Heart Development, Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in a Giant Danio (Devario malabaricus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the Giant Danio Devario Malabaricus
2.2. Animals Breeding and Rearing
2.3. Morphometric Analysis
2.4. Wholemount Lectin Staining and Immunostaining Procedures
2.5. Tissue Imaging and Image Analysis
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cardiac Development in the Giant Danio Devario Malabaricus
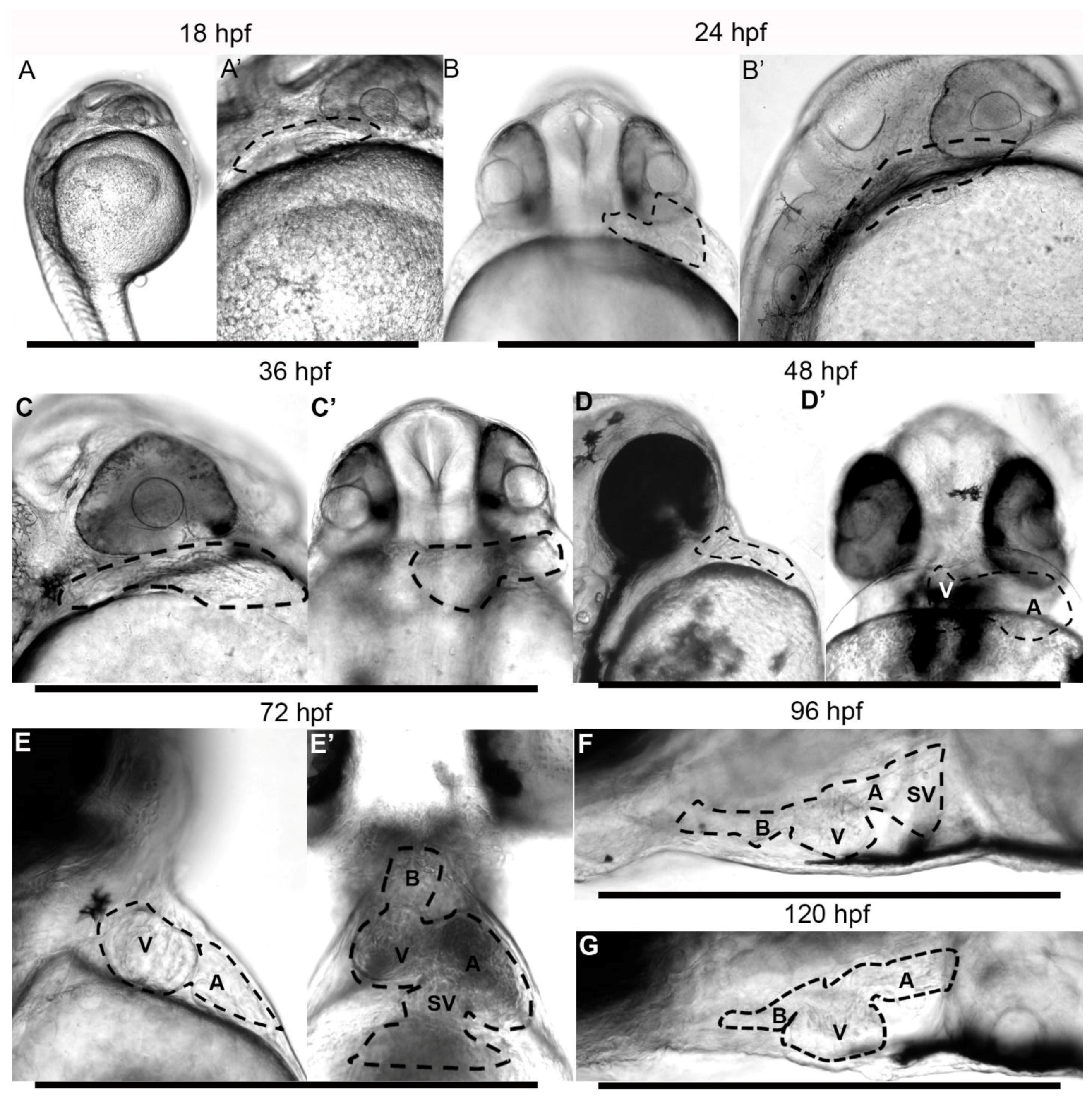
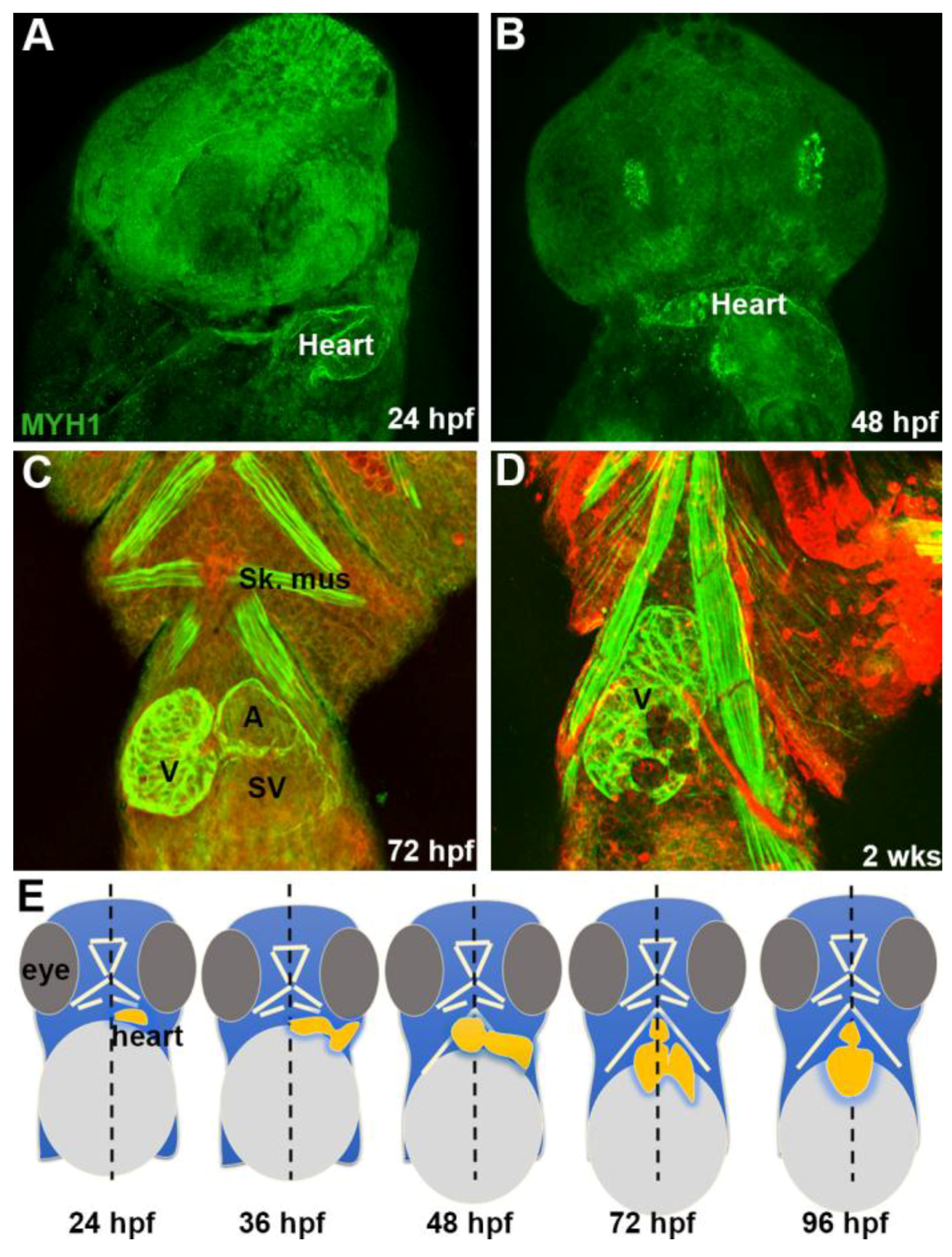
3.2. Embryonic Stage (Fertilization to 1.5 Days Post-Fertilization)
3.3. Early Larvae (36–72 h Post Fertilization)
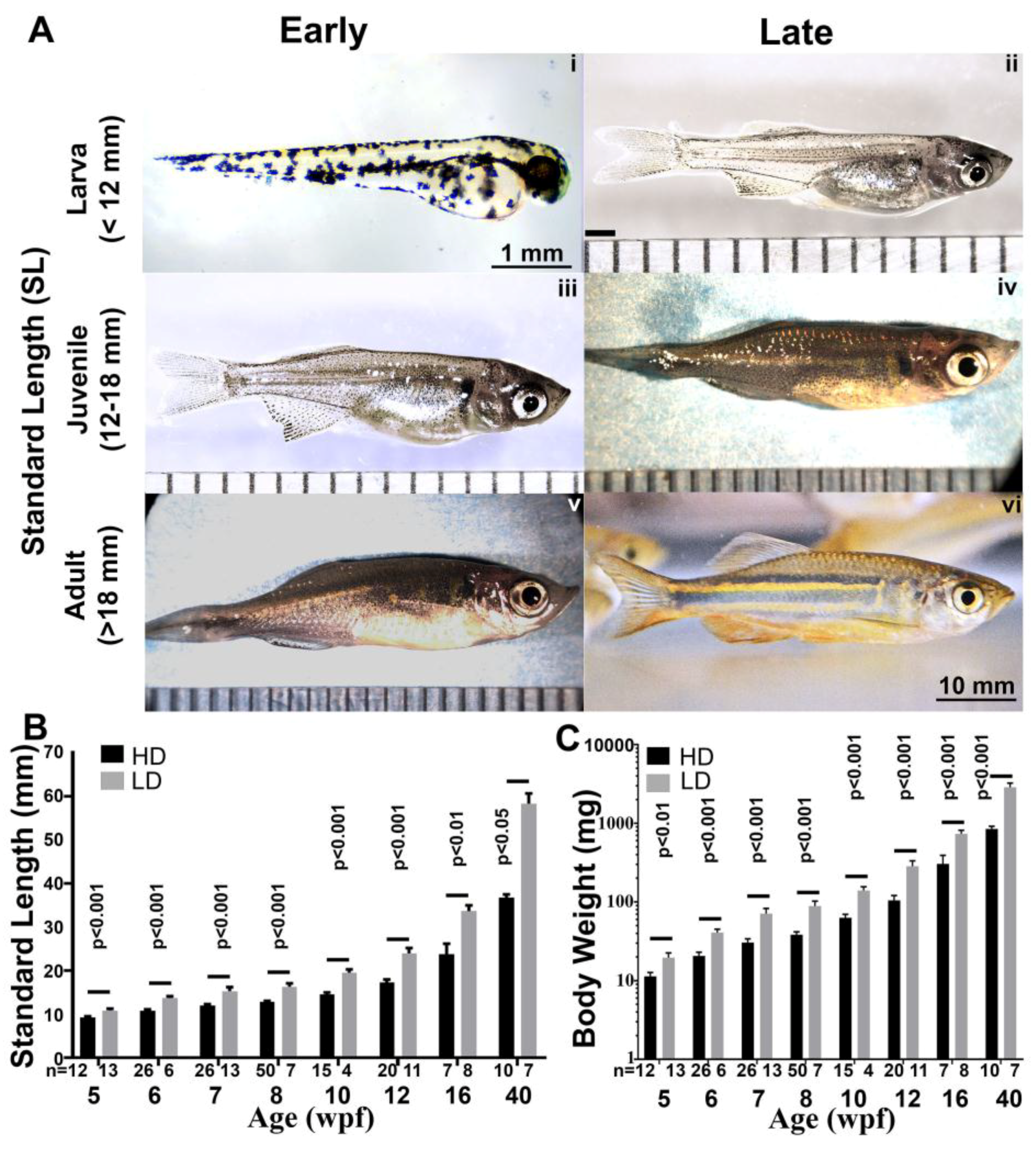
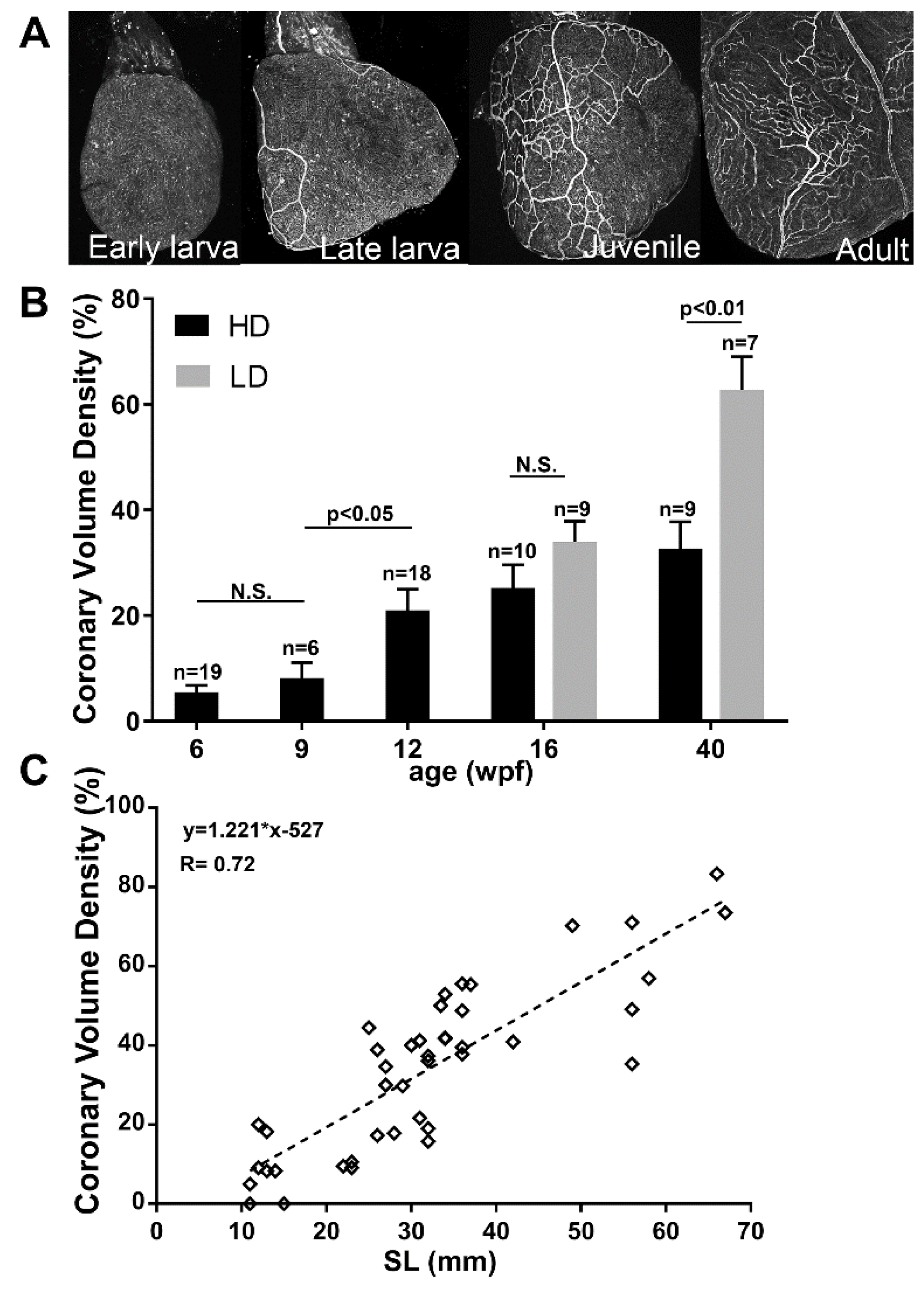
3.4. Growth Parameters in Post Embryonic DM
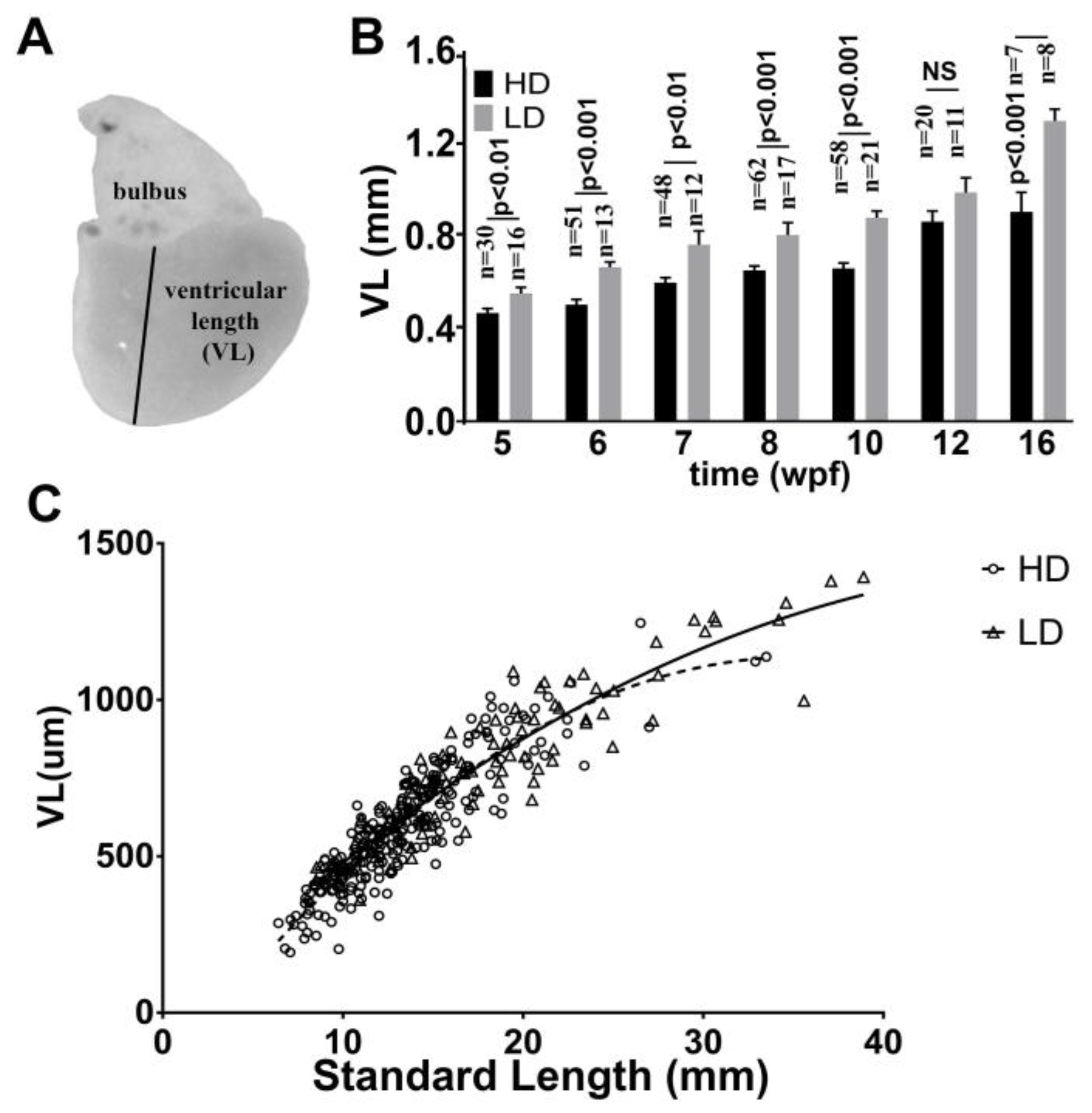
3.5. Ventricular Growth in Post Embryonic DM
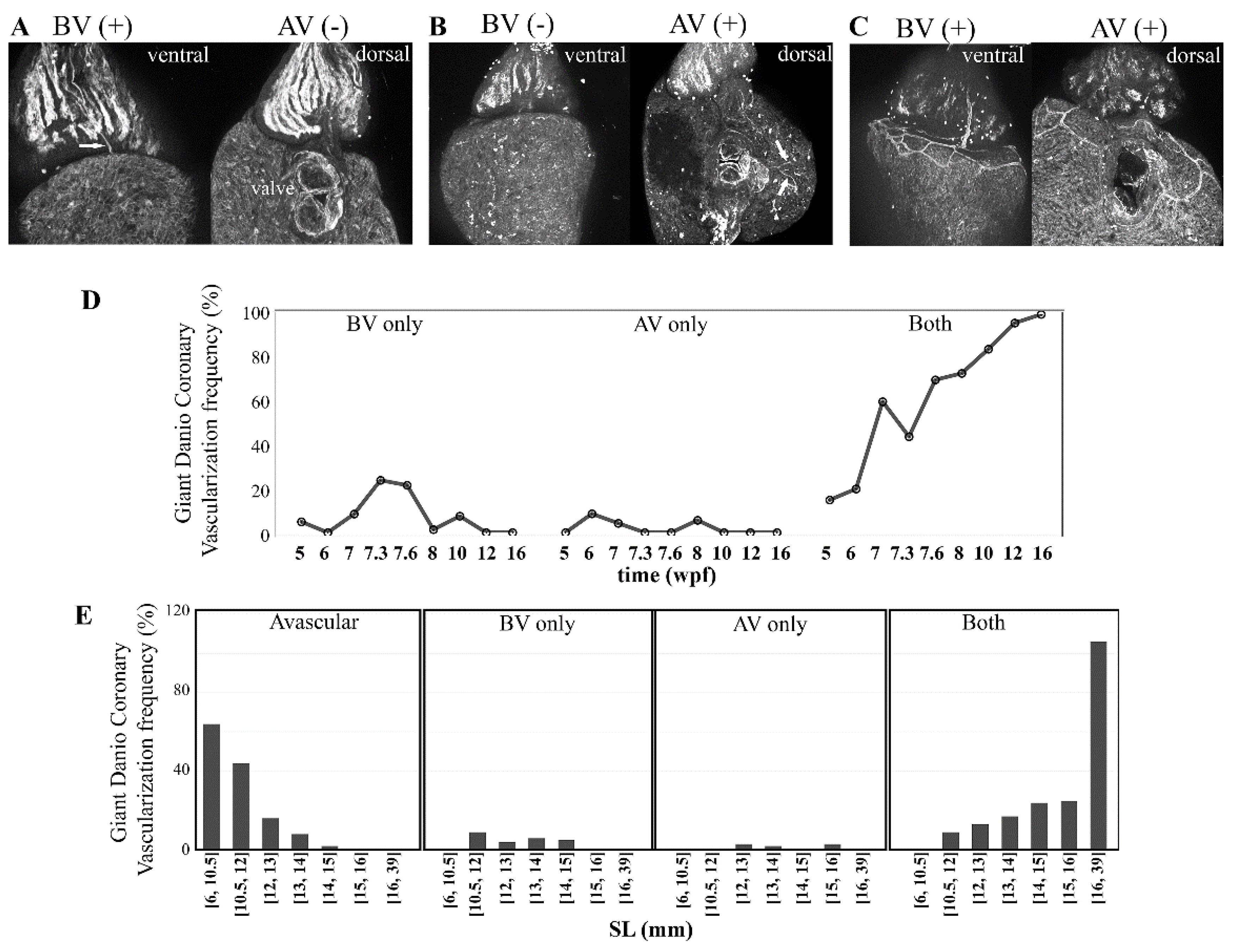
3.6. Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in the Post-Embryonic DM
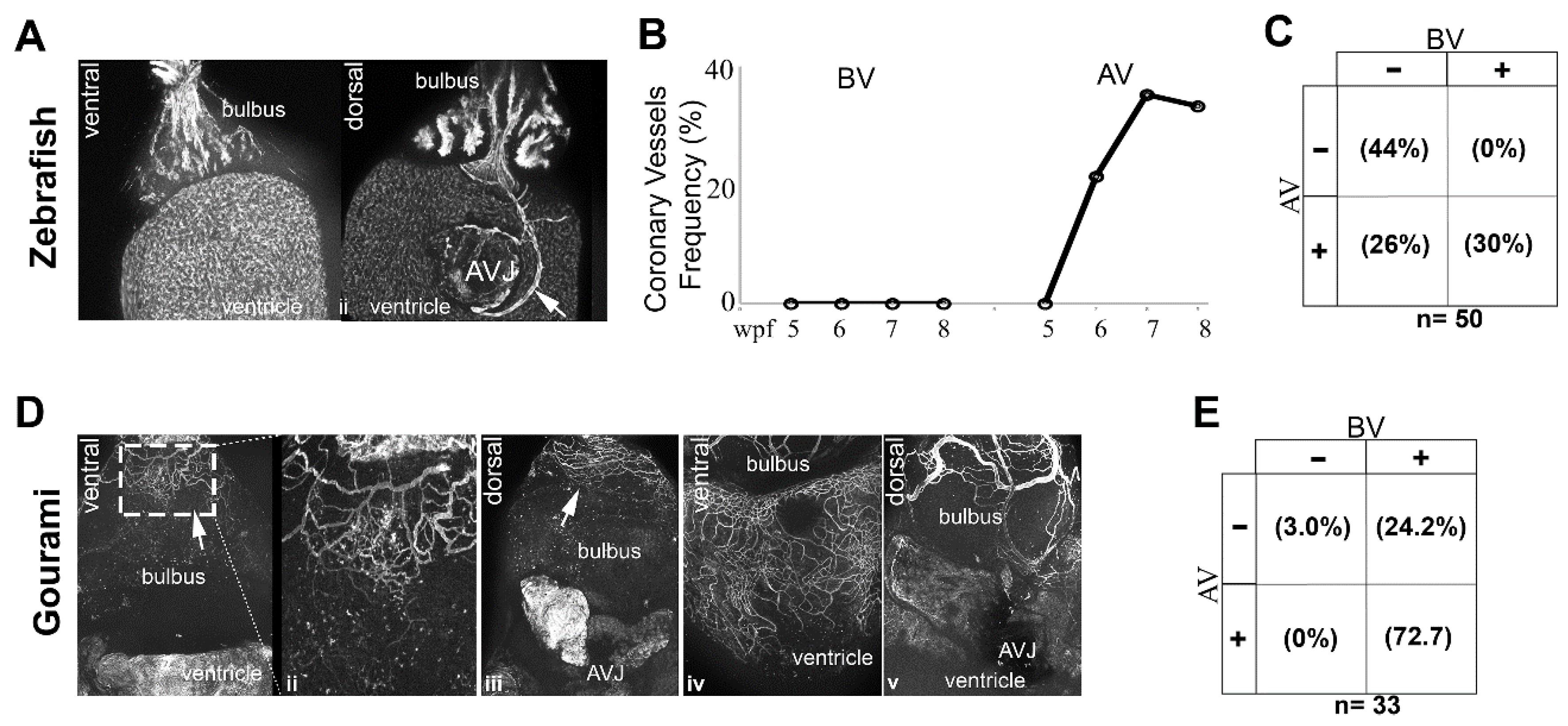
3.7. Origin of Coronary Vessels in the Giant Danio, Zebrafish and Gourami
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komuro, I.; Izumo, S. Csx: A murine homeobox-containing gene specifically expressed in the developing heart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8145–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonissen, K.F.; Drysdale, T.A.; Lints, T.J.; Harvey, R.P.; Krieg, P.A. Xnkx-2.5, a xenopus gene related to nkx-2.5 and tinman: Evidence for a conserved role in cardiac development. Dev. Biol. 1994, 162, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.G.; Patterson, V.L.; Grimes, D.T.; Burdine, R.D. Modeling syndromic congenital heart defects in zebrafish. Curr. Top. Dev. Boil. 