Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanistic Innovations in Small-Molecule GLP-1RAs
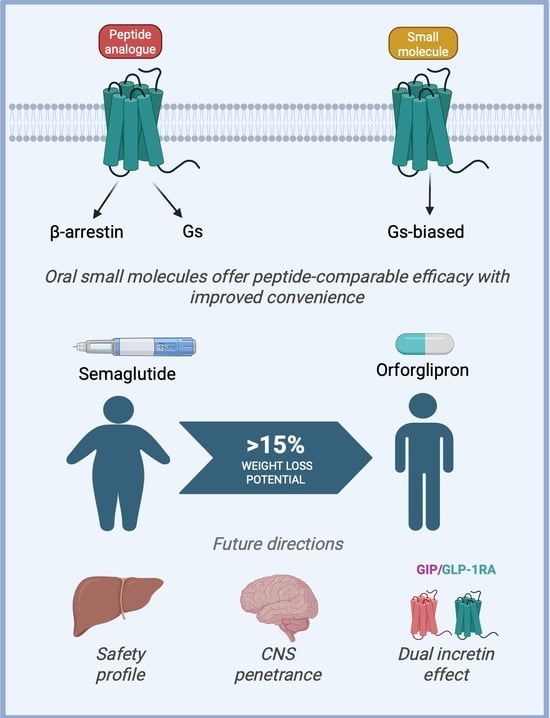
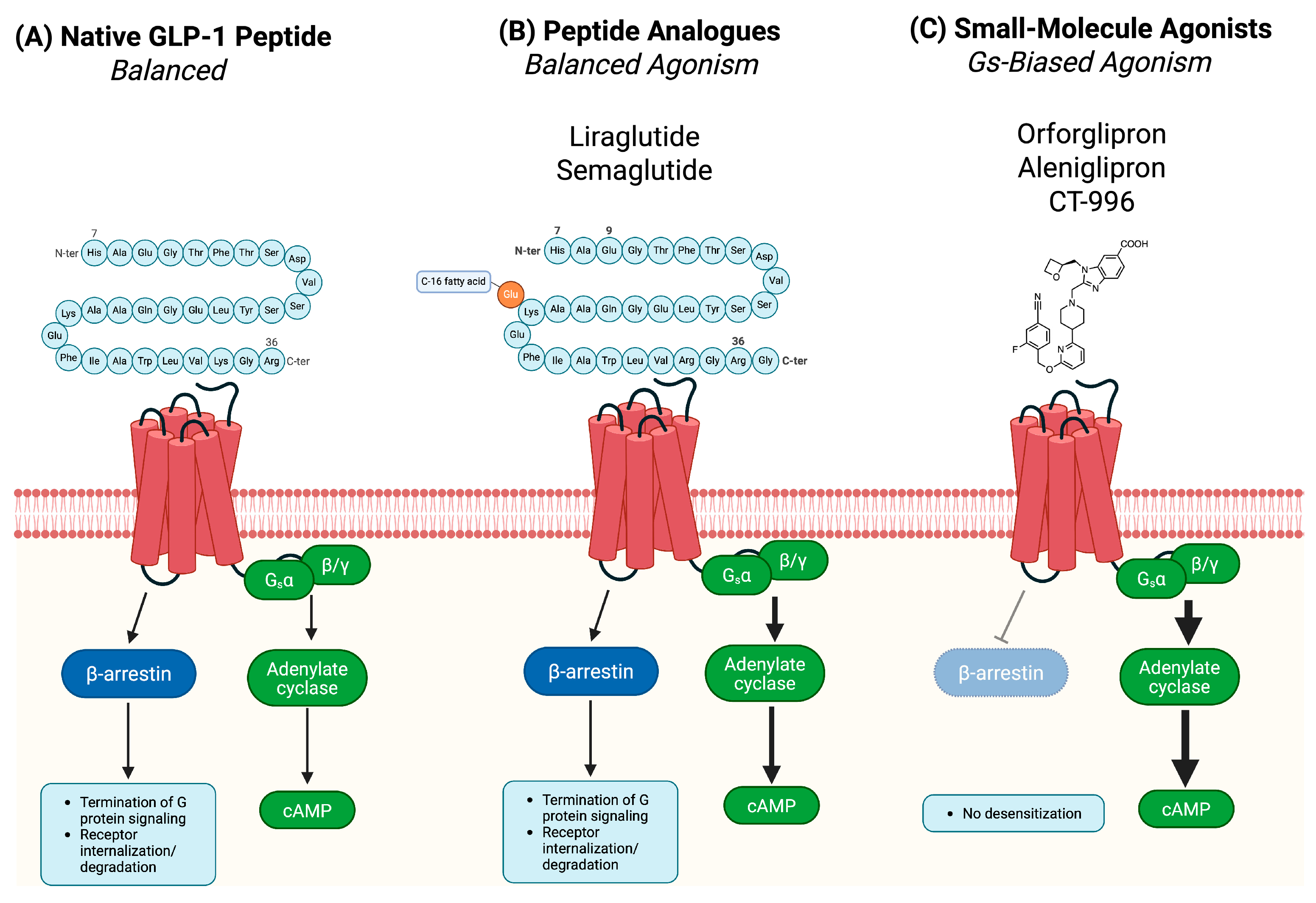
2.1. Gs-Biased Agonism: Preferential G Protein Signaling and Therapeutic Relevance
2.2. Non-Canonical Binding and Allosteric Modulation in Small-Molecule GLP-1R Agonism
| Ligand (Representative Compound) | Molecular Class | Binding Site Location | GLP-1R Domains Engaged | Signaling Bias | Pharmacological Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 (native peptide) | Endogenous peptide | Canonical orthosteric (dual-site model) | Extracellular domain (ECD) + TM1, TM2, TM7 | Balanced (Gs + β-arrestin) | Reference ligand; activates both Gs and β-arrestin pathways [18] |
| Liraglutide | Peptide analogue | Canonical orthosteric | ECD + TM core bundle | Balanced | Long-acting; maintains native GLP-1 signaling profile [20] |
| Semaglutide | Peptide analogue | Canonical orthosteric | ECD + TM core bundle | Balanced | High GLP-1R affinity; acylated for prolonged action [7] |
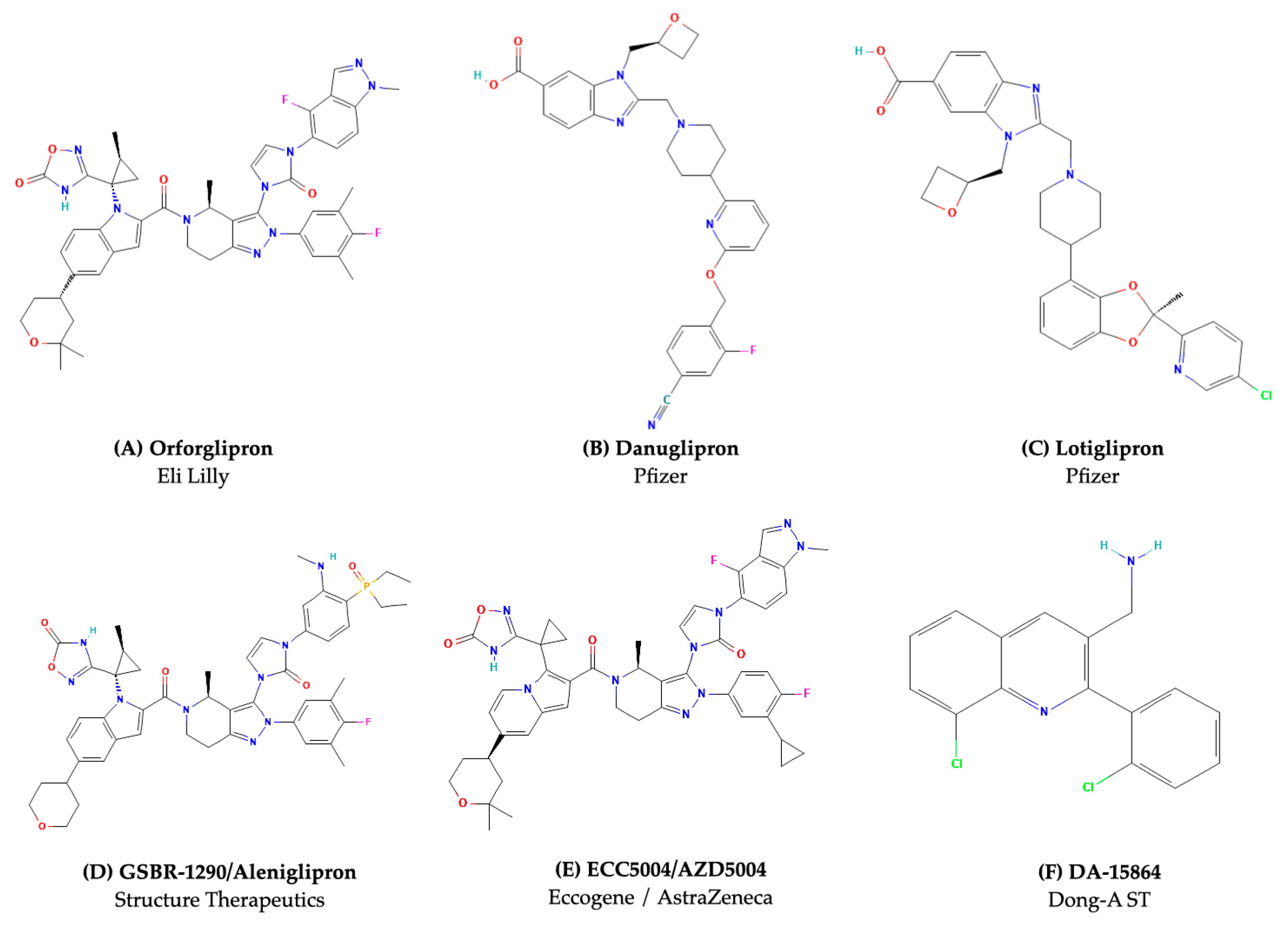
| Orforglipron (LY3502970) | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes (deep TM pocket) | TM1, TM2, TM3, TM5, TM7 | Gs-biased | Strong Gs activation; negligible β-arrestin recruitment [45] |
| Danuglipron (PF-06882961) | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes (TM cavity) | TM1, TM2, TM7 | Gs-biased | Robust cAMP signaling; limited β-arrestin activity [46] |
| Lotiglipron | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Gs-biased | Designed for potent cAMP activation; discontinued due to liver toxicity [47] |
| GSBR-1290 (Aleniglipron) | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM1, TM2, TM7 | Gs-biased | Selective Gs activator; minimal receptor internalization [38] |
| CT-996 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM core (specific residues not fully disclosed) | Gs-biased | Avoids β-arrestin recruitment; long pharmacokinetic half-life [48] |
| ECC5004 (AZD5004) | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding mode | TM domain | Gs-biased | Enhances cAMP; minimal β-arrestin coupling [49] |
| TERN-601 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Gs-biased | Preclinical candidate; strong cAMP response [50] |
| GS-4571 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Gs-biased | Stimulates insulinotropic cAMP pathway in β-cells [51] |
| DA-15864 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Gs-biased | Investigated for metabolic and neurological applications [52] |
| MLX-7505 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Gs-biased | Early-stage development; bias profile under investigation [53] |
| RGT-075 | Small molecule | Non-canonical orthosteric binding modes | TM domain | Balanced | Full agonist; dual activation of Gs and β-arrestin pathways [54] |
| BETP (PAM) | Positive allosteric modulator | Allosteric (extracellular TM cleft) | TM domain, near ECL2 | Modulates Gs (not an agonist) | Enhances endogenous GLP-1 response; no intrinsic activity; explored in combination therapy [41] |
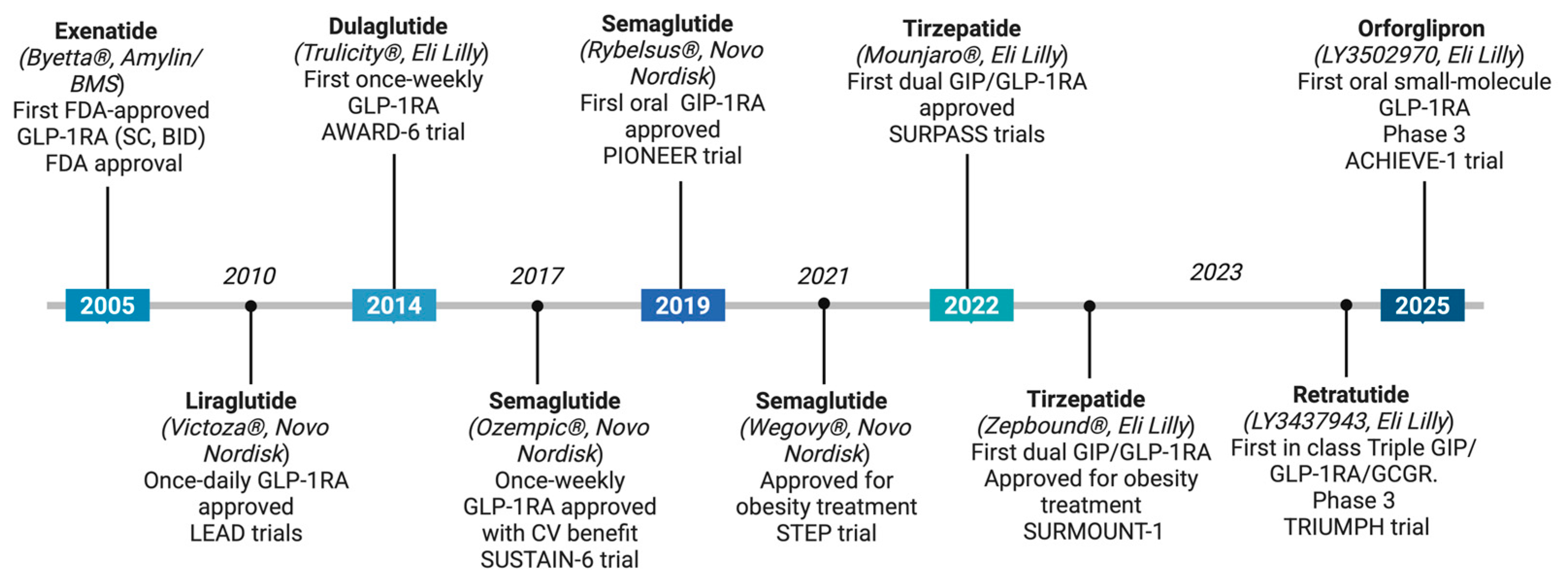
3. Clinical Development and Leading Candidates of Small-Molecule GLP-1RAs
3.1. Orforglipron (Eli Lilly): A Clinically Advanced Oral G Protein-Biased GLP-1RA in Phase 3 Trials
3.2. Danuglipron and Lotiglipron (Pfizer): The Collapse of a Promising Class
3.3. GSBR-1290/Aleniglipron (Structure Therapeutics): Allosteric Gs-Biased Agonist with Hepatic Safety
3.4. CT-996 (Roche/Carmot Therapeutics): Fast-Onset Candidate with Food-Independent Absorption
3.5. ECC5004/AZD5004 (Eccogene/AstraZeneca): Primate-Selective Molecule with Simplified Dosing
3.6. TERN-601 (Terns Pharmaceuticals): Low-Burden Oral Option for Weight-Centric Therapy
3.7. GS-4571 (Gilead Sciences) and Emerging Preclinical Candidates: Expanding the Oral GLP-1RA Pipeline
4. Redefining Metabolic Therapy: Clinical Promise of Small-Molecule GLP-1RAs
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Hepatic Safety and Structural Liability
5.2. Pharmacodynamic Variability and Clinical Differentiation
5.3. Integration into Clinical Practice and Guidelines
