Study of Wide-Field-of-View X-ray Observations of the Virgo Cluster Using the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observations and Data Reduction
LEIA Observations
- Since the digital number (DN) of each event was only subtracted by the corresponding row’s median value on-board, the ground processing pipeline further subtracted the bias residual of each pixel stored in CALDB.
- The position of each event was converted to the celestial coordinates (J2000) using the satellite attitude and alignment matrix between the detector and the satellite. The nonlinear distortion due to the non-spherical shape of MPO was also corrected for in this step according to the result of the on-ground calibration performed at IHEP.
- The anomalous pixels stored in CALBD and their nearby pixels were flagged. New anomalous pixels (hot and flickering) were also searched for and flagged.
- A grade and a single PHA value were assigned to the event according to the DNs of the pixels around the event.
- The Pulse-Invariant (PI) value of each event was calculated according to the gain stored in CALDB.
- Single, double, triple, and quadruple events without any anomalous flag were selected for further processing. The geomagnetic cut-off rigidity (COR) was employed to remove the high background interval in the high-latitude region, i.e., . The earth elevation angle was required to be larger than 10 degrees to remove the effect of earth occultation. The angular distance to the nominal pointing should be smaller than 0.2 degrees to ensure the stabilization of the satellite.
- The pipeline generated an exposure map that accounts for bad CMOS pixels and columns, attitude variations, and telescope vignetting (optional) for event files.
- An image in the 0.5–4.0 keV band was accumulated for each CMOS using the cleaned events, and source detection was performed on each image to generate a source catalog.
