Persistent Changes in Hormones and Growth Factors Involved in Ageing in Patients That Recovered from Severe COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Volunteers
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
| Human Insulin (INS) | MBS704195 |
| Human Transforming Growth Factor Beta | MBS266143 |
| Human Insulin-like Growth Factors 1 Long R3 | MBS733937 |
| Human BDNF | MBS2515054 |
| Human NGF | MBS2509465 |
| Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor | MBS021279 |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 | MBS459282 |
| Human Oxytocin | MBS703338 |
| Human GH | MBS2513456 |
| Human Acylated ghrelin | MBS166226 |
| Human SARS-Cov-2 SPIKE | NBP3-11407 |
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of Severe COVID-19 Patients
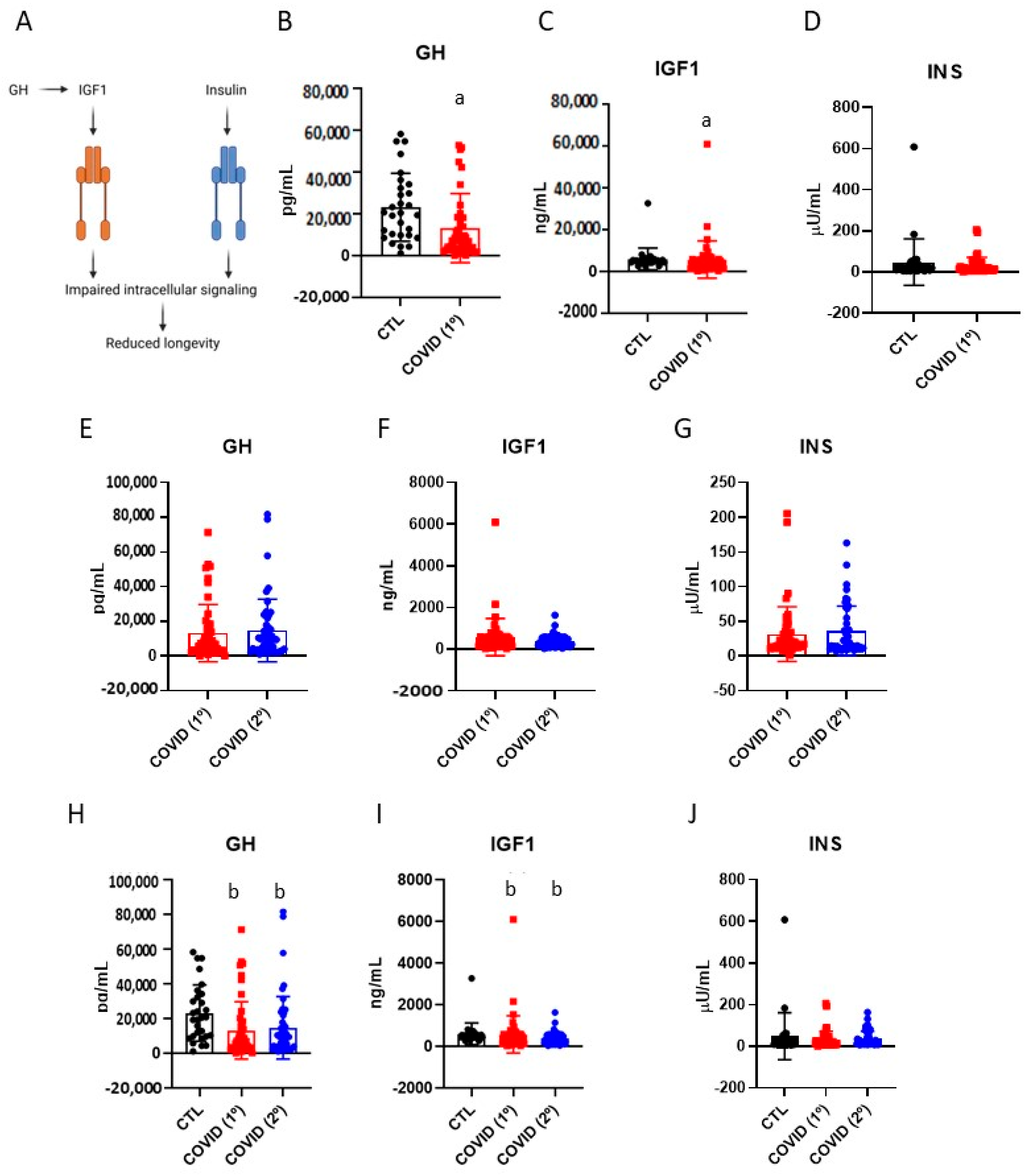
3.2. Blood Levels of Growth Hormone, Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Insulin in Patients Recovered from Severe COVID-19
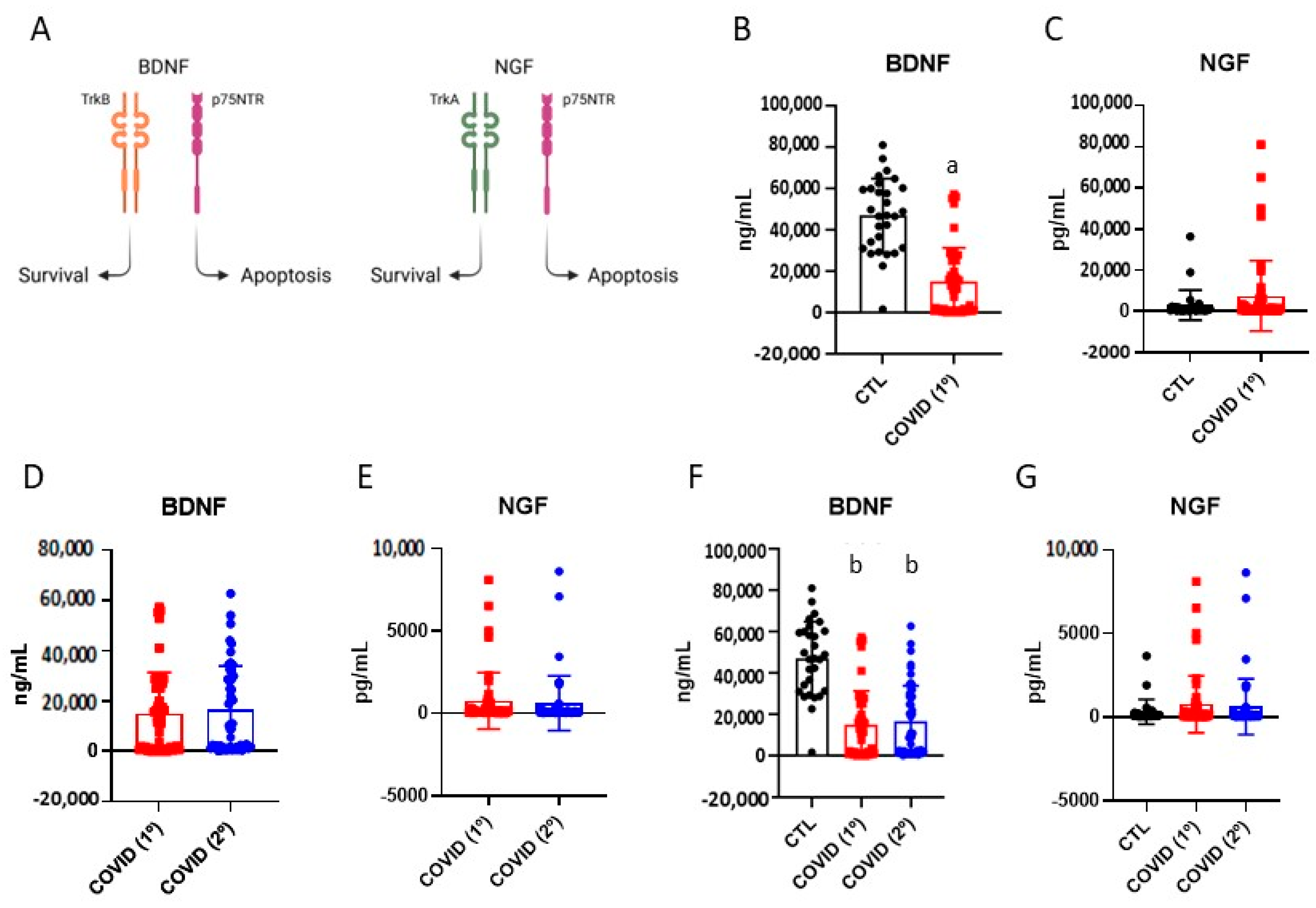
3.3. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Nerve Growth Factor in Patients Recovered from Severe COVID-19
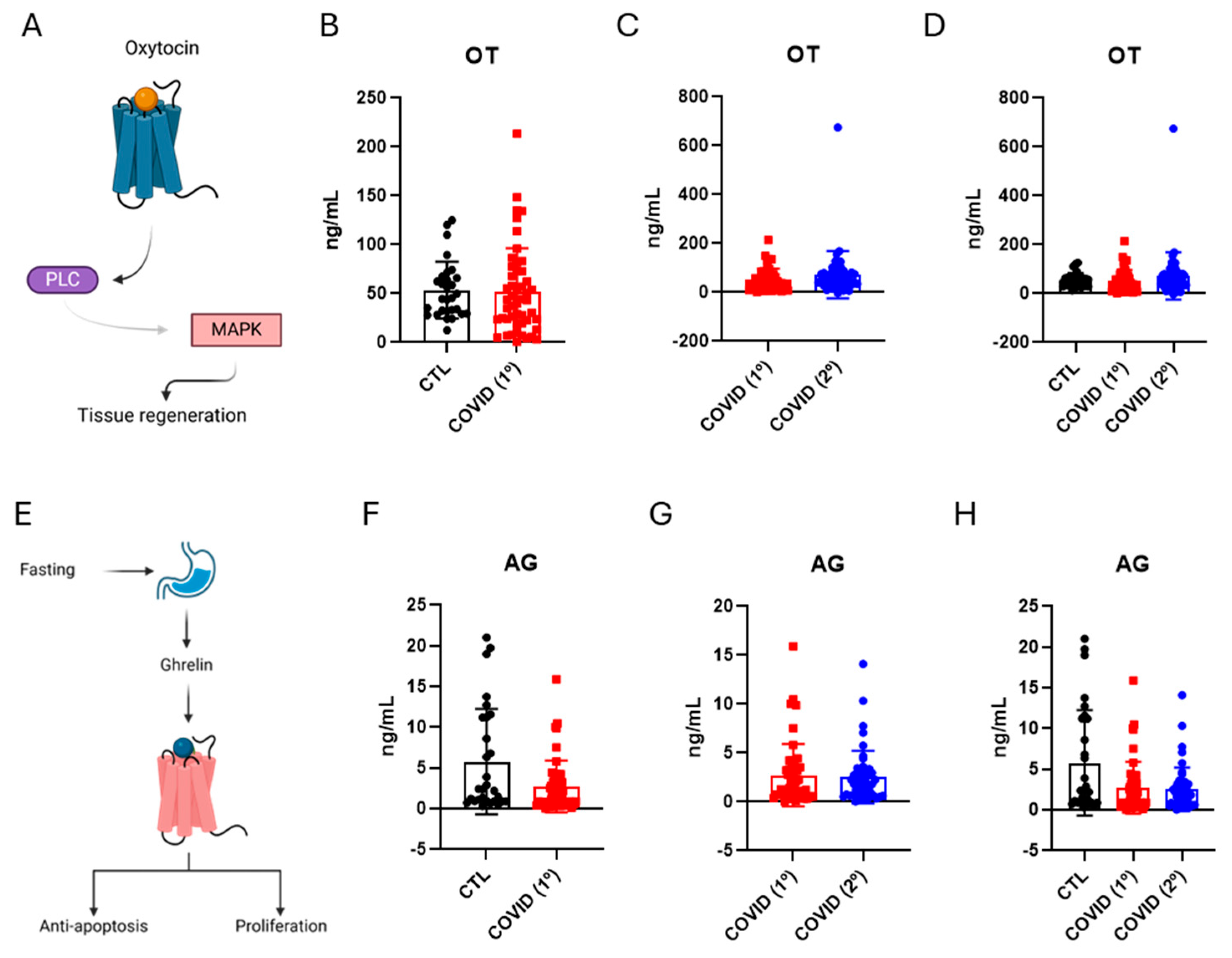
3.4. Oxytocin and Ghrelin Levels in Patients Recovered from Severe COVID-19
3.5. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor, Fibroblast Growth Factor-1, and Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Levels in Patients Recovered from Severe COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | Acylated Ghrelin |
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| CNPq | National Council for Scientific and Technological Research and Development |
| COVID | Coronavirus Disease |
| FGF-1 | Fibroblast Growth Factor-1 |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 |
| NGF | Nerve Growth Factor |
| OCRC | Obesity and Comorbidities Research Center |
| OT | Oxytocin |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta |
| Trka | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A |
| Trkb | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B |
| UNT | Universal Trial Number |
References
- Chen, H.; Yin, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, D.; Wang, Z.; Baimayangji; Chen, L.; et al. Alcohol Consumption and Accelerated Biological Ageing in Middle-Aged and Older People: A Longitudinal Study from Two Cohorts. Addiction 2024, 119, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Kitwiroon, N.; Beevers, S.; Barratt, B.; Brayne, C.; Cerin, E.; Franklin, R.; Houlden, V.; Woods, B.; Abozied, E.Z.; et al. The Longitudinal Associations between Ambient Air Pollution Exposure and Dementia in the UK: Results from the Cognitive Function and Ageing Study II and Wales. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.M.; Shyne, A.; Gunn, D.A.