5.4. Market Competition and Therapeutic Positioning
6. Patent and Innovation Landscape
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| AEs | Adverse events |
| cAMP | Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CVOT | Cardiovascular outcomes trial |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| EPAC2 | Exchange protein activated by cAMP 2 |
| ECL | Extracellular loop |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| GCGR | Glucagon Receptor |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GIAEs | Gastrointestinal adverse events |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP-1RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| MR | Modified release |
| PAM | Positive allosteric modulator |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| QD | Once daily (quaque die) |
| SAEs | Serious adverse events |
| SGLT2i | Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor |
| SNAC | Sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino] caprylate |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TM | Transmembrane |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Lien, N.; Vuong, C.; Schmitt, M.H.; Soorya, Y.; Abubakar, B.A.; Muiznieks, L.; Embry, N.; Siddaiah, H.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Mediated Weight Loss and Diabetes Mellitus Benefits: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e76101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiz, A.; Filion, K.B.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Peters, T.M.; Eisenberg, M.J. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Induced Weight Loss: A Review of Central and Peripheral Pathways in Appetite and Energy Regulation. Am. J. Med. 2025, 138, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawami, K.; Tanaka, A.; Node, K. Updated evidence on cardiovascular and renal effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists and combination therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors and finerenone: A narrative review and perspectives. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; McHugh, K.J. Strategies for overcoming protein and peptide instability in biodegradable drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 199, 114904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.F. The development of oral semaglutide, an oral GLP-1 analog, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Int. 2020, 11, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, F.K.; Aroda, V.R.; do Vale, R.D.; Holst-Hansen, T.; Laursen, P.N.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubino, D.M.; Garvey, W.T.; OASIS 1 Investigators. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A.; Edmonds, D.J.; Fortin, J.P.; Kalgutkar, A.S.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Loria, P.M.; Saxena, A.R.; Bagley, S.W.; Buckeridge, C.; Curto, J.M.; et al. A small-molecule oral agonist of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8208–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melson, E.; Ashraf, U.; Papamargaritis, D.; Davies, M.J. What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, C.; Savage, E.E.; Christopoulos, A.; Miller, L.J.; Sexton, P.M.; Wootten, D. Minireview: Signal bias, allosterism, and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1R: Implications for drug discovery. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; De Block, C.; Brown, K.; Wang, H.; Thomas, M.K.; Zeytinoglu, M.; Maldonado, J.M. Tirzepatide improved markers of islet cell function and insulin sensitivity in people with T2D (SURPASS-2). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, M.; Dunn, J.P.; Kushner, R.F.; Cao, D.; Harris, C.; Gibble, T.H.; Stefanski, A.; Griffin, R. Body composition changes during weight reduction with tirzepatide in the SURMOUNT-1 study of adults with obesity or overweight. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, F.S.; Douros, J.D.; Gabe, M.