4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Plant Material
2.1.2. Chemicals
2.2. Extraction and Isolation
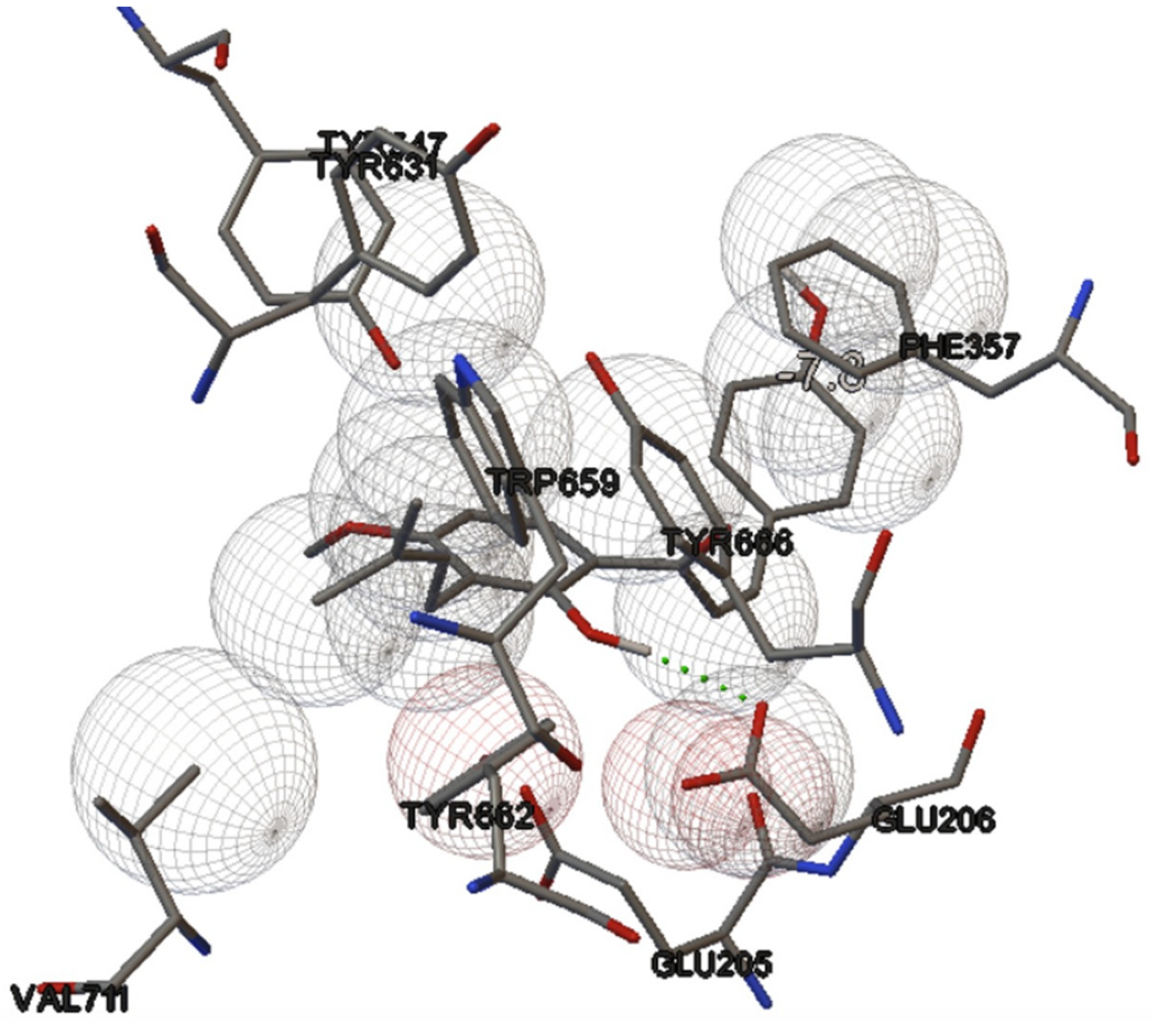
2.3. In Silico Study
2.3.1. Protein Preparation
2.3.2. Ligand Preparation
2.3.3. Validation of the Docking Simulation
2.3.4. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.4. In Vitro Study
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) Assay
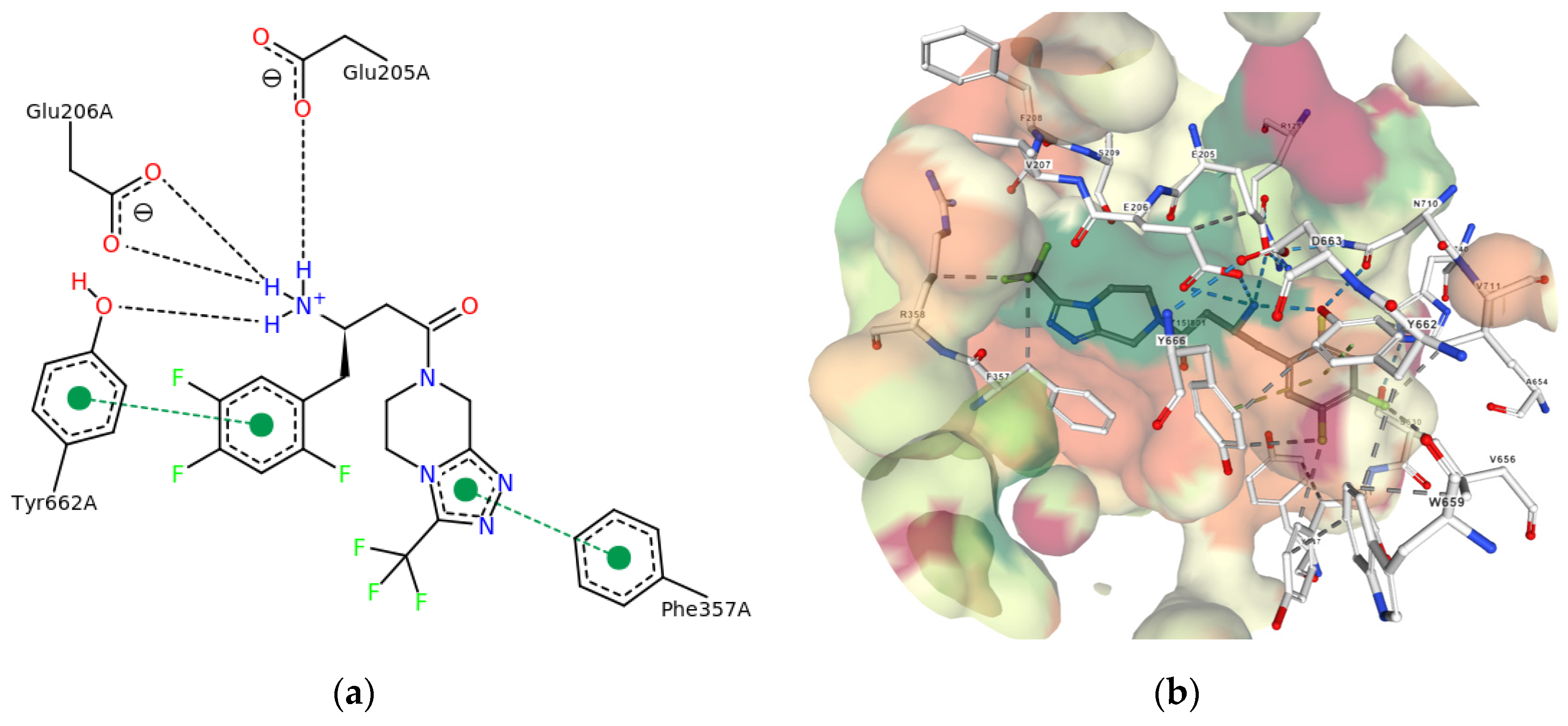
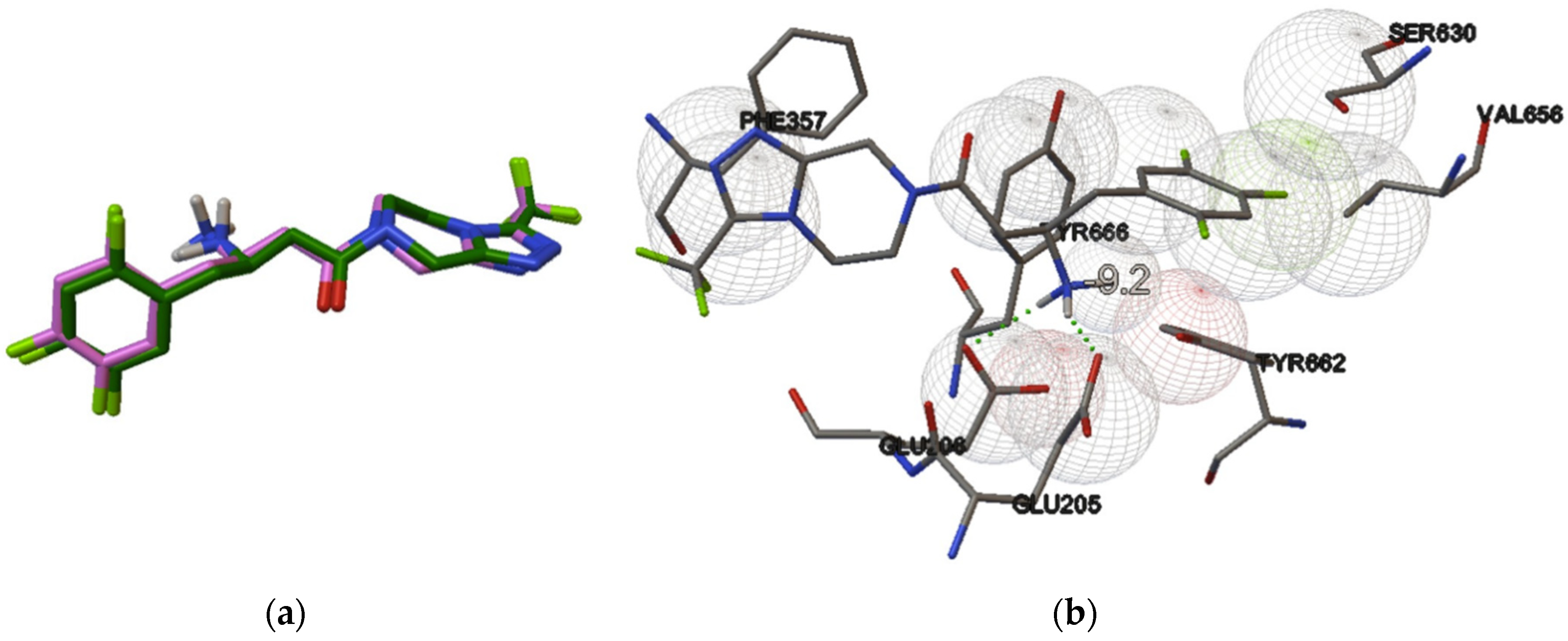
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicker, D. DPP-4 Inhibitors: Impact on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; ISBN 9782930229812. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Indonesian Report on Basic Health Research; Ministry of Health (Indonesia): Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018; ISBN 978-602-8937-24-5.
- Deacon, C.F. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A comparative review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Kemmeries, G.; Holst, J.J.; Meier, J.J. Rapid tachyphylaxis of the glucagon-like peptide 1-induced deceleration of gastric emptying in humans. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Bandeira-echtler, E. Emerging Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokoba, A.B.; Obateru, O.A.; Olokoba, L.B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Current Trends. Oman Med. J. 