Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal malignancies due to underlying co-morbid cirrhosis and chemo-resistance. Vaccination and improved treatment for hepatitis are the most effective means to reduce the burden of liver cancer worldwide. Expression of biomarkers such as AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), DDK1 (Dickkopf WNT Signaling Pathway Inhibitor 1) and microRNAs in blood are being tested for early screening of liver cancer. Since 2008, sorafenib has been used as the standard molecular targeting agent for HCC. However, overall outcomes for sorafenib alone or in combination with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors are unsatisfactory. Whether simultaneously or sequentially, addiction switches and compensatory pathway activation in HCC, induced by sorafenib treatment, may induce acquired resistance. Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) and metadherin (MTDH) have been shown to be master regulators of different aspects of tumorigenesis, including angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis and drug resistance. Elevated expression of both FOXM1 and MTDH is known to be a consequence of both activating mutations in oncogenes such as PI3K, Ras, myc and loss of function mutations in tumor suppressor genes such as p53 and PTEN in various types of cancers including HCC. The role of FOXM1 and MTDH as potential prognostic markers as well as therapeutic targets in HCC will be discussed. In addition, microRNAs (miRNAs), endogenous small non-coding RNAs involved in the regulation of gene expression, are involved in HCC and interact with both FOXM1 and MTDH in several ways. Thus, altered expression of miRNAs in HCCs will also be discussed as potential tools for diagnosis, prognosis and therapy in HCC.
1. PI3K/Akt Pathway Is Involved in the Sorafenib Resistance
Hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) are genetically heterogeneous tumors. TP53 mutations have been found in HCC, especially in HCC patients with HCV or HBV positive [1]. In addition to prior HBV/HCV infection, metabolic abnormalities such as diabetes and obesity are also involved in HCC carcinogenesis. In contrast to other epithelial cancers such as breast, ovarian and colon, no mutations of common oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes except TP53 have been identified in HCC cells. However, many growth factor receptors such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) as well as key oncogenic signaling pathways related to proliferation and angiogenesis such as Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK (MAPK), phoshoinositol-3 kinase (PI3k)/Akt/mTOR, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (c-Met), insulin growth factor receptor(IGF), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog and Notch have been shown to be involved in hepatocarcinogenesis [2,3]. Therefore, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib has been used to block both tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis by targeting Raf-1/B-Raf kinases and VEGFR-2/-3 and PDGFR-β tyrosine kinases. Sorafenib administration has led to significant improvement in overall survival (OS) in patients with advanced HCC but disease stabilization does not last due to acquired resistance [4,5,6]. Understanding the mechanism of sorafenib resistance would improve sorafenib therapy in patients with HCC. One mechanism of sorafenib resistance in cultured HCC cells may be associated with a switch from the MAPK pathway to the parallel PI3K/Akt pathway when vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), Ret, c-kit and the downstream MAPK pathway are inhibited by sorafenib inhibition of tyrosine kinases. Activation of Akt and upregulation of phosphorylation of its downstream targets, including S6K and 4EBP1, have been shown in sorafenib treated HCC cells [7]. In HCC cells in which resistance is the result of long-term exposure to sorafenib, increased expression of phosphorylated Akt and the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K was observed. Sorafenib resistance could be reversed by knockdown of Akt or by administration of the Akt inhibitor MK-2206 [8]. In addition to the above described mechanisms, multidrug resistance protein 2 (MDRP2) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) also appear to be involved in acquired resistance to sorafenib in HCC [9,10,11].
Activation of the oncogenic signaling pathway PI3K/Akt can induce expression of both FOXM1 and MTDH, two critical master regulator genes involved in metastasis and drug resistance in numerous solid tumors including HCC [8,12]. FOXM1 expression can also be induced by other mechanisms including (i) increased transcription through the action of transcription factors E2F, c-Myc, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) [13,14,15]; (ii) loss transcription repression due to mutations in the tumor suppressor p53 (seen in approximately half of HCC patients) [16,17,18] and (iii) decreased expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) such as miR-149 and miR-134 which down-regulate FOXM1 post-transcriptionally [19,20]. Bioinformatic analyses of genome-wide transcriptional sequencing data in HCC have identified alterations of the FOXM1 transcription network including downstream FOXM1 effectors AURKB, BIRC5, CCNB1, CCNB2 and NEK2 [21,22].
2. FOXM1 is Essential for the Development of HCC
Conditionally deleted FOXM1 mouse hepatocytes are highly resistant to developing HCC in response to a Diethylnitrosamine (DEN)/Phenobarbital (PB) liver tumor-induction protocol suggesting a pivotal role for FOXM1 in HCC development [23,24]. HBV-associated hepatocarcinogenesis involves the activation of FOXM1 expression by hepatitis B virus X (HBx) through the ERK/CREB pathway [25]. Induction of MMP-7, RhoC, and ROCK1 expression by FOXM1 can promote hepatoma cell invasion and metastasis [25]. FOXM1 expression was highly correlated with the recurrence and poor survival of patients with HBV-HCC after surgical resection. Another downstream effector of FOXM1, acid phosphatase 5 (ACP5), is also involved in progression and metastasis of HCC mediated by FOXM1. Knockdown of ACP5 significantly reduced FOXM1-mediated invasion and lung metastases [26]. Co-expression of ACP5 and FOXM1 was associated with poor prognosis. Overexpression of miR-135a favors invasive and metastatic behavior in vitro. MiR-135a is transcribed by FOXM1 and metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1) was identified as a direct target of miR-135a [27]. Further analysis revealed the relevance of miR-135a with respect to the prognosis and survival of HCC patients with Portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT). PVTT has been correlated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and 50%–80% of HCC is accompanied by portal vein invasion. MiR-135a is highly over-expressed in PVTT [27].
3. FOXM1 Acts as a Therapeutic Target of HCC
Thiazole compounds, Siomycin A and thiostrepton, and other proteasome inhibitors such as bortezomib, have been shown to repress transcription of FOXM1 at both the mRNA and protein levels in cancer cells [28]. These agents could be attractive therapeutic drugs to overcome drug resistance when combined with standard regimens for cancers with FOXM1 overexpression. FOXM1 is also an inhibitory target of tumor suppressor gene p19 (ARF) [23,29,30]. A p19(ARF) position 26-44 peptide fragment containing nine D-Arg residues to enhance cellular uptake was sufficient to significantly reduce FOXM1 transcriptional activity. HCC in both wild-type mice or in Arf(−/−)Rosa26-FOXM1 Tg mice was induced by diethylnitrosamine/phenobarbital. These HCC-bearing mice were then injected daily with the cell-penetrating ARF(26-44) peptide inhibitor to pharmacologically reduce FOXM1 activity. After 4 weeks of this treatment, HCC regions displayed reduced tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis within the HCC region but not in the adjacent normal liver tissue. Significant downregulation of FOXM1 to normal cell levels has been reached in cancer cells by depleting NPM1, an interacting partner of FOXM1 [31]. Peptides or small molecules specifically targeting the interaction between FOXM1 and NPM1 could potentially lead to a FOXM1 targeted therapy. Various DNA repair genes including BRIP1 (BRCA1-associated BACH1 helicase), Rad51, XRCC1 (X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1) and BRCA2 (breast cancer-associated gene 2) have been transcriptionally regulated by FOXM1 [32,33,34,35]. The function of FOXM1 as transcription regulator of DNA repair genes indicates that FOXM1 might be targeted to increase the sensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage induced by chemotherapy and radiotherapy (Figure 1A).
