A Simplified Kinematics and Kinetics Formulation for Prismatic Tensegrity Robots: Simulation and Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction and Related Work
1.1. Tensegrity Kinematics and Kinetics
1.2. Prismatic Tensegrity Structures
1.3. Contribution and Paper Structure
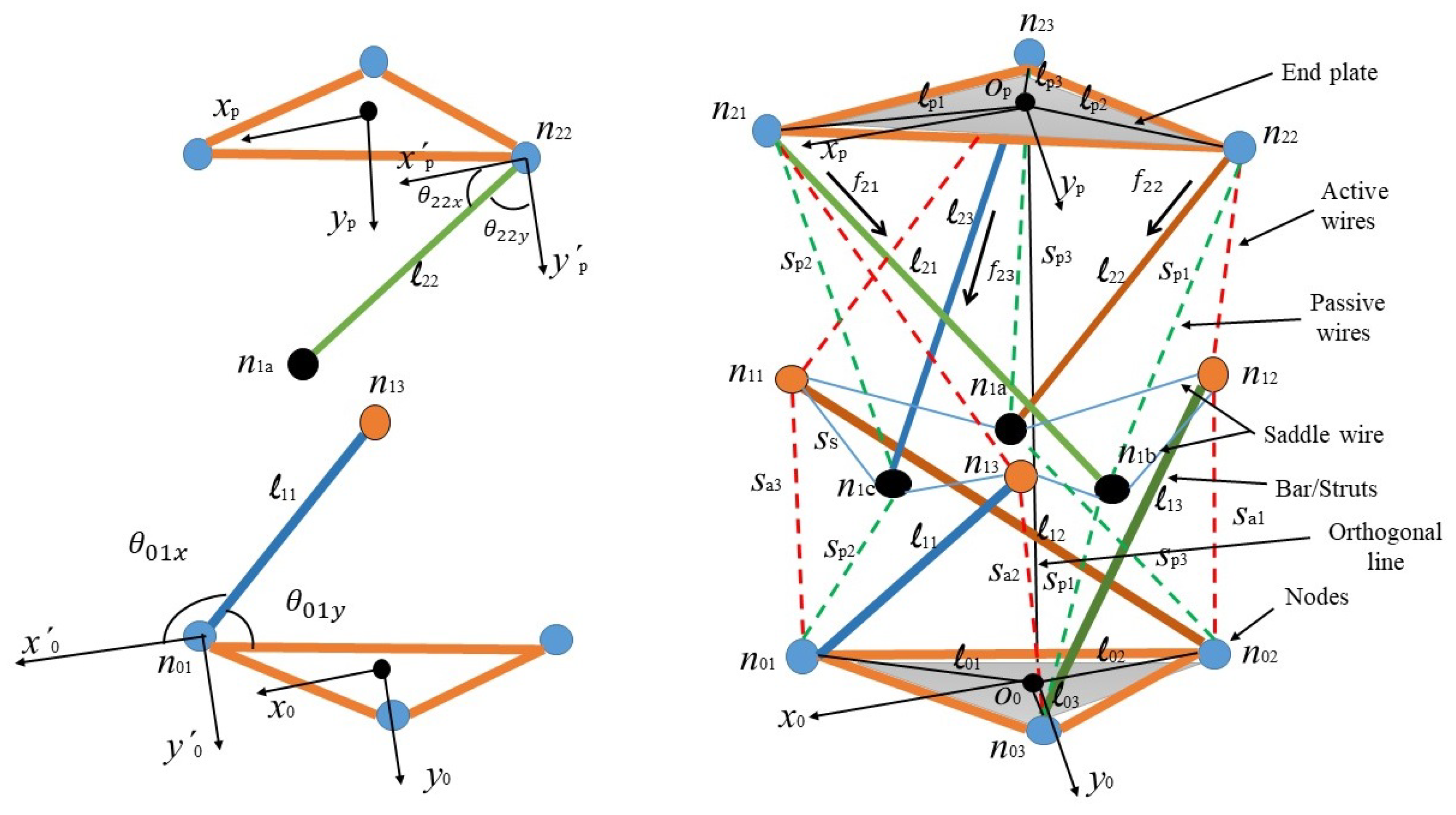
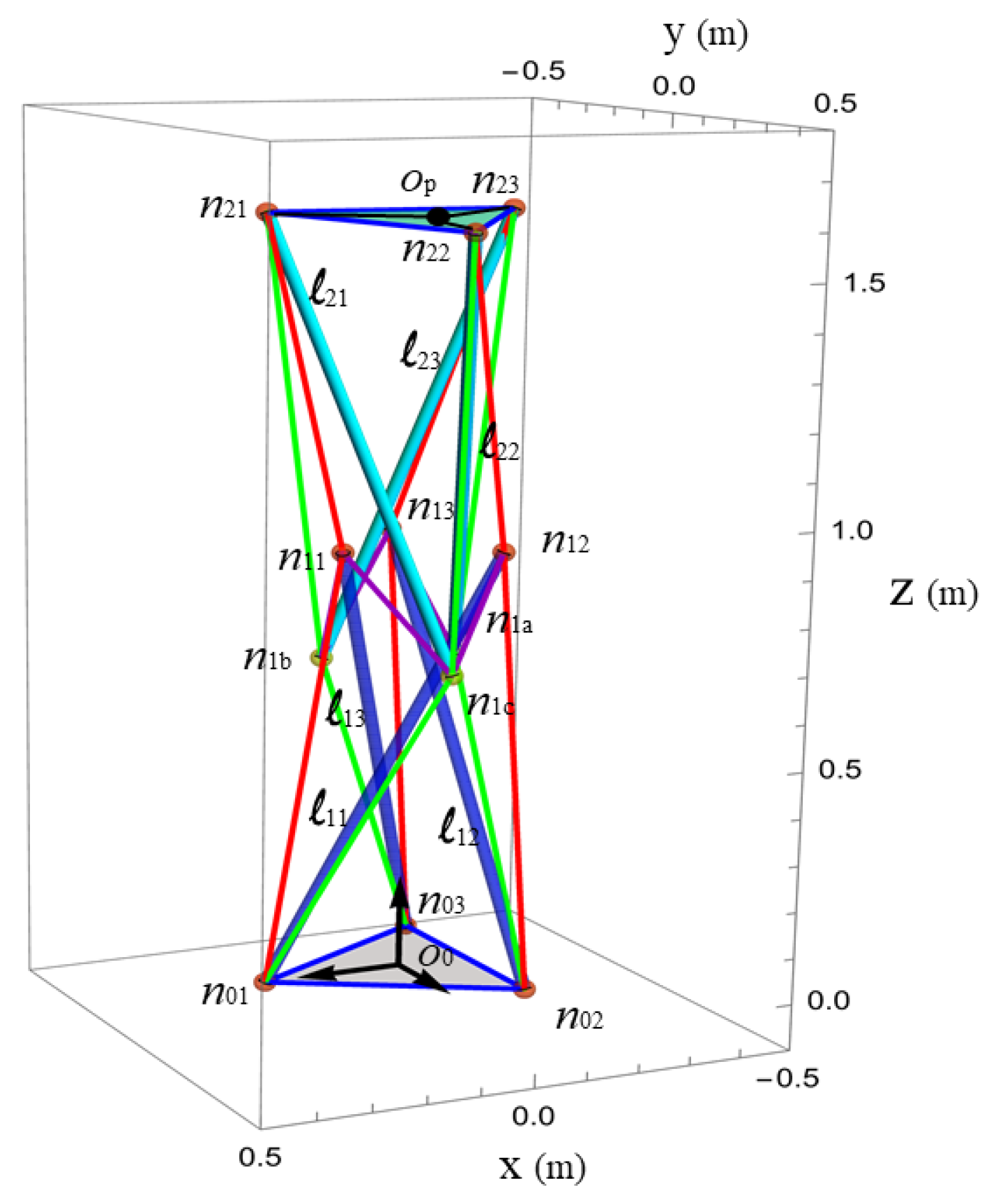
2. Case Study
Experimental Setup and Initial Posture Calibration
- The line that connects the centers of the upper plate and base plate should be perpendicular to the ground while the upper plate is kept on a horizontal plane.