2012, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Wang, L.; Beconi, M.; Eiermann, G.J.; Fisher, M.H.; He, H.; Hickey, G.J.; Kowalchick, J.E.; Leiting, B.; Lyons, K.; et al. (2R)-4-Oxo-4-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin- 7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: A Potent, Orally Active Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 141, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilleßen, P.; Celner, J.; Kretschmann, A.; Pfeifer, A.; Racké, K.; Mayer, P. Metabolic role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) in primary human (pre)adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition on Microvascular Diabetes Complications. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2884–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; Avogaro, A. Cardiovascular effects of DPP-4 inhibition: Beyond GLP-1. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2011, 55, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Metcalfe, D.; McTernan, P.G. Obesity and Diabetes:Lipids, “Nowhere to run to”. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Li, Q.; Bi, K.S. Bioactive Flavonoids in Medicinal Plants: Structure, Activity and Biological Fate. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 13, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.; Ohnogi, H.; Nagamine, K.; Kudo, Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Tanabe, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Sagawa, H.; Kato, I. Antidiabetic Activities of Chalcones Isolated from a Japanese Herb, Angelica keiskei. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6013–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Ashida, H. Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) Extract Prevents Adiposity in High-fat Diet-fed C57BL/6 Mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Fujinami, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Amano, A.; Ishigami, A.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, N.; Ito, F.; Mori, T.; Sawada, M.; et al. Two chalcones, 4-Hydroxyderricin and Xanthoangelol, Stimulate GLUT4-dependent Glucose Uptake through the LKB1/AMP-activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihisa, T.; Tokuda, H.; Ukiya, M.; Iizuka, M.; Schneider, S.; Ogasawara, K.; Mukainaka, T.; Iwatsuki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nishino, H. Chalcones, Coumarins, and Flavanones from the Exudate of Angelica keiskei and Their Chemopreventive Effects. Cancer Lett. 2003, 201, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L. Natural Medicine: The Genus Angelica. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1479–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, N. Compounds from Angelica keiskei with NQO1 Induction, DPPH Scavenging and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, L.K.; Cech, N.B. A Review of the Medicinal Uses and Pharmacology of Ashitaba. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Son, Y.K.; Kim, G.H.; Hwang, K.H. Xanthoangelol and 4-Hydroxyderricin are the Major Active Principles of the Inhibitory Activities Against Monoamine Oxidases on Angelica keiskei K. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Software news and Update AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levita, J.; Rositama, M.R.; Alias, N.; Khalida, N.; Saptarini, N.M.; Megantara, S. Discovering COX-2 Inhibitors from Flavonoids and Diterpenoids. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Riyanti, S.; Suganda, A.G.; Sukandar, E.Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV Inhibitory Activity of some Indonesian Medicinal Plants. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 375–377. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Z. Determination of 4-Hydroxyderricin and Xanthoangelol in Different Parts of Angelica keiskei by HPLC-PDA. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Bonini, S.A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M.; Mastinu, A. Cannabimimetic plants: Are they new cannabinoidergic modulators? Planta 2019, 249, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashier, D.S.; Sharma, A.; Dahiya, N.; Singh, S.; Khadka, A. Lorcaserin: A novel antiobesity drug. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2014, 5, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xing, C. Diverse Molecular Targets for Chalcones with Varied Bioactivities. Med. Chem. 2015, 5, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.A.; Kumbhar, S.S.; Katti, V.S.; Choudhari, P.B.; Bhatia, M.S. 3D QSAR and pharmacophore modelling on chalcones as antileishmanial agents potential trypanothione reductase Inhibitors. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Arulmozhiraja, S.; Matsuo, N.; Ishitsubo, E.; Okazaki, S.; Shimano, H.; Tokiwa, H. Comparative Binding Analysis of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) with Antidiabetic Drugs -An Ab Initio Fragment Molecular Orbital Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
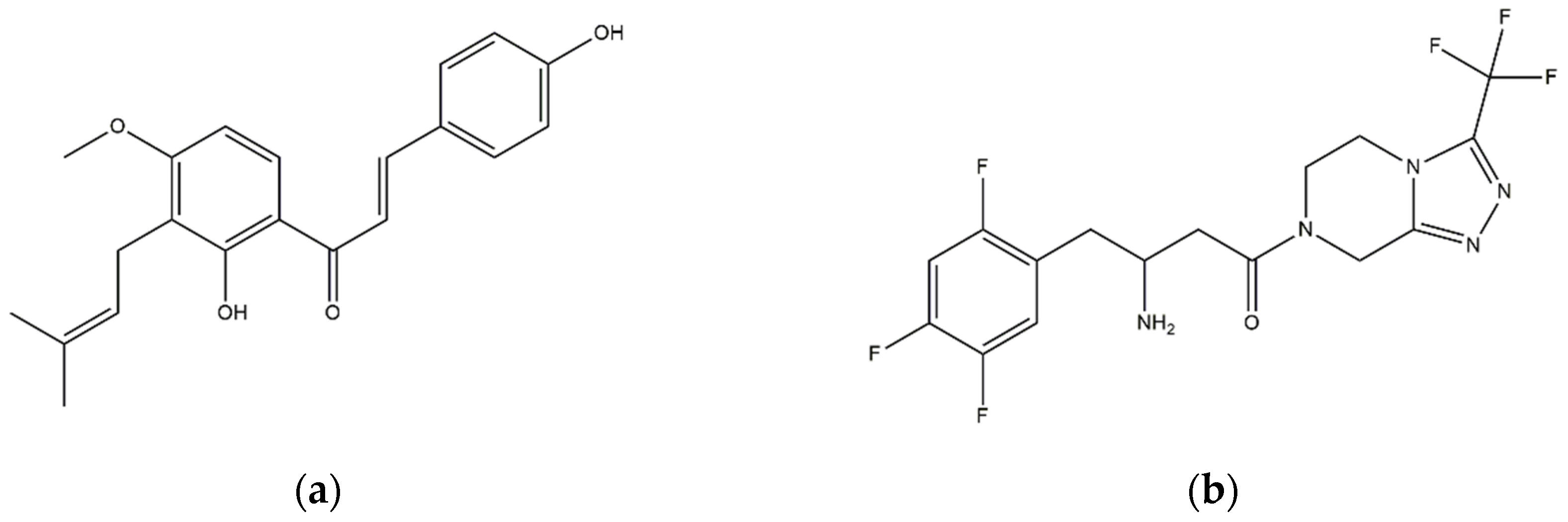
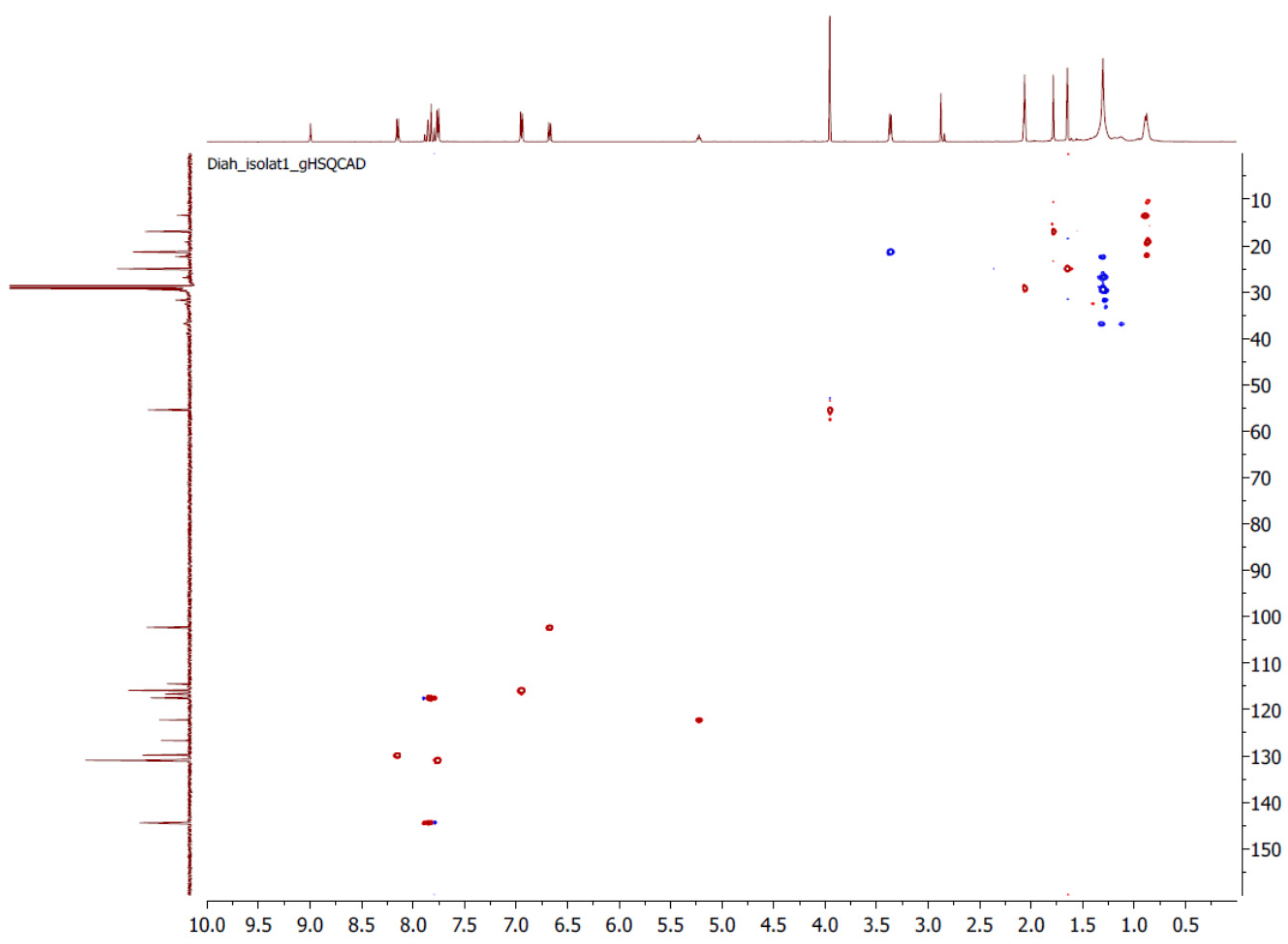
| 4-HD [23] (solvent CDCl3) | |||
| δ C (ppm) | δ H (ppm) | CH (HSQC) | Position |
| - | 1.60 | (3H,s,4″-CH3) | 4″ |
| - | 3.31 | (1H, d, J = 7.0 Hz,1″-H) | 1″ |
| - | 1.71 | (3H, s, 5″-CH3) | 5″ |
| - | 3.82 | (3H, s, 4-OCH3) | 4′ |
| - | 6.41 | (1H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, 5′-H) | 5′ |
| - | 6.79 | (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, 3,5-H) | 3,5 |
| - | 7.36 | (1H, d, J = 15.4 Hz, α) | α |
| - | 7.70 | (2H, d, J = 9.4 Hz, 2,6-H) | 2,6 |
| - | 5.30 | (1H, t, J = 7.0 Hz, 2″-H) | 2″ |
| - | 7.70 | (1H, d, J = 9.4 Hz, 6′-H) | 6′ |
| - | 7.72 | (1H, d, J = 15.4 Hz, β) | β |
| - | 13.38 | (1H, s, 2′-OH) | 2′ |
| Compound 1 (4-HD) (solvent (CD3)2CO) | |||
| δ C (ppm) | δ H (ppm) | CH (HSQC) | Position |
| 17.88 | 1.63 | (3H,s, -CH3) | 4″ |
| 22.27 | 3.36 | (1H,d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1″-H) | 1″ |