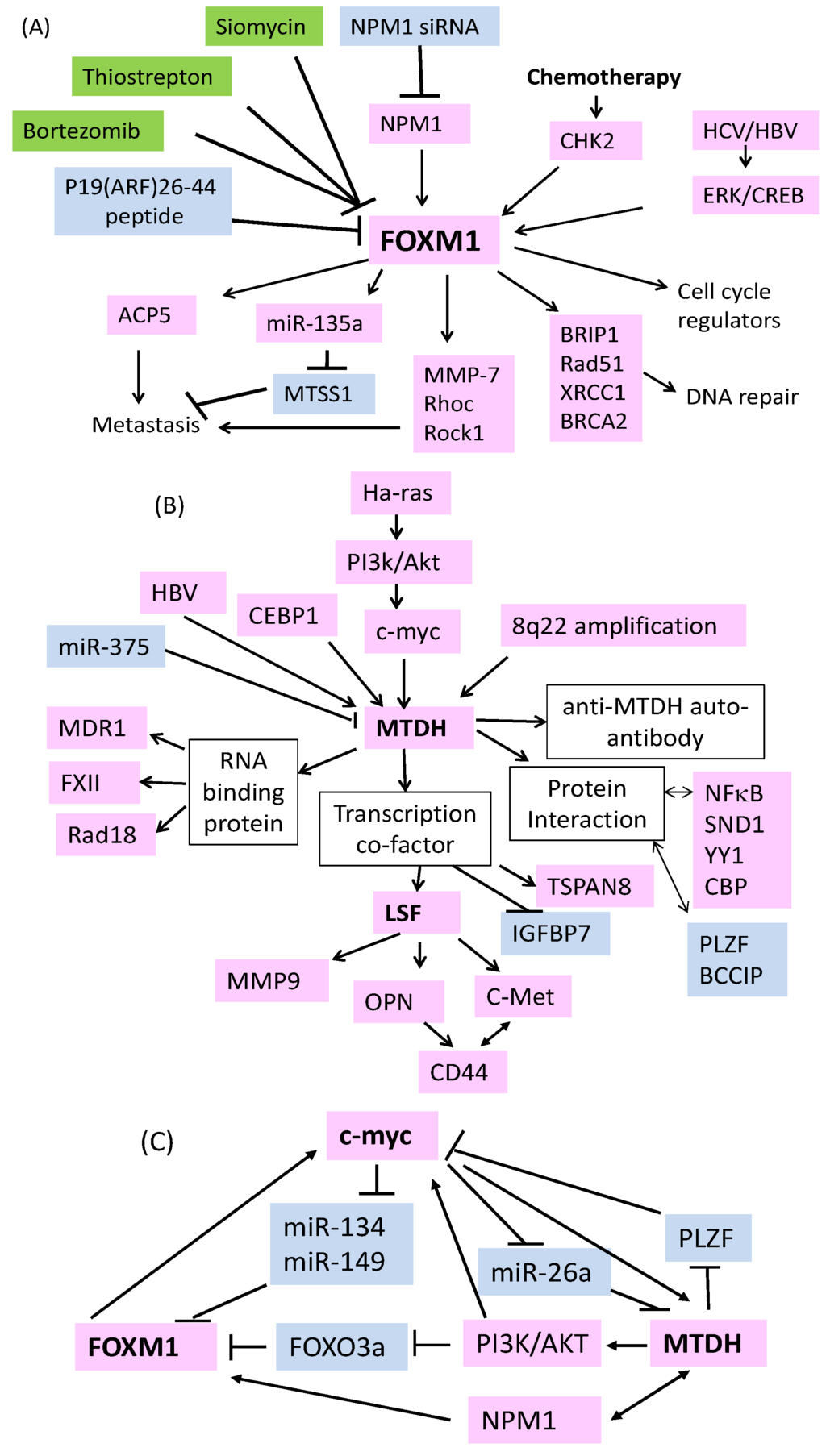
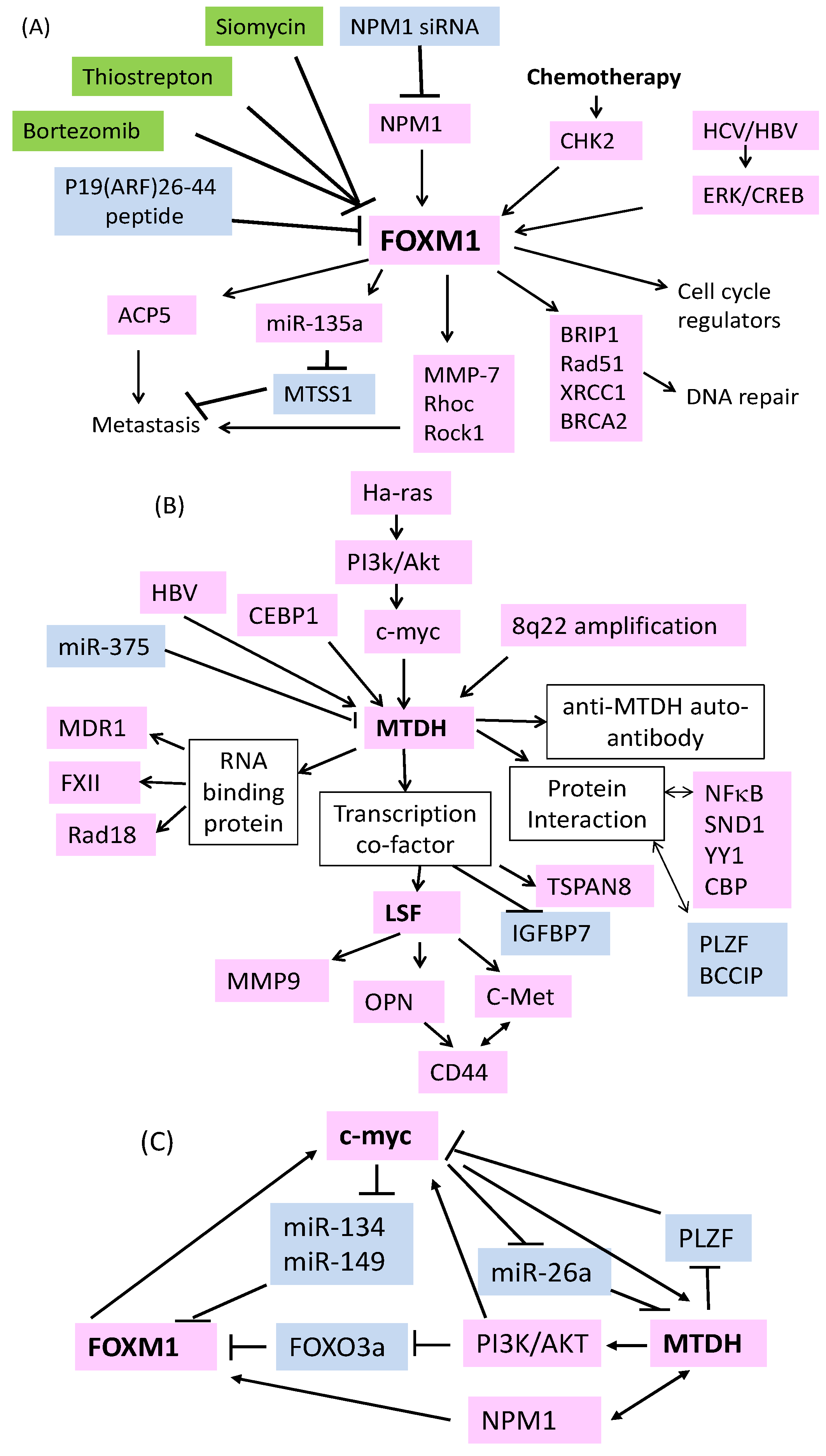
Figure 1.
