Abstract
A Multi-Phase Transport (AMPT) model is used to study the elliptic flow fluctuations of identified particles using participant and spectator event planes. The elliptic flow measured using the first order spectator event plane is expected to give the elliptic flow relative to the true reaction plane which suppresses the flow fluctuations. However, the elliptic flow measured using the second-order participant plane is expected to capture the elliptic flow fluctuations. Our study shows that the first order spectator event plane could be used to study the elliptic flow fluctuations of the identified particles in the AMPT model. The elliptic flow fluctuations magnitude shows weak particle species dependence and transverse momentum dependence. Such observation will have important implications for understanding the source of the elliptic flow fluctuations.
1. Introduction
Many studies of the ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and the Large Hadron Collider show that an exotic state of matter named Quark-Gluon Plasma (QGP) is created in these collisions. A large number of studies are focused on identifying the dynamical evolution and the transport properties of the QGP.
In heavy-ion collisions, the produced particle azimuthal anisotropy measurements have been used in various studies to show the viscous hydrodynamic response of the QGP to the initial energy density spatial distribution produced in the early stages of the collisions [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. The azimuthal anisotropy of the particles emitted relative to the reaction plane can be described by the Fourier expansion [15,16] of the final-state azimuthal angle distribution,
The first Fourier harmonic, , is the directed flow; is called the elliptic flow, and is the triangular flow, etc. A wealth of information on the characteristics of the QGP has been gained via the anisotropic flow studies of directed and elliptic flow [17,18,19], higher-order flow harmonics [10,20,21,22,23], flow fluctuations [24,25,26] and different flow harmonics correlations [21,27,28,29,30,31].
Hydrodynamic studies suggest that anisotropic flow stems from the evolution of the medium in the presence of initial-state anisotropies, determined by the eccentricities . The and flow harmonics are recognized to be linearly correlated to and , respectively [7,28,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Therefore for these flow harmonics,
where encodes knowledge about the medium properties such as the specific shear viscosity () of the QGP. Accurate extraction of requires certain restrictions on the initial-state models employed in such extractions. Such constraints can be achieved via measurements of the flow harmonics and the event-by-event flow fluctuations [39]. Flow fluctuations could be arising from several sources: one of which has attracted considerable attention is the initial eccentricity fluctuations [40,41,42]. Recent theoretical studies have begun to take into account initial conditions that include energy density fluctuations, initial flow [13,37,43], and the full shear stress tensor [44] at and at > 0 [45,46,47,48]. Also, the partonic structure inside the nucleons has been considered in Reference [49].
Recently, Reference [50] presented more realistic event-by-event fluctuating initial conditions, Initial Conserved Charges in Nuclear Geometry (ICCING), of not only the initial energy density profile but also the initial conserved charges of baryon number (B), strangeness (S), and electric charge (Q) density distributions. This work pointed out that while baryon number and electric charge have almost the same geometries to the energy density profile, the initial strangeness distribution is considerably more eccentric. Such an effect predicts that the elliptic flow fluctuations will be larger for the strange and multi-strange hadrons. This effect can be detected experimentally via studying the elliptic flow fluctuations of the identified hadrons.
The ratio between four-particles elliptic flow, , and the two-particles elliptic flow, , is often used to estimate the strength of the elliptic flow fluctuations as a fraction of the measured flow harmonic strength [51,52]. However, important caveats to studying the elliptic flow fluctuations using () for the identified hadrons are, first, the demand for high statistical power, and second, the multi-strange hadron identification process [53]. Consequently, the ratio of is of limited experimental use for carrying out these investigations for the multi-strange hadrons.
In this work, we investigate an alternative validation scheme, which employs the use of the first-order spectator event plane, , along with the second-order event plane to study the elliptic flow fluctuations of the identified hadrons. Here, the underlying notion is that (with respect to the spectator first-order event plane) will reduce the elliptic flow fluctuations due to the strong correlations between the and the true reaction plane. Therefore, the ratio is expected to reflect the elliptic flow fluctuations.
For RHIC highest energy and using the STAR detector, we propose a similar investigation to be performed using the first-order spectator event plane from spectator neutrons, measured by the zero-degree calorimeters (ZDC) [54] and the second-order event plane using the new installed Event-Plane-Detector (EPD) [55]. Consequently, we think that conducting a similar experimental study will reveal important information about the elliptic flow fluctuations and will shed light on the ICCING scenario suggested in Reference [50].
2. Method
The current study is conducted with simulated events for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV, collected using the AMPT [56] model with the string-melting mechanism and hadronic cascade on. The AMPT model, which has been widely employed to study relativistic heavy-ion collisions [56,57,58,59,60,61,62,62], includes four main dynamical components: initial condition, parton cascade, hadronization, and hadronic rescatterings. The initial conditions take into account soft string excitations and the phase space distributions of minijet partons, which are produced by the Heavy-Ion Jet Interaction Generator model (HIJING) [63] in which the Glauber model with multiple nucleon scatterings are used to define the heavy-ion collisions initial state.
The partons scatterings are handled according to the Zhang’s Parton Cascade (ZPC) model [64], which contain only two-body elastic scatterings with a cross-section defined as:
where = 0.47 is the strong coupling constant, is the screening mass and s and t are the Mandelstam variables. In the AMPT with the string-melting mechanism, the excited strings and minijet partons are melted into partons. The partons scatterings will lead to local energy density fluctuations, which are equivalent to the local transverse density of participant nucleons.
