Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations Are Regulated by miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374-5p in O9-1 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Search
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) Incorporation Assay
2.6. Immunocytochemical Analysis
2.7. Terminal 2′-Deoxyuridine, 5′-Triphosphate (dUTP) Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Staining
2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.9. Taqmann Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of a Set of Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations
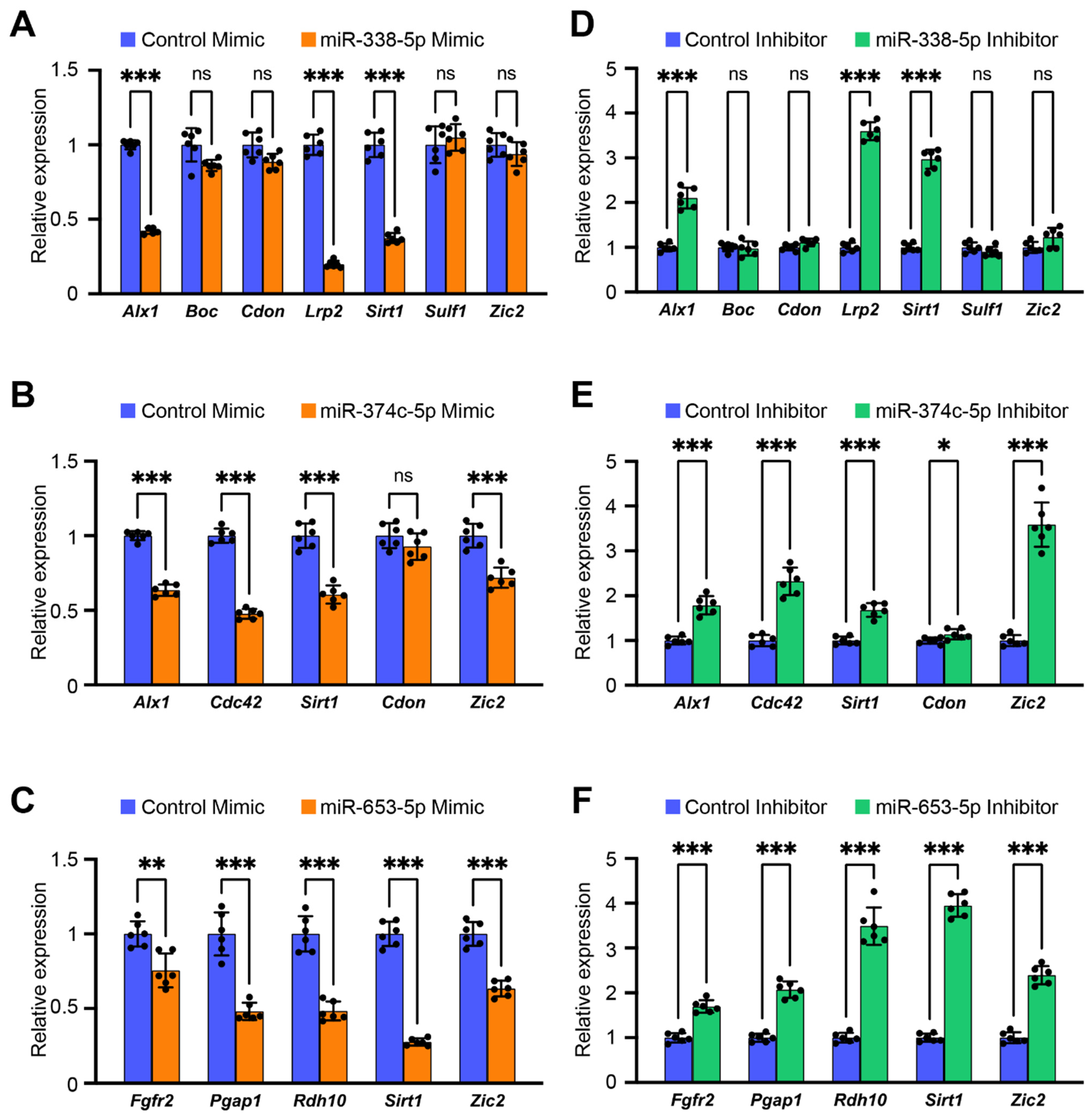
3.2. Overexpression of miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374c-5p Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Suppresses Expression of Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations in O9-1 Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twigg, S.R.; Wilkie, A.O. New insights into craniofacial malformations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, R50–R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suzuki, A.; Sangani, D.R.; Ansari, A.; Iwata, J. Molecular mechanisms of midfacial developmental defects. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2016, 245, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iwaya, C.; Suzuki, A.; Iwata, J. MicroRNAs and Gene Regulatory Networks Related to Cleft Lip and Palate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yankee, T.N.; Oh, S.; Winchester, E.W.; Wilderman, A.; Robinson, K.; Gordon, T.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; VanOudenhove, J.; Scott, D.A.; Leslie, E.J.; et al. Integrative analysis of transcriptome dynamics during human craniofacial development identifies candidate disease genes. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chai, Y.; Maxson, R.E., Jr. Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2006, 235, 2353–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoux, M.; Rijli, F.M. Molecular mechanisms of cranial neural crest cell migration and patterning in craniofacial development. Development 2010, 137, 2605–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Suzuki, H.I. Systems and Synthetic microRNA Biology: From Biogenesis to Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stavast, C.J.; Erkeland, S.J. The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation. Cells 2019, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehy, N.T.; Cordes, K.R.; White, M.P.; Ivey, K.N.; Srivastava, D. The neural crest-enriched microRNA miR-452 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal signaling in the first pharyngeal arch. Development 2010, 137, 4307–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zehir, A.; Hua, L.L.; Maska, E.L.; Morikawa, Y.; Cserjesi, P. Dicer is required for survival of differentiating neural crest cells. Dev. Biol. 2010, 340, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, T.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, L. Wnt1-cre-mediated conditional loss of Dicer results in malformation of the midbrain and cerebellum and failure of neural crest and dopaminergic differentiation in mice. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 2, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Yoshioka, H.; Summakia, D.; Desai, N.G.; Jun, G.; Jia, P.; Loose, D.S.; Ogata, K.; Gajera, M.V.; Zhao, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses mouse lip mesenchymal cell proliferation through the regulation of genes associated with cleft lip in the mouse. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suzuki, A.; Abdallah, N.; Gajera, M.; Jun, G.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z.; Iwata, J. Genes and microRNAs associated with mouse cleft palate: A systematic review and bioinformatics analysis. Mech. Dev. 2018, 150, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, W.; Brouwer, C. Pathview: An R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1830–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, F.; Simon, L.; Suzuki, A.; Iwaya, C.; Jia, P.; Iwata, J.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal MicroRNA-Gene Expression Network Related to Orofacial Clefts. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Otsuka-Tanaka, Y.; Oommen, S.; Kawasaki, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Imam, N.; Jalani-Ghazani, F.; Hindges, R.; Sharpe, P.; Ohazama, A. Oral lining mucosa development depends on mesenchymal microRNAs. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, K. Dicer activity in neural crest cells is essential for craniofacial organogenesis and pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis. Mech. Dev. 2011, 128, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, M.; Tao, L.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal miR-653-5p suppresses laryngeal papilloma progression by inhibiting BZW2. Clinics 2023, 78, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qi, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Tao, X. Long non-coding RNA PRNCR1 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting the miR-653-5p/ELF2 axis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Qi, Q.; Hou, S.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C. Exosomal circular RNA hsa_circ_007293 promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells through regulation of the microRNA-653-5p/paired box 6 axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10136–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, L.; Qian, J.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X. Circular RNA AGFG1 motivates breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and glycolysis by controlling microRNA-653-5p/14-3-3 protein epsilon. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2023, 70, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Gong, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S. CircARL8B Contributes to the Development of Breast Cancer Via Regulating miR-653-5p/HMGA2 Axis. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 1648–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F. miR-653-5p suppresses the growth and migration of breast cancer cells by targeting MAPK6. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Z.; Fan, H.; Chen, W.; Xiao, J.; Ma, X.; Ni, P.