Exploring the Regulation of Tmem182 Gene Expression in the Context of Retinoid X Receptor Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.3. Western Analysis
2.4. Reverse Transcription PCR Analysis
2.5. Quantitative ChIP Analysis
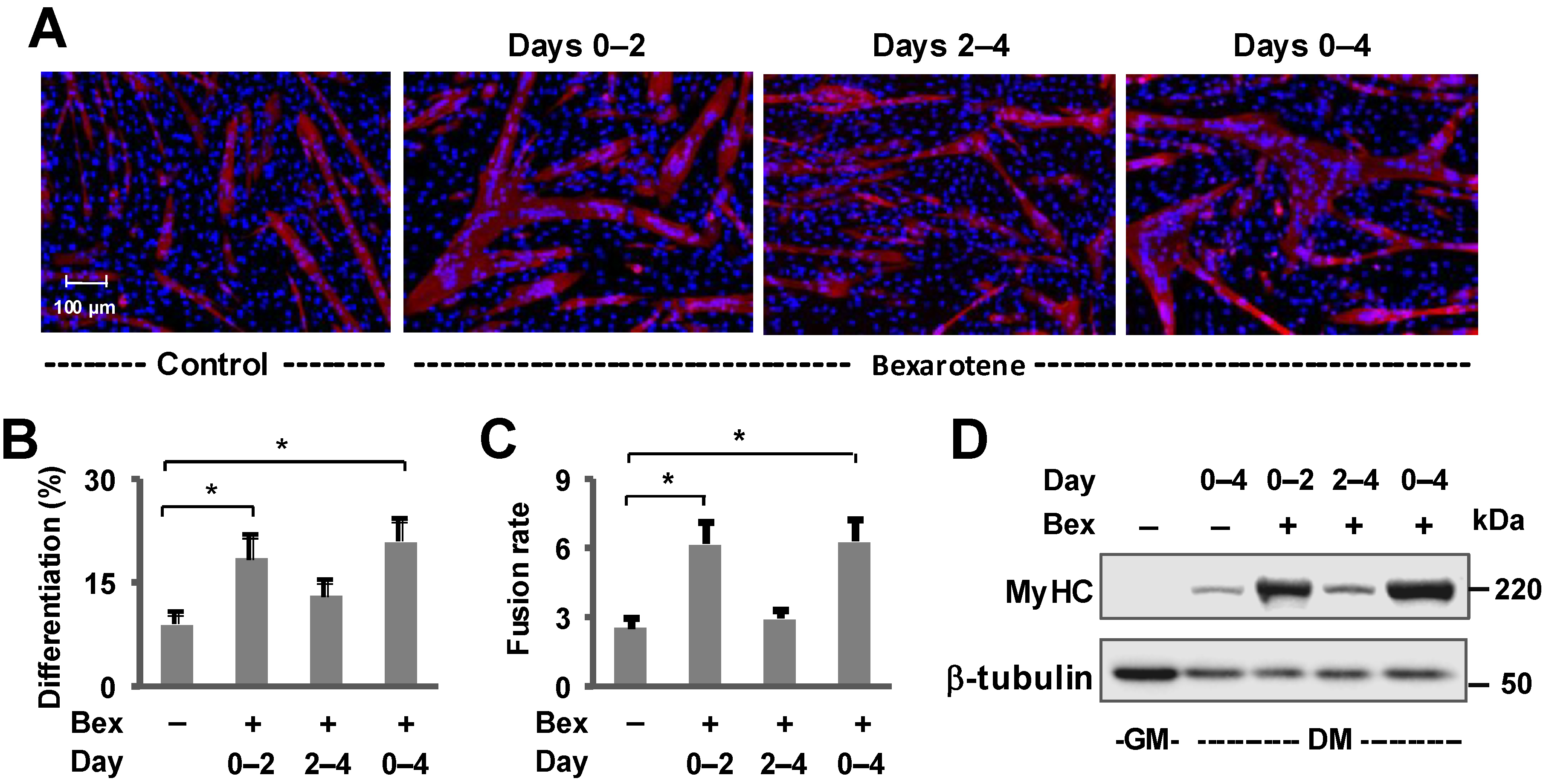
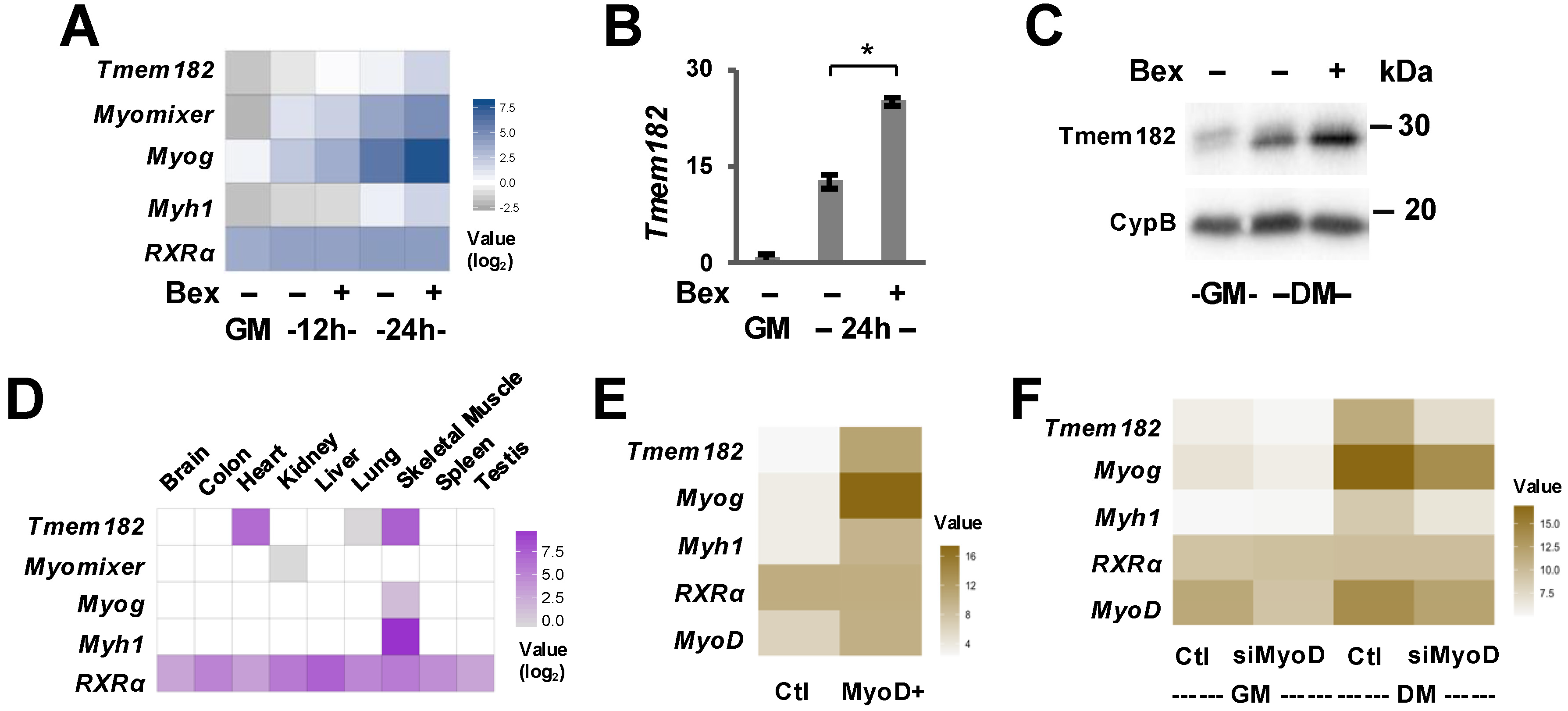
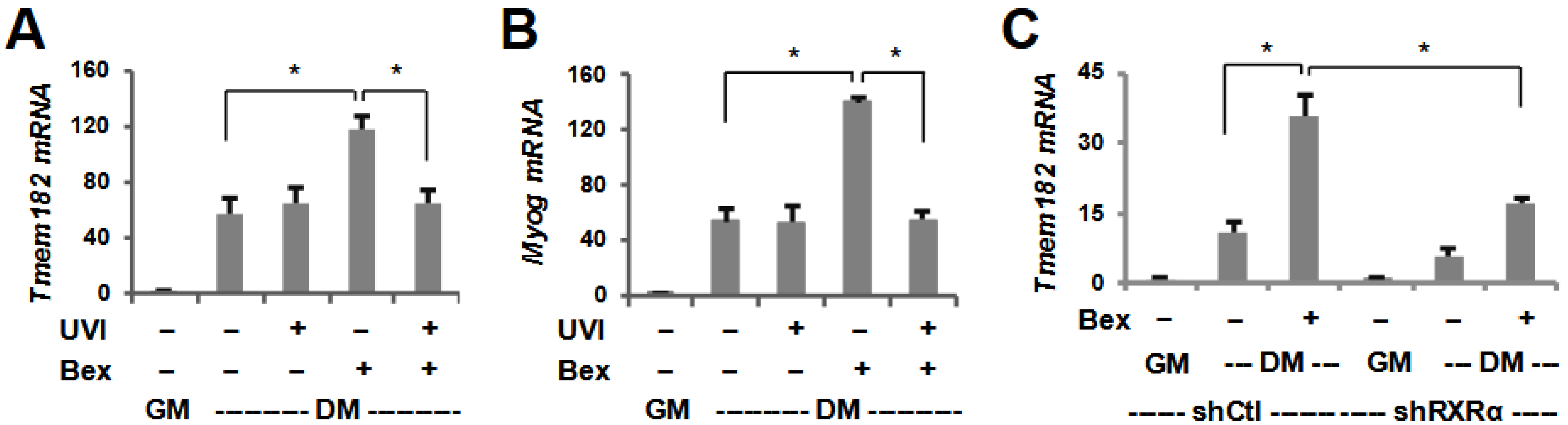
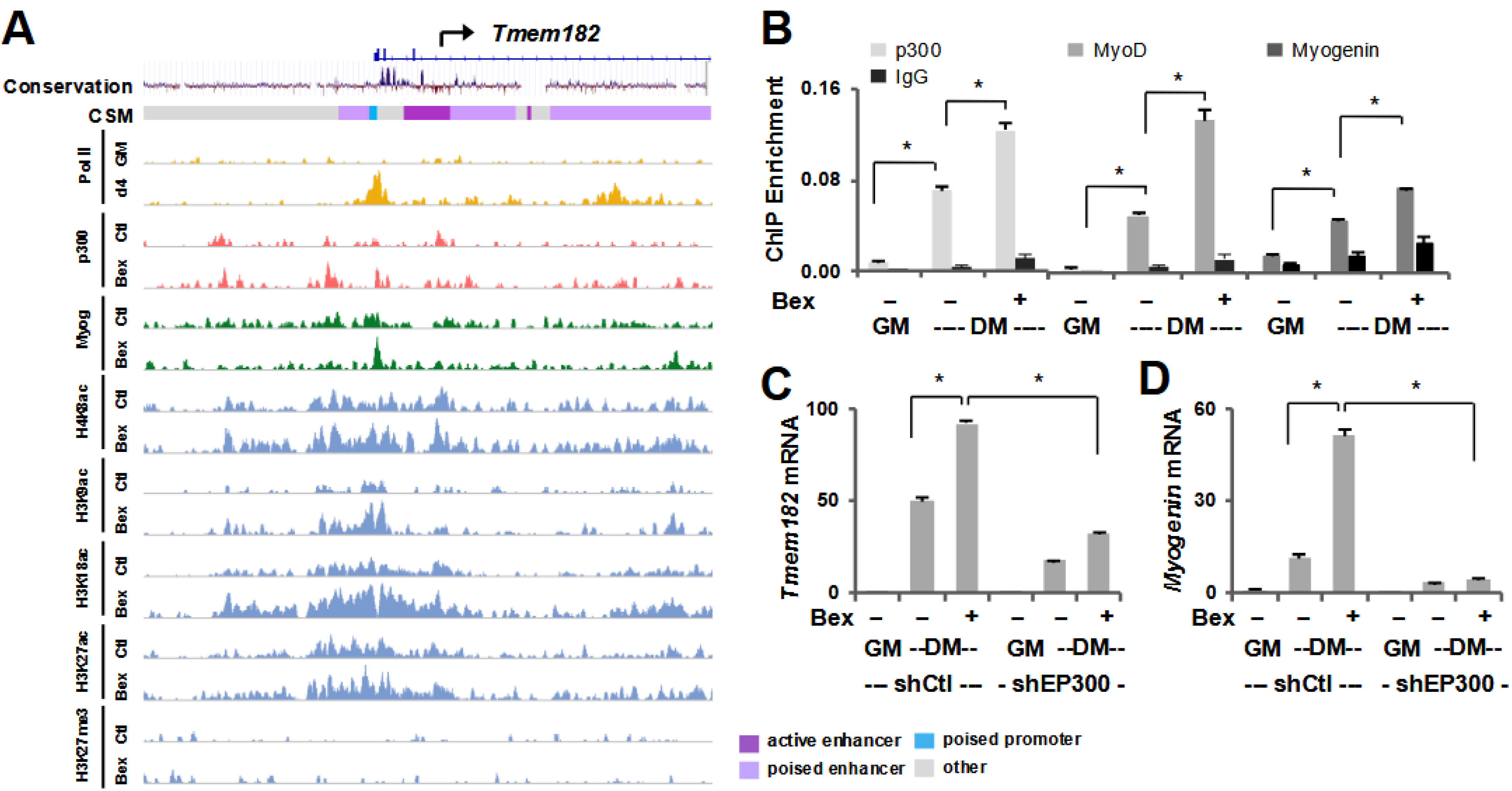
3. Results
3.1. Tmem182 Is a Rexinoid-Responsive Target and Expressed in Skeletal Muscle
3.2. The Regulation of Tmem182 Expression
3.3. Tmem182 Expression Is p300-Dependent
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, T.; Buschhausen-Denker, G.; Bober, E.; Tannich, E.; Arnold, H.H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Weintraub, H.; Lassar, A.B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell 1987, 51, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, S.J.; Konieczny, S.F. Identification of MRF4: A new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D.G.; Olson, E.N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorelli, V.; Caretti, G. Mechanisms underlying the transcriptional regulation of skeletal myogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, D.A.; Tapscott, S.J. Molecular distinction between specification and differentiation in the myogenic basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, M.A.; Jaenisch, R. The MyoD family of transcription factors and skeletal myogenesis. BioEssays 1995, 17, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, A.; Morris, J.H.; Rudnicki, M.; Braun, T.; Arnold, H.H.; Klein, W.H.; Olson, E.N. Myogenin’s functions do not overlap with those of MyoD or Myf-5 during mouse embryogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1995, 172, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassar-Duchossoy, L.; Gayraud-Morel, B.; Gomès, D.; Rocancourt, D.; Buckingham, M.; Shinin, V.; Tajbakhsh, S. Mrf4 determines skeletal muscle identity in Myf5:Myod double-mutant mice. Nature 2004, 431, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, P.S. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seale, P.; Sabourin, L.A.; Girgis-Gabardo, A.; Mansouri, A.; Gruss, P.; Rudnicki, M.A. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell 2000, 102, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, P.S.; Golding, J.P.; Nagata, Y.; Hudon, V.; Partridge, T.A.; Beauchamp, J.R. Muscle satellite cells adopt divergent fates. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissi, V.