Abstract
Autonomous vehicles are a continuously rising technology in several industry sectors. Examples of these technologies lie in the advances in self-driving cars and can be linked to extraterrestrial exploration, such as NASA’s Mars Exploration Rovers. These systems present a leading methodology allowing for increased task performance and capabilities, which are no longer limited to active human support. However, these robotic systems may vary in shape, size, locomotion capabilities, and applications. As such, this report presents a systematic literature review (SLR) regarding hybrid autonomous robotic vehicles focusing on leg–wheel locomotion. During this systematic review of the literature, a considerable number of articles were extracted from four different databases. After the selection process, a filtered sample was reviewed. A brief description of each document can be found throughout this report.
1. Introduction
Autonomous robots have been perfected over the years and are preferred for several applications. Examples include increasing productivity and efficiency in the agriculture sector and tunnel inspection for structural assessment [1]. These systems also allow for safer, faster, and more reliable performance in industrial settings. Such applications include the following:
- Collaboration Robots:These are used in several industries to work between robot and human tasks such as sorting and picking.
- Inventory Transportation Robots:These are used to transport inventory within a facility.
- Scalable Storage Picking Robots:These are mainly used to retrieve items from or place items in storage, allowing the operator to access the products quickly.
- AGVs—Automatic Guided Vehicles:These are used in applications such as self-driving forklifts.
Autonomous hybrid vehicles are robotic devices capable of different types of locomotion. As such, some vehicles are even capable of moving through different terrains, environments, and conditions without needing additional human support. However, these features are not applicable to all hybrid vehicles. The progressive advancement in these technologies has become a leading study subject in robotics.
Hybrid vehicles can exhibit different types of locomotion, such as ground, air, and water. The following list presents some examples:
- AGVs—Autonomous Guided Vehicles.
- AUVs—Autonomous Underwater Vehicles.
- UAVs—Unmanned Aerial Vehicles.
Hybrid robots can be used in many industries, such as manufacturing, transportation, and search-and-rescue missions. In manufacturing, for example, hybrid robots can move around the factory floor easily and manipulate objects with high precision. They can also be used in transportation, such as autonomous delivery vehicles, which can navigate through complex environments and make decisions on the fly. In search-and-rescue operations, hybrid robots can navigate through challenging terrain and provide real-time information to the rescue team.
Integrating hybrid technology in robots can also significantly increase their capabilities in machine learning and computer vision. These robots can recognize and interpret their environment, make decisions, and act autonomously. This enables the robot to perform tasks that were once only possible for humans, such as recognizing and identifying objects and obstacles and making decisions based on that information, such as path planning and obstacle avoidance.
However, some challenges must be overcome before hybrid robots can be widely adopted. Ensuring the safe operation of hybrid robots in unpredictable environments remains a primary concern, necessitating robust adaptive mechanisms. Additionally, the high cost associated with hybrid robotics poses a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in resource-constrained applications.
This work aims to present a systematic literature review of robotic autonomous hybrid vehicles that use wheel–leg technology. With these data, we can better understand how these implementations have been perfected over the past 20 years. Also, we can scout for possible implementations and methodologies to be applied in future works regarding this particular locomotion system.
Structured methodically, this document delineates the methodology employed for data collection, paper selection, and data classification in Section 2, followed by the presentation of the analysis results in Section 3. Section 4 provides a detailed description of the obtained findings, while Section 5 encapsulates conclusive insights drawn from this study, paving the way for further exploration and advancement in the field of robotic autonomous hybrid vehicles.
2. Method
Systematic literature reviews (SLRs) organize scientific works to answer a particular research question in a way that is transparent and reproducible while seeking to include all published evidence on the topic and evaluating the quality of this evidence. SLRs have become a significant methodology in disciplines such as public-policy research, health science, and engineering [2].
The research for this SLR was performed according to the systematic literature methodology presented in [3,4,5]. This work is divided into three stages: planning, conducting, and reporting the review.
Preliminary research was conducted using Google Scholar to verify whether such an SLR already existed. After a thorough search, no document of this nature was found. As such, this systematic review can be considered new research.
2.1. Planning
Starting the SLR planning involved identifying and establishing the research questions this work aims to investigate. These research questions (RQ) are as follows:
- RQ1—Are there recent robotic implementations with legged–wheeled technologies?
- RQ2—Are the recently published works on legged–wheeled robots tested on realistic simulators?
- RQ3—Are the recently published works on legged–wheeled robots tested through a physical prototype?
2.2. Search Process
The used data sources include Scopus, IEEE Digital Library (IEEE Xplore), ScienceDirect, and SpringerLink. All websites were accessed on 10 August 2023.
Research terms—robotic vehicles; autonomous; hybrid; wheeled–legged or legged–wheeled.
- ScopusWebsite: https://www.scopus.com( TITLE-ABS-KEY ( robotic AND vehicles ) ) AND ( ( ( ( autonomous ) ) AND ( hybrid ) ) AND ( ( wheeled–legged ) OR (legged-wheeled) ) )
- IEEE Digital LibrarySearch within results: (“All Metadata”: Robotic vehicles) + “Autonomous” + “hybrid” + “wheeled-legged”AND(“All Metadata”: Robotic vehicles) + “Autonomous” + “hybrid” + “legged-wheeled”Both search processes produced the same results.
- ScienceDirectWebsite: https://www.sciencedirect.com/Search String: robotic vehicles AND “autonomous” AND “hybrid” AND (“wheeled-legged” OR “legged-wheeled”)
- Springer LinkWebsite: https://link.springer.com/Search string: robotic AND vehicles AND autonomous AND hybrid AND (wheeled-legged OR legged-wheeled)
The databases used in this review were selected due to the following reasons:
- They are well-known and established databases in the robotics field.
- It is possible to use a search string as well as Boolean operators to improve the results of the search process.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion of the acquired papers rested on them meeting all the inclusion criteria, present in Table 1. An article was considered in the review if these criteria were met. However, if any of the exclusion criteria were met, the work was excluded from the study.

Table 1.
Inclusion criteria.
An important note about the nomenclature used in this SLR lies in the multiple definitions of leg-and- wheel robot implementations. Since there is no fixed general termination for this type of locomotion, both “legged-wheeled” and “wheeled-legged” nomenclatures must be used in the search process to account for different name use by multiple authors.
Inclusion criteria:
The exclusion criteria, as opposed to the inclusion criteria, are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Exclusion criteria.
2.4. Quality Assessment
With the inclusion and exclusion criteria defined, a set of questions was determined to assess the overall quality of the work regarding this literature review, as shown in Table 3. Each question is answered with a Boolean answer of “Yes” or “No” and scored with 1 or 0 points, respectively. As such, the maximum possible score is 5 points.

Table 3.
Quality questions.
