Abstract
The relativistic jets of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) might be powered by a black-hole (BH) hyperaccretion system. The inherent asymmetry in these jets generates recoil forces, inducing oscillations and positional deviations of the BH from equilibrium. In this study, we explore the influence of different initial BH mass, spin, and mass accretion rate, as well as their evolutions on the dynamical properties of BH under the effect of asymmetric jets. Our results reveal that the initial mass and accretion rate significantly impact the BH’s acceleration, velocity, and displacement, while the different initial spin plays a negligible role in shaping the overall dynamical evolution. Additionally, we calculate the gravitational wave (GW) strains associated with the asymmetric jets, finding that the resulting GW signals are too weak to be detected, even for nearby GRBs. These findings provide critical insights into the dynamical response of BHs to asymmetric jets and the associated GW radiation, advancing our understanding of BH physics in GRBs.
1. Introduction
On 17 August 2017, the gravitational wave (GW) event GW170817 was detected by aLIGO and Virgo, followed by the identification of its electromagnetic counterparts through subsequent observations [1]. This joint detection of GWs and electromagnetic signals marked the dawn of the multimessenger astronomy era. This breakthrough has significantly influence diverse research fields, including gravitational physics, cosmology, high-energy astrophysics, and nuclear physics.
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) arise from massive collapsars and compact object mergers, often associated with core-collapse supernovae (CCSNe) and kilonovae, respectively [1,2,3,4,5,6]. GRBs evolve through three stages: (1) the collapse of massive stars or the merging of compact binaries leads to the formation of the “central engine”, maybe consisting of a black hole (BH) surrounded by a hyperaccretion disk; (2) the central engine generates intermittent ultra-relativistic jets; and (3) energy dissipation within these relativistic jets produces prompt gamma-ray emission and multi-band afterglows. It is widely believed that these jets are powered either by the Blandford–Znajek (BZ) process [7] or by the neutrino annihilation process [8,9,10,11] of the central engines. However, distinguishing between these two mechanisms based solely on electromagnetic observations remains challenging. Multimessenger radiation can offer complementary insights into the same astrophysical sources, addressing limitations inherent to studying these events through a single channel.
The prompt phase-light curves of GRBs are frequently variable and irregular [2,12,13], reflecting the inherently inhomogeneous activity of the central engine. This variability arises from several factors: (1) accretion instabilities, where fluctuations in the accretion rate onto the BH generate intermittent jets [2]; (2) magnetic processes, such as reconnection events in the accretion disk or jet, releasing energy sporadically [13]; and (3) feedback mechanisms, where energy released by the jet interacts with the surrounding material, creating a feedback loop that enhances variability [14]. In a BH hyperaccretion scenario, it is reasonable to assume that random asymmetric jets may be irregular in direction, luminosity, or morphology, rather than being neatly collimated and symmetric along the rotational axis, and are generated during the accretion process or the interaction with the ejecta, envelopes, and circumstellar environment. GWs can be produced during GRB events in three distinct phases. The first phase involves GW radiation generated during the formation of a compact object, typically associated with compact binary mergers or collapsar events. In this phase, the asymmetric collapse of a massive star or the merger of two compact objects results in GWs that carry away angular momentum and energy, potentially detectable by future GW detectors [15,16,17,18,19]. The second phase arises from the acceleration of relativistic ejecta, which occurs during the GRB’s central engine activity. As the ejecta is accelerated to ultra-relativistic velocities, gravitational radiation is emitted due to the high velocities and complex dynamics of the system [20,21,22,23]. The third is from the central engine [11]. GWs can also be emitted when asymmetric bipolar jets exert a net recoil force on the central BH. In this work, we investigates the production of GWs triggered by asymmetric jets in GRBs and explores the dynamic activities of central BH.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we explore models of BH hyperaccretion systems with asymmetric jets and their role in GW production in GRBs. In Section 3, we present the results on the dynamical properties of BH hyperaccretion systems, focusing on variations in the initial BH mass, spin, and mass accretion rate, as well as the gravitational radiation generated by asymmetric jets. A brief summary is given in Section 4.
2. Model
A GRB event typically emits asymmetric jets. The luminosity of the jet directed towards Earth is denoted as , while the luminosity of the jet propagating in the opposite direction is expressed as . The asymmetry in the jet luminosities can be quantified as [24]
where represents the asymmetry factor. We assume random variations within of at each point in time which is a random integer multiple of as well as the typically minimum timescales of the GRB pulses. of corresponds to the typical amplitude difference of GRB light curves. Following Kumar et al. (2008) [25], we expect to decline approximately as in the scenario of massive collapsars. Then, using the fitting formula of neutrino annihilation luminosity in Popham et al. (1999) [8], we can obtain the luminosity of the jet, starting with an initial value of and decaying over time, which can be expressed as
The jet luminosity can be roughly considered as the initial neutrino annihilation luminosity, which is related to the mass accretion rate by , where [9]. Consequently, this asymmetry induces a recoil force on the central compact object, given by
where c is the speed of light. The recoil force generated by the random variations in luminosity asymmetry of GRBs significantly affects the dynamical properties of the BH. The recoil force exhibits random oscillations with both positive and negative values, stabilizing around zero as the luminosity decreases. Consequently, the BH eventually reaches a steady state with minor random fluctuations. The corresponding acceleration of the BH can be expressed as [26]
where M is the BH mass. The velocity and displacement are then derived by integrating the acceleration, where and , and corresponds the initial states. The BH mass evolves with time due to mass accretion and is described by [26]
where is the mass accretion rate of the BH, which starts with an initial value of and correlates with time, which determines the evolution of the jet luminosity.