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Controlling nuclear receptors: The circular logic of cofactor cycles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.-F.; Shikama, N.; Henzen, C.; Desbaillets, I.; Lutz, W.; Marino, S.; Wittwer, J.; Schorle, H.; Gassmann, M.; Eckner, R. Differential role of p300 and CBP acetyltransferase during myogenesis: p300 acts upstream of MyoD and Myf5. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5186–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polesskaya, A.; Naguibneva, I.; Fritsch, L.; Duquet, A.; Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Robin, P.; Vervisch, A.; Pritchard, L.L.; Cole, P.; Harel-Bellan, A. CBP/p300 and muscle differentiation: No HAT, no muscle. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6816–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francetic, T.; Le May, M.; Hamed, M.; Mach, H.; Meyers, D.; Cole, P.A.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Regulation of Myf5 Early Enhancer by Histone Acetyltransferase p300 during Stem Cell Differentiation. Mol. Biol. 2012, 1, 1000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Khilji, S.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Stepwise acetyltransferase association and histone acetylation at the Myod1 locus during myogenic differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.H.; Smolik, S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Polesskaya, A.; Filleur, S.; Ferreira, R.; Duquet, A.; Robin, P.; Vervish, A.; Trouche, D.; Cabon, F.; Harel-Bellan, A. CBP/p300 histone acetyl-transferase activity is important for the G1/S transition. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, N.G.; Özdag, H.; Caldas, C. p300/CBP and cancer. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yu, L.-R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Kasper, L.H.; Lee, J.-E.; Wang, C.; Brindle, P.K.; Dent, S.Y.R.; Ge, K. Distinct roles of GCN5/PCAF-mediated H3K9ac and CBP/p300-mediated H3K18/27ac in nuclear receptor transactivation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blow, M.J.; McCulley, D.J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Akiyama, J.A.; Holt, A.; Plajzer-Frick, I.; Shoukry, M.; Wright, C.; Chen, F.; et al. ChIP-Seq identification of weakly conserved heart enhancers. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar-Zaidi, B.; Cowper-Sal·lari, R.; Corradin, O.; Saiakhova, A.; Bartels, C.F.; Balasubramanian, D.; Myeroff, L.; Lutterbaugh, J.; Jarrar, A.; Kalady, M.F.; et al. Epigenomic enhancer profiling defines a signature of colon cancer. Science 2012, 336, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzman, N.D.; Stuart, R.K.; Hon, G.; Fu, Y.; Ching, C.W.; Hawkins, R.D.; Barrera, L.O.; Van Calcar, S.; Qu, C.; Ching, K.A.; et al. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asp, P.; Blum, R.; Vethantham, V.; Parisi, F.; Micsinai, M.; Cheng, J.; Bowman, C.; Kluger, Y.; Dynlacht, B.D. Genome-wide remodeling of the epigenetic landscape during myogenic differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E149–E158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khilji, S.; Hamed, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Loci-specific histone acetylation profiles associated with transcriptional coactivator p300 during early myoblast differentiation. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Hayes, J.J.; Pruss, D.; Wolffe, A.P. A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell 1993, 72, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-Resolution Profiling of Histone Methylations in the Human Genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin Modifications and Their Function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 2007, 447, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, G.C.; Hawkins, R.D.; Ren, B. Predictive chromatin signatures in the mammalian genome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, R195–R201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsall, J.; Gupta, V.; O’Neill, L.P.; Turner, B.M.; Nightingale, K.P. Genes Are Often Sheltered from the Global Histone Hyperacetylation Induced by HDAC Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zang, C.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Schones, D.E.; Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, A.I.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Retinoid x receptor heterodimers in the metabolic syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Irimia, M.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, H.Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Lee, L.J.; Slobodeniuc, V.; Kutter, C.; Watt, S.; Colak, R.; et al. The Evolutionary Landscape of Alternative Splicing in Vertebrate Species. Science 2012, 338, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, H.