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Watson, R.E.B. Epigenetics and Ultraviolet Radiation: Implications for Skin Ageing and Carcinogenesis. Ski. Skin. Health Dis. 2024, 4, e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Cho, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.C.; Han, S.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.P.; et al. Causal Linkage of T obacco Smoking with Ageing: Mendelian Randomization Analysis towards Telomere Attrition and Sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialasche, F.; Polidori, M.C.; Monastero, R.; Ercolani, S.; Camarda, C.; Cecchetti, R.; Mecocci, P. Biomarkers of Oxidative and Nitrosative Damage in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Woodroofe, M.N. Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in Neurodegeneration and Repair. Immunology 2014, 141, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, L.; Noe, M.; Pahlavan, A.; Werzen, A.; Seung, H.; Yoo, Y.C.J.; Tyson, P.; Narayanan, S.; Turan, S.; Turan, O.M.; et al. Increased Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Pregnancy in a Multicenter Propensity Score-Matched Study. J. Perinat. Med. 2023, 51, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkodaymi, M.S.; Omrani, O.A.; Fawzy, N.A.; Shaar, B.A.; Almamlouk, R.; Riaz, M.; Obeidat, M.; Obeidat, Y.; Gerberi, D.; Taha, R.M.; et al. Prevalence of Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome Symptoms at Different Follow-up Periods: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Herman, E.; Ahmed, A.; Anderson, J.; Selph, S.; Dana, T.; Williams, L.; Ivlev, I. Long COVID Definitions and Models of Care: A Scoping Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.-L. Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Its Roles in Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, A.; Barbi, V.; Zamperla, M.G.; Atlante, S.; Forleo, L.; Nesta, M.; Massetti, M.; Pontecorvi, A.; Nanni, S.; Farsetti, A.; et al. Evidence for Biological Age Acceleration and Telomere Shortening in COVID-19 Survivors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, F.; Asghary, A.; Zolbanin, N.M.; Faraji, F.; Jafari, R. Immunosenescence and Inflammaging in COVID-19. Viral Immunol. 2023, 36, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Ran, D.; Davalos, V.; Planas-Serra, L.; Pujol, A.; Esteller, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, H. Accelerated Biological Aging in COVID-19 Patients. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatinelli, J.; Matacchione, G.; Giuliani, A.; Ramini, D.; Rippo, M.R.; Procopio, A.D.; Bonafè, M.; Olivieri, F. Circulating Biomarkers of Inflammaging as Potential Predictors of COVID-19 Severe Outcomes. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2022, 204, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridoss, M.; Ayyasamy, L.; Bagepally, B.S. Is COVID-19 Severity Associated with Telomere Length? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Juárez, G.E.; Genis-Mendoza, A.D.; Martínez-López, J.N.I.; Fresan, A.; Tovilla-Zaráte, C.A.; Nolasco-Rosales, G.A.; la Cruz, G.I.J.-D.; Ramos, D.R.; Villar-Soto, M.; Mejía-Ortiz, P.; et al. Exploring the Relationship between Telomere Length and Cognitive Changes in Post-COVID-19 Subjects. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.R.; de Carvalho, R.M.; Cirino, H.d.S.; Martins, R.; Furtado, C.L.M.; Santana, B.A.A.; Calado, R.T.; Ferriani, R.A.; dos Reis, R.M. Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Sperm Telomere Length. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2025, 42, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrantonaki, E.; Schönknecht, P.; Hossini, A.M.; Kaiser, E.; Katsouli, M.-M.; Adjaye, J.; Schröder, J.; Zouboulis, C.C. Skin and Brain Age Together: The Role of Hormones in the Ageing Process. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.; Gauvreau, K.; Mattie, H. Principles of Biostatistics, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-0-429-34051-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yonker, L.M.; Swank, Z.; Bartsch, Y.C.; Burns, M.D.; Kane, A.; Boribong, B.P.; Davis, J.P.; Loiselle, M.; Novak, T.; Senussi, Y.; et al. Circulating Spike Protein Detected in Post–COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Myocarditis. Circulation 2023, 147, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junnila, R.K.; List, E.O.; Berryman, D.E.; Murrey, J.W.; Kopchick, J.J. The GH/IGF-1 Axis in Ageing and Longevity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambataro, F.; Murty, V.P.; Lemaitre, H.S.; Reed, J.D.; Das, S.; Goldberg, T.E.; Callicott, J.H.; Weinberger, D.R.; Mattay, V.S. BDNF Modulates Normal Human Hippocampal Ageing [Corrected]. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, A.K. Spatially Restricted Actions of BDNF. Neuron 2002, 36, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffmeijer, R.; van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J. Ageing and Oxytocin: A Call for Extending Human Oxytocin Research to Ageing Populations—A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2013, 59, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, A.S.; Nevala, W.K.; Dronca, R.S.; Leontovich, A.A.; Shuster, L.; Markovic, S.N. Normal Ageing Is Associated with an Increase in Th2 Cells, MCP-1 (CCL1) and RANTES (CCL5), with Differences in sCD40L and PDGF-AA between Sexes. ClinExp Immunol. 2012, 170, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegertjes, R.; Thielen, N.; van Caam, A.; van Laar, M.; van Beuningen, H.; Koenders, M.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P.; van de Loo, F.; Davidson, E.B. Increased IL-6 Receptor Expression and Signaling in Ageing Cartilage Can Be Explained by Loss of TGF-β-Mediated IL-6 Receptor Suppression. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-T.; Kazui, H.; Ikeda, M.; Huang, C.