In the string-melting version and when partons stop interacting with each other, a quark coalescence model is used to couple partons into hadrons. Consequently, the partonic matter is then converted into hadronic matter and the hadronic interactions are given by the A Relativistic Transport (ART) model [65], which incorporates both elastic and inelastic scatterings for baryon–baryon, baryon–meson, and meson–meson interactions.
In this work, the centrality intervals are defined by selecting the impact parameter distribution, then the AMPT events are analyzed using (i) the event plane method and (ii) the multi-particle cumulant technique [66,67,68,69]. Using both methods, particle of interest (POI) comes from pseudorapidities , which matches the STAR experiment pseudorapidity acceptance, and with transverse momentum .
The second-order event plane (), is estimated from the azimuthal distribution of final-state particles. The elliptic flow that will be obtained using this method will then be corrected with the corresponding event plane resolution ( ()) [16]. The is reconstructed in a pseudorapidity range of , which matches the STAR experiment EPD acceptance, and :
where is the final-state azimuthal angle of particle i, and is its weight. The weight is chosen to be equal to . Also, the first order spectator plane is constructed using the AMPT spectator x and y position information. Using the spectator or the event planes we can give the elliptic flow as:
where () and () represent the resolution of the event planes. The event planes resolution is calculated using the two-subevent method [16].
On the other hand, the standard (subevents) cumulant methods framework is discussed in References [66,67,68,69]. In the standard cumulant method, the n-particle cumulants are constructed using particles from the acceptance. Thus the constructed two- and four-particle correlations can be written as:
where, represents the average over all particles in a single event, and then in average over all events, n is the harmonic number and expresses the azimuthal angle of the particle. Then the four-particle elliptic flow harmonic can be given as:
In general, when the flow fluctuation is smaller than the true reaction plan elliptic flow one can write [70,71]:
Then the ratio can be used to estimate the strength of the elliptic flow fluctuations as a fraction of the measured flow harmonic (large value of indicates less fluctuations whereas a smaller value indicates large fluctuations),
The reliability of this elliptic flow fluctuations extraction will depend on the strength of the correlations between the spectator plane and the reaction plane.
3. Results and Discussion
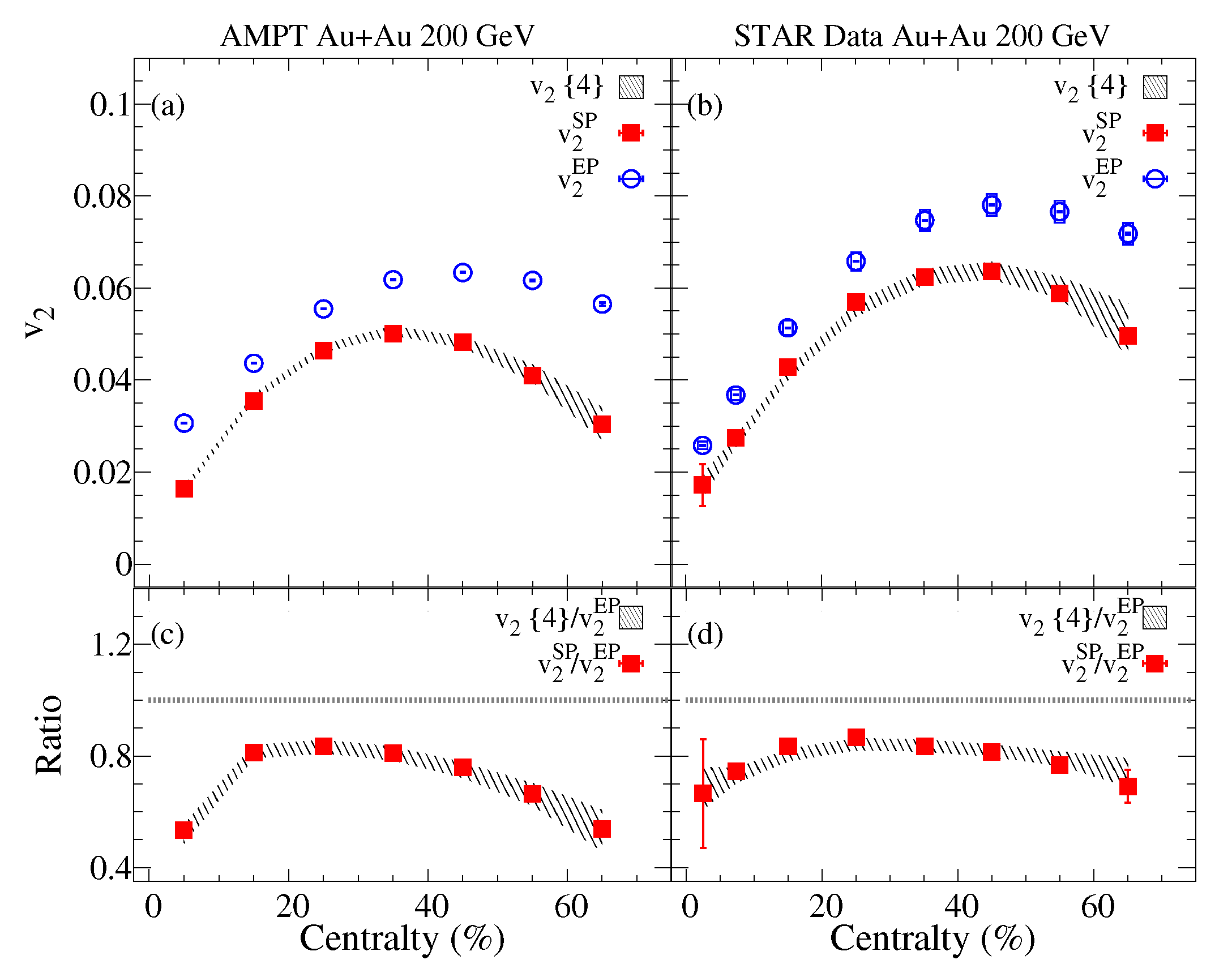
Panel (a) of Figure 1 compares the centrality dependence of the four-particle elliptic flow () with the elliptic flow measured with respect to the event plane () and spectators plane (). The comparison of the and the shows larger magnitudes for . By contrast, the values for show good agreement with . Qualitatively, one expects such patterns due to the respective flow fluctuations contributions to and . The experimental measurements for charge hadrons reported by the STAR experiment, shown in Figure 1b [18,72], also show good agreement between and (), consistent with the AMPT simulations. Here, no attempt was made to improve the agreement between the model and the experimental results by varying the model parameters to influence the flow magnitude and its associated fluctuations [73,74,75,76]. We defer such an investigation to a future study. The ratio , presented in panel (c) from AMPT, and data panel (d) serves as a metric for elliptic flow fluctuations. The decrease from central to peripheral collisions, consistent with the patterns expected when initial-state eccentricity fluctuations dominate. Note, however, that other sources of fluctuations could contribute.