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L. MicroRNA-653-5p Promotes Gastric Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting the SOCS6-STAT3 Pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 655580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; Yu, Y.; Gu, C. Circular circRANGAP1 Contributes to Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Increasing COL11A1 Expression Through Sponging miR-653-5p. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 2580–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Jiang, P.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 Induces Gefitinib Resistance of Lung Adenocarcinoma Through the miR-653-5p/AGR2 Axis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, G.; Xiog, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, W.; Tang, T.; Sun, J.; Li, J. miR-374c-5p regulates PTTG1 and inhibits cell growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ding, B.; Lou, W.; Fan, W.; Pan, J. Exosomal miR-374c-5p derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via the LIMK1-Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1038–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
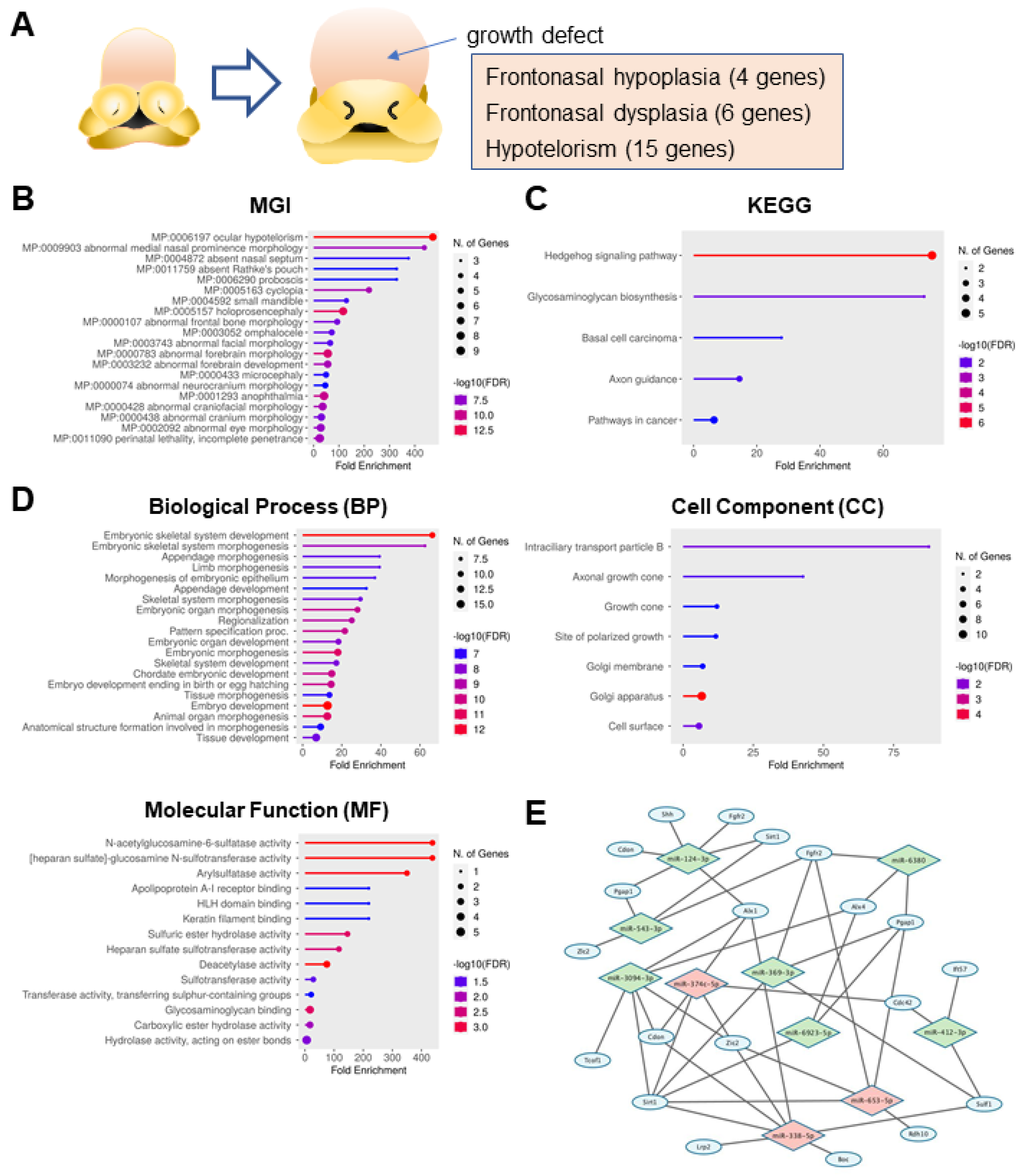

| Gene Symbol | References (PMID) | Chromosome | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontonasal hypoplasia (4 genes) | |||
| Bmp4 | 24785830 | 14 | bone morphogenetic protein 4 |
| Cdc42 | 28326341 | 4 | cell division cycle 42 |
| Ndst1 | 16020517 | 18 | N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 1 |
| Rdh10 | 17473173 | 1 | retinol dehydrogenase 10 (all-trans) |
| Frontonasal dysplasia (6 genes) | |||
| Alx1 | 35127681 | 10 | ALX homeobox 1 |
| Alx3 | 19409524 | 3 | aristaless-like homeobox 3 |
| Alx4 | 25673119 | 2 | aristaless-like homeobox 4 |
| Fgfr2 | 11274405 | 7 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 |
| Ndst3 | 18385133 | 3 | N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 3 |
| Tcof1 | 16938878 | 18 | treacle ribosome biogenesis factor 1 |
| Hypotelorism (15 genes) | |||
| Boc | 21183473 | 16 | biregional cell adhesion molecule-related/downregulated by oncogenes (Cdon) binding protein |
| Cdon | 21183473 | 9 | cell adhesion molecule-related/downregulated by oncogenes |
| Disp1 | 15269168 | 1 | dispatched RND transporter family member 1 |
| Ift27 | 25446516 | 15 | intraflagellar transport 27 |
| Ift57 | 17027958 | 16 | intraflagellar transport 57 |
| Lrp2 | 26107939 | 2 | low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 2 |
| Nosip | 25546391 | 7 | nitric oxide synthase-interacting protein |
| Pgap1 | 10529425 | 1 | post-GPI attachment to proteins 1 |
| Shh and Sulf1 and Sulf2 | 18213582 | 5 | sonic hedgehog |
| 1 | sulfatase 1 | ||
| 2 | sulfatase 2 | ||
| Shh and Six3 | 18694563 | 17 | sine oculis-related homeobox 3 |
| Sirt1 | 28273169 | 10 | sirtuin 1 |
| Wdr11 | 29263200 | 7 | WD repeat domain 11 |
| Zic2 | 29992973 | 14 | zinc finger protein of the cerebellum 2 |
| Enrichment FDR | Gene Number | Pathway Genes | Pathway | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGI enrichment | ||||
| 1.70 × 10−15 | 7 | 13 | MP:0006197 ocular hypotelorism | Ift27, Sirt1, Disp1, Ift57, Wdr11, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 1.01 × 10−8 | 4 | 8 | MP:0009903 abnormal medial nasal prominence morphology | Tcof1, Rdh10, Wdr11, Pgap1 |