The BH spin parameter, , is defined as [26]
where J represents the angular momentum of the BH. The angular momentum also evolves with the mass accretion rate, as given by [26]
Here, and are the specific energy and angular momentum at the marginally stable orbit, respectively, defined as
and
where is the radius of the marginally stable orbit, given by
where
and
Using the above equations, the evolution of the BH spin parameter can be derived as [26]
For the BH-disk system, although the weak gravitational field and Newtonian limit are invalid, the BH is approximated as a bulk object and treated dynamically similar to the NS-disk system. By simulating the waveform under trace-reversed metric perturbation and using the same formalism as for the NS-disk case, the GW amplitude is estimated approximately, providing a rough calculation without requiring a full relativistic treatment [24,27]. The amplitude of GWs for the BH-disk case can be estimated as
where = 10 kpc represents the distance between the wave source and Earth, and R denotes the radius of the BH’s outer horizon [10]. The expression for R is given by
We explore the dynamical properties of BHs and the gravitational strains that arise in the asymmetric jets. From the BH’s mass and the net luminosity of the jet, we can calculate the acceleration, velocity, and displacement of the BH relative to equilibrium. Furthermore, the initial conditions of the BH’s mass, spin, and mass accretion rate affect the BHs’ dynamical properties and their gravitational radiation emission.
3. Results
The results presented in this section were derived through analytical modeling and numerical calculations. The evolution of the BH’s dynamical properties under the influence of random asymmetric jets was modeled using the motion equations derived above.
3.1. The Effect of Initial Mass Accretion Rates
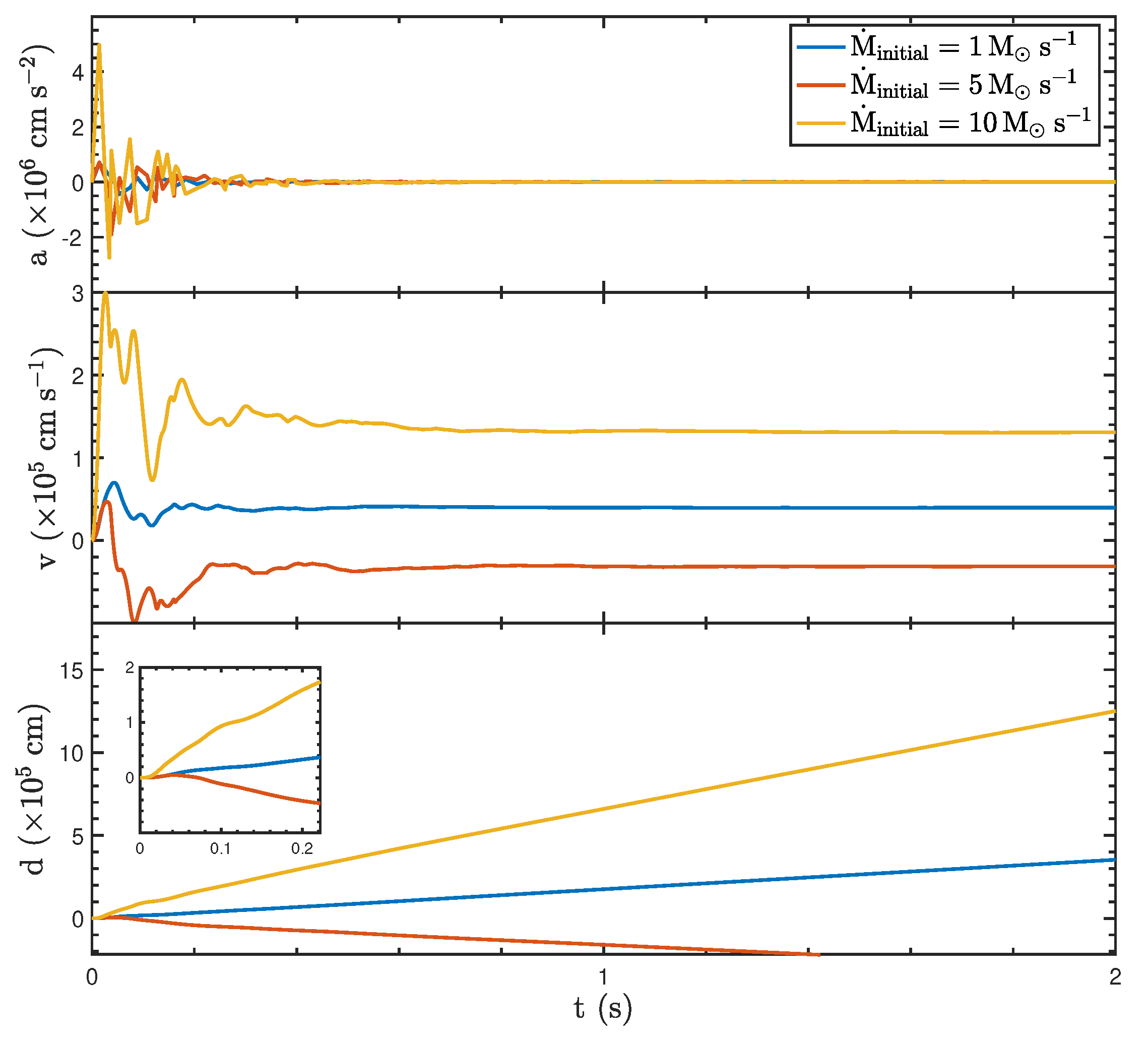