Mechanisms regulating the overexpression of FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1), MTDH (metadherin) and downstream effectors and strategies used to target FOXM1 in HCC (Hepatocellular carcinoma). (A) Thiazole compounds siomycin and thiostrepton, proteasome inhibitors (highlighted in green boxes), ARF peptides and NPM1 siRNA (highlighted in blue boxes) can reduce the expression of FOXM1. Chemotherapy can increase FOXM1 stability via CHK2. HBV/HCV can increase FOXM1 through ERK/CREB.Up-regulated FOXM1 subsequently controls cell cycle transition, DNA repair and metastasis via positive (pink boxes) or negative (blue boxes) regulating downstream effectors. (B) Multiple mechanisms including chromosome amplification at 8q22, Ras, PI3K/Akt, myc activation, increased CEBP1, reduced miR-375, and HBV infection can cause up-regulation of MTDH. Increased MTDH can regulate various downstream effectors to control drug resistance and metastasis via RNA or protein interactions. Increased expression of anti-MTDH auto-antibody, TSPAN8 and reduced expression of IGFBP7 in HCC patient blood might be used as poor prognosis biomarker. (C) Multiple feedback loops are involved in the expression regulation of MTDH, FOXM1 and c-myc in HCC.
Figure 1.
Mechanisms regulating the overexpression of FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1), MTDH (metadherin) and downstream effectors and strategies used to target FOXM1 in HCC (Hepatocellular carcinoma). (A) Thiazole compounds siomycin and thiostrepton, proteasome inhibitors (highlighted in green boxes), ARF peptides and NPM1 siRNA (highlighted in blue boxes) can reduce the expression of FOXM1. Chemotherapy can increase FOXM1 stability via CHK2. HBV/HCV can increase FOXM1 through ERK/CREB.Up-regulated FOXM1 subsequently controls cell cycle transition, DNA repair and metastasis via positive (pink boxes) or negative (blue boxes) regulating downstream effectors. (B) Multiple mechanisms including chromosome amplification at 8q22, Ras, PI3K/Akt, myc activation, increased CEBP1, reduced miR-375, and HBV infection can cause up-regulation of MTDH. Increased MTDH can regulate various downstream effectors to control drug resistance and metastasis via RNA or protein interactions. Increased expression of anti-MTDH auto-antibody, TSPAN8 and reduced expression of IGFBP7 in HCC patient blood might be used as poor prognosis biomarker. (C) Multiple feedback loops are involved in the expression regulation of MTDH, FOXM1 and c-myc in HCC.
4. Role of MTDH as an RNA Binding Protein in Drug Resistance
MTDH has also been shown to play a critical role in DNA damage response (DDR) in a transgenic mouse model with hepatocyte-specific expression of MTDH (Alb/MTDH) [36,37]. Compared to control hepatocytes, reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and delayed activation of ATM, ATR, CHK1 and CHK2 have been observed in Alb/MTDH hepatocytes following isolation and culture. Endogenous MTDH is mainly distributed in the nucleus or nucleolus in hepatocytes of wild type mice, however, MTDH is mainly localized at cytoplasm in hepatocytes of the transgenic (Alb/MTDH) mouse model. Our previous report in which we used RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation followed by microarray analysis (RIP-chip) showed that MTDH can associate with various mRNA targets including multiple members of the Fanconi Anemia pathway (FANCA, FANCC, FANCD2, FANCI) and functionally related Rad18 [38]. MTDH might function as a RNA binding protein to regulate the levels of important DNA repair factors at the post-transcriptional level. Previous work has shown that MTDH can promote translation of the multiple drug resistance gene MDR1 and the angiogenesis gene factor XII (FXII) [36,39,40]. Therefore, targeting MTDH might impair the ability of cancer cells to rapidly repair their DNA and increase therapeutic efficacy.
5. Mechanisms of MTDH Overexpression in HCC
Overexpression of MTDH is detected in >90% of HCC patients by immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays (TMAs) and the level of MTDH expression is negatively correlated with overall survival and cumulative recurrence rates [41]. MTDH was identified by characterizing the copy number aberration (CNA) landscape in HCC from the recurrent focal amplification peaks [42] as one of the oncogenic drivers playing a significant role in HCC growth and survival. Multivariate analyses of 288 HCC patients revealed that high MTDH expression was an independent predictor of shorter disease-free survival (DFS) after curative hepatectomy [43]. MTDH overexpression in HCC was associated with elevated copy numbers due to gains of large regions of chromosome 8q22. Transcription of MTDH is induced by direct binding of c-myc to the MTDH promoter upon activation of Ha-ras/PI3K/Akt signaling [44]. Overexpression of MTDH in HCC cells might evade apoptosis and increase cell growth through the regulation of PLZF repression on the activation of c-myc, which can activate transcription of MTDH through a positive feedback loop [45]. MTDH is a confirmed target of miR375 for post-transcriptional regulation. MiR-375 has been shown to be downregulated in 60 human HCC compared to normal adjacent tissues [46]. Downregulation of N-cadherin and snail, upregulation of E-cadherin, and translocation of β-catenin by depletion expression of MTDH in HCC cell lines indicates that MTDH may promote HCC metastasis through the induction of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process [47,48]. Moreover, MTDH overexpression was correlated with clinicopathologic characters including cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, chemoresistance, angiogenesis and poor clinical outcome [40,49,50]. A gradual increase in MTDH expression in normal liver tissue to hepatitis B and HBV-related HCC tissue levels was observed [51]. Significant correlation between MTDH expression with the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC, seventh edition) stage, T classification, N classification, vascular invasion, and histological differentiation was seen in the HBV-related HCC patients. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1 (CEBP1) binds to the 3'-UTR of MTDH mRNA and promotes its translation. Monoubiquitination of MTDH protein in cancer cells leads to increased stabilization and cytoplasmic accumulation. In summary, MTDH overexpression in human HCC is caused by multiple mechanisms, such as genomic amplification at 8q22 as well as myc mediated transcription activation and reduced post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs, monoubiquitination and association with CEBP1 (Figure 1B). HCC with steatotic features was induced by the carcinogen N-nitrosodiethylamine in a transgenic mouse with hepatocyte-specific expression of MTDH (Alb/MTDH), but not in wild-type (WT) mice. Novel aspects of MTDH function, including induction of steatosis, inhibition of senescence, and activation of the coagulation pathway to augment aggressive hepatocarcinogenesis have been observed in hepatocyte-specific MTDH transgenic mice [36]. Inhibition of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine was also observed in MTDH knockout mice [52].