-W.; Huang, S.-H.; Hsu, S.-W.; Chang, W.-N.; Chang, C.-C. Genetic Interaction of APOE and FGF1 Is Associated with Memory Impairment and Hippocampal Atrophy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budni, J.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; Mina, F.; Garcez, M.L.; Zugno, A.I. The Involvement of BDNF, NGF and GDNF in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Alonso-Alvarez, C. Oxidative Stress as a Life-history Constraint: The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Shaping Phenotypes from Conception to Death. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkur, A.K.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; Van De Veen, W.; Brüggen, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 and Mechanisms of Immunopathological Changes in COVID-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Narayanan, A.; Vesterbacka, J.; Blennow, O.; Chen, P.; Gao, Y.; Gabarrini, G.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Buggert, M.; Manoharan, L.; et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiome on Immunological Responses to COVID-19 Vaccination in Healthy Controls and People Living with HIV. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, J.; Peyssonnaux, C.; Singh, K.K.; Edeas, M. Mitochondria and Microbiota Dysfunction in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Mitochondrion 2020, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Hsin, H.; Libina, N.; Kenyon, C. Regulation of the Caenorhabditis Elegans Longevity Protein DAF-16 by Insulin/IGF-1 and Germline Signaling. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.D.; Tissenbaum, H.A.; Liu, Y.; Ruvkun, G. Daf-2, an Insulin Receptor-like Gene That Regulates Longevity and Diapause in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Science 1997, 277, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, N.D.; Brywe, K.G.; Isgaard, J. Aspects of Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Related to Neuroprotection, Regeneration, and Functional Plasticity in the Adult Brain. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, H.; Eizirik, D.L. Resistance to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Matter of Hormesis? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 8, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z. Do Deficiencies in Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Shorten or Prolong Longevity? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taieb, A.; Nassim, B.H.S.; Asma, G.; Jabeur, M.; Ghada, S.; Asma, B.A. The Growing Understanding of the Pituitary Implication in the Pathogenesis of Long COVID-19 Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Adv. Respir. Med. 2024, 92, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.T.; Zhou, F.; Xie, W.Q.; Wang, S.