To explore the effects of different initial mass accretion rates on the BH properties, we consider 1, 5, and 10 . While accretion rates beyond 10 are not explored in this study, they may be excluded due to physical constraints inherent to GRB progenitor systems or the limitations of the numerical models employed. For context, GRBs arising from collapsar or compact binary merger scenarios are generally expected to exhibit accretion rates within this range [8]m where the initial BH mass and the spin parameter are and , respectively. As shown in Figure 1, at a low accretion rate of (blue curve), the BH experiences minimal oscillations in acceleration, velocity, and displacement. The acceleration, velocity, and displacement remain nearly constant at zero, indicating weak recoil forces and stable dynamical properties, maintaining the BH close to its equilibrium position. At a middle-point accretion rate of (red curve), the acceleration exhibits pronounced oscillations during the early phase (), driven by the increased asymmetry in the jet luminosity. These oscillations gradually decay over time. The velocity undergoes significant fluctuations, reflecting the strong recoil forces acting on the BH, before stabilizing to an approximately constant value. The displacement indicates a noticeable positional shift due to the recoil effect. At a high accretion rate of (yellow curve), the dynamic impact is further amplified. The acceleration exhibits the largest oscillation amplitude, particularly in the early phase (), as the jet asymmetry becomes more pronounced. This leads to strong velocity oscillations, whose peak has a higher value compared to the moderate accretion rate. The displacement reaches its maximum value, with a rapid increase during the early phase, showing the strongest recoil effect among the three scenarios.
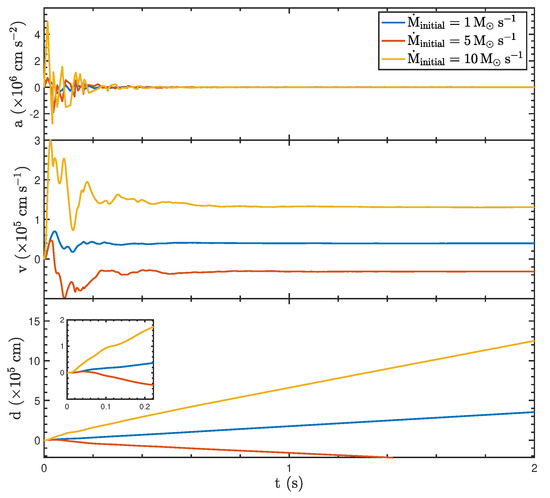
Figure 1.
The dynamic properties of the BH with different initial mass accretion rates of 1, 5, and 10 , an initial mass of , and a spin parameter of .
Overall, as increases, the asymmetric luminosity-driven recoil force intensifies, resulting in more significant fluctuations in acceleration and velocity during the initial stages and the greater displacement of the BH from its equilibrium position during the early phase. These results highlight the critical role of the accretion rate in shaping the dynamical properties of BHs.
