Abstract
Berberine, a natural isoquinoline alkaloid, has been shown to improve glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and blood pressure regulation. However, its poor bioavailability has limited widespread clinical use. ToBeRock® is a self-emulsifying formulation designed to enhance the bioaccessibility of berberine. This retrospective, real-world pilot study conducted through community pharmacies with pharmaceutical care services aimed to evaluate the metabolic and hemodynamic effects of ToBeRock® in adults with impaired fasting glucose (IFG). Sixty adults with IFG (FPG 100–125 mg/dL) were enrolled through territorial pharmacies offering pharmaceutical services. Patients were retrospectively grouped into two cohorts: a Low-Dose Group (ToBeRock® 1 capsule/day) and a High-Dose Group (ToBeRock® 2 capsules/day). Capillary blood sampling and in-pharmacy blood pressure measurements were recorded at baseline (T0), 4 weeks (T1), and 8 weeks (T2). Evaluated parameters included fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides), systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP/DBP), and oxidative stress markers (FORT, FORD). Both cohorts showed statistically significant reductions in fasting glucose (p < 0.001), LDL (p = 0.036 Low-Dose/p = 0.039 High-Dose), and triglycerides (p = 0.012/0.009) after 8 weeks of treatment. The High-Dose Group experienced a greater improvement in HbA1c (−0.26%, p = 0.041) and a mild but statistically significant increase in HDL (p = 0.049). Improvements in oxidative balance were observed with significant reductions in FORT (p = 0.019/0.011), increases in FORD (p = 0.033/0.008), and a favorable shift in the REDOX index (p = 0.012/0.006). Systolic blood pressure decreased by −6.3 mmHg in the Low-Dose Group (p = 0.031) and −7.6 mmHg in the High-Dose Group (p = 0.048), while diastolic pressure dropped by −3.9 mmHg (p = 0.044) and −4.2 mmHg (p = 0.051), respectively. This real-world, retrospective analysis highlights the potential clinical benefit of ToBeRock® in improving glycemic, lipid, oxidative, and hemodynamic profiles. The High-Dose Group demonstrated more consistent and significant results, supporting the dose-responsive efficacy of the bioavailable formulation and the value of pharmacy-based monitoring of nutraceutical interventions.
1. Introduction
Impaired fasting glucose (IFG), defined as fasting plasma glucose levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL, represents a prediabetic condition associated with increased cardiometabolic risk and a high likelihood of progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). IFG affects a substantial proportion of the adult population worldwide: in 2021, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimated that 319 million people globally had impaired fasting glucose, a figure expected to rise to 454 million by 2045 [1].
Beyond glycemic dysregulation, individuals with IFG frequently present with other components of the metabolic syndrome, including dyslipidemia, abdominal obesity, and elevated blood pressure, which synergistically increase the risk of cardiovascular events [2]. In contemporary clinical settings, the initial identification of IFG frequently occurs within community pharmacy environments [3,4]. These pharmacy-based screening platforms enable opportunistic detection of early dysglycemic states in asymptomatic individuals, particularly during non-targeted cardiovascular risk screening programs [5,6]. Within this paradigm, the territorial pharmacist emerges as a peripheral healthcare sentinel, capable of contributing to the subclinical phenotyping of metabolic risk through the integration of point-of-care biochemical data, anthropometric indices, and patient-reported information. This positioning not only facilitates the prompt identification of latent metabolic dysregulation but also enables the initiation of structured interventions, including nutritional and lifestyle counseling, nutraceutical recommendations based on mechanistic plausibility and clinical evidence, and, where indicated, algorithm-guided referral to primary or specialist medical services [7].
The pharmacist’s role in this context is consistent with the principles of proactive risk stratification, territorial predictive prevention, and translational implementation of precision public health and may constitute a pivotal node in delaying or preventing the transition from IFG to overt glucose intolerance or atherogenic dysmetabolism. In this context, lifestyle intervention remains the cornerstone of IFG management; however, the need for early, non-pharmacologic strategies capable of improving metabolic profiles has stimulated growing interest in functional and nutraceutical approaches [8,9,10].