2017, 124, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, B.; Wang, T.; Christoffels, V.M.; Moorman, A.F. Evolution and development of the building plan of the vertebrate heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, M.C.; Stainier, D.Y. Cardiovascular development. Prospects for a genetic approach. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stainier, D.Y.; Fishman, M.C. The zebrafish as a model system to study cardiovascular development. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1994, 4, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Pristyazhnyuk, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ozato, K. The see-through medaka: A fish model that is transparent throughout life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10046–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hano, T.; Oshima, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Tanaka, M.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Ozato, K.; Nassef, M.; Shimasaki, Y.; Honjo, T. In ovo nanoinjection of nonylphenol affects embryonic development of a transgenic see-through medaka (Oryzias latipes), olvas-GFP/STII-YI strain. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Sedmera, D.; Yost, H.J.; Clark, E.B. Structure and function of the developing zebrafish heart. Anat. Rec. 2000, 260, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, K.D.; Wilson, L.G.; Keating, M.T. Heart regeneration in zebrafish. Science 2002, 298, 2188–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Poss, K.D. Cardiac regenerative capacity and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 719–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleman, C.; Holtzman, N.G. Analysis of postembryonic heart development and maturation in the zebrafish, danio rerio. Dev. Dyn. 2012, 241, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Morioka, M.; Kimura, S.; Tasaki, M.; Inohaya, K.; Kudo, A. Differential reparative phenotypes between zebrafish and medaka after cardiac injury. Dev. Dyn. 2014, 243, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icardo, J.M.; Guerrero, A.; Duran, A.C.; Domezain, A.; Colvee, E.; Sans-Coma, V. The development of the sturgeon heart. Anat. Embryol. 2004, 208, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, A.C.; Duran, A.C.; Sans-Coma, V.; Hami, D.; Santoro, M.M.; Torres, M. Phylogeny informs ontogeny: A proposed common theme in the arterial pole of the vertebrate heart. Evol. Dev. 2010, 12, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midttun, B. Ultrastructure of the junctional region of the fish heart ventricle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1983, 76, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.M. Morphology and innervation of the fish heart. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 1985, 89, 1–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agnisola, C.; Tota, B. Structure and function of the fish cardiac ventricle: Flexibility and limitations. Cardioscience 1994, 5, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Biermann, C.H.; Orti, G. The phylogenetic position of the zebrafish (Danio rerio), a model system in developmental biology: An invitation to the comparative method. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1993, 252, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biga, P.R.; Meyer, J. Growth hormone differentially regulates growth and growth-related gene expression in closely related fish species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2009, 154, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullander, S.O.; Rahman, M.M.; Noren, M.; Mollah, A.R. Devario in Bangladesh: Species diversity, sibling species, and introgression within danionin cyprinids (Teleostei: Cyprinidae: Danioninae). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullander, S.O. Devario fangae and Devario myitkyinae, two new species of danionin cyprinids from northern Myanmar (Teleostei: Cyprinidae: Danioninae). Zootaxa 2017, 4227, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, G.; Shirakami, H.; Hirano, Y.; Oba, M.; Yoshinaga, H.; Khieokhajonkhet, A.; Nagasaka, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Ushio, H. Diversity of lipid distribution in fish skeletal muscle. Zool. Sci. 2016, 33, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poling, K.R.; Brunjes, P.C. Sensory deafferentation and olfactory bulb morphology in the zebrafish and related species. Brain Res. 2000, 856, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braekevelt, C.R. Fine structure of the retinal epithelium and tapetum lucidum in the giant danio (Danio malabaricus) (teleost). Anat. Embryol. 1980, 158, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D.G.; Mattson, M.P. Horizontal cell electrical coupling in the giant danio: Synaptic modulation by dopamine and synaptic maintenance by calcium. Brain Res. 1996, 718, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roessel, P.; Palacios, A.G.; Goldsmith, T.H. Activity of long-wavelength cones under scotopic conditions in the cyprinid fish danio aequipinnatus. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1997, 181, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.L.; Beyer, E.C.; McMahon, D.G. Cloning and functional expression of a novel gap junction channel from the retina of danio aquipinnatus. Vis. Neurosci. 