3.2. The Effect of Initial Spins
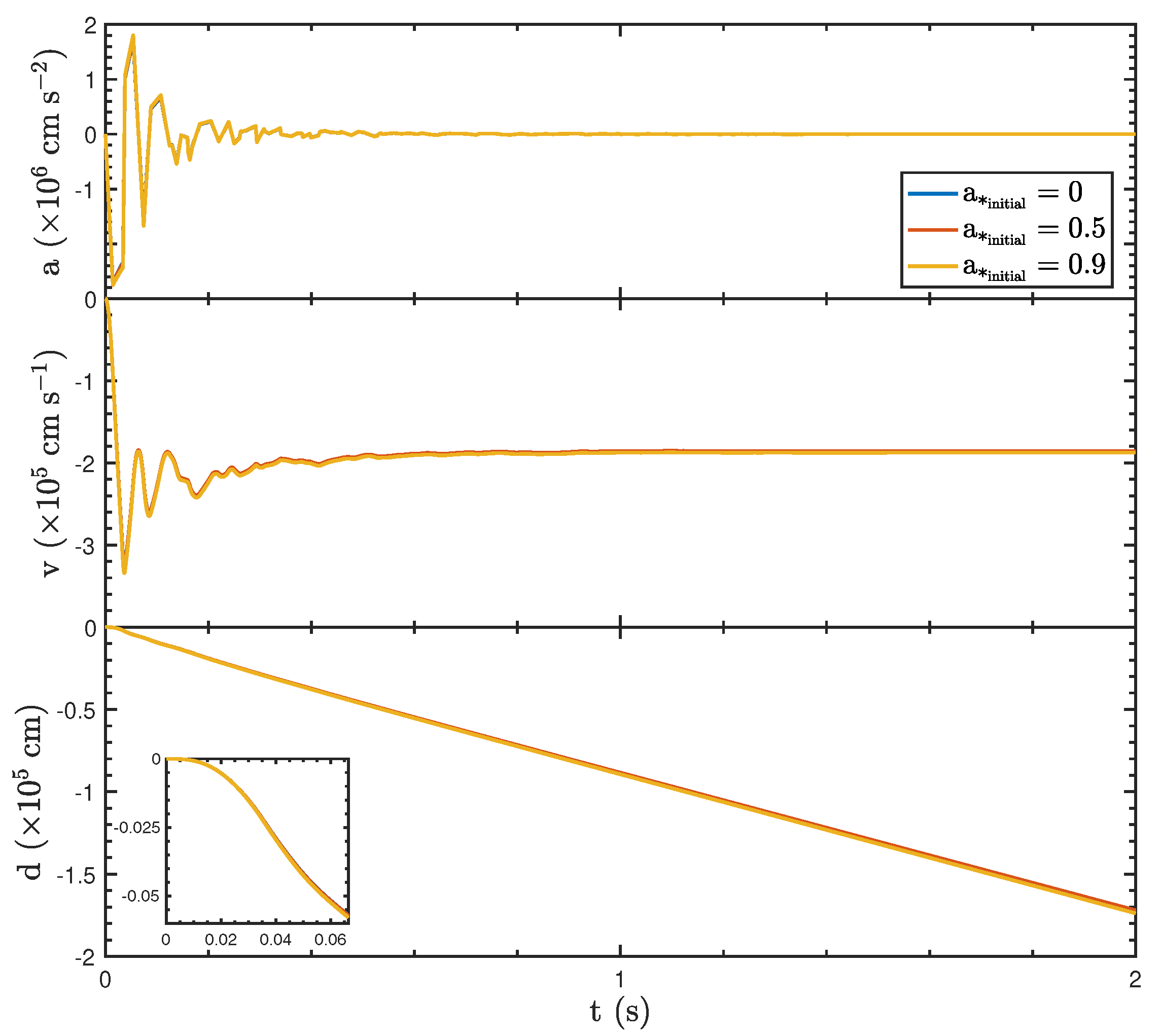
The dynamical properties of the BH under different initial spin parameters ()—0, 0.5, and 0.9—reveal the minimal influence of spin on the BH’s acceleration, velocity, and displacement, where the initial BH mass and initial mass accretion rate are and , respectively. As shown in Figure 2, the acceleration (a) exhibits oscillatory behavior during the early phase () due to asymmetric jet luminosity. However, the amplitude and frequency of these oscillations remain consistent across all spin values, stabilizing to near zero over time (). Similarly, the velocity (v), derived by integrating the acceleration, follows a uniform trend for all spins, showing initial fluctuations before settling to a constant negative value. Consequently, the displacement (d), obtained from the velocity, exhibits a linear decrease after the initial oscillatory phase, with no significant divergence in the trajectories for different spin values. The inset plot highlights the early evolution of displacement, confirming that variations in do not significantly affect the BH’s positional dynamics. These results suggest that the BH with different initial spin exerts only a negligible influence in shaping recoil processes during GRBs, given the very quick evolution of the BH spin for the hyperaccretion case.
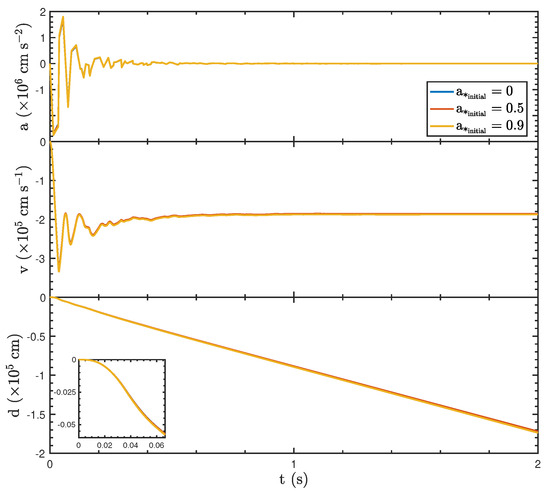
Figure 2.
The dynamic properties of the BH with different initial spin parameters, specifically , , and , while its initial mass and initial mass accretion rate are and , respectively.