Among these, berberine, a plant-derived isoquinoline alkaloid, has shown promising results in subjects with IFG and metabolic syndrome [11,12]. Berberine exerts multiple metabolic effects: it improves insulin sensitivity, enhances glucose uptake via AMPK activation, and exerts favorable effects on lipid metabolism and inflammatory markers [13]. Clinical studies have demonstrated its ability to reduce fasting glucose, HbA1c, total cholesterol, and LDL-C in prediabetic individuals [14].
Nevertheless, the therapeutic application of berberine has been historically limited by its poor oral bioavailability, due to low intestinal solubility, efflux by P-glycoprotein, and extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism (Figure 1) [15]. To enhance its clinical effectiveness, ToBeRock®, a high-bioaccessibility formulation based on a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS), has been developed. This system promotes micellar dispersion of berberine in the intestinal lumen (Figure 1), improving absorption and systemic exposure. The co-formulation with tocotrienols may further support cellular uptake and antioxidant activity, offering a multi-targeted nutraceutical approach to managing early metabolic dysfunction.
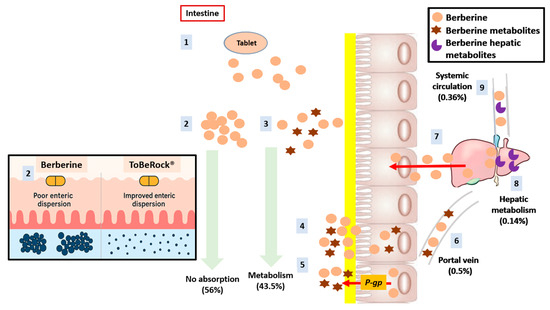
Figure 1.
Berberine route after oral supplementation (adapted from Colletti A et al. 2022 [13]). After ingestion, the tablet disintegrates and releases the BBR particles (1). However, about 56% of BBR is not absorbed in the GI tract due to self-aggregation (2). In addition, intestinal metabolism (operated by both gut microbiota and CYP450) is responsible for 43.5% of total BBR-particles (3). Finally, the poor permeability (4), P-gp-mediated efflux (5) and hepatobiliary re-excretion (7) also contribute to the reduction in bioavailability. Only 0.5% of BBR enter the portal circulation (6) and 0.36% arrive in the systemic circulation (9).
Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the metabolic effects of a novel high-bioaccessibility berberine formulation (ToBeRock®), administered at two different dosages, in individuals with IFG. The study was conducted in a real-world, pharmacy-based setting to reflect the practical applicability of nutraceutical interventions in early cardiometabolic risk management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
This was a retrospective study which involved 60 volunteers (Figure 2) retrospectively enrolled through three community pharmacies located in Italy, as part of a structured pharmacy-based metabolic screening and follow-up program. Participants eligible for this retrospective study were adults aged between 40 and 70 years, with a body mass index (BMI) ranging from 25 to 32 kg/m2 and impaired fasting glucose (FPG 100–125 mg/dL). The inclusion criteria were defined according to the American Diabetes Association Standards of Care in Diabetes 2025, which establishes an impaired fasting glucose (100–125 mg/dL) range [16]; the WHO 2006 criteria for intermediate hyperglycemia [17]; and the 2023 ESC guidelines defining cardiovascular risk and comorbidities to be excluded [18].
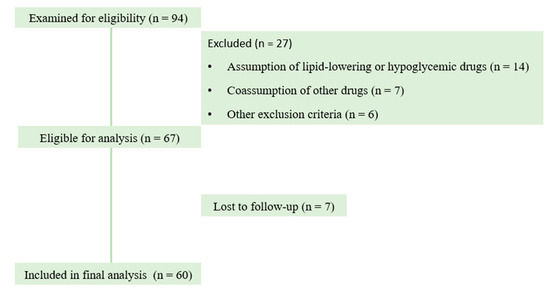
Figure 2.
Flowchart of participants in the study.