1998, 15, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.Y.; Adolph, A.R.; Dowling, J.E. Retinal bipolar cell input mechanisms in giant danio. I. Electroretinographic analysis. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfgang, M.J.; Anderson, J.M.; Grosenbaugh, M.A.; Yue, D.K.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Near-body flow dynamics in swimming fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2303–2327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bak-Coleman, J.; Court, A.; Paley, D.A.; Coombs, S. The spatiotemporal dynamics of rheotactic behavior depends on flow speed and available sensory information. J. Exp. Boil. 2013, 216, 4011–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butail, S.; Salerno, P.; Bollt, E.M.; Porfiri, M. Classification of collective behavior: A comparison of tracking and machine learning methods to study the effect of ambient light on fish shoaling. Behav. Res. Methods 2015, 47, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Ramanujam, S.N.; Mahapatra, B.K. Breeding and development of ornamental hill stream fish Devario aequipinnatus (McClelland) in captivity. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Biga, P.R.; Goetz, F.W. Zebrafish and giant danio as models for muscle growth: Determinate vs. Indeterminate growth as determined by morphometric analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 291, R1327–R1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafontant, P.J.; Burns, A.R.; Grivas, J.A.; Lesch, M.A.; Lala, T.D.; Reuter, S.P.; Field, L.J.; Frounfelter, T.D. The giant danio (D. aequipinnatus) as a model of cardiac remodeling and regeneration. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manalo, T.; May, A.; Quinn, J.; Lafontant, D.S.; Shifatu, O.; He, W.; Gonzalez-Rosa, J.M.; Burns, G.C.; Burns, C.E.; Burns, A.R.; et al. Differential lectin binding patterns identify distinct heart regions in giant danio (Devario aequipinnatus) and zebrafish (Danio rerio) hearts. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2016, 64, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.L.; Agnew, M.K.; Hirt, M.V.; Sado, T.; Schneider, L.M.; Freyhof, J.; Sulaiman, Z.; Swartz, E.; Vidthayanon, C.; Miya, M.; et al. Systematics of the subfamily danioninae (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 57, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graser, R.; O’HUigin, C.; Vincek, V.; Meyer, A.; Klein, J. Trans-species polymorphism of class IIMhc loci in danio fishes. Immunogenetics 1996, 44, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S. On the breeding habits and development of a cyprinid, danio (danio) malabaricus (Jordan) in ceylon. Ceylon J. Sci. 1938, VI, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Stainier, D.Y.; Lee, R.K.; Fishman, M.C. Cardiovascular development in the zebrafish. I. Myocardial fate map and heart tube formation. Development 1993, 119, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Pater, E.; Clijsters, L.; Marques, S.R.; Lin, Y.F.; Garavito-Aguilar, Z.V.; Yelon, D.; Bakkers, J. Distinct phases of cardiomyocyte differentiation regulate growth of the zebrafish heart. Development 2009, 136, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parichy, D.M.; Elizondo, M.R.; Mills, M.G.; Gordon, T.N.; Engeszer, R.E. Normal table of postembryonic zebrafish development: Staging by externally visible anatomy of the living fish. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 2975–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, M.R.; Bussmann, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Osorio, A.; Burns, C.G.; Burns, C.E.; Sucov, H.M.; Siekmann, A.F.; Lien, C.L. Chemokine-guided angiogenesis directs coronary vasculature formation in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, A.A.; Holdway, J.E.; Major, R.J.; Poss, K.D. Regulated addition of new myocardial and epicardial cells fosters homeostatic cardiac growth and maintenance in adult zebrafish. Development 2008, 135, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Red-Horse, K.; Ueno, H.; Weissman, I.L.; Krasnow, M.A. Coronary arteries form by developmental reprogramming of venous cells. Nature 2010, 464, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.I.; Sharma, B.; Akerberg, B.N.; Numi, H.J.; Kivela, R.; Saharinen, P.; Aghajanian, H.; McKay, A.S.; Bogard, P.E.; Chang, A.H.; et al. The sinus venosus contributes to coronary vasculature through VEGFC-stimulated angiogenesis. Development 2014, 141, 4500–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Pu, W.T.; Zhou, B. Cellular origin and developmental program of coronary angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yu, W.; He, L.; Yang, Z.; Yan, Y.; et al. Vessel formation. De novo formation of a distinct coronary vascular population in neonatal heart. Science 2014, 345, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pu, W.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Tian, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.M.; Sucov, H.M.; et al. Endocardium minimally contributes to coronary endothelium in the embryonic ventricular free walls. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1880–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andres, A.V.; Munoz-Chapuli, R.; Sans-Coma, V. Development of the coronary arteries and cardiac veins in the dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula). Anat. Rec. 1993, 235, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shifatu, O.; Glasshagel-Chilson, S.; Nelson, H.M.; Patel, P.; Tomamichel, W.; Higginbotham, C.; Evans, P.K.; Lafontant, G.S.; Burns, A.R.; Lafontant, P.J. Heart Development, Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in a Giant Danio (Devario malabaricus). J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6030019
Shifatu O, Glasshagel-Chilson S, Nelson HM, Patel P, Tomamichel W, Higginbotham C, Evans PK, Lafontant GS, Burns AR, Lafontant PJ. Heart Development, Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in a Giant Danio (Devario malabaricus). Journal of Developmental Biology. 2018; 6(3):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleShifatu, Olubusola, Sarah Glasshagel-Chilson, Hannah M. Nelson, Purva Patel, Wendy Tomamichel, Clay Higginbotham, Paula K. Evans, Gregory S. Lafontant, Alan R. Burns, and Pascal J. Lafontant. 2018. "Heart Development, Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in a Giant Danio (Devario malabaricus)" Journal of Developmental Biology 6, no. 3: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6030019
APA StyleShifatu, O., Glasshagel-Chilson, S., Nelson, H. M., Patel, P., Tomamichel, W., Higginbotham, C., Evans, P. K., Lafontant, G. S., Burns, A. R., & Lafontant, P. J. (2018). Heart Development, Coronary Vascularization and Ventricular Maturation in a Giant Danio (Devario malabaricus). Journal of Developmental Biology, 6(3), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6030019