MTDH is primarily located in the membrane and the cytoplasm of HCC cells compared to nuclear distribution in normal hepatocytes. Autoantibodies against tumor-associated antigens present in the blood of cancer patients can be developed as biomarkers. As a consequence of overexpression of MTDH in cancer cell membranes, elevated levels of anti-MTDH antibody in the serum of cancer patients was detected [53]. Anti-MTDH antibody at titers of ≥1:50 from the sera of liver cancer patients was detected in 48 out of 96 (50%) HCC patients by ELISA using the lung-homing domain (aa 381–443) of human MTDH as the antigen [53,54]. In contrast, no anti-MTDH antibody was detected in the serum of 230 normal controls. Anti-MTDH antibody was detected in eight of 31 (26%) stage I and II HCC patients and in 40 of 65 (62%) stage III and IV HCC patients.
6. Signal Transduction Pathways Activated by MTDH
Activation of the Akt and NF-κB pathways are the two major signal transduction pathways correlated with MTDH and drug resistance in HCC [55]. Although the detailed mechanism of PI3K/Akt pathway activation by MTDH is unclear, involvement of MTDH has been confirmed by several laboratories. MTDH may play a role in the chronic inflammatory changes preceding HCC development by activating the NF-κB pathway. MTDH was seen to interact with the p65 subunit of NF-κB as well as with CREB-binding protein (CBP) [56]. Though MTDH itself does not have a DNA-binding domain, MTDH may function as a transcriptional coactivator in the NF-κB complex bound to IL-8 promoter as a bridging factor among NF-κB, CBP, and basal transcription machinery to activate downstream genes of NF-κB pathway. Further, MTDH is involved in Wnt/β-catenin signaling through inducing ERK42/44 activation and is associated with protective autophagy by inducing AMPK activation.
7. MTDH Regulation of Downstream Genes in HCC
Genes downstream of MTDH were identified via an Affymetrix oligonucleotide microarray by comparing differential gene expression in control and exogenous MTDH expressing HepG2 cells. One cluster of genes in the Wnt signaling pathway, including lymphoid-enhancing factor 1/T cell factor 1 (LEF1/TCF1), CTBP2 and APC, were regulated by MTDH. A second cluster of genes downstream of MTDH was associated with chemoresistance including drug-metabolizing enzymes, such as dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD), cytochrome P4502B6 (CYP2B6), dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (AKR1C2), and the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC11 (also known as MRP8). Transcription factor CP2 (TFCP2, also known as LSF) was also significantly upregulated by MTDH in HCC cells. Other important genes downstream of MTDH include claudin 4 (CLDN4), tetraspanin 8 (TSPAN8), transgelin (TAGLN, a suppressor of MMP-9), IGF-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) and pyruvate kinase (PK).
Late SV40 factor (LSF) was up-regulated by MTDH in HCC [41]. LSF is a ubiquitous transcription factor, first identified as a transcriptional activator of the major late Simian Virus 40 promoter. LSF belongs to the LSF/CP2 family related to grainyhead family of proteins and is involved in many biological functions, including regulation of cellular proliferation, viral promoters and drug resistance. Similar to MTDH, LSF overexpression is detected in more than 90% of human HCC patients, compared to normal hepatocytes. A network of proteins including osteopontin (OPN), Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and c-Met were identified as downstream effectors of LSF in LSF-induced hepatocarcinogenesis [41,57,58]. A small molecule inhibitor of LSF, Factor Quinolinone inhibitor 1 (FQI1), was identified by a high throughput screening [59]. FQI1 can profoundly inhibit viability in human HCC cell lines in vitro and markedly inhibit growth of human HCC xenografts as well as angiogenesis in vivo. MET/HGF targeted anticancer therapies with tivantinib, cabozantinib, onartuzumab, crizotinib, rilotumumab, and ficlatuzumab have shown encouraging results in clinical trials. Patients with high MTDH and LSF expression may benefit from targeted MET /HGF inhibitor treatment.
Tspan8 (also called D6.1A/CO-029 cancer antigen) is associated with metastasis and pro-angiogenesis. Tspan8 is another gene upregulated by MTDH in HCC cells [36]. Tspan8 expression is induced 30-fold in liver after DEN treatment of MTDH transgenic mice compared to wild type mice. Tspan8 contributes to a selective recruitment of proteins and mRNA into extra-cellular microvesicles called exosomes. This includes CD49d, which is implicated in exosome-endothelial cell (EC) binding and EC internalization. EC uptake of Tspan8-CD49d complex-containing exosomes was accompanied by enhanced EC proliferation, migration, sprouting, and maturation of EC progenitors. Tumor-derived exosomes containing the Tspan8 can efficiently induce angiogenesis.
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) is a downstream gene repressed by MTDH in HCC cells [60]. IGFBP7 is a secreted member of the IGFBP family. The IGFBP family (IGFBP1-7), two growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) and their receptors (IGF-IR and IGF-IIR) are components of IGF signal transduction pathway. Using an immunohistochemical approach in tissue microarray, high IGFBP7 expression was detected in normal human liver while a significantly decreased expression was seen in 104 HCC patients. Thus, IGFBP7 downregulation might be a prognostic marker for aggressive HCC. Although stable overexpression of IGFBP7 in aggressive human HCC cells resulted in modest inhibition compared to controls, profound inhibition of tumorigenesis by IGFBP7-overexpression was observed in a subcutaneous xenograft assay using athymic nude mice. Marked inhibition of angiogenesis and induction of senescence may cause the difference in the IGFBP7 in vitro effect. Replication-incompetent adenovirus-delivered IGFBP7 (Ad.IGFBP7) potently induces apoptosis in multiple HCC cell lines in vitro and profoundly inhibits primary tumor growth and metastasis in vivo [60].
8. MicroRNAs in HCC: Drug Resistance and Beyond
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (21–23 nucleotide) RNA species whose role in both normal cellular functions and human diseases, particularly cancers, is well established [61]. A direct role for miRNAs in HCC drug resistance has been shown. Over-expression of miR-122, the liver-specific miRNA, in HCC cells, including Hep3B, HepG2 and Huh7, increased sensitivity to adriamycin and vincristine [62]. More generally, use of several drug resistant Huh7 HCC sublines identified an array of significant miRNA expression changes when compared to control Huh7 cells [63]. Among the miRNAs displaying significant differential expression were miR-146a/b and miR-181d. Both of these miRNA families have been shown in other cancers to influence chemoresistance [63].
In addition to therapeutic resistance, a number of studies have implicated miRNAs in various aspects of HCC development and pathology. One of the most direct demonstrations of the role of miRNAs in HCC is related to the tight linkage of several miRNAs to the hyperactivation of the Myc oncogene that is characteristic of both HCC and the rare childhood hepatoblastoma (HB) [64]. MiRNAs miR-100, miR-125b, miR-26, miR-23a/b, miR-371 and let-7a are all validated Myc targets and all are important effectors of Myc-mediated oncogenesis in HCC. Hou et al. [65] examined the miRNAomes of both normal human liver tissues (n = 3) and hepatocellular carcinomas (n = 3) using next-generation deep sequencing. They found that the majority of miRNA expression in both samples could be accounted for by very few miRNAs. Among the most abundantly expressed miRNAs was the liver-specific miR-122 [66] and miR-192. Giordano and Columbano [67] note that miR-21 is the most over-expressed miRNA in HCC as compared with normal tissues.