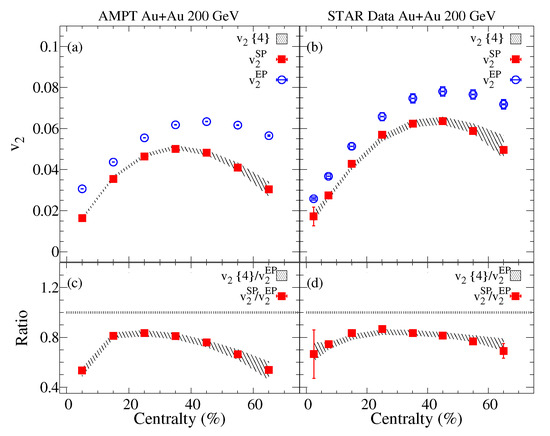
Figure 1.
The charged particles centrality dependence of and are compared to the four-particles elliptic flow (hashed band) for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the A Multi-Phase Transport (AMPT) model panel (a). The charged particles centrality dependence of and are compared to for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the STAR experiment [18,72] panel (b). The elliptic flow fluctuations represented by the ratios and are presented in panels (c,d).
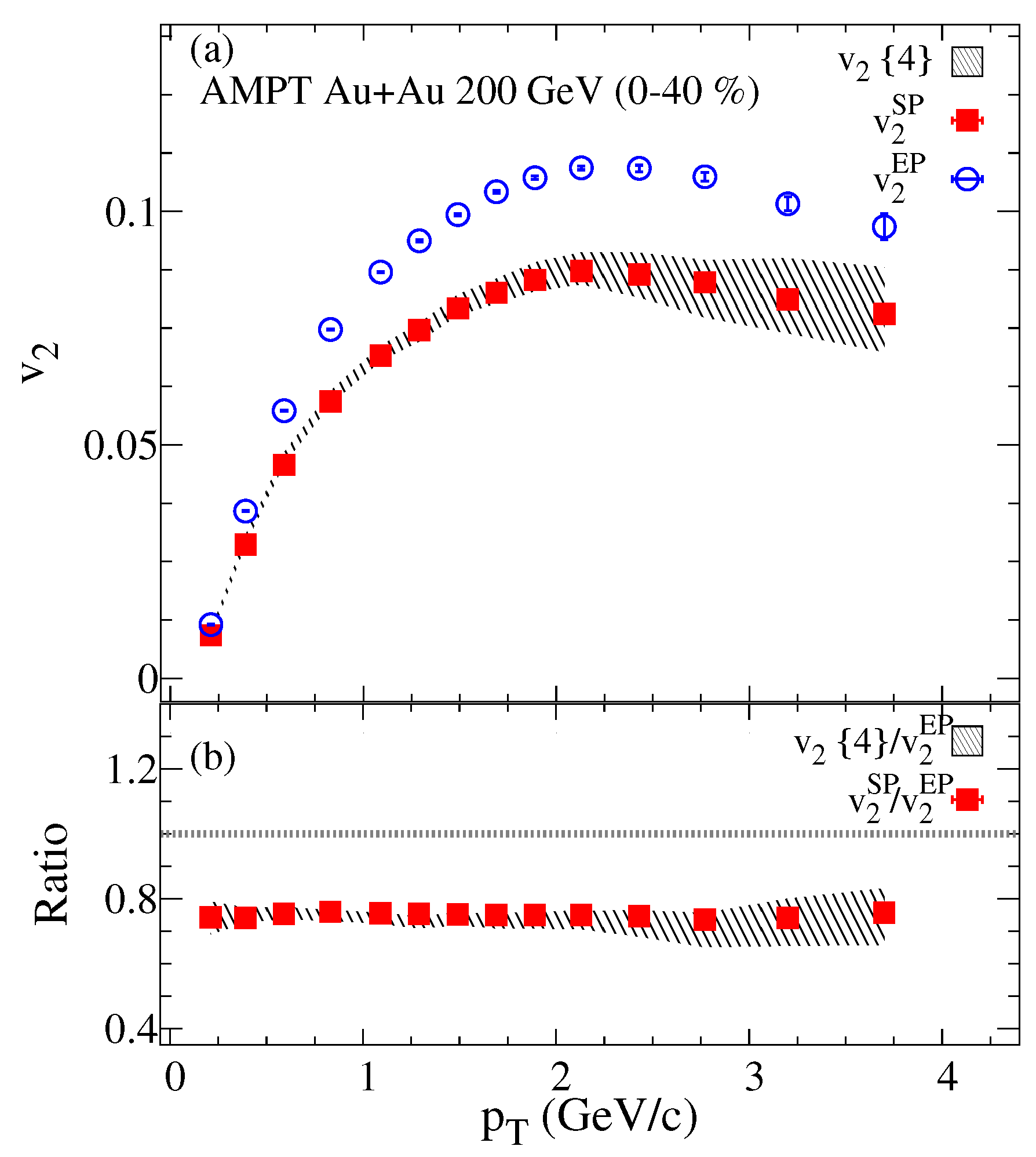
The transverse momentum dependence of the , and are shown in Figure 2. This differential comparison further reflects the effect of the elliptic flow fluctuations on the which is highlighted in the ratio between and . Also a good agreement (within the errors) has been observed between the and . The ratio , presented in panel (b) presents the strength of the elliptic flow fluctuations which shows no dependence, consistent with the preliminary STAR measurements [77].
