Abstract
There is an urgent need for scientists to verify the pharmacological properties of medicinal plants. Leucophyllum frutescens (Lf) belongs to the family Scrophulariaceae, and it is used in the treatment of airway diseases such as cough, tuberculosis, and asthma. The methanolic extract of the aerial parts of Lf allows for the isolation and identification of verbascoside (Vb). This study aimed to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of Vb, a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside (CPG), on post-necrotic liver damage induced by thioacetamide (TA) via in vivo and in silico studies, with the latter considering a cancerous process. The aerial parts of Lf were extracted by maceration using hexane methanol (5 L/500 g/8 days). Vb was isolated from methanol extract at approximately 30%. Wistar rats were intragastrically pretreated or not with a single dose of Vb (20 mg/kg) for four days. On the fourth day, a single dose of TA (6.6 mmol/kg) was intraperitoneally injected. Blood samples and parameters related to liver damage, like AST and ALT, were obtained. Vb significantly reduced the level of liver injury following thioacetamide-induced necrosis. This was corroborated by in silico assay and docking studies, demonstrating that Vb can interact with a HeLa target through hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions, achieving better performance than commercial chemotherapeutic Taxol®, by 0.34 kcal/mol. AST and ALT were significantly lower in the rats pretreated with Vb. Furthermore, Vb did not induce cytotoxicity and had a median lethal dose (LD50) greater than 5000 mg/kg. These results suggest that Vb may be used as an alternative to reduce liver damage.
1. Introduction
The liver is one of the organs most likely to be damaged due to contact with xenobiotics (drugs, alcohol, abuse drugs, environmental toxins, and others) [1], leading to a very high incidence of liver diseases. Cirrhosis, fatty liver, chronic hepatitis, and cancer have high mortality rates in Mexico and worldwide [2]. Liver cancer is a significant problem, especially in less developed regions; it is considered one of the most common malignant cancers in humans and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide [3]. Owing to the high incidence of liver diseases, different experimental models have been designed to determine the mechanisms by which liver lesions develop. One model utilized to demonstrate the hepatic response against the aggressive attack of a hepatotoxic drug is a single dose of thioacetamide (TA) [4]. TA is a potent hepatotoxic agent that, when administered at doses of 500 mg/kg to rats, initiates severe hepatocellular perivenous necrosis, increasing the activity of the ALT and AST enzymes. The increased activities of these enzymes in serum may be interpreted as hepatocyte damage or changes in their membrane permeability, indicating severe hepatocellular damage [5], both of which have been associated with hepatocellular carcinoma [6]. The latter effect may be due to its ability to alter the function of tubulin and, consequently, affect the formation and stability of microtubules. These changes in microtubules may interfere with cellular division processes and regulate cell proliferation [7].
Treatment of liver pathologies is not only costly due to disease but also as due to subsequent complications. Moreover, the use of drugs to treat some liver diseases sometimes may not be the best option, as they can cause hepatotoxicity and deteriorate the condition of the patient [1]. Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) has provided empirical knowledge on the use of plants for many treatments. It has been crucial for designing phytochemical studies, where the main objective is identifying the molecules responsible for therapeutic effects and designing biological studies that aim to explain the mechanisms of action through the molecules mentioned above [8].
Thousands of people worldwide prefer medicinal plants to drugs for the reasons mentioned above. This, coupled with their benefits, make them a more affordable option with fewer or less severe consequences—if any [9]. Alternative therapies have been scarcely explored; thus, additional research is crucial to generate new proposals and less costly treatments with fewer adverse effects [9]. Additionally, pharmacological and toxicological research is necessary to establish therapeutic doses and provide a better basis for the suitable utilization of medicinal plants.
In this study, a compound isolated from Leucophyllum frutescens (Lf), a species commonly known as “cenizillo”, was investigated [10]. This species belongs to the Scrophulariaceae family and is used in traditional medicine for airway diseases, such as cough, tuberculosis, fever, and asthma. It is also used as an antioxidant, vasodilator, and analgesic (rheumatic pain). In the traditional medicine of Mexico, Lf is also used to treat liver and bladder disorders [11], and its antiproliferative effect on cancer cells has been evaluated [12]. However, research does not exist to corroborate all these targets of verbascoside (Vb) effects. In Mexico, methanol extract from the aerial parts of Lf allowed for the isolation and identification of Vb, which was isolated in approximately 30% of the total extract. Moreover, to support the experimental results, an in silico assay was performed to determine the principal interactions between the studied ligands and the selected receptor using computational methods described by Díaz-Cervantes and coworkers [13,14].
To validate the use of this plant in Mexican traditional medicine as a hepatoprotective agent, we evaluated the effect of Vb against post-necrotic liver damage induced by thioacetamide (TA) through in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The aerial parts of Leucophyllum frutescens were collected in Metztitlán Municipality, Hidalgo State, México, in June 2013 and identified by Professor Manuel González Ledesma. A voucher specimen (Vargas-Mendoza D 01 Leucophyllum frutescens) is preserved at the Herbarium of Biological Research Centre, Autonomous University of Hidalgo, Pachuca, Hidalgo, Mexico.