All participants provided informed consent prior to inclusion. Exclusion criteria included a personal history of cardiovascular disease or equivalent risk conditions; obesity defined as BMI > 32 kg/m2; current or recent use of hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic medications or dietary supplements affecting glucose or lipid metabolism; uncontrolled diabetes mellitus; pregnancy or lactation; and known pathologies of the thyroid, liver, kidneys, or skeletal muscle. Furthermore, any medical or surgical condition that could interfere with regular participation and compliance with the study protocol constituted a reason for exclusion.
Participants were excluded from this analysis if they had incomplete data or missed scheduled visits, or if they reported the use of non-trial drugs during the treatment with nutraceuticals.
Participants received the treatment for 2 months. Volunteers were evaluated at time zero (T = 0), after 4 weeks (T = 1) and after 8 weeks of supplementation (T = 2) for clinical status, in addition to being evaluated for compliance and the tolerability of the products. Parameters assessed at baseline (T0), 4 weeks (T1), and 8 weeks (T2) included metabolic (fasting plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and serum uric acid) and hemodynamic parameters (systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP)), lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Oxidative stress biomarkers (FORT, FORD, and REDOX index) were measured at T0 and T2.
Informed written consent for using personal data for the present investigation was obtained from all the subjects.
The timeline of the study is described in detail in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Study timeline.
2.2. Treatment
Each patient was treated with ToBeRock® at a dosage of 1 or 2 capsules a day for eight weeks (T0–T2). Throughout the entire period of treatment, patients were directed to take the designated supplement at approximately the same time each day, in fed state.
ToBeRock® is a patent food supplement based on a high-purity dry extract of Berberis aristata (97% berberine), providing 242.5 mg of berberine per capsule, in combination with tocotrienols (29.75 mg vitamin E per capsule). From a technological standpoint, ToBeRock® adopts a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) to improve intestinal solubilization and micellar dispersion of berberine, a compound known for its low aqueous solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism (Figure 4) [19]. The presence of emulsifying agents such as polysorbate 80 and sorbitan esters favors rapid emulsification in the intestinal lumen, enhancing bioaccessibility and pre-systemic absorption [20]. The tocotrienol component also contributes to membrane fluidity and cellular uptake, supporting the nutraceutical’s multi-target metabolic action.
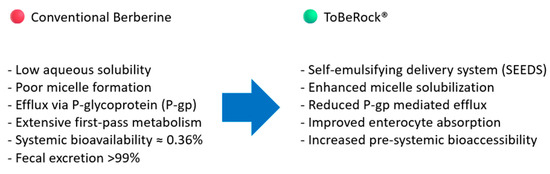
Figure 4.
Pharmacokinetic differences between conventional berberine and ToBeRock®.
2.3. Efficacy Assessment
The primary outcome of the study was to evaluate the use of ToBeRock® at a dosage of 1 or 2 capsules a day for 8 weeks in subjects with impaired fasting glucose. Secondary outcomes included changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), uric acid, lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides), systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP), oxidative stress biomarkers (FORT, FORD, REDOX index), and hepatic safety parameters (ALT, AST). All parameters were assessed at baseline, week 4, and week 8 to monitor both metabolic and vascular effects as well as overall safety status. Oxidative stress biomarkers were measured only in T0 and T2.
Measurements were conducted using validated devices in pharmacy settings. Capillary blood samples were analyzed using the CLINI5® diagnostic platform (Callegari S.p.A., Parma, Italy), a compact, validated, pharmacy-based point-of-care system for multiparametric biochemical evaluation [21,22]. The device employs photometric and kinetic colorimetric methods on whole blood samples obtained via fingertip puncture. The following parameters were assessed using reagent-specific test strips and disposable cuvettes. Fasting plasma glucose and uric acid were measured through enzymatic colorimetric reactions with endpoint detection at 520–550 nm. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was determined via a boronate affinity chromatography-based immunoturbidimetric assay, with results expressed in % (NGSP/DCCT-aligned). Lipid profile components, including total cholesterol and triglycerides, were assessed enzymatically (CHOD-PAP and GPO-PAP methods, respectively). LDL-C was calculated using the Friedewald formula ([LDL-C] = [Total Cholesterol] − [HDL-C] − [Triglycerides/5], expressed in mg/dL) [23]. Despite this method remaining standard in community of pharmacies and preventive settings, it presents well-recognized limitations, particularly in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Recent studies have evaluated the accuracy of Friedewald-derived LDL-C compared with direct assays and alternative equations, highlighting contexts in which novel approaches such as the Martin-Hopkins or Sampson equations may provide superior precision [23,24,25,26]. Transaminases (ALT and AST) were measured using kinetic UV methods, monitoring the rate of NADH oxidation at 340 nm over a fixed interval.