While the vast majority of miRNA studies in cancers have focused on the role of particular miRNAs, in particular cancers or cancer processes, the advent of The Cancer Genome Atlas project has made it possible to examine multiple biologic and genetic characteristics in numerous cancers simultaneously [68,69,70]. These, in turn, have allowed researchers to re-examine previous, more focused studies in a much broader context.
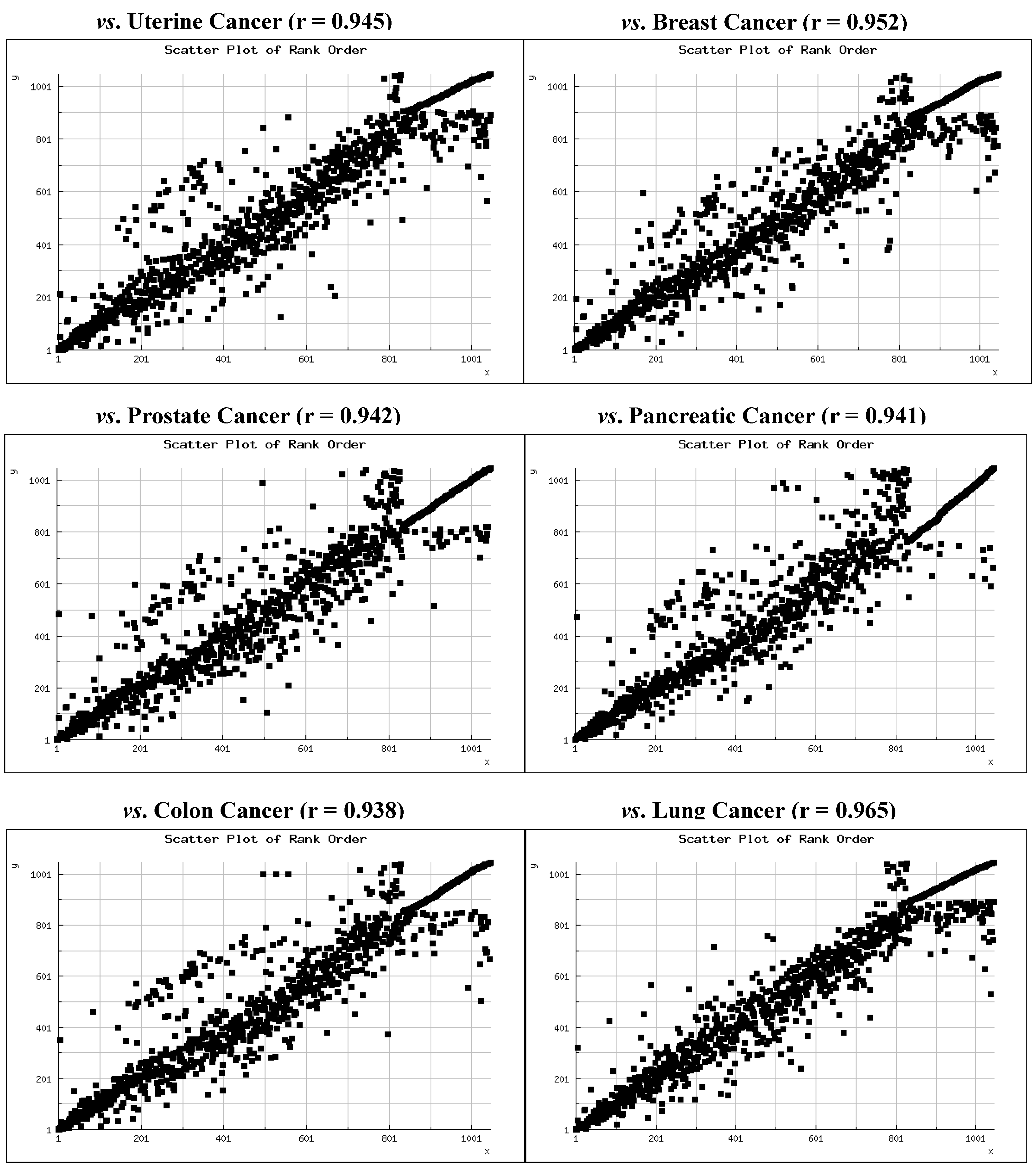
We recently compared expression levels of 1,046 miRNAs in seven cancers using deep sequencing profiles of hundreds of tumors produced by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project [71]. Expression levels were compared via Spearman Rank Order Correlation [72] and included uterine corpus adenocarcinoma (n = 415 patients), ovarian serous adenocarcinoma (n = 970 patients), breast adenocarcinoma (n = 770 patients), prostate adenocarcinoma (n = 286 patients), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (n = 62 patients), colorectal adenocarcinoma (n = 478 patients), and lung adenocarcinoma (n = 482 patients). The patterns we observed show that overall miRNA expression is very highly correlated among the cancers (mean ρ = 0.94 ± 0.03). We also observed that all of the most highly expressed miRNAs among these cancers are members of evolutionarily ancient miRNA families, the vast majority of which appeared in animal genomes prior to the emergence of land animals 380 million years ago.
TCGA has produced similar miRNA expression data on 197 patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We have incorporated these data into our previous analyses and compared expression levels with those of uterine corpus adenocarcinoma, breast adenocarcinoma, prostate adenocarcinoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, colorectal adenocarcinoma, and lung adenocarcinoma. Rank order scatter plots and correlations are shown in Figure 2. Again, the Spearman Rank Order Correlations are very high (mean ρ = 0.95 ± 0.01) and all are statistically significant (p < 0.0001).