2.2. Extraction and Purification
The extraction procedure previously described by Balderas-Renteria was followed [15]. Air-dried aerial parts (0.5 kg) were subjected to maceration with methanol at a ratio of 5 L per 500 g of plant material for a period of eight days. Afterward, the solvent was evaporated under vacuum, resulting in approximately 80 g of residue, which corresponds to an extraction yield of approximately 16%.
Thirty grams of methanol extract was purified on a Sephadex LH-20 (1000 g) column (6 × 60 cm) using H2O, H2O:MeOH (9:1, 4:1, 7:3, 3:2, 1:1, 2:3, 3:7, 1:4, 1:9), and MeOH as eluents. In other words, gradient elution was performed with the intention that, as the eluent concentration increased, the analyte would become bound to the mobile phase, move through the column, and ultimately be eluted. Fractions of 500 mL of each polarity were collected and marked as “A–K”. They were evaporated and analyzed by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) (EtOAc:MeOH:H2O at 5:1.8:0.4) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Fractions “D, E, and F” gave 1.2 g, 4.9 g, and 2.5 g, respectively. A single spot was shown on the TLC using 1% FeCl3 in MeOH as the developing solution. These fractions were collected and analyzed by 1H, 13C, 1D, and 2D NMR.
NMR measurements were performed at 400 MHz for 1H and at 100 MHz for 13C on a VARIAN 400 spectrometer from CDCl3, CD3OH, and DMSO-d6 solutions. Column chromatography (CC) was carried out on Merck silica gel 60 (Aldrich, 230–400 mesh ASTM), and Sephadex LH-20 TLC (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was carried on aluminum sheets with silica gel 60 F254 (Merck, Darmstadt, Alemania) and sprayed on using 5% methanolic FeCl3 and/or 1% methanolic diphenylboric acid-β-ethylamino ester.
2.3. Animals
Experiments were performed on adult male Wistar rats that were two months old (200–220 g) and obtained from Bioterio-UAEH. The animals were housed in a climate- and light-controlled room with a 12 h light/dark cycle. Rats were allowed access to food (standard pellet diet) and water ad libitum. All experiments were internally approved by the Ethical Institutional Committee for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals with official certificate No. 5-12-2013 and were carried out following the Official Mexican Norm for Animal Care and Handing NOM-062-ZOO-1999 [16]. The number of experimental animals was kept to a minimum, and at the end of the study, the animals were sacrificed in a CO2 chamber.
2.4. Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity Study
Adult male Wistar rats were acclimated in an animal room for two weeks before use. Throughout these two weeks, the rats were supplied with food and water ad libitum. The Wistar rats were intragastrically pretreated or not with a single dose of Vb (20 mg/kg) for four days. On the fourth day, they were intraperitoneally injected with a single dose of TA (6.6 mmol/kg) that was freshly dissolved in 0.9% NaCl [17]. Blood samples were obtained from the rats 0, 24, and 48 h following TA intoxication. Untreated animals received 0.5 mL of 0.9% NaCl. Experiments were performed on three groups: the control group, rats treated with a single dose of TA, and rats pretreated with Vb and treated with a single dose of TA (Vb + TA). Each experiment was performed in duplicate in four different animals and followed the international criteria for the use and care of experimental animals outlined in The Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals in Toxicology, as adopted by the Society of Toxicology in 1989.
2.5. Processing of Samples
Samples were obtained from the control group 0, 24, and 48 h following TA intoxication in both Vb-pretreated and non-pretreated animals. The rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation; blood was collected from the hearts, kept at 4 °C for 24 h, and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min; and serum was obtained as the supernatant and stored at −70 °C until required.
2.6. Determination of AST and ALT
Enzymatic determination was performed in serum under optimal temperature conditions and substrate and cofactor concentrations. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities were determined in serum following the methods of Rej and Horder [18] and Murray [19]. The activities of these enzymes were determined using spectrophotometric methods. AST activity was quantitatively determined by measuring the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm at 25 °C, which was produced by the oxidation of NADH to NAD+ in the coupled reaction of the reduction of oxaloacetate to malate and catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase. Similarly, the activity of ALT was determined by measuring the decrease in absorbance in the coupled reaction of the reduction of pyruvate into lactate and catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase.
2.7. In Silico Predictions of Bioactivity
In the in silico predictions, the SMILE code for Vb was used, which was obtained from the PubChem database “https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/” (accessed on 10 January 2023). The PASS online server [20] was used for the analysis of biological activity.
2.8. Cell Cultures
To evaluate the antiproliferative effects of Vb on malignant cells, we used HeLa (human cervix adenocarcinoma cells) and MeT-5A (human mesothelium cells) cells. HeLa cells were grown in Ham’s F12 Nutrient Mixture (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and RPMI 1640 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 2.38 g/L HEPES, 0.11 g/L pyruvate sodium, and 2.5 g/L glucose. Additionally, 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 microg/mL streptomycin, and 0.25 mg/mL amphotericin B (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) were added to both media. The cells were cultured at 37 °C in a moist atmosphere of 5% CO2.