Capillary blood from the fingertip was also used to perform the Free Oxygen Radicals Test (FORT) and Free Oxygen Radical Defense (FORD) assays.
The FORT (FORM, CR 2000, Callegari) assesses the presence of hydroperoxides (ROOH), which are reactive oxygen species derived from the metabolism of lipids, amino acids, and nucleic acids. In the presence of transition metals (e.g., Fe2+), these hydroperoxides are decomposed into alkoxyl and peroxyl radicals via the Fenton reaction. These radicals oxidize a chromogen (a phenylenediamine derivative, 2CrNH2), producing a colored radical cation measurable at 505 nm. The absorbance correlates with hydroperoxide concentration via the Beer–Lambert law. Results are expressed in FORT units (1 FORT = 0.26 mg/L H2O2). Intra-assay and inter-assay coefficients of variation (CVs) were 3.7% and 6.2%, respectively.
The FORD test evaluates antioxidant defenses using a colored and stable radical cation formed from 4-amino-N,N-diethylaniline sulfate in an acidic environment (pH 5.2) in the presence of FeCl3. Antioxidants in the sample reduce the radical, causing a decrease in absorbance at 505 nm, proportional to antioxidant concentration. Quantification is achieved by comparison with a Trolox standard curve. Intra-assay and inter-assay CVs were 4.2% and 6.6%, respectively.
All measurements were performed under standard pharmacy conditions within 2 min from sample collection, ensuring high reproducibility and clinical reliability for field screening applications.
Blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) was measured using the Microlife WatchBP Office device, a clinically validated oscillometric monitor recommended by the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) [27]. The device performs three consecutive automated measurements in accordance with international guidelines and includes atrial fibrillation (AFIB) detection. All assessments were carried out under standardized conditions in a seated position, after at least five minutes of rest, in the pharmacy setting.
2.4. Assessment of Safety and Tolerability
Tolerability and safety were assessed using continuous monitoring over the period of treatment to detect any adverse events and evaluate the clinical safety of the supplement. Treatment compliance and the occurrence of adverse effects were monitored using a diary sheet organized on tables with the possibility for patients to indicate their assumptions of whether they were undergoing nutraceutical treatment and eventual side effects.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Personal data and physiological/pathological anamnesis were only collected at the enrolment visit (T−0), and treatment compliance data were collected in T1 and T2.
Data were systematically entered into an electronic sheet (Excel 2023, Microsoft 2023, Windows 2003, Redmond, WA, USA) throughout the study period. The entries underwent a double check for errors and were subsequently processed using GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 software. Descriptive data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Normality of distribution was verified using the Shapiro–Wilk test. To evaluate the effects of treatment over time, a two-way repeated measures ANOVA was performed, followed by Bonferroni—adjusted post hoc corrections tests, when appropriate. Significant interactions were further explored with independent-sample t-tests at each time point. Furthermore, inter-group comparisons were evaluated using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline values. A significance level of <0.05 was deemed statistically significant for all conducted tests.
3. Results
Ninety-four volunteers were examined for eligibility, of which 60 completed the study (Figure 1). Twenty-seven subjects were excluded due to concomitant pathologies (thyroid disease and/or diabetes type II) and/or assumption of other drugs. Seven participants were lost to follow-up.