- Each node in the upper plate is connected to one active wire and one passive wire. Defining the corresponding initial tensions , , for active wires and , , for passive wires, the following condition should be satisfied:
3. Proposed Formulation of Tensegrity Kinematics and Kinetics
3.1. Node Coordinates
3.2. Definition of the Constraint Equations
- (a)
- Three coordinates describing the position of the center of the top plate:
- (b)
- Three angles describing the rotation of the top plate:
- (c)
- Twelve angles defining the rotation of the six universal joints:
- (d)
- Three forces , defining the axial forces of the bars connected to the top plate;
- (e)
- The (scalar) tension of the saddle wire .
- (CE1) The magnitude of moment vectors at the nodes , , and applied by bars , , and , respectively, must be zero (three equations).
- (CE2) The magnitude of the moment vectors at nodes , , and applied by bars , , and , respectively, must be zero (three equations).
- (CE3) The sum of the forces applied to nodes , and must be equal to the opposite gravity vector applied to the mass center of the top plate (three equations).
- (CE4) The sum of the force vectors applied to nodes , , and must be equal to the opposite gravity vector applied to the nodes due to the weight of the end plate and the bars (nine equations).
- (CE5) The resultant moment vector applied to the center of the top plate must be a zero vector (three equations).
- (CE6) The length of the saddle wire is constant (one equation).
3.2.1. Formulation of CE1
3.2.2. Formulation of CE2
3.2.3. Formulation of CE3
3.2.4. Formulation of CE4
3.2.5. Formulation of CE5
3.2.6. Formulation of CE6
3.3. Inverse Kinematics
4. Experimental Validation
4.1. Determination of the Initial Posture
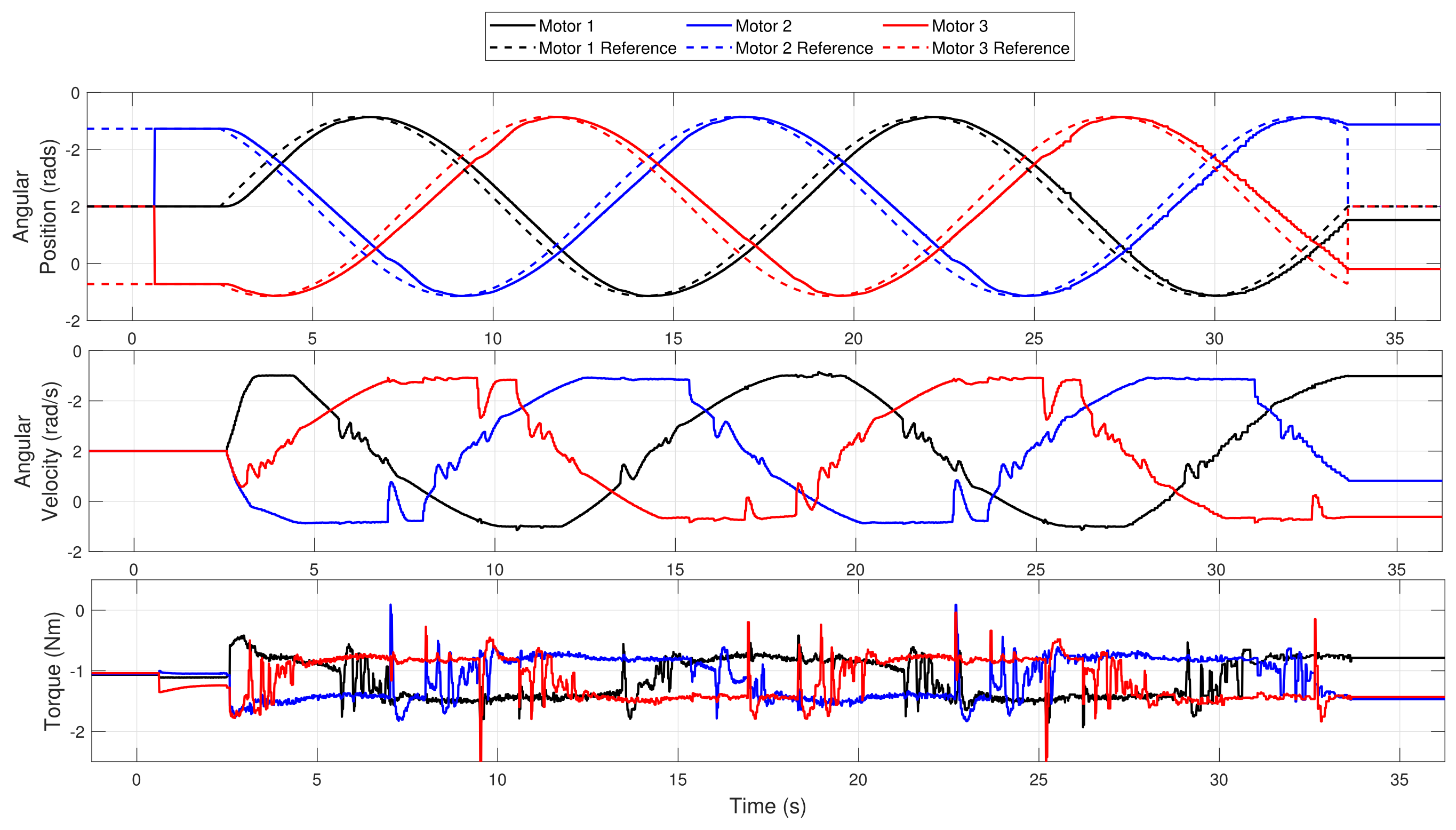
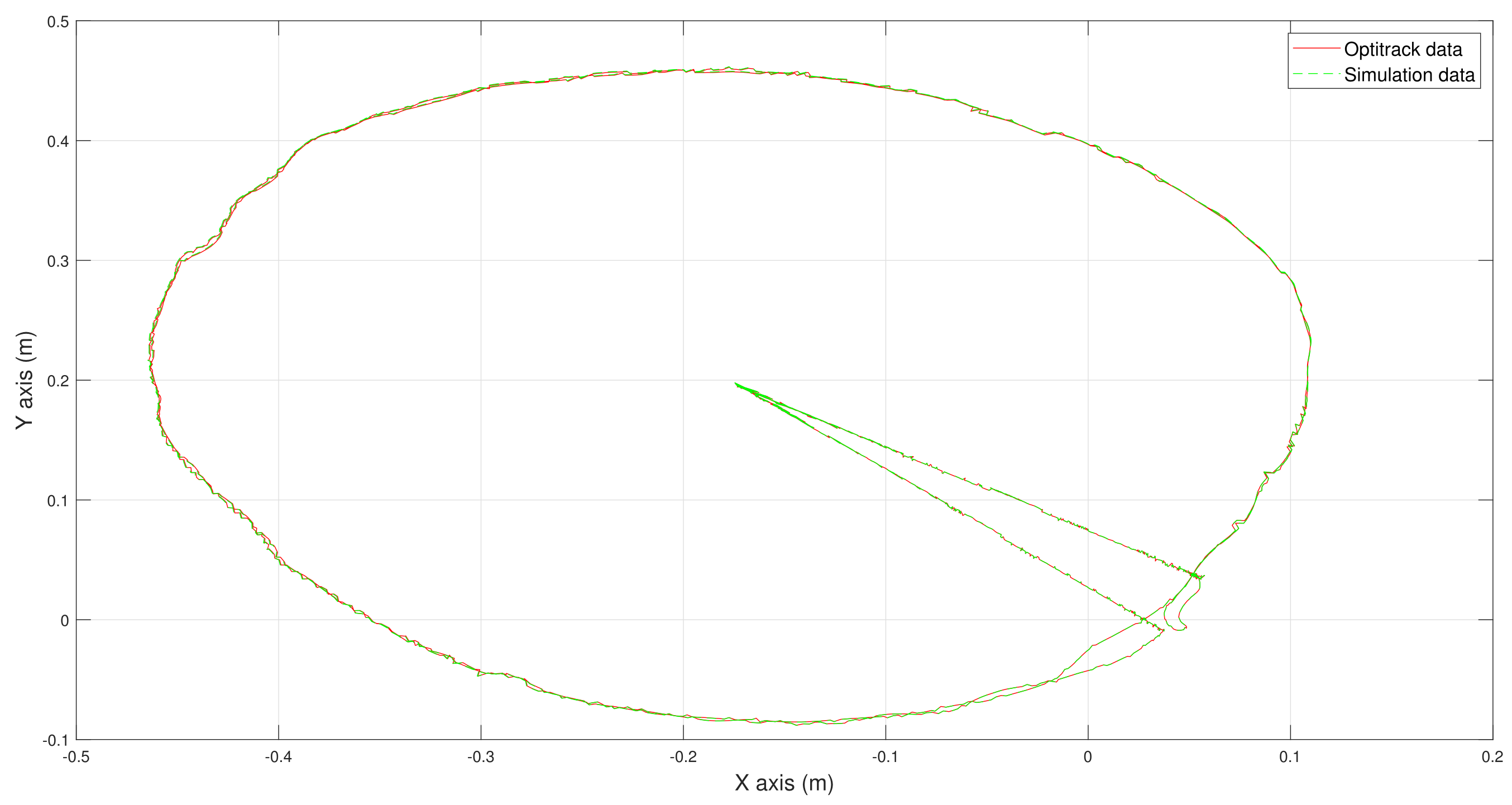
4.2. Experiments and Control Strategy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mathematical Notations List
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| Bar length | |
| Triangle length | |
| Spring constant | |
| Top plate mass | |
| Bar mass | |
| Node mass | |
| g | Gravitation vector |
| Passive wire tension | |
| Initial passive wire tension | |
| Active wire tension | |
| Initial active wire tension | |
| Saddle wire tension | |
| Base nodes | |
| Mid nodes | |
| Upper nodes | |
| Rotational angles | |
| Base universal joint angles | |
| Top plate universal joint angles | |
| Top plate rotation angle | |
| Axial forces applied from the top plate | |
| Top plate positioning of the center | |
| Upper plate origin | |
| Torque vector from the base | |
| Torque vector from top plate | |
| Passive wire length | |
| Passive wire initial stretch | |
| q | 22 internal variables |
| 19 internal variables except , , | |
| 22 constraints | |
| Desired active wire tension | |
| Desired end-effector position | |
| Desired variables to reach desired end-effector position |
References
