Gravitational Lensing of Continuous Gravitational Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gravitational Lensing of Gravitational Waves
2.1. Strong Gravitational Lensing in Brief
2.2. Wave Optics Regime
3. Effects of the Gravitational Wave Lensing of Continuous Waves
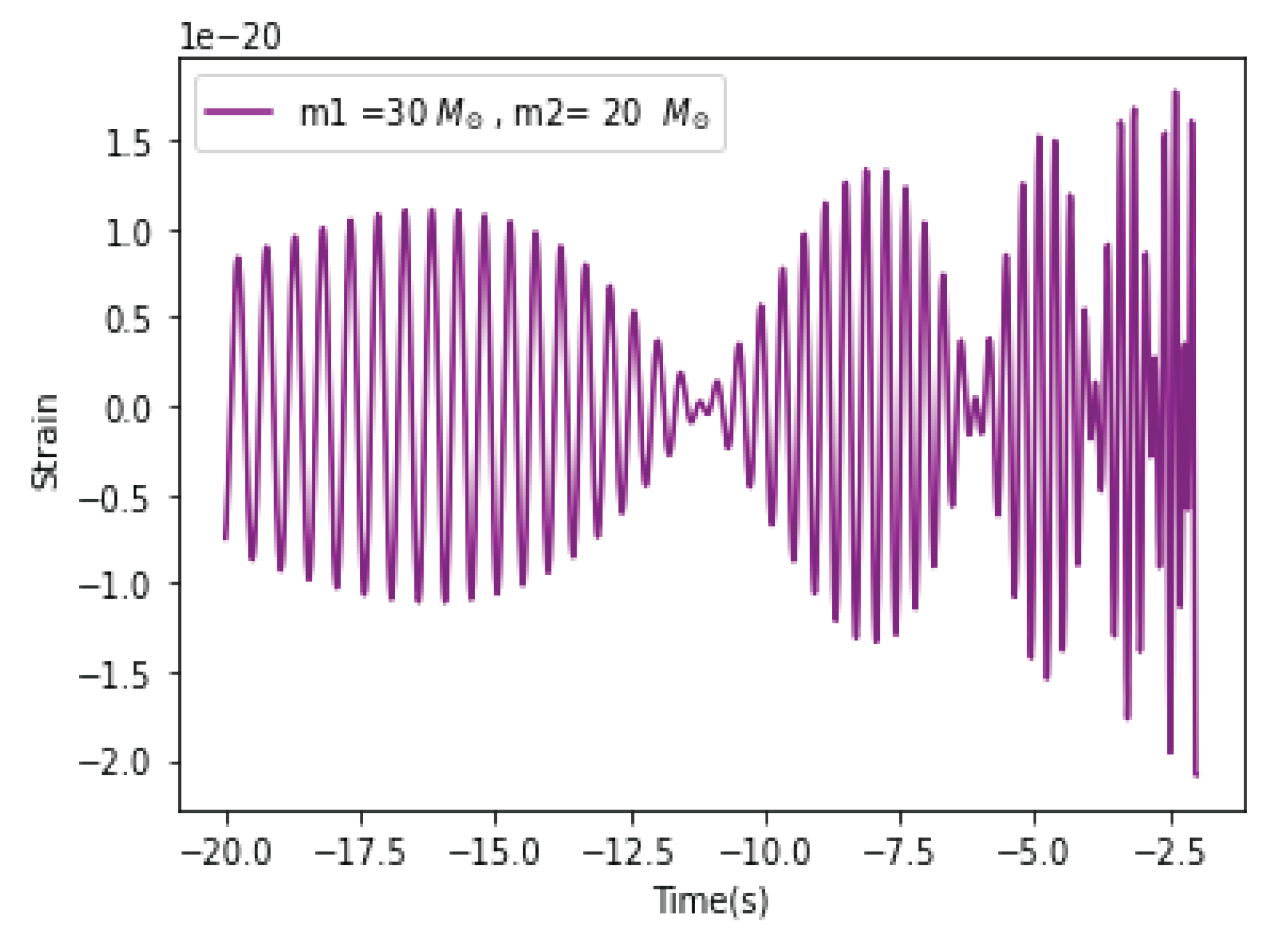
3.1. Beat Patterns
3.2. Diffractive Microlensing
- w > 1, to have enough amplification;
- y < 3, to detect fringes before they are damped;
- , to see a fringe pattern.