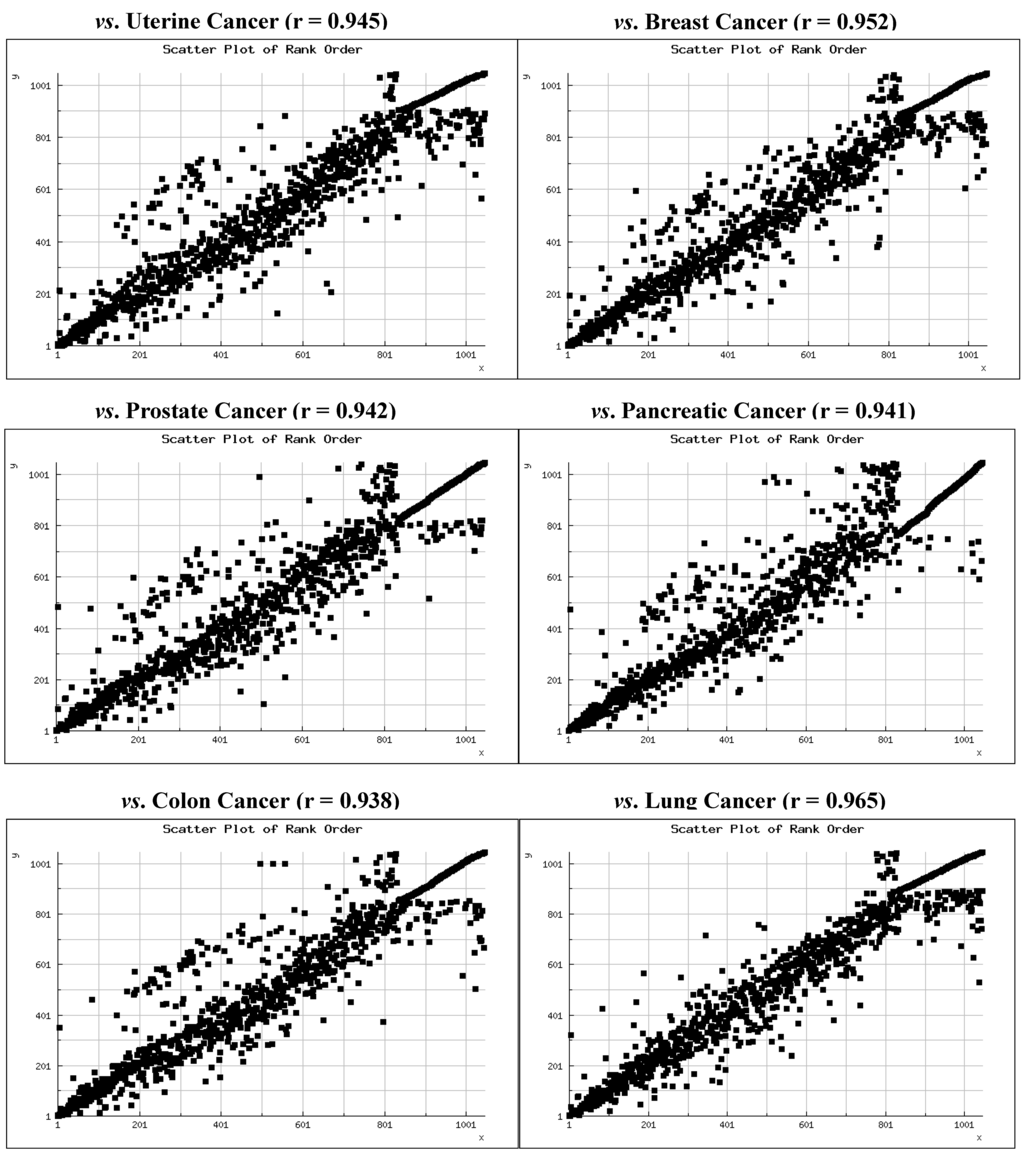
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of the expression rank of 1,046 miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma versus six adenocarcinomas with the Spearman Rank Correlation for each. All correlations are significant (p < 0.001).
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of the expression rank of 1,046 miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma versus six adenocarcinomas with the Spearman Rank Correlation for each. All correlations are significant (p < 0.001).
Moreover, the previously seen pattern of domination by ancient miRNA families is obtained in HCC as well. Budhu et al. [73] identified 19 miRNAs related to metastasis in HCC. Consistent with our prior observation, only one of these 19 miRNAs, miR-148, is a member of a miRNA family whose emergence in animal genomes occurred more recently than 380 million years ago.
In TCGA HCC data, miR-21 is the most highly expressed miRNA and it ranks either first or second in each of the other tumors as well. Indeed, miR-21 has been called the most dysregulated miRNA in cancer and noted the many biological processes, both normal and pathologic, in which miR-21 plays a major role [74]. In the HCC TCGA data, both miR-122 and miR-192 were very highly expressed. In comparison with data from the six other cancers, miR-192 was also highly expressed whereas, not surprisingly, miR-122 was barely detected. Interestingly, among the most highly expressed miRNAs in other tumors are the five members of the miR-200 family (miR-200a,b,c; miR-141 and miR-429). In the HCC TCGA data, members of the miR-200 family are barely expressed. These miRNAs are involved in the crucial epithelial to mesenchymal transition and are routinely over-expressed in adenocarcinomas [75]. HCC is not an adenocarcinoma and its etiology is tied to exposure to certain viruses such as hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as well as other liver-specific pathologies such as cirrhosis. Takahashi et al. [76] note that miR-200a is down-regulated in chronic liver tissue injury, including HCV infection. Thus, the very different expression pattern of the miR-200 family members in HCC compared to other cancers is related to the difference in the route of carcinogenesis in HCC. Other miRNAs displaying HCC-specific expression in the TCGA rankings are miR-194-1,2, miR-217, and miR-885. It has been shown in mice that miR-217 levels are dramatically increased in liver cells in response to chronic ethanol exposure and that such increases result in excess fat accumulation [77]. Chronic alcohol exposure in humans leads to cirrhosis, a well-established HCC precursor. MiR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells but over-expression in liver cancer cells in mice inhibits metastases [78]. Finally, miR-885 has been reported to activate the tumor suppressor p53 and to inhibit proliferation and survival [79]. Thus, it is not surprising to see that this miRNA exhibits quite low expression in adenocarcinoma TCGA ranks. That it is substantially more highly expressed in HCC by comparison is puzzling since the rate of p53 mutation in HCC is very low except in areas of the world where aflatoxin-contaminated foods are routinely consumed [80]. However, Gui et al. [81] identified significantly high levels of circulating miR-885 to be characteristic of both cirrhosis and HCC. Thus, miR-885 may well be important to a liver-specific pathologic process independent of p53.
9. Conclusions
In summary, the mechanisms of the drug resistance in HCC are complicated and remain unclear. Genetic heterogeneity may be the primary resistance mechanism of HCC to chemotherapy. Multiple mechanisms can induce the overexpression of FOXM1 and MTDH, two pivotal master regulators involved in drug resistance and metastasis. As shown in Figure 1C, there are several positive feedback loops between the activation of FOXM1 and MTDH. First, MTDH can activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, suppressing FOXO3a mediated transcription repression to FOXM1 and activating c-myc [82,83]. MTDH may also activate FOXM1 by interacting with NPM1 [31,38]. Second, MTDH can release the transcription repression to c-myc by interacting with the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF) [45]. C-myc can directly increase MTDH transcription and inhibits the suppression by miR-26a [84]. Third, FOXM1 can directly regulate c-myc transcription and c-myc can release the suppression of FOXM1 by miR-134 and miR-149 [19,84]. Chemotherapy can also simultaneously activate the addiction switches and compensatory pathways, such as FOXM1 protein stability induction by CHK2, leading to acquired resistance and metastasis [85,86]. Further investigation of the feedback loops of FOXM1, MTDH, c-myc and microRNAs will better our understanding of the mechanisms of drug resistance in HCC and inform strategies for mitigating it.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by NIH Grant R01CA99908 to Kimberly K. Leslie, the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research Development Fund, and Institutional Research Grant no. IRG-77-004-31 from the American Cancer Society to Shujie Yang, administered through the Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Iowa.