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Wainscott, D.B.; Suter, T.M.; Capozzi, M.E.; van der Velden, W.J.; Stutsman, C.; Cardona, G.R.; et al. Tirzepatide is an imbalanced and biased dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of care in diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. S1), S181–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022: A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2753–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.L. The development of Byetta (exenatide) from the venom of the Gila monster as an anti-diabetic agent. Toxicon 2012, 59, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Nissen, S.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Zinman, B.; Daniels, G.H.; Pocock, S.; Steinberg, W.M.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Mann, J.F.; et al. Design of the liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (LEADER) trial. Am. Heart J. 2013, 166, 823–830.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.; Frid, A.; Hermansen, K.; Shah, N.S.; Tankova, T.; Mitha, I.H.; Zdravkovic, M.; Düring, M.; Matthews, D.R.; LEAD-2 Study Group. Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride, and placebo, all in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes: The LEAD (Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes)-2 study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, K.M.; Povedano, S.T.; Forst, T.; González, J.G.; Atisso, C.; Sealls, W.; Fahrbach, J.L. Once-weekly dulaglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes (AWARD-6): A randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Saugstrup, T.; Buse, J.B.; Donsmark, M.; Zacho, J.; Davies, M.J. Incorporating and interpreting regulatory guidance on estimands in diabetes clinical trials: The PIONEER 1 randomized clinical trial as an example. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K.; SURPASS-2 Investigators. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L.; et al. Triple-hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity—A phase 2 trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Nagendra, L.; Anne, B.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, M.; Kamrul-Hasan, A.B.M. Orforglipron, a novel non-peptide oral daily glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist as an anti-obesity medicine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2024, 10, e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, F.; Li, Z. Non-peptide agonists and positive allosteric modulators of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors: Alternative approaches for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Bermudez, M. Allosteric coupling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2513–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liang, Y.-L.; Belousoff, M.J.; Deganutti, G.; Fletcher, M.M.; Willard, F.S.; Bell, M.G.; Christe, M.E.; Sloop, K.W.; Inoue, A.; et al. Activation of the GLP-1 receptor by a non-peptidic agonist. Nature 2020, 577, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B. The therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor biased agonism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 492–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Structure Therapeutics. GSBR-1290 demonstrates Gs-biased signaling and favorable GI tolerability: Phase 2a clinical results. In Proceedings of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Annual Meeting, Hamburg, Germany, 9–13 September 2024. Abstract. [Google Scholar]
- Haggag, A.Z.; Xu, J.; Butcher, L.; Pagnussat, S.; Davies, G.; Lundqvist, S.; Wang, W.; Van Zuydam, N.; Nelander, K.; Jha, A.; et al. Non-clinical and first-in-human characterization of ECC5004/AZD5004, a novel once-daily, oral small-molecule GLP-1 receptor agonist. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Zhong, W.; Yuan, D.; et al. Structural insights into the activation of GLP-1R by a small molecule agonist. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sun, B.; Yoshino, H.; Feng, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; Nagao, S.; Wainscott, D.