A total of 60 participants with impaired fasting glucose (FPG 100–125 mg/dL) were retrospectively evaluated and assigned to either a low-dose (1 capsule/day, n = 30) or high-dose (2 capsules/day, n = 30) ToBeRock® group. Baseline characteristics including sex, age, and BMI were homogeneous across groups (Table 1). As indicated in Table 2, progressive reduction in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) was observed in both groups at week 4 and week 8. In the low-dose group, FPG decreased from 112.4 ± 6.1 mg/dL at baseline to 106.2 ± 5.4 mg/dL at week 4 and 103.8 ± 4.7 mg/dL at week 8 (p < 0.001 vs. baseline). In the high-dose group, FPG declined from 113.1 ± 6.4 mg/dL to 104.8 ± 5.0 mg/dL at week 4 and 100.9 ± 4.3 mg/dL at week 8 (p < 0.001 vs. baseline; p = 0.015 vs. low-dose at week 8). HbA1c levels also declined over time, but no significant intra-group or inter-group differences were observed at week 4 or week 8.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study population.

Table 2.
Changes in Metabolic Parameters from Baseline to Week 8.
Total cholesterol and LDL-C showed significant reductions in both groups by week 8. LDL-C decreased from 134 ± 29 mg/dL to 115 ± 25 mg/dL in the low-dose group (p = 0.014 vs. baseline) and from 136 ± 31 mg/dL to 106 ± 23 mg/dL in the high-dose group (p < 0.001 vs. baseline). Triglyceride levels also dropped significantly (low-dose: 152 ± 35 to 132 ± 28 mg/dL; high-dose: 158 ± 37 to 124 ± 26 mg/dL; p = 0.028 and p < 0.001 vs. baseline, respectively). HDL-C increased significantly only in the high-dose group (from 47 ± 11 to 51 ± 9 mg/dL; p = 0.030 vs. baseline); no significant change was seen in the low-dose group (from 48 ± 10 to 50 ± 9 mg/dL; p = ns).
Serum uric acid levels, AST/ALT ratio, and BMI remained stable in both groups over the study period (p = ns for all comparisons). ALT showed a significant reduction only at week 8 in the high dose group (ALT: low-dose p = ns, high-dose p = 0.032 vs. baseline; AST: low-dose p = ns, high-dose p = 0.072 vs. baseline).
At week 8, FORT levels decreased significantly (low-dose: 353 ± 52 to 312 ± 47 U CARR, p = 0.034; high-dose: 357 ± 55 to 298 ± 43 U CARR, p < 0.001 vs. baseline). Concurrently, FORD increased significantly (low-dose: 1.62 ± 0.38 to 1.88 ± 0.36 mmol Trolox eq., p = 0.033; high-dose: 1.59 ± 0.34 to 2.02 ± 0.33, p = 0.013). The REDOX index decreased from 218 ± 43 to 166 ± 32 (low-dose) and from 225 ± 45 to 147 ± 30 (high-dose), confirming a significant oxidative balance improvement (p < 0.001 for both groups; p = 0.021 vs. low-dose at week 8) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Oxidative stress and hepatic markers (week 0 vs. week 8).
SBP decreased significantly from 132.1 ± 9.8 mmHg to 125.8 ± 8.6 mmHg in the low-dose group (p = 0.016 vs. baseline), and from 133.6 ± 10.3 to 126.0 ± 7.7 mmHg in the high-dose group (p = 0.003 vs. baseline). DBP also declined significantly at week 8: low-dose from 84.2 ± 6.3 to 80.3 ± 5.3 mmHg (p = 0.02 vs. baseline), high-dose from 85.1 ± 6.6 to 80.9 ± 5.1 mmHg (p = 0.016 vs. baseline) (Table 4). No significant differences were observed between groups for blood pressure reductions at week 8.

Table 4.
Changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP/DBP).
No adverse events were reported during the study period. Treatment was well tolerated, and compliance exceeded 95% in both groups.
4. Discussion
The results of this retrospective real-world study showed that a high-bioaccessibility formulation of berberine and Vitamin E (ToBeRock®), administered either at 1 or 2 capsules per day, exerts favorable effects on FPG, lipid profile, blood pressure regulation, and oxidative stress in subjects with impaired fasting glucose (IFG). The inclusion of vitamin E in the formulation may contribute synergistically not only to enhancing intestinal bioaccessibility of berberine via improved micellar dispersion, but also to modulating oxidative stress and vascular stiffness through pleiotropic antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects at the endothelial level.
