Germ Granules in Animal Oogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Inductive and Inherited Determination of Germ Line Cells
3. Diversity of RNP Granules in Germline Cells
GG Nomenclature Problems
4. P-Granules in Caenorhabditis elegans
5. Drosophila GG
5.1. Sponge Bodies
5.2. Polar Granules
5.3. Nuage
6. Zebrafish GG
7. Xenopus GG
Xenopus Bb Composition
8. Birds
9. GG in Mammalian Oocytes
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, T.W.; Kato, M.; Xie, S.; Wu, L.C.; Mirzaei, H.; Pei, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, Y.; Allen, J.; Xiao, G.; et al. Cell-Free Formation of RNA Granules: Bound RNAs Identify Features and Components of Cellular Assemblies. Cell 2012, 149, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.C.; Brangwynne, C.P. Getting RNA and Protein in Phase. Cell 2012, 149, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondele, M.; Sachdev, R.; Heinrich, S.; Wang, J.; Vallotton, P.; Fontoura, B.M.A.; Weis, K. DEAD-Box ATPases Are Global Regulators of Phase-Separated Organelles. Nature 2019, 573, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metschnikoff, E. Über Die Entwicklung Der Cecidomyidenlarven Aus Dem Pseudovum. Arch. Naturg. I 1865, 31, 304. [Google Scholar]
- Enukashvily, N.I.; Dobrynin, M.A.; Chubar, A.V. RNA-Seeded Membraneless Bodies: Role of Tandemly Repeated RNA. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 126, pp. 151–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strome, S.; Wood, W.B. Immunofluorescence Visualization of Germ-Line-Specific Cytoplasmic Granules in Embryos, Larvae, and Adults of Caenorhabditis Elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Updike, D.L.; Strome, S. A Genomewide RNAi Screen for Genes That Affect the Stability, Distribution and Function of P Granules in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Genetics 2009, 183, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilsch-Bräuninger, M.; Schwarz, H.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. A Sponge-like Structure Involved in the Association and Transport of Maternal Products during Drosophila Oogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, A.P. Assembly of the Drosophila Germ Plasm. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001, 203, 187–213. [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, A.P. Polar Granules of Drosophila. 3. The Continuity of Polar Granules during the Life Cycle of Drosophila. J. Exp. Zool. 1971, 176, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, K.; Wallace, R.A.; Sarka, A.; Qi, X. Stages of Oocyte Development in the Zebrafish, Brachydanio Rerio. J. Morphol. 1993, 218, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, A.E.; Hartung, O.; Rothhämel, S.; Ferreira, E.; Jenny, A.; Marlow, F.L. Oocyte Polarity Requires a Bucky Ball-Dependent Feedback Amplification Loop. Development 2014, 141, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaut, H.; Pelegri, F.; Bohmann, K.; Schwarz, H.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Zebrafish Vasa RNA but Not Its Protein Is a Component of the Germ Plasm and Segregates Asymmetrically before Germline Specification. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloc, M.; Bilinski, S.; Chan, A.P.; Allen, L.H.; Zearfoss, N.R.; Etkin, L.D. RNA Localization and Germ Cell Determination in Xenopus. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001, 203, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Dougherty, M.T.; Bilinski, S.; Chan, A.P.; Brey, E.; King, M.L.; Patrick, C.W.; Etkin, L.D. Three-Dimensional Ultrastructural Analysis of RNA Distribution within Germinal Granules of Xenopus. Dev. Biol. 2002, 241, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunekawa, N.; Naito, M.; Sakai, Y.; Nishida, T.; Noce, T. Isolation of Chicken Vasa Homolog Gene and Tracing the Origin of Primordial Germ Cells. Development 2000, 127, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, H.G.; Lim, J.M.; Ono, T.; Han, J.Y. DAZL Expression Explains Origin and Central Formation of Primordial Germ Cells in Chickens. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.L.; Pelegri, F. Primordial Germ Cell Specification in Vertebrate Embryos: Phylogenetic Distribution and Conserved Molecular Features of Preformation and Induction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 730332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepling, M.E.; Wilhelm, J.E.; O’Hara, A.L.; Gephardt, G.W.; Spradling, A.C. Mouse Oocytes within Germ Cell Cysts and Primordial Follicles Contain a Balbiani Body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaja, N.; Sassone-Corsi, P. The Chromatoid Body: A Germ-Cell-Specific RNA-Processing Centre. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertig, A.T. The Primary Human Oocyte: Some Observations on the Fine Structure of Balbiani’s Vitelline Body and the Origin of the Annulate Lamellae. Am. J. Anat. 1968, 122, 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemes, H.E.; Fawcett, D.W.; Dym, M. Unusual Features of the Nuclear Envelope in Human Spermatogenic Cells. Anat. Rec. 1978, 192, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, R.; Nistal, M.; Amat, P.; Rodríguez, M.C. Ultrastructural Observations on Nucleoli and Related Structures during Human10.1038/Nrm2081. Anat. Embryol. 1986, 174, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, R.; Nistal, M.; Amat, P.; Rodriguez, M.C. Presence of Ribonucleoproteins and Basic Proteins in the Nuage and Intermitochondrial Bars of Human Spermatogonia. J. Anat. 1985, 143, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamieson-Lucy, A.; Mullins, M.C. The Vertebrate Balbiani Body, Germ Plasm, and Oocyte Polarity. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 135, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Reunov, A. Structures Related to the Germ Plasm in Mouse. Zygote 2006, 14, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Seydoux, G. Germ Cell Development in C. Elegans. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 757, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontems, F.; Stein, A.; Marlow, F.; Lyautey, J.; Gupta, T.; Mullins, M.C.; Dosch, R. Bucky Ball Organizes Germ Plasm Assembly in Zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüpbach, T.; Wieschaus, E. Maternal-Effect Mutations Altering the Anterior-Posterior Pattern of the Drosophila Embryo. Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol. 1986, 195, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, P. Dead-Box Proteins: A Family Affair—Active and Passive Players in RNP-Remodeling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4168–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, E. The Function and Regulation of Vasa-like Genes in Germ-Cell Development. Genome Biol. 2000, 1, reviews1017.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruzelska, J.; Kotecki, M.; Kusz, K.; Spik, A.; Firpo, M.; Reijo Pera, R.A. Conservation of a Pumilio-Nanos Complex from Drosophila Germ Plasm to Human Germ Cells. Dev. Genes Evol. 2003, 213, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.K.; Moore-Jarrett, T.; Ruley, H.E. PUM2, a Novel Murine Puf Protein, and Its Consensus RNA-Binding Site. RNA 2001, 7, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Köprunner, M.; Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; Raz, E. A Zebrafish Nanos-Related Gene Is Essential for the Development of Primordial Germ Cells. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2877–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, K.; Seydoux, G. Nos-1 and Nos-2, Two Genes Related to Drosophila Nanos, Regulate Primordial Germ Cell Development and Survival in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Development 1999, 126, 4861–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginter-Matuszewska, B.; Kusz, K.; Spik, A.; Grzeszkowiak, D.; Rembiszewska, A.; Kupryjanczyk, J.; Jaruzelska, J. NANOS1 and PUMILIO2 Bind MicroRNA Biogenesis Factor GEMIN3, within Chromatoid Body in Human Germ Cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 136, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; King, M.L. Repressive Translational Control in Germ Cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomi, M.C.; Mannen, T.; Siomi, H. How Does the Royal Family of Tudor Rule the PIWI-Interacting RNA Pathway? Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, T.; Lasko, P. Drosophila Tudor Is Essential for Polar Granule Assembly and Pole Cell Specification, but Not for Posterior Patterning. Genesis 2004, 40, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, A.; Tiedau, D.; Firooznia, A.; Müller-Reichert, T.; Jessberger, R. Tdrd6 Is Required for Spermiogenesis, Chromatoid Body Architecture, and Regulation of MiRNA Expression. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megosh, H.B.; Cox, D.N.; Campbell, C.; Lin, H. The Role of PIWI and the MiRNA Machinery in Drosophila Germline Determination. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaja, N.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Jaskiewicz, L.; Kimmins, S.; Parvinen, M.; Filipowicz, W.; Sassone-Corsi, P. The Chromatoid Body of Male Germ Cells: Similarity with Processing Bodies and Presence of Dicer and MicroRNA Pathway Components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eno, C.; Pelegri, F. Germ Cell Determinant Transmission, Segregation, and Function in the Zebrafish Embryo; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2268-5. [Google Scholar]
- De Felici, M. The Formation and Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in Mouse and Man. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2016, 58, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.L.; Defalco, T. Of Mice and Men: In Vivo and in Vitro Studies of Primordial Germ Cell Specification. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2017, 35, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seervai, R.N.H.; Wessel, G.M. Lessons for Inductive Germline Determination. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seydoux, G.; Schedl, T. The Germline in C. Elegans: Origins, Proliferation, and Silencing. Int. Rev. Cytol 2001, 203, 139–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schisa, J.A.; Pitt, J.N.; Priess, J.R. Analysis of RNA Associated with P Granules in Germ Cells of C. Elegans Adults. Development 2001, 128, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conine, C.C.; Batista, P.J.; Gu, W.; Claycomb, J.M.; Chaves, D.A.; Shirayama, M.; Mello, C.C. Argonautes ALG-3 and ALG-4 Are Required for Spermatogenesis-Specific 26G-RNAs and Thermotolerant Sperm in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3588–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Reinke, V.A.C. Elegans Piwi, PRG-1, Regulates 21U-RNAs during Spermatogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claycomb, J.M.; Batista, P.J.; Pang, K.M.; Gu, W.; Vasale, J.J.; van Wolfswinkel, J.C.; Chaves, D.A.; Shirayama, M.; Mitani, S.; Ketting, R.F.; et al. The Argonaute CSR-1 and Its 22G-RNA Cofactors Are Required for Holocentric Chromosome Segregation. Cell 2009, 139, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Fields, B.D.; Spracklin, G.; Shukla, A.; Phillips, C.M.; Kennedy, S. Spatiotemporal Regulation of Liquid-like Condensates in Epigenetic Inheritance. Nature 2018, 557, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznicki, K.A.; Smith, P.A.; Leung-Chiu, W.M.A.; Estevez, A.O.; Scott, H.C.; Bennett, K.L. Combinatorial RNA Interference Indicates GLH-4 Can Compensate for GLH-1; These Two P Granule Components Are Critical for Fertility in C. Elegans. Development 2000, 127, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Vallandingham, J.; Shiu, P.; Li, H.; Hunter, C.P.; Mak, H.Y. The DEAD Box Helicase RDE-12 Promotes Amplification of RNAi in Cytoplasmic Foci in C. Elegans. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updike, D.L.; Hachey, S.J.; Kreher, J.; Strome, S. P Granules Extend the Nuclear Pore Complex Environment in the C. Elegans Germ Line. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnik, E.A.; Updike, D.L. Membraneless Organelles: P Granules in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Traffic 2019, 20, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Shirayama, M.; Conte, D., Jr.; Vasale, J.; Batista, P.J.; Claycomb, J.M.; Moresco, J.J.; Youngman, E.; Keys, J.; Stoltz, M.J.; et al. Distinct Argonaute-Mediated 22G-RNA Pathways Direct Genome Surveillance in the C. Elegans Germline. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.; Smith, J.; Chen, B.C.; Schmidt, H.; Rasoloson, D.; Paix, A.; Lambrus, B.G.; Calidas, D.; Betzig, E.; Seydoux, G. Regulation of RNA Granule Dynamics by Phosphorylation of Serine-Rich, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in C. Elegans. eLife 2014, 3, e04591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R.; Shim, E.; Kohara, Y.; Singson, A.; Blackwell, T. Cgh-1, a Conserved Predicted RNA Helicase Required for Gametogenesis and Protection from Physiological Germline Apoptosis in C. Elegans. Dev. 2001, 128, 3221–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Keiper, B.D.; Kawasaki, I.; Fan, Y.; Kohara, Y.; Rhoads, R.E.; Strome, S. An Isoform of ElF4E Is a Component of Germ Granules and Is Required for Spermatogenesis in C. Elegans. Dev. 2001, 128, 3899–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.; Piano, F.; Davis, R.E. Caenorhabditis Elegans Decapping Proteins: Localization and Functional Analysis of Dcp1, Dcp2, and DcpS during Embryogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5880–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Eckmann, C.R.; Courson, D.S.; Rybarska, A.; Hoege, C.; Gharakhani, J.; Jülicher, F.; Hyman, A.A. Germline P Granules Are Liquid Droplets That Localize by Controlled Dissolution/Condensation. Science 2009, 324, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berleth, T.; Burri, M.; Thoma, G.; Bopp, D.; Richstein, S.; Frigerio, G.; Noll, M.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. The Role of Localization of Bicoid RNA in Organizing the Anterior Pattern of the Drosophila Embryo. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Amikura, R.; Hanyu, K.; Kobayashi, S. Me31B Silences Translation of Oocyte-Localizing RNAs through the Formation of Cytoplasmic RNP Complex during Drosophila Oogenesis. Dev. 2001, 128, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snee, M.J.; Macdonald, P.M. Bicaudal C and Trailer Hitch Have Similar Roles in Gurken MRNA Localization and Cytoskeletal Organization. Dev. Biol. 2009, 328, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snee, M.J.; Macdonald, P.M. Dynamic Organization and Plasticity of Sponge Bodies. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, J.E.; Hilton, M.; Amos, Q.; Henzel, W.J. Cup Is an EIF4E Binding Protein Required for Both the Translational Repression of Oskar and the Recruitment of Barentsz. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.D.; Fan, S.J.; Hsu, W.S.; Chou, T. Bin Drosophila Decapping Protein 1, DDcp1, Is a Component of the Oskar MRNP Complex and Directs Its Posterior Localization in the Oocyte. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cuevas, M.; Lee, J.K.; Spradling, A.C. Alpha-Spectrin Is Required for Germline Cell Division and Differentiation in the Drosophila Ovary. Development 1996, 122, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, B.; Ackerman, L.; Barbel, S.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Identification of a Component of Drosophila Polar Granules. Development 1988, 103, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Nusslein-Volhard, C. The Maternal Gene Nanos Has a Central Role in Posterior Pattern Formation of the Drosophila Embryo. Development 1991, 112, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, A.K.; Yan, N.; Arn, E.; Harrison, D.; Macdonald, P.M. Localization-Dependent Oskar Protein Accumulation Control after the Initiation of Translation. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.N.; Macdonald, P.M. Aubergine Encodes a Drosophila Polar Granule Component Required for Pole Cell Formation and Related to ElF2C. Development 2001, 128, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardsley, A.; McDonald, K.; Boswell, R.E. Distribution of Tudor Protein in the Drosophila Embryo Suggests Separation of Functions Based on Site of Localization. Development 1993, 119, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, K.L.; Kai, T. Unique Germ-Line Organelle, Nuage, Functions to Repress Selfish Genetic Elements in Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6714–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardane, L.S.; Saito, K.; Nishida, K.M.; Miyoshi, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Nagami, T.; Siomi, H.; Siomi, M.C. A Slicer-Mediated Mechanism for Repeat-Associated SiRNA 5′ End Formation in Drosophila. Science 2007, 315, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findley, S.D.; Tamanaha, M.; Clegg, N.J.