3.3. The Effect of Initial Mass of the BH
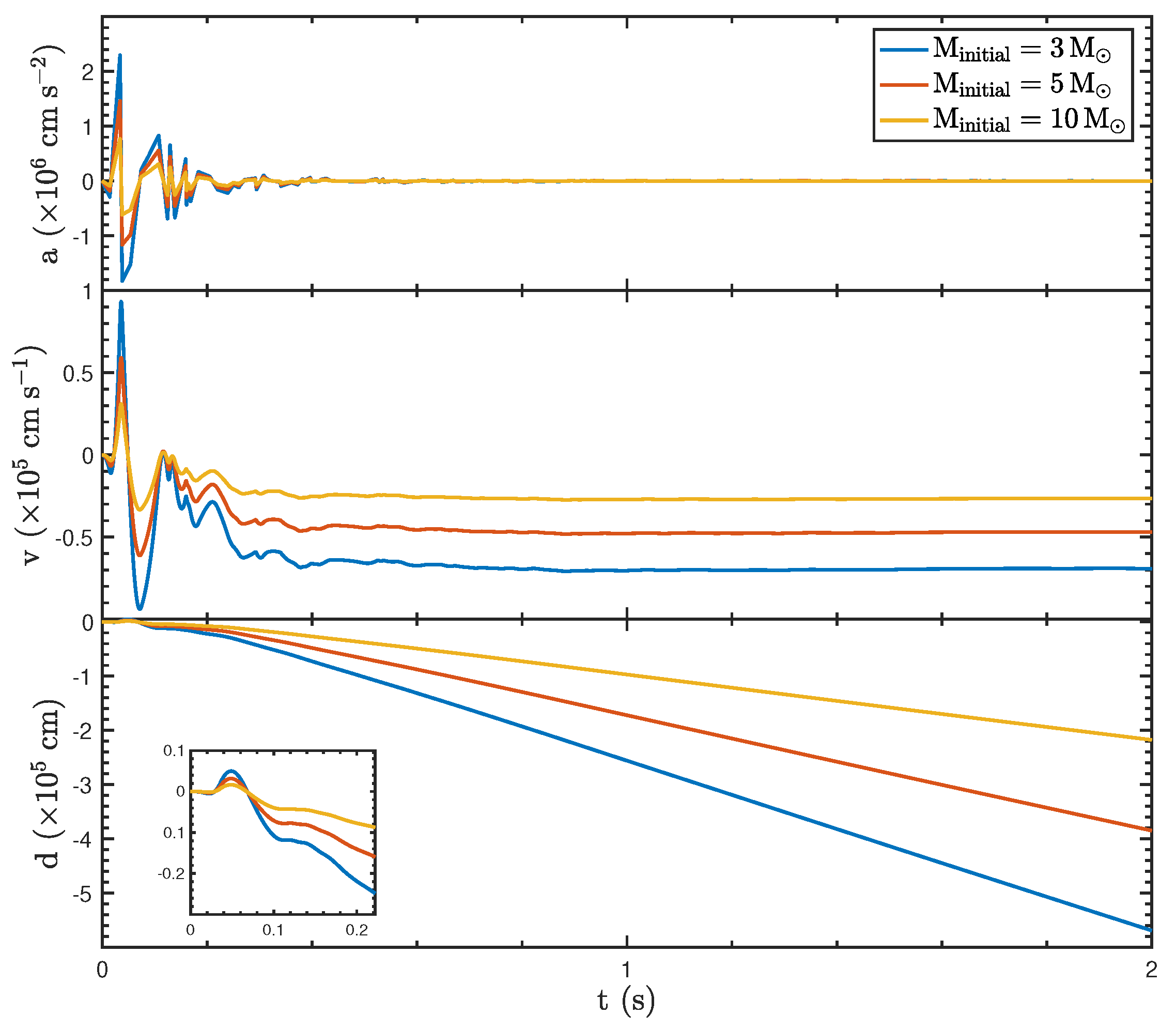
The dynamical properties of BHs under varying initial masses ( = 3, 5, and 10 ) with an initial mass accretion rate and a spin parameter are and , respectively, demonstrating the significant influence of mass on their response to asymmetric jet luminosity, as shown in Figure 3. The acceleration (a) exhibits oscillatory behavior in the early phase () due to the recoil force. Lower-mass BHs experience larger oscillation amplitudes, while higher-mass BHs show smaller amplitudes, reflecting the inverse relationship between mass and acceleration for a given recoil force. The velocity (v), derived from the acceleration, also shows mass-dependent behavior: BHs with lower masses exhibit larger velocity fluctuations and reach a more negative steady-state value compared to higher-mass BHs, which have reduced velocity amplitudes due to greater inertia. Similarly, the displacement (d), calculated by integrating the velocity, indicates that lower-mass BHs experience greater positional shifts, while higher-mass BHs exhibit more modest displacements, as highlighted in the inset.