Several improvements were already detectable after 4 weeks, and most parameters exhibited a progressive benefit over the 8-week observation period. These findings align with prior evidence regarding the pleiotropic metabolic actions of berberine, including AMPK activation, LDL receptor upregulation, and anti-inflammatory effects [28].
The significant reduction in FPG value, particularly in the high-dose group, reinforces the potential of berberine as a non-pharmacological option for managing early glyco-metabolic dysregulation. Conversely, no significant reduction in HbA1c was observed, probably due to the short observation period and the relatively low baseline HbA1c levels of the study population. Furthermore, clinically meaningful reductions in triglycerides and LDL-C were observed, with a slight but significant increase in HDL-C only in the high-dose group. These findings are consistent with recent meta-analyses indicating that berberine may exert lipid-lowering effects comparable to statins in mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia [29].
The inclusion of oxidative stress parameters adds a novel translational dimension. The significant reduction in FORT and REDOX index, along with the increase in FORD, suggests that ToBeRock® exerts systemic antioxidant effects, potentially contributing to its vascular and metabolic benefits. The high-dose group achieved stronger improvements in redox balance and a significant superiority over the low-dose group in REDOX index, indicating a dose-dependent trend. Additionally, both dosages were associated with mild but statistically significant reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure at week 8. However, no significant inter-group differences were observed, suggesting that the blood pressure-lowering effect may not be dose-dependent within the tested range. Although the antihypertensive mechanism of berberine is not fully elucidated, proposed pathways include endothelial nitric oxide synthesis, renin-angiotensin modulation, and sympathetic tone reduction [30].
Interestingly, despite the overall superiority of the high-dose group in certain parameters, the low-dose group also showed significant improvements in glycemic, lipid, and oxidative stress markers. This may be explained by the optimized bioaccessibility profile of the formulation, which, even at lower dosages, ensures adequate enteric bioaccessibility to berberine. Such pharmacokinetic efficiency may have contributed to the absence of statistically significant inter-group differences for some endpoints. This observation highlights the importance of formulation technology in enhancing the clinical efficacy of nutraceutical interventions, potentially allowing lower doses to achieve meaningful clinical benefits [13]. The superior efficacy of ToBeRock® compared with conventional berberine is mainly attributable to the SEDDS [20], which enhances intestinal solubilization, micellar dispersion, and absorption of berberine, thereby increasing its systemic bioaccessibility. In addition, the inclusion of vitamin E, besides providing complementary antioxidant and endothelial protective effects, may also act as a lipophilic co-carrier within the formulation, further favoring micellar incorporation and enteric bioaccessibility of berberine. This dual contribution may explain the overall metabolic and vascular improvements observed with ToBeRock®.
ALT and AST showed mild reductions only in the high-dose group at week 8, without significant hepatotoxicity signals. Overall, liver enzymes and uric acid levels remained within normal ranges, supporting the hepatic safety of this formulation over the short term. No participants experienced adverse events, and treatment adherence exceeded 95% in both arms, an essential finding in the context of preventive medicine and pharmacy-based interventions.
This study has several strengths, including the real-world pharmacy-based setting, short-term longitudinal design with 4- and 8-week endpoints, and the integration of clinical, biochemical, and redox-related parameters. The inclusion of a capillary-based point-of-care approach reflects practical applicability in community screening and management of subclinical metabolic dysfunctions. All hematochemical and redox parameters were assessed using the CLINI5® diagnostic platform (Callegari S.p.A., Parma, Italy), a compact, validated, pharmacy-based point-of-care system for multiparametric biochemical evaluation, whose accuracy and clinical applicability have been demonstrated in peer-reviewed studies. Its use allows rapid, minimally invasive, and reliable measurements, enabling effective monitoring in real-life preventive settings and enhancing the translational value of nutraceutical interventions.
