Physical Reinforcement Learning with Integral Temporal Difference Error for Constrained Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Robot Dynamics and the Problem Statement
2.2. The Actor–Critic Learning Control Problem
3. Learning Actor–Critic Design
3.1. The Value Function and the Temporal Difference Error
3.2. The Critic Neural Network
3.3. The Actor Neural Network
3.4. Model-Free Actor–Critic Control Design
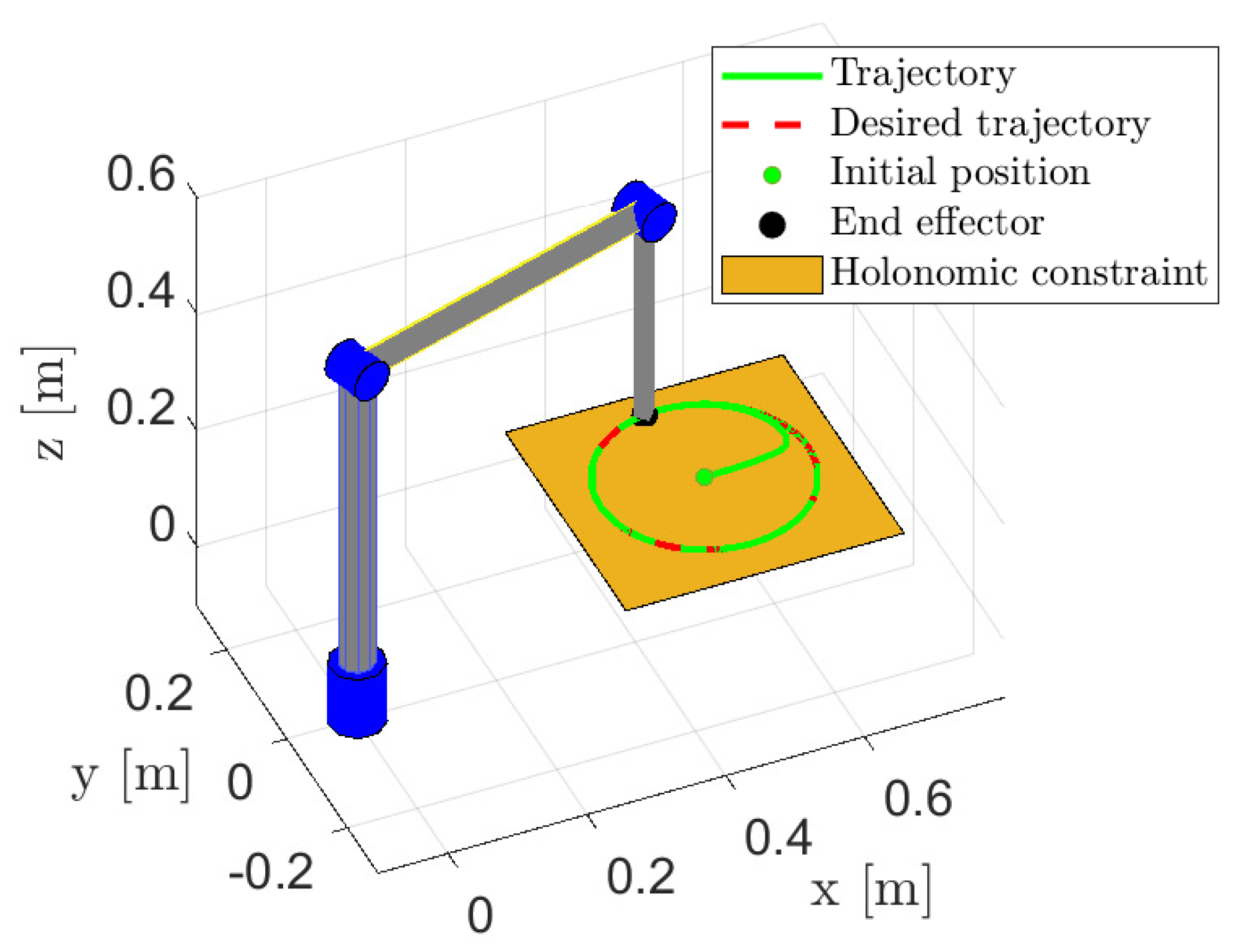
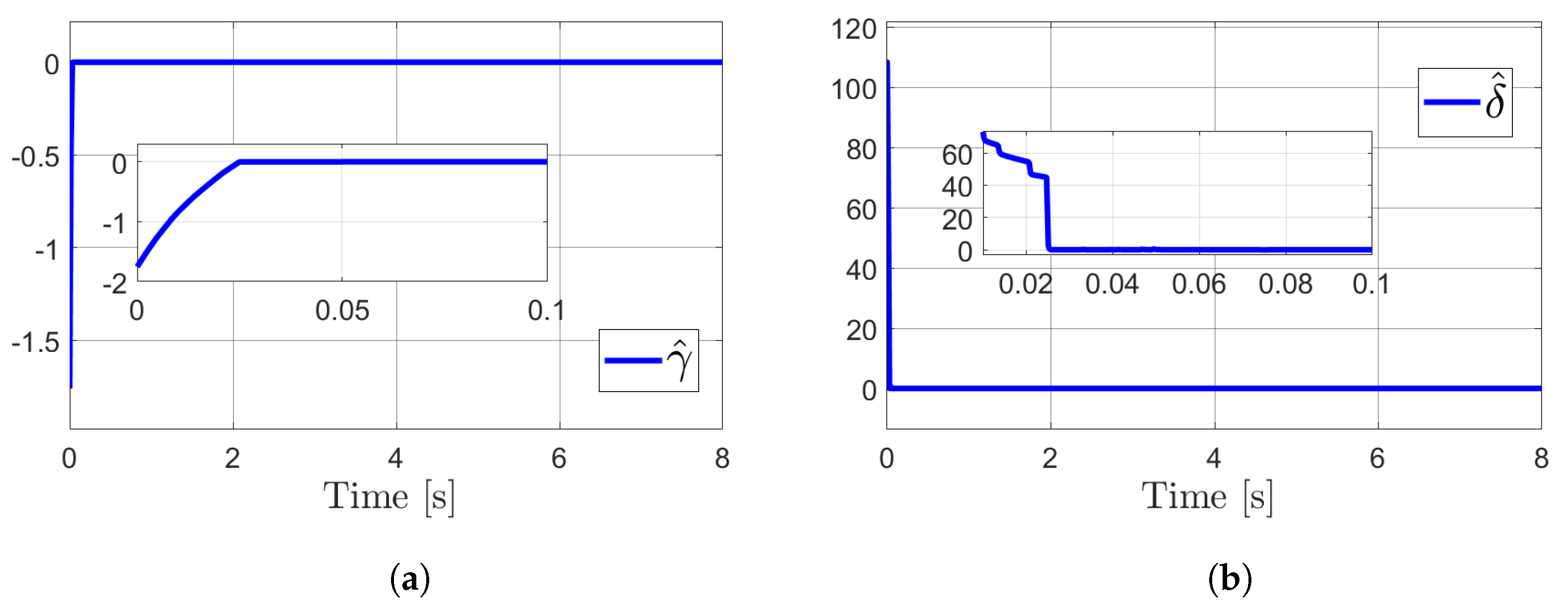
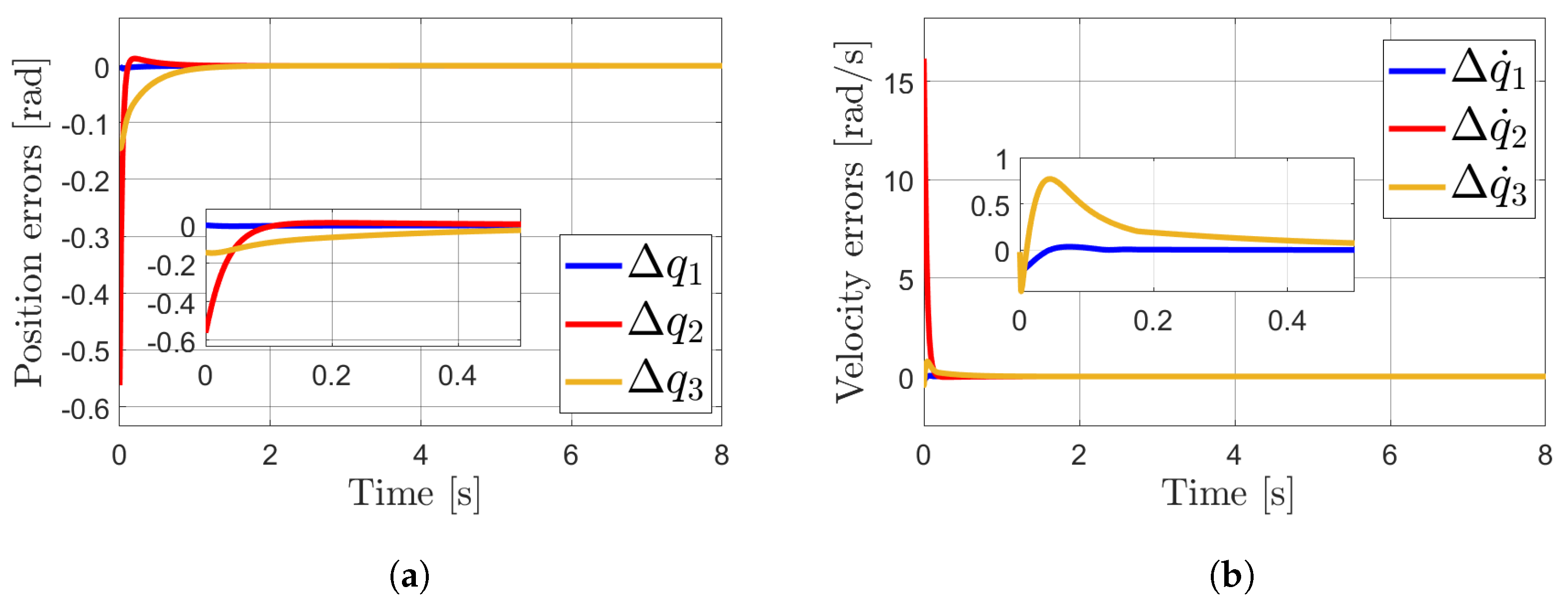
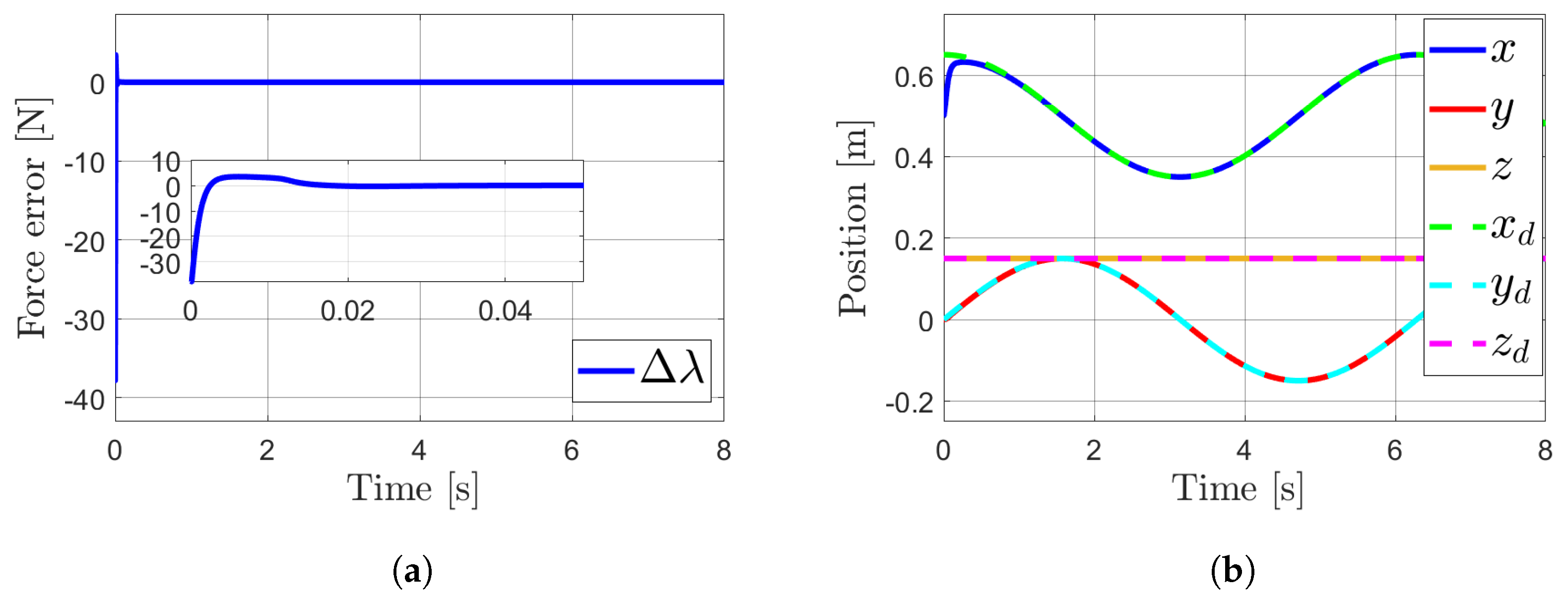
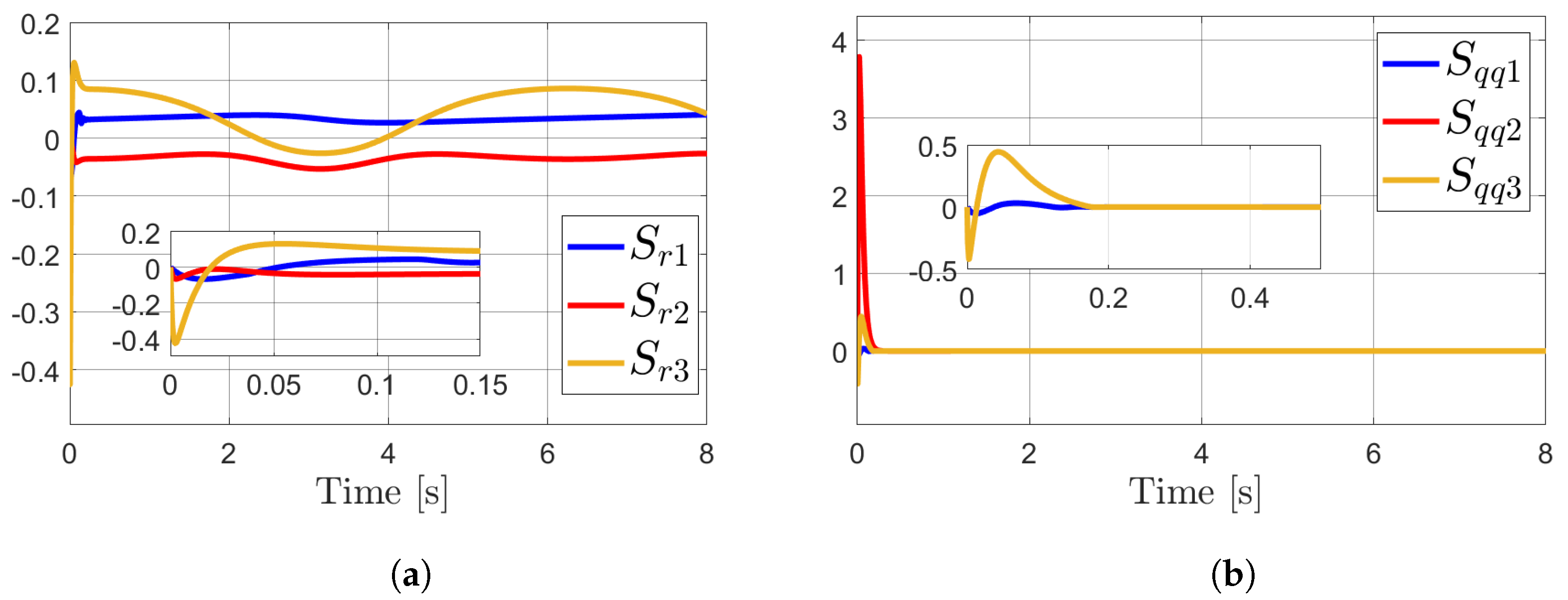
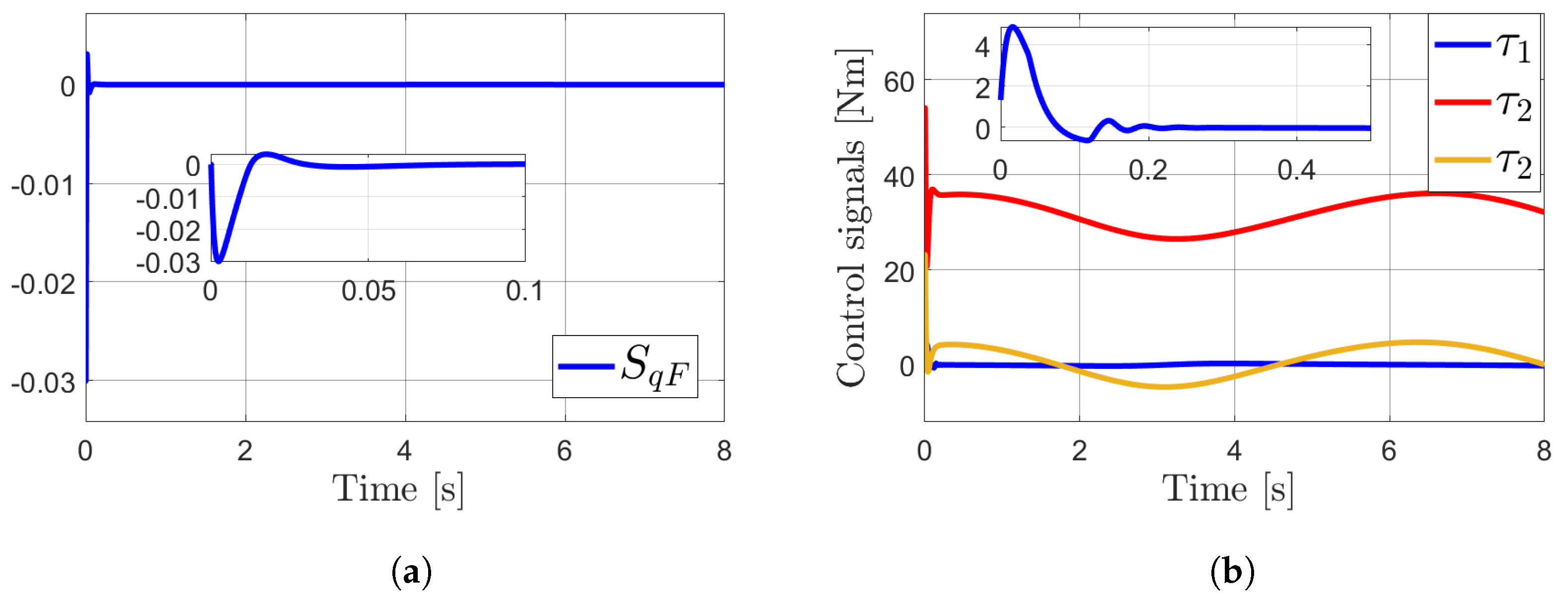
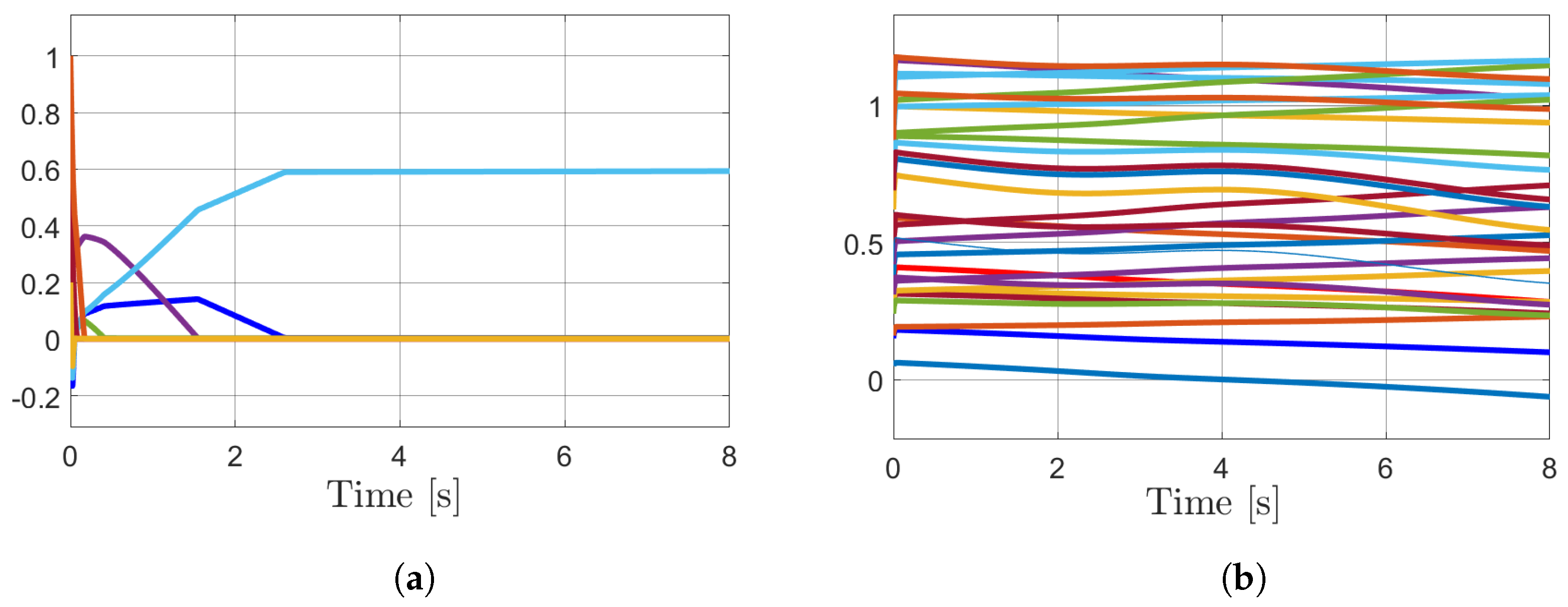
4. Simulations
Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proofs of the Propositions and Theorem
Appendix A.1. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix A.2. Proof of the Theorem
References
- Gu, S.; Yang, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, G.; Walter, F.; Wang, J.; Knoll, A. A Review of Safe Reinforcement Learning: Methods, Theories, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 11216–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Garcia, L.; Parra-Vega, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, R. Automatic reinforcement for robust model-free neurocontrol of robots without persistent excitation. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2024, 38, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaverini, S.; Siciliano, B.; Villani, L. A survey of robot interaction control schemes with experimental comparison. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 1999, 4, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N. Impedance Control: An Approach to Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 1984 American Control Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 June 1984; pp. 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.C.; Huang, A.C. Adaptive Impedance Control of Robot Manipulators based on Function Approximation Technique. Robotica 2004, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClamroch, N.; Wang, D. Feedback stabilization and tracking of constrained robots. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1988, 33, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Vega, V.; Arimoto, S.; Liu, Y.; Naniwa, T. Model-based adaptive hybrid control for robot manipulators under holonomic constraints. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1994, 27, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Hsia, T. Neural network impedance force control of robot manipulator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, C.P.; Doulgeri, Z.; Rovithakis, G.A. Neuro-Adaptive Force/Position Control With Prescribed Performance and Guaranteed Contact Maintenance. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Yang, C.; He, W.; Chen, C.L.P. Force Sensorless Admittance Control With Neural Learning for Robots With Actuator Saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 3138–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barto, A.G.; Sutton, R.S.; Anderson, C.W. Looking Back on the Actor–Critic Architecture. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, C.; Li, Z. Reinforcement Learning Control of a Flexible Two-Link Manipulator: An Experimental Investigation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 7326–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Dao, P.N.; Loc, P.T.; Huy, T.Q. Sliding Variable-based Online Adaptive Reinforcement Learning of Uncertain/Disturbed Nonlinear Mechanical Systems. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2021, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Huang, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, C. Adaptive dynamic programming-based controller with admittance adaptation for robot–environment interaction. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420924610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, M.; Zou, Y.b.; Xiao, J.d.; Chen, S.y. Robotic Curved Surface Tracking with a Neural Network for Angle Identification and Constant Force Control based on Reinforcement Learning. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liao, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. A novel impedance control method of rubber unstacking robot dealing with unpredictable and time-variable adhesion force. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Han, S.; Tao, B.; Yin, Z.; Ding, H. Model-Based Actor−Critic Learning of Robotic Impedance Control in Complex Interactive Environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13225–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrusquía, A.; Yu, W.; Soria, A. Position/force control of robot manipulators using reinforcement learning. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2019, 46, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.N.; Do, D.K.; Nguyen, D.K. Adaptive Reinforcement Learning-Enhanced Motion/Force Control Strategy for Multirobot Systems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5560277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.N.; Liu, Y.C. Adaptive reinforcement learning in control design for cooperating manipulator systems. Asian J. Control 2022, 24, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katić, D.M.; Rodić, A.D.; Vukobratović, M.K. Hybrid dynamic control algorithm for humanoid robots based on reinforcement learning. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. Theory Appl. 2008, 51, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormushev, P.; Calinon, S.; Caldwell, D.G. Reinforcement Learning in Robotics: Applications and Real-World Challenges. Robotics 2013, 2, 122–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Nageotte, F.; Zanne, P.; de Mathelin, M.; Dresp-Langley, B. Deep Reinforcement Learning for the Control of Robotic Manipulation: A Focussed Mini-Review. Robotics 2021, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Garcia, L.; Parra-Vega, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, R.; Vázquez-García, C.E. A Novel Actor—Critic