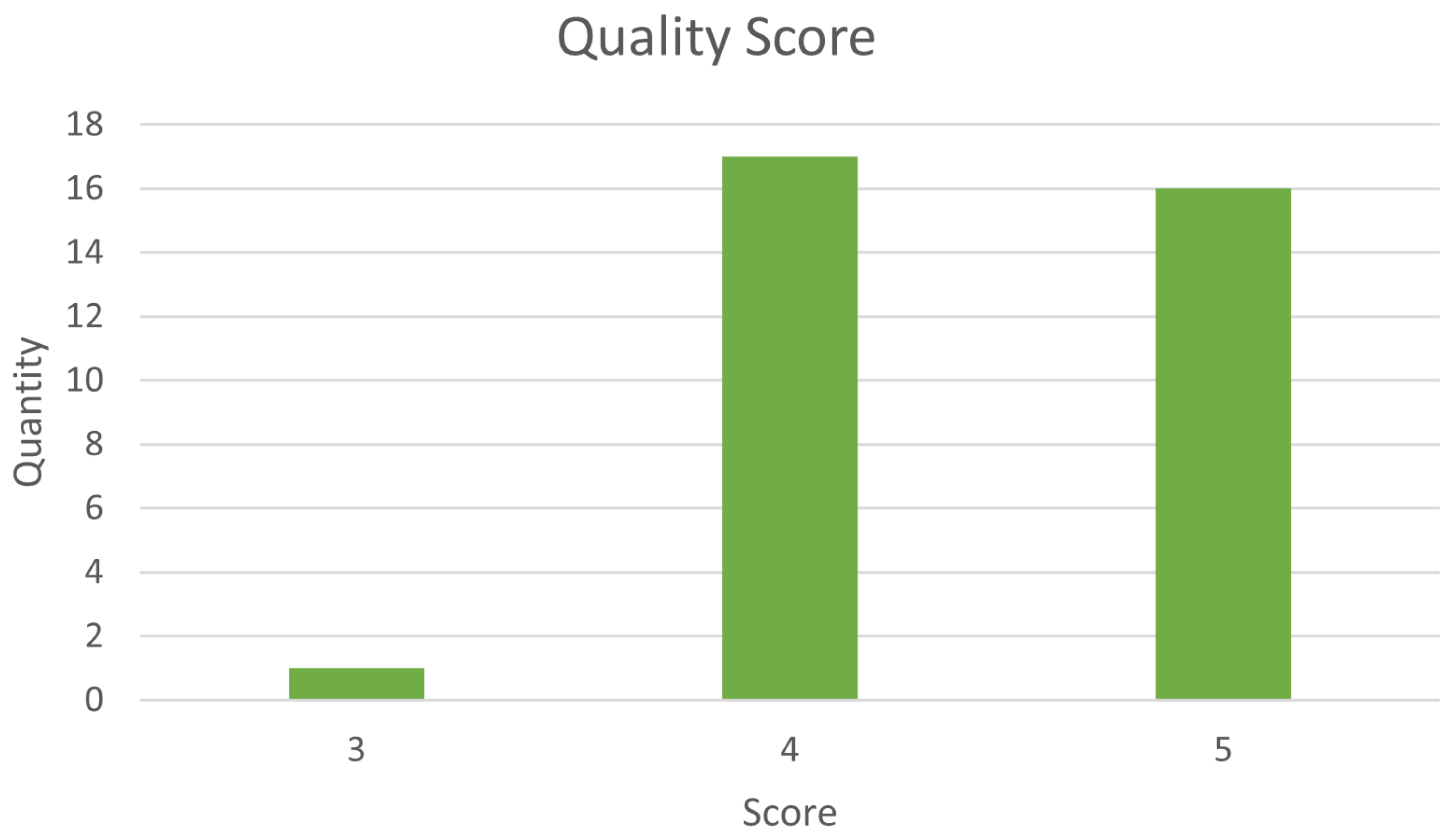
After analyzing the papers for the answer to the quality questions, ten papers scored 3 or less points, as shown in the graph of Figure 1. As such, these works were excluded from this review.
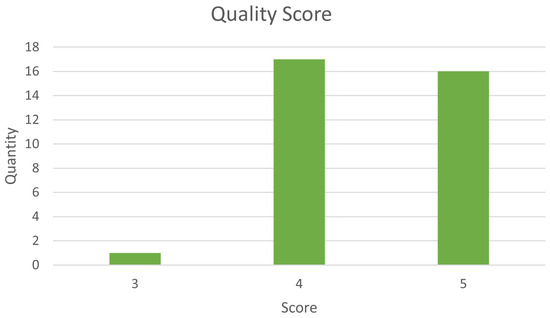
Figure 1.
Quality results.
To further evaluate the selected papers, a set of data questions was used to assess the results and procedures of each work, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Data questions.
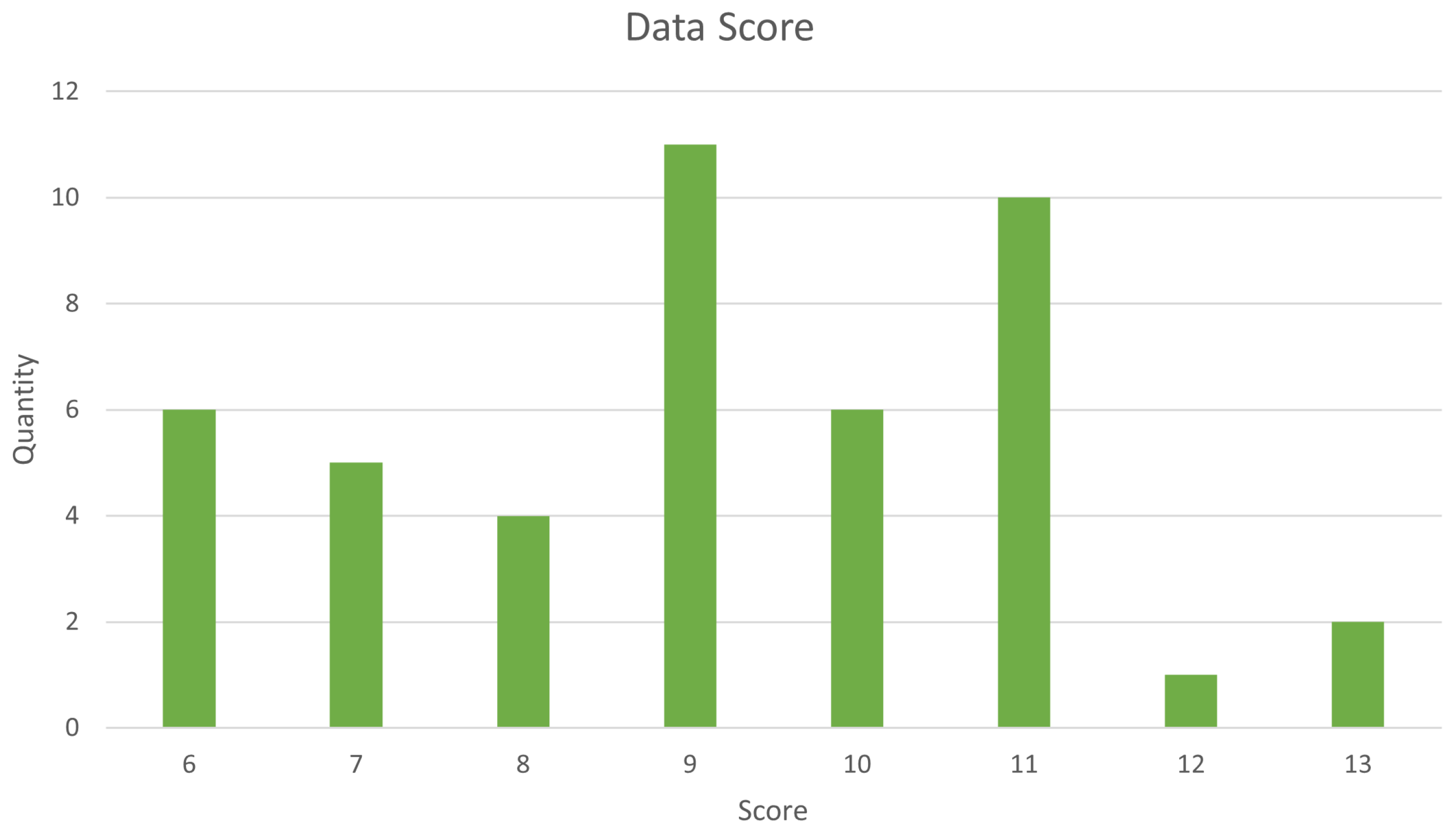
Data questions DQ1 and DQ3 to DQ7 are to be met with one of the following responses: “Yes” (Y), “No” (N), or “Yes but not entirely” (YN). Question DQ2, on the other hand, is meant to be answered with “NEW” or “OLD.” The results of this evaluation are shown in Figure 2.