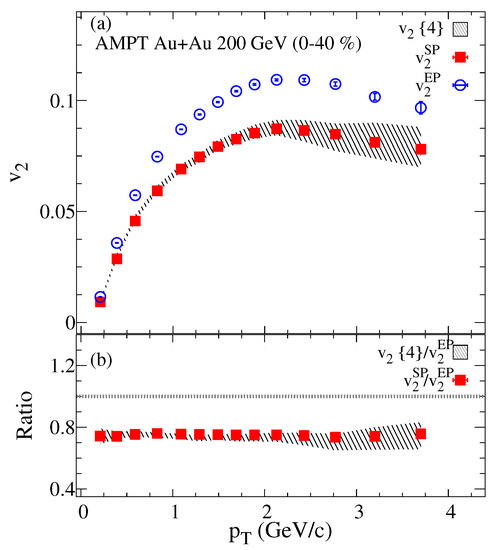
Figure 2.
The charged particles dependence of and are compared to the four-particles elliptic flow (hashed band) panel (a). The ratios and are presented in panel (b) for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the AMPT model.
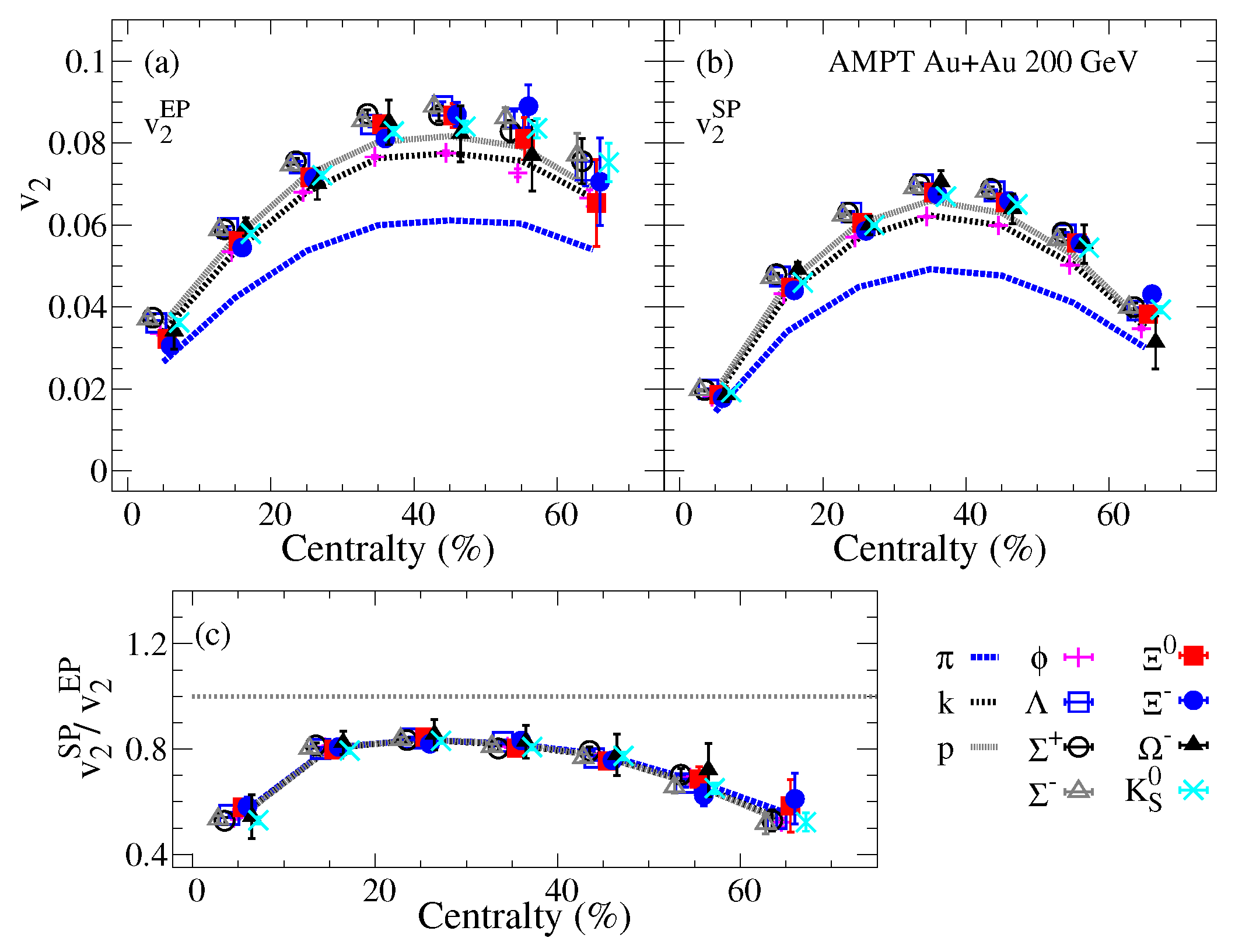
The centrality dependence of the identified particles panel (a), panel (b) and panel (c) are shown in Figure 3 for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the AMPT model. The results of and show the mass ordering effect on the observed magnitude. This mass ordering effect, which cancels out for the ratio , presented in panel (c) indicates the domination of the initial-state eccentricity fluctuations in the AMPT model.