2.9. Inhibition Growth Assay
HeLa and MeT-5A (5 × 104) cells were seeded into each well of a 24-well cell culture plate. After incubation for 24 h, various concentrations of Vb were added, and the cells were incubated under standard conditions for an additional 48 h. A trypan blue assay was performed to determine cell viability. Cytotoxicity data were expressed as GI50 values, that is, the concentration of the test agent that induces a 50% reduction in cell number compared to control cultures. HeLa (human cervix adenocarcinoma) and Met-5A (human mesothelium) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA).
2.10. Docking Assays
Owing to Tubulin’s significant role in the cellular cytoskeleton, which plays a critical role in cell division, maintaining cellular shape and function, and the potential impact of interfering with its microtubule formation and stability on cell proliferation, we performed a docking analysis with this molecular target and Vb. Avogadro software was used to model Vb and was optimized at the UFF level [21]. The optimized molecules were coupled with the selected target (PDB code: 1JFF) [22] using the MoldockScore scoring function [23] with the Molegro Virtual Docker (MVD) package [24]. Tubulin (HeLa target) [25] was used to perform the docking studies. The docking assay was carried out using a fixed target and a genetic algorithm to search for the poses, while the scoring function evaluated the ligand–receptor interactions considering the classical interactions of Coulombic and Lennard-Jones interactions. This was implemented in MVD software. The target was corrected (by adding hydrogen atoms and missing sites of residues) using the same computational package. Finally, to complete the study, the normal modes of the selected tubulin were used to analyze the possible conformations of the protein and its interactions with the studied ligands. This analysis was performed using the ElNemo server following the normal-mode vector to consider this the target [26].
2.11. Acute Toxicity Test
The method described by the OECD-423 guideline [27] was employed in determining Vb’s median lethal dose (LD50) in rats. Vb was suspended in the vehicle (distilled water), and the concentrations were adjusted to orally administer 0.5 mL/100 g body weight. For the acute toxicity study, the rats were divided into two groups, each comprising three randomly weighed rats. Animals in the first group received Vb at an oral dose of 5000 mg/kg. Rats in the second group (control) were treated orally only with distilled water and kept under the same conditions. In both groups, rats were weighed and observed for mortality, abnormal behavior, and other toxic signs during the first 30 min and periodically for 24 h, with particular attention during the first 4 h and afterward, then daily for 14 days [28]. The number of deaths was recorded, and the LD50 value was determined. All surviving animals were sacrificed at the end of each experiment, autopsied, and examined macroscopically for any pathological changes compared with those of the control group.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The results were calculated as the means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M) of four experimental observations in duplicate (four animals). Differences between groups were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA), and a post hoc Tukey test was performed to identify significant differences between treatments. For statistical analysis, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Active Compounds of Leucophyllum frutescens
Fractions “D, E, and F” weighed 1.2 g, 4.9 g, and 2.5 g, respectively. One spot was shown on the TLC using 1% FeCl3 in MeOH as the developing solution. These fractions were collected and analyzed by 1H, and 13C, 1D, and 2D NMR. We were able to recognize Vb (Figure 1 and Figure 2) as the principal component, comprising 8.6 g of a single compound, which accounted for 28% from the extract and 5% from a vegetal source.
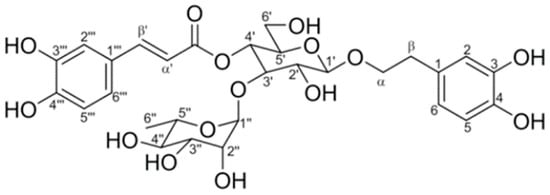
Figure 1.
Verbascoside chemical structure.
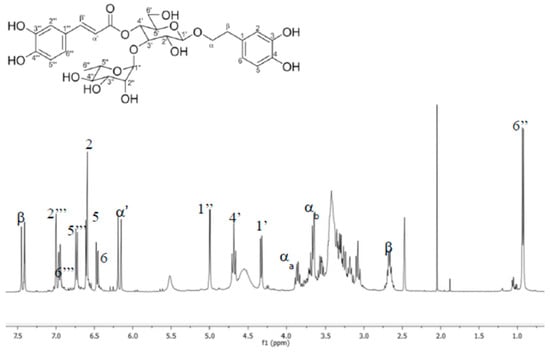
Figure 2.
HMBC spectra of verbascoside.
