Regularity of a General Class of “Quantum Deformed” Black Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (Schwarzschild): Not regular;
- : Metric–regular;
- : Christoffel–symbol–regular;
- : Curvature–regular.
2. Geometric Analysis
2.1. Metric Components
2.2. Event Horizons
2.3. Christoffel Symbols of the Second Kind
2.4. Orthonormal Components
2.5. Riemann Tensor
2.6. Ricci Tensor
2.7. Ricci Scalar
2.8. Einstein Tensor
2.9. Weyl Tensor
2.10. Weyl Scalar
2.11. Kretschmann Scalar
3. Surface Gravity and Hawking Temperature
4. Stress-Energy Tensor
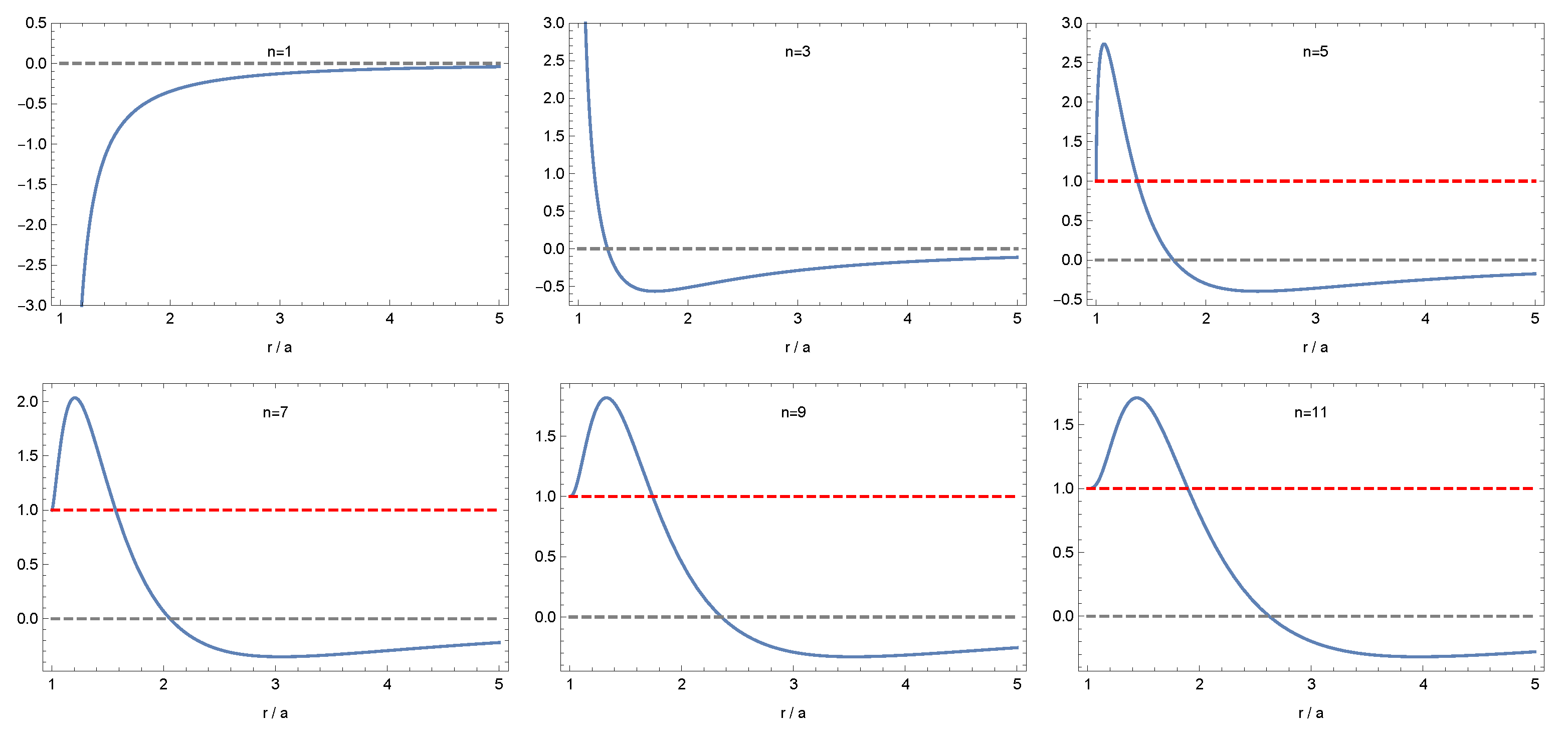
5. Energy Conditions
5.1. Null Energy Condition
5.2. Weak Energy Condition
5.3. Strong Energy Condition
5.4. Dominant Energy Condition
6. ISCO and Photon Sphere Analysis
6.1. Photon Orbits
6.2. ISCOs
6.3. Summary
- ;
- ;
- .