Motor Reinforcement Learning for Continuum Soft Robots. Robotics 2023, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Vega, V.; Arimoto, S. A passivity-based adaptive sliding mode position-force control for robot manipulators. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 1996, 10, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doya, K. Temporal Difference Learning in Continuous Time and Space. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Proceedings of the 1995 Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 27–30 November 1995; Touretzky, D., Mozer, M., Hasselmo, M., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; Volume 8, pp. 1073–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, G.J.; Mahmoudi, S.; Brown, K. Pavlovian learning and conditioned reinforcement. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2023, 56, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, T.; Barto, A. Lyapunov design for safe reinforcement learning control. In Safe Learning Agents: Papers from the 2002 AAAI Symposium, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 25–27 March 2002; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
| Control Law | Performance Metrics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Proposal | 4.796 × 10−4 | 9.194 × 10−2 | 258.8 | 142.9 |
| Neurocontroller | 7.142 × 10−4 | 9.246 × 10−2 | 259 | 151.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantoja-Garcia, L.; Parra-Vega, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, R. Physical Reinforcement Learning with Integral Temporal Difference Error for Constrained Robots. Robotics 2025, 14, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080111
Pantoja-Garcia L, Parra-Vega V, Garcia-Rodriguez R. Physical Reinforcement Learning with Integral Temporal Difference Error for Constrained Robots. Robotics. 2025; 14(8):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080111
Chicago/Turabian StylePantoja-Garcia, Luis, Vicente Parra-Vega, and Rodolfo Garcia-Rodriguez. 2025. "Physical Reinforcement Learning with Integral Temporal Difference Error for Constrained Robots" Robotics 14, no. 8: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080111
APA StylePantoja-Garcia, L., Parra-Vega, V., & Garcia-Rodriguez, R. (2025). Physical Reinforcement Learning with Integral Temporal Difference Error for Constrained Robots. Robotics, 14(8), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080111