Verbascoside: amber amorphous powder; mp 139–142 °C; m; 1H NMR (400 MHz) DMSO-d6: δ 7.582 (d, 1, J = 15.8 Hz, H-β′), 7.054 (d, 1, J = 1.96 Hz, H-2″′), 6.92 (dd, 1, J = 8.32, 2.0 Hz, H-6″′), 6.76 (d, 1, J = 8.32 Hz, H-5″′), 6.69 (d, 1, J = 1.8 Hz, H-2), 6.67 (d, 1, J = 8.04 Hz, H-5), 6.53 (dd, 1, J = 8.04, 1.8 Hz, H-6), 6.26 (d, 1, J = 15.8 Hz H-α′), 5.02 (br, s 1 H-1″), 4.71 (t, 1, J = 9.27 Hz, H-4′), 4.35 (d, 1, J = 7.64 Hz, H-1′), 3.88 (c, 1, J = 924, H-αa), 2.65 (m, 1, H-β), 0.95 (d, 3, J = 6.16 Hz, 6”), 13C NMR (100 MHz) DMSO-d6: δ 166.98 (COO), 148.32 (C-4″′), 146.68 (C-β’), 145.34 (C-3″′), 144.63 (C-3), 143.18 (C-4), 130.08 (C-1), 126.25 (C-1′″), 121.94 (C-6″′), 119.96 (C-6′), 115.78 (C-α′), 115.19 (C-2), 114.99 (C-5), 113.90 (C-2″′), 113.26 (C-5″′), 102.69 (C-1′), 101.62 (C-1″), 80.33 (C-3′), 74.72 (C-2′), 74.46 (C-5′), 72.37 (C-4″), 70.91 (C-α), 70.86 (C-2″), 70.62 (C-3″), 69.12 (C-4′), 69.02 (C-5″), 60.90 (C-6′), 35.12 (C-β) and 17.14 (C-6″).
3.2. In Silico Approaches to Biological Activity
Prior to the in vitro and in vivo experiments, an in silico analysis was conducted using the PASS online server to evaluate the biological effects of Vb found in Leucophyllum frutescens. This analysis revealed a high probability of hepatoprotective activity of Vb, as well as its potential as an aspartyl transferase inhibitor. Additionally, promising anticariogenic effects were identified, as shown in Table 1. These results led to expectations regarding the biological effects of the component, providing a strong foundation for the subsequent experiments.

Table 1.
Biological activities determined by PASS.
3.3. Liver Damage Biomarkers (AST and ALT)
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the effects of Vb pretreatment on levels of AST and ALT, respectively, in the sera of rats intoxicated with a single sublethal dose of TA 0, 24, and 48 h following TA intoxication. Significant increases in AST and ALT levels were observed at 24 and 48 h in the group that received TA compared to the group without TA, which confirms enzymatic activity as a marker of liver damage. Pretreatment with Vb in the rat model of TA-induced hepatoxicity resulted in significant decreases in AST and ALT levels, delaying liver injury at 24 and 48 h. According to the results, Vb demonstrated a hepatoprotective effect.
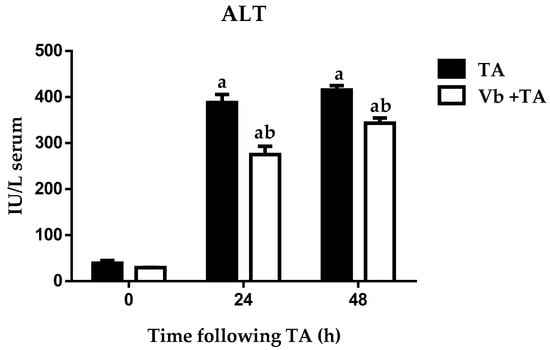
Figure 3.
Effect of verbascoside pretreatment on levels of ALT activity in serum of rats intoxicated with one sublethal dose of thioacetamide (TA). Samples were obtained 0, 24, and 48 h following thioacetamide (TA) administration. The results are expressed in IU/L serum. Bars indicate the mean ± S.E.M of four determinations in duplicate from four rats. Differences against the control are expressed as (a), and differences due to Vb are expressed as (b) p < 0.05.
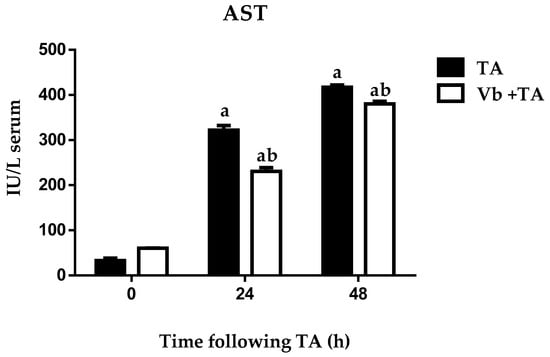
Figure 4.
Effect of verbascoside pretreatment on levels of AST activity in serum of rats intoxicated with one sublethal dose of thioacetamide (TA). Samples were obtained 0, 24, and 48 h following thioacetamide (TA) administration. The results are expressed in IU/L serum. Bars indicate the mean ± S.E.M of four determinations in duplicate from four rats. Differences against the control are expressed as (a), and differences due to Vb are expressed as (b) p < 0.05.
3.4. In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity
The antiproliferative activity of Vb was evaluated by an in vitro assay performed on a human tumor cell line, HeLa (cervix adenocarcinoma), and on non-tumorigenic human cells, MeT5A (mesothelium). Compared to the control culture, the percentage of viable cells was above 50% for all tested concentrations (10–500 μM) in both cell types, indicating the inability of Vb to induce any significant cytotoxicity up to 500 μM.
3.5. Docking Assay
The docking assay for Vb was compared with Taxol®, as shown in Figure 5A, as well as with the normal modes of tubulin following the vector presented in Figure 5B. The main energies of interaction between the selected HeLa target and the studied molecules (including the energies in the normal modes) are shown in Table 2.