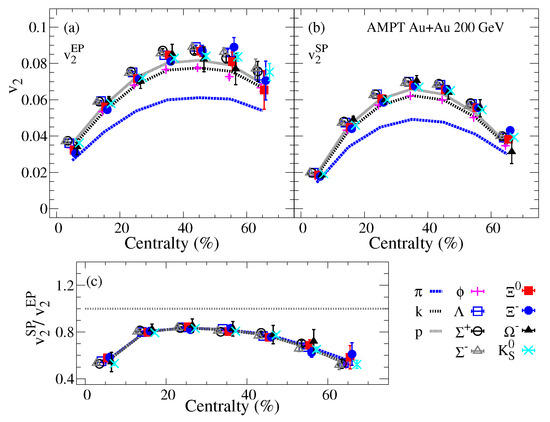
Figure 3.
The identified particles centrality dependence of the elliptic flow harmonic with respect to participant and spectator event planes panels (a,b) respectively. The elliptic flow fluctuations represented by the ratio are presented in panel (c) for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the AMPT model.
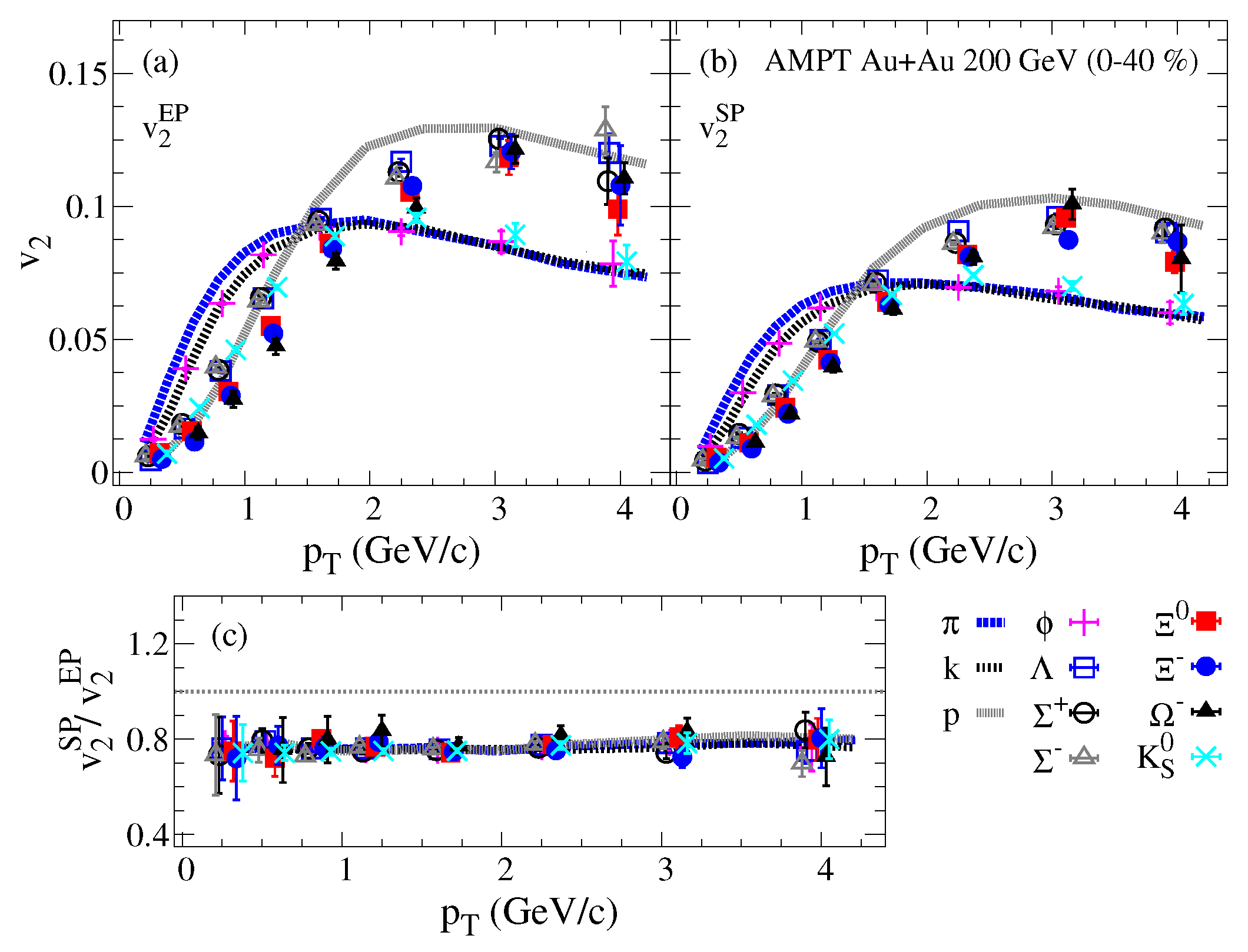
Figure 4 compares the dependence of the identified particles panel (a), panel (b) and panel (c) for % Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the AMPT model. The ratios panel (c) (elliptic flow fluctuations) show week sensitivity to the increase. The and vs. show the expected mass ordering dependence, which cancels out for the ratio vs. , presented in panel (c), which further suggests that the elliptic flow fluctuations in the AMPT model are governed by initial-state fluctuations.