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Droz, B.A.; et al. Structural basis for GLP-1 receptor activation by LY3502970, an orally active nonpeptide agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29959–29967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Shi, S.; Guan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, F.; Lei, H.; Lin, X. Discovery of GSBR-1290, a highly potent, orally available, novel small molecule GLP-1 receptor agonist. Diabetes 2023, 72 (Suppl. S1), 760-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Whiteaker, P. Mechanism of allosteric modulation of the Cys-loop receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2592–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Wainscott, D.B.; Stutsman, C.; Marín, A.; Ficorilli, J.; Cabrera, O.; Willard, F.S.; Sloop, K.W. Positive allosteric modulation of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor by diverse electrophiles. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10700–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, F.S.; Ho, J.D.; Sloop, K.W. Discovery and pharmacology of the covalent GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) allosteric modulator BETP: A novel tool to probe GLP-1R pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 88, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, N.; Wu, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, T. Targeting cryptic allosteric sites of G protein-coupled receptors as a novel strategy for biased drug discovery. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 212, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Chen, L.-N.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zou, X.; Ye, C.; Dai, A.; Liu, Q.; Huang, W.; Sun, X.; et al. Molecular insights into ago-allosteric modulation of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Lu, J.; Willars, G.B. Allosteric modulation of the activity of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) metabolite GLP-1 9–36 amide at the GLP-1 receptor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, E.; Ma, X.; Liu, R.; Robins, D.; Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Haupt, A.; Benson, C. Orforglipron (LY3502970), a novel, oral non-peptide glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist: A phase 1b, multicentre, blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, multiple-ascending-dose study in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Gorman, D.N.; Esquejo, R.M.; Bergman, A.; Chidsey, K.; Buckeridge, C.; Griffith, D.A.; Kim, A.M. Danuglipron (PF-06882961) in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending-dose phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckeridge, C.; Tsamandouras, N.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, S.; Brown, L.S.; Hernandez-Illas, M.; Saxena, A.R. Once-daily oral small-molecule glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist lotiglipron (PF-07081532) for type 2 diabetes and obesity: Two randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-ascending-dose phase 1 studies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, M.V.; Wabnitz, P.; Wu, J.; Toussaint Touson, S.; Elliott, M.A.; Chang, C.C.; Lickliter, J. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of CT-996, an Oral Small-Molecule, Signal-Biased GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Over 4 Weeks in Adults With Obesity. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Madrid, Spain, 11 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- AstraZeneca. Weight Management Virtual Event: IR Presentation. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/content/dam/az/Investor_Relations/events/Weight-Management-Virtual-Event-IR-presentation.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Terns Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Terns Pharmaceuticals Announces Positive Phase 1 Clinical Trial Results for TERN-601. 2024. Available online: https://ir.ternspharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/terns-pharmaceuticals-announces-positive-phase-1-clinical-trial/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Vogel, J.E.N.; Seung, M.; Marchand, B.; Bhangre, N.; Mukherjee, J.I.T.; Ammann, S.E.; Armstrong, M.; Brizgys, G.; Chin, E.; Chou, C.