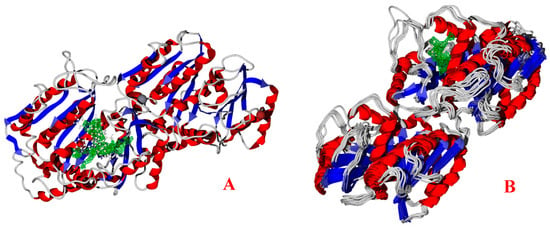
Figure 5.
(A) Docking between the tubulin (Hela target) and the studied molecules in static crystalized conformation and (B) normal modes of the studied tubulin. The green grid indicates the best interaction cavity of the target.

Table 2.
Principal interaction energies in kcal/mol.
The hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions are key in ligand–target docking, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
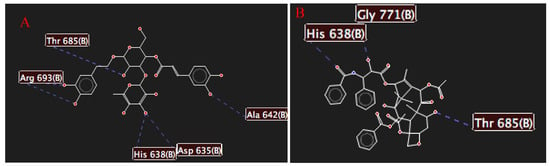
Figure 6.
Hydrogen bond interactions between (A) the selected target and verbascoside and between (B) the selected target and Taxol®.
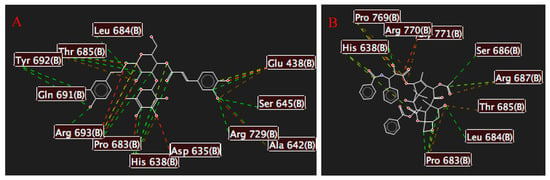
Figure 7.
Electrostatic interactions between (A) the selected target and verbascoside and between (B) the selected target and Taxol®. Green lines depict attractive interactions, and red lines indicate repulsive interactions.
3.6. Toxicity Study
Vb was found to be non-toxic because the treatment did not cause any deaths within 14 days after administration in either treatment. Therefore, the estimated LD50 was above 5000 mg/kg. The evaluated animals did not show any major changes in behavior; body weight; or macroscopic morphology of the heart, lungs, liver, or kidneys compared with to those in the control group.
4. Discussion
In this study, acetoside (a phenylethanoid glycoside compound), known as Vb, from the aerial parts of Lf. was verified by NMR and compared with the results of previous studies [29]. The Vb yield was approximately 30% of the total extract. Moreover, studies have shown that the yield of acetoside in other medicinal plants, such as Cistanches spp., Castilleja spp., and Plantago spp. [30,31], varies between 0.63 and 0.93% [32], which is not consistent with the results obtained in our study. These results suggest that the extraction and isolation used in our study effectively produced Vb.
In the present study, we examined the correlation between Vb and the levels of AST and ALT in rats intoxicated with one sublethal dose of TA to simulate what occurs clinically during liver damage. We used TA to induce acute and chronic liver injury [4], and TA was chosen as the highest dose, with survival above 90% [17]. The rats in this study showed significant increases in AST and ALT levels in response to the TA administration compared to those in the control group. These results are consistent with previous studies, which reported an increase in the levels of these enzymes in correlation with damage to the structural integrity of the liver [33,34]. This indicates the presence of necrosis of hepatocytes, resulting in a deficiency of transaminase, structural alterations, and interference with the integrity of the hepatocytes. AST and ALT levels are ideal to study because they simulate the clinical characteristics of human pathology [5].
Our study revealed the hepatoprotective effect of Vb from Lf against TA-induced hepatotoxicity for the first time. Vb + TA resulted in a significant decrease in ALT and AST serum levels, which is representative of hepatic damage. These in vivo evaluations were correlated with in silico analyses, showing a probability of Vb being hepatoprotective. The results are consistent with previous studies that have shown that Vb exhibits a potent hepatoprotective effect against some hepatotoxicants, such as carbon tetrachloride, D-galactosamine, and lipopolysaccharide [15,33,34,35,36,37,38], as it inhibited the serum levels of ALT and AST. These results can be attributed to the ability of Vb to conserve liver cell membrane integrity against necrotic damage by TA, the reduction in the rate of transaminase release, and cellular membrane stabilization [39].
However, the mechanisms by which Vb protects against TA-induced hepatotoxicity are unclear. In recent years, studies have shown that liver injury is a complex process involving multiple factors, including oxygen free radical responses, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory responses [40]. TA-induced hepatotoxicity involves multiple mechanisms, including metabolic activation by CYP2E1, leading to the formation of the reactive metabolites S-oxide (TASO) and S-dioxide (TASO2) [41,42]. These active intermediates lead to the formation of adducts of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which promotes lipid and protein peroxidation and mitochondrial damage [5]. Vb has been shown to suppress P450 2E1 protein levels [37]; inhibit apoptosis in D-GalN and LPS-induced liver injury [38]; and decrease the serum level of various enzymes, such as alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transferase enzymes, and total and direct bilirubin [35]. In addition, Vb increases the total serum protein and albumin, attenuates lipid peroxidation, and increases GSH in the liver [19]. Vb also inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of nitric oxide and scavenges both superoxide radicals and DPPH radicals [35]. This suggests that the hepatoprotective effect of Vb may be associated with other molecular mechanisms associated with its various pharmacological activities, such as anti-tumor, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antinephritic, and antimetastatic activities [39,43,44,45,46,47,48]. However, further studies are necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
Moreover, cytotoxicity studies have been performed on natural products (extracts or pure compounds) to determine their ability to act as antitumor agents, owing to their extreme structural diversity and chemical complexity and because they act pleiotropically to modulate several cellular signaling pathways [49]. This study revealed, for the first time, that Vb is not cytotoxic against a human tumor cell line, HeLa, or non-tumorigenic human cells. However, other studies have reported that Vb exhibited cytotoxic effects against other human cancer cell lines [50,51] and demonstrated marginal toxicity against human peripheral blood mononuclear cells [52]. These discrepancies may be attributed to the ability of Vb to act independently of the tumor genetic background, suggesting that its antitumor effect may involve modulation of oncogenic signaling pathways and other mechanisms. Notably, its antitumor effect was found to surpass the modulation of these oncogenic signaling pathways, making it a promising candidate for further investigation and potential therapeutic development.