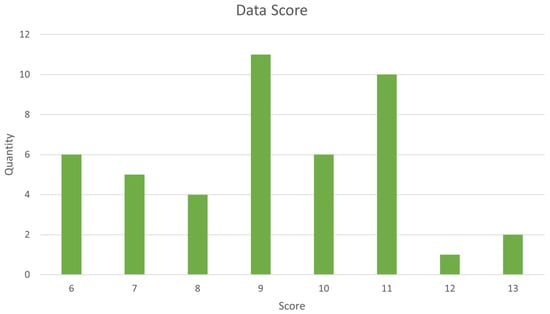
Figure 2.
Data results.
3. Results
This section presents the results acquired from the search of the databases. The final database search was conducted on 10 August 2023, to obtain the most updated version of this research.
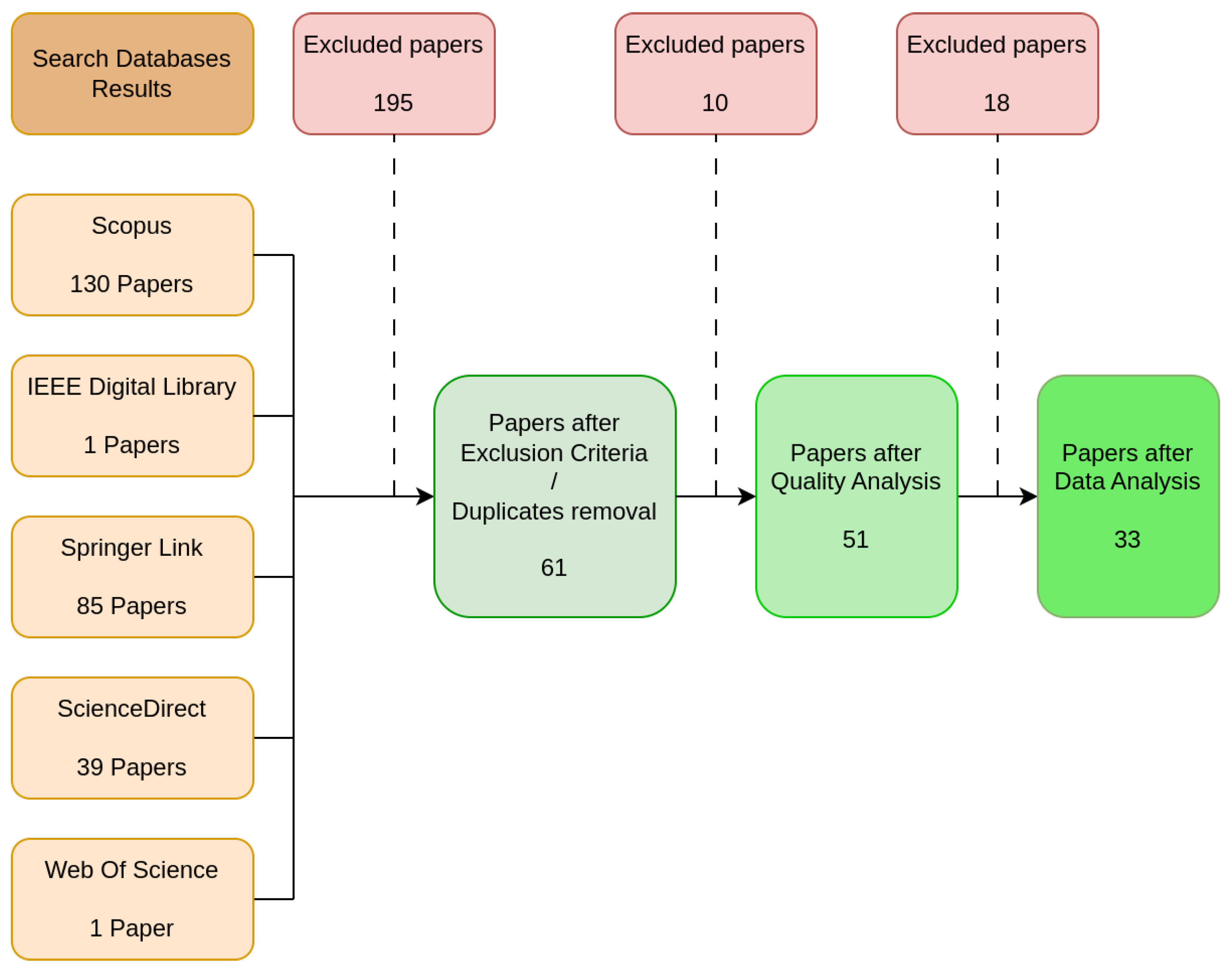
In total, we obtained 256 scientific articles: 130 from the Scopus search; 1 from the IEEE Digital Library; 85 from SpringerLink; 36 from ScienceDirect; and 1 from Web Of Science. Given the reduced results, duplicate items were verified using EndNote, and 7 duplicate items were found and excluded.
Following the inclusion and exclusion criteria analysis, 188 items were removed for not meeting these parameters after analyzing the title, abstract, and overall content.