-H.; et al. 1625-P: GS-4571, an oral small molecule GLP-1R agonist, improves glucose tolerance and suppresses food intake in obese diabetic cynomolgus monkeys. Diabetes 2024, 73 (Suppl. S1), 1625-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Kim, M.K.; Son, M.H. The development of non-peptide glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearss, D.J.; Lin, C.; Medley, K.; Vankayalapati, H. 1139-P: Discovery of a Potent, Orally Efficacious Small Molecule Agonist of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor. Diabetes 2024, 73 (Suppl. S1), 1139-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, X.; Huang, W.; Guo, W.; Lin, J.; Zhong, W. 753-P: RGT-075, an Orally Efficacious Small Molecule GLP-1R Full Agonist in Cynomolgus Monkey Models. Diabetes 2022, 71 (Suppl. S1), 753-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikirica, M.V.; Martin, A.A.; Wood, R.; Leith, A.; Piercy, J.; Higgins, V. Reasons for Discontinuation of GLP1 Receptor Agonists: Data from a Real-World Cross-Sectional Survey of Physicians and Their Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Frias, J.P.; Brown, L.S.; Gorman, D.N.; Vasas, S.; Tsamandouras, N.; Birnbaum, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron for Glycemic Control Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2314493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Yu, H. Research Progress and Future Prospects of Small-Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs). Metab. Target Organ Damage 2025, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Blevins, T.; Connery, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Raha, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.; et al. Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Inc. Pfizer Provides Update on GLP-1-RA Clinical Development Program. Press Release. 2023. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-provides-update-glp-1-ra-clinical-development (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Frias, J.P.; Hsia, S.; Eyde, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Konig, M.; Kazda, C.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Pratt, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Orforglipron in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Randomised, Dose-Response, Phase 2 Study. Lancet 2023, 402, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Pamporis, K.; Stachteas, P.; Bougioukas, K.I.; Klisic, A.; Fragakis, N.; Rizzo, M. Safety and efficacy of the new, oral, small-molecule, GLP-1 receptor agonists orforglipron and danuglipron for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metabolism 2023, 149, 155710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, E.; Ma, X.; Liu, R.; Robins, D.; Haupt, A.; Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Benson, C. Orforglipron (LY3502970), a novel, oral non-peptide glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist: A Phase 1a, blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, single- and multiple-ascending-dose study in healthy participants. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, R.; Pratt, E.J.; Benson, C.T.; Bhattachar, S.N.; Sloop, K.W. Effect of Food Consumption on the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Once-Daily Orally Administered Orforglipron (LY3502970), a Non-Peptide GLP-1 Receptor Agonist. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloop, K.W.; Cox, A.L.; Wainscott, D.B.; White, A.; Droz, B.A.; Stutsman, C.; Showalter, A.D.; Suter, T.M.; Dunbar, J.D.; Snider, B.M.; et al. The Pharmacological Basis for Nonpeptide Agonism of the GLP-1 Receptor by Orforglipron. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadp5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütkemeyer, C.; Pasqualotto, E.; Ferreira, R.O.M.; Chavez, M.P.; Petris, I., Jr.; Dos Santos, H.V.; Wille, J.M.; Hohl, A.; Ronsoni, M.F.; van de Sande-Lee, S. Effects of Once-Daily Oral Orforglipron on Weight and Metabolic Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 68, e230469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eli Lilly and Company. A Study of Orforglipron (LY3502970) in Adult Participants with Type 2 Diabetes and Inadequate Glycemic Control with Diet and Exercise Alone (ACHIEVE-1). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05971940?term=ORFORGLIPRON&aggFilters=status:com&rank=4 and https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/413375; (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Eli Lilly and Company. A Study of Orforglipron (LY3502970) Compared with Oral Semaglutide in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes. Available online: https://trials.lilly.com/es-AR/trial/424335 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Eli Lilly’s Announcement Regarding Oral GLP-1 Orforglipron (Statistically Significant Efficacy and a Safety Profile Consistent with Injectable GLP-1 Medicines in Phase III ACHIEVE-1 for Type 2 Diabetes). News Release, 18 April 2025. Available online: https://www.chugai-pharm.co.jp/english/news/detail/20250418083000_1152.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Fatima, H.; Rangwala, H.S.; Mustafa, M.S.; Shafique, M.A.; Abbas, S.R.; Rizwan, A.; Fadlalla Ahmed, T.K.; Arshad, A. Evaluating Glycemic Control Efficacy and Safety of the Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3567–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil, R. Companies Seek Second GLP-1 Revolution—In Pill Form. Science 2025, 388, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Inc. Pfizer Provides Update on Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron. Press Release. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-provides-update-oral-glp-1-receptor-agonist (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Amin, N.B.; Frederich, R.; Tsamandouras, N.; Haggag, A.Z.; Schuster, T.; Zmuda, W.; Palmer, A.; Vasas, S.; Buckley, G.; Smith, T.R.; et al. Evaluation of an Oral Small-Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist, Lotiglipron, for Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Dose-Ranging, Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xing, W.; Jiang, W.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Q.; Ren, P.; Zhang, H.; et al. Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Profiles of a Novel GLP-1 Receptor Biased Agonist—SAL0112. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yun, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, T.; Xu, T.; Shen, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, K. Discovery of Novel 5,6-Dihydro-1,2,4-Triazine Derivatives as Efficacious Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7988–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Ibarra, L.; Yue, H.; Barth, A.; Bach, M.A. 767-P: A Phase 1b/2a Study of the Safety and Tolerability of GSBR-1290, a Novel Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist (GLP-1RA), in Healthy Overweight/Obese Volunteers (HOV) and Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Diabetes 2024, 73 (Suppl. S1), 767-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasherbrum Bio Inc., a Wholly Owned Subsidiary of Structure Therapeutics. A Phase 2b, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Range Finding Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Multiple Doses of GSBR-1290 in Participants Living with Obesity or Overweight with at Least One Weight-Related Comorbidity. Available online: https://www.centerwatch.com/clinical-trials/listings/NCT06693843/a-phase-2b-dose-range-finding-study-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-multiple-doses-of-gsbr-1290-in-participants-living-with-obesity-or-overweight-with-at-least-one-weight-related-comorbidity (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Roche. [Ad Hoc Announcement Pursuant to Art. 53 LR] Roche Announces Positive Phase I Results of Its Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist CT-996 for the Treatment of People with Obesity. Press Release. Available online: https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2024-07-17 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Chugai Therapeutics, a Roche Company. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1 Study Evaluating the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Single and Multiple Doses of CT-996 in Overweight/Obese Participants and in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05814107 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Luo, J.; Rodriguez, R.; Hergarden, A.; Tracy, T.; Lam, D.; Garai, S.; Marshall, D.; Hansen, S.K.; Chakravarthy, M. 771-P: Efficacy of CT-996, an Oral Small Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in Human GLP-1 Receptor Knockin Mice and Obese Cynomolgus Monkeys. Diabetes 2024, 73 (Suppl. S1), 771-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche. IRP 2024 Presentation: Pipeline Update Including CT-996. Available online: https://assets.roche.com/f/176343/x/a04e4301c3/irp250424-a.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- AstraZeneca. A Phase I, Two-Part Study in Healthy Volunteers Consisting of a Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multiple Ascending Dose Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of AZD5004 and a Randomized, Open-Label, Two-Way Cross-Over Study to Compare the Relative Bioavailability of Two Oral Tablet Strengths of AZD5004. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05654831 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Liang, Y.L.; Khoshouei, M.; Glukhova, A.; Furness, S.G.B.; Zhao, P.; Clydesdale, L.; Koole, C.; Truong, T.T.; Thal, D.M.; Lei, S.; et al. Phase-Plate Cryo-EM Structure of a Biased Agonist-Bound Human GLP-1 Receptor–Gs Complex. Nature 2018, 555, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccogene Inc. Eccogene Receives Milestone Payment of $60 Million from AstraZeneca Following Dosing of the First Patient in Global Phase 2b Program of ECC5004/AZD5004 for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Press Release. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/10/23/2779676/0/en/Eccogene-Receives-Milestone-Payment-of-60-Million-from-AstraZeneca.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Waldron, J. Tern’s Oral GLP-1 Shows 5% Weight Loss at One Month at Highest Dose. 2024. Available online: https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/terns-oral-glp-1-shows-5-weight-loss-1-month-highest-dose (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Terns Pharmaceuticals Inc. Terns Pharmaceuticals Provides Program Updates and Announces Design of FALCON Phase 2 Clinical Trial of TERN-601. 2025. Available online: https://ir.ternspharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/terns-pharmaceuticals-provides-program-updates-and-announces-0/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Gilead Sciences Inc. Study of GS-4571 in Healthy Participants, Nondiabetic Obese Participants, and Nonobese Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) (Study ID: GS-US-506-6610). Available online: https://www.gileadclinicaltrials.com/study?nctid=NCT06562907 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Ozmosi. GS-4571 Drug Profile. Available online: https://pryzm.ozmosi.com/product/gs-4571 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Gilead Sciences Inc. Small Molecule GLP-1R Agonists and Uses Thereof (Patent Filing). 2023. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023045678A1 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Zhi, L.; Xue, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, M.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; He, P.; et al. Novel Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist S6 Stimulates Insulin Secretion from Rat Islets. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 664802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, I.G.; Im, A.R.; Lee, D.G.; Choi, W.G.; Jang, E.; Park, J.S.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; An, K.; et al. 93-LB: Discovery of ID110521156, a Small Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes 2023, 72 (Suppl. S1), 93-LB. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 137319706, Orforglipron. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/137319706 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 134611040, Danuglipron. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/134611040 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 146609022, Lotiglipron. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/146609022 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 164809721, Aleniglipron. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/164809721 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 167350327, GLP-1 Receptor Agonist 14. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/167350327 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 59264634, (8-Chloro-2-(2-chlorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl)methanamine. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/59264634 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes—State-of-the-Art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhiary, R.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Gabriele, S.; Beall, R.F.; Tu, S.S.; Feldman, W.B. Patents and Regulatory Exclusivities on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. JAMA 2023, 330, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Du, Y.; Lou, J.; Gurbuz, S.; Thomas, M.K.; Hartman, M.L.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and Glucagon Receptor Agonist, for People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo- and Active-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Phase 2 Trial Conducted in the USA. Lancet 2023, 402, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Agent | Developer | Clinical Stage | HbA1c Reduction | Weight Loss | Mechanism | Tolerability | Dosing/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orforglipron [28,58,64,66,67,68] | Eli Lilly | Phase 3 (T2DM, obesity) | ~1.2–1.7% | Up to 14.7% (36w) | G protein-biased; partial β-arrestin | GI AEs; 10–17% discontinuation | Once daily; food-independent |
| Danuglipron [56,57] | Pfizer | Discontinued (April 2025) | ~1.16% | 4–5.5 kg (16w) | G protein-biased; allosteric | GI AEs; hepatotoxicity (late) | BID; QD formulation abandoned |
| Lotiglipron [47,59,72] | Pfizer | Discontinued (2023) | ~1.0–1.6% | ~5.4% | G protein-biased | ALT/AST ↑; hepatotoxicity | Once daily; program halted |
| GSBR-1290 (aleniglipron) [75,76] | Structure Therapeutics | Phase 2b (ongoing) | ~1.0% | Up to 6.2% (12w) | G protein-biased; allosteric | Mild GI AEs; no hepatotoxicity | Once daily; no permeation enhancer |
| CT-996 [48,77,79] | Roche/Carmot | Phase 2 (initiated) | Not reported | 6.1% (4w) | G protein-biased; transmembrane site | Well tolerated; no SAEs | QD; food-independent; rapid onset |
| ECC5004 (AZD5004) [34] | Eccogene/AstraZeneca | Phase 2b (per sponsor) | ~2.2 mmol/L (FPG) | ~2.5–3.0 kg (28d) | G protein-biased; primate-selective | Mild GI AEs; no hepatotoxicity | QD; food-independent; primate efficacy only |
| TERN-601 [50] | Terns Pharmaceuticals | Phase 1 completed | Trend only | Up to 5.5% (28d) | G protein-biased | No SAEs or discontinuations | QD; dose-escalation tested |
| GS-4571 [51] | Gilead Sciences | Phase 1 (ongoing) | Preclinical only | 6.5% (preclinical) | Presumed Gs-biased; CNS-penetrant | No human data | Structure unpublished |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saldívar-Cerón, H.I.; Vargas-Camacho, J.A.; León-Cabrera, S.; Briseño-Díaz, P.; Castañeda-Ramírez, A.E.; Muciño-Galicia, A.E.; Díaz-Domínguez, M.R. Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020026
Saldívar-Cerón HI, Vargas-Camacho JA, León-Cabrera S, Briseño-Díaz P, Castañeda-Ramírez AE, Muciño-Galicia AE, Díaz-Domínguez MR. Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2025; 93(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaldívar-Cerón, Héctor Iván, Jorge Arturo Vargas-Camacho, Sonia León-Cabrera, Paola Briseño-Díaz, Ari Evelyn Castañeda-Ramírez, Axel Eduardo Muciño-Galicia, and María Regina Díaz-Domínguez. 2025. "Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies" Scientia Pharmaceutica 93, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020026
APA StyleSaldívar-Cerón, H. I., Vargas-Camacho, J. A., León-Cabrera, S., Briseño-Díaz, P., Castañeda-Ramírez, A. E., Muciño-Galicia, A. E., & Díaz-Domínguez, M. R. (2025). Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanistic Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 93(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020026