- The light curve and spectrum of each source in the catalog were extracted. The pipeline also generated the corresponding Response Matrix File (RMF) and Ancillary Response Function (ARF) file, which accounted for the effective area, vignetting correction, and PSF correction.
3. Results
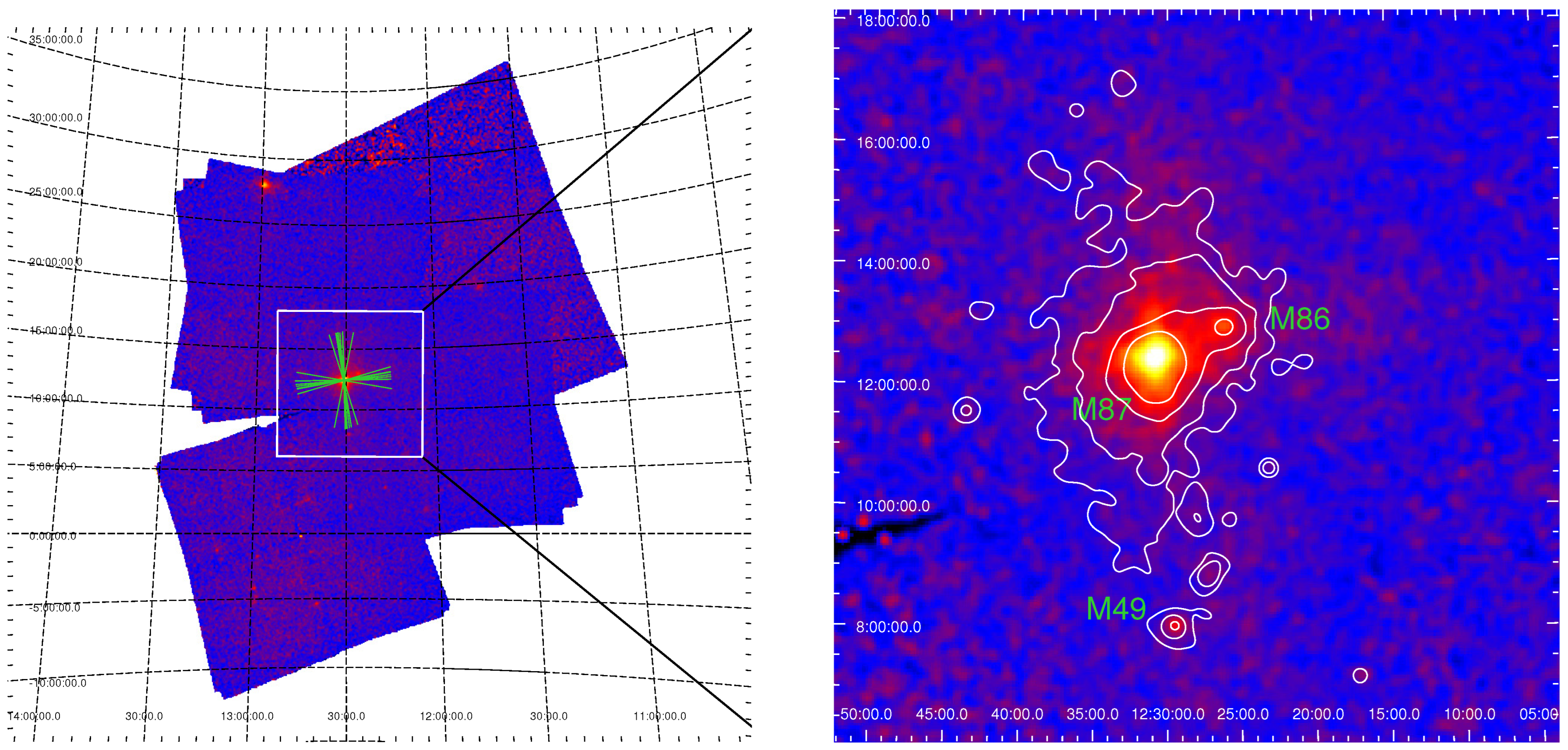
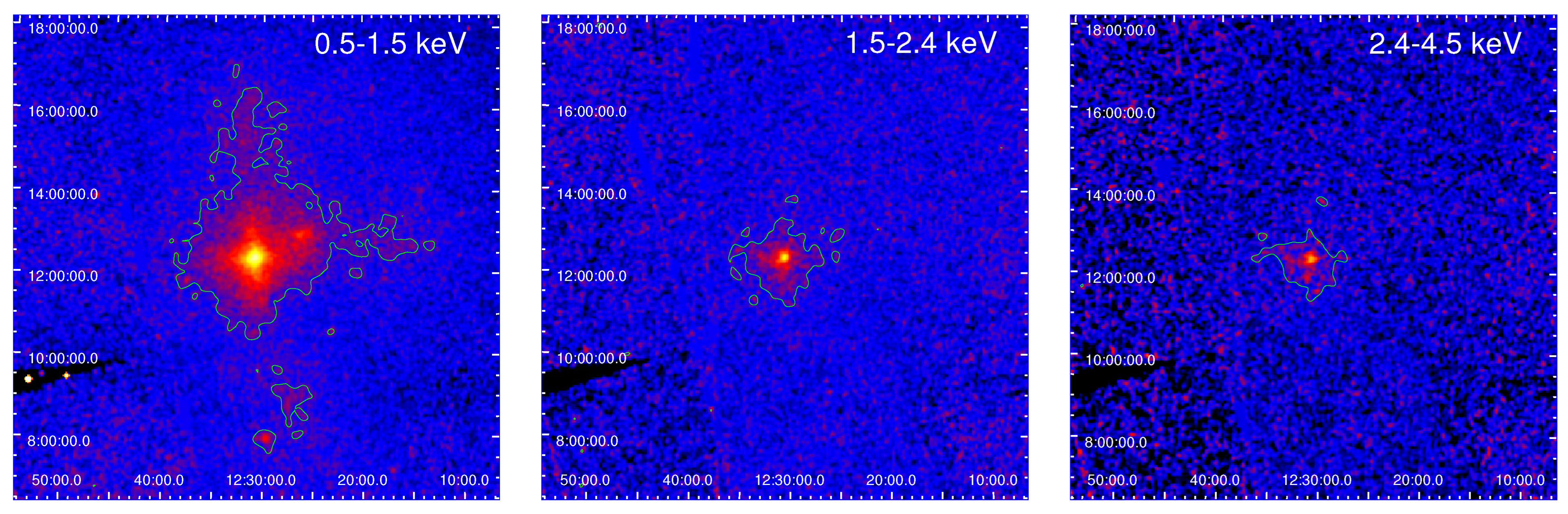
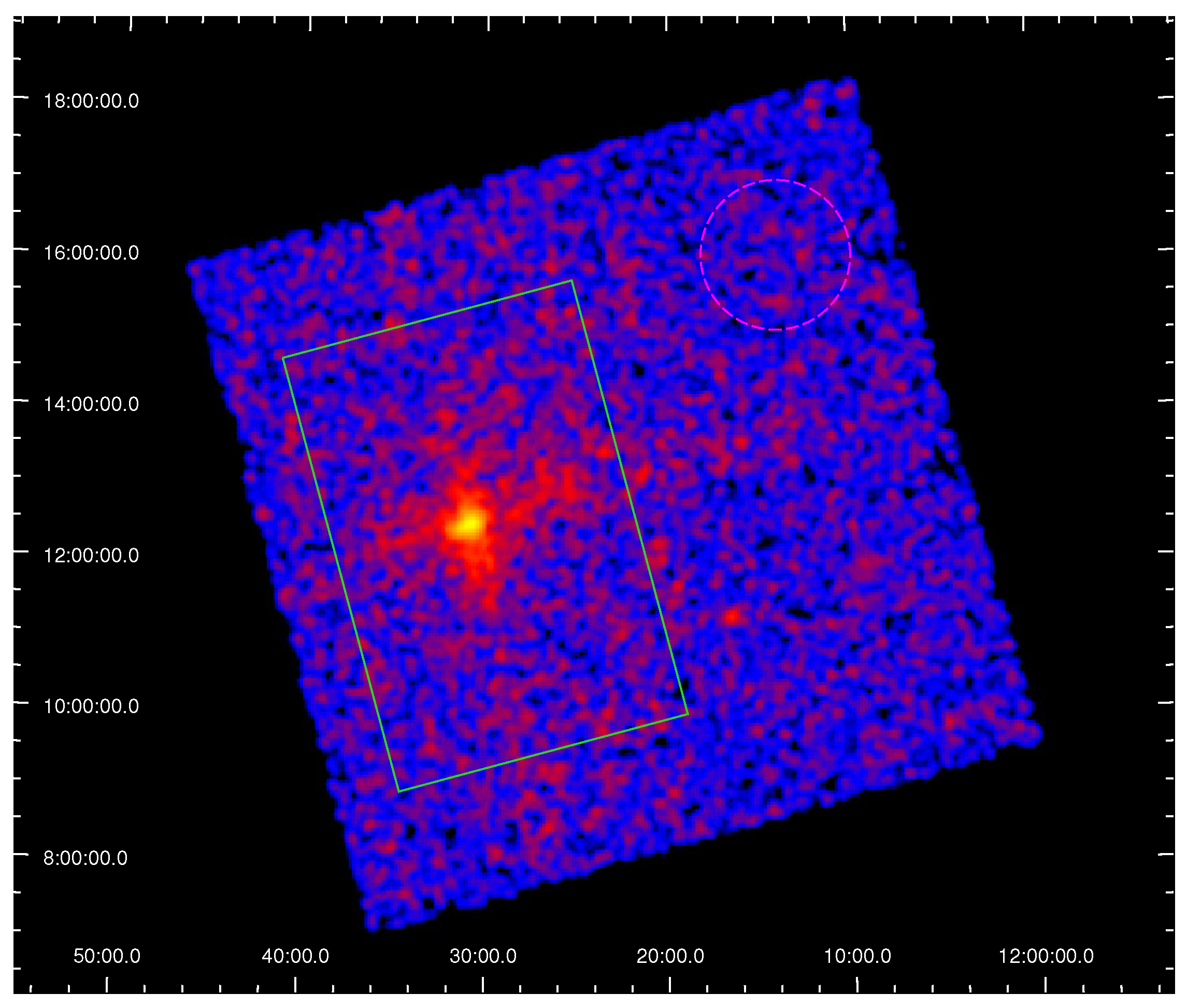
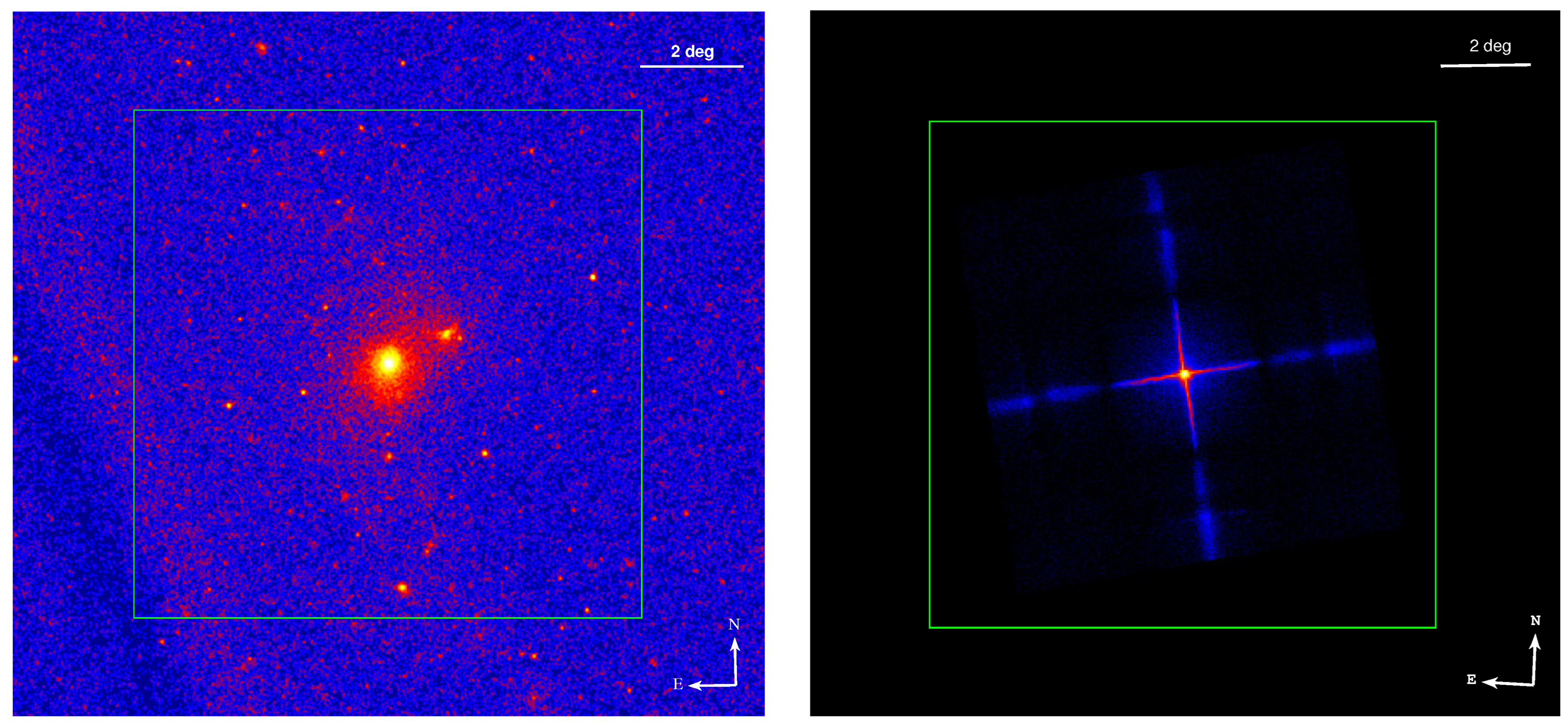
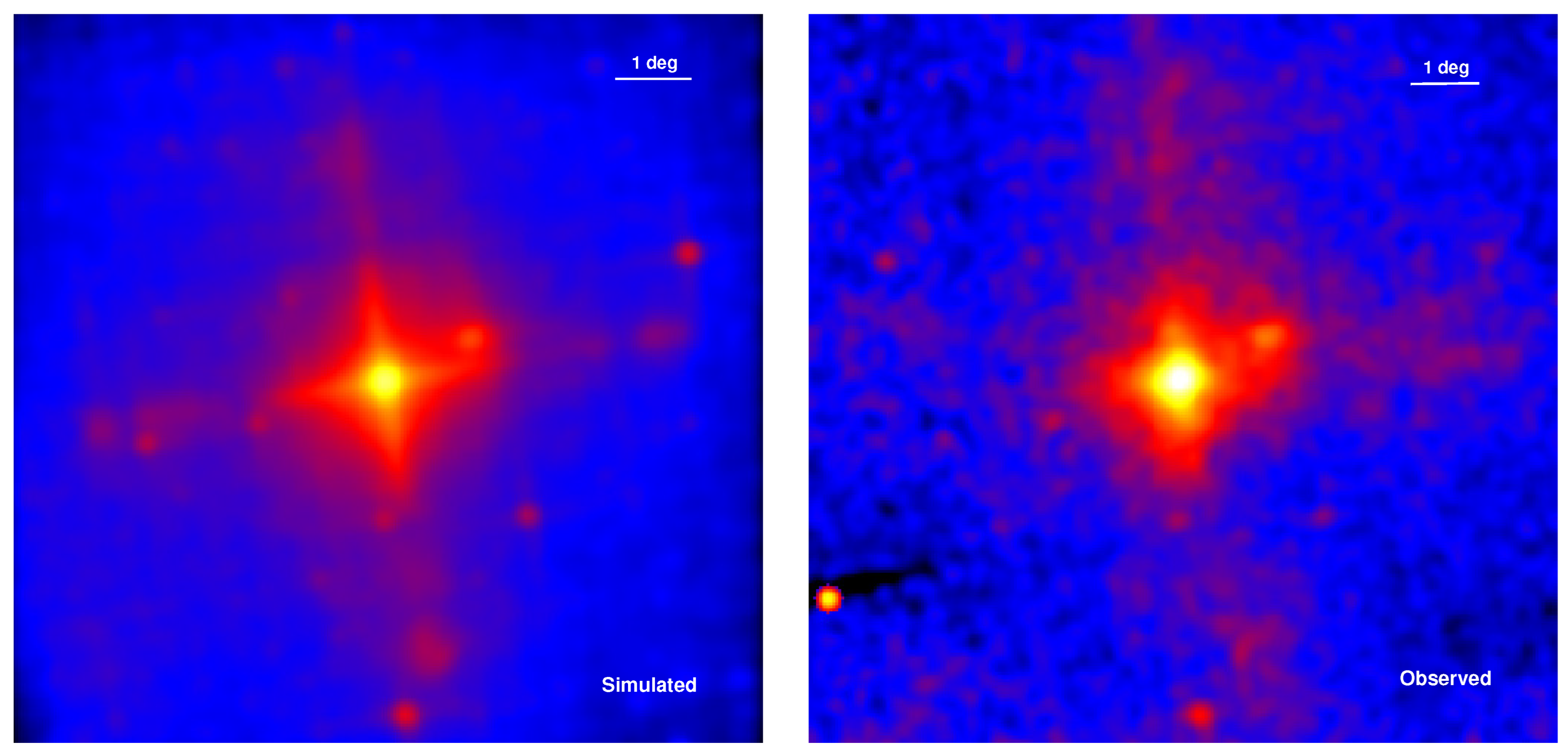
3.1. The X-ray Image
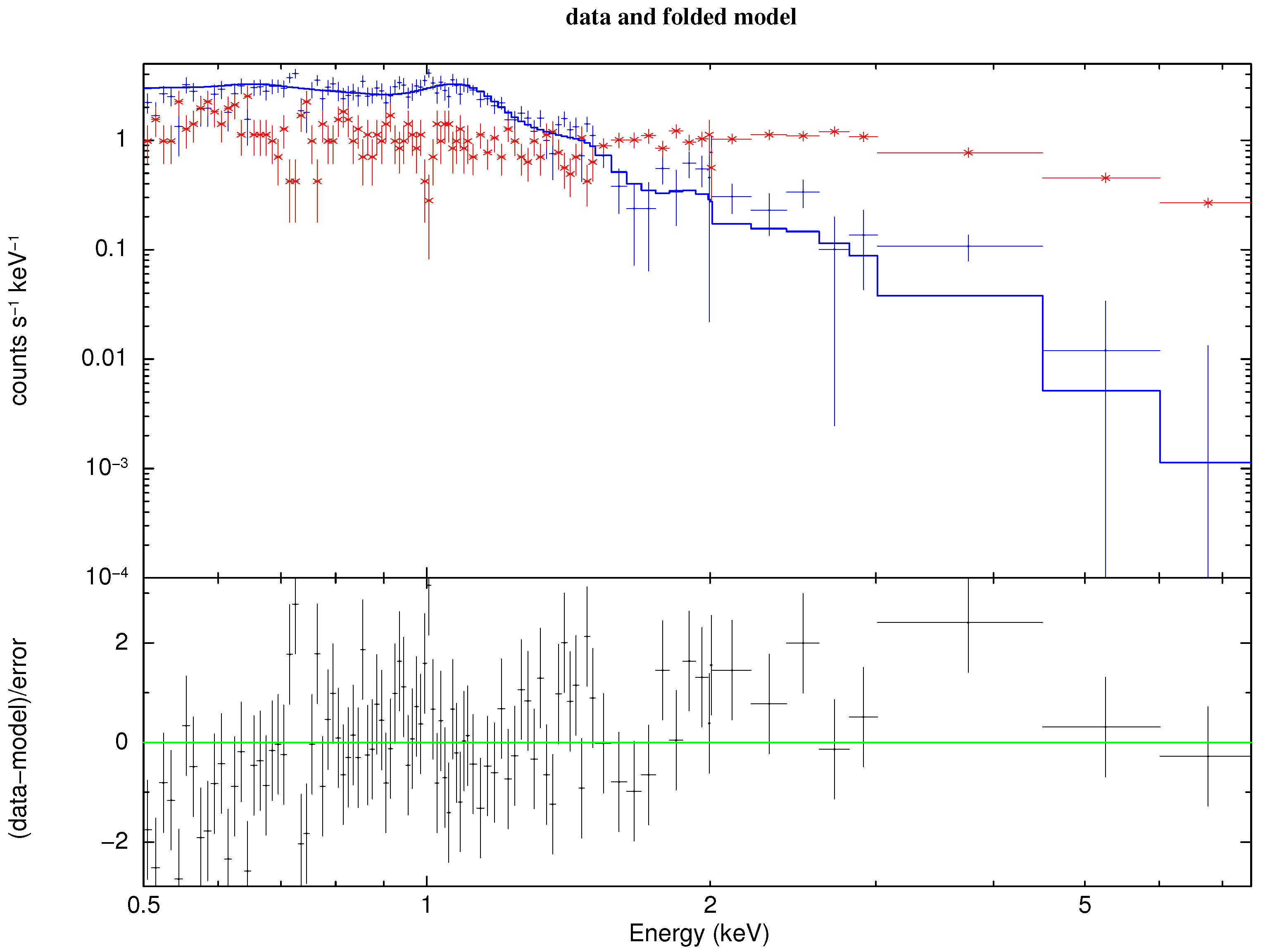
3.2. LEIA Spectrum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The images match the ROSAT PSPC images. Galaxies, including M87, M86, and M49, can be clearly seen from the merged LEIA image in the 0.5–4.5 keV band.
- The LEIA images show an arm structure caused by the PSF effect of the LEIA instrument.
- We extracted the LEIA spectrum and determined the average temperature of the FoV ( keV ) and found it to be consistent with the overall temperature ( keV) within a 1∘ radius of M87, as measured by ROSAT, and the average temperature of (∼2.3 keV) obtained by XMM-Newton.
- Above 1.5 keV, the spectrum is dominated by the background, with the image primarily showing the central point source and its PSF effects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Available online: http://montage.ipac.caltech.edu/ (accessed on 19 May 2024). |
References
- Angel, J.R.P. Lobster eyes as X-ray telescopes. Astrophys. J. 1979, 233, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.W.; Stevenson, A.W.; Nugent, K.A.; Chapman, H.; Steenstrup, S. On the concentration, focusing, and collimation of x-rays and neutrons using microchannel plates and configurations of holes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1989, 60, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.N.; Nugent, K.A.; Wilkins, S.W. X-ray focusing using square channel-capillary arrays. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1991, 62, 1542–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.W.; Lees, J.E.; Pearson, J.F.; Sims, M.R.; Roxburgh, K. X-ray focusing using microchannel plates. In Proceedings of the Multilayer and Grazing Incidence X-ray/EUV Optics; Hoover, R.B., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; Volume 1546, pp. 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.W.; Brunton, A.N.; Lees, J.E.; Pearson, J.F.; Feller, W.B. X-ray focusing using square-pore microchannel plates First observation of cruxiform image structure. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 1993, 324, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Willingale, R.; Ling, Z.; Feng, H.; Li, H.; Ji, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S. Ray tracing simulations for the wide-field x-ray telescope of the Einstein Probe mission based on Geant4 and XRTG4. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2014: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; Takahashi, T., den Herder, J.W.A., Bautz, M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 9144, p. 91444E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, R.; Sveda, L.; Pína, L.; Inneman, A.; Semencova, V.; Skulinova, M. LOBSTER: New space x-ray telescopes. In Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priedhorsky, W.C.; Peele, A.G.; Nugent, K.A. An X-ray all-sky monitor with extraordinary sensitivity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 279, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.W.; Brunton, A.N.; Bannister, N.P.; Pearson, J.F.; Ward, M.; Stevenson, T.J.; Watson, D.J.; Warwick, B.; Whitehead, S.; O’Brian, P.; et