Cell Fate Decision Making through Oriented Cell Division
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cell Polarity Complexes Controlling Cell Fate Decisions
2.1. The Par/aPKC Complex
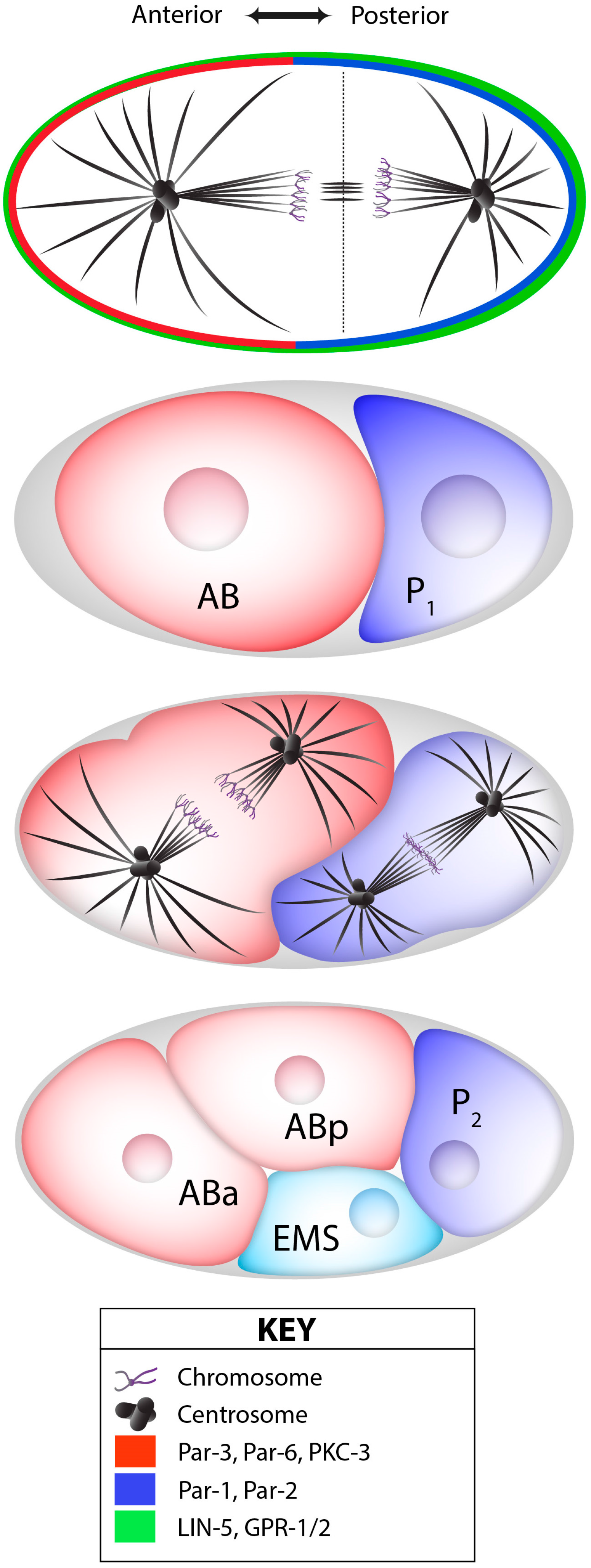
2.2. The Notch/Numb Pathway
3. Spindle Orientation Complexes Controlling Cell Fate Decisions
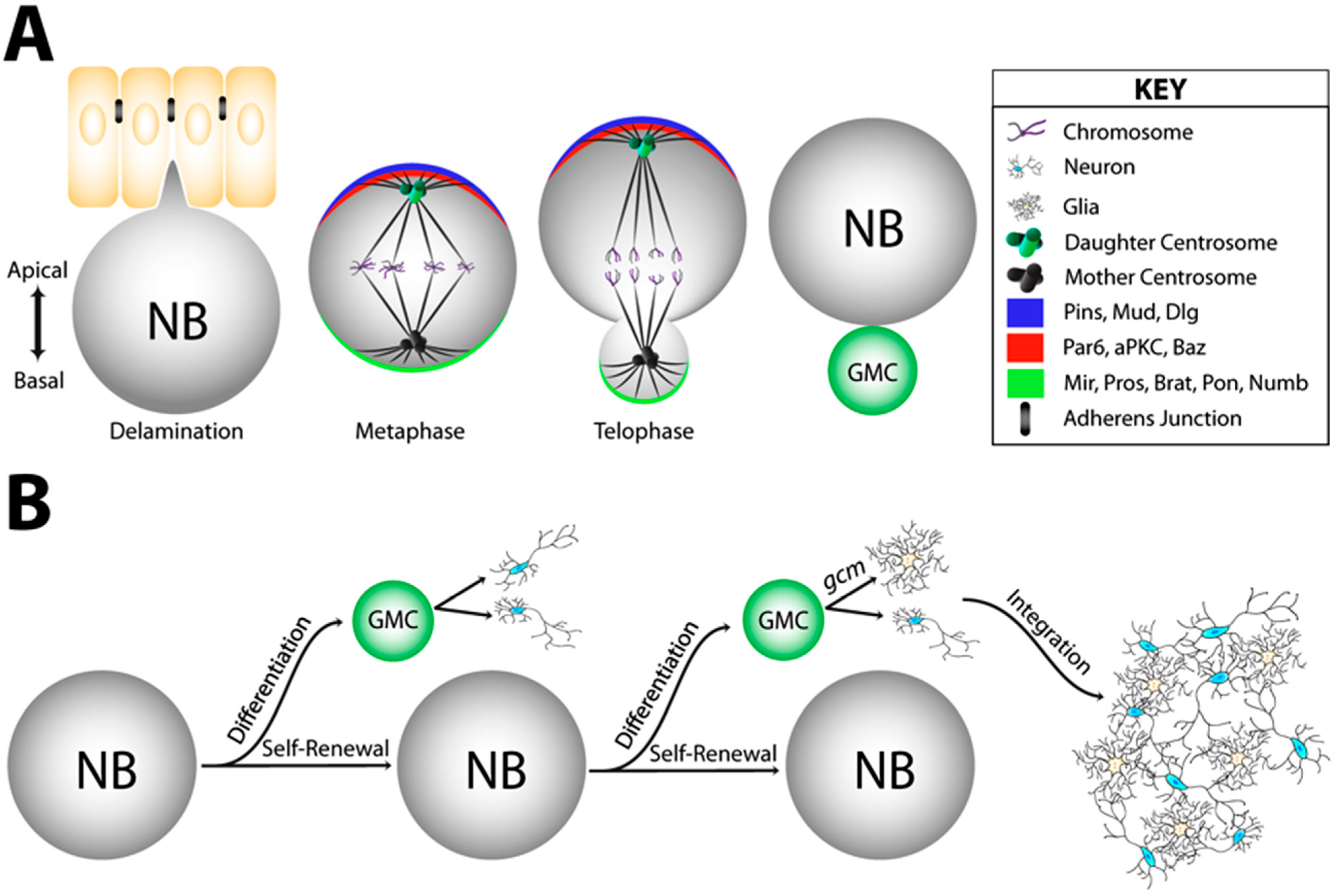
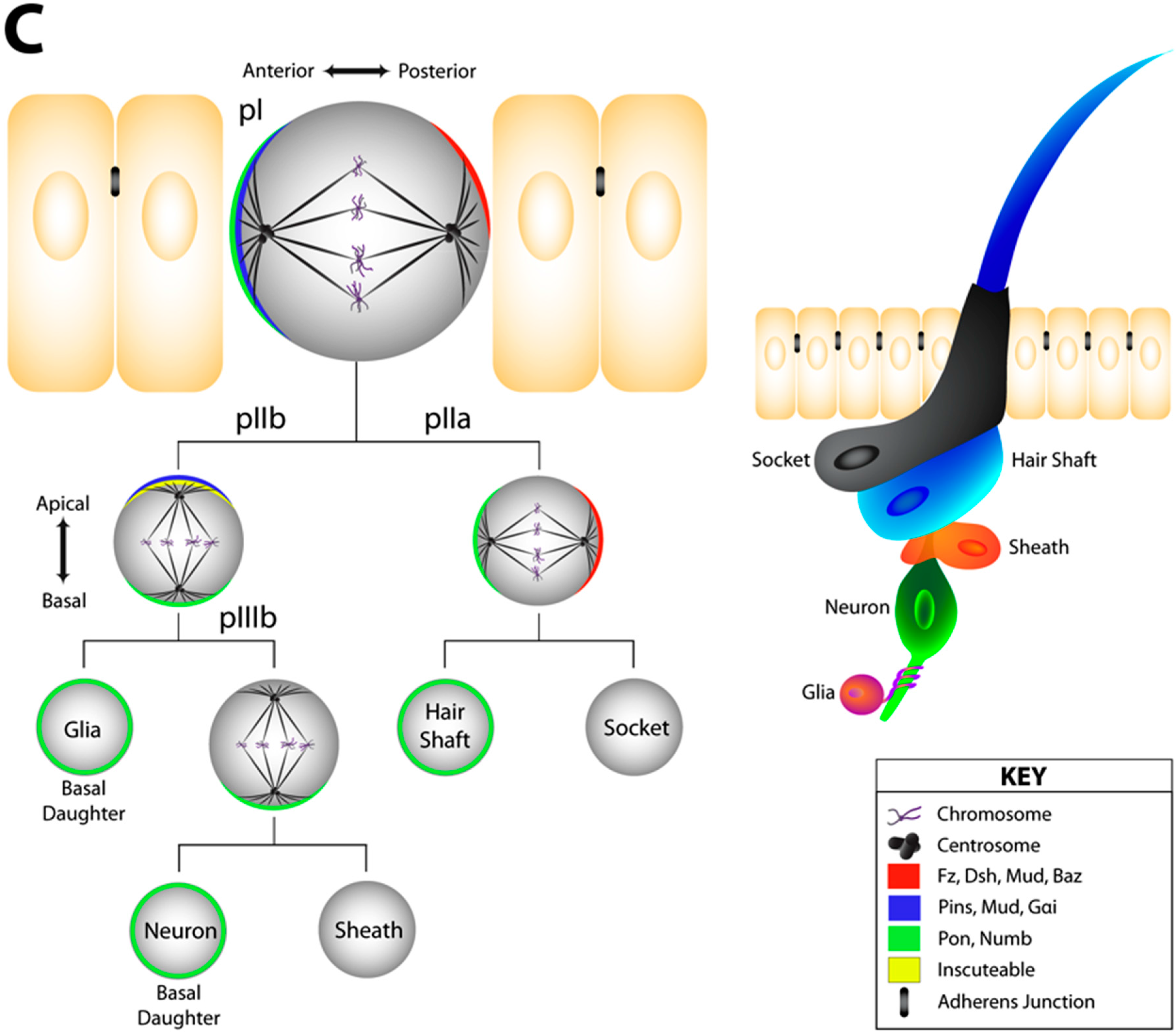
3.1. The Pins/Mud/Dlg Complex
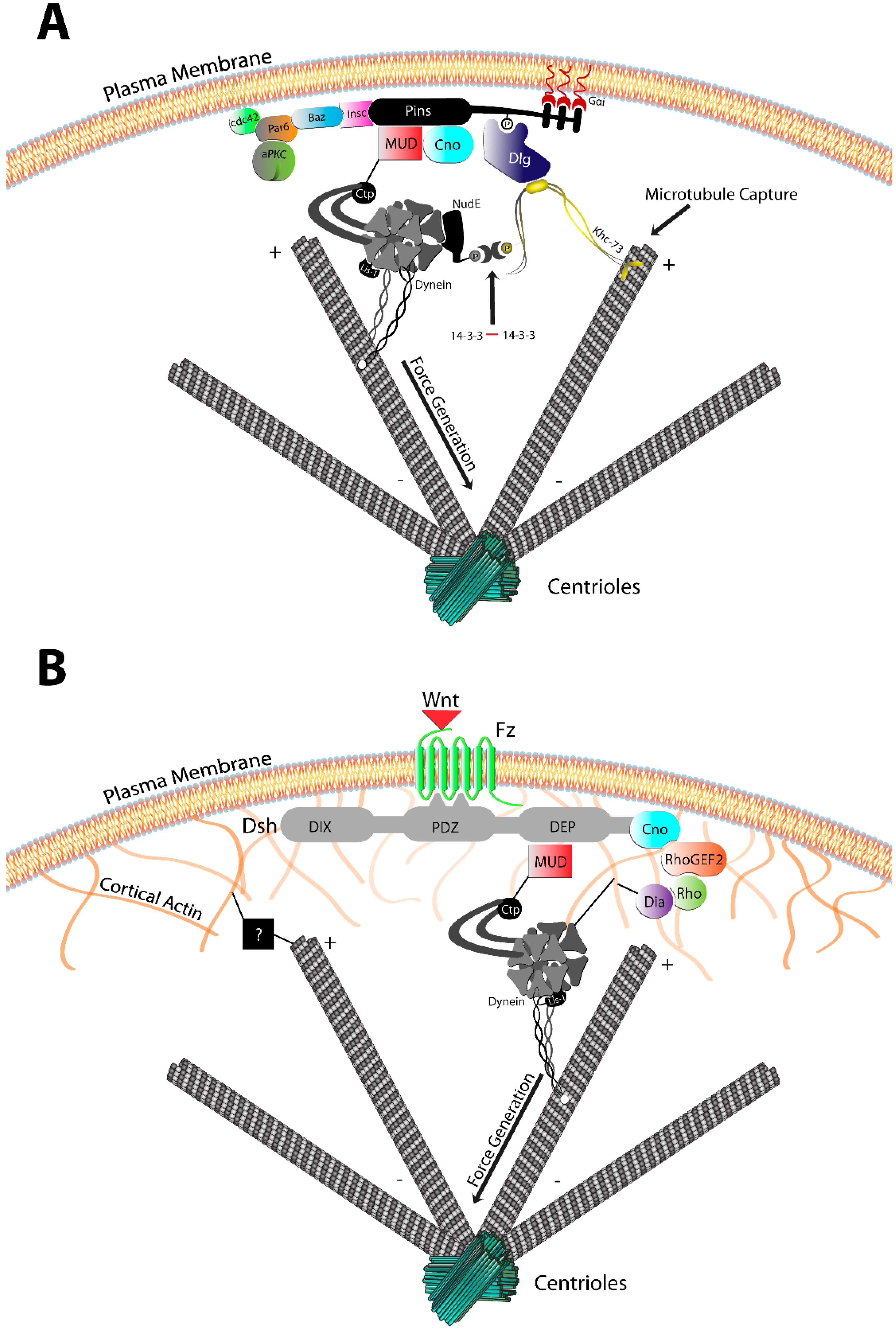
3.2. The Frizzled/Dsh Complex
4. Cell Fate Decisions Made Through Oriented Cell Divisions
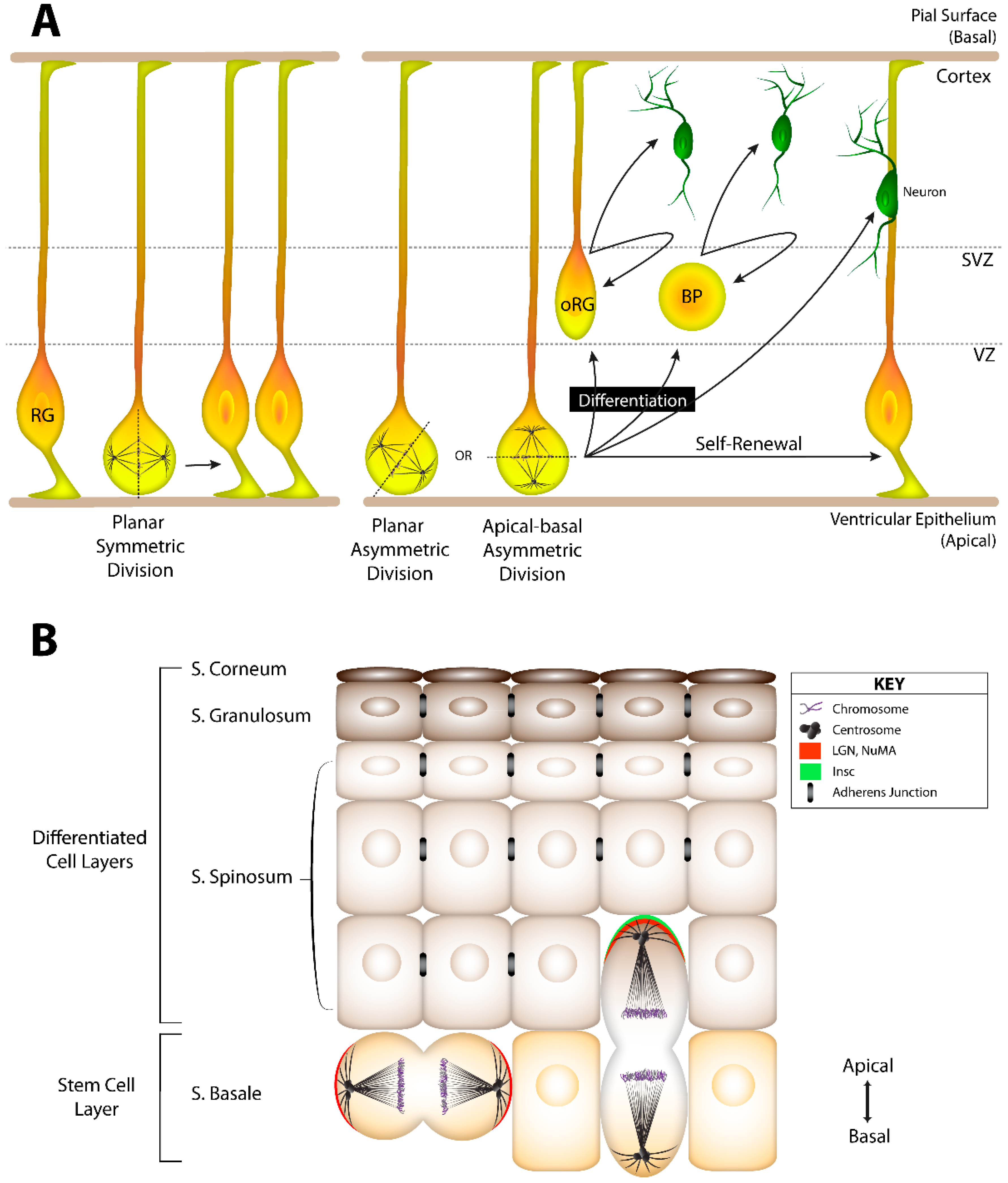
4.1. Cell Fate Decisions in the Developing Brain
4.2. Cell Fate Decisions in Epithelial Tissue
4.3. Cell Fate Decisions in the Germ Line
4.4. Cell Fate Decisions in T-cell Selection

5. Emerging Evidence for Centrosome Asymmetry
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergstralh, D.T.; St Johnston, D. Spindle orientation: What if it goes wrong? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noatynska, A.; Gotta, M.; Meraldi, P. Mitotic spindle (dis)orientation and disease: Cause or consequence? J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheeks, R.J.; Canman, J.C.; Gabriel, W.N.; Meyer, N.; Strome, S.; Goldstein, B. C. C. elegans Par proteins function by mobilizing and stabilizing asymmetrically localized protein complexes. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca, A.A.; Schetter, A.; Aceto, D.; Kemphues, K.; Seydoux, G. Polarization of the C. elegans zygote proceeds via distinct establishment and maintenance phases. Development 2003, 130, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, E.; Nance, J.; Priess, J.R. Cortical flows powered by asymmetrical contraction transport par proteins to establish and maintain anterior-posterior polarity in the early C. elegans embryo. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motegi, F.; Zonies, S.; Hao, Y.; Cuenca, A.A.; Griffin, E.; Seydoux, G. Microtubules induce self-organization of polarized par domains in caenorhabditis elegans zygotes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrasek, Z.; Hoege, C.; Mashaghi, A.; Ohrt, T.; Hyman, A.A.; Schwille, P. Characterization of protein dynamics in asymmetric cell division by scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Boyd, L.; Seydoux, G. Stabilization of cell polarity by the C. elegans ring protein Par-2. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, A.; Morton, D.; Kemphues, K. The C. elegans homolog of Drosophila Lethal giant larvae functions redundantly with PAR-2 to maintain polarity in the early embryo. Development 2010, 137, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoege, C.; Constantinescu, A.T.; Schwager, A.; Goehring, N.W.; Kumar, P.; Hyman, A.A. Lgl can partition the cortex of one-cell Caenorhabditis elegans embryos into two domains. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulston, J.E.; Schierenberg, E.; White, J.G.; Thomson, J.N. The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 1983, 100, 64–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, H. Control of cell polarity and asymmetric division in C. elegans. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2012, 101, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Betschinger, J.; Mechtler, K.; Knoblich, J.A. The Par complex directs asymmetric cell division by phosphorylating the cytoskeletal protein Lgl. Nature 2003, 422, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Robinson, K.J.; Doe, C.Q. Lgl, Pins and aPKC regulate neuroblast self-renewal versus differentiation. Nature 2006, 439, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, M.M.; Albertson, R.; Shih, H.P.; Lee, C.Y.; Doe, C.Q. Drosophila aPKC regulates cell polarity and cell proliferation in neuroblasts and epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwood, S.X.; Chabu, C.; Penkert, R.R.; Doe, C.Q.; Prehoda, K.E. Cdc42 acts downstream of Bazooka to regulate neuroblast polarity through Par-6 aPKC. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3200–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Chan, L.N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M. PDZ domains of Par-3 as potential phosphoinositide signaling integrators. Molecular cell 2007, 28, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.G.; Harris, T.J. Interactions between the PDZ domains of Bazooka (Par-3) and phosphatidic acid: In vitro characterization and role in epithelial development. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeshima-Kataoka, H.; Skeath, J.B.; Nabeshima, Y.; Doe, C.Q.; Matsuzaki, F. Miranda directs prospero to a daughter cell during Drosophila asymmetric divisions. Nature 1997, 390, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.P.