The remaining 61 works were analyzed for quality assessment. Having excluded ten papers, as described in Section 2.4, due to the quality questions analysis, we were left with 51 papers. Each work was evaluated with a numerical score. Each work was scored for the answers to each of the data questions. Questions DQ1 and DQ3 through DQ7 were scored with 0, 1, or 2 points if the answer was “N”, “YN”, or “Y”, respectively. For question DQ2, the answer is scored with 1 point for “NEW” or 0 points for “OLD”. Additionally, the selected articles related to each of the research questions are presented in Table 5. The answers and corresponding scores of the analysis of each finalist work are presented in Table 6. With this scoring method, the maximum possible score is 13 points. As such, for the remainder of this literature review, papers with scores equal to or greater than nine were considered, leaving 33 papers to be analyzed. The overall Search process and the paper selection and filtering are presented in Figure 3.

Table 5.
Research questions results.

Table 6.
Data questions results.
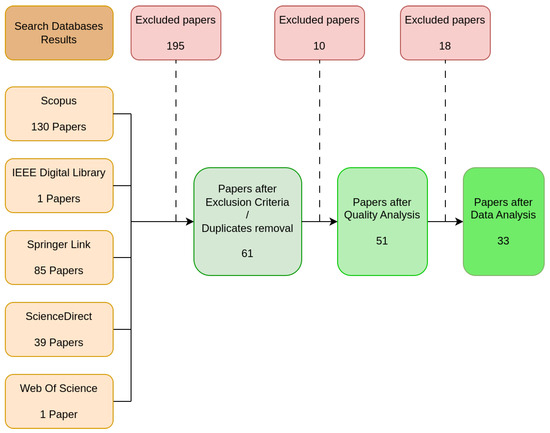
Figure 3.
Paper selection process.
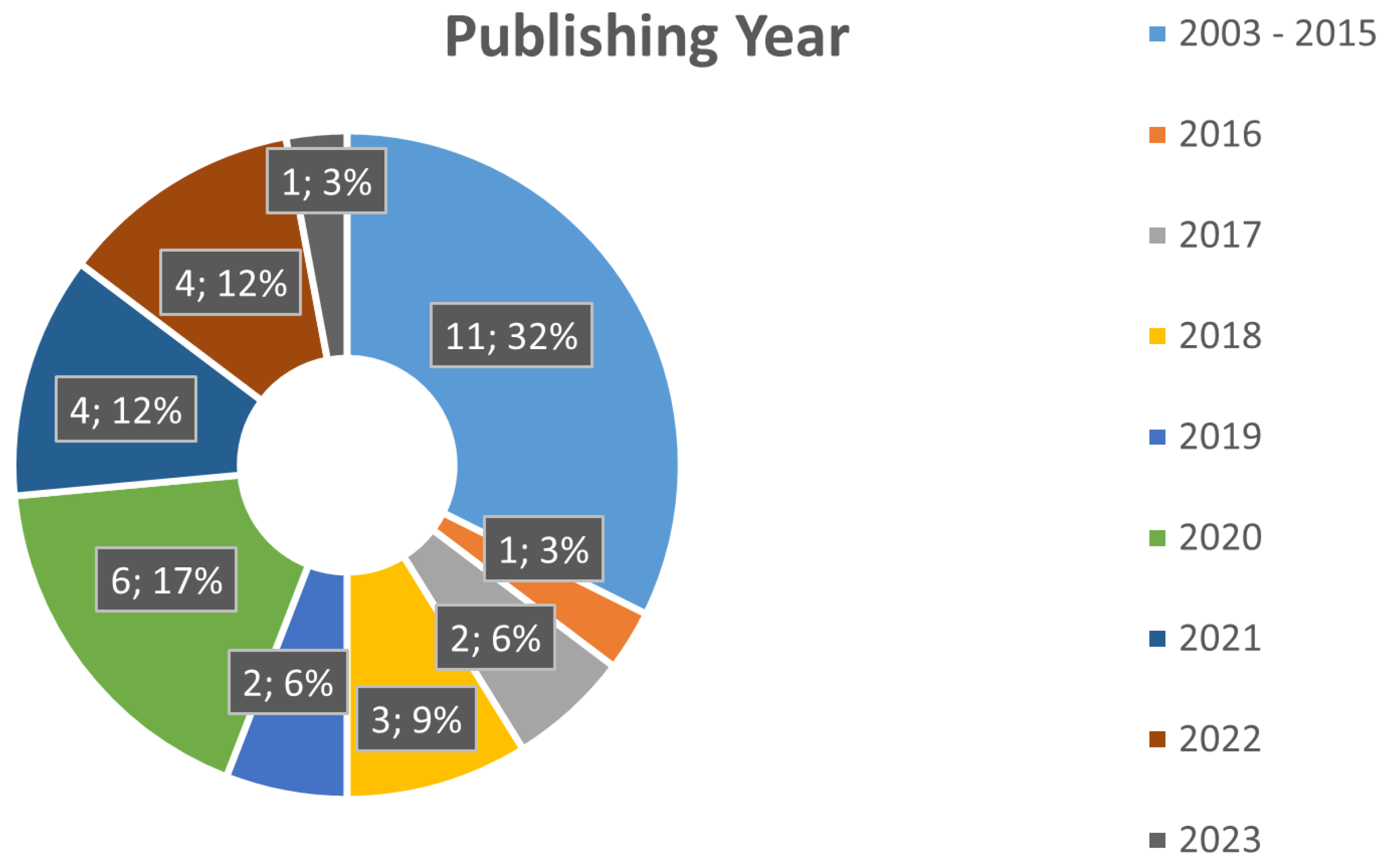
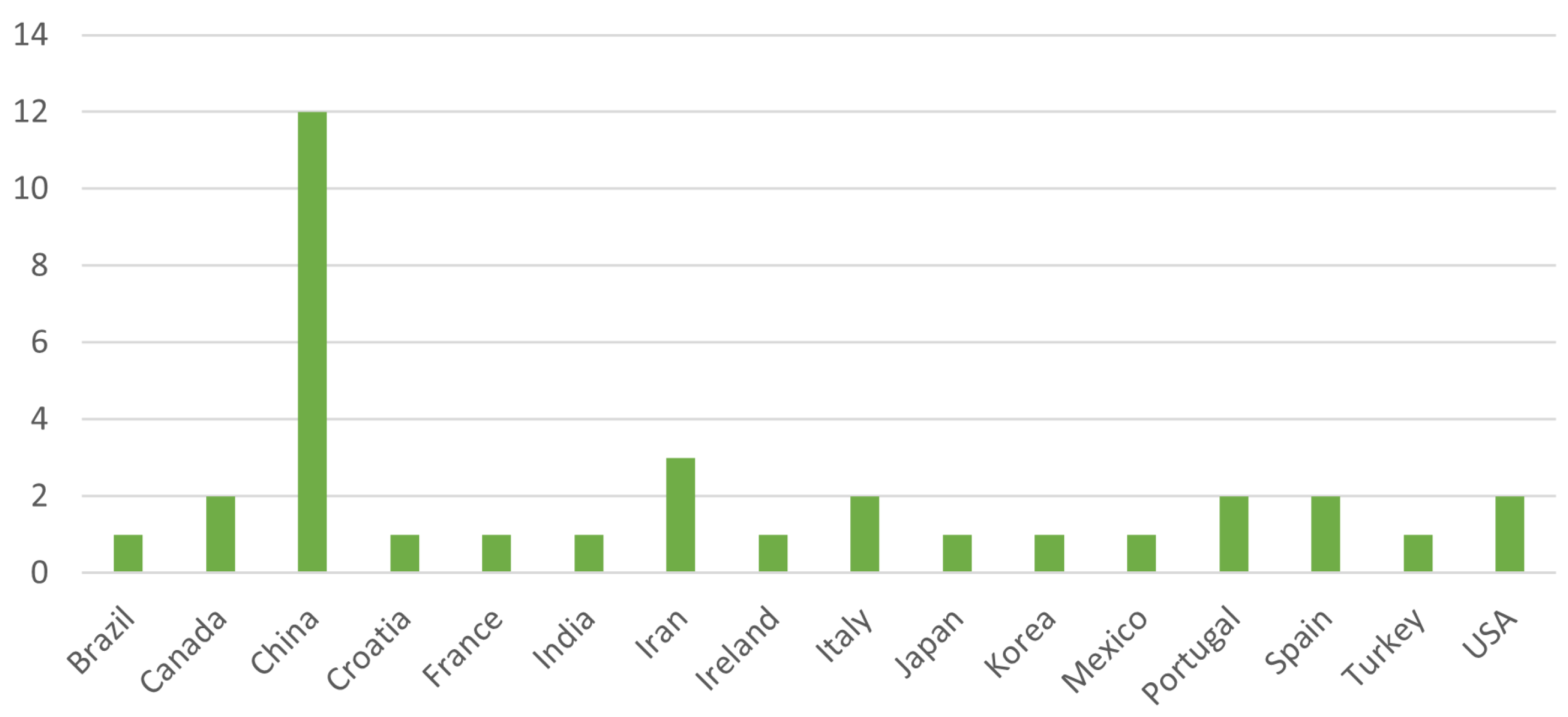
The relevant works were also analyzed for their publication year and research location, as presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively. With a quick analysis of these items, we can infer that there has been a surge of papers in this particular field from 2020 to the present day, comprising 12 of the 29 selected works. Additionally, we notice higher interest in this area of expertise in countries such as China and Iran, which comprise 40.3% of the selected works.
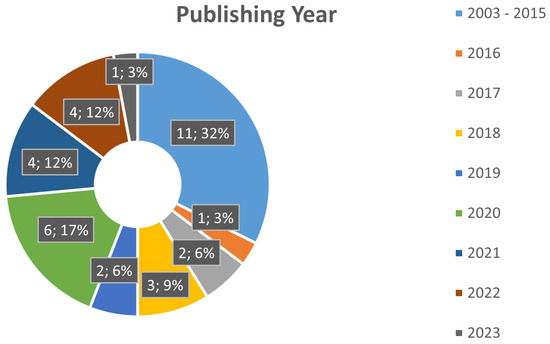
Figure 4.
Papers’ Publishing Year Distribution.
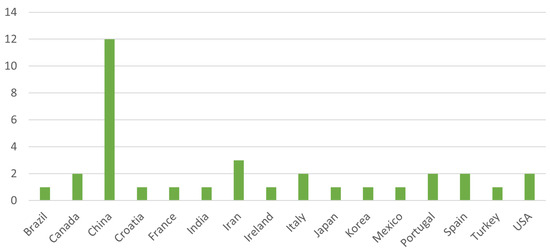
Figure 5.
Papers’ Research Country Distribution.
4. Analysis
The intersection of robotics and locomotion has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, paving the way for innovative solutions in various industries. Among these advancements, legged–wheeled robots have garnered considerable attention due to their unique ability to navigate diverse terrains with agility and precision. As we delve into the literature surrounding these fascinating machines, it becomes evident that they represent a convergence of cutting-edge technology and sophisticated design principles. This discussion aims to explore the evolution, applications, and challenges associated with legged–wheeled robots, offering insights gleaned from a systematic review of pertinent research literature.
4.1. Leg–Wheel Implementations
This section delves into the realm of legged–wheeled robots, a unique category of robotic systems blending both leg and wheel functionalities. Recognized for their versatility and adaptability, these robots demand thorough investigation into their mechanical complexities, operational capabilities, and scholarly significance within the robotics domain. Here, we aim to dissect the essence of legged–wheeled robotics, offering insights into its technological intricacies and scholarly discourse to enhance the scientific comprehension of this emerging field.