However, certain limitations must be acknowledged: the retrospective, non-randomized design, with the absence of a placebo group, introduces potential selection and confounding biases. In addition, the short duration (8 weeks) does not allow evaluation of long-term cardiometabolic outcomes or sustainability of effects. Moreover, LDL-C values were estimated using the Friedewald formula through a validated pharmacy-based point-of-care platform. While this method is widely employed in community and preventive settings, it is known to have limitations compared with direct assays, particularly in subjects with higher triglyceride levels. Nevertheless, the use of a standardized calculation ensured internal consistency across all participants, allowing the detection of clinically relevant lipid trends within this real-world context.
Future studies should aim to validate these findings in larger, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with longer follow-up durations and the inclusion of hard endpoints such as diabetes conversion rates, endothelial function, or cardiovascular biomarkers. Investigating the mechanistic correlations (e.g., AMPK phosphorylation, gut microbiota modulation, epigenetic signaling) would further support the translational relevance of berberine-based interventions. From a practical perspective, the pharmacist-led model of identifying and managing IFG with evidence-based nutraceuticals warrants structured implementation within territorial health systems. However, challenges remain in terms of regulatory recognition, reimbursement frameworks, and the standardization of nutraceutical formulations, which require harmonization across clinical, industrial, and public health sectors.
5. Conclusions
This real-world study demonstrates that a high-bioaccessibility berberine formulation (ToBeRock®) is safe, well-tolerated, and effective in improving glycemic, lipid, hemodynamic, and oxidative stress parameters in individuals with impaired fasting glucose. The observed dose-dependent effects support its potential use as a frontline nutraceutical in early cardiometabolic prevention. Further randomized trials are warranted to confirm and extend these findings over longer durations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.; methodology, V.C.; software, V.C.; validation, A.C., V.C. and A.M.; formal analysis, A.M. and V.C.; investigation, A.C.; data curation, V.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C., E.R. and M.P.; writing—review and editing, A.C., A.M., V.C. and G.C.; visualization, V.C. and A.M.; supervision, G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons concerning the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation). At the end of the study, data were collected and entered into a secure electronic system anonymously, and stored at the Department of Drug Science and Technology for a period not exceeding that necessary for the purposes for which they were collected or subsequently processed as required by applicable regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| FPG | Fasting Plasma Glucose |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
| IFG | Impaired Fasting Glucose |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| FORT | Free Oxygen Radicals Test |
| FORD | Free Oxygen Radicals Defence |
| REDOX Index | Ratio between FORT and FORD values (oxidative balance index) |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, P.; Baldessin, L.; Pagliacci, S. Prediabetes, Undiagnosed Diabetes and Diabetes Risk in Italy in 2017–2018: Results from the First National Screening Campaign in Community Pharmacies. J. Public Health 2022, 44, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, S.; Holt, R.; Portlock, J.; Price, H. The Role of Community Pharmacists and Their Position in the Delivery of Diabetes Care: An Update for Medical Professionals. Postgrad. Med. J. 2020, 96, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krass, I.; Twigg, M.J.; Mitchell, B.; Carter, R.; Mohebbi, M.; Shih, S.T.F.; Trinder, P.; Versace, V.L.; Wilson, F.; McNamara, K.; et al. Pharmacy diabetes screening trial (PDST): Outcomes of a national clustered randomized controlled trial comparing three screening methods for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in community pharmacy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 197 (Suppl. 1), 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krass, I.; Versace, M.J.; McNamara, K. Participant and GP Perspectives and Experiences of Screening for Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Community Pharmacy During the Pharmacy Diabetes Screening Trial. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.R.; de Oliveira, M.G.G.; Camargo, M.S.; Moreira, P.M.B.; de Castro, P.R.; Aguiar, E.C.; Mistro, S. Improving Pharmaceutical Practice in Diabetes Care Using Point-of-Care Glycated Haemoglobin Testing in the Community Pharmacy. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2024, 32, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, M.; Patti, A.M.; Giglio, R.V.