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Miranda is required for the asymmetric localization of prospero during mitosis in Drosophila. Cell 1997, 90, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Ackerman, L.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Modes of protein movement that lead to the asymmetric localization of partner of numb during Drosophila neuroblast division. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Rothenberg, M.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Partner of Numb colocalizes with Numb during mitosis and directs Numb asymmetric localization in Drosophila neural and muscle progenitors. Cell 1998, 95, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Percival-Smith, A.; Li, C.; Jia, C.Y.; Gloor, G.; Li, S.S. A novel transmembrane protein recruits numb to the plasma membrane during asymmetric cell division. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11304–11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwood, S.X.; Prehoda, K.E. aPKC phosphorylates Miranda to polarize fate determinants during neuroblast asymmetric cell division. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Lau, K.M.; Rahmani, Z.; Dho, S.E.; Brothers, G.; She, Y.M.; Berry, D.M.; Bonneil, E.; Thibault, P.; Schweisguth, F.; et al. aPKC-mediated phosphorylation regulates asymmetric membrane localization of the cell fate determinant Numb. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz-Peitz, F.; Nishimura, T.; Knoblich, J.A. Linking cell cycle to asymmetric division: Aurora-A phosphorylates the Par complex to regulate Numb localization. Cell 2008, 135, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Andersen, R.O.; Cabernard, C.; Manning, L.; Tran, K.D.; Lanskey, M.J.; Bashirullah, A.; Doe, C.Q. Drosophila Aurora-A kinase inhibits neuroblast self-renewal by regulating aPKC/Numb cortical polarity and spindle orientation. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, T.; Takizawa, K.; Nitta, K.; Hotta, Y. Glial cells missing: A binary switch between neuronal and glial determination in drosophila. Cell 1995, 82, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.W.; Fetter, R.D.; Tear, G.; Goodman, C.S. Glial cells missing: A genetic switch that controls glial versus neuronal fate. Cell 1995, 82, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.M.; Datta, A.; Rodriguez-Fraticelli, A.E.; Peranen, J.; Martin-Belmonte, F.; Mostov, K.E. A molecular network for de novo generation of the apical surface and lumen. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, D.M.; Mostov, K.E. From cells to organs: Building polarized tissue. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yamanaka, T.; Sasaki, K.; Mizuno, K.; Sawada, H.; Yonemura, S.; Ohno, S. Interaction between Par-3 and the aPKC-Par-6 complex is indispensable for apical domain development of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musch, A.; Cohen, D.; Yeaman, C.; Nelson, W.J.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E.; Brennwald, P.J. Mammalian homolog of Drosophila tumor suppressor lethal (2) giant larvae interacts with basolateral exocytic machinery in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, T.; Horikoshi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Maniwa, R.; Nagai, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Hirose, T.; Ishikawa, H.; et al. Par-6 regulates aPKC activity in a novel way and mediates cell-cell contact-induced formation of the epithelial junctional complex. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Veligodskiy, A.; Berge, U.; Lucas, M.S.; Kroschewski, R. Rock-mediated contractility, tight junctions and channels contribute to the conversion of a preapical patch into apical surface during isochoric lumen initiation. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3649–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Wu, H.; Chan, L.N.; Zhang, M. Par-3-mediated junctional localization of the lipid phosphatase PTEN is required for cell polarity establishment. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23440–23449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassama-Diagne, A.; Yu, W.; ter Beest, M.; Martin-Belmonte, F.; Kierbel, A.; Engel, J.; Mostov, K. Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate regulates the formation of the basolateral plasma membrane in epithelial cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Belmonte, F.; Mostov, K. Phosphoinositides control epithelial development. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Stein, W.; Ramrath, A.; Grimm, A.; Muller-Borg, M.; Wodarz, A. Direct association of Bazooka/Par-3 with the lipid phosphatase pten reveals a link between the Par/aPKC complex and phosphoinositide signaling. Development 2005, 132, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahama, S.; Hirose, T.; Ohno, S. aPKC restricts the basolateral determinant Ptdins(3,4,5)P3 to the basal region. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgan, J.; Kaji, N.; Jin, D.; Hall, A. Par6B and atypical PKC regulate mitotic spindle orientation during epithelial morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12461–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Du, Q.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Balsbaugh, J.L.; Maitra, S.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Macara, I.G. Par3 controls epithelial spindle orientation by aPKC-mediated phosphorylation of apical Pins. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collu, G.M.; Hidalgo-Sastre, A.; Brennan, K. Wnt-Notch signalling crosstalk in development and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3553–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoblich, J.A.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. The N terminus of the Drosophila Numb protein directs membrane association and actin-dependent asymmetric localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13005–13010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshiro, T.; Yagami, T.; Zhang, C.; Matsuzaki, F. Role of cortical tumour-suppressor proteins in asymmetric division of Drosophila neuroblast. Nature 2000, 408, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Manning, L.; Albertson, R.; Doe, C.Q. The tumour-suppressor genes lgl and dlg regulate basal protein targeting in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nature 2000, 408, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roegiers, F.; Younger-Shepherd, S.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Two types of asymmetric divisions in the Drosophila sensory organ precursor cell lineage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frise, E.; Knoblich, J.A.; YoungerShepherd, S.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. The Drosophila Numb protein inhibits signaling of the Notch receptor during cell-cell interaction in sensory organ lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11925–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, L.; Vodovar, N.; Schweisguth, F. Endocytosis by Numb breaks Notch symmetry at cytokinesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutterer, A.; Knoblich, J.A. Numb and alpha-Adaptin regulate sanpodo endocytosis to specify cell fate in Drosophila external sensory organs. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolini, E.; Puri, C.; Salcini, A.E.; Gagliani, M.C.; Pelicci, P.G.; Tacchetti, C.; di Fiore, P.P. Numb is an endocytic protein. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldmacher-Voss, B.; Reugels, A.M.; Pauls, S.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. A 90-degree rotation of the mitotic spindle changes the orientation of mitoses of zebrafish neuroepithelial cells. Development 2003, 130, 3767–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reugels, A.M.; Boggetti, B.; Scheer, N.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. Asymmetric localization of Numb:EGFP in dividing neuroepithelial cells during neurulation in Danio rerio. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggetti, B.; Jasik, J.; Takamiya, M.; Strahle, U.; Reugels, A.M.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. NBP, a zebrafish homolog of human Kank3, is a novel numb interactor essential for epidermal integrity and neurulation. Dev. Biol. 2012, 365, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bultje, R.S.; Castaneda-Castellanos, D.R.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N.; Kriegstein, A.R.; Shi, S.H. Mammalian Par3 regulates progenitor cell asymmetric division via Notch signaling in the developing neocortex. Neuron 2009, 63, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishell, G.; Kriegstein, A.R. Neurons from radial glia: The consequences of asymmetric inheritance. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhong, W.; Jan, Y.N.; Temple, S. Asymmetric Numb distribution is critical for asymmetric cell division of mouse cerebral cortical stem cells and neuroblasts. Development 2002, 129, 4843–4853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oegema, K.; Mitchison, T.J. Rappaport rules: Cleavage furrow induction in animal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4817–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanon, I.; Gonzalez-Gaitan, M. Oriented cell division in vertebrate embryogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.S.; Johnston, C.A. Molecular pathways regulating mitotic spindle orientation in animal cells. Development 2013, 140, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, X.; Bellaiche, Y. Mitotic spindle orientation in asymmetric and symmetric cell divisions during animal development. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor-Bergmann, A.; Goddard, G.; Woolner, S. Force and the spindle: Mechanical cues in mitotic spindle orientation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.M. Cell adhesion in regulation of asymmetric stem cell division. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siller, K.H.; Doe, C.Q. Spindle orientation during asymmetric cell division. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaiche, Y.; Radovic, A.; Woods, D.F.; Hough, C.D.; Parmentier, M.L.; O’Kane, C.J.; Bryant, P.J.; Schweisguth, F. The Partner of Inscuteable/Discs-large complex is required to establish planar polarity during asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Cell 2001, 106, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Shevchenko, A.; Knoblich, J.A. A protein complex containing inscuteable and the Galpha-binding protein Pins orients asymmetric cell divisions in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, B.; Boone, J.Q.; Stevens, N.R.; Brand, A.H.; Doe, C.Q. Regulation of spindle orientation and neural stem cell fate in the Drosophila optic lobe. Neural Dev. 2007, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechler, T.; Fuchs, E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote stratification and differentiation of mammalian skin. Nature 2005, 437, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.; Petronczki, M.; Dorner, D.; Forte, M.; Knoblich, J.A. Heterotrimeric G proteins direct two modes of asymmetric cell division in the Drosophila nervous system. Cell 2001, 107, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Morin, X.; Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; Chia, W. Analysis of partner of inscuteable, a novel player of Drosophila asymmetric divisions, reveals two distinct steps in inscuteable apical localization. Cell 2000, 100, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, K.; Willard, F.S.; Colombo, K.; Johnston, C.A.; McCudden, C.R.; Siderovski, D.P.; Gonczy, P. RIC-8 is required for GPR-1/2-dependent Galpha function during asymmetric division of C. elegans embryos. Cell 2004, 119, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, K.; Grill, S.W.; Kimple, R.J.; Willard, F.S.; Siderovski, D.P.; Gonczy, P. Translation of polarity cues into asymmetric spindle positioning in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Science 2003, 300, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werts, A.D.; Roh-Johnson, M.; Goldstein, B. Dynamic localization of C. elegans TPR-GoLoco proteins mediates mitotic spindle orientation by extrinsic signaling. Development 2011, 138, 4411–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, D.; Shioi, G.; Shitamukai, A.; Mori, A.; Kiyonari, H.; Miyata, T.; Matsuzaki, F. Neuroepithelial progenitors undergo LGN-dependent planar divisions to maintain self-renewability during mammalian neurogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Spindle orientation in mammalian cerebral cortical development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, X.; Jaouen, F.; Durbec, P. Control of planar divisions by the G-protein regulator LGN maintains progenitors in the chick neuroepithelium. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siller, K.H.; Doe, C.Q. Lis1/dynactin regulates metaphase spindle orientation in Drosophila neuroblasts. Dev. Biol. 2008, 319, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siller, K.H.; Serr, M.; Steward, R.; Hays, T.S.; Doe, C.Q. Live imaging of Drosophila brain neuroblasts reveals a role for Lis1/dynactin in spindle assembly and mitotic checkpoint control. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5127–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, S.K.; Neumuller, R.A.; Novatchkova, M.; Du, Q.; Knoblich, J.A. The Drosophila NuMA Homolog Mud regulates spindle orientation in asymmetric cell division. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.A.; Hirono, K.; Prehoda, K.E.; Doe, C.Q. Identification of an Aurora-A/PinsLINKER/Dlg spindle orientation pathway using induced cell polarity in S2 cells. Cell 2009, 138, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siller, K.H.; Cabernard, C.; Doe, C.Q. The NuMA-related Mud protein binds Pins and regulates spindle orientation in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotak, S.; Busso, C.; Gonczy, P. Cortical dynein is critical for proper spindle positioning in human cells. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabernard, C.; Doe, C.Q. Apical/basal spindle orientation is required for neuroblast homeostasis and neuronal differentiation in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C. Spindle orientation, asymmetric division and tumour suppression in Drosophila stem cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, S.E.; Doe, C.Q. Microtubule-induced Pins/Galphai cortical polarity in Drosophila neuroblasts. Cell 2005, 123, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.A.; Doe, C.Q.; Prehoda, K.E. Structure of an enzyme-derived phosphoprotein recognition domain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstralh, D.T.; Lovegrove, H.E.; St Johnston, D. Discs large links spindle orientation to apical-basal polarity in Drosophila epithelia. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadaoui, M.; Machicoane, M.; di Pietro, F.; Etoc, F.; Echard, A.; Morin, X. Dlg1 controls planar spindle orientation in the neuroepithelium through direct interaction with LGN. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.H.; Hanada, T.; Chishti, A.H. The effector domain of human dLg tumor suppressor acts as a switch that relieves autoinhibition of kinesin-3 motor GAKIN/KIF13B. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 10039–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.S.; Prehoda, K.E. A NudE/14–3-3 pathway coordinates dynein and the kinesin Khc73 to position the mitotic spindle. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, G.P.; Fletcher, G.C.; Brain, R.; Thompson, B.J. Aurora kinases phosphorylate Lgl to induce mitotic spindle orientation in Drosophila epithelia. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.A.; Moreira, S.; Ventura, G.; Sunkel, C.E.; Morais-de-Sa, E. Aurora A triggers Lgl cortical release during symmetric division to control planar spindle orientation. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.J.; Sahai, E. MST kinases in development and disease. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 210, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicoane, M.; de Frutos, C.A.; Fink, J.; Rocancourt, M.; Lombardi, Y.; Garel, S.; Piel, M.; Echard, A. SLK-dependent activation of ERMs controls LGN-NuMA localization and spindle orientation. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 205, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keder, A.; Rives-Quinto, N.; Aerne, B.L.; Franco, M.; Tapon, N.; Carmena, A. The hippo pathway core cassette regulates asymmetric cell division. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, E.B.; Sanchez, D.; Johnston, C.A. Warts phosphorylates Mud to promote Pins-mediated mitotic spindle orientation in Drosophila, independent of yorkie. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2751–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.; Mlodzik, M. Planar cell polarity signaling: From fly development to human disease. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, M.; Concha, M.L.; Heisenberg, C.P. Non-canonical wnt signalling and regulation of gastrulation movements. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H. The intestinal crypt, a prototype stem cell compartment. Cell 2013, 154, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaiche, Y.; Gho, M.; Kaltschmidt, J.A.; Brand, A.H.; Schweisguth, F. Frizzled regulates localization of cell-fate determinants and mitotic spindle rotation during asymmetric cell division. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gho, M.; Schweisguth, F. Frizzled signalling controls orientation of asymmetric sense organ precursor cell divisions in Drosophila. Nature 1998, 393, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, N.C.; Ellis, G.C.; Bowerman, B.; Garriga, G. MOM-5 frizzled regulates the distribution of DSH-2 to control C. elegans asymmetric neuroblast divisions. Dev. Biol. 2005, 284, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanon, I.; Abrami, L.; Holtzer, L.; Heisenberg, C.P.; van der Goot, F.G.; Gonzalez-Gaitan, M. Anthrax toxin receptor 2a controls mitotic spindle positioning. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 15, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segalen, M.; Johnston, C.A.; Martin, C.A.; Dumortier, J.G.; Prehoda, K.E.; David, N.B.; Doe, C.Q.; Bellaiche, Y. The Fz-Dsh planar cell polarity pathway induces oriented cell division via Mud/NuMA in Drosophila and zebrafish. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.A.; Manning, L.; Lu, M.S.; Golub, O.; Doe, C.Q.; Prehoda, K.E. Formin-mediated actin polymerization cooperates with Mushroom body defect (Mud)-dynein during Frizzled-Dishevelled spindle orientation. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4436–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunda, P.; Baum, B. The actin cytoskeleton in spindle assembly and positioning. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Bagonis, M.; Danuser, G.; Pellman, D. Direct microtubule-binding by myosin-10 orients centrosomes toward retraction fibers and subcortical actin clouds. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, J.; Cramer, L.P.; Baum, B.; McGee, K.M. Myosin II-dependent cortical movement is required for centrosome separation and positioning during mitotic spindle assembly. Cell 2004, 117, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applewhite, D.A.; Grode, K.D.; Keller, D.; Zadeh, A.D.; Slep, K.C.; Rogers, S.L. The spectraplakin short stop is an actin-microtubule cross-linker that contributes to organization of the microtubule network. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, A.; Karakesisoglou, I.; Wong, E.; Vaezi, A.; Fuchs, E. Acf7: An essential integrator of microtubule dynamics. Cell 2003, 115, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.D.; Dewey, E.B.; Johnston, C.A. Dishevelled binds the Discs large “Hook” domain to activate GukHolder-dependent spindle positioning in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, D.; Ran, J.; Gao, J.; Suo, S.; Sun, S.C.; Zhou, J. CYLD regulates spindle orientation by stabilizing astral microtubules and promoting dishevelled-NuMA-dynein/dynactin complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejima, K.; Kang, S.; Mitani, S.; Cosman, P.C.; Chisholm, A.D. Syndecan defines precise spindle orientation by modulating Wnt signaling in C. elegans. Development 2014, 141, 4354–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doe, C.Q. Neural stem cells: Balancing self-renewal with differentiation. Development 2008, 135, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabernard, C.; Prehoda, K.E.; Doe, C.Q. A spindle-independent cleavage furrow positioning pathway. Nature 2010, 467, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Steward, R.; Luo, L. Drosophila Lis1 is required for neuroblast proliferation, dendritic elaboration and axonal transport. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chenn, A.; McConnell, S.K. Cleavage orientation and the asymmetric inheritance of Notch1 immunoreactivity in mammalian neurogenesis. Cell 1995, 82, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, J.J.; Tseng, H.C.; Zhou, Y.; Frank, C.L.; Xie, Z.; Tsai, L.H. Cdk5rap2 interacts with pericentrin to maintain the neural progenitor pool in the developing neocortex. Neuron 2010, 66, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, J.L.; Kosodo, Y.; Enard, W.; Paabo, S.; Huttner, W.B. Aspm specifically maintains symmetric proliferative divisions of neuroepithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10438–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, J.D.; Colombo, K.; Molina-Calavita, M.; Keryer, G.; Zala, D.; Charrin, B.C.; Dietrich, P.; Volvert, M.L.; Guillemot, F.; Dragatsis, I.; et al. Huntingtin is required for mitotic spindle orientation and mammalian neurogenesis. Neuron 2010, 67, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyre, E.; Jaouen, F.; Saadaoui, M.; Haren, L.; Merdes, A.; Durbec, P.; Morin, X. A lateral belt of cortical LGN and NuMA guides mitotic spindle movements and planar division in neuroepithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postiglione, M.P.; Juschke, C.; Xie, Y.; Haas, G.A.; Charalambous, C.; Knoblich, J.A. Mouse inscuteable induces apical-basal spindle orientation to facilitate intermediate progenitor generation in the developing neocortex. Neuron 2011, 72, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingling, J.; Youn, Y.H.; Darling, D.; Toyo-Oka, K.; Pramparo, T.; Hirotsune, S.; Wynshaw-Boris, A. Neuroepithelial stem cell proliferation requires Lis1 for precise spindle orientation and symmetric division. Cell 2008, 132, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosodo, Y.; Roper, K.; Haubensak, W.; Marzesco, A.M.; Corbeil, D.; Huttner, W.B. Asymmetric distribution of the apical plasma membrane during neurogenic divisions of mammalian neuroepithelial cells. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaffrey, L.M.; Macara, I.G. Epithelial organization, cell polarity and tumorigenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsushima, M.; Toyoshima, F.; Nishida, E. Dual role of Cdc42 in spindle orientation control of adherent cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 2816–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, F.; Nishida, E. Integrin-mediated adhesion orients the spindle parallel to the substratum in an EB1- and myosin X-dependent manner. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolner, S.; O’Brien, L.L.; Wiese, C.; Bement, W.M. Myosin-10 and actin filaments are essential for mitotic spindle function. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, L.E.; Zegers, M.M.P.; Mostov, K.E. Opinion—Building epithelial architecture: Insights from three-dimensional culture models. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, E.; Legue, E.; Doyen, A.; Nato, F.; Nicolas, J.F.; Torres, V.; Yaniv, M.; Pontoglio, M. Defective planar cell polarity in polycystic kidney disease. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.E.; Beronja, S.; Pasolli, H.A.; Fuchs, E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote Notch-dependent epidermal differentiation. Nature 2011, 470, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartlick, O.; Mumcu, P.; Julicher, F.; Gonzalez-Gaitan, M. Understanding morphogenetic growth control—Lessons from flies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Insights from development. Development 2012, 139, 3471–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, Y.; Meyer, E.J.; Kroesen, A.; McKinney, S.A.; Gibson, M.C. Epithelial junctions maintain tissue architecture by directing planar spindle orientation. Nature 2013, 500, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, J.S.; Cuningham, J.C.; Peifer, M. Acentrosomal Drosophila epithelial cells exhibit abnormal cell division, leading to cell death and compensatory proliferation. Dev. Cell 2014, 30, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tanwar, P.S.; Raftery, L.A. Drosophila follicle cells: Morphogenesis in an eggshell. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Minan, A.; Martin-Bermudo, M.D.; Gonzalez-Reyes, A. Integrin signaling regulates spindle orientation in Drosophila to preserve the follicular-epithelium monolayer. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.M.; Jones, D.L.; Fuller, M.T. Orientation of asymmetric stem cell division by the apc tumor suppressor and centrosome. Science 2003, 301, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiger, A.A.; Jones, D.L.; Schulz, C.; Rogers, M.B.; Fuller, M.T. Stem cell self-renewal specified by JAK-STAT activation in response to a support cell cue. Science 2001, 294, 2542–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulina, N.; Matunis, E. Control of stem cell self-renewal in Drosophila spermatogenesis by JAK-STAT signaling. Science 2001, 294, 2546–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, M.; Venkei, Z.G.; Yamashita, Y.M. The polarity protein Baz forms a platform for the centrosome orientation during asymmetric stem cell division in the Drosophila male germline. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Borgne, R.; Bellaiche, Y.; Schweisguth, F. Drosophila E-cadherin regulates the orientation of asymmetric cell division in the sensory organ lineage. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metz, P.J.; Arsenio, J.; Kakaradov, B.; Kim, S.H.; Remedios, K.A.; Oakley, K.; Akimoto, K.; Ohno, S.; Yeo, G.W.; Chang, J.T. Regulation of asymmetric division and CD8+ T lymphocyte fate specification by protein kinase Czeta and protein kinase Clambda/iota. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.H.; Sidhu, S.S.; Chan, A.C. Regulation of a late phase of T cell polarity and effector functions by Crtam. Cell 2008, 132, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Palanivel, V.R.; Kinjyo, I.; Schambach, F.; Intlekofer, A.M.; Banerjee, A.; Longworth, S.A.; Vinup, K.E.; Mrass, P.; Oliaro, J.; et al. Asymmetric T lymphocyte division in the initiation of adaptive immune responses. Science 2007, 315, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocca, M.L.; Barnett, B.E.; Burkhardt, J.K.; Chang, J.T.; Reiner, S.L. Cutting edge: Asymmetric memory T cell division in response to rechallenge. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4145–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, E.D.; Oliaro, J.; Kallies, A.; Belz, G.T.; Filby, A.; Hogan, T.; Haynes, N.; Ramsbottom, K.M.; van Ham, V.; Kinwell, T.; et al. Regulation of asymmetric cell division and polarity by Scribble is not required for humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.G.; Koehli, S.; Hausmann, B.; Schmaler, M.; Zehn, D.; Palmer, E. T cell affinity regulates asymmetric division, effector cell differentiation, and tissue pathology. Immunity 2012, 37, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliaro, J.; van Ham, V.; Sacirbegovic, F.; Pasam, A.; Bomzon, Z.; Pham, K.; Ludford-Menting, M.J.; Waterhouse, N.J.; Bots, M.; Hawkins, E.D.; et al. Asymmetric cell division of T cells upon antigen presentation uses multiple conserved mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, K.; Shimoni, R.; Charnley, M.; Ludford-Menting, M.J.; Hawkins, E.D.; Ramsbottom, K.; Oliaro, J.; Izon, D.; Ting, S.B.; Reynolds, J.; et al. Asymmetric cell division during T cell development controls downstream fate. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 210, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, B.E.; Ciocca, M.L.; Goenka, R.; Barnett, L.G.; Wu, J.M.; Laufer, T.M.; Burkhardt, J.K.; Cancro, M.P.; Reiner, S.L. Asymmetric B cell division in the germinal center reaction. Science 2012, 335, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaunat, O.; Granja, A.G.; Barral, P.; Filby, A.; Montaner, B.; Collinson, L.; Martinez-Martin, N.; Harwood, N.E.; Bruckbauer, A.; Batista, F.D. Asymmetric segregation of polarized antigen on B cell division shapes presentation capacity. Science 2012, 335, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, L.; Yamashita, Y.M. Centrosome asymmetry and inheritance during animal development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubinet, C.; Cabernard, C. Control of asymmetric cell division. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 31, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, E.A.; Raff, J.W. Centrioles, centrosomes, and cilia in health and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, L.; Vanselow, K.; Skogs, M.; Toyoda, Y.; Lundberg, E.; Poser, I.; Falkenby, L.G.; Bennetzen, M.; Westendorf, J.; Nigg, E.A.; et al. Novel asymmetrically localizing components of human centrosomes identified by complementary proteomics methods. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, M.; Leisner, C.; Chen, D.; Manatschal, C.; Wegleiter, T.; Ouellet, J.; Lindstrom, D.; Gottschling, D.E.; Vogel, J.; Barral, Y. Spindle pole bodies exploit the mitotic exit network in metaphase to drive their age-dependent segregation. Cell 2012, 148, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.; Tanaka, T.U.; Nasmyth, K.; Schiebel, E. Modes of spindle pole body inheritance and segregation of the Bfa1p-Bub2p checkpoint protein complex. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6359–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.M.; Mahowald, A.P.; Perlin, J.R.; Fuller, M.T. Asymmetric inheritance of mother versus daughter centrosome in stem cell division. Science 2007, 315, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Turkel, N.; Hemati, N.; Fuller, M.T.; Hunt, A.J.; Yamashita, Y.M. Centrosome misorientation reduces stem cell division during ageing. Nature 2008, 456, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tsai, J.W.; Imai, J.H.; Lian, W.N.; Vallee, R.B.; Shi, S.H. Asymmetric centrosome inheritance maintains neural progenitors in the neocortex. Nature 2009, 461, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conduit, P.T.; Raff, J.W. Cnn dynamics drive centrosome size asymmetry to ensure daughter centriole retention in Drosophila neuroblasts. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januschke, J.; Llamazares, S.; Reina, J.; Gonzalez, C. Drosophila neuroblasts retain the daughter centrosome. Nature Commun. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januschke, J.; Reina, J.; Llamazares, S.; Bertran, T.; Rossi, F.; Roig, J.; Gonzalez, C. Centrobin controls mother-daughter centriole asymmetry in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Ramdas Nair, A.; Cabernard, C. The centriolar protein Bld10/Cep135 is required to establish centrosome asymmetry in Drosophila neuroblasts. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januschke, J.; Gonzalez, C. The interphase microtubule aster is a determinant of asymmetric division orientation in Drosophila neuroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerit, D.A.; Smyth, J.T.; Rusan, N.M. Organelle asymmetry for proper fitness, function, and fate. Chromosome Res. 2013, 21, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehnly, H.; Canton, D.; Bucko, P.; Langeberg, L.K.; Ogier, L.; Gelman, I.; Santana, L.F.; Wordeman, L.; Scott, J.D. A mitotic kinase scaffold depleted in testicular seminomas impacts spindle orientation in germ line stem cells. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dewey, E.B.; Taylor, D.T.; Johnston, C.A. Cell Fate Decision Making through Oriented Cell Division. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 129-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb3040129
Dewey EB, Taylor DT, Johnston CA. Cell Fate Decision Making through Oriented Cell Division. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2015; 3(4):129-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb3040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleDewey, Evan B., Danielle T. Taylor, and Christopher A. Johnston. 2015. "Cell Fate Decision Making through Oriented Cell Division" Journal of Developmental Biology 3, no. 4: 129-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb3040129
APA StyleDewey, E. B., Taylor, D. T., & Johnston, C. A. (2015). Cell Fate Decision Making through Oriented Cell Division. Journal of Developmental Biology, 3(4), 129-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb3040129