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E.; Gill, P.E. Optimization of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 4687–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Dobah, Y.; Scarpa, F.; Fraternali, F.; Skelton, R.E. Tensegrity cell mechanical metamaterial with metal rubber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 031906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ohsaki, M. Stability conditions for tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 3875–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabelhaus, A.P.; Bruce, J.; Caluwaerts, K.; Manovi, P.; Firoozi, R.F.; Dobi, S.; Agogino, A.M.; SunSpiral, V. System design and locomotion of SUPERball, an untethered tensegrity robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2867–2873. [Google Scholar]
- Calladine, C.R. Buckminster Fuller’s “tensegrity” structures and Clerk Maxwell’s rules for the construction of stiff frames. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1978, 14, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibert, A.; Pellegrino, S. Review of form-finding methods for tensegrity structures. Int. J. Space Struct. 2003, 18, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Advanced form-finding of tensegrity structures. Comput. Struct. 2010, 88, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Lee, J. Form-finding of tensegrity structures with multiple states of self-stress. Acta Mech. 2011, 222, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, R.; Skelton, R.E. Globally stable tensegrity compressive structures for arbitrary complexity. Compos. Struct. 2017, 179, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.E.; Montuori, R.; Pecoraro, V. Globally stable minimal mass compressive tensegrity structures. Compos. Struct. 2016, 141, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, M.; Russo, S.; Sinatra, R. A novel parallel manipulator architecture for manufacturing applications. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2003, 10, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assal, S.F. Self-organizing approach for learning the forward kinematic multiple solutions of parallel manipulators. Robotica 2012, 30, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kwak, Y.K.; Smith, C.C. Development of a parallel wire mechanism for measuring position and orientation of a robot end-effector. Mechatronics 1998, 8, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi-zanganeh, K.; Angeles, J. Real-time direct kinematics of general six-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulators with minimum-sensor data. J. Robot. Syst. 1995, 12, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jiao, L. Forward kinematics of a general Stewart parallel manipulator using the genetic algorithm. J. Xidian Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2003, 30, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Guo, F. Kinematic and static analysis of a novel tensegrity robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 149, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, M.; Gosselin, C.M. Kinematic and static analysis of a 3-PUPS spatial tensegrity mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H. Static and dynamic analyses of tensegrity structures. Part 1. Nonlinear equations of motion. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2001, 38, 3599–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Maurin, B.; Motro, R. Form-finding of nonregular tensegrity systems. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Gan, B.; Fujita, K.; Kurokawa, J. A Genetic Algorithm Based Form-Finding for Tensegrity Structure. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, K. Form-finding of tensegrity structures via genetic algorithm. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagitz, M.; Mirats Tur, J. Finite element based form-finding algorithm for tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 3235–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, G.G.; Bungartz, H.J.; Mohrdieck, C. Numerical form-finding of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 6855–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, S.H.; Mirats Tur, J.M. Tensegrity frameworks: Static analysis review. Mech. Mach. Theory 2008, 43, 859–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, C.; Corless, M.; Skelton, R.E. Linear dynamics of tensegrity structures. Eng. Struct. 2002, 24, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroughi, S.; Khodaparast, H.H.; Friswell, M.I. Non-linear dynamic analysis of tensegrity structures using a co-rotational method. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2015, 69, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.E.; De Oliveira, M.C. Tensegrity Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nagase, K.; Skelton, R. Network and vector forms of tensegrity system dynamics. Mech. Res. Commun. 2014, 59, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.; Skelton, R.E. Nonminimal dynamics of general class k tensegrity systems. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2015, 15, 1450042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeyev, D.; Zhakatayev, A.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Varol, H.A. Generalized dynamics of stacked tensegrity manipulators. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63472–63484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Skelton, R.E. Tensegrity system dynamics with rigid bars and massive strings. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2019, 46, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Chen, M.; Majji, M.; Skelton, R.E. MOTES: Modeling of tensegrity structures. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, P.D.; Chiaverini, S.; Antonelli, G. Handling robot constraints within a Set-Based Multi-Task Priority Inverse Kinematics Framework. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7477–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, A.; Ha, J. A geometric tracking of rank-1 manipulability for singularity-robust collision avoidance. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2021, 14, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Azar, A.T.; Abbas, N.E.; Ezzeldin, M.A.; Ammar, H.H. Experimental kinematic modeling of 6-dof serial manipulator using hybrid deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, Cairo, Egypt, 8–10 April 2020; pp. 