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.T.; Gao, L.; Wu, Z.B. A Potential Impact of SARS-CoV-2 on Pituitary Glands and Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors. Endocrine 2021, 72, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capatina, C.; Poiana, C.; Fleseriu, M. Pituitary and SARS CoV-2: An Unremitting Conundrum. Best. Pr. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosi, G.; Cremaschi, A.; Giavoli, C.; Ferrante, E.; Mantovani, G. Hypopituitarism and COVID-19. Pituitary 2024, 27, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moises, T.; Dreier, A.; Flohr, S.; Esser, M.; Brauers, E.; Reiss, K.; Merken, D.; Weis, J.; Krüttgen, A. Tracking TrkA’s Trafficking: NGF Receptor Trafficking Controls NGF Receptor Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 35, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.S.; Lane, M.A.; Ingram, D.K.; Mattison, J.A.; Elahi, D.; Tobin, J.D.; Muller, D.; Metter, E.J. Biomarkers of Caloric Restriction May Predict Longevity in Humans. Science 2002, 297, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, B.; Beyazyüz, E.; Beyazyüz, M.; Çelikkol, A.; Albayrak, Y. Long-Lasting Cognitive Effects of COVID-19: Is There a Role of BDNF? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 273, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, C.; Ferraguti, G.; Tarani, L.; Tarani, F.; Messina, M.P.; Fiore, M. Nerve Growth Factor and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in COVID-19. Biology 2024, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, S.; Chini, B.; Grinevich, V. Lifespan Oxytocin Signaling: Maturation, Flexibility, and Stability in Newborn, Adolescent, and Aged Brain. Dev. Neurobiol. 2017, 77, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, C.; Cousin, W.; Upadhyayula, P.; Chen, R.Y.; Chooljian, M.S.; Li, J.; Kung, S.; Jiang, K.P.; Conboy, I.M. Oxytocin Is an Age-Specific Circulating Hormone That Is Necessary for Muscle Maintenance and Regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.X.; Brubaker, P.L. Ghrelin, the Proglucagon-Derived Peptides and Peptide YY in Nutrient Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Mansour, A.; Reizine, F.; Mismetti, P.; Gouin-Thibault, I.; Cognasse, F. Platelet-Derived sCD40L: Specific Inflammatory Marker for Early-Stage Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, J.; Shang, F.; Zang, K.; Ji, T. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor B Attenuates Lethal Sepsis through Inhibition of Inflammatory Responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrey, A.C.; Qeadan, F.; A Middleton, E.; Pinchuk, I.V.; A Campbell, R.; Beswick, E.J. Cytokine Release Syndrome in COVID- 19: Innate Immune, Vascular, and Platelet Pathogenic Factors Differ in Severity of Disease and Sex. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.; Lizneva, D.; Yuen, T. The Role of PDGF-BB in the Bone-Vascular Relationship during Aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e153644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wirt, S.E.; Bottino, R.; Schorle, H.; Sage, J.; Kim, S.K. PDGF Signalling Controls Age- Dependent Proliferation in Pancreatic β-Cells. Nature 2011, 478, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Yang, M. Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors in the Treatment of Diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.L.; Eltoukhy, M.M.; Shalaby, R.E.; Okasha, K.M.; El-Shanshoury, M.R.; Attia, M.A.; Hantera, M.S.; Hilal, A.; Eid, M.A. COVID-19 Severity Shifts the Cytokine Milieu Toward a Proinflammatory State in Egyptian Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023, 43, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrou, A.; Aslanidis, T.; Makedou, K.; Mitsianis, A.; Thisiadou, A.; Karalazou, P.; Chatzopoulos, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kalis, A.; Giagkoulis, D.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 in COVID-19: An Observational Study. Cureus 2023, 5, e42561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. TGF-β Signaling in Health, Disease and Therapeutics. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistnes, M. Hitting the Target! Challenges and Opportunities for TGF-β Inhibition for the Treatment of Cardiac Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ask, K.; Bonniaud, P.; Maass, K.; Eickelberg, O.; Margetts, P.J.; Warburton, D.; Groffen, J.; Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M. Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Mediated by TGF-β Isoform 1 but Not TGF-Β3. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatler, A.L.; Jenkins, G. TGF-β Activation and Lung Fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synenki, L.; Chandel, N.S.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Donnelly, H.K.; Topin, J.; Eisenbart, J.; Jovanovic, B.; Jain, M. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid from Patients with Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Induces Myofibroblast Differentiation. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, E.; Casitas, R.; Díaz-García, E.; García-Tovar, S.; Galera, R.; Torres-Vargas, M.; Fernández-Velilla, M.; López-Fernández, C.; Añón, J.M.; Quintana-Díaz, M.; et al. TGF-Β1 Overexpression in Severe COVID-19 Survivors and Its Implications for Early- Phase Fibrotic Abnormalities and Long-Term Functional Impairment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1401015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frischbutter, S.; Durek, P.; Witkowski, M.; Angermair, S.; Treskatsch, S.; Maurer, M.; Radbruch, A.; Mashreghi, M. Serum TGF- β as a Predictive Biomarker for Severe Disease and Fatality of COVID-19. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2350433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivancevic-Simonovic, S.; Minic, R.; Cupurdija, V.; Stanojevic-Pirkovic, M.; Milosevic-Djordjevic, O.; Jakovljevic, V.; Mihaljevic, O. Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGF-Β1) in COVID-19 Patients: Relation to Platelets and Association with the Disease Outcome. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G. The Role of Proteases in Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | p-Value | ||||