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Maelstrom, a Drosophila Spindle-Class Gene, Encodes a Protein That Colocalizes with Vasa and RDE1/AGO1 Homolog, Aubergine, in Nuage. Development 2003, 130, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.S.; Kai, T. Repression of Retroelements in Drosophila Germline via PiRNA Pathway by the Tudor Domain Protein Tejas. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qi, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, H. PAPI, a Novel TUDOR-Domain Protein, Complexes with AGO3, ME31B and TRAL in the Nuage to Silence Transposition. Development 2011, 138, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, F.L.; Mullins, M.C. Bucky Ball Functions in Balbiani Body Assembly and Animal-Vegetal Polarity in the Oocyte and Follicle Cell Layer in Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2008, 321, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Aguirre, M.; Zhang, H.; Jamieson-Lucy, A.; Mullins, M.C. Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 (Macf1) Domain Function in Balbiani Body Dissociation and Nuclear Positioning. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roovers, E.F.; Kaaij, L.J.T.; Redl, S.; Bronkhorst, A.W.; Wiebrands, K.; de Jesus Domingues, A.M.; Huang, H.-Y.; Han, C.-T.; Riemer, S.; Dosch, R.; et al. Tdrd6a Regulates the Aggregation of Buc into Functional Subcellular Compartments That Drive Germ Cell Specification. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 285–301.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eno, C.; Hansen, C.L.; Pelegri, F. Aggregation, Segregation, and Dispersal of Homotypic Germ Plasm RNPs in the Early Zebrafish Embryo. Dev. Dyn. 2019, 248, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.W.; Zhang, J.; Maines, J.Z.; Wasserman, S.A.; King, M. Lou A Xenopus DAZ-like Gene Encodes an RNA Component of Germ Plasm and Is a Functional Homologue of Drosophila Boule. Development 1998, 125, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.; Woodland, H.R. Xpat, a Gene Expressed Specifically in Germ Plasm and Primordial Germ Cells of Xenopus Laevis. Mech. Dev. 1998, 73, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zearfoss, N.R.; Chan, A.P.; Kloc, M.; Allen, L.H.; Etkin, L.D. Identification of New Xlsirt Family Members in the Xenopus Laevis Oocyte. Mech. Dev. 2003, 120, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, H.; Houston, D.W.; Bubunenko, M.; Mosquera, L.; King, M. Lou DEADSouth Is a Germ Plasm Specific DEAD-Box RNA Helicase in Xenopus Related to EIF4A. Mech. Dev. 2000, 95, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, H.; Rothhämel, S.; Shimizu, T.; Kim, C.-H.; Yonemura, S.; Marlow, F.L.; Hibi, M. Syntabulin, a Motor Protein Linker, Controls Dorsal Determination. Development 2010, 137, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Komazaki, S.; Miyoshi, O.; Asashima, M. Immunocytochemical Study of Activin Type IB Receptor (XALK4) in Xenopus Oocytes. Dev. Growth Differ. 2003, 45, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viel, A.; Armand, M.J.; Callen, J.C.; Gomez De Gracia, A.; Denis, H.; le Maire, M. Elongation Factor 1 Alpha (EF-1 Alpha) Is Concentrated in the Balbiani Body and Accumulates Coordinately with the Ribosomes during Oogenesis of Xenopus Laevis. Dev. Biol. 1990, 141, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forristall, C.; Pondel, M.; Chen, L.; King, M.L. Patterns of Localization and Cytoskeletal Association of Two Vegetally Localized RNAs, Vg1 and Xcat-2. Development 1995, 121, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguero, T.; Zhou, Y.; Kloc, M.; Chang, P.; Houliston, E.; King, M. Lou Hermes (Rbpms) Is a Critical Component of RNP Complexes That Sequester Germline RNAs during Oogenesis. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannese, M.; Cagliani, R.; Pardini, C.L.; Boncinelli, E. Xotx1 Maternal Transcripts Are Vegetally Localized in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. Mech. Dev. 2000, 90, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Grotjahn, D.; Welch, E.; Lyman-Gingerich, J.; Holguin, C.; Dimitrova, E.; Abrams, E.W.; Gupta, T.; Marlow, F.L.; Yabe, T.; et al. Hecate/Grip2a Acts to Reorganize the Cytoskeleton in the Symmetry-Breaking Event of Embryonic Axis Induction. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takeda, A.; Mise, K.; Okuno, T.; Suzuki, T.; Minami, N.; Imai, H. Stage-Specific Expression of MicroRNAs during Xenopus Development. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Shirato, Y.; Bilinski, S.; Browder, L.W.; Johnston, J. Differential Subcellular Sequestration of Proapoptotic and Antiapoptotic Proteins and Colocalization of Bcl-x(L) with the Germ Plasm, in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. Genesis 2007, 45, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boke, E.; Ruer, M.; Wühr, M.; Coughlin, M.; Lemaitre, R.; Gygi, S.P.; Alberti, S.; Drechsel, D.; Hyman, A.A.; Mitchison, T.J. Amyloid-like Self-Assembly of a Cellular Compartment. Cell 2016, 166, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Houston, D.W. Role of Maternal Xenopus Syntabulin in Germ Plasm Aggregation and Primordial Germ Cell Specification. Dev. Biol. 2017, 432, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.K.; Knowles, B.B. Controlling Endogenous Retroviruses and Their Chimeric Transcripts during Natural Reprogramming in the Oocyte. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. S1), S47–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, Y.; Tsunekawa, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Satoh, M.; Noce, T. Expression and Intracellular Localization of Mouse Vasa-Homologue Protein during Germ Cell Development. Mech. Dev. 2000, 93, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Baibakov, B.; Dean, J. A Subcortical Maternal Complex Essential for Preimplantation Mouse Embryogenesis. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurttas, P.; Vitale, A.M.; Fitzhenry, R.J.; Cohen-Gould, L.; Wu, W.; Gossen, J.A.; Coonrod, S.A. Role for PADI6 and the Cytoplasmic Lattices in Ribosomal Storage in Oocytes and Translational Control in the Early Mouse Embryo. Development 2008, 135, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepling, M.E. A Novel Maternal MRNA Storage Compartment in Mouse Oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuma, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Kitamura, K.; Kasai, S.; Fujioka, M.; Hiyoshi, M.; Takamune, K.; Noce, T.; Nakatsuji, N. Tdrd1/Mtr-1, a Tudor-Related Gene, Is Essential for Male Germ-Cell Differentiation and Nuage/Germinal Granule Formation in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15894–15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, Y.; Speed, R.M.; Gautier, P.; Semple, C.A.; Maratou, K.; Turner, J.M.A.; Cooke, H.J. Mouse MAELSTROM: The Link between Meiotic Silencing of Unsynapsed Chromatin and MicroRNA Pathway? Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albamonte, M.S.; Willis, M.A.; Albamonte, M.I.; Jensen, F.; Espinosa, M.B.; Vitullo, A.D. The Developing Human Ovary: Immunohistochemical Analysis of Germ-Cell-Specific VASA Protein, BCL-2/BAX Expression Balance and Apoptosis. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 23, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, P.S.; Bayne, R.A.L.; Robinson, L.L.L.; Fulton, N.; Anderson, R.A. Developmental Changes in Expression of Myeloid Cell Leukemia-1 in Human Germ Cells during Oogenesis and Early Folliculogenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ouyang, J.P.T.; Seydoux, G. Nuage Condensates: Accelerators or Circuit Breakers for SRNA Silencing Pathways? RNA 2022, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strome, S.; Lehmann, R. Germ versus Soma Decisions: Lessons from Flies and Worms. Science 2007, 316, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updike, D.; Strome, S. P Granule Assembly and Function in Caenorhabditis Elegans Germ Cells. J. Androl. 2010, 31, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönczy, P.; Rose, L.S. Asymmetric Cell Division and Axis Formation in the Embryo. WormBook 2005, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.N.; Schisa, J.A.; Priess, J.R. P Granules in the Germ Cells of Caenorhabditis Elegans Adults Are Associated with Clusters of Nuclear Pores and Contain RNA. Dev. Biol. 2000, 219, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schisa, J.A. New Insights into the Regulation of RNP Granule Assembly in Oocytes. Int. Rev. Cell Mol Biol. 2012, 295, 233–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiledjian, M.; Dreyfuss, G. Primary Structure and Binding Activity of the HnRNP U Protein: Binding RNA through RGG Box. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntharalingam, M.; Wente, S.R. Peering through the Pore: Nuclear Pore Complex Structure, Assembly, and Function. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruidl, M.E.; Smith, P.A.; Kuznicki, K.A.; McCrone, J.S.; Kirchner, J.; Rousell, D.L.; Strome, S.; Bennett, K.L. Multiple Potential Germ-Line Helicases Are Components of the Germ-Line-Specific P Granules of Caenorhabditis Elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13837–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmell, M.A.; Dokshin, G.A.; Skaletsky, H.; Hu, Y.C.; van Wolfswinkel, J.C.; Igarashi, K.J.; Bellott, D.W.; Nefedov, M.; Reddien, P.W.; Enders, G.C.; et al. A Widely Employed Germ Cell Marker Is an Ancient Disordered Protein with Reproductive Functions in Diverse Eukaryotes. eLife 2016, 5, e19993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leacock, S.W.; Reinke, V. MEG-1 and MEG-2 Are Embryo-Specific P-Granule Components Required for Germline Development in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Genetics 2008, 178, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.S.; Putnam, A.; Lu, T.; He, S.; Ouyang, J.P.T.; Seydoux, G. Recruitment of MRNAs to P Granules by Condensation with Intrinsically-Disordered Proteins. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boag, P.R.; Atalay, A.; Robida, S.; Reinke, V.; Blackwell, T.K. Protection of Specific Maternal Messenger RNAs by the P Body Protein CGH-1 (Dhh1/RCK) during Caenorhabditis Elegans Oogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.P.T.; Folkmann, A.; Bernard, L.; Lee, C.-Y.; Seroussi, U.; Charlesworth, A.G.; Claycomb, J.M.; Seydoux, G. P Granules Protect RNA Interference Genes from Silencing by PiRNAs. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trcek, T.; Lehmann, R. Germ Granules in Drosophila. Traffic 2019, 20, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Fuller, M.T. Stem Cell Niches. In Essentials of Stem Cell Biology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 59–79. ISBN 9780124104273. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.N.; Cant, K.; Cooley, L. Morphogenesis of Drosophila Ovarian Ring Canals. Development 1994, 120, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastock, R.; St Johnston, D. Drosophila Oogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R1082–R1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Diehl-Jones, W.; Lasko, P. Localization of Vasa Protein to the Drosophila Pole Plasm Is Independent of Its RNA-Binding and Helicase Activities. Development 1994, 120, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.; Sheth, U. P Bodies and the Control of MRNA Translation and Degradation. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, R. Germ Plasm Biogenesis—An Oskar-Centric Perspective. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2016, 116, 679–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, T.; Liu, N.; Arkov, A.; Lehmann, R.; Lasko, P. Isolation of New Polar Granule Components in Drosophila Reveals P Body and ER Associated Proteins. Mech. Dev. 2008, 125, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkov, A.L.; Wang, J.Y.S.; Ramos, A.; Lehmann, R. The Role of Tudor Domains in Germline Development and Polar Granule Architecture. Development 2006, 133, 4053–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, P.F.; Ashburner, M. Posterior Localization of Vasa Protein Correlates with, but Is Not Sufficient for, Pole Cell Development. Genes Dev. 1990, 4, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerdell, J.R.; Yamaguchi, S.; Carthew, R.W. RNAi Is Activated during Drosophila Oocyte Maturation in a Manner Dependent on Aubergine and Spindle-E. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalova, F.; Parfenov, V. Immunomorphological Localization of Vasa Protein and Pre-MRNA Splicing Factors in Panorpa Communis Trophocytes and Oocytes. Cell Biol. Int. 2003, 27, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Gall, J.G. U Bodies Are Cytoplasmic Structures That Contain Uridine-Rich Small Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins and Associate with P Bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11655–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Davies, S.E.; Liu, J.L. The Spinal Muscular Atrophy Protein SMN Affects Drosophila Germline Nuclear Organization through the U Body-P Body Pathway. Dev. Biol. 2009, 332, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelfinger, D.; Arndt-Jovin, D.J.; Lührmann, R.; Achsel, T. The Human LSm1-7 Proteins Colocalize with the MRNA-Degrading Enzymes Dcp1/2 and Xrn1 in Distinct Cytoplasmic Foci. RNA 2002, 8, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, V.; Szöllösi, D.; Kloc, M. The Balbiani Body: Asymmetry in the Mammalian Oocyte. Genesis 2000, 26, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Bilinski, S.; Etkin, L.D. The Balbiani Body and Germ Cell Determinants: 150 Years Later. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2004, 59, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlow, F.L. Maternal Control of Development in Vertebrates: My Mother Made Me Do It! Developmental Biology; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Theusch, E.V.; Brown, K.J.; Pelegri, F. Separate Pathways of RNA Recruitment Lead to the Compartmentalization of the Zebrafish Germ Plasm. Dev. Biol 2006, 292, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.T.; Estridge, B.H.; Kloc, M.; Wolfe, K.G.; Bilinski, S.M. Balbiani Bodies in Cricket Oocytes: Development, Ultrastructure, and Presence of Localized RNAs. Differentiation 2001, 67, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, J.N. Oogenesis in Xenopus Laevis (Daudin) I. Stages of Oocyte Development in Laboratory Maintained Animals. J. Morphol. 1972, 136, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignotte, F.; Tourte, M.; Mounolou, J.C. Segregation of Mitochondria in the Cytoplasm of Xenopus Vitellogenic Oocytes. Biol. Cell 1987, 60, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Bilinski, S.; Dougherty, M.T.; Brey, E.M.; Etkin, L.D. Formation, Architecture and Polarity of Female Germline Cyst in Xenopus. Dev. Biol. 2004, 266, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boke, E.; Mitchison, T.J. The Balbiani Body and the Concept of Physiological Amyloids. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Butler, A.; Owens, D.; King, M.L.; Aguero, T. Methods for Isolating the Balbiani Body/Germplasm from Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 1920, pp. 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Mitchison, T.J.; Hyman, A.A. Active Liquid-like Behavior of Nucleoli Determines Their Size and Shape in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4334–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škugor, A.; Tveiten, H.; Johnsen, H.; Andersen, Ø. Multiplicity of Buc Copies in Atlantic Salmon Contrasts with Loss of the Germ Cell Determinant in Primates, Rodents and Axolotl. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, L.; Salzer, M.C.; Duran, J.M.; Zaffagnini, G.; De Guirior, C.; Angeles Martínez-Zamora, M.; Böke, E. Comparative analysis of vertebrates reveals that mouse primordial oocytes do not contain a Balbiani body. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 135, jcs259394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein Folding and Misfolding. Nature 2003, 426, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, N.; Mukherjee, C. Germ Cell Ribonucleoprotein Granules in Different Clades of Life: From Insects to Mammals. WIREs RNA 2021, 12, e1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, S.E.; Mowry, K.L. Organizing the Oocyte: RNA Localization Meets Phase Separation. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 140, pp. 87–118. ISBN 9780128152201. [Google Scholar]
