Exploring Neutrino Masses (g − 2)μ,e in Type I+II Seesaw in Le–Lα-Gauge Extended Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model with Hybrid Seesaw Scenario
2.1. Vacuum Stability and Unitarity Criteria
2.2. Scalar Mass Spectrum
3. Neutrino Mass Generation
3.1. Model-A
3.2. Model B
4. Numerical Analysis
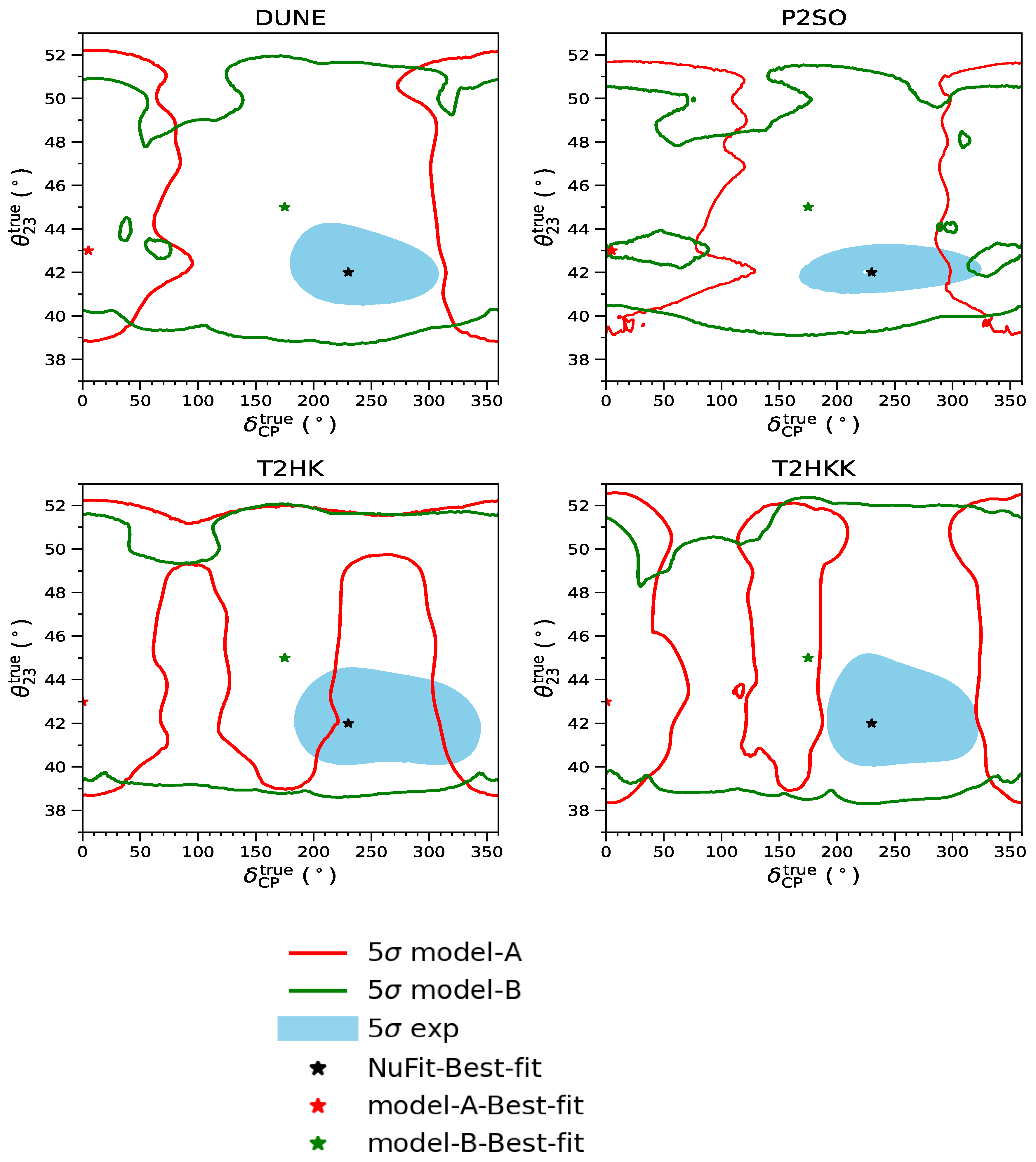
5. Testing the Models in Upcoming Long-Baseline Experiments
5.1. Experimental Details
5.2. Simulation Details
5.3. Results
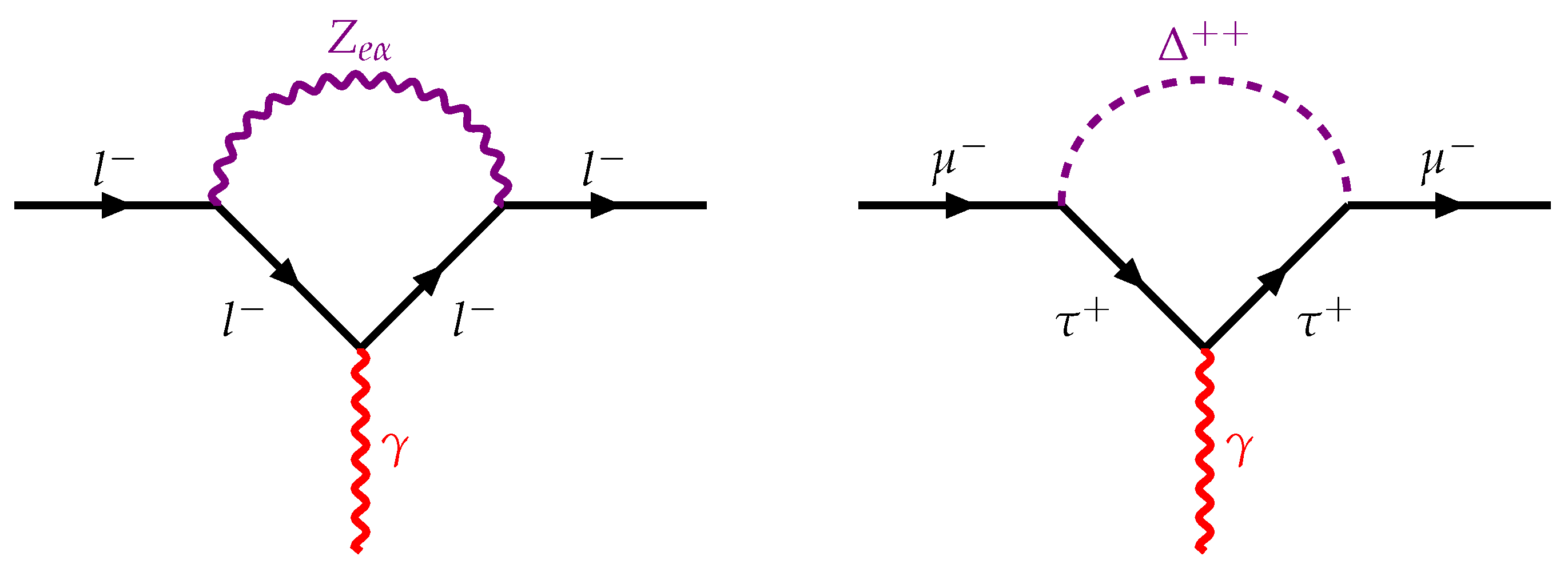
6. Electron and Muon
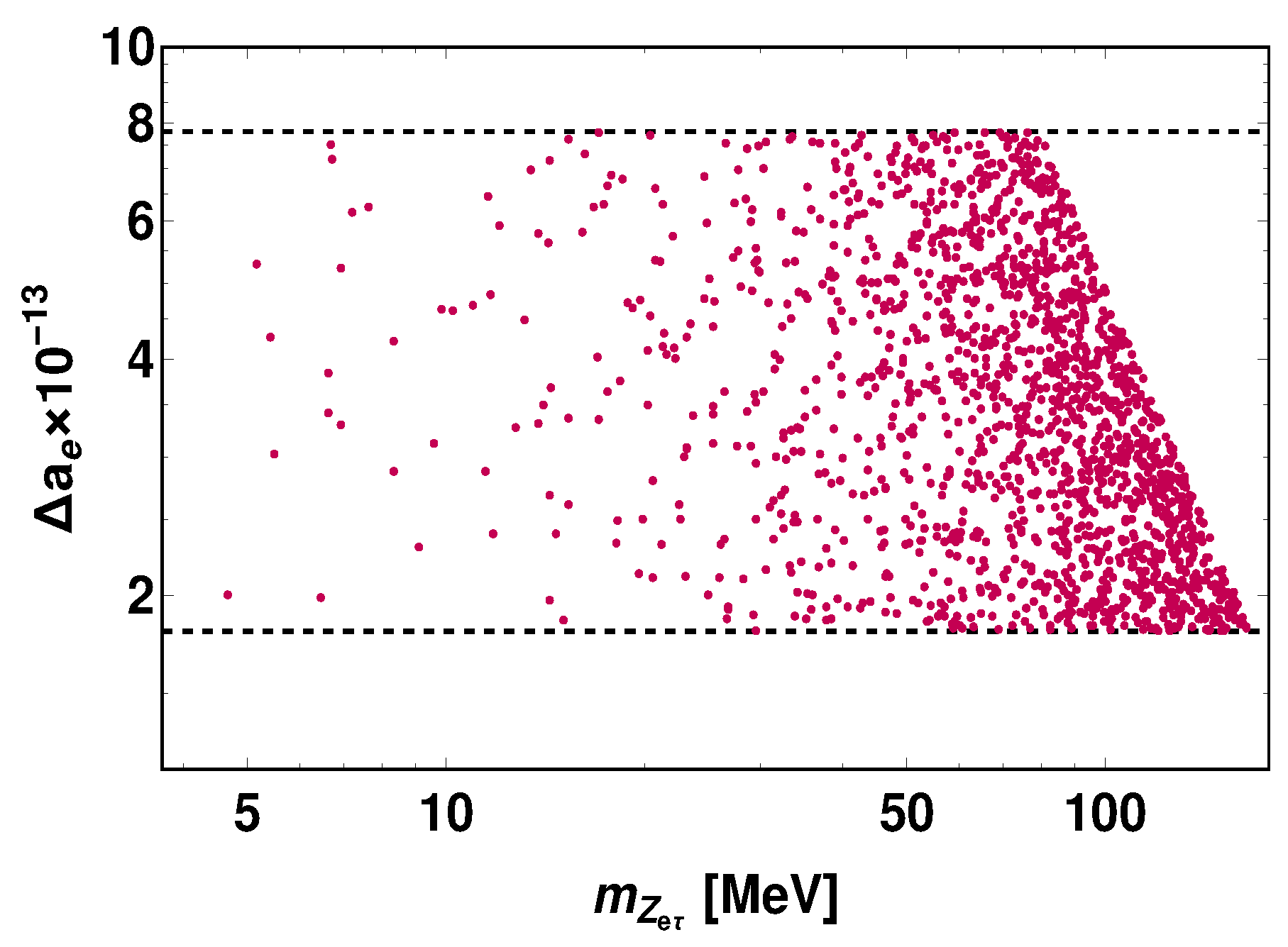
6.1. Electron
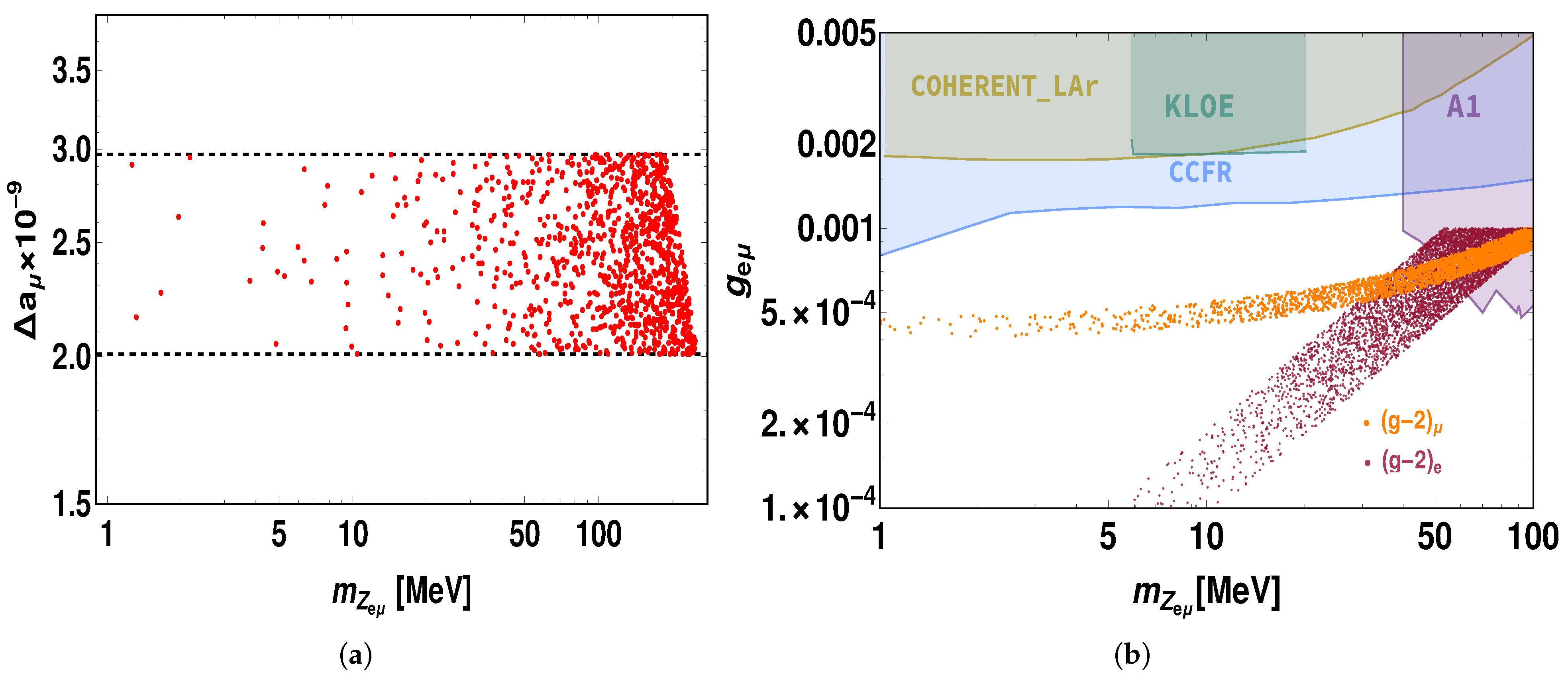
6.2. Muon
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minkowski, P. μ→ eγ at a rate of one out of 109 muon decays? Phys. Lett. B 1977, 67, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, T. Horizontal gauge symmetry and masses of neutrinos. Conf. Proc. C 1979, 7902131, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gell-Mann, M.; Ramond, P.; Slansky, R. Complex Spinors and Unified Theories. Conf. Proc. C 1979, 790927, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Brdar, V.; Helmboldt, A.J.; Iwamoto, S.; Schmitz, K. Type-I Seesaw as the Common Origin of Neutrino Mass, Baryon Asymmetry, and the Electroweak Scale. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 075029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, O.G.; Valle, J.W.F. Neutrino oscillations and the seesaw origin of neutrino mass. Nucl. Phys. B 2016, 908, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, G.C.; Penedo, J.T.; Pereira, P.M.F.; Rebelo, M.N.; Silva-Marcos, J.I. Type-I Seesaw with eV-Scale Neutrinos. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramond, P. The Family Group in Grand Unified Theories. arXiv 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, J.; Valle, J.W.F. Neutrino Masses in SU(2) x U(1) Theories. Phys. Rev. D 1980, 22, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, R.N.; Senjanovic, G. Neutrino Masses and Mixings in Gauge Models with Spontaneous Parity Violation. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.P.; Li, L.F. Neutrino Masses, Mixings and Oscillations in SU(2) x U(1) Models of Electroweak Interactions. Phys. Rev. D 1980, 22, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Sarkar, U. Neutrino masses and leptogenesis with heavy Higgs triplets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5716–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antusch, S.; King, S.F. Type II Leptogenesis and the neutrino mass scale. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 597, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S. A Minimal Type II Seesaw Model. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 076002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhrib, A.; Benbrik, R.; Chabab, M.; Moultaka, G.; Peyranere, M.C.; Rahili, L.; Ramadan, J. The Higgs Potential in the Type II Seesaw Model. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.F.; de, S. Pires, C.A.; Rodrigues da Silva, P.S. Inverse type II seesaw mechanism and its signature at the LHC and ILC. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 769, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Ning, G.Z. Radiative Neutrino Mass in Type III Seesaw Model. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 073003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E. Pathways to naturally small neutrino masses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R.; Lew, H.; He, X.G.; Joshi, G.C. Seesaw Neutrino Masses Induced by a Triplet of Leptons. Z. Phys. C 1989, 44, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Huang, J. TeV Scale Models of Neutrino Masses and Their Phenomenology. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 26, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinsky, M.; Romao, J.C.; Valle, J.W.F. Novel supersymmetric SO(10) seesaw mechanism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 161801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E. Deciphering the Seesaw Nature of Neutrino Mass from Unitarity Violation. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2009, 24, 2161–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzocchi, F.; Cerdeno, D.G.; Munoz, C.; Valle, J.W.F. Calculable inverse-seesaw neutrino masses in supersymmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 051701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E. Radiative inverse seesaw mechanism for nonzero neutrino mass. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 013013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyla, P.; Barnett, R.M.; Beringer, J.; Dahl, O.; Dwyer, D.A.; Groom, D.E.; Lin, C.J.; Lugovsky, K.S.; Pianori, E.; Robinson, D.J. Review of Particle Physics. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2020, 2020, 083C01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, A.; Farzan, Y. Explaining the ANITA events by a Le–Lτ gauge model. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 12, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.H.; He, X.G.; Wu, L.; Yang, J.M. Leptophilic dark matter in gauged U(1)Le–Lμ model in light of DAMPE cosmic ray e++e− excess. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Feng, L.; Guo, X.; Shang, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.; Zu, L. Explaining the DAMPE data with scalar dark matter and gauged U(1)Le–Lμ interaction. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, A.S.; Mohanty, S. Constraints on flavor dependent long range forces from atmospheric neutrino observations at super-Kamiokande. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 584, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Dighe, A.; Joshipura, A.S. Constraints on flavor-dependent long range forces from solar neutrinos and KamLAND. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 093005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Agarwalla, S.K. Universe’s Worth of Electrons to Probe Long-Range Interactions of High-Energy Astrophysical Neutrinos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 061103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Poddar, T.; Mohanty, S.; Jana, S. Constraints on long range force from perihelion precession of planets in a gauged Le-Lμ,τ scenario. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannike, K. Vacuum stability conditions from copositivity criteria. Eur. Phys. J. C 2012, 72, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, K.P.; Majumdar, D.; Rakshit, S. A possible explanation of low energy γ-ray excess from galactic centre and Fermi bubble by a Dark Matter model with two real scalars. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.W.; Quigg, C.; Thacker, H.B. Weak interactions at very high energies: The role of the Higgs-boson mass. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 16, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Santamaria, A. Updated scalar sector constraints in the Higgs triplet model. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, I.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.C.; Maltoni, M.; Schwetz, T.; Zhou, A. The fate of hints: Updated global analysis of three-flavor neutrino oscillations. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmuth, K.A.; Petcov, S.T.; Rodejohann, W. UPMNS = . Phys. Lett. B 2007, 654, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, P.H.; Petcov, S.T.; Rodejohann, W. On deviations from bimaximal neutrino mixing. Nucl. Phys. B 2004, 687, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, B.; Acciarri, R.; Acero, M.A.; Adamov, G.; Adams, D.; Adinolfi, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmed, J.; Alion, T.; Monsalve, S.A.; et al. Experiment Simulation Configurations Approximating DUNE TDR. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.04797. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, D.K.; Ghosh, M.; Majhi, R.; Mohanta, R. Study of light sterile neutrino at the long-baseline experiment options at KM3NeT. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 075039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ahn, S.H.; Aihara, H.; Aimi, A.; Akutsu, R.; Andreopoulos, C.; Anghel, I.; Anthony, L.H.; Antonova, M. Physics potentials with the second Hyper-Kamiokande detector in Korea. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2018, 2018, 063C01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Aihara, H.; Aimi, A.; Akutsu, R.; Andreopoulos, C.; Anghel, I.; Anthony, L.H.; Antonova, M.; Ashida, Y.; Aushev, V. Hyper-Kamiokande Design Report. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.04163. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.; Lindner, M.; Winter, W. Simulation of long-baseline neutrino oscillation experiments with GLoBES (General Long Baseline Experiment Simulator). Comput. Phys. Commun. 2005, 167, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.; Kopp, J.; Lindner, M.; Rolinec, M.; Winter, W. New features in the simulation of neutrino oscillation experiments with GLoBES 3.0: General Long Baseline Experiment Simulator. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 177, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.H.; Yu, C.; Zhong, W.; Estey, B.; Müller, H. Measurement of the fine-structure constant as a test of the Standard Model. Science 2018, 360, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Nio, M. Revised and Improved Value of the QED Tenth-Order Electron Anomalous Magnetic Moment. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 036001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Yao, Z.; Cladé, P.; Guellati-Khélifa, S. Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion. Nature 2020, 588, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, G.F.; Paradisi, P.; Passera, M. Testing new physics with the electron g-2. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Y.M.; Banerjee, D.; Bernhard, J.; Burtsev, V.E.; Chumakov, A.G.; Cooke, D.; Crivelli, P.; Depero, E.; Dermenev, A.V.; Donskov, S.V. Constraints on New Physics in Electron g − 2 from a Search for Invisible Decays of a Scalar, Pseudoscalar, Vector, and Axial Vector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 211802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.R.; Whisnant, K.; Young, B.L. Second Order Corrections to the Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment in Alternative Electroweak Models. Phys. Rev. D 1985, 31, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguillard, D.P.; Albahri, T.; Allspach, D.; Anisenkov, A.; Badgley, K.; Baeßler, S.; Bailey, I.; Bailey, L.; Baranov, V.A.; Barlas-Yucel, E.; et al. Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.20 ppm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 161802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.W.; Bousquet, Q.; Brown, H.N.; Bunce, G.; Carey, R.M.; Cushman, P.; Danby, G.T.; Debevec, P.T.; Deile, M.; Deng, H.; et al. Final Report of the Muon E821 Anomalous Magnetic Moment Measurement at BNL. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 072003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Asmussen, N.; Benayoun, M.; Bijnens, J.; Blum, T.; Bruno, M.; Caprini, I.; Calame, C.C.; Cè, M.; Colangelo, G.; et al. The anomalous magnetic moment of the muon in the Standard Model. Phys. Rep. 2020, 887, 1–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmannshofer, W.; Chen, C.Y.; Bhupal Dev, P.S.; Soni, A. Lepton flavor violating Z’ explanation of the muon anomalous magnetic moment. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 762, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, C.; Patra, S.; Pritimita, P.; Senapati, S.; Yajnik, U.A. Neutrino mass, mixing and muon g − 2 explanation in U(1)Lμ–Lτ extension of left-right theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.; Okada, H. Inverse seesaw and (g − 2) anomalies in B − L extended two Higgs doublet model. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.; Rashed, A.; Moretti, S. The Dark Z′ and Sterile Neutrinos Behind Current Anomalies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegerlehner, F.; Nyffeler, A. The Muon g-2. Phys. Rep. 2009, 477, 1–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Foldenauer, P.; Jaeckel, J. Hunting All the Hidden Photons. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, B.; Albahri, T.; Al-Kilani, S.; Allspach, D.; Alonzi, L.P.; Anastasi, A.; Anisenkov, A.; Azfar, F.; Badgley, K.; Baeßler, S.; et al. Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.46 ppm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 141801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.M.; Shaevitz, M.H.; Bolton, T. Precision measurements with high-energy neutrino beams. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.R.; Rabinowitz, S.A.; Arroyo, C.; Bachmann, K.T.; Blair, R.E.; Foudas, C.; King, B.J.; Lefmann, W.C.; Leung, W.C.; Oltman, E.; et al. Neutrino tridents and W Z interference. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 3117–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmannshofer, W.; Gori, S.; Pospelov, M.; Yavin, I. Neutrino Trident Production: A Powerful Probe of New Physics with Neutrino Beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 091801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Dutta, M.; Mahapatra, S.; Sahu, N. Lepton anomalous magnetic moment with singlet-doublet fermion dark matter in a scotogenic U(1)Lμ-Lτ model. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 015029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KLOE-2 Collaboration. Search for light vector boson production in e+e−→μ+μ−γ interactions with the KLOE experiment. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 736, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, H.; Achenbach, P.; Ayerbe Gayoso, C.; Bernauer, J.C.; Böhm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Debenjak, L.; Denig, A.; Distler, M.O.; Esser, A.; et al. Search for Light Gauge Bosons of the Dark Sector at the Mainz Microtron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 251802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, H.; Achenbach, P.; Ayerbe Gayoso, C.; Beranek, T.; Beričič, J.; Bernauer, J.C.; Böhm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Correa, L.; Debenjak, L.; et al. Search at the Mainz Microtron for Light Massive Gauge Bosons Relevant for the Muon g − 2 Anomaly. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 221802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodas, A.; Coy, R.; King, S.J.D. Solving the electron and muon g − 2 anomalies in Z′ models. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fields | Model A: | Model B: | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | ||
| S | 1 | 1 |
| Model A | Model B | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Range | Parameters | Range |
| (in TeV) | (in TeV) | ||
| (in TeV) | (in TeV) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panda, P.; Mishra, P.; Behera, M.K.; Singirala, S.; Mohanta, R. Exploring Neutrino Masses (g − 2)μ,e in Type I+II Seesaw in Le–Lα-Gauge Extended Model. Universe 2024, 10, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100387
Panda P, Mishra P, Behera MK, Singirala S, Mohanta R. Exploring Neutrino Masses (g − 2)μ,e in Type I+II Seesaw in Le–Lα-Gauge Extended Model. Universe. 2024; 10(10):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100387
Chicago/Turabian StylePanda, Papia, Priya Mishra, Mitesh Kumar Behera, Shivaramakrishna Singirala, and Rukmani Mohanta. 2024. "Exploring Neutrino Masses (g − 2)μ,e in Type I+II Seesaw in Le–Lα-Gauge Extended Model" Universe 10, no. 10: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100387
APA StylePanda, P., Mishra, P., Behera, M. K., Singirala, S., & Mohanta, R. (2024). Exploring Neutrino Masses (g − 2)μ,e in Type I+II Seesaw in Le–Lα-Gauge Extended Model. Universe, 10(10), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100387