7. Regge–Wheeler Analysis
8. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazakov, D.; Solodukhin, S. On quantum deformation of the Schwarzschild solution. Nucl. Phys. B 1994, 429, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodukhin, S.N. “Nongeometric” contribution to the entropy of a black hole due to quantum corrections. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 51, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodukhin, S.N. Two-dimensional quantum-corrected eternal black hole. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Olmedo, J.; Singh, P. Quantum extension of the Kruskal spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 126003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Can quantum-corrected btz black hole anti-evaporate? Mod. Phys. Lett. A 1998, 13, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, R.V.; Neves, J. Bardeen regular black hole as a quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black hole. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1950048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaslavskii, O.B. Near-extremal and extremal quantum-corrected two-dimensional charged black holes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, 2687–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.F.; Khalil, M.M. Black hole with quantum potential. Nucl. Phys. B 2016, 909, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmet, X.; El-Menoufi, B.K. Quantum corrections to Schwarzschild black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjalal, M. Shahjalal Phase transition of quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black hole in rainbow gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 784, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.-J.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.-X. Quantum tunneling and remnant from a quantum-modified Schwarzschild space–time close to Planck scale. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjalal, M. Thermodynamics of quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black hole surrounded by quintessence. Nucl. Phys. B 2019, 940, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamzadeh, S.; Nozari, K. Tunneling of massless and massive particles from a quantum deformed Schwarzschild black hole surrounded by quintessence. Nucl. Phys. B 2020, 959, 115136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, M.R.; Linder, E.V. Schwarzschild Metric with Planck Length. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.01333. [Google Scholar]
- Nozari, K.; Hajebrahimi, M. Geodesic Structure of the Quantum-Corrected Schwarzschild Black Hole Surrounded by Quintessence. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.14775. [Google Scholar]
- Nozari, K.; Hajebrahimi, M.; Saghafi, S. Quantum corrections to the accretion onto a Schwarzschild black hole in the background of quintessence. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, D.J.; Moynihan, N.; Das, S.; Haque, S.S.; Underwood, B. Towards the Raychaudhuri equation beyond general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.G.; Tseytlin, A. Scalar-tensor quantum gravity in two dimensions. Nucl. Phys. B 1992, 382, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T. When is gttgrr = −1? Class. Quantum Gravity 2007, 24, 5717–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, V.V. Quintessence and black holes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2003, 20, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. The Kiselev black hole is neither perfect fluid, nor is it quintessence. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 37, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonserm, P.; Ngampitipan, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Decomposition of the total stress energy for the generalized Kiselev black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 024022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Non-singular general-relativistic gravitational collapse. In Proceedings of the GR5 Conference, Tbilisi, Georgia, 9–13 September 1968; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, T.A.; Bergmann, P.G. Stellar collapse without singularities? Phys. Rev. D 1983, 28, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, A. Regular black holes and topology change. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 7615–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A. Regular magnetic black holes and monopoles from nonlinear electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Sarbach, O. Stability properties of black holes in self-gravitating nonlinear electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayon-Beato, E.; Garcia, A. Four parameter regular black hole solution. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2005, 37, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.A. Formation and Evaporation of Nonsingular Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 031103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A.; Fabris, J.C. Regular Phantom Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 251101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A.; Dehnen, H.; Melnikov, V.N. Regular black holes and black universes. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2007, 39, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.P.S.; Zaslavskii, O.B. Quasi-black holes: Definition and general properties. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 084030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoldi, S. Spherical black holes with regular center: A Review of existing models including a recent realization with Gaussian sources. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0802.0330. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, J.P.S.; Zanchin, V.T. Regular black holes: Electrically charged solutions, Reissner-Nordström outside a de Sitter core. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A.; Konoplya, R.A.; Zhidenko, A. Instabilities of wormholes and regular black holes supported by a phantom scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambi, C.; Modesto, L. Rotating regular black holes. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 721, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Black hole evaporation without an event horizon. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.4098. [Google Scholar]