Therefore, it is important to consider these results when searching for new therapeutic alternatives to prevent liver damage and to determine other parameters of liver damage and different cancer cell lines and their mechanisms of action.
Figure 5A shows the interaction of a commercial drug, Taxol®, and the studied molecule, Vb, with the HeLa target. When all the cavities of the target were tested, the green-colored cavity was found to be the best interacting cavity. Figure 5B shows the normal modes of the studied tubulin, considering that the structure was obtained following the vector of the normal mode. In the site around the interacting cavity, a notable opening of this site is visible, separating the residues and opening the active site.
Regarding the interaction energies, Table 2 shows that while Taxol® has a total energy of −205.85 kcal/mol compared to −161.23 kcal/mol for Vb, and the molecule size plays a crucial role in the improved interaction of the last molecule. This is important because LE is generally a better parameter to compare the interaction of two or more molecules with a selected target. Despite the use of LE, in prior works, this parameter has been shown to correlate with experimental results [53]. A more negative value of LE indicates an improved interaction. Thus, Vb has a better interaction than Taxol®, with LE values of −3.66 and −3.32 kcal/mol, respectively [21,22,23,24,25,54].
These results were corroborated using the normal modes of the studied tubulin, in which all conformations of the protein showed adequate values of LE (see Table 2), including the case of the normal mode, which is the opening of the active site, with LE values of −2.75 kcal/mol for Taxol® and −4.11 for Vb. We determined that Vb interacts better with the HeLa target than Taxol®, as shown in Table 2. LE is a crucial parameter; however, hydrogen bond energy also plays a crucial role in ligand–target interactions. For example, in the static mode, the value for Vb is −9.21 kcal/mol, while for Taxol®, it is −6.27 kcal/mol [21,22,23,24,25,54].
We analyzed these interactions, and Figure 6 shows the primary amino acid residues that interact with the studied molecules, Thr 685 and His 638, which are common in both cases. However, Vb presents two more interactions than Taxol®, resulting in more hydrogen bond interactions. Figure 7 presents similar behavior of the hydrogen bonds, with Vb generating more attractive interactions compared to Taxol® [21,22,23,24,25,54]. Thus, the selected target has more interactions with Vb. Taxol® was used as a control drug in the case of in silico assays.
Finally, the acute toxicity results revealed the non-toxic nature of Vb. The oral LD50 value for Vb was above 5000 mg/kg. Animals tolerated the 5000 mg/kg dose well, and there were no toxic symptoms or deaths during the experimental period. Postmortem examinations showed the macroscopic morphology of the liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, and stomach, with normal color and morphology compared with the vehicle. These results are consistent with those reported in previous studies [35]. Generally, Vb can be classified as a non-toxic treatment, with an oral LD50 higher than 4 g/kg considered safe [55].