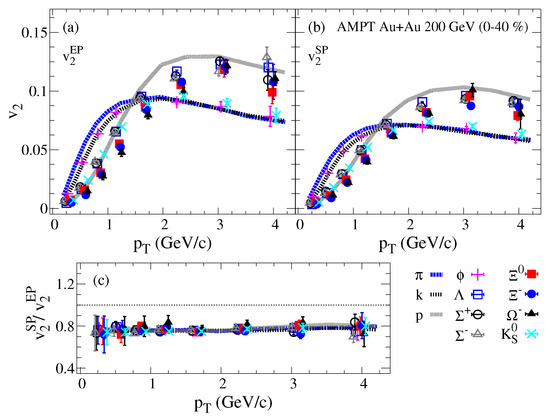
Figure 4.
The identified particles dependence of the elliptic flow harmonic with respect to participant and spectator event planes panels (a,b) respectively. The elliptic flow fluctuations represented by the ratio are presented in panel (c) for Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV from the AMPT model.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we studied the centrality and transverse momentum dependence of the identified particles , and the elliptic flow fluctuations presented by the ratio using the AMPT model. The magnitude of the elliptic flow fluctuations is observed to increase from central to mid-central collisions, consistent with the patterns expected from the initial-state eccentricity fluctuations; a weak dependence is also observed. The centrality and dependence of the identified particles and show the expected mass ordering. However, the elliptic flow fluctuations show no particle species dependence. The integrated and differential elliptic flow fluctuation results indicate the domination of the effect of the initial-state eccentricity fluctuations as expected in the AMPT model. It is suggested that similar investigations of experimental data could display important insight on the ICCING scenario in heavy-ion collisions.
Author Contributions
N.M.; conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, and writing—original draft preparation. X.S., Z.Y., O.E., and R.L.: writing—review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the US Department of Energy under contract DE-FG02-94ER40865 (N.M., X.S., Z.Y. and O.E.) and DE-FG02-87ER40331.A008 (R.L.).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jacquelyn Noronha-Hostler for the useful discussion and Emily Racow for the language check.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heinz, U.W.; Kolb, P.F. Early thermalization at RHIC. Nucl. Phys. 2002, A702, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Heinz, U.W.; Kharzeev, D.; Lacey, R.; Nara, Y. Hadronic dissipative effects on elliptic flow in ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Lett. 2006, B636, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovinen, P.; Kolb, P.F.; Heinz, U.W.; Ruuskanen, P.V.; Voloshin, S.A. Radial and elliptic flow at RHIC: Further predictions. Phys. Lett. 2001, B503, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Tsuda, K. Collective flow and two pion correlations from a relativistic hydrodynamic model with early chemical freeze out. Phys. Rev. 2002, C66, 054905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romatschke, P.; Romatschke, U. Viscosity Information from Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: How Perfect is the Fluid Observed at RHIC? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 172301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzum, M. Flow fluctuations and long-range correlations: Elliptic flow and beyond. J. Phys. 2011, G38, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Bass, S.A.; Heinz, U.; Hirano, T.; Shen, C. 200 A GeV Au+Au collisions serve a nearly perfect quark-gluon liquid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 192301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Heinz, U.W.; Liu, J. Mode-coupling effects in anisotropic flow in heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2016, C93, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, N. Beam energy dependence of the anisotropic flow coefficients vn. PoS 2018, CPOD2017, 005. [Google Scholar]
- Magdy, N. Viscous Damping of Anisotropic Flow in 7.7–200 GeV Au+Au Collisions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 779, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, B.; Jeon, S.; Gale, C. Anisotropic flow in = 2.76 TeV Pb+Pb collisions at the LHC. Phys. Lett. 2011, B702, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaney, D.; Yan, L. Non linearities in the harmonic spectrum of heavy ion collisions with ideal and viscous hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 2012, C86, 044908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardim, F.G.; Grassi, F.; Luzum, M.; Ollitrault, J.Y. Anisotropic flow in event-by-event ideal hydrodynamic simulations of = 200 GeV Au+Au collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 202302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, R.A.; Reynolds, D.; Taranenko, A.; Ajitanand, N.N.; Alexander, J.M.; Liu, F.H.; Gu, Y.; Mwai, A. Acoustic scaling of anisotropic flow in shape-engineered events: Implications for extraction of the specific shear viscosity of the quark gluon plasma. J. Phys. 2016, G43, 10LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, S.; Zhang, Y. Flow study in relativistic nuclear collisions by Fourier expansion of Azimuthal particle distributions. Z. Phys. C 1996, 70, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poskanzer, A.M.; Voloshin, S.A. Methods for analyzing anisotropic flow in relativistic nuclear collisions. Phys. Rev. 1998, C58, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, N. Beam-energy dependence of the azimuthal anisotropic flow from RHIC. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09640. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, J.; Adamczyk, L.; Adams, J.R.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Alekseev, I.; Anderson, D.M.; Aoyama, R.; et al. Azimuthal Harmonics in Small and Large Collision Systems at RHIC Top Energies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 172301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, N. Collision system and beam energy dependence of anisotropic flow fluctuations. Nucl. Phys. 2019, A982, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, L.; Adams, J.R.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Ajitanand, N.N.; Alekseev, I.; Anderson, D.M.; Aoyama, R.; et al. Azimuthal anisotropy in Cu+Au collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. 2018, C98, 014915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, L.