- Mathura, V.S.; Soman, K.V.; Varma, T.K.; Braun, W.A. Multimeric Model for Murine Anti-Apoptotic Protein Bcl-2 and Structural Insights for Its Regulation by Post-Translational Modification. J. Mol. Modeling 2003, 9, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, D.C.; Mira, A. Mitochondria and Germ-Cell Death. Nature 1999, 400, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavial, F.; Acloque, H.; Bachelard, E.; Nieto, M.A.; Samarut, J.; Pain, B. Ectopic Expression of Cvh (Chicken Vasa Homologue) Mediates the Reprogramming of Chicken Embryonic Stem Cells to a Germ Cell Fate. Dev. Biol. 2009, 330, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasley, A.; Chavez, S.; Danilchik, M.; Wühr, M.; Pelegri, F. Vertebrate Embryonic Cleavage Pattern Determination. In Vertebrate Development: Maternal to Zygotic Control; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Pelegri, F., Danilchik, M., Sutherland, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 117–171. ISBN 978-3-319-46095-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.-F.; Cheng, S.-F.; Wang, L.-Q.; Yin, S.; De Felici, M.; Shen, W. DAZ Family Proteins, Key Players for Germ Cell Development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantú, A.V.; Laird, D.J. Wnt and Bmp Fit Germ Cells to a T. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kloc, M.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Borsuk, E.; Kubiak, J.Z. Polarity and Asymmetry during Mouse Oogenesis and Oocyte Maturation. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2012, 55, 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mestrah, M.; Castle, P.E.; Borossa, G.; Kan, F.W.K. Subcellular Distribution of ZP1, ZP2, and ZP3 Glycoproteins during Folliculogenesis and Demonstration of Their Topographical Disposition within the Zona Matrix of Mouse Ovarian Oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 66, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoodbhoy, T.; Avilés, M.; Baibakov, B.; Epifano, O.; Jiménez-Movilla, M.; Gauthier, L.; Dean, J. ZP2 and ZP3 Traffic Independently within Oocytes Prior to Assembly into the Extracellular Zona Pellucida. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 7991–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wang, Z.B.; Quan, S.; Huang, X.; Tong, J.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Guo, L.; Wei, Y.C.; Ouyang, Y.C.; Hou, Y.; et al. GM130, a Cis-Golgi Protein, Regulates Meiotic Spindle Assembly and Asymmetric Division in Mouse Oocyte. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Monnot, S.; Gigarel, N.; Samuels, D.C.; Burlet, P.; Hesters, L.; Frydman, N.; Frydman, R.; Kerbrat, V.; Funalot, B.; Martinovic, J.; et al. Segregation of MtDNA throughout Human Embryofetal Development: M.3243A>G as a Model System. Hum. Mutat 2011, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivkova, R.; Panevska, M.; Delimitreva, S.; Markova, M.; Nikolova, V.; Chakarova, I.; Tenev, T.; Hadzhinesheva, V.; Mainhard, K.; Vatev, I. Investigation of Cytokeratin and Vimentin Intermediate Filaments in Polycystic Ovaries (PCOS)—Presence and Specific Structure of Balbiani Body in Primordial Follicles. Akusherstvo Ginekol. 2013, 52, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrynin, M.A.; Korchagina, N.M.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Shafranskaya, D.; Ostromyshenskii, D.I.; Shunkina, K.; Stepanova, I.; Kotova, A.V.; Podgornaya, O.I.; Enukashvily, N.I. Human Pericentromeric Tandemly Repeated DNA Is Transcribed at the End of Oocyte Maturation and Is Associated with Membraneless Mitochondria-Associated Structures. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman-Kay, J.D.; Mittag, T. From Sequence and Forces to Structure, Function, and Evolution of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Structure 2013, 21, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nott, T.J.; Petsalaki, E.; Farber, P.; Jervis, D.; Fussner, E.; Plochowietz, A.; Craggs, T.D.; Bazett-Jones, D.P.; Pawson, T.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; et al. Phase Transition of a Disordered Nuage Protein Generates Environmentally Responsive Membraneless Organelles. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.R.; Milin, A.N.; Moosa, M.M.; Onuchic, P.L.; Deniz, A.A. Reentrant Phase Transition Drives Dynamic Substructure Formation in Ribonucleoprotein Droplets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11354–11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaskivuo, T.E.; Anttonen, M.; Herva, R.; Billig, H.; Dorland, M.; te Velde, E.R.; Stenbäck, F.; Heikinheimo, M.; Tapanainen, J.S. Survival of Human Ovarian Follicles from Fetal to Adult Life: Apoptosis, Apoptosis-Related Proteins, and Transcription Factor GATA-4. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albamonte, M.I.; Albamonte, M.S.; Stella, I.; Zuccardi, L.; Vitullo, A.D. The Infant and Pubertal Human Ovary: Balbiani’s Body-Associated VASA Expression, Immunohistochemical Detection of Apoptosis-Related BCL2 and BAX Proteins, and DNA Fragmentation. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albamonte, M.I.; Albamonte, M.S.; Bou-Khair, R.M.; Zuccardi, L.; Vitullo, A.D. The Ovarian Germinal Reserve and Apoptosis-Related Proteins in the Infant and Adolescent Human Ovary. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudson, C.M.; Tung, K.S.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Brown, G.A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bax-Deficient Mice with Lymphoid Hyperplasia and Male Germ Cell Death. Science 1995, 270, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felici, M.; Lobascio, A.M.; Klinger, F.G. Cell Death in Fetal Oocytes: Many Players for Multiple Pathways. Autophagy 2008, 4, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yang, Y.; Xing, D. Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL Play Important Roles in the Crosstalk between Autophagy and Apoptosis. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.K.; Lorthongpanich, C.; Chew, T.G.; Tan, C.W.G.; Shue, Y.T.; Balu, S.; Gounko, N.; Kuramochi-Miyagawa, S.; Matzuk, M.M.; Chuma, S.; et al. The Nuage Mediates Retrotransposon Silencing in Mouse Primordial Ovarian Follicles. Development 2013, 140, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