Researchers from FEUP (Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto) present the design and modeling of a robotic legged–wheeled system meant to be applied in a hybrid robotic vehicle [7]. Their work focuses on the design, modeling, and control of a legged–wheeled mechanism, its build, and its successful validation through physical scenarios. However, as mentioned in the authors’ conclusions, this design can still be improved in regard to low frequencies, which are not yet well accounted for by the model. Moreover, their work is further developed to include the modeling, and overall control of a vehicle with leg–wheel capabilities [6]. The system was simulated using the SimTwo simulator and successfully validated through a physical prototype in indoor environments, with low errors between the simulation and physical results. This work still needs to be completed and requires zr-axis control of the robot, testing algorithms for trajectory control and planning (with obstacle detection and avoidance), and the development of a gait-planning framework for the robot. Additionally, improvements to the data acquisition feature can be made, adding vision sensors to account for obstacle avoidance.
To further explore leg–wheel technologies, researchers from the University of Huelva have developed R3HC [8], which is a hybrid hexapod designed for patrolling in areas with small surfaces with obstacles and/or some unevenness. The robot is based on the Cassino Hexapod robot series with a twisting joint on each leg. The robot is capable of turning around its axis and following dynamic trajectories. Additionally, preliminary experiments have been successfully conducted.
While focusing on motion and kinematics, researchers from the Istituto Italiano di Technologia introduced the derivation of legged–wheeled motion kinematics [9] without imposing constraints on the camber angles of the wheels. CENTAURO—a legged–wheeled centaur-like robot—was used to test a kinematics control scheme proposed to address a structural singularity as the non-holonomy of a system deteriorates.
Researchers from National Taiwan University (NTU) present a quadruped robot with novel leg–wheel transformable climbs [11]. Their work focuses on the transformation strategy, modeling, and kinematics. The proposed strategies aim to maintain stability and prevent leg slippage in kinematic constraint. Additionally, the robot works with low power consumption.
Guardian, presented in [12], is a four-wheeled–legged robot capable of motion on granular terrain. The paper presents Guardian’s design, and a link design scheme for the robot’s legs, thus reducing the leg weight and increasing the load capacity. Additionally, the robot is also able to climb over tall obstacles.
Researchers from National University of Defense Technology introduced an innovative six-wheeled mobile robot [32] featuring a reconfigurable body and self-adaptive obstacle-climbing mechanisms. It has the capability to transition between three locomotion states, offering terrain adaptability, obstacle-crossing ability, and portability. The robot was tested through simulation and a physical prototype, presenting good results regarding its portability, obstacle-crossing capabilities, and adaptability.