Author Contributions
X.M., and S.Y. wrote part 1 to 7, E.J.D and B.M.S wrote part 8, X.M.,E.J.D and K.K.L edited the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Meerzaman, D.M.; Yan, C.; Chen, Q.R.; Edmonson, M.N.; Schaefer, C.F.; Clifford, R.J.; Dunn, B.K.; Dong, L.; Finney, R.P.; Cultraro, C.M.; et al. Genome-wide transcriptional sequencing identifies novel mutations in metabolic genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2014, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Qu, X. SL1122-37, a novel derivative of sorafenib, has greater effects than sorafenib on the inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and prevention of angiogenesis. Biosci. Trends 2013, 7, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Scartozzi, M.; Faloppi, L.; Svegliati Baroni, G.; Loretelli, C.; Piscaglia, F.; Iavarone, M.; Toniutto, P.; Fava, G.; De Minicis, S.; Mandolesi, A.; et al. VEGF and VEGFR genotyping in the prediction of clinical outcome for HCC patients receiving sorafenib: The ALICE-1 study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 125, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Greten, T.F.; Manns, M.P.; Malek, N. Sorafenib for the treatment of HCC--the beginning of a new era in the treatment of HCC. Z. Gastroenterol. 2009, 47, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Tang, Y.F.; Yao, T.J.; Chiu, J.; Leung, R.; Chan, P.; Cheung, T.T.; Chan, A.C.; Pang, R.W.; Poon, R.; et al. The outcomes and safety of single-agent sorafenib in the treatment of elderly patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Oncologist 2011, 16, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.K.; Ng, L.; Lam, C.S.; Wong, S.K.; Wan, T.M.; Cheng, N.S.; Yau, T.C.; Poon, R.T.; Pang, R.W. The Enhanced metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib resistance. PLoS One 2013, 8, e78675. [Google Scholar]
- Gedaly, R.; Angulo, P.; Hundley, J.; Daily, M.F.; Chen, C.; Evers, B.M. PKI-587 and sorafenib targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MAPK pathways synergistically inhibit HCC cell proliferation. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 176, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.F.; Chen, H.L.; Tai, W.T.; Feng, W.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; Cheng, A.L. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Sheng, H.; Saxena, R.; Skill, N.J.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Yu, M.; Nakshatri, H.; Maluccio, M.A. NF-kappaB inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its potential as adjunct to sorafenib based therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009, 278, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanik, T.; Kohler, B.C.; Boger, R.J.; Worns, M.A.; Heeger, S.; Otto, G.; Hovelmeyer, N.; Galle, P.R.; Schuchmann, M.; Waisman, A.; et al. Down- regulation of CYLD as a trigger for NF-kappaB activation and a mechanism of apoptotic resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H.; Chiang, I.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, F.T.; Chen, H.W.; Chen, C.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Lin, W.J.; Hwang, J.J. Simultaneous imaging of temporal changes of NF-kappaB activity and viable tumor cells in Huh7/NF-kappaB-tk-luc2/rfp tumor-bearing mice. In Vivo 2013, 27, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, B.; Sun, X.Y. Mechanisms of resistance to sorafenib and the corresponding strategies in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Hikosaka, K.; Sultana, N.; Sharkar, M.T.; Noritake, H.; Kimura, W.; Wu, Y.X.; Kobayashi, Y.; Uezato, T.; Miura, N. Liver tumor formation by a mutant retinoblastoma protein in the transgenic mice is caused by an upregulation of c-Myc target genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Mo, P.; Huang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tian, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The TNF-alpha/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.D.; Brooks, L., 3rd; Zhang, X.; Mahoney, J.M.; Martyanov, V.; Wood, T.A.; Sherlock, G.; Cheng, C.; Whitfield, M.L. Identification of cell cycle-regulated genes periodically expressed in U2OS cells and their regulation by FOXM1 and E2F transcription factors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, A.M.; Prives, C. Pro-proliferative FoxM1 is a target of p53-mediated repression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 4295–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, B.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. p53 negatively regulates expression of FoxM1. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3425–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millour, J.; de Olano, N.; Horimoto, Y.; Monteiro, L.J.; Langer, J.K.; Aligue, R.; Hajji, N.; Lam, E.W. ATM and p53 regulate FOXM1 expression via E2F in breast cancer epirubicin treatment and resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Fu, Z.; Ying, J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W. miR-134 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3761–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, J.; Cao, R. miR-149 Inhibits Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells EMT by Targeting FOXM1. Biochem. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 506731. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, H.; Lv, J.; Ying, T.; Jin, S.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Yuan, B.; Yang, Q. Gene-gene interaction network analysis of ovarian cancer using TCGA data. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Creighton, C.J.; Dayaram, T.; Shuck, R.; Shinbrot, E.; Xi, L.; Gibbs, R.A.; Wheeler, D.A.; Donehower, L.A. Effects of TP53 mutational status on gene expression patterns across 10 human cancer types. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichenko, V.V.; Major, M.L.; Wang, X.; Petrovic, V.; Kuechle, J.; Yoder, H.M.; Dennewitz, M.B.; Shin, B.; Datta, A.; Raychaudhuri, P.; et al. Foxm1b transcription factor is essential for development of hepatocellular carcinomas and is negatively regulated by the p19ARF tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Gusarova, G.; Wang, Z.; Carr, J.R.; Li, J.; Kim, K.H.; Qiu, J.; Park, Y.D.; Williamson, P.R.; Hay, N.; et al. Deregulation of FoxM1b leads to tumour metastasis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Fan, D.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K. Upregulated FoxM1 expression induced by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Tang, G.; et al. ACP5, a direct transcriptional target of FoxM1, promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, W.; Shi, J.; Li, N.; Yu, X.; Xue, J.; Fu, X.; Chu, K.; Lu, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. MicroRNA-135a contributes to the development of portal vein tumor thrombus by promoting metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, U.G.; Zipfel, P.A.; Tyler, D.S.; Gartel, A.L. Novel anticancer compounds induce apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.H.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Major, M.L.; Raychaudhuri, P. New and unexpected: Forkhead meets ARF. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarova, G.A.; Wang, I.C.; Major, M.L.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Ackerson, T.; Petrovic, V.; Costa, R.H. A cell-penetrating ARF peptide inhibitor of FoxM1 in mouse hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, U.G.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Nucleophosmin interacts with FOXM1 and modulates the level and localization of FOXM1 in human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41425–41433. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Jennings, N.B.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Peng, G.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, K.; Leem, S.H.; Lin, S.Y.; et al. FOXM1 mediates Dox resistance in breast cancer by enhancing DNA repair. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, A.; Huang, Z.; Huang, S. FoxM1 inhibition sensitizes resistant glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by downregulating the expression of DNA-repair gene Rad51. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongkow, P.; Karunarathna, U.; Khongkow, M.; Gong, C.; Gomes, A.R.; Yague, E.; Monteiro, L.J.; Kongsema, M.; Zona, S.; Man, E.P.; et al. FOXM1 targets NBS1 to regulate DNA damage-induced senescence and epirubicin resistance. Oncogene 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.J.; Khongkow, P.; Kongsema, M.; Morris, J.R.; Man, C.; Weekes, D.; Koo, C.Y.; Gomes, A.R.; Pinto, P.H.; Varghese, V.; et al. The Forkhead Box M1 protein regulates BRIP1 expression and DNA damage repair in epirubicin treatment. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4634–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Emdad, L.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Chen, D.; Gredler, R.; Shen, X.N.; Robertson, C.L.; Dumur, C.I.; Hylemon, P.B.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC in liver cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 120, 193–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhu, D.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Brachova, P.; Leslie, K.K. Cytoplasmic Metadherin (MTDH) provides survival advantage under conditions of stress by acting as RNA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4485–4491. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, B.K.; Chen, D.; Su, Z.Z.; Gredler, R.; Yoo, J.; Shah, K.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Molecular mechanism of chemoresistance by astrocyte elevated gene-1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Thiel, K.W.; Leslie, K.K. Drug resistance mediated by AEG- 1/MTDH/LYRIC. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 120, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Emdad, L.; Su, Z.Z.; Villanueva, A.; Chiang, D.Y.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Mills, A.S.; Waxman, S.; Fisher, R.A.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lim, H.Y.; Shi, S.; Lee, J.; Deng, S.; Xie, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pocalyko, D.; Yang, W.J.; et al. Genomic landscape of copy number aberrations enables the identification of oncogenic drivers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 58, 706–717. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.; Hyeon, J.; Park, C.K. Metadherin is a prognostic predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy. Gut Liver 2013, 7, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17390–17395. [Google Scholar]
- Thirkettle, H.J.; Mills, I.G.; Whitaker, H.C.; Neal, D.E. Nuclear LYRIC/AEG-1 interacts with PLZF and relieves PLZF-mediated repression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; Chang, Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Tang, F.; Li, P.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hao, M.; Sheng, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, J.; Hu, C. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel biomarker of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in two China regions. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Dai, Z.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G.H.; Yu, L.; Ding, Z.B.; Shi, G.M.; Ke, A.W.; Yang, X.R.; et al. Metadherin promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through induction of epithelial- mesenchymal transition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7294–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Advances in Cancer Research. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC Implicated in Multiple Human Cancers; Academic Press (ELSEVIER): San Diego, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: Clinical significance. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 120, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Liu, W.; You, N.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Zhao, G.; Yang, P.; Wang, D.; Dou, K. Prognostic significance of metadherin overexpression in hepatitis B virus- related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, C.L.; Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, A.; Rajasekaran, D.; Akiel, M.; Shen, X.N.; Arkun, K.; Ghosh, S.; Mark, M.A.; et al. Analyzing the role of Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 (AEG-1) in hepatocarcinogenesis using a knockout mouse model. In Presented at the 2014 Annual of the American Association of cancer Research (AACR), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–9 April 2014.