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Laudet, V. Principles for modulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le May, M.; Mach, H.; Lacroix, N.; Hou, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Contribution of retinoid X receptor signaling to the specification of skeletal muscle lineage. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26806–26812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSudais, H.; Aabed, K.; Nicola, W.; Dixon, K.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Retinoid X Receptor-selective Signaling in the Regulation of Akt/Protein Kinase B Isoform-specific Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3090–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khilji, S.; Hamed, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Dissecting myogenin-mediated retinoid X receptor signaling in myogenic differentiation. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Khilji, S.; Dixon, K.; Blais, A.; Ioshikhes, I.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Insights into interplay between rexinoid signaling and myogenic regulatory factor-associated chromatin state in myogenic differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11236–11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuninger, D.; Kuzmickas, R.; Peng, B.; Pintar, J.E.; Rotwein, P. Gene discovery by microarray: Identification of novel genes induced during growth factor-mediated muscle cell survival and differentiation. Genomics 2004, 84, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; He, D.; Liang, S.; Luo, Q.; et al. TMEM182 interacts with integrin beta 1 and regulates myoblast differentiation and muscle regeneration. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1704–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Smas, C.M. Expression and regulation of transcript for the novel transmembrane protein Tmem182 in the adipocyte and muscle lineage. BMC Res. Notes 2008, 1, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morihara, H.; Yokoe, S.; Wakabayashi, S.; Takai, S. TMEM182 inhibits myocardial differentiation of human iPS cells by maintaining the activated state of Wnt/β-catenin signaling through an increase in ILK expression. FASEB BioAdvances 2024, 6, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millay, D.P.; O’Rourke, J.R.; Sutherland, L.B.; Bezprozvannaya, S.; Shelton, J.M.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 2013, 499, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, P.; Ramirez-Martinez, A.; Li, H.; Cannavino, J.; McAnally, J.R.; Shelton, J.M.; Sánchez-Ortiz, E.