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Ajitanand, N.N.; Alekseev, I.; Anderson, D.M.; Aoyama, R.; Aparin, A.; et al. Harmonic decomposition of three-particle azimuthal correlations at energies available at the BNL Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. Phys. Rev. 2018, C98, 034918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, B.; Roland, G. Collision geometry fluctuations and triangular flow in heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2010, C81, 054905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrchyan, S.; Khachatryan, V.; Sirunyan, A.M.; Tumasyan, A.; Adam, W.; Bergauer, T.; Dragicevic, M.; Eroe, J.; Fabjan, C.; Friedl, M.; et al. Measurement of higher-order harmonic azimuthal anisotropy in PbPb collisions at = 2.76 TeV. Phys. Rev. 2014, C89, 044906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, B.; Back, B.B.; Baker, M.D.; Ballintijn, M.; Barton, D.S.; Betts, R.R.; Bindel, R.; Busza, W.; Chetluru, V.; Garcia, E.; et al. Importance of correlations and fluctuations on the initial source eccentricity in high-energy nucleus-nucleus collisions. Phys. Rev. 2008, C77, 014906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, B.; Roland, C.; Seals, H.; Wolfs, F.L.H.; Roland, G.; Verdier, R.; Loizides, C.; Holynski, R.; Manly, S.; Li, W.; et al. Non-flow correlations and elliptic flow fluctuations in gold-gold collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. 2010, C81, 034915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollitrault, J.Y.; Poskanzer, A.M.; Voloshin, S.A. Effect of flow fluctuations and nonflow on elliptic flow methods. Phys. Rev. 2009, C80, 014904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.; Adamczyk, L.; Adams, J.R.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Ajitanand, N.N.; Alekseev, I.; Anderson, D.M.; et al. Correlation Measurements Between Flow Harmonics in Au+Au Collisions at RHIC. Phys. Lett. 2018, B783, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Heinz, U.W. Event-by-event shape and flow fluctuations of relativistic heavy-ion collision fireballs. Phys. Rev. 2011, C84, 024911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adare, A.; Afanasiev, S.; Aidala, C.; Ajitanand, N.N.; Akiba, Y.; Al-Bataineh, H.; Alexander, J.; Aoki, K.; Aramaki, Y.; Atomssa, E.T.; et al. Measurements of Higher-Order Flow Harmonics in Au+Au Collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 252301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aad, G.; Abbott, B.; Abdallah, J.; Khalek, S.A.; Aben, R.; Abi, B.; Abolins, M.; AbouZeid, O.S.; Abramowicz, H.; Abreu, H.; et al. Measurement of event-plane correlations in = 2.76 TeV lead-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector. Phys. Rev. 2014, C90, 024905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aad, G.; Abajyan, T.; Abbott, B.; Abdallah, J.; Khalek, S.A.; Abdelalim, A.A.; Aben, R.; Abi, B.; Abolins, M.; AbouZeid, O.S.; et al. Measurement of the correlation between flow harmonics of different order in lead-lead collisions at = 2.76 TeV with the ATLAS detector. Phys. Rev. 2015, C92, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, H.; Denicol, G.S.; Holopainen, H.; Huovinen, P. Event-by-event distributions of azimuthal asymmetries in ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2013, C87, 054901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardim, F.G.; Noronha-Hostler, J.; Luzum, M.; Grassi, F. Effects of viscosity on the mapping of initial to final state in heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2015, C91, 034902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Centrality dependence of mapping the hydrodynamic response to the initial geometry in heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2015, C92, 024904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, H.; Niemi, H.; Eskola, K.J. Event-by-event hydrodynamics and elliptic flow from fluctuating initial state. Phys. Rev. 2011, C83, 034901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.Y.; Petersen, H.; Bass, S.A.; Muller, B. Translation of collision geometry fluctuations into momentum anisotropies in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2010, C82, 064903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, C.; Jeon, S.; Schenke, B.; Tribedy, P.; Venugopalan, R. Event-by-event anisotropic flow in heavy-ion collisions from combined Yang-Mills and viscous fluid dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 012302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lacey, R.A. Acoustic scaling of linear and mode-coupled anisotropic flow; implications for precision extraction of the specific shear viscosity. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, N.; Dinh, P.M.; Ollitrault, J.Y. A New method for measuring azimuthal distributions in nucleus-nucleus collisions. Phys. Rev. 2001, C63, 054906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Snellings, R. Eccentricity fluctuations and its possible effect on elliptic flow measurements. arXiv 2003, arXiv:0312008. [Google Scholar]
- Manly, S.; Phobos, C. System size, energy and pseudorapidity dependence of directed and elliptic flow at RHIC. Nucl. Phys. 2006, A774, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, S.A. Toward the energy and the system size dependece of elliptic flow: Working on flow fluctuations. In Proceedings of the 22nd Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (WWND 2006), La Jolla, CA, USA, 11–19 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gardim, F.G.; Grassi, F.; Hama, Y.; Luzum, M.; Ollitrault, J.Y. Directed flow at mid-rapidity in event-by-event hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 2011, C83, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, B.; Shen, C.; Tribedy, P. Hybrid Color Glass Condensate and hydrodynamic description of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider small system scan. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 803, 135322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, K. Strings, pomerons, and the venus model of hadronic interactions at ultrarelativistic energies. Phys. Rep. 1993, 232, 87–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Schenke, B. Dynamical initial state model for relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 97, 024907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Asakawa, M.; Hirano, T.; Kitazawa, M.; Morita, K.; Murase, K.; Nara, Y.; Nonaka, C.; Ohnishi, A. Dynamically integrated transport approach for heavy-ion collisions at high baryon density. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 98, 024909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohs, J.; Ryu, S.; Elfner, H. Particle Production via Strings and Baryon Stopping within a Hadronic Transport Approach. J. Phys. G 2020, 47, 065101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinheimer, J.; Mitrovski, M.; Schuster, T.; Petersen, H.; Bleicher, M.; Stoecker, H. Strangeness fluctuations and MEMO production at FAIR. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 676, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Sievert, M.D.; Wertepny, D.E.; Noronha-Hostler, J. Initial state fluctuations of QCD conserved charges in heavy-ion collisions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.10272. [Google Scholar]