Rolling-Wolf [13] is a wheeled–legged Robot with high structural stability. Actuated with ball screws and sliders, it can provide more excellent structure stability, force distribution, and hauling capacity than previous wheeled–legged robots. A particularity of this implementation is the optimization of the structure’s parameters using an Archive-based Micro Genetic Algorithm (AMGA) through Isight and Matlab software. This approach considerably increased the robot’s maximum lifting weight and decreased its maximum driving forces.
TRREx, presented in [33], is the Transforming Roving-Rolling Explorer, which is a cylindrical robot with an armadillo-inspired design with retractable legs meant for planetary exploration. This work presents the modeling, building, and testing of TRREx. The robot’s validation was performed using simulation and validated with mathematical models. Additionally, a prototype was also tested. During testing, the results proved the mathematical model’s ability to predict the physical prototype’s behavior.
Transleg [14] is a legged–wheeled robot which adopts a wire-driven method to reduce the system’s weight and simplify it’s overall structure. The robot’s design is presented. The system is validated using simulation and a physical prototype.
PAW [15] is a quadruped robotic platform with four springy legs with rotary actuation at the hips and driven wheels mounted at the distal ends of the legs. The robot’s locomotion aim to use its spring for motions such as bounding, galloping, and jumping.
Presenting a wheeled–legged robot with an active waist joint, the authors of [16] propose a robot system capable of crawling locomotion and turning movement in the legged mode. The system can achieve velocities of 17.2 m/min in wheeled mode and 10.4 m/min in legged mode while presenting mobility efficiencies of up to 96.3% and overall robot efficiency of 75.2%. However, the obstacle-climbing height of the robot is limited to 10 cm. The proposed improvements include integrating infrared sensors to allow for the automatic adjustment of the waist joint.
Land Devil Ray (LDR) [26] is a prototype of a transformable wheeled–legged robot meant for search-and-rescue missions. The wheeled–legged transformation mechanism works with a “hinge type multi-four-bar linkage mechanism” with only one actuator allowing each leg to act as a trigger for others. The robot is capable of passive transformation according to the environment’s terrain conditions. Finally, the system can climb to heights of 2.8 times its wheel radius and proves a successful prototype.
Wheelleg [37], developed at the Università di Catania, is a hybrid robot whose kinematics, dynamics, and control are reported in this work—comprising two pneumatically actuated legs and two rear wheels actuated by different DC motors. The proposed model is successfully tested and validated through simulation using a Matlab calculation code. As such, it is possible to plan different trajectories for each joint.
Researchers from UPMC Univ Paris conduct a motion kinematics analysis of a wheeled legged rover over a 3D surface with posture adaptation [28]. The main goal is to control the system’s overall stability and posture. The model is tested through virtual and physical experiments, and proves successful. The model is generic and capable of accounting for multiple features, such as slippage velocities and the usage of internal or external parameters. However, one limitation is its assumption of continuous contact with the ground.
FUHAR [30] is a transformable wheeled–legged robot for search and rescue whose design, analysis, and evaluation are presented in this paper. The robot is capable of quickly switching from leg to wheel mode, capable of adapting to different terrains, and capable of climbing obstacles. The mode transformation is stable and carried out through a multi-four-bar mechanism, with each leg able to transform independently. Finally, the system is validated through a built prototype.
VTFIC [17] is a strategy for vibration control based on variable target force impedance control meant to be applied to wheeled–legged robots, and has been widely investigated for adapting to undulating slope terrain. Its main goal is to improve stability in the process of dynamic motion on rough ground. This is achieved by increasing the end-forces’ tracking speed and accuracy by changing the target force of impedance control. The proposed stability and convergence algorithm is proven and tested through simulation and experimental procedures. Applications of this work include load transportation and work requiring fast wheel motion.
The fascinating research on legged-wheel robots presented provides valuable insights into their design, functionality, and real-world applications. Through meticulous research and experimentation, scientists are advancing our understanding of these hybrid systems, uncovering new possibilities for their use in various fields. Despite the challenges and complexities involved, ongoing efforts in this area promise to drive further innovation and unlock the full potential of legged-wheel robots in robotics and beyond.
4.2. Leg Implementations
Legged robots have emerged as a cornerstone of robotics research, embodying the quest to replicate and enhance human mobility. In reviewing the literature, it is evident that these robots offer exceptional adaptability and promise across diverse applications. From bipedal to quadrupedal designs, they blend engineering ingenuity with biological inspiration.
RoMiRAMT-II [19] is a Rotational-Leg-type Miniature Robot with an Actuated Middle Joint and a Tail proposed by the authors of this work. The design is bio-inspired and was carefully selected between a series of possible candidates by comparing their performance using the V-REP 3D simulator. The middle joint is used for lifting or lowering the robot’s lower body, and geometric analysis of the system verifies its effectiveness. Additionally, a tail is used to prevent cases of flipping of the robot and allows for the climbing of more significant obstacles. Finally, the robot can climb heights up to 106cm, which is a relatively high value because it is 2.5 times greater than its leg length.
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University present a new six-parallel-legged walking robot and a 6-DOF parallel kinematic machine (PKM) tool [34]. This system is capable of high mobility, precision, and terrain adaptability. The system’s motion is divided into three hierarchical layers: leg, body, and head motion. The motion of each layer and the whole robot is successfully tested through simulations and an actual prototype to validate the overall system.
While developing and studying a more complex system with a greater number of legs, researchers from Tarbiat Modares University focus on behavior-based control and navigation for an autonomous hexapod robot using a hybrid automaton [20]. The transition between different behaviors relies solely on sensory data, with no representation of the environment included. Their findings indicate that improving the smoothness of the robot’s motion would negatively impact its ability to track the reference point with precision and its reaction speed, and vice versa. Additionally, simulation tests validate the effectiveness of the navigation algorithm in generating optimal paths by seamlessly transitioning between different modes. The robot also demonstrates its capability to follow a reference point using various gaits.
“HyLMoR” [36] is a Hybrid Locomotion Mobile Robot, an integration of quadrotor and quadruped systems. The system is capable of ground and aerial locomotion. The design, build, and choice of materials for the robot’s construction were based on mathematical calculations. The prototype was successfully built and tested. However, early tests proved less promising than later ones, which still need improvement, signaling that the project is in an early stage and requires some perfecting.
While differing from other leg shapes in this review, ePaddle [29,31] is presented as an eccentric paddle mechanism. ePaddle is an amphibious robot with a race-walking gait divided into four phases: stepping, landing, shifting, and lifting. Additionally, the detailed kinematics for each phase are given and a motion planning method is proposed and tested through simulation on a virtual four-ePaddle robot in two different scenarios: walking on a straight line and tracking a circular curve path. The results of these simulations proved successful. In comparison with previous mechanisms, this module features higher reliability and efficiency. As such, this paper proposes a legged walking gait for a quadruped or hexapod robot based on ePaddle-EGM modules. One prototype has been built as of 2015, and tests still need to be concluded, with some features still needing validation.
Legged robots are crucial in robotics research, aiming to imitate and enhance human movement. Our review of the literature shows their versatility and potential across various areas. Whether they walk on two or four legs, these robots combine engineering and biology to shape the future of robotics.