| 25.89 | 1.77 | (3H,s, -5″-CH3) | 5″ |
| 56.32 | 3.95 | (3H,s, 4′-OCH3) | 4′ |
| 103.19 | 6.67 | (1H,d, J = 9.1 Hz, 5′-H) | 5′ |
| 116.79 | 6.93 | (2H,d, J = 8.6 Hz, 3,5-H) | 3,5 |
| 117.60 | 7.73 | (1H,d, J = 15.4 Hz, α) | α |
| 118.38 | 7.80 | (2H,d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2,6-H) | 2,6 |
| 123.16 | 5.21 | (1H,t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2″-H) | 2″ |
| 127.59 | - | - | - |
| 130.76 | 8.13 | (1H,d, J = 9.1 Hz, 6′-H) | 6′ |
| 131.84 | - | - | 3″ |
| 145.35 | 7.84 | (1H,d, J = 15.4 Hz, β) | β |
| - | 13.76 | (1H,s, 2′-OH) | 2′ |
| 161.06 | - | - | - |
| 163.38 | - | - | - |
| 163.79 | - | - | - |
| 164.14 | - | - | - |
| 164.18 | - | - | - |
| 193.46 | - | (C=O) | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aulifa, D.L.; Adnyana, I.K.; Levita, J.; Sukrasno, S. 4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87040030
Aulifa DL, Adnyana IK, Levita J, Sukrasno S. 4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2019; 87(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleAulifa, Diah Lia, I Ketut Adnyana, Jutti Levita, and Sukrasno Sukrasno. 2019. "4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV" Scientia Pharmaceutica 87, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87040030
APA StyleAulifa, D. L., Adnyana, I. K., Levita, J., & Sukrasno, S. (2019). 4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 87(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87040030