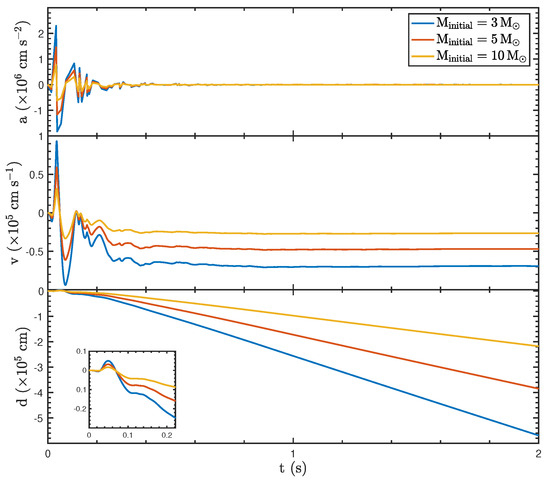
Figure 3.
The dynamic properties of the BH with different initial BH masses ( = 3, 5, and 10 ), an initial mass accretion rate of , and a spin parameter of .
Notably, differences in the initial BH mass affect only the magnitude of the dynamical parameters (acceleration, velocity, and displacement) and do not influence their temporal evolution trends. Since the initial luminosity is directly related to the mass accretion rate, the time-dependent change in luminosity remains consistent across the three cases. Consequently, the recoil force exhibits a similar trend over time for each scenario.
These results emphasize that the initial mass of the BH is a critical parameter in determining its dynamic response. Lower-mass BHs are more susceptible to recoil-induced acceleration, velocity changes, and positional shifts, whereas higher-mass BHs resist such effects due to their larger inertia. This study highlights the fundamental role of BH mass in modulating the observable dynamical properties of GRB systems and provides key insights into the recoil processes driven by asymmetric jet luminosity.
3.4. GW Production in BH Hyperaccretion System with Asymmetric Jets
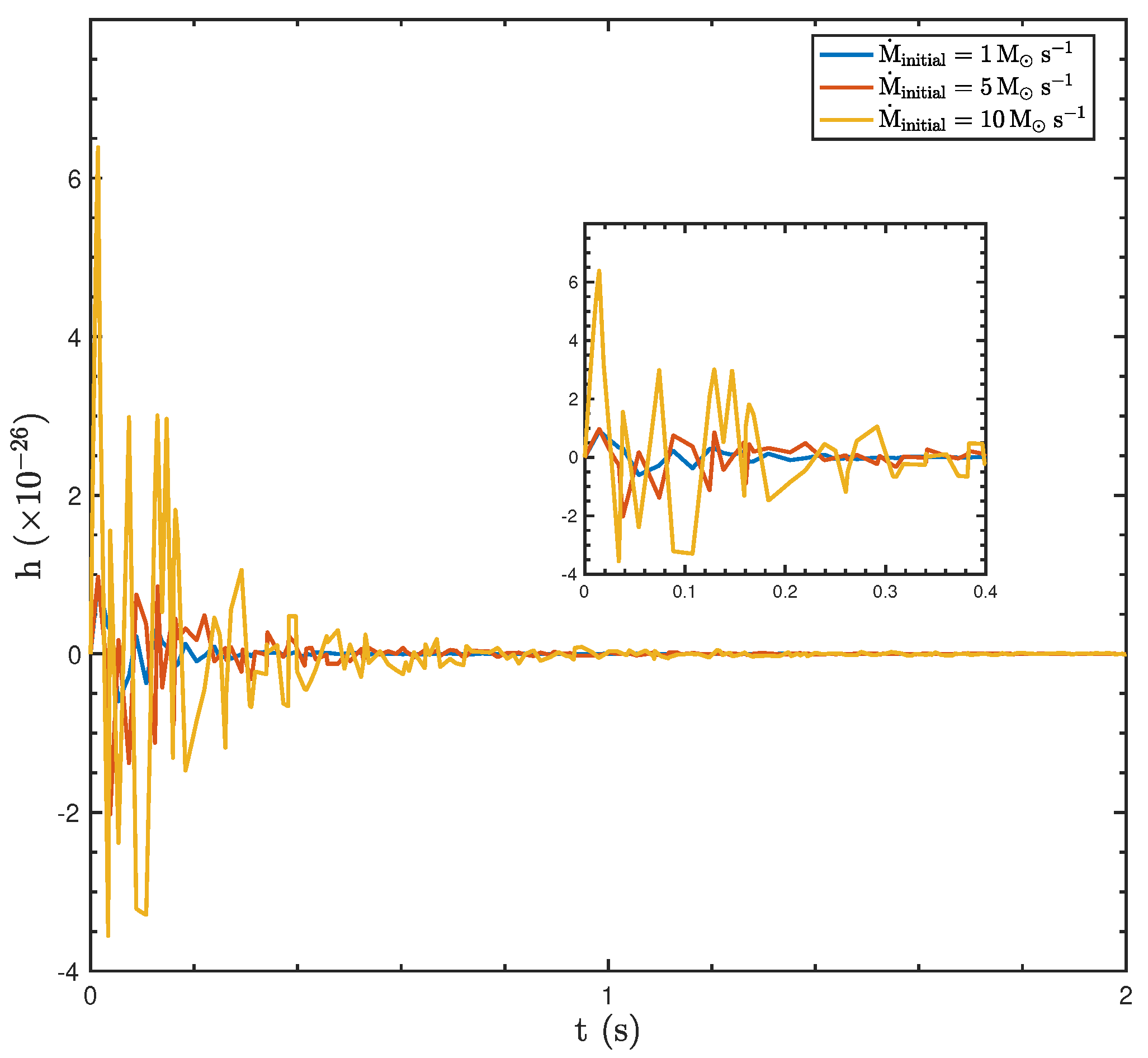
The GW amplitude generated by a BH–disk system exhibits significant variation depending on the initial mass accretion rate ( = 1, 5, and 10 ), where the initial BH mass and the spin parameter are and , respectively, as shown in Figure 4. GWs are produced by the expansion and compression of space–time caused by the acceleration of a massive object, such as a BH, with the recoil force arising from asymmetric jet luminosity playing a key role in the process. At a low accretion rate (), the GW amplitude remains nearly zero, reflecting negligible jet asymmetry and weak or undetectable GW signals. The maximum amplitude of the peaks for this accretion rate is . For a moderate accretion rate (), the GW amplitude exhibits noticeable oscillations during the early phase (), driven by jet asymmetry and the corresponding dynamic recoil forces. These oscillations diminish over time, and the amplitude stabilizes near zero as the jet luminosity decays. The maximum amplitude of the peaks in this case is . At a high accretion rate (), the GW amplitude displays the largest initial oscillations and sharp peaks, reaching up to , reflecting enhanced jet asymmetry and stronger recoil forces. However, such a signal remains challenging to detect with current gravitational wave observatories. Over time, the oscillations gradually subside, and the amplitude stabilizes.
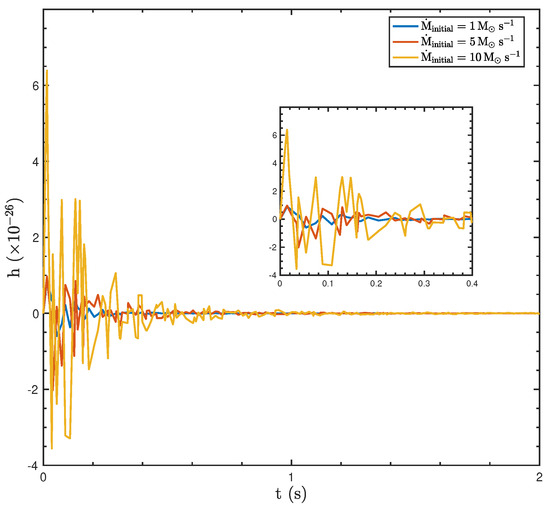
Figure 4.
The amplitude of GWs generated by asymmetric jets of BH hyperaccretion with varying initial mass accretion rates 1, 5, and 10 , an initial mass of , and a spin of .
