Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Thermodynamic Solubility Measurement
2.2.2. Determination of Effective Permeability (Pe) with PAMPA
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
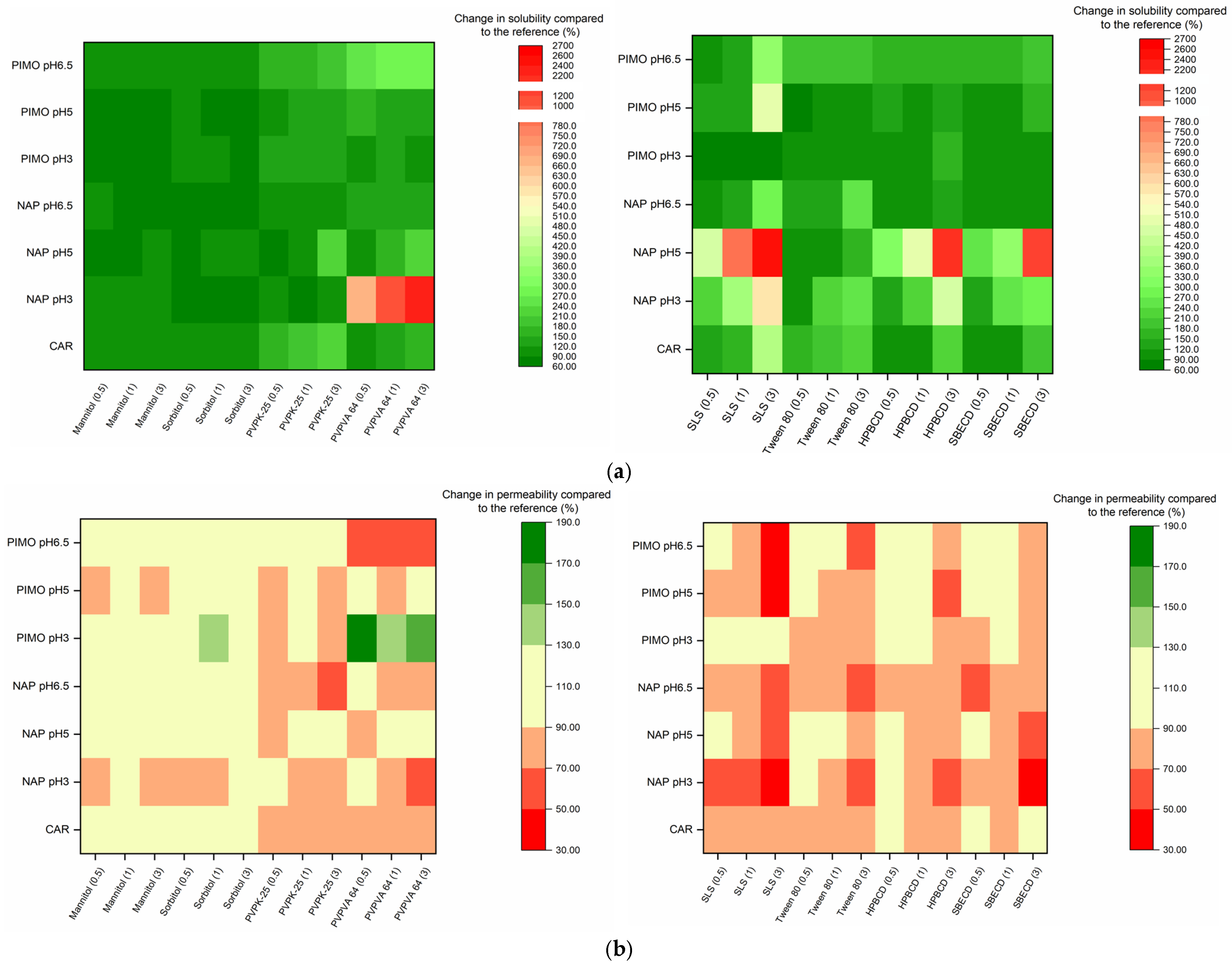
3.1. Equilibrium Solubility
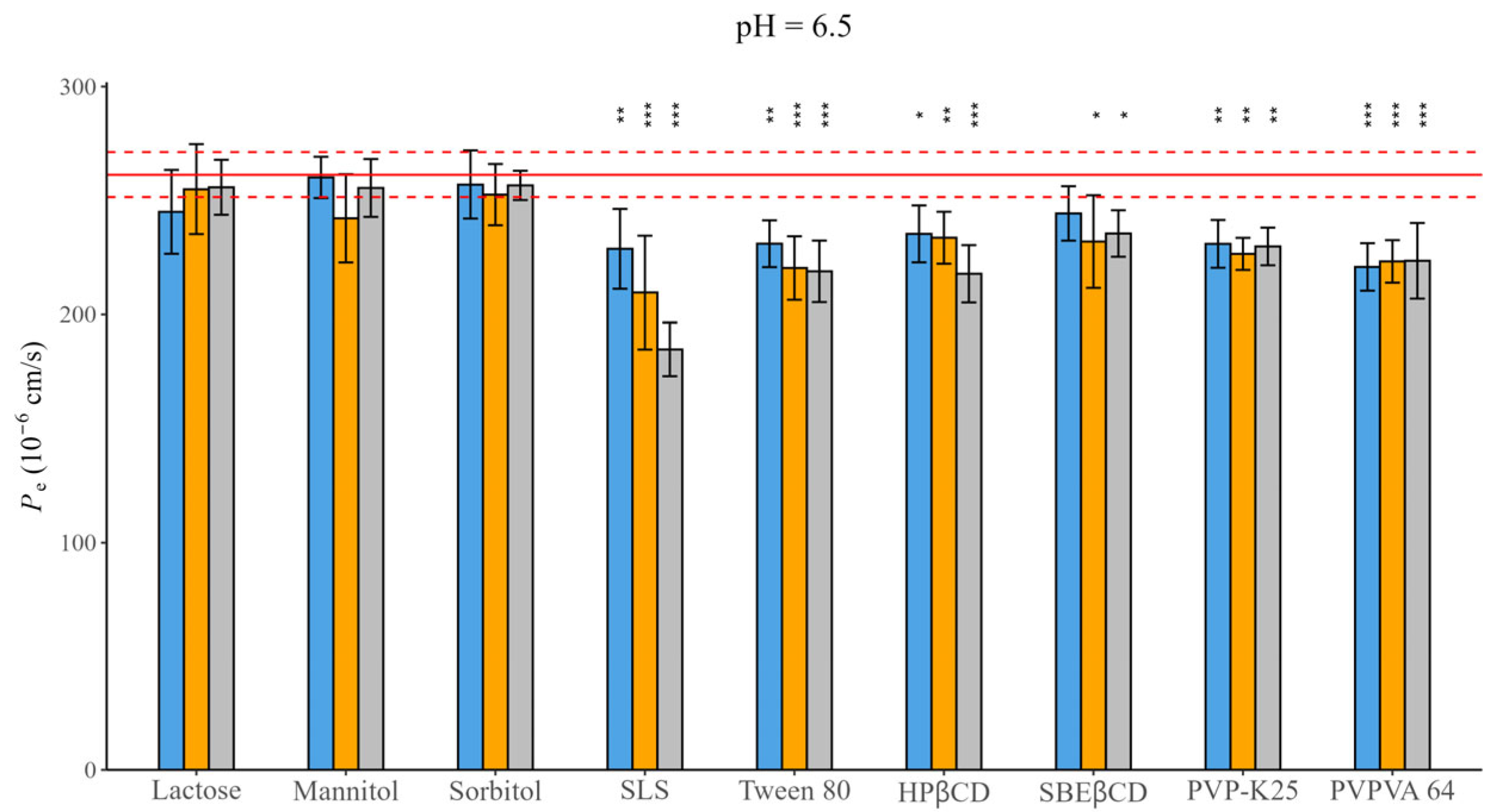
3.2. Effective Permeability
4. Discussion
4.1. Fillers
4.2. Surfactants
4.3. Polymers
4.4. Cyclodextrins
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| API | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients |
| Pe | Effective Permeability |
| PAMPA | Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay |
| SSF | Saturated Shake Flask Method |
| CAR | Carbamazepine |
| NAP | Naproxen |
| PIMO | Pimobendan |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutical Classification System |
| CDs | Cyclodextrins |
| HPβCD | Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin |
| SBEβCD | Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin |
| PVP-K25 | Polyvinylpyrrolidone K25 |
| PVPVA 64 | Polyvinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate 64 |
| SLS | Sodium Lauryl Sulphate |
| Tween 80 | Polysorbat 80 |
| CMC | Critical Micelle Concentration |
References
- Khan, K.U.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F.; Suhail, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ijaz, S. Overview of Nanoparticulate Strategies for Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayun, B.; Lin, X.; Choi, H.J. Challenges and Recent Progress in Oral Drug Delivery Systems for Biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascone, S.; Lamberti, G.; Marra, F.; Titomanlio, G.; d’Amore, M.; Barba, A.A. Gastrointestinal Behavior and ADME Phenomena: I. In Vitro Simulation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation Design for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs Based on Biopharmaceutics Classification System: Basic Approaches and Practical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 46, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamba, I.; Sombié, C.B.; Yabré, M.; Zimé-Diawara, H.; Yaméogo, J.; Ouédraogo, S.; Lechanteur, A.; Semdé, R.; Evrard, B. Pharmaceutical Approaches for Enhancing Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 204, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, P.; He, W. Solubilization Techniques Used for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 4683–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Magdum, C.; Jadge, D.; Jagtap, R. Solubility Enhancement Technique: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Csicsák, D.; Szolláth, R.; Kádár, S.; Ambrus, R.; Bartos, C.; Balogh, E.; Antal, I.; Köteles, I.; Tőzsér, P.; Bárdos, V.; et al. The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.M.; Hoffman, A.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Solubility-Permeability Interplay in Using Cyclodextrins as Pharmaceutical Solubilizers: Mechanistic Modeling and Application to Progesterone. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, A.; Beig, A.; Lindley, D.; Miller, J.M. The Solubility–Permeability Interplay and Oral Drug Formulation Design: Two Heads Are Better than One. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Beig, A.; Krieg, B.J.; Carr, R.A.; Borchardt, T.B.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L.; Dahan, A. The Solubility-Permeability Interplay: Mechanistic Modeling and Predictive Application of the Impact of Micellar Solubilization on Intestinal Permeation. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Agbaria, R.; Dahan, A. Oral Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs: The Tradeoff between Solubility Increase and Permeability Decrease When Using Cyclodextrin-Based Formulations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. The Interaction of Nifedipine with Selected Cyclodextrins and the Subsequent Solubility-Permeability Trade-Off. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Lindley, D.; Dahan, A. Striking the Optimal Solubility-Permeability Balance in Oral Formulation Development for Lipophilic Drugs: Maximizing Carbamazepine Blood Levels. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Lindley, D.; Carr, R.A.; Zocharski, P.; Agbaria, R.; Dahan, A. Head-To-Head Comparison of Different Solubility-Enabling Formulations of Etoposide and Their Consequent Solubility-Permeability Interplay. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, S.; Geoghegan, C.; Brayden, D.J. Safety of Surfactant Excipients in Oral Drug Formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 202, 115086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, H.M.S.H.; Maw, P.D.; Loftsson, T.; Jansook, P. A Current Overview of Cyclodextrin-Based Nanocarriers for Enhanced Antifungal Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kádár, S.; Tőzsér, P.; Nagy, B.; Farkas, A.; Nagy, Z.K.; Tsinman, O.; Tsinman, K.; Csicsák, D.; Völgyi, G.; Takács-Novák, K.; et al. Flux-Based Formulation Development—A Proof of Concept Study. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, B.M.; Rahman, S.N.R.; Pawde, D.M.; Goswami, A.; Shunmugaperumal, T. Orally Administered Drug Solubility-Enhancing Formulations: Lesson Learnt from Optimum Solubility-Permeability Balance. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine-Shamir, N.; Dahan, A. Ethanol-Based Solubility-Enabling Oral Drug Formulation Development: Accounting for the Solubility-Permeability Interplay. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qiao, N.; Wang, K. Influence of Sodium Lauryl Sulfate and Tween 80 on Carbamazepine-Nicotinamide Cocrystal Solubility and Dissolution Behaviour. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Panigrahi, P.P. Solubility Enhancement of Etoricoxib by Cosolvency Approach. ISRN Phys. Chem. 2012, 2012, 820653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA—Inactive Ingredients Database. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/inactive-ingredients-database-download (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Avdeef, A. Absorption and Drug Development: Solubility, Permeability and Charge State, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, C.A.S.; Holm, R.; Jørgensen, S.A.; Andersson, S.B.E.; Artursson, P.; Beato, S.; Borde, A.; Box, K.; Brewster, M.; Dressman, J.; et al. Early Pharmaceutical Profiling to Predict Oral Drug Absorption: Current Status and Unmet Needs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethorst, D.; Mols, R.; Duchateau, G.; Tack, J.