- Frolov, V.P. Information loss problem and a ‘black hole’ model with a closed apparent horizon. JHEP 2014, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Do Black Holes Exist? arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.6981. [Google Scholar]
- Balart, L.; Vagenas, E.C. Regular black holes with a nonlinear electrodynamics source. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 124045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, T.; Pacilio, C.; Rovelli, C.; Speziale, S. On the effective metric of a Planck star. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 47, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Notes on nonsingular models of black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-Y.; Wang, X. Construction of regular black holes in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 124027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P.; Zelnikov, A. Quantum radiation from an evaporating nonsingular black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Remarks on non-singular black holes. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 168, 01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.A.; Chimento, S.; Ortín, T.; Ruipérez, A. Regular stringy black holes? Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Models for the nonsingular transition of an evaporating black hole into a white hole. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.06683. [Google Scholar]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Di Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Pacilio, C.; Visser, M. On the viability of regular black holes. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Di Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Visser, M. Phenomenological aspects of black holes beyond general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 124009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Di Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Visser, M. Opening the Pandora’s box at the core of black holes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 145005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Di Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Visser, M. Geodesically complete black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 084047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Di Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Pacilio, C.; Visser, M. Inner horizon instability and the unstable cores of regular black holes. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.; Hopper, S.; Macedo, C.F.B.; Palenzuela, C.; Pani, P. Gravitational-wave signatures of exotic compact objects and of quantum corrections at the horizon scale. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 084031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Barceló, C.; Liberati, S.; Sonego, S. Small, dark, and heavy: But is it a black hole? PoS 2009, 75, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Black holes in general relativity. PoS 2009, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Wiltshire, D.L. Stable gravastars—An alternative to black holes? Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, C.; Liberati, S.; Sonego, S.; Visser, M. Black Stars, Not Holes. Sci. Am. 2009, 301, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Black-bounce to traversable wormhole. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Martín-Moruno, P.; Visser, M. Vaidya spacetimes, black-bounces, and traversable wormholes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.S.N.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Dynamic thin-shell black-bounce traversable wormholes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 124035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Regular Black Holes with Asymptotically Minkowski Cores. Universe 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.; Lobo, F.S.N.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Thin-shell traversable wormhole crafted from a regular black hole with asymptotically Minkowski core. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 064054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Photon Spheres, ISCOs, and OSCOs: Astrophysical Observables for Regular Black Holes with Asymptotically Minkowski Cores. Universe 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonserm, P.; Ngampitipan, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Exponential metric represents a traversable wormhole. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barausse, E.; Berti, E.; Hertog, T.; Hughes, S.A.; Jetzer, P.; Pani, P.; Sotiriou, T.P.; Tamanini, N.; Witek, H.; Yagi, K.; et al. Prospects for fundamental physics with LISA. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2020, 52, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Physical observability of horizons. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 127502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Information Preservation and Weather Forecasting for Black Holes. arxiv 2014, arXiv:1401.5761. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, F.S.N.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Silva, M.V.D.S.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Novel black-bounce geometries. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2009.12057. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, M. Dirty black holes: Thermodynamics and horizon structure. Phys. Rev. D 1992, 46, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_condition (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Tipler, F.J. Energy conditions and spacetime singularities. Phys. Rev. D 1978, 17, 2521–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, A. Geodesic focusing, energy conditions and singularities. Class. Quantum Gravity 1987, 4, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkhammer, G. Averaged energy conditions for free scalar fields in flat spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 1991, 43, 2542–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.H.; Roman, T.A. Averaged energy conditions and quantum inequalities. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 51, 4277–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Lorentzian Wormholes: From Einstein to Hawking; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fewster, C.J.; Roman, T.A. Null energy conditions in quantum field theory. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, C.; Visser, M. Twilight for the energy conditions? Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2002, 11, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Energy Conditions in the Epoch of Galaxy Formation. Science 1997, 276, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.; Barceló, C. Energy conditions and their cosmological implications. arXiv 1999, arXiv:gr-qc/0001099. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, M. Gravitational vacuum polarization. II. Energy conditions in the Boulware vacuum. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 5116–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, T.A. Some thoughts on energy conditions and wormholes. arXiv 2004, arXiv:gr-qc/0409090. [Google Scholar]
- Cattoen, C.; Visser, M. Cosmological milestones and energy conditions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 68, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Energy conditions and galaxy formation. arXiv 1997, arXiv:gr-qc/9710010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewster, C.J.; Galloway, G.J. Singularity theorems from weakened energy conditions. Class. Quantum Gravity 2011, 28, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaslavskii, O. Regular black holes and energy conditions. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 688, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moruno, P.; Visser, M. Classical and Semi-classical Energy Conditions. Black Hole Phys. 2017, 189, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Moruno, P.; Visser, M. Semiclassical energy conditions for quantum vacuum states. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 2013, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moruno, P.; Visser, M. Classical and quantum flux energy conditions for quantum vacuum states. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel, E. A Primer on Energy Conditions. Einstein Stud. 2017, 13, 43–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moruno, P.; Visser, M. Semi-classical and nonlinear energy conditions. In Proceedings of the 14th Marcel Grossmann Meeting, Rome, Italy, 12–18 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-M. Geodesics and periodic orbits around quantum-corrected black holes. Phys. Dark Universe 2020, 30, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Guo, M.; Feng, X.H. Influence of Quantum Correction on the Black Hole Shadows, Photon Rings and Lensing Rings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00657. [Google Scholar]
- Boonserm, P.; Ngampitipan, T.; Visser, M. Regge-Wheeler equation, linear stability, and greybody factors for dirty black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachi, A.; Lemos, J.P.S. Quasinormal modes of regular black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 24034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.; Correa, J. Quasinormal modes of the Bardeen black hole: Scalar perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, Á.; Panotopoulos, G. Quasinormal modes of an improved Schwarzschild black hole. Phys. Dark Universe 2020, 30, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplya, R. Quantum corrected black holes: Quasinormal modes, scattering, shadows. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 804, 135363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Bouetou, B.T.; Kofane, T.C. Quasinormal modes of a quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black hole: Gravitational and Dirac perturbations. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X. Electromagnetic quasinormal mode of quantum corrected Schwarzschild black hole. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2016, 6, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Thomas, B.B.; Kofané, T.C. Quasinormal modes of scalar perturbation around a quantum-corrected Schwarzschild black hole. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 350, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 1 | globally violated | globally violated | globally violated | globally violated |
| 3 | globally violated | |||
| 5 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| n | NEC | WEC | SEC | DEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 1 | globally violated | globally violated | globally violated | globally violated |
| 3 | same as NEC | globally violated | ||
| 5 | same as NEC | |||
| 7 | same as NEC | |||
| 9 | same as NEC | |||
| 11 | same as NEC | |||
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berry, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Regularity of a General Class of “Quantum Deformed” Black Holes. Universe 2021, 7, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7060165
Berry T, Simpson A, Visser M. Regularity of a General Class of “Quantum Deformed” Black Holes. Universe. 2021; 7(6):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7060165
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerry, Thomas, Alex Simpson, and Matt Visser. 2021. "Regularity of a General Class of “Quantum Deformed” Black Holes" Universe 7, no. 6: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7060165
APA StyleBerry, T., Simpson, A., & Visser, M. (2021). Regularity of a General Class of “Quantum Deformed” Black Holes. Universe, 7(6), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7060165