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bajraktari, G.; Bianchi, C.; Çalık, A.N.; Djuric, D.M.; Ezhov, M.; et al. The Role of Nutraceuticals in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Colletti, A. Nutraceuticals and Cholesterol Lowering: Clinical Evidence in the Management of Hyperlipidemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Angelini, F.; Belli, L.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Da Ros, R.; De Pergola, G.; Gaudio, G.V.; Lupi, A.; Sartore, G.; et al. Nutraceuticals and Supplements in Management of Prediabetes and Diabetes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Hwang, J.; Nasreen, I.; Sicignano, D.; Pasupuleti, V.; Snow-Caroti, K.; White, C.M. Impact of Berberine or Berberine Combination Products on Lipoprotein, Triglyceride and Biological Safety Marker Concentrations in Patients with Hyperlipidemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diet. Suppl. 2024, 21, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Jia, W. Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Dyslipidemia with the Natural Plant Alkaloid Berberine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, A.; Fratter, A.; Pellizzato, M.; Cravotto, G. Nutraceutical Approaches to Dyslipidaemia: The Main Formulative Issues Preventing Efficacy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Lu, F. Berberine in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 591654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Hao, H.P.; Xie, H.G.; Lai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, G. Extensive Intestinal First-Pass Elimination and Predominant Hepatic Distribution of Berberine Explain Its Low Plasma Levels in Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-X.; Tang, D.; Feng, L.; Zheng, Z.-G.; Wang, R.-S.; Wu, A.-G.; Duan, T.-T.; He, B.; Zhu, Q. Development of Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Oral Bioavailability Enhancement of Berberine Hydrochloride. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. S1), S27–S49. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 1–50. ISBN 9241594934. [Google Scholar]
- ESC Scientific Document Group. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4043–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.W.; Kotta, S.; Ansari, S.H.; Sharma, R.K.; Ali, J. Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System (SNEDDS) of the Poorly Water-Soluble Grapefruit Flavonoid Naringenin: Design, Characterization, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorgis, L.; Zeller, M.; Vergely, C.; Sicard, P.; Buffet, P.; L’Huillier, I.; Beer, J.C.; Cottin, Y.; Rochette, L. Validation of assessment of circulate oxidative stress markers by the Free Oxygen Radicals Testing (FORT)assay among patients with acute myocardial infarction. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. Suppl. 2011, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danciu, A.M.; Ghitea, T.C.; Bungau, A.F.; Vesa, C.M. The Relationship Between Oxidative Stress, Selenium, and Cumulative Risk in Metabolic Syndrome. In Vivo 2023, 37, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, Without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, P.R.; Akinkuolie, A.O.; Chu, A.Y.; Shah, S.H.; Kraus, W.E.; Craig, D.; Padmanabhan, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M.; Chasman, D.I.; et al. Atherogenic Lipoprotein Determinants of Cardiovascular Disease and Residual Risk Among Individuals with Low Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, M.; Ling, C.; Sun, Q.; Harb, R.; Ashmaig, M.; Warnick, R.; Sethi, A.; Fleming, J.K.; Otvos, J.D.; Meeusen, J.W.; et al. A New Equation for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients with Normolipidemia and/or Hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyakumar, V.; Park, J.; Golozar, A.; Lazo, M.; Quispe, R.; Guallar, E.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Jones, S.R.; Martin, S.S. Fasting Versus Nonfasting and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Accuracy. Circulation 2018, 137, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Alpert, B.; Mieke, S.; Asmar, R.; Atkins, N.; Eckert, S.; Frick, G.; Friedman, B.; Graßl, T.; Ichikawa, T.; et al. A Universal Standard for the Validation of Blood Pressure Measuring Devices. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sureda, A.; Jafari, S.; Memariani, Z.; Tewari, D.; Annunziata, G.; Barrea, L.; Hassan, S.T.S.; Šmejkal, K.; Malaník, M.; et al. Berberine in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1923–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Song, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Berberine for Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phytomedicine 2023, 117, 154891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rubio, K.G.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Robles-Cervantes, J.A. Berberine Reduces Vascular Stiffness in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2016, 10, S68–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).