4.3. Wheel Implementations
Wheeled robots represent the backbone of robotics, epitomizing efficient mobility and practical utility. Exploring the literature dedicated to these machines reveals their versatility across diverse applications, from exploration to industrial automation. This discussion aims to delve into the wealth of research surrounding wheeled robots, highlighting their evolution and functionalities, and the array of challenges and opportunities they offer.
With the novelty of adjustable wheelbases, researchers from the National University of Defense Technology propose a six-wheel driving system with an adjustable wheelbase [10]. The system is capable of adjusting its axle load and accommodating for uneven terrains. The final system design proved capable of enhancing the traction performance, obstacle-crossing performance, and trench-crossing performance of an unmanned vehicle, among other findings.
With a focus on terrain adaptability, authors form University of Tehran propose an adjustable wheel meant for soft terrains [23]. In addition, a simulator was also built to compare its performance with other mobile robots on soft and more complex terrains. One of the main conclusions of this work is that the wheel’s radius significantly affects the traction force and sinkage if the type of wheel is not accounted for. As such, the need for an adjustable wheel is clear so that the robot can dynamically adapt to different terrains. Another conclusion is that a smaller wheel radius allows for better vehicle steering. Finally, the mechanism is simulated and shows the ability to adapt to different terrains and climb small obstacles.
Regarding motion kinematics, authors from Iran University of Science and Technology present the development, motion equations, and simulation of a wheeled robot used for space exploration and rescue operations [22]. It is meant to extend the capabilities of mobile robots. Motion equations were derived using a G-A formulation, and dynamic equations were obtained in a generic form. Using ADAMS for simulation purposes and validation, the system is now at the prototype-building stage and is undergoing testing for real scenarios.
With a focus on terrain and control, researchers from Trinity College Dublin present a wheeled robot capable of moving through human-centered environments while still being able to cross through different terrains [24]. Examples of terrain adaptability include crevice crossing and step climbing. Using electro-pneumatic control, the robot has great joint compliance and mass distribution. The system has been successfully tested and validated in simulated and natural environments.
Focusing on the mathematical element of a model robot, researchers from Universidad Panamericana campus Bonaterra aim to present a mathematical model [25] for a differential-drive model robot with two active fixed wheels and a passive steering wheel. The robot’s control is based on sonar sensors, which can map received stimui through BAWMR (Behavior Architecture for a Wheeled Mobile Robot) and alter the motor’s DC voltages, thus altering the movement of the robot.
Once more, the collective efforts discussed here emphasize the fundamental role of wheeled robots in pushing the boundaries of robotics forward. They offer a glimpse into the vast possibilities these machines hold across various fields, serving as catalysts for continued innovation and progress in the realm of robotics.
4.4. Other Implementations
Beyond wheeled and legged robots lie a diverse array of innovative machines in robotics. From aerial drones to specialized task-oriented robots, this discussion explores their functionalities, applications, and unique contributions, as revealed in the literature.
AZIMUT [18], as presented by the authors, is a mobile robotic platform with four independent leg–track–wheel articulations intended for, but not limited to, indoor use. As such, this system, as the first prototype of this project, attempts to combine all three locomotion alternatives: legs, wheels, and tracks. The testing of this implementation lies mainly on flat surfaces and stairs.
EspeleoRobô [21], developed in Instituto Tecnologico Vale (ITV), which is a robot hybrid vehicle meant for inspection services in confined spaces and is capable of wireless communication, and whose first prototype was built in 2015. The primary purpose of this work is the proposal of strategies for the path planning and navigational control of a vehicle. These strategies rely on image reconstruction techniques to work correctly in GPS-blocked locations. These strategies are tested through simulation and real cave scenarios, producing positive results, and could benefit from embedded lighting devices on the robot to improve light settings. As such, the technology with the most desirable results is LiDAR-SLAM.
With a focus on trajectory generation, researchers at Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics propose a Back-Stepping-Based Trajectory-Tracking Controller for an existing spherical mobile robot (BHQ-2) [35]. The goal lies in solving the robot’s dynamic trajectory tracking problem. Lyapunov’s function validates the back-stepping algorithm’s convergence. Finally, it is concluded that the controller can successfully plan the linear or circular motions of the system.
Stair-Climbing Mobility Systems (SCMSs) are hybrid systems combining wheels and sliders. Researchers at the University of Castilla-La Mancha aim to improve the performance of these systems in a climbing or descending motion on stairs with geometrical imperfections [27]. The two proposed improvements are redesigning the climbing and positioning mechanisms and incorporating laser sensors. Experiments are performed with both regular and improved systems. The results show the overall system’s higher precision, performance, and speed. The introduction of laser sensors enables a trajectory generation algorithm based on a more precise stair geometry analysis, allowing for a faster and safer motion of the SCM.
RolLeapO [38] is a spherical robot with rolling and leaping capabilities and comprises two individual semi-spheres that allow for its movement. The leaping ability is achieved through a “five-bar mechanism" and its release/retract storage mechanism. The robot was modeled as a two-wheeled pendulum model, and its dynamics were analyzed with the Lagrangian method. RolLeapO was tested through simulation and built for experimental validation. The results show that the average leaping height is 25.4 cm, close to the sphere’s diameter, outperforming other similar robots.
In essence, these examples underscore the breadth of innovation and ingenuity within the field of robotics, with each machine offering unique solutions to complex challenges. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of technological advancement, the possibilities for robotics in various domains are virtually limitless, promising a future defined by unprecedented capabilities and applications.
5. Conclusions
In the present report, a comprehensive systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted to explore the landscape of Hybrid Robotic Vehicles, with a particular emphasis on legged–wheeled applications. The primary objective was to assess the existing solutions and advancements in this technology, both in development and already established.
A thorough search across multiple renowned databases yielded a substantial pool of 102 papers, all of which were subjected to rigorous filtering based on predefined research questions (RQs). This meticulous screening process ensured that only the most relevant and pertinent literature was included in the review. Following the initial filtration, the papers underwent further scrutiny using specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, as well as quality questions, resulting in the identification of 29 documents deemed suitable for inclusion.
The selected works were subjected to a detailed analysis, employing a set of data questions to evaluate their performance and relevance to the research objectives. Each paper was meticulously examined, with particular attention paid to its proposed locomotion system and publication year, and the geographic location of the research. The findings of this analysis are comprehensively presented in Section 3 and Section 4 of this report.
In conclusion, this document represents a significant contribution to the understanding of robotic vehicles, particularly in the realm of legged–wheeled applications. By providing a comprehensive review of the existing literature and highlighting key advancements and trends, this report serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners alike, paving the way for further exploration and innovation in this exciting field of robotics.
This detailed analysis of the selected papers highlights both the achievements and the ongoing challenges in designing and implementing legged–wheeled robots. While some designs exhibit impressive capabilities in navigating challenging terrains and adapting to dynamic environments, others still require refinement, particularly in terms of stability, control, and obstacle avoidance. Furthermore, the integration of advanced sensors, tools and control algorithms continues to play a crucial role in improving the performance and autonomy of these robots.