| 2.83 × 10−6 | 3 | 7 | MP:0004872 absent nasal septum | Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2 |
| 3.62 × 10−6 | 3 | 8 | MP:0011759 absent Rathke’s pouch | Bmp4, Fgfr2, Pgap1 |
| 3.62 × 10−6 | 3 | 8 | MP:0006290 proboscis | Ndst1, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 3.84 × 10−9 | 5 | 20 | MP:0005163 cyclopia | Shh, Disp1, Wdr11, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 1.50 × 10−6 | 4 | 27 | MP:0004592 small mandible | Ift27, Tcof1, Wdr11, Pgap1 |
| 1.01 × 10−12 | 8 | 60 | MP:0005157 holoprosencephaly | Shh, Lrp2, Disp1, Cdon, Six3, Wdr11, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 1.64 × 10−7 | 5 | 47 | MP:0000107 abnormal frontal bone morphology | Shh, Tcof1, Disp1, Fgfr2, Alx4 |
| 5.49 × 10−7 | 5 | 61 | MP:0003052 omphalocele | Ift27, Bmp4, Lrp2, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 8.23 × 10−7 | 5 | 67 | MP:0003743 abnormal facial morphology | Disp1, Fgfr2, Wdr11, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| 9.08 × 10−12 | 9 | 141 | MP:0000783 abnormal forebrain morphology | Shh, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Disp1, Alx1, Cdon, Wdr11, Pgap1 |
| 4.79 × 10−9 | 7 | 110 | MP:0003232 abnormal forebrain development | Bmp4, Tcof1, Lrp2, Six3, Ndst1, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 2.87 × 10−6 | 5 | 89 | MP:0000433 microcephaly | Shh, Tcof1, Wdr11, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 3.62 × 10−6 | 5 | 95 | MP:0000074 abnormal neurocranium morphology | Shh, Tcof1, Disp1, Fgfr2, Alx4 |
| 1.08 × 10−10 | 9 | 191 | MP:0001293 anophthalmia | Shh, Bmp4, Tcof1, Lrp2, Six3, Wdr11, Ndst1, Zic2, Pgap1 |
| 4.79 × 10−9 | 8 | 196 | MP:0000428 abnormal craniofacial morphology | Shh, Sirt1, Tcof1, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Cdon, Six3, Wdr11 |
| 1.64 × 10−7 | 7 | 200 | MP:0000438 abnormal cranium morphology | Shh, Cdc42, Tcof1, Fgfr2, Six3, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| 2.05 × 10−8 | 8 | 246 | MP:0002092 abnormal eye morphology | Shh, Sirt1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| 6.25 × 10−9 | 9 | 324 | MP:0011090 perinatal lethality, incomplete penetrance | Shh, Ift27, Sirt1, Bmp4, Lrp2, Cdon, Alx4, Wdr11, Pgap1 |
| KEGG enrichment | ||||
| 2.80 × 10−7 | 5 | 58 | Hedgehog signaling pathway | Shh, Boc, Lrp2, Disp1, Cdon |
| 8.51 × 10−3 | 2 | 24 | Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis | Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 2.93 × 10−2 | 2 | 63 | Basal cell carcinoma | Shh, Bmp4 |
| 1.87 × 10−2 | 3 | 181 | Axon guidance | Shh, Cdc42, Boc |
| 3.11 × 10−2 | 4 | 542 | Pathways in cancer | Shh, Cdc42, Bmp4, Fgfr2 |
| GO enrichment (BP) | ||||
| 1.64 × 10−13 | 10 | 132 | Embryonic skeletal system development | Shh, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 2.84 × 10−9 | 7 | 98 | Embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis | Alx3, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 4.78 × 10−8 | 7 | 156 | Appendage morphogenesis | Shh, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Alx1, Alx4 |
| 4.78 × 10−8 | 7 | 156 | Limb morphogenesis | Shh, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Alx1, Alx4 |