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that Vb exhibits potent hepatoprotective action upon TA-induced hepatic damage in rats and is non-toxic. The results suggest that Vb isolated from Leucophyllum frutescens may be a new alternative therapeutic for the treatment of liver injury. Therefore, further study is required through clinical studies to establish adequate doses in humans. The results of the docking studies demonstrated that Vb can interact with a HeLa target through hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions, surpassing commercial chemotherapeutic Taxol® by 0.34 kcal/mol.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B. and O.A.J.-M.; methodology, L.D.V. and A.N.G.-A.; software, E.D.-C., J.V.E.-J. and J.C.O.-Z.; data curation, C.V.-V. and V.M.M.-P.; formal analysis, O.A.J.-M. and M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, O.A.J.-M., M.B., L.D.V., E.D.-C. and J.V.E.-J.; writing—review and editing, O.A.J.-M., M.B., L.D.V., E.D.-C. and J.V.E.-J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present research received funds from CONACYT, Mexico. LDV and ANG-A are grateful to University of Padova -Dotazione Ordinaria Ricerca (DOR) 2022 for financial support. E.D.-C. acknowledges funding from Convocatoria Institucional de Investigación Científica (CIIC) 2023 for project number 270/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Autonomous of Hidalgo State University, Health Sciences Institute (CICUAL07-2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Pharmacology, Pharmacognosy and Botany Department of Pharmacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pandit, A.; Sachdeva, T.; Bafna, P. Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of disease: Mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and therapeutic implications. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroentero Hepatol. 2004, 1, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, T.; Sheikh, N. An overview of thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxin Rev. 2013, 32, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilakapati, J.; Korrapati, M.C.; Hill, R.A.; Warbritton, A.; Latendresse, J.R.; Mehendale, H.M. Toxicokinetics and toxicity of thioacetamide sulfoxide: A metabolite of thioacetamide. Toxicology 2007, 230, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Fujii, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Yafune, A.; Hayashi, S.M.; Suzuki, K.; Shibutani, M. Involvement of multiple cell cycle aberrations in early preneoplastic liver cell lesions by tumor promotion with thioacetamide in a two-stage rat hepatocarcinogenesis model. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, G.; Park, H.J.; Jiang, P.P.; Sit, W.H.; van Griensven, L.J.; Wan, J.M. Protective effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extracts against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: A proteomics analysis. Chin. Med. 2012, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luper, S.N.D. A review of plants used in the treatment of liver disease: Part 1. Altern. Med. Rev. 1998, 3, 410–421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Recent advances in natural products from plants for treatment of liver diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.J.S.; Verde, S.M.J.; Heredia, N. Traditional uses and scientific knowledge of medicinal plants from México and Central America. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2001, 8, 37–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.M.M. Plantas Medicinales del Noreste de México, 1st ed.; El Sol, S.A., de C., V., Eds.; Grupo Vitro, Club Ecológico Novaterra, IMSS: Monterrey, NL, México, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.E.; Al-Megrin, W.A. Biological Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Leucophyllum frutescens and Russelia equisetiformis Extracts. Nanomater. Basel. 2021, 11, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cervantes, E.; Cortés-García, C.J.; Chacón-García, L.; Suárez-Castro, A. Molecular docking and pharmacophoric modelling of 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles as inhibitors of two proteins present in cancer, the ABL and the mutated T315I kinase. Silico Pharmacol. 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Tejada, E.P.; Albino-Flores, A.; Mejía-Benavides, J.E.; Fuentes-Ocampo, L.; Diaz-Cervantes, E. Tio2 as a Nanocarrier of Antibiotics (Quinolones): A Molecular Docking Assay. In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Recent Advances in Nanotechnology (RAN’21), Virtual, 14–16 June 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderas-Renteria, I.; Camacho-Corona, M.R.; Carranza-Rosales, P.; Lozano-Garza, H.G.; Castillo-Nava, D.; Alvarez-Mendoza, F.J.; Tamez-Cantú, E.M. Hepatoprotective effect of Leucophyllum frutescens on Wistar albino rats intoxicated with carbon tetrachloride. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Official Mexican Norm NOM 0062-ZOO-1999; Technical Specifications for the Production, Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Diario Oficial de la Federación: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001; pp. 107–165.
- Sanz, N.; Díez-Fernández, C.; Andrés, D.; Cascales, M. Hepatotoxicity and aging: Endogenous antioxidant systems in hepatocytes from 2-, 6-, 12-, 18- and 30-month-old rats following a necrogenic dose of thioacetamide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1587, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, R.; Horder, M. Aspartate aminotransferase. L-aspartate: 2-oxoglutarate aminotranferase, EC 2.6.2.1. Routine, U.V. method. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Verlag-CHemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1987; pp. 416–424. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R. Alanine aminotransferase. In Clinical Chemistry: Theory, Analysis, and Correlation, 2nd ed.; C.V. Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1989; pp. 898–989. [Google Scholar]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Druzhilovskii, D.S.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Prediction of the biological activity spectra of organic compounds using the PASS online web resource. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2014, 50, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, W.D.; Cieplak, P.; Bayly, C.I.; Gould, I.R.; Merz, J.K.M.; Ferguson, D.M.; Spellmeyer, D.C.; Fox, T.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A. A Second Generation Force Field for the Simulation of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Organic Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5179–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, J.; Li, H.; Downing, K.H.; Nogales, E. Refined Structure of αβ-Tubulin at 3.5 Å Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 313, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, C. GEMDOCK: A generic evolutionary method for molecular docking. Proteins 2004, 55, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Olvera, D.; García-González, A.N.; Morales-Salazar, I.; Islas-Jácome, A.; Rojas-Aguirre, Y.; Ibarra, I.A.; Díaz-Cervantes, E.; Alcaraz-Estrada, S.L.; González-Zamora, E. Synthesis of Pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-ones via Multicomponent Reactions and In Vitro–In Silico Studies Against SiHa, HeLa, and CaSki Human Cervical Carcinoma Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhre, K.; Sanejouand, Y.H. ElNemo: A normal mode web server for protein movement analysis and the generation of templates for molecular replacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W610–W614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Guidelines Number 425 for Testing Chemicals; Acute Oral Toxicity-Up and Down Procedure; OECD: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, C.S.; Weil, S.C. Principles and Methods of Toxicology, 2nd ed.; Hays, A.W., Ed.