Looking ahead, the research community can leverage the insights gained from this review to further advance the field of legged–wheeled robotics. Future efforts may focus on refining existing designs, developing novel control strategies, and exploring new applications, such as search-and-rescue missions or planetary exploration. By continuing to push the boundaries of innovation, researchers can unlock the full potential of legged-wheeled robots and pave the way for their widespread adoption in various industries and domains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.F.G. and V.H.P.; methodology, D.F.G. and V.H.P.; validation, D.F.G.; formal analysis, D.F.G. and V.H.P.; investigation, D.F.G.; writing—original draft preparation, D.F.G.; writing—review and editing, D.F.G. and V.H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Loupos, K.; Doulamis, A.D.; Stentoumis, C.; Protopapadakis, E.; Makantasis, K.; Doulamis, N.D.; Amditis, A.; Chrobocinski, P.; Victores, J.; Montero, R.; et al. Autonomous robotic system for tunnel structural inspection and assessment. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2018, 2, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lame, G. Systematic Literature Reviews: An Introduction. In Proceedings of the Design Society: International Conference on Engineering Design, Delft, The Netherlands, 5–8 August 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B. Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews; Keele University: Keele, UK, 2004; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.A.; Budgen, D. Evidence-Based Software Engineering and Systematic Reviews; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; EBSE: Menen, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, V.H.; Gonçalves, J.; Costa, P. Design, Modeling, and Control of a Single Leg for a Legged-Wheeled Locomotion System with Non-Rigid Joint. Actuators 2021, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.H.; Soares, I.N.; Rocha, M.; Lima, J.; Gonçalves, J.; Costa, P. Design, Modeling, and Control of an Autonomous Legged-Wheeled Hybrid Robotic Vehicle with Non-Rigid Joints. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bravo, F.; Villadoniga, P.; Carbone, G. Design and Operation of a Novel Hexapod Robot for Surveillance Tasks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics, Torino, Italy, 6–8 June 2017; Ferraresi, C., Quaglia, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Kameduła, M.; Kashiri, N.; Tsagarakis, N.G. Wheeled motion kinematics and control of a hybrid mobility CENTAURO robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 128, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, F. Enhancing the Passing Ability of Unmanned Vehicles Using a Variable-Wheelbase Driving System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115871–115885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Yu, W.S.; Lin, P.C. A Wheel to Leg Transformation Strategy in a Leg-Wheel Transformable Robot. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Seattle, WA, USA, 28–30 June 2023; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, T.; Yue, X. The Wheel-legged Robot for Guanular Terrain: Guardian. In Proceedings of the 2022 28th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Nanjing, China, 16–18 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. Design and optimization of wheel-legged robot: Rolling-Wolf. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 27, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Song, G.; Qiao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H. Design and Implementation of a Leg–Wheel Robot: Transleg. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharf, I. Dynamic Locomotion with a Wheeled-Legged Quadruped Robot. In Brain, Body and Machine; Angeles, J., Boulet, B., Clark, J.J., Kövecses, J., Siddiqi, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Song, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. A Wheel-legged Robot with Active Waist Joint: Design, Analysis, and Experimental Results. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 83, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Stewart-Inspired Vibration Isolation Control for a Wheel-legged Robot via Variable Target Force Impedance Control. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 106, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, F.; Létourneau, D.; Arsenault, M.; Bergeron, Y.; Cadrin, R.; Gagnon, F.; Legault, M.A.; Millette, M.; Paré, J.F.; Tremblay, M.C.; et al. Multi-Modal Locomotion Robotic Platform Using Leg-Track-Wheel Articulations. Auton. Robot. 2005, 18, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.; Bae, J. Design and Analysis of a Rotational Leg-type Miniature Robot with an Actuated Middle Joint and a Tail (RoMiRAMT-II). J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, M.; Sadedel, M.; Davarpanah, A. Behavior-Based Navigation of an Autonomous Hexapod Robot Using a Hybrid Automaton. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 102, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpúrua, H.; Rezende, A.; Potje, G.; Júnior, G.P.d.C.; Fernandes, R.; Miranda, V.; Filho, L.W.d.R.; Domingues, J.; Rocha, F.; de Sousa, F.L.M.; et al. Towards Semi-autonomous Robotic Inspection and Mapping in Confined Spaces with the EspeleoRobô. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 101, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, E.; Dehkordi, S.F.; Korayem, M.H. Reconfigurable Mobile Robot with Adjustable Width and Length: Conceptual Design, Motion Equations and Simulation. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 99, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Alipour, K. New Adaptive Segmented Wheel for Locomotion Improvement of Field Robots on Soft Terrain. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 97, 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinn, C.; Cullinan, M.F.; Otubela, M.; Kelly, K. Design of a terrain adaptive wheeled robot for human-orientated environments. Auton. Robot. 2019, 43, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mata, C.; Velázquez, R.; Gutiérrez, C.A. A Differential-Drive Mobile Robot Driven by an Ethology Inspired Behaviour Architecture. Procedia Technol. 2012, 3, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Guan, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, J.; Duan, W. An optional passive/active transformable wheel-legged mobility concept for search and rescue robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 107, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocoteco, J.; Morales, R.; Feliu, V. Improving the climbing/descent performance of stair-climbing mobility systems confronting architectural barriers with geometric disturbances. Mechatronics 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, C.; Benamar, F.; Plumet, F. Motion kinematics analysis of wheeled–legged rover over 3D surface with posture adaptation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, Y. Planning of Legged Race-walking Gait for an ePaddle-based Amphibious Robot. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertyüz, İ.; Tanyıldızı, A.K.; Taşar, B.; Tatar, A.B.; Yakut, O. FUHAR: A transformable wheel-legged hybrid mobile robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 133, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Luo, J.; Gong, Z. Non-reciprocating legged gait for robot with epicyclic-gear-based eccentric paddle mechanism. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 68, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wei, G.; Shang, J. A Portable Six-Wheeled Mobile Robot With Reconfigurable Body and Self-Adaptable Obstacle-Climbing Mechanisms. J. Mech. Robot. 2022, 14, 051010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, L.; Mazzoleni, A.; Gemmer, T.; Ferguson, S. Modeling, construction and experimental validation of actuated rolling dynamics of the cylindrical Transforming Roving-Rolling Explorer (TRREx). Acta Astronaut 2017, 132, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Gao, F. A novel six-legged walking machine tool for in-situ operations. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 15, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Zengbo, L.; Yao, C. A Back-stepping Based Trajectory Tracking Controller for a Non-chained Nonholonomic Spherical Robot. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2008, 21, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, M.; Nair, A.R.; Krishnan, A. Design, Manufacturing and Testing of a Hybrid Locomotion Mobile Robot “HyLMoR”. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 24, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, M.; Muscato, G.; Sinatra, R. Kinematics, dynamics and control of a hybrid robot Wheeleg. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2003, 45, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Chang, C.L.; Ho, J.H.; Lin, P.C. Design and implementation of a novel spherical robot with rolling and leaping capability. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 171, 104747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).