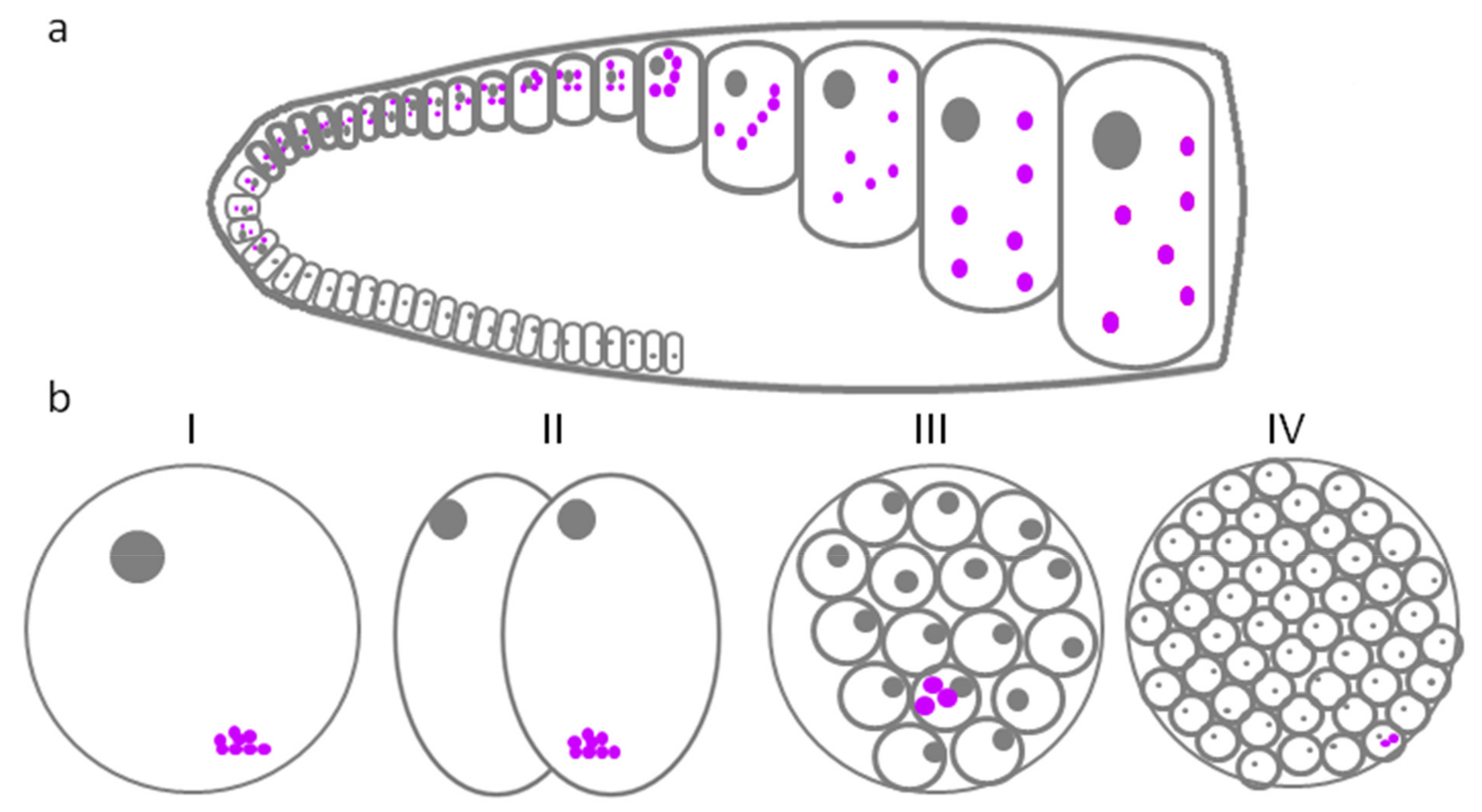
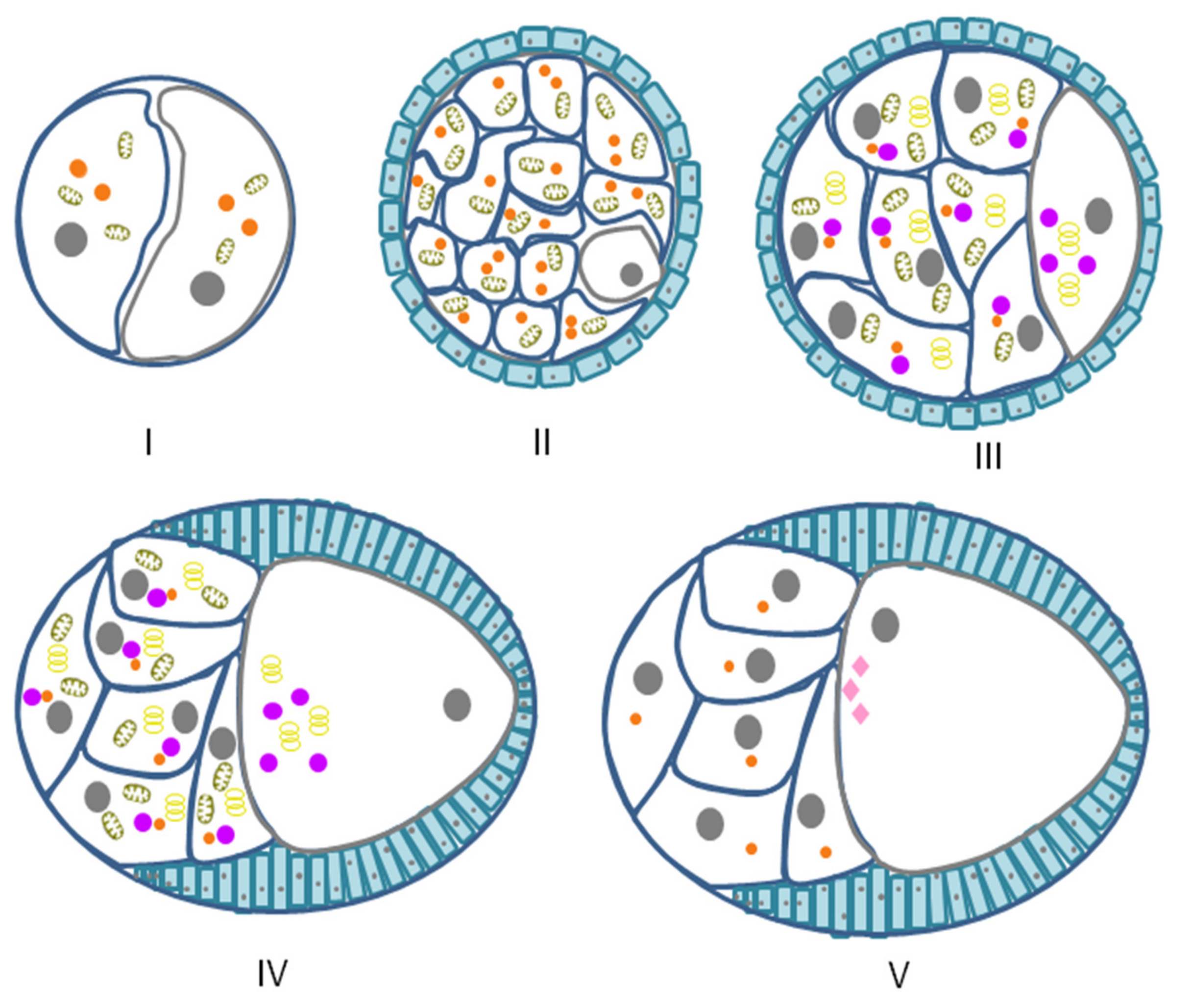
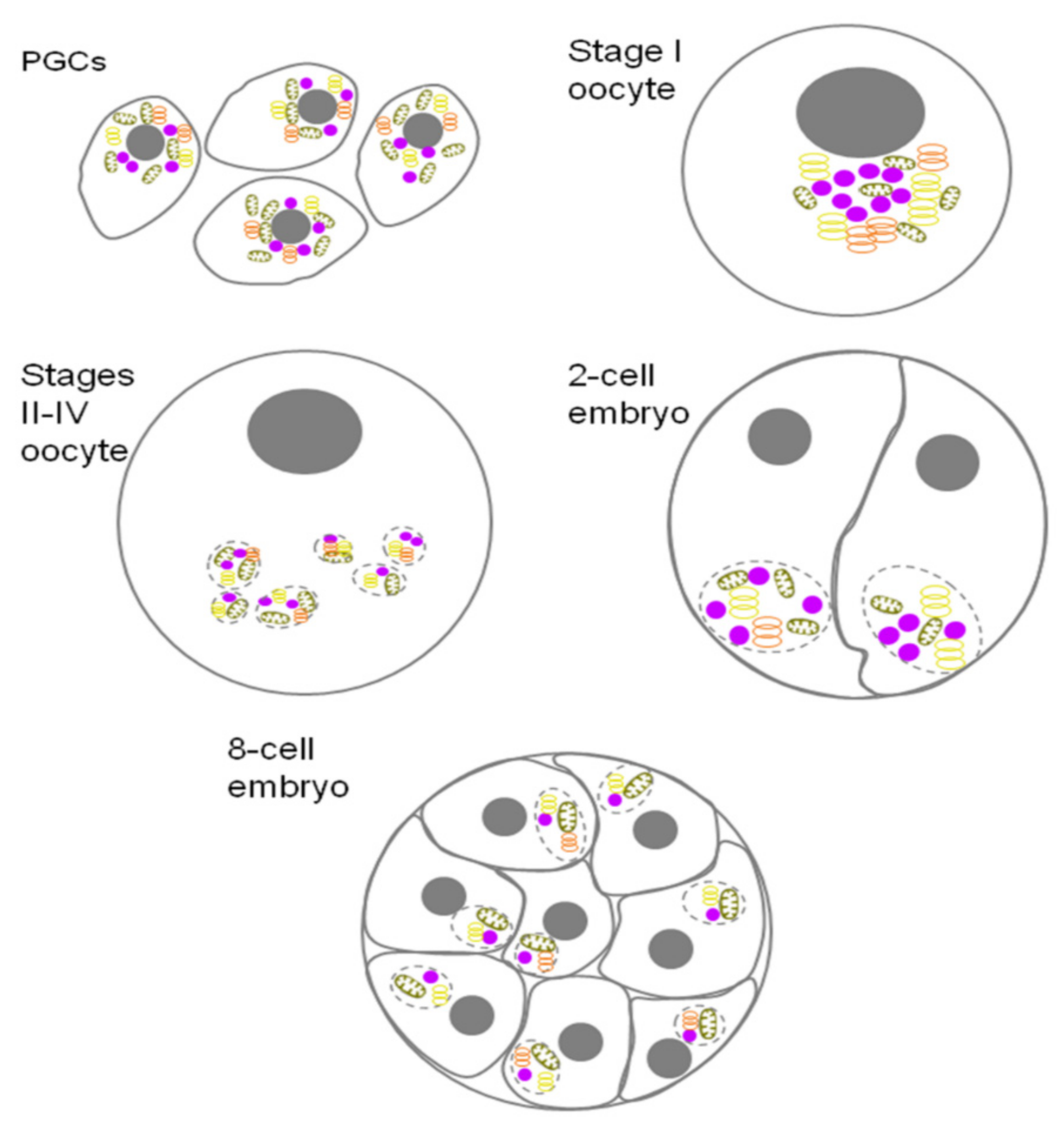
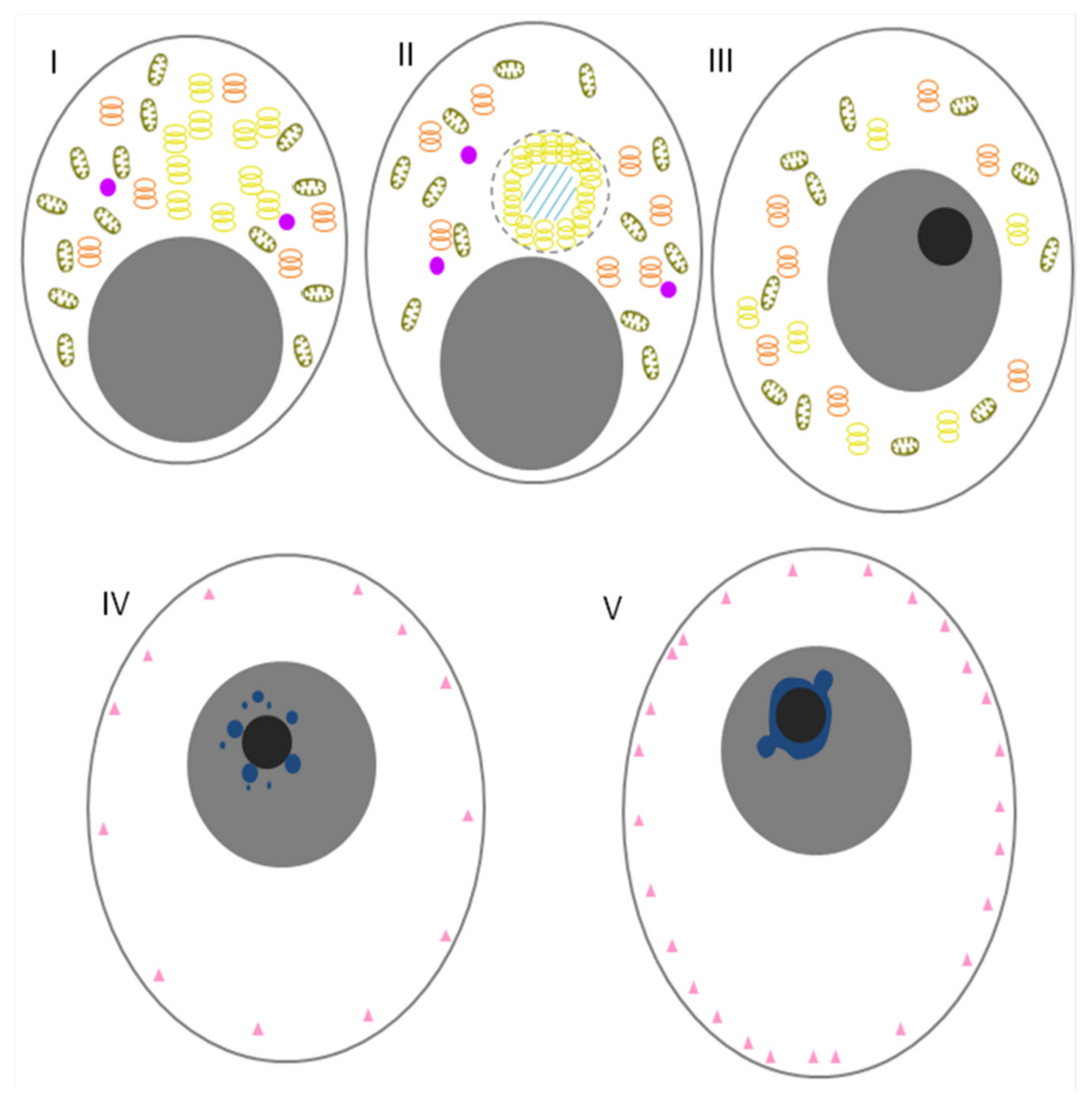
| Species | Type of Cells | Stage of Development | Historical Name of the Structure | Modern Name of the Structure | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caenorhabditis elegans | Cells of germ line at all stages of development | Four larval stages and an adult | P-granules | P-granules/nuage | [6,7] |
| Drosophila melanogaster | In oocytes and nurse cells | All stages of oogenesis | Sponge bodies | GG | [8] |
| In nurse cells | All stages of oogenesis | Nuage | Nuage | [9,10] | |
| In oocytes and embryos | Late stages of oogenesis and early embryogenesis | Polar granules | GG | [9,10] | |
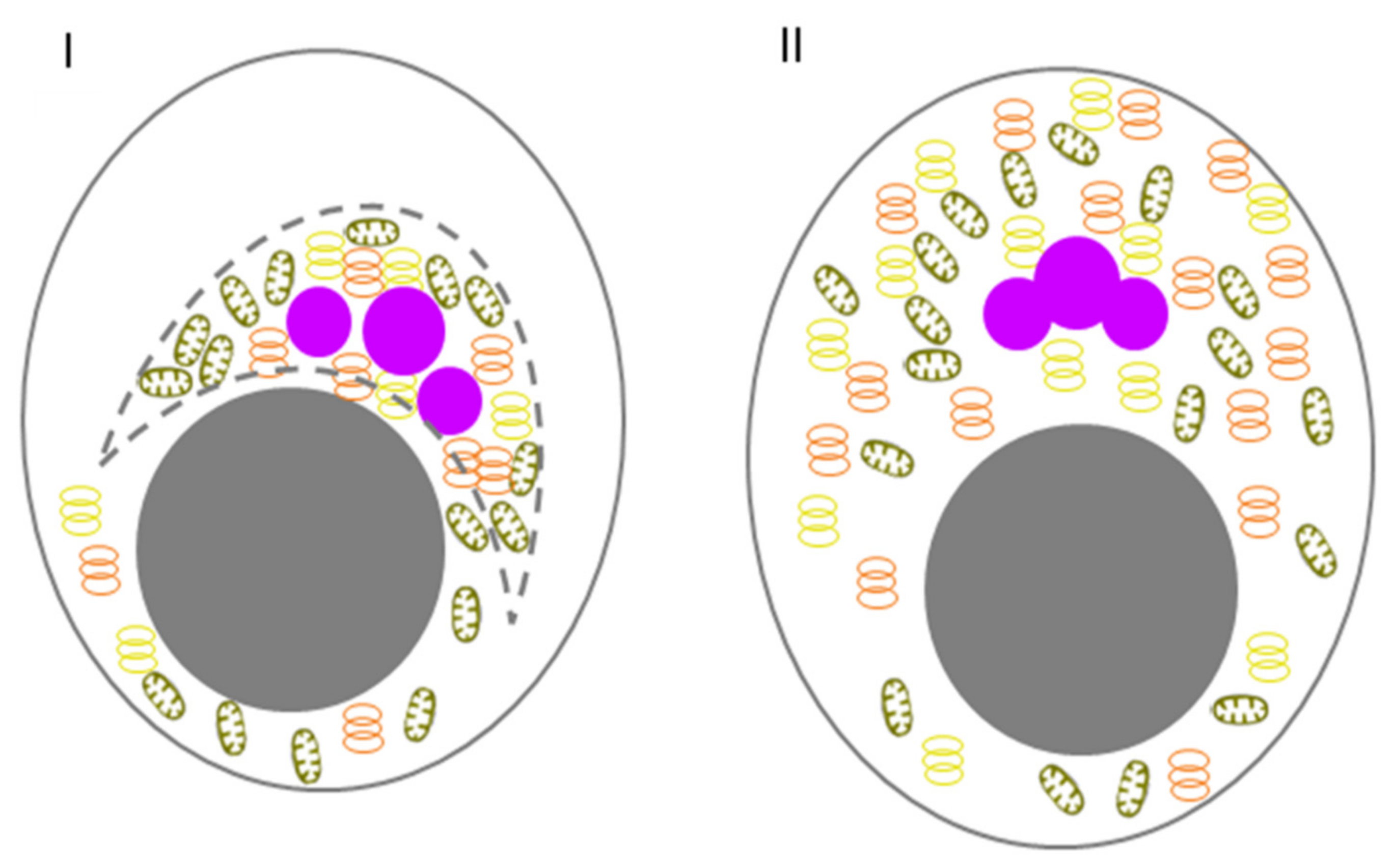
| Danio rerio | Primary oocytes | From stage Ia (zygotene) to stage Ib (diplotene) of oocytes development | Nuage/intermitochondrial cement | Bb | [11,12] |
| Embryos | From zygote to 32-cell embryo | GG as part of germ plasm islands | Nuage-like structures | [12,13] | |
| Xenopus laevis | PGC and early oocytes | From PGC to I stage of oocytes development | Mitochondrial cloud and subsequent stages of its development | Nuage | [14] |
| Oocytes | From I to Vl stage of oocytes development | GG as part of Bb | GG | [14,15] | |
| Late oocytes and early embryos | From Vl stage of oocytes development to 8 cell embryo | Small GG as part of germ plasm «islands» | GG | [14,15] | |
| Embryos | From eight cell embryo to PGC | GG as part of germ plasm ‘islands’ | GG | [15] | |
| Gallus gallus | Oocytes | Oocytes | Mitochondrial cloud | CVH-positive structures | [16,17,18] |
| Early embryos | From embryo stage I to stage X | Mitochondrial cloud | CVH-positive structures | [16] | |
| Mus musculus | Oogonia and oocytes of primary follicles | Early stages of oogenesis | Nuage | Nuage | [19] |
| Spermatocytes | Spermatogenesis | chromatoid body | Nuage/chromatoid body | [20] | |
| Homo sapiens | Oogonia | Early stages of oogenesis | Nuage | Nuage | [21] |
| Spermatidsspermatocytes | Spermatogenesis | Chromatoid body | Nuage | [22,23,24] |
| Species | Modern Name of the Structure | Marker RNA | Marker Protein |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. elegans | Nuage/P-granules | mRNA Nos-2 [35,48] 26G siRNA-3[49] piRNA (21U) [50] 22G-siRNA [51] | ZNFX-1 and WAGO-4 [52] GLH-1, 2, 3, 4 [53] RDE-12 [54] PGL-1, PGL-3 [53,55] LAF-1, VBH-1, CAR-1, CSR-1, ALG-3, ALG-4, and HRDE-1 [56] WAGO-1 [57] MEG-1, MEG-2, MEG-3, and MEG-4 [58] Nanos [35] PUM 2 [33] CGH-1 [59]IFE-1(EIF4E) [60] DCP-2 [61] DCR-1, DRH-3, EGO-1, CSR-1, and PRG-1 [51] PGL-3, MEX-5 И PAR-1 [62] |
| Drosophila melanogaster | GG/sponge bodies | mRNA Bicoid [63] | Exuperantia И Me31B [8,63,64] Bruno (in nurse cells), Orb (in oocytes) [8,64,65,66] EIF4e [64] Cup [67] Dcp1 and Dcp2 [68] Nanos [37] PUM 2 [33] α-spectrin [69] |
| GG/polar granules | Vasa [70] Oskar [71] Dcp1 И Me31B [64,72] Aubergine [73] Tudor [74] EIF4A [64] PIWI, DICER-1 И dFMRP (fragile X mental retardation protein) [41] α-spectrin [69] | ||
| Nuage | Small interference RNA (siRNAs) [75] | Vasa [70] Ago3 [76] Aubergine [73] Maelstrom, Spindle-E [77] Krimp, Tejas, and PAPI [75,78,79] α-spectrin [69] | |
| Danio rerio | Bb | Vasa, Nanos1, Dazl [12] | Buc [28,80] Vasa [13] Hermes [12] Macf1 [81] Tudor (Tdrd6) [82] |
| Nuage-like structures | Dazl, Dnd, Nos-3, Rgs14a, Vasa [83] Brul [43] | Nanos 1 [34] | |
| Xenopus laevis | Nuage/mitochondrial cloud | Xdazl [84] Xpat [85] Xlsirts [86] DEADSouth [87] Fingers И XFACS [15] Syntabulin [88] | XALK4 [89] EF-1 [90] Tudor (Tdrd6) [12] Nanos, Pumilio [37] |
| GG | Xcat2, Vg1 [91] Xdazl, Xpat, Xlsirts [15] Hermes, Nanos1, Vasa and Dazl [92] Xwnt11, VegT [14] Xotx1 [93] mRNA glutamate receptor interacting protein 2a (Grip2a) [94] | XVLG1 [95] EIF4A [87] Kox1 [15] Bcl-xL [96] XALK4 [89] XVelo [97] Rbpms2 [82] Tudor (Tdrd6) [12] Macf1 [81] Nanos, Pumilio [37] | |
| Small GG as part of germ plasm islands | Xcat2, Vg1 [91] Xdazl, Xpat, Xlsirts [15] mRNA Glutamate receptor interacting protein 2a (Grip2a) [94] RNA Syntabulin [98] | XVelo [97] Tudor (Tdrd6) [12] Nanos, Pumilio [37] | |
| Gallus gallus | CVH-positive structures | CVH (chicken Vasa homolog)[16] | |
| Mus musculus | Nuage | mRNA Dnajc11, Spin1 [99], piwiRNA [99] | MVH [100] PADI6, NLRP5 И FILIA [101,102] DDX6, CPEB, YBX2 (MSY2), (Exon junction complex, EJC), DCP1A [103] TDRD1 [104] Nanos1, Pumilio2, Gemin3 [36] Maelstrom [105] |
| Homo sapiens | Nuage | DDX4 [42] BAX (oogony and oocytes) [106] BCL2 (only oogonia) [106] Mcl-1 [107] Nanos, Pumilio И Gemin3 [36] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrynin, M.A.; Bashendjieva, E.O.; Enukashvily, N.I. Germ Granules in Animal Oogenesis. J. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040043
Dobrynin MA, Bashendjieva EO, Enukashvily NI. Germ Granules in Animal Oogenesis. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2022; 10(4):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrynin, Mikhail A., Ekaterina O. Bashendjieva, and Natella I. Enukashvily. 2022. "Germ Granules in Animal Oogenesis" Journal of Developmental Biology 10, no. 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040043
APA StyleDobrynin, M. A., Bashendjieva, E. O., & Enukashvily, N. I. (2022). Germ Granules in Animal Oogenesis. Journal of Developmental Biology, 10(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040043