- Giacalone, G.; Noronha-Hostler, J.; Ollitrault, J.Y. Relative flow fluctuations as a probe of initial state fluctuations. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 054910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, P.; Mantovani Sarti, V.; Noronha, J.; Noronha-Hostler, J.; Parotto, P.; Vazquez, I.P.; Ratti, C. Effect of the QCD equation of state and strange hadronic resonances on multiparticle correlations in heavy ion collisions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, L.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Alekseev, I.; Aparin, A.; Arkhipkin, D.; Aschenauer, E.C.; Averichev, G.S.; et al. Centrality and transverse momentum dependence of elliptic flow of multistrange hadrons and ϕ meson in Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 062301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.; Strobele, H.; Denisov, A.; Garcia, E.; Murray, M.; White, S. The RHIC zero-degree calorimeters. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 2001, A461, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Ewigleben, A.; Garrett, S.; He, W.; Huang, T.; Jacobs, P.M.; Ju, X.; Lisa, M.A.; Lomnitz, M.; Pak, R.; et al. The STAR Event Plane Detector. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.05243. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.W.; Ko, C.M.; Li, B.A.; Zhang, B.; Pal, S. A Multi-phase transport model for relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2005, C72, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L.; Lin, Z.W. Predictions for = 5.02 TeV Pb+Pb Collisions from a Multi-Phase Transport Model. Phys. Rev. 2016, C93, 054911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L. Decomposition of the jet fragmentation function in high-energy heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 2013, C88, 021902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L. Medium modifications of jet shapes in Pb+Pb collisions at = 2.76 TeV within a multiphase transport model. Phys. Rev. 2014, C89, 024902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzdak, A.; Ma, G.L. Elliptic and triangular flow in p+Pb and peripheral Pb+Pb collisions from parton scatterings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 252301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.W.; Huo, P.; Jia, J.; Ma, G.L. Multiparticle azimuthal cumulants in p+Pb collisions from a multiphase transport model. Phys. Rev. 2018, C98, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, N.; Nie, M.W.; Huang, L.; Ma, G.L.; Lacey, R. An extended (ΔS2) correlator for detecting and characterizing the Chiral Magnetic Wave. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.02396. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.N.; Gyulassy, M. HIJING: A Monte Carlo model for multiple jet production in p p, p A and A A collisions. Phys. Rev. 1991, D44, 3501–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. ZPC 1.0.1: A Parton cascade for ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1998, 109, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.A.; Ko, C.M. Formation of superdense hadronic matter in high-energy heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. 1995, C52, 2037–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilandzic, A.; Snellings, R.; Voloshin, S. Flow analysis with cumulants: Direct calculations. Phys. Rev. 2011, C83, 044913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandzic, A.; Christensen, C.H.; Gulbrandsen, K.; Hansen, A.; Zhou, Y. Generic framework for anisotropic flow analyses with multiparticle azimuthal correlations. Phys. Rev. 2014, C89, 064904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhou, M.; Trzupek, A. Revealing long-range multiparticle collectivity in small collision systems via subevent cumulants. Phys. Rev. 2017, C96, 034906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdošová, K. Investigations of anisotropic collectivity using multi-particle correlations in pp, p–Pb and Pb–Pb collisions. Nucl. Phys. 2017, A967, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R. Elliptic Flow: A Brief Review. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, S.A.; Poskanzer, A.M.; Tang, A.; Wang, G. Elliptic flow in the Gaussian model of eccentricity fluctuations. Phys. Lett. 2008, B659, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Anisotropic flow in Au Au and Cu Cu at 62-GeV and 200-GeV. Nucl. Phys. A 2006, 774, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Ma, G.; Ma, Y. Anisotropic flow and flow fluctuations for Au + Au at = 200 GeV in a multiphase transport model. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 044907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L.; Bzdak, A. Long-range azimuthal correlations in proton–proton and proton–nucleus collisions from the incoherent scattering of partons. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 739, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Nasim, M. Scaling of elliptic flow in heavy-ion collisions with the number of constituent quarks in a transport model. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 93, 034908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, K.; Singha, S.; Nasim, M.; Mohanty, B. Study of re-scattering effect on elliptic flow and production of resonances using AMPT. DAE Symp. Nucl. Phys. 2017, 62, 962–963. [Google Scholar]
- Magdy, N. Collision System Dependence of Anisotropic Flow, Flow Fluctuations and Mixed Harmonic Correlations at STAR Energies; Quark Matter; Quark Matter; Stony Brook University: Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).