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Bi, Q.; Yue, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. A review on tensegrity structures-based robots. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 168, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.S.; Booth, J.W.; Baines, R.L.; Wang, K.; Vespignani, M.; Bekris, K.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Tensegrity Robotics. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintchev, S.; Zappetti, D.; Willemin, J.; Floreano, D. A Soft Robot for Random Exploration of Terrestrial Environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 7492–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Liu, R.; Lin, X.; Li, C.; Guo, H.; Ye, Z.; Wang, C. Configuration Design and Gait Planning of a Six-Bar Tensegrity Robot. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Nabae, H.; Endo, G.; Suzumori, K. New soft robot hand configuration with combined biotensegrity and thin artificial muscle. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4345–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, K.; Shin, D.; Ogai, Y. Design of a Movable Tensegrity Arm with Springs Modeling an Upper and Lower Arm. Actuators 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Post, M.A. A Symmetric Three Degree of Freedom Tensegrity Mechanism with Dual Operation Modes for Robot Actuation. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, H. Swimming performance of a tensegrity robotic fish. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kawaguchi, K.; Feng, J. Prismatic tensegrity structures with additional cables: Integral symmetric states of self-stress and cable-controlled reconfiguration procedure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 4294–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guest, S.; Ohsaki, M. Symmetric prismatic tensegrity structures: Part I. Configuration and stability. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Cao, Y.P.; Gao, H. A Monte Carlo form-finding method for large scale regular and irregular tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmia, A.; Kelaiaia, R.; Chemori, A.; Company, O. On Robust Mechanical Design of a PAR2 Delta-Like Parallel Kinematic Manipulator. J. Mech. Robot. 2021, 14, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaiaia, R.; Zaatri, A.; Company, O. Multiobjective Optimization of 6-dof UPS Parallel Manipulators. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 1885–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshmukhametov, A.; Koganezawa, K.; Yamamoto, Y. A novel discrete wire-driven continuum robot arm with passive sliding disc: Design, kinematics and passive tension control. Robotics 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshmukhametov, A.N.; Koganezawa, K.; Buribayev, Z.; Amirgaliyev, Y.; Yamamoto, Y. Study on multi-section continuum robot wire-tension feedback control and load manipulability. Ind. Robot Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2020, 47, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.E.; Jay, L.O.; Leonard, M.W.; Petzold, L.R.; Sharma, V. An SQP method for the optimal control of large-scale dynamical systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 120, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.J. Interior point methods for optimal control of discrete time systems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1993, 77, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingley, J.; Boyd, S. CVXGEN: A code generator for embedded convex optimization. Optim. Eng. 2012, 13, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschueren, R.; Frison, G.; Kouzoupis, D.; Frey, J.; Duijkeren, N.v.; Zanelli, A.; Novoselnik, B.; Albin, T.; Quirynen, R.; Diehl, M. acados—A modular open-source framework for fast embedded optimal control. Math. Program. Comput. 2022, 14, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Bar length | 1000 mm | |
| Triangle length | 450 mm | |
| Spring constant | 1800 N/m | |
| Top plate mass | 0.86 kg | |
| Bar mass | 0.18 kg | |
| Node mass | 0.1 kg | |
| Gravitation vector | g | m/s |
| Passive wire tension | 90 N | |
| Active wire tension | 65 N | |
| Saddle wire tension | 120 N |
| Nodes | Simulation | Experiment | Difference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | ||
| Base plate | 250 | 0 | 0 | 267 | 1 | 1.6 | 17 | 1 | 1.6 | |
| −130 | −225 | 0 | −127 | −232 | 1.6 | 3 | 7 | 1.6 | ||
| −130 | 225 | 0 | −127 | 232 | 1.6 | 3 | 7 | 1.6 | ||
| Mid nodes | 144 | 50 | 920 | 148 | 49 | 921 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |
| −50 | −150 | 920 | −56 | −148 | 872 | 6 | 2 | 48 | ||
| −130 | 110 | 910 | −120 | 130 | 901 | 10 | 20 | 9 | ||
| 125 | −70 | 673 | 112 | −64 | 684 | 13 | 6 | 11 | ||
| 135 | −70 | 662 | 122 | −68 | 677 | 13 | 2 | 15 | ||
| −14 | 150 | 671 | −12 | 142 | 651 | 2 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Upper plate | 18 | 257 | 1590 | 17 | 218 | 1620 | 1 | 39 | 30 | |
| −250 | −104 | 1600 | −260 | −101 | 1614 | 10 | 3 | 14 | ||
| 197 | −156 | 1600 | 178 | −160 | 1602 | 19 | 4 | 2 | ||
| Nodes | Average Error (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Base plate | 1.6 | |
| 1.6 | ||
| 1.6 | ||
| Mid nodes | 0.76 | |
| 0.89 | ||
| 1.0 | ||
| 0.73 | ||
| 1.1 | ||
| 0.42 | ||
| Upper plate | 0.156 | |
| 0.653 | ||
| 0.327 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeshmukhametov, A.; Koganezawa, K. A Simplified Kinematics and Kinetics Formulation for Prismatic Tensegrity Robots: Simulation and Experiments. Robotics 2023, 12, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12020056
Yeshmukhametov A, Koganezawa K. A Simplified Kinematics and Kinetics Formulation for Prismatic Tensegrity Robots: Simulation and Experiments. Robotics. 2023; 12(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeshmukhametov, Azamat, and Koichi Koganezawa. 2023. "A Simplified Kinematics and Kinetics Formulation for Prismatic Tensegrity Robots: Simulation and Experiments" Robotics 12, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12020056
APA StyleYeshmukhametov, A., & Koganezawa, K. (2023). A Simplified Kinematics and Kinetics Formulation for Prismatic Tensegrity Robots: Simulation and Experiments. Robotics, 12(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12020056