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Control of muscle formation by the fusogenic micropeptide myomixer. Science 2017, 356, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.E.; Goh, Q.; Kurosaka, M.; Gamage, D.G.; Petrany, M.J.; Prasad, V.; Millay, D.P. Myomerger induces fusion of non-fusogenic cells and is required for skeletal muscle development. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vashisht, A.A.; O’Rourke, J.; Corbel, S.Y.; Moran, R.; Romero, A.; Miraglia, L.; Zhang, J.; Durrant, E.; Schmedt, C.; et al. The microprotein Minion controls cell fusion and muscle formation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.; Russell, C.; Chen, P.; Burge, C.B. Evolutionary dynamics of gene and isoform regulation in Mammalian tissues. Science 2012, 338, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, I.; Yang, D.; Girgis, J.; Gunasekharan, A.; Phenix, H.; Kærn, M.; Blais, A. Genome-wide association between Six4, MyoD, and the histone demethylase Utx during myogenesis. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4738–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, D.; Nishi, M.; Fukada, S.-I.; Doi, M.; Okamura, H.; Uezumi, A.; Zhang, L.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, M.; Ichimura, A.; et al. Gm7325 is MyoD-dependently expressed in activated muscle satellite cells. Biomed. Res. Tokyo Jpn. 2017, 38, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; You, W.; Wang, Y.; Shan, T. The regulatory role of Myomaker and Myomixer–Myomerger–Minion in muscle development and regeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2019, 77, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahoum, V.; Perez, E.; Germain, P.; Rodriguez-Barrios, F.; Manzo, F.; Kammerer, S.; Lemaire, G.; Hirsch, O.; Royer, C.A.; Gronemeyer, H.; et al. Modulators of the structural dynamics of the retinoid X receptor to reveal receptor function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17323–17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Hamed, M.; Lacroix, N.; Li, Q. Molecular Basis for the Regulation of Transcriptional Coactivator p300 in Myogenic Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, H.M.; Pavlath, G.K.; Hardeman, E.C.; Chiu, C.P.; Silberstein, L.; Webster, S.G.; Miller, S.C.; Webster, C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science 1985, 230, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I.; Huang, X.; Jones, S.; Zhang, L.; Hatcher, R.; Gao, B.; Zhang, P. Dynamic gene expression during the onset of myoblast differentiation in vitro. Genomics 2003, 82, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doynova, M.D.; Markworth, J.F.