al. LOBSTER-ISS: An imaging x-ray all-sky monitor for the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the X-ray and Gamma-Ray Instrumentation for Astronomy XII; Flanagan, K.A., Siegmund, O.H.W., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 4497, pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Amati, L.; Cannizzo, J.K.; Cordier, B.; Gehrels, N.; Ghirlanda, G.; Götz, D.; Produit, N.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. Perspectives on Gamma-Ray Burst Physics and Cosmology with Next Generation Facilities. Space Sci. Rev. 2016, 202, 235–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.; Hutchinson, I.; Lerman, H.; Feldman, C.; McHugh, M.; Lodge, A.; Willingale, R.; Beardmore, A.; Speight, R.; Drumm, P. The soft x-ray imager on THESEUS: The transient high energy survey and early universe surveyor. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2020: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; den Herder, J.W.A., Nikzad, S., Nakazawa, K., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 11444, p. 114442L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunce, E.J.; Martindale, A.; Lindsay, S.; Muinonen, K.; Rothery, D.A.; Pearson, J.; McDonnell, I.; Thomas, C.; Thornhill, J.; Tikkanen, T.; et al. The BepiColombo Mercury Imaging X-ray Spectrometer: Science Goals, Instrument Performance and Operations. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, D.; Meuris, A.; Pinsard, F.; Doumayrou, E.; Tourrette, T.; Osborne, J.P.; Willingale, R.; Sykes, J.M.; Pearson, J.F.; Duigou, J.M.L.; et al. The microchannel x-ray telescope status. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2016: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; den Herder, J.W.A., Takahashi, T., Bautz, M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 9905, p. 99054L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, C.; Willingale, R.; Pearson, J.; Butcher, G.; Peterson, P.; Crawford, T.; Houghton, P.; Speight, R.; Lodge, A.; Bicknell, C.; et al. Calibration of the flight model lobster eye optic for SVOM. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2022: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; den Herder, J.W.A., Nikzad, S., Nakazawa, K., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2022; Volume 12181, p. 121811P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembay, S.; Branduardi-Raymont, G.; Drumm, P.; Escoubet, C.P.; Genov, G.; Gow, J.; Hall, D.; Holland, A.; Hudec, R.; Mas-Hesse, J.M.; et al. The Soft X-ray Imager (SXI) on the SMILE Mission. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016; p. SM44A-04. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.X.; Sun, X.J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, S.L.; Jin, G.; Zhang, S.N.; Zhang, X.F.; Chang, J.B.; Chen, F.S.; Chen, Y.F.; et al. The Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy Onboard the SATech-01 Satellite. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 23, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ling, Z.X.; Sun, X.J.; Sun, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.D.; Xue, Y.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Dai, Y.F.; Jia, Z.Q.; et al. First Wide Field-of-view X-ray Observations by a Lobster-eye Focusing Telescope in Orbit. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 941, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonry, J.L.; Dressler, A.; Blakeslee, J.P.; Ajhar, E.A.; Fletcher, A.B.; Luppino, G.A.; Metzger, M.R.; Moore, C.B. The SBF Survey of Galaxy Distances. IV. SBF Magnitudes, Colors, and Distances. Astrophys. J. 2001, 546, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhringer, H.; Briel, U.G.; Schwarz, R.A.; Voges, W.; Hartner, G.; Trümper, J. The structure of the Virgo cluster of galaxies from Rosat X-ray images. Nature 1994, 368, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truemper, J. ROSAT: A New Look at the X-ray Sky. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1992, 33, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Matsushita, K.; Yamasaki, N.Y.; Ohashi, T.; Ishida, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Böhringer, H.; Matsumoto, H. Temperature Map of the Virgo Cluster of Galaxies Observed with ASCA. Astrophys. J. 2001, 549, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, O.; Werner, N.; Simionescu, A.; Allen, S.W.; Böhringer, H. X-ray spectroscopy of the Virgo Cluster out to the virial radius. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, M.; Emsellem, E.; Krajnović, D.; McDermid, R.M.; Scott, N.; Verdoes Kleijn, G.A.; Young, L.M.; Alatalo, K.; Bacon, R.; Blitz, L.; et al. The ATLAS3D project—I. A volume-limited sample of 260 nearby early-type galaxies: Science goals and selection criteria. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, D.; Svinkin, D.S.; Delaunay, J.; Tanvir, N.R.; Gao, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.F.; et al. Soft X-ray prompt emission from a high-redshift gamma-ray burst EP240315a. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, B.; Soida, M.; Beck, R.; Chung, A.; Urbanik, M.; Chyży, K.T.; Otmianowska-Mazur, K.; Kenney, J.D.P. Large-scale radio continuum properties of 19 Virgo cluster galaxies. The influence of tidal interactions, ram pressure stripping, and accreting gas envelopes. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.A.; Fabian, A.C.; Forman, W.; Jones, C.; Stern, C. Ram-Pressure Stripping of the Multiphase Interstellar Medium of the Virgo Cluster Elliptical Galaxy M86 (NGC 4406). Astrophys. J. 1991, 375, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binggeli, B.; Tammann, G.A.; Sandage, A. Studies of the Virgo Cluster. VI. Morphological and Kinematical Structure of the Virgo Cluster. Astron. J. 1987, 94, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, A.; Böhringer, H.; Brüggen, M.; Finoguenov, A. The gaseous atmosphere of M 87 seen with XMM-Newton. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 465, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Belsole, E.; Finoguenov, A.; Böhringer, H. XMM-Newton observation of M 87. I. Single-phase temperature structure of intracluster medium. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 386, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molendi, S. On the Temperature Structure of M87. Astrophys. J. 2002, 580, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalberla, P.M.W.; Burton, W.B.; Hartmann, D.; Arnal, E.M.; Bajaja, E.; Morras, R.; Pöppel, W.G.L. The Leiden/Argentine/Bonn (LAB) Survey of Galactic HI. Final data release of the combined LDS and IAR surveys with improved stray-radiation corrections. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 440, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, S.; Willingale, R.; Ling, Z. Geant4 simulations of a wide-angle x-ray focusing telescope. Exp. Astron. 2017, 43, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, M.; Pointecouteau, E.; Pratt, G.W. The structural and scaling properties of nearby galaxy clusters. II. The M-T relation. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 441, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacconi, R.; Gursky, H.; Paolini, F.R.; Rossi, B.B. Evidence for x Rays From Sources Outside the Solar System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1962, 9, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Component | Parameters | LEIA |