| Control | COVID-19/1º | ||||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Sex | 0.5448 * | ||||
| Male | 14 | 50 | 28 | 57.14 | |
| Female | 14 | 50 | 21 | 42.86 | |
| Comorbidities | 0.2027 * | ||||
| Yes | 8 | 28.57 | 8 | 16.33 | |
| No | 20 | 71.43 | 41 | 83.67 | |
| Obesity | 0.9656 * | ||||
| No | 13 | 46.43 | 23 | 46.94 | |
| Yes | 15 | 53.57 | 26 | 53.06 | |
| Hypertension | 0.0634 * | ||||
| No | 11 | 39.29 | 30 | 61.22 | |
| Yes | 17 | 60.71 | 19 | 38.78 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.0003 * | ||||
| No | 16 | 57.14 | 45 | 91.84 | |
| Yes | 12 | 42.86 | 4 | 8.16 | |
| Diabetes | 1.0000 * | ||||
| No | 20 | 71.43 | 35 | 71.43 | |
| Yes | 8 | 28.57 | 14 | 28.57 | |
| Asthma | 1.0000 ** | ||||
| No | 26 | 92.86 | 45 | 91.84 | |
| Yes | 2 | 7.14 | 4 | 8.16 | |
| Respiratory disease | 0.5311 ** | ||||
| No | 28 | 100 | 47 | 95.92 | |
| Yes | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4.08 | |
| Hypothiroidism | 0.1937 ** | ||||
| No | 22 | 78.57 | 44 | 89.8 | |
| Yes | 6 | 21.43 | 5 | 10.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuchi-Cabral, A.; Palma, A.C.; Nogueira, G.A.; Oliveira, H.C.; Fusco, S.F.B.; Moretti, M.L.; Velloso, L.A.; Araujo, E.P. Persistent Changes in Hormones and Growth Factors Involved in Ageing in Patients That Recovered from Severe COVID-19. Diseases 2025, 13, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070209
Cuchi-Cabral A, Palma AC, Nogueira GA, Oliveira HC, Fusco SFB, Moretti ML, Velloso LA, Araujo EP. Persistent Changes in Hormones and Growth Factors Involved in Ageing in Patients That Recovered from Severe COVID-19. Diseases. 2025; 13(7):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070209
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuchi-Cabral, Alice, André C. Palma, Guilherme A. Nogueira, Henrique Ceretta Oliveira, Suzimar F. Benato Fusco, Maria L. Moretti, Licio A. Velloso, and Eliana P. Araujo. 2025. "Persistent Changes in Hormones and Growth Factors Involved in Ageing in Patients That Recovered from Severe COVID-19" Diseases 13, no. 7: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070209
APA StyleCuchi-Cabral, A., Palma, A. C., Nogueira, G. A., Oliveira, H. C., Fusco, S. F. B., Moretti, M. L., Velloso, L. A., & Araujo, E. P. (2025). Persistent Changes in Hormones and Growth Factors Involved in Ageing in Patients That Recovered from Severe COVID-19. Diseases, 13(7), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070209