| 6.96 × 10−8 | 7 | 166 | Morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium | Shh, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Lrp2, Ift57, Alx1 |
| 1.35 × 10−7 | 7 | 188 | Appendage development | Shh, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Alx1, Alx4 |
| 2.49 × 10−8 | 8 | 237 | Skeletal system morphogenesis | Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 2.20 × 10−10 | 10 | 312 | Embryonic organ morphogenesis | Shh, Alx3, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Six3, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 5.79 × 10−10 | 10 | 348 | Regionalization | Shh, Bmp4, Lrp2, Disp1, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4, Pgap1 |
| 2.20 × 10−10 | 11 | 446 | Pattern specification proc. | Shh, Alx3, Bmp4, Lrp2, Disp1, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4, Pgap1 |
| 1.08 × 10−8 | 10 | 478 | Embryonic organ development | Shh, Alx3, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Six3, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.76 × 10−11 | 13 | 632 | Embryonic morphogenesis | Shh, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.80 × 10−8 | 10 | 508 | Skeletal system development | Shh, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Fgfr2, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.61 × 10−10 | 13 | 765 | Chordate embryonic development | Shh, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.75 × 10−10 | 13 | 781 | Embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching | Shh, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.11 × 10−7 | 10 | 639 | Tissue morphogenesis | Shh, Cdc42, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Six3 |
| 1.64 × 10−13 | 17 | 1169 | Embryo development | Shh, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Disp1, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| 1.76 × 10−11 | 15 | 1041 | Animal organ morphogenesis | Shh, Cdc42, Sulf2, Alx3, Sulf1, Bmp4, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4, Ndst1 |
| 1.24 × 10−7 | 12 | 1144 | Anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis | Shh, Cdc42, Sulf1, Sirt1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon |
| 2.49 × 10−8 | 15 | 1900 | Tissue development | Shh, Cdc42, Sulf2, Sulf1, Sirt1, Bmp4, Tcof1, Rdh10, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Ift57, Alx1, Cdon, Six3, Alx4 |
| GO enrichment (CC) | ||||
| 1.50 × 10−2 | 2 | 20 | Intraciliary transport particle B | Ift27, Ift57 |
| 2.56 × 10−2 | 2 | 41 | Axonal growth cone | Boc, Lrp2 |
| 3.78 × 10−2 | 3 | 218 | Growth cone | Sirt1, Boc, Lrp2 |
| 3.78 × 10−2 | 3 | 225 | Site of polarized growth | Sirt1, Boc, Lrp2 |
| 3.78 × 10−2 | 4 | 502 | Golgi membrane | Cdc42, Ift27, Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 2.48 × 10−5 | 11 | 1449 | Golgi apparatus | Shh, Cdc42, Sulf2, Ift27, Sulf1, Lrp2, Ndst3, Ift57, Alx1, Wdr11, Ndst1 |
| 1.60 × 10−2 | 6 | 926 | Cell surface | Shh, Sulf2, Sulf1, Lrp2, Fgfr2, Cdon |
| GO enrichment (MF) | ||||
| 3.98 × 10−4 | 2 | 4 | N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase activity | Sulf2, Sulf1 |
| 3.98 × 10−4 | 2 | 4 | [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine N-sulfotransferase activity | Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 4.44 × 10−4 | 2 | 5 | Arylsulfatase activity | Sulf2, Sulf1 |