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Characterization of Human Duodenal Fluids in Fasted and Fed State Conditions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdeef, A. The Rise of PAMPA. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansy, M.; Senner, F.; Gubernator, K. Physicochemical High Throughput Screening: Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeation Assay in the Description of Passive Absorption Processes. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, E.; Comer, J.E.A.; Takács-Novák, K. Study of Equilibrium Solubility Measurement by Saturation Shake-Flask Method Using Hydrochlorothiazide as Model Compound. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veseli, A.; Žakelj, S.; Kristl, A. A Review of Methods for Solubility Determination in Biopharmaceutical Drug Characterization. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W. Practical Aspects of Solubility Determination in Pharmaceutical Preformulation. In Solvent Systems and Their Selection in Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects; Augustijns, P., Brewster, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume VI. [Google Scholar]
- Tőzsér, P.; Kovács, L.L.; Kádár, S.; Csicsák, D.; Sóti, P.; Völgyi, G.; Sinkó, B.; Nagy, Z.K.; Borbás, E. The Effect of Surfactants and PH Modifying Agents on the Dissolution and Permeation of Pimobendan. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeef, A.; Fuguet, E.; Llinàs, A.; Ràfols, C.; Bosch, E.; Völgyi, G.; Verbic, T.; Boldyreva, E.; Takács-Novák, K. Equilibrium Solubility Measurement of Ionizable Drugs—Consensus Recommendations for Improving Data Quality. Admet Dmpk 2016, 4, 117–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völgyi, G.; Csicsák, D.; Takács-Novák, K. Right Filter-Selection for Phase Separation in Equilibrium Solubility Measurement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.T.; Margarit, M.V.; Salcedo, G.E. Characterization and Solubility Study of Solid Dispersions of Flunarizine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Il Farm. 2002, 57, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinkó, B.; Kökösi, J.; Avdeef, A.; Takács-Novák, K. A PAMPA Study of the Permeability-Enhancing Effect of New Ceramide Analogues. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Massik, M.A.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Galal, S.; Daabis, N.A. Towards a Universal Dissolution Medium for Carbamazepine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine-Shamir, N.; Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. The Solubility, Permeability and the Dose as Key Factors in Formulation Development for Oral Lipophilic Drugs: Maximizing the Bioavailability of Carbamazepine with a Cosolvent-Based Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völgyi, G.; Baka, E.; Box, K.J.; Comer, J.E.A.; Takács-Novák, K. Study of PH-Dependent Solubility of Organic Bases. Revisit of Henderson-Hasselbalch Relationship. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 673, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Goel, A.; Sharma, S.; Parmar, M. Solubility enhancement techniques with special emphasis on hydrotrophy. Int. J. Pharma Prof. Res. 2010, 1, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fine-Shamir, N.; Dahan, A. Solubility-Enabling Formulations for Oral Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs: Considering the Solubility-Permeability Interplay for Accelerated Formulation Development. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinier, V.; Aubry, J.M. Sugar-Based Hydrotropes: Preparation, Properties and Applications. Carbohydr. Chem. 2014, 40, 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah Ali, H.; Kamal Omer, H. Solubility Enhancement of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug Using Hydrotropy and Mixed Hydrotropy-Based Solid Dispersion Techniques. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 2022, 7161660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, B.W.; Albers, E. Effect of Hydrotropic Substances on the Complexation of Sparingly Soluble Drugs with Cyclodextrin Derivatives and the Influence of Cyclodextrin Complexation on the Pharmacokinetics of the Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 80, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.P.; Srinivas, N.R.; Babu, R.J. Use of Sorbitol as Pharmaceutical Excipient in the Present Day Formulations–Issues and Challenges for Drug Absorption and Bioavailability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.L.; Straughn, A.B.; Sadrieh, N.; Meyer, M.; Faustino, P.J.; Ciavarella, A.B.; Meibohm, B.; Yates, C.R.; Hussain, A.S. A Modern View of Excipient Effects on Bioequivalence: Case Study of Sorbitol. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuguet, E.; Ràfols, C.; Rosés, M.; Bosch, E. Critical Micelle Concentration of Surfactants in Aqueous Buffered and Unbuffered Systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 548, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattachar, S.N.; Risley, D.S.; Werawatganone, P.; Aburub, A. Weak Bases and Formation of a Less Soluble Lauryl Sulfate Salt/Complex in Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) Containing Media. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 412, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolten, D.; Lietzow, R.; Türk, M. Solubility of Ibuprofen, Phytosterol, Salicylic Acid, and Naproxen in Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Y.; Shi, X.B.; Chang, J.H.; Wang, R.X.; Zhou, J.Y.; Liu, P. Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Glycyrrhetinic Acid: Using Soluplus, PVP, and PVPVA as the Polymer Matrix to Enhance Solubility, Bioavailability, and Stability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, K.; Qiao, N.; Yardley, V.; Li, M. Investigating Permeation Behavior of Flufenamic Acid Cocrystals Using a Dissolution and Permeation System. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4257–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, M.M.; Olesen, N.E.; Holm, P.; Langguth, P.; Holm, R.; Rades, T. Influence of Polymer Molecular Weight on Drug–Polymer Solubility: A Comparison between Experimentally Determined Solubility in PVP and Prediction Derived from Solubility in Monomer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2905–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornells, E.; Fuguet, E.; Mañé, M.; Ruiz, R.; Box, K.; Bosch, E.; Ràfols, C. Effect of Vinylpyrrolidone Polymers on the Solubility and Supersaturation of Drugs; a Study Using the Cheqsol Method. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.E.; Tao, J.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Yu, L. Solubilities of Crystalline Drugs in Polymers: An Improved Analytical Method and Comparison of Solubilities of Indomethacin and Nifedipine in PVP, PVP/VA, and PVAc. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.; Simonova, O.; Perlovich, G. Mechanistic Insight in Permeability through Different Membranes in the Presence of Pharmaceutical Excipients: A Case of Model Hydrophobic Carbamazepine. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarević, D.; Kachrimanis, K.; Djurić, Z.; Ibrić, S. Influence of Hydrophilic Polymers on the Complexation of Carbamazepine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 78, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Roy, S.; Kumar, A.; Mahmood, S.; Khodapanah, N.; Thomas, S.; Agatemor, C.; Ghosal, K. Physicochemical Characterization, Molecular Docking, and in Vitro Dissolution of Glimepiride-Captisol Inclusion Complexes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19968–19977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Agbaria, R.; Dahan, A. The Use of Captisol (SBE7-β-CD) in Oral Solubility-Enabling Formulations: Comparison to HPβCD and the Solubility-Permeability Interplay. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cyclodextrins: Effects on Drug Permeation through Biological Membranes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbás, E.; Nagy, Z.K.; Nagy, B.; Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Tsinman, O.; Tsinman, K.; Sinkó, B. The Effect of Formulation Additives on in Vitro Dissolution-Absorption Profile and in Vivo Bioavailability of Telmisartan from Brand and Generic Formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bárdos, V.; Szolláth, R.; Tőzsér, P.; Mirzahosseini, A.; Sinkó, B.; Angi, R.; Takács-Novák, K. Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020019
Bárdos V, Szolláth R, Tőzsér P, Mirzahosseini A, Sinkó B, Angi R, Takács-Novák K. Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2025; 93(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleBárdos, Vivien, Rita Szolláth, Petra Tőzsér, Arash Mirzahosseini, Bálint Sinkó, Réka Angi, and Krisztina Takács-Novák. 2025. "Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs" Scientia Pharmaceutica 93, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020019
APA StyleBárdos, V., Szolláth, R., Tőzsér, P., Mirzahosseini, A., Sinkó, B., Angi, R., & Takács-Novák, K. (2025). Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 93(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020019