- Chen, X.; Dong, K.; Long, M.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H. Serum anti-AEG-1 auto-antibody is a potential novel biomarker for malignant tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Medine, E.I.; Odaci, D.; Gacal, B.N.; Gacal, B.; Sakarya, S.; Unak, P.; Timur, S.; Yagci, Y. A new approach for in vitro imaging of breast cancer cells by anti-metadherin targeted PVA-pyrene. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdad, L.; Das, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Hu, B.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: Signaling pathways, downstream genes, interacting proteins, and regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 120, 75–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Park, E.S.; Emdad, L.; Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Fisher, P.B. Molecular basis of nuclear factor-kappaB activation by astrocyte elevated gene-1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Emdad, L.; Gredler, R.; Fuller, C.; Dumur, C.I.; Jones, K.H.; Jackson-Cook, C.; Su, Z.Z.; Chen, D.; Saxena, U.H.; et al. Transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8357–8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Gredler, R.; Chen, D.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. c-Met activation through a novel pathway involving osteopontin mediates oncogenesis by the transcription factor LSF. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Santhekadur, P.K.; Rajasekaran, D.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, R.; Chen, D.; Schaus, S.E.; Hansen, U.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. The transcription factor LSF: A novel oncogene for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 269–285. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Yoo, B.K.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Gredler, R.; Bhutia, S.K.; Das, S.K.; Fuller, C.; Su, Z.Z.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6693–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptman, N.; Glavac, D. MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs: Prospects in diagnostics and therapy of cancer. Radiol. Oncol. 2013, 47, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, F.; Ma, L.; Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y.; Bian, X.; Bie, P.; et al. MicroRNA-122 sensitizes HCC cancer cells to adriamycin and vincristine through modulating expression of MDR and inducing cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett. 2013, 310, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Gao, M.; Huang, A. Differential miRNA expression profiles in hepatocellular cells and drug-resistant sublines. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 29, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Buendia, M.A.; Bourre, L.; Cairo, S. Myc target miRs and liver cancer: Small molecules to get Myc sick. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Grosshans, H. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122: Biology and therapeutic potential. Prog. Drug Res. 2011, 67, 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, S.; Columbano, A. MicroRNAs: New tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology 2013, 57, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoth, C.; McLellan, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Vandin, F.; Ye, K.; Niu, B.; Lu, C.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; McMichael, J.F.; et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 2013, 502, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Hei, N.; Liang, H. Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level properties of prognostic genes across cancer types. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3231. [Google Scholar]
- Devor, E.J.; Schickling, B.M.; Leslie, K.K. microRNA expression patterns across seven cancers are highly correlated and dominated by evolutionarily ancient families. Biomedical. Rep. 2014, 2, 384–387. [Google Scholar]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhu, A.; Jia, H.L.; Forgues, M.; Liu, C.G.; Goldstein, D.; Lam, A.; Zanetti, K.A.; Ye, Q.-H.; Qin, L.-X.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarswamy, R.; Volkmann, I.; Thum, T. Regulation and function of miR-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Develop. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.; Wen, H.-J.; Patel, T. microRNAs in liver disease: From diagnostics to therapeutics. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Hu, M.; Zhang, R.; Shen, Z.; Flatow, L.; You, M. MicroRNA-217 promotes ethanol-induced fat accumulation in hepatocytes by down-regulating SIRT1. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9817–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, S.; Tian, Y.; Jove, R.; Xu, R.; Huang, W. miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice. Hepatology 2010, 52, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasyeva, E.A.; Mestdagh, P.; Kumps, C.; Vandesompele, J.; Ehemann, V.; Theissen, J.; Fischer, M.; Zapatka, M.; Brors, B.; Savelyeva, L.; et al. MicroRNA miR-885-5p targets CDK2 and MCM5, activates p53 and inhibits proliferation and survival. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Phillips, T.D.; Jolly, S.E.; Williams, J.H.; Phillips, T.D.; Jolly, P.E.; Stiles, J.K.; Jolly, C.M.; Aggarwal, D. Human aflotoxicosis in developing countries: A review of toxicology, exposure, potential health consequences and interventions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.; Tian, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Run, W.; Tian, L.; Jia, X.; Gao, Y. Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.S.; Brosens, J.J.; Schwenen, H.D.; Lam, E.W. FOXO and FOXM1 in cancer: The FOXO-FOXM1 axis shapes the outcome of cancer chemotherapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lam, E.W. Role of the forkhead transcription factor FOXO-FOXM1axis in cancer and drug resistance. Front. Med. 2012, 6, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, X.X.; He, J.R.; Zhou, C.X.; Guo, M.; He, M.; Li, M.F.; Chen, G.Q.; Zhao, Q. Pathologically decreased miR-26a antagonizes apoptosis and facilitates carcinogenesis by targeting MTDH and EZH2 in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierstra, I.; Alves, J. FOXM1c transactivates the human c-myc promoter directly via the two TATA boxes P1 and P2. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4645–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Raychaudhuri, P.; Costa, R.H. Chk2 mediates stabilization of the FoxM1 transcription factor to stimulate expression of DNA repair genes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