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Vickers, M.H.; O’Sullivan, J.M. Linkages between changes in the 3D organization of the genome and transcription during myotube differentiation in vitro. Skelet. Muscle 2017, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, R.; Holtzer, H. Mitosis and the process of differentiation of myogenic cells in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1969, 41, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezel, W.; Dupé, V.; Mark, M.; Dierich, A.; Kastner, P.; Chambon, P. RXR gamma null mice are apparently normal and compound RXR alpha +/-/RXR beta -/-/RXR gamma -/- mutant mice are viable. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9010–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, P.; Grondona, J.M.; Mark, M.; Gansmuller, A.; LeMeur, M.; Decimo, D.; Vonesch, J.L.; Dollé, P.; Chambon, P. Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: Convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell 1994, 78, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, F.J.; Seaver, K.J.; Fishburn, A.L.; Htet, S.L.; Tapscott, S.J. In vitro transcription system delineates the distinct roles of the coactivators pCAF and p300 during MyoD/E47-dependent transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khilji, S.; Hamed, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Exploring the Regulation of Tmem182 Gene Expression in the Context of Retinoid X Receptor Signaling. J. Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13040034
Khilji S, Hamed M, Chen J, Li Q. Exploring the Regulation of Tmem182 Gene Expression in the Context of Retinoid X Receptor Signaling. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2025; 13(4):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhilji, Saadia, Munerah Hamed, Jihong Chen, and Qiao Li. 2025. "Exploring the Regulation of Tmem182 Gene Expression in the Context of Retinoid X Receptor Signaling" Journal of Developmental Biology 13, no. 4: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13040034
APA StyleKhilji, S., Hamed, M., Chen, J., & Li, Q. (2025). Exploring the Regulation of Tmem182 Gene Expression in the Context of Retinoid X Receptor Signaling. Journal of Developmental Biology, 13(4), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13040034