|---|---|---|
| WABS | nH ( cm2) | 2.13 (frozen) |
| APEC | KT (keV) | |
| Abun (metal abundances) | 0.30 (frozen) | |
| z (redshift) | 0.00428 (frozen) | |
| norm | ||
| /DOF | 187.62/151 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, W.-C.; Jia, S.-M.; Zhao, H.-H.; Yu, H.; Pan, H.-W.; Li, C.-K.; Cheng, Y.-L.; Weng, S.-S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Study of Wide-Field-of-View X-ray Observations of the Virgo Cluster Using the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy. Universe 2024, 10, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10070300
Feng W-C, Jia S-M, Zhao H-H, Yu H, Pan H-W, Li C-K, Cheng Y-L, Weng S-S, Chen Y, Liu Y, et al. Study of Wide-Field-of-View X-ray Observations of the Virgo Cluster Using the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy. Universe. 2024; 10(7):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10070300
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Wen-Cheng, Shu-Mei Jia, Hai-Hui Zhao, Heng Yu, Hai-Wu Pan, Cheng-Kui Li, Yu-Lin Cheng, Shan-Shan Weng, Yong Chen, Yuan Liu, and et al. 2024. "Study of Wide-Field-of-View X-ray Observations of the Virgo Cluster Using the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy" Universe 10, no. 7: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10070300
APA StyleFeng, W.-C., Jia, S.-M., Zhao, H.-H., Yu, H., Pan, H.-W., Li, C.-K., Cheng, Y.-L., Weng, S.-S., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Ling, Z.-X., & Zhang, C. (2024). Study of Wide-Field-of-View X-ray Observations of the Virgo Cluster Using the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy. Universe, 10(7), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10070300