3.3. Poisson–Arago Spot
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punturo, M.; Abernathy, M.; Acernese, F.; Allen, B.; Andersson, N.; Arun, K.; Barone, F.; Barr, B.; Barsuglia, M.; Beker, M.; et al. The Einstein Telescope: A third-generation gravitational wave observatory. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 194002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, S.; Sigg, D.; Ballmer, S.W.; Barsotti, L.; Mavalvala, N.; Evans, M. Gravitational wave detector with cosmological reach. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzmann, K.; for the LISA Study Team. LISA—An ESA cornerstone mission for a gravitational wave observatory. Class. Quant. Grav. 1997, 14, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Seoane, P.; Audley, H.; Babak, S.; Baker, J.; Barausse, E.; Bender, P.; Berti, E.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M.; Bortoluzzi, D.; et al. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00786. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, N.; Kawamura, S.; Nakamura, T. Possibility of Direct Measurement of the Acceleration of the Universe Using 0.1 Hz Band Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Antenna in Space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 221103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Nakamura, T.; Ando, M.; Seto, N.; Tsubono, K.; Numata, K.; Takahashi, R.; Nagano, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Musha, M.; et al. The Japanese space gravitational wave antenna—DECIGO. Class. Quant. Grav. 2006, 23, S125–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Ando, M.; Seto, N.; Sato, S.; Nakamura, T.; Tsubono, K.; Kanda, N.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoyama, J.; Funaki, I.; et al. The Japanese space gravitational wave antenna: DECIGO. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 094011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, B. Concepts and status of Chinese space gravitational wave detection projects. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.T. Gravitational Lensing of Gravitational Waves from Inspiraling Binaries by a Point Mass Lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Nakamura, T. Wave Effects in the Gravitational Lensing of Gravitational Waves from Chirping Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2003, 595, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Biesiada, M.; Gavazzi, R.; Piórkowska, A.; Zhu, Z.H. Cosmology with strong-lensing systems. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Biesiada, M.; Yao, M.; Zhu, Z.H. Limits on the power-law mass and luminosity density profiles of elliptical galaxies from gravitational lensing systems. MNRAS 2016, 461, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Biesiada, M.; Zhu, Z.H. Strongly lensed gravitational waves from intrinsically faint double compact binaries—Prediction for the Einstein Telescope. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereno, M.; Sesana, A.; Bleuler, A.; Jetzer, P.; Volonteri, M.; Begelman, M.C. Strong Lensing of Gravitational Waves as Seen by LISA. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 251101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piórkowska-Kurpas, A.; Hou, S.; Biesiada, M.; Ding, X.; Cao, S.; Fan, X.; Kawamura, S.; Zhu, Z.H. Inspiraling Double Compact Object Detection and Lensing Rate: Forecast for DECIGO and B-DECIGO. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Ehlers, J.; Falco, E.E. Gravitational Lenses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treu, T.; Koopmans, L.V.E. Massive Dark Matter Halos and Evolution of Early-Type Galaxies toz≈1. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treu, T.; Koopmans, L.V.E.; Bolton, A.S.; Burles, S.; Moustakas, L.A. Erratum: “The Sloan Lens ACS Survey. II. Stellar Populations and Internal Structure of Early-Type Lens Galaxies” (ApJ, 640, 662 [2006]). Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J.; Biesiada, M.; Liu, Y.; Lian, Y. Testing the cosmic curvature at high redshifts: The combination of LSST strong lensing systems and quasars as new standard candles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Bartelmann, M. Lectures on Gravitational Lensing. arXiv 1996, arXiv:astro–ph/9606001. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardeau, F. Gravitation lenses. In Theoretical and Observational Cosmology; NATO Advanced Study Institute (ASI) Series C; Lachièze-Rey, M., Ed.; Springer-Science+Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 541, p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Fan, X.L.; Liao, K.; Zhu, Z.H. Gravitational wave interference via gravitational lensing: Measurements of luminosity distance, lens mass, and cosmological parameters. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 064011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaranowski, P.; Krolak, A. Analysis of Gravitational-Wave Data. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore, M. Gravitational Waves. Volume 1: Theory and Experiments; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-19-857074-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Fan, X.L.; Ding, X.; Biesiada, M.; Zhu, Z.H. Precision cosmology from future lensed gravitational wave and electromagnetic signals. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesiada, M.; Ding, X.; Piórkowska, A.; Zhu, Z.H. Strong gravitational lensing of gravitational waves from double compact binaries—Perspectives for the Einstein Telescope. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ding, X.; Biesiada, M.; Liao, K.; Zhu, Z.H. How Does the Earth’s Rotation Affect Predictions of Gravitational Wave Strong Lensing Rates? Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Liao, K.; Ding, X.; You, Z.; Cao, Z.; Biesiada, M.; Zhu, Z.H. Event rate predictions of strongly lensed gravitational waves with detector networks and more realistic templates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 509, 3772–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Gravitational Microlensing by the Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. 