The oscillatory behavior of the GW amplitude closely follows the evolution of the recoil force, as the two are proportional. Higher accretion rates produce stronger and more pronounced oscillations in the GW amplitude due to greater jet asymmetry and recoil forces, while lower accretion rates reduce recoil forces, and correspondingly smaller GW amplitudes. As the accretion rate decreases further and approaches zero, the recoil force and acceleration nearly vanish, resulting in negligible GW radiation. At this stage, the BH stabilizes dynamically, exhibiting only minor random fluctuations, and the jets become nearly symmetric. This symmetry leads to the gradual decline and dissipation of GW radiation.
These findings highlight the critical role of the accretion rate in shaping GW radiation and the interplay between accretion dynamics, jet asymmetry, and recoil forces. Current GW detection observatories, such as LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA, have sensitivities that can detect strains on the order of to for typical sources like binary BH and NS mergers [18,28,29]. These limits are significantly higher than the predicted GW amplitudes from BH hyperaccretion systems driven by asymmetric jets, which are on the order of . This provides valuable insights into the detectability of GWs from BH–disk systems and their connection to GRBs, emphasizing the importance of jet and accretion-driven processes in the generation of observable GW signals.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the dynamical properties of BH driven by asymmetric jets in GRBs, focusing on the interaction and evolution of the mass accretion rate, luminosity, spin, and initial mass. We examined how variations in these parameters affect the acceleration, velocity, and distance of the BH. Our findings highlight that random fluctuations in both luminosity and mass accretion rate induce complex, oscillatory motion in the BH trajectory, with stabilizing effects as the accretion rate decays over time. Additionally, we demonstrated that the initial mass of the BH plays a critical role in determining the magnitude of its acceleration, while variations in spin have minimal impact on long-term dynamics.
Furthermore, we explored the generation of GW radiation resulting from the accelerated motion of the BH. The amplitude of the wave radiation, directly related to the recoil force, was shown to depend on the mass accretion rate and luminosity. As the accretion rate decreases, the intensity of GW emission also declines, ultimately leading to a near-stable BH state with minimal GW production. This study provides insights into the relationship between BH dynamics and GW signals, contributing to the field of multi-messenger astrophysics.