| 4.63 × 10−2 | 1 | 4 | Apolipoprotein A-I receptor binding | Cdc42 |
| 4.63 × 10−2 | 1 | 4 | HLH domain binding | Sirt1 |
| 4.63 × 10−2 | 1 | 4 | Keratin filament binding | Sirt1 |
| 1.94 × 10−3 | 2 | 12 | Sulfuric ester hydrolase activity | Sulf2, Sulf1 |
| 2.64 × 10−3 | 2 | 15 | Heparan sulfate sulfotransferase activity | Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 3.98 × 10−4 | 3 | 35 | Deacetylase activity | Sirt1, Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 3.12 × 10−2 | 2 | 61 | Sulfotransferase activity | Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 4.63 × 10−2 | 2 | 82 | Transferase activity, transferring sulphur-containing groups | Ndst3, Ndst1 |
| 1.94 × 10−3 | 4 | 202 | Glycosaminoglycan binding | Shh, Sulf2, Sulf1, Bmp4 |
| 1.20 × 10−2 | 3 | 152 | Carboxylic ester hydrolase activity | Ndst3, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| 2.11 × 10−2 | 5 | 742 | Hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds | Sulf2, Sulf1, Ndst3, Ndst1, Pgap1 |
| miRNA Family | q-Value Bonferroni | q-Value FDR B and H | Hit Count in Query List | Target Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-338-5p | 5.66 × 10−5 | 1.26 × 10−4 | 7 | Alx1, Boc, Cdon, Lrp2, Sirt1, Sulf1, Zic2 |
| miR-653-5p | 8.68 × 10−4 | 9.98 × 10−3 | 5 | Fgfr2, Pgap1, Rdh10, Sirt1, Zic2 |
| miR-374c-5p | 2.95 × 10−2 | 1.55 × 10−2 | 5 | Alx1, Cdc42, Cdon, Sirt1, Zic2 |
| miR-543-3p | 1.15 × 10−2 | 2.64 × 10−2 | 4 | Fgfr2, Zlc2, Sirt1, Pgap1 |
| miR-124-3p | 5.85 × 10−2 | 2.64 × 10−2 | 6 | Alx1, Cdon, Fgfr2, Shh, Sirt1, Pgap1 |
| miR-6923-5p | 1.17 × 10−1 | 3.38 × 10−2 | 3 | Alx4, Pgap1, Sirt1 |
| miR-3094-3p | 1.33 × 10−1 | 3.49 × 10−2 | 6 | Alx1, Alx4, Cdon, Sirt1, Tcof1, Zic2 |
| miR-6380 | 2.30 × 10−1 | 3.77 × 10−2 | 3 | Alx4, Fgfr2, Pgap1 |
| miR-369-3p | 2.81 × 10−1 | 4.17 × 10−2 | 4 | Fgfr2, Pgap1, Sirt1, Sulf1 |
| miR-412-3p | 3.16 × 10−1 | 4.34 × 10−2 | 3 | Cdc42, Ift57, Sulf1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwaya, C.; Yu, S.; Iwata, J. Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations Are Regulated by miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374-5p in O9-1 Cells. J. Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb12030019
Iwaya C, Yu S, Iwata J. Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations Are Regulated by miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374-5p in O9-1 Cells. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2024; 12(3):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb12030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwaya, Chihiro, Sunny Yu, and Junichi Iwata. 2024. "Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations Are Regulated by miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374-5p in O9-1 Cells" Journal of Developmental Biology 12, no. 3: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb12030019
APA StyleIwaya, C., Yu, S., & Iwata, J. (2024). Genes Related to Frontonasal Malformations Are Regulated by miR-338-5p, miR-653-5p, and miR-374-5p in O9-1 Cells. Journal of Developmental Biology, 12(3), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb12030019