1986, 304, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Biesiada, M.; Fan, X.L. The Wave Nature of Continuous Gravitational Waves from Microlensing. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.H.; Hannuksela, O.A.; Herrera-Martín, A.; Diego, J.M.; Broadhurst, T.; Li, T.G.F. Discovering intermediate-mass black hole lenses through gravitational wave lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 083005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Shin, C.S. Gravitational-Wave Fringes at LIGO: Detecting Compact Dark Matter by Gravitational Lensing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 041103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, P.; Vitale, S.; Loeb, A. Detecting stellar lensing of gravitational waves with ground-based observatories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, R.; Refsdal, S.; Stabell, R. Astrophysical applications of gravitational micro-lensing. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 166, 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, R.; Ostriker, J.P. Pulsar Populations and Their Evolution. Astrophys. J. 1990, 352, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D.; Schramm, D.N.; Truran, J.W. On Relative Supernova Rates and Nucleosynthesis Roles. Astrophys. J. 1989, 339, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Gravitational Microlensing of the Galactic Bulge Stars. Astrophys. J. 1991, 371, L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Gravitational Microlensing by the Globular Cluster Stars. Acta Astron. 1994, 44, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrukowicz, P.; Minniti, D.; Jetzer, P.; Alonso-García, J.; Udalski, A. The first confirmed microlens in a globular cluster. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 744, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaranowski, P.; Królak, A. Searching for gravitational waves from known pulsars using the and statistics. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 194015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguri, M. Strong gravitational lensing of explosive transients. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2019, 82, 126901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, X. Poisson-Arago spot for gravitational waves. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2021, 64, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regge, T.; Wheeler, J.A. Stability of a Schwarzschild Singularity. Phys. Rev. 1957, 108, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, Y.; Noda, S.; Sakai, Y. Wave optics in spacetimes with compact gravitating object. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 064037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiziev, P.P. Exact solutions of Regge–Wheeler equation and quasi-normal modes of compact objects. Class. Quant. Grav. 2006, 23, 2447–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.K.Y.; Wong, K.W.K.; Broadhurst, T.; Li, T.G.F. Precise LIGO lensing rate predictions for binary black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 023012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, T.; Diego, J.M.; Smoot, G.F., III. Twin LIGO/Virgo Detections of a Viable Gravitationally-Lensed Black Hole Merger. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.03190. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, A.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. Search for lensing signatures in the gravitational-wave observations from the first half of LIGO-Virgo’s third observing run. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.06384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P.; Berry, C.; Bianconi, M.; Farr, W.M.; Jauzac, M.; Massey, R.; Richard, J.; Robertson, A.; Sharon, K.; Vecchio, A.; et al. Strong-lensing of Gravitational Waves by Galaxy Clusters. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2017, 13, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.L.; Rodney, S.A.; Treu, T.; Strolger, L.G.; Foley, R.J.; Jha, S.W.; Selsing, J.; Brammer, G.; Bradač, M.; Cenko, S.B.; et al. Deja vu all over again: The reappearance of supernova refsdal. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, S.S.; Zackay, B.; Mao, S.; Lu, Y. Detecting lensing-induced diffraction in astrophysical gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, A.K.; Bagla, J.S. Gravitational lensing of gravitational waves: Wave nature and prospects for detection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 492, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Meena, A.K.; More, A.; Bose, S.; Bagla, J.S. Gravitational lensing of gravitational waves: Effect of microlens population in lensing galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 4869–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Li, P.; Yu, H.; Biesiada, M.; Fan, X.L.; Kawamura, S.; Zhu, Z.H. Lensing rates of gravitational wave signals displaying beat patterns detectable by DECIGO and B-DECIGO. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, F.R. Nonlinear Gravitational Waves and Solitons. In Nonlinear Systems, Vol. 1: Mathematical Theory and Computational Methods; Carmona, V., Cuevas-Maraver, J., Fernández-Sánchez, F., García-Medina, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 207–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biesiada, M.; Harikumar, S. Gravitational Lensing of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Universe 2021, 7, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7120502
Biesiada M, Harikumar S. Gravitational Lensing of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Universe. 2021; 7(12):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7120502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiesiada, Marek, and Sreekanth Harikumar. 2021. "Gravitational Lensing of Continuous Gravitational Waves" Universe 7, no. 12: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7120502
APA StyleBiesiada, M., & Harikumar, S. (2021). Gravitational Lensing of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Universe, 7(12), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7120502