Overall, this study enhances the understanding of BH dynamics in GRBs and offers insights into the relationship between asymmetric jet-driven motion and GW generation. The weak GW signal reflects the limited asymmetry and energy of these jets, contrasting with the stronger emissions from binary mergers. Detecting such nearby faint signals would require future detectors with enhanced sensitivity, such as the Einstein Telescope [30]. Our results underscore the importance of mass accretion dynamics in shaping BH behavior and highlight the potential for observing GW radiation from these processes with current and future detectors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L.; methodology, T.L.; software, Z.-O.Y.; validation, Z.-O.Y., Y.-Q.Q. and T.L.; formal analysis, Z.-O.Y. and Y.-Q.Q.; investigation, Z.-O.Y.; data curation, Z.-O.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.-O.Y. and Y.-Q.Q.; writing—review and editing, Y.-Q.Q. and T.L.; visualization, Z.-O.Y.; supervision, T.L.; project administration, T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 12173031, 12494572 and 12221003.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated in this work will be shared upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Z.-O.Y. acknowledges support from the Undergraduate Innovation Program of Xiamen University Malaysia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Gravitational Waves and Gamma-Rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, A.I.; Woosley, S.E. Collapsars: Gamma-Ray Bursts and Explosions in “Failed Supernovae”. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; Poznanski, D.; Kasen, D.; Barnes, J.; Zaltzman, M.; Vasylyev, S.; Maoz, D.; et al. Optical Emission from a Kilonova Following a Gravitational-Wave-Detected Neutron Star Merger. Nature 2017, 551, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Simon, J.D.; Ulloa, N.; Kasen, D.; et al. Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the Optical Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source. Science 2017, 358, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D. Kilonovae. Living Rev. Relativ. 2017, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. The Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-139-22653-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic Extraction of Energy from Kerr Black Holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popham, R.; Woosley, S.E.; Fryer, C. Hypernovae and Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gu, W.-M.; Xue, L.; Lu, J.-F. Structure and Luminosity of Neutrino-cooled Accretion Disks. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Fukue, J.; Mineshige, S. Black Hole Accretion Disks: Towards a New Paradigm; Kyoto University Press: Kyoto, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Gu, W.-M.; Zhang, B. Neutrino-Dominated Accretion Flows as the Central Engine of Gamma-Ray Bursts. New Astron. Rev. 2017, 79, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A. Gamma-Ray Bursts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 33, 415–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, H. The Internal-collision-induced Magnetic Reconnection and Turbulence (ICMART) Model of Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2011, 726, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Piran, T.; Sari, R. Can Internal Shocks Produce the Variability in Gamma-Ray Bursts? Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, C.L.; New, K.C.B. Gravitational Waves from Gravitational Collapse. Living Rev. Relativ. 2003, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, K.; Sato, K.; Takahashi, K. Explosion Mechanisms, Neutrino Bursts, and Gravitational Waves in Core-Collapse Supernovae. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.D. The Gravitational Wave Signature of Core-collapse Supernovae. Class. Quantum Gravity 2009, 26, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalis, E.B.; Ori, A. Emission of Gravitational Radiation from Ultrarelativistic Sources. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 064018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. Gravitational Radiation from Gamma-Ray Bursts. arXiv 2001, arXiv:astro-ph/0102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. Gamma-Ray Bursts-A Primer for Relativists. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2002, 34, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sago, N.; Ioka, K.; Nakamura, T.; Yamazaki, R. Gravitational Wave Memory of Gamma-Ray Burst Jets. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Li, X.-D.; Hu, Y.-M.; Peng, F.-K.; Li, M. Gravitational Waves Induced by the Asymmetric Jets of Gamma-ray Bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Narayan, R.; Johnson, J.L. Mass Fall-Back and Accretion in the Central Engine of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 388, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.-J.; Liu, T.; Gu, W.-M.; Lin, D.-B.; Sun, M.-Y.; Wu, X.-F.; Lu, J.-F. Time Evolution of Flares in GRB 130925A: Jet Precession in a Black Hole Accretion System. Astrophys. J. 2014, 781, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, J.; Anderson, W. Gravitational-Wave Physics and Astronomy: An Introduction to Theory, Experiment, and Data Analysis; Wiley Series on Cosmology; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3527408863. [Google Scholar]
- Acernese, F.; Agathos, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Aisa, D.; Allemandou, N.; Allocca, A.; Amarni, J.; Astone, P.; Balestri, G.; Ballardin, G.; et al. Advanced Virgo: A Second-Generation Gravitational-Wave Detector. Class. Quantum Gravity 2014, 32, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, T.; Ando, M.; Arai, K.; Arai, Y.; Araki, S.; Araya, A.; Aritomi, N.; Aso, Y.; Bae, S.; Bae, Y.; et al. Overview of KAGRA: Detector Design and Construction History. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2021, 2021, 05A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hild, S.; Abernathy, M.; Acernese, F.E.; Amaro-Seoane, P.; Andersson, N.; Arun, K.; Barone, F.; Barr, B.; Barsuglia, M.; Beker, M.; et al. Sensitivity Studies for Third-Generation Gravitational Wave Observatories. Class. Quantum Gravity 2011, 28, 094013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).