 2012, 57, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, F.; Nepolean, T.; Vishwakarma, A.K.; Pandey, N.; Prasanna, B.M.; Gupta, H.S. Mapping and Validation of Microsatellite Markers Linked to Sugary1 and Shrunken2 Genes in Maize (Zea mays L. ). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simla, S.; Lertrat, K.; Suriharn, B. Carbohydrate Characters of Six Vegetable Waxy Corn Varieties as Affected by Harvest Time and Storage Duration. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the Number of Clusters of Individuals Using the Software STRUCTURE: A Simulation Study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for Association Mapping of Complex Traits in Diverse Samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Genetic Distance between Populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A Website and Program for Visualizing STRUCTURE Output and Implementing the Evanno Method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.-S.; Xu, J.-Y.; He, W.-M.; Yang, T.-L. PopLDdecay: A Fast and Effective Tool for Linkage Disequilibrium Decay Analysis Based on Variant Call Format Files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Wang, Q.; Peiffer, J.; Li, M.; Bradbury, P.J.; Gore, M.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT: Genome Association and Prediction Integrated Tool. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SNP | Chr | Position (V4) | –log10(p) Value | MAF | R2 | Candidate Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AX-91593662 | 3 | 218,476,619 | 7.99 | 0.33 | 0.17 | - |
| AX-91593878 | 3 | 219,463,930 | 7.42 | 0.31 | 0.16 | - |
| AX-91849634 | 3 | 22,005,7126 | 13.81 | 0.33 | 0.18 | Zm00001d044129 (Shrunken2) |
| AX-90850969 | 3 | 220,099,694 | 9.74 | 0.34 | 0.17 | - |
| AX-90866628 | 4 | 42,950,506 | 8.1 | 0.48 | 0.16 | - |
| AX-90877243 | 4 | 83,464,190 | 7.5 | 0.05 | 0.11 | - |
| AX-91612113 | 4 | 83,465,341 | 8.37 | 0.05 | 0.16 | - |
| AX-91346854 | 4 | 83,501,441 | 7.37 | 0.07 | 0.11 | - |
| AX-91617781 | 4 | 115,510,176 | 7.46 | 0.05 | 0.17 | - |
| AX-90975122 | 5 | 213,164,020 | 7.26 | 0.07 | 0.10 | - |
| AX-91411958 | 7 | 159,043,703 | 7.34 | 0.09 | 0.09 | - |
| AX-91740905 | 7 | 159,053,605 | 7.34 | 0.09 | 0.11 | - |
| Markers | Chr | Position (V.4) | SNPs | Unextended Primer (UEP) Sequence (5′---3′) a | UEP Mass (Da) | Call 1 | Mass 1 (Da) | Call 2 | Mass 2 (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AX_90540251 | 3 | 219,980,272 | G/A | tGTGATCTTGAAGAATGCAA | 6180 | G | 6427.2 | A | 6507.1 |
| Sh2_rs129520792 | 3 | 219,980,689 | A/G | ccccgGCTTCTTCTTCAGTTTCATAG | 7839.1 | A | 8110.3 | G | 8126.3 |
| Sh2_rs828195672 | 3 | 219,983,718 | C/G | AATTCTTTGAAAAACCAAAGG | 6446.2 | G | 6693.4 | C | 6733.5 |
| Sh2_rs831139887 | 3 | 219,983,940 | C/T | gtatcGTGATATCAGCATCGTCCT | 7318.8 | C | 7565.9 | T | 7645.9 |
| Sh2_rs802264642 | 3 | 219,984,110 | C/T | CCTGTATTTCTTTAGGATTATTACA | 7612 | T | 7883.2 | C | 7899.2 |
| AX_91593984 | 3 | 219,984,862 | T/A | cccgACCACTTCGATTATGG | 6052.9 | A | 6324.2 | T | 6380 |
| AX_91593975 | 3 | 219,985,438 | A/T | cccTCAAATAGGGTCATCT | 5747.8 | T | 6019 | A | 6074.9 |
| Sh2_rs844805326 | 3 | 219,985,637 | C/T | gTTGGTGGTAGAGTTGCT | 5616.6 | T | 5887.9 | C | 5903.9 |
| Sh2_rs806747225 | 3 | 219,985,795 | A/G | AGTGCAAACTGCATATCT | 5482.6 | C | 5729.8 | T | 5809.7 |
| Sh2_rs277282298 | 3 | 219,989,285 | G/A | ACCACTACCACCAACA | 4748.1 | C | 4995.3 | T | 5075.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruanjaichon, V.; Khammona, K.; Thunnom, B.; Suriharn, K.; Kerdsri, C.; Aesomnuk, W.; Yongsuwan, A.; Chaomueang, N.; Thammapichai, P.; Arikit, S.; et al. Identification of Gene Associated with Sweetness in Corn (Zea mays L.) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Development of a Functional SNP Marker for Predicting Sweet Corn. Plants 2021, 10, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061239
Ruanjaichon V, Khammona K, Thunnom B, Suriharn K, Kerdsri C, Aesomnuk W, Yongsuwan A, Chaomueang N, Thammapichai P, Arikit S, et al. Identification of Gene Associated with Sweetness in Corn (Zea mays L.) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Development of a Functional SNP Marker for Predicting Sweet Corn. Plants. 2021; 10(6):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061239
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuanjaichon, Vinitchan, Kanogporn Khammona, Burin Thunnom, Khundej Suriharn, Chalong Kerdsri, Wanchana Aesomnuk, Arweewut Yongsuwan, Naraporn Chaomueang, Paradee Thammapichai, Siwaret Arikit, and et al. 2021. "Identification of Gene Associated with Sweetness in Corn (Zea mays L.) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Development of a Functional SNP Marker for Predicting Sweet Corn" Plants 10, no. 6: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061239
APA StyleRuanjaichon, V., Khammona, K., Thunnom, B., Suriharn, K., Kerdsri, C., Aesomnuk, W., Yongsuwan, A., Chaomueang, N., Thammapichai, P., Arikit, S., Wanchana, S., & Toojinda, T. (2021). Identification of Gene Associated with Sweetness in Corn (Zea mays L.) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Development of a Functional SNP Marker for Predicting Sweet Corn. Plants, 10(6), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061239