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 292–293. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Jiang, S.; Luo, P.; Wu, J.; Gao, P. Isolation, Purification and Structure Identification of Antioxidant Compound from the Roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague and its Life Span Prolonging Effect in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tsao, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, R.; Young, J.C.; Zhu, H.; Deng, Z.; Xie, M.; Fu, Z. Isolation and purification of acteoside and isoacteoside from Plantago psyllium L. by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 2005, 1063, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Numata, A.; Takemura, T.; Ode, R.H.; Narula, A.S.; Schmidt, J.M.; Cragg, G.M.; Pase, C.P. Antineoplastic agents, 107. Isolation of acteoside and isoacteoside from Castilleja linariaefolia. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzutti, S.; Ferreira, S.R.S.; Herrero, M.; Ibanez, E. Intensified aqueous-based processes to obtain bioactive extracts from Plantago major and Plantago lanceolata. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2017, 119, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Hernández, T.A.; Santos-López, J.A.; Benedí, J.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Velázquez-González, C.; De la O-Arciniega, M.; Jaramillo-Morales, O.A.; Bautista, M. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Croton hypoleucus Extract in an Induced-Necrosis Model in Rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Vázquez-Velasco, M.; González-Torres, L.; Benedí, J.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Morales-González, J.A.; Jaramillo-Morales, O.A.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Bautista, M. Effect of Extract and Ellagic Acid from Geranium schiedeanum on the Antioxidant Defense System in An Induced-Necrosis Model. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldesoky, A.; Abdel-Rahman, R.; Ahmed, O.; Soliman, G.; Saeedan, A.; Elzorba, H.; Elansary, A.; Hattori, M. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective potential of Plantago major growing in Egypt and its major phenylethanoid glycoside, acteoside. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hase, K.; Tezuka, Y.; Namba, T.; Kadota, S. Acteoside inhibits apoptosis in D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Woo, E.R.; Choi, C.Y.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, D.G.; You, H.J.; Jeong, H.G. Protective effect of acteoside on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 2004, 9, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Ma, L.; Yan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Z.; Huang, Y. Protective effect of acteoside on immunological liver injury induced by Bacillus Calmette-Guerin plus lipopolysaccharide. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchyshak, T.; Yakovenko, T.; Shmarakov, I.; Tkachuk, Z. The potential protective effect of oligoribonucleotides-d-mannitol complexes against thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Pharm. Basel 2018, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramahia, S.K.; Apte, U.; Mehendale, H.M. Cytochrome P4502E1 induction increases thioacetamide liver injury in diet-restricted rats. Drug Metab. Diapos 2001, 269, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Hajovsky, H.; Hu, G.; Koen, Y.; Sarma, D.; Cui, W.; Moore, D.S.; Staudinger, J.L.; Hanzlik, R.P. Metabolism and Toxicity of Thioacetamide and Thioacetamide S -Oxide in Rat Hepatocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Inoue, M.; Ogihara, Y.; Saracoglu, I. Antimetastatic activity of acteoside, a phenylethanoid glycoside. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.F.; Lin, L.C.; Chen, C.F. Acteoside protects endothelial cells against free radical-induced oxidative stress. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.A.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, T.H.; Kim, Y.C. Acteoside and its aglycones protect primary cultures of rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C. Acteoside protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against-amyloid-induced cell injury. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, P.; Iijima, R.; Han, J.; Shigemori, H.; Yokota, S.; Isoda, H. Inhibitory effect of acteoside isolated from Cistanche tubulosa on chemical mediator release and inflammatory cytokine production by RBL-2H3 and KU812 cells. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Chunhua, M.; Shumin, W. Effects of acteoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 285, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, G.A.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Pezzuto, J.M. Separation, structure elucidation and bioassay of cytotoxic natural products, In: Bioactive Natural Products: Detection, Isolation and Structure Determination; Colegate, S.M., Molyneux, R.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 99–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Feng, Y.; Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Sui, H.; Chai, N.; Chen, X.; Liu, N.; Ji, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Verbascoside promotes apoptosis by regulating HIPK2-p53 signaling in human colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 5, 14–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Ha, J.; Lee, K.T. Acteoside inhibits human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cell proliferation via inducing cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and differentiation into monocyte. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulou, A.; Samara, P.; Tsitsilonis, O.; Skaltsa, H. Polar constituents of Marrubium thessalum Boiss. & Heldr. (Lamiaceae) and their cytotoxic/cytostatic activity. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Salazar, I.; Montes-Enríquez, F.P.; Garduño-Albino, C.E.; García-Sánchez, M.A.; Ibarra, I.A.; Rojas-Aguirre, Y.; García-Hernández, M.E.; Sarmiento-Silva, R.E.; Alcaraz-Estrada, S.L.; Díaz-Cervantes, E.; et al. Synthesis of bis-furyl-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-ones via Ugi-Zhu reaction and in vitro activity assays against human SARS-CoV-2 and in silico studies on its main proteins. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanwell, M.; Curtis, D.; Lonie, D.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminformatics 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.L.; Ferenz, R.L.; Burgess, B.A. Estimation of acute oral toxicity in rats by determination of the approximate lethal dose rather than the LD50. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1986, 6, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).