Early CytoSorb Hemoadsorption in a Neutropenic Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Septic Shock and ARDS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Patient Background
2.2. Admission and Chemotherapy
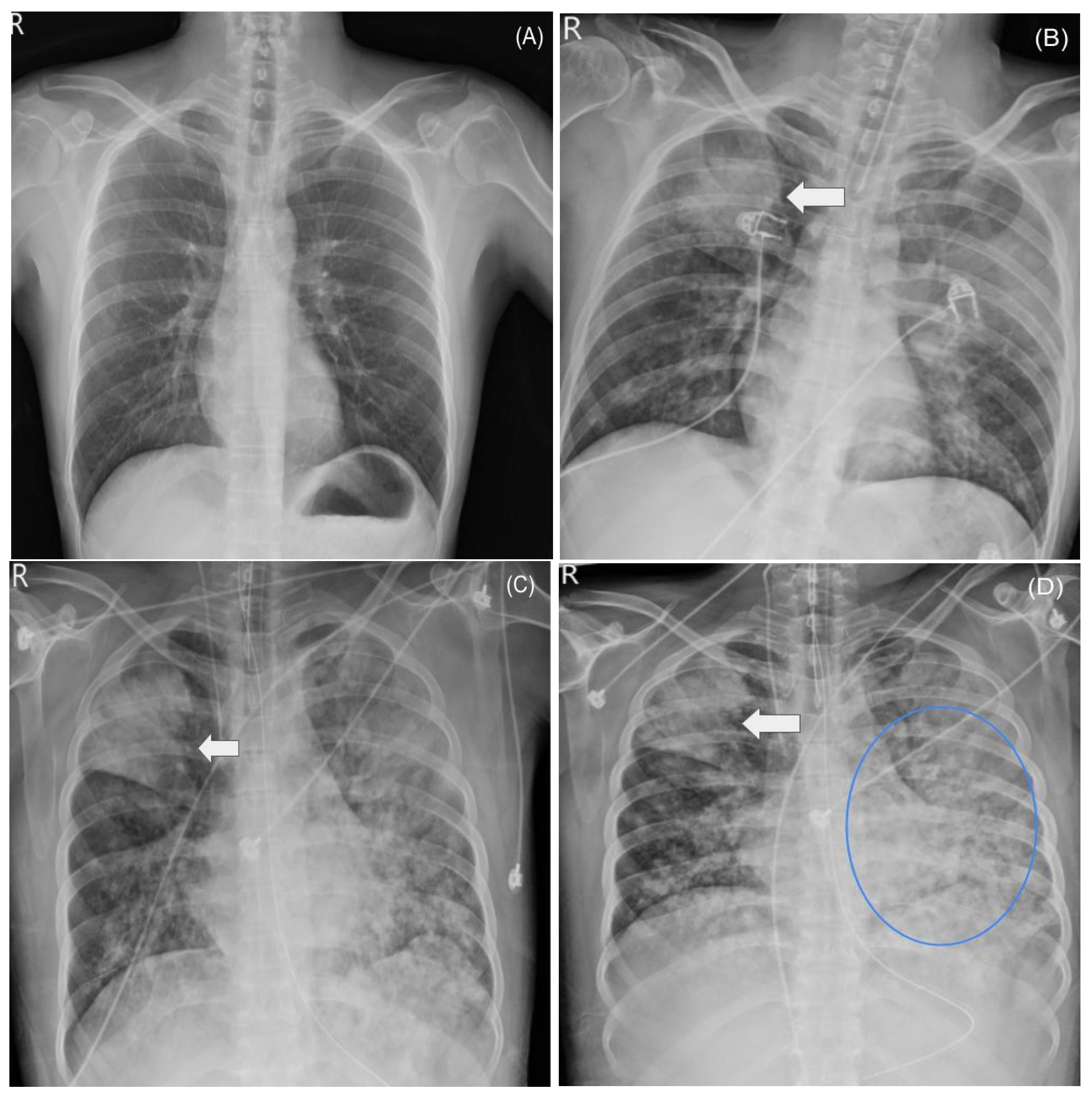
2.3. ICU Course and ARDS
2.4. Infection Control and Antimicrobial Management
| Drug (Generic Name) | Start Date | Stop Date | Dosage | Route | Indication | Microbiology Result (MIC) | Rationale/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 3 April 2025 | 4 April 2025 | 4.5 g q8h | IV | Empiric | CRPA R (≥16)/Staph. spp. + | Initial FN, stopped after CRPA ID |
| Fluconazole | 3 April 2025 | 5 April 2025 | 200 mg qd | PO | Empiric | — | Added for possible fungal infection |
| Brosym (Cefoperazone/Sulbactam) | 4 April 2025 | 5 April 2025 | 2 g q12h | IV | Escalation | — | Deterioration under initial therapy |
| Meropenem | 5 April 2025 | 6 April 2025 | 500 mg q8h | IV | Escalation | CRPA R (≥8) | Severe sepsis/respiratory failure |
| Colistin | 5 April 2025 | 10 April 2025 | 9 MIU LD, 4.5 MIU q12h | IV | Targeted | CRPA S (MIC 0.5) | Combined with CAZ/AVI salvage |
| Ceftazidime–Avibactam | 5 April 2025 | 8 April 2025 | 2.5 g q8h | IV | Targeted | CRPA R (—) | Institutional salvage protocol/XDR |
| Amikacin | 6 April 2025 | 10 April 2025 | 250 mg qd | IV | Escalation | CRPA R (≥64) | Added for double coverage |
| Teicoplanin | 6 April 2025 | 10 April 2025 | 200 mg q12h → qd | IV | Gram + | MR-CNS S | For catheter/skin coinfection |
| Isavuconazole | 6 April 2025 | 10 April 2025 | 200 mg q8h → qd | IV | Empiric | — | Added for suspected fungal infection |
| ICU Day | Date | Mechanical Ventilation | Prone Position | CWH (CRRT) | CytoSorb™ | Vasopressor | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 April 2025 | Start | Start | Intubation, ICU admission | |||
| 2 | 6 April 2025 | Yes | Start | Start | Start | Yes | Severe shock, ARDS diagnosis |
| 3 | 7 April 2025 | Yes | Yes | Yes | End | Yes | BAL performed. persistent ARDS |
| 4 | 8 April 2025 | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| 5 | 9 April 2025 | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| 6 | 10 April 2025 | Yes (to death) | End (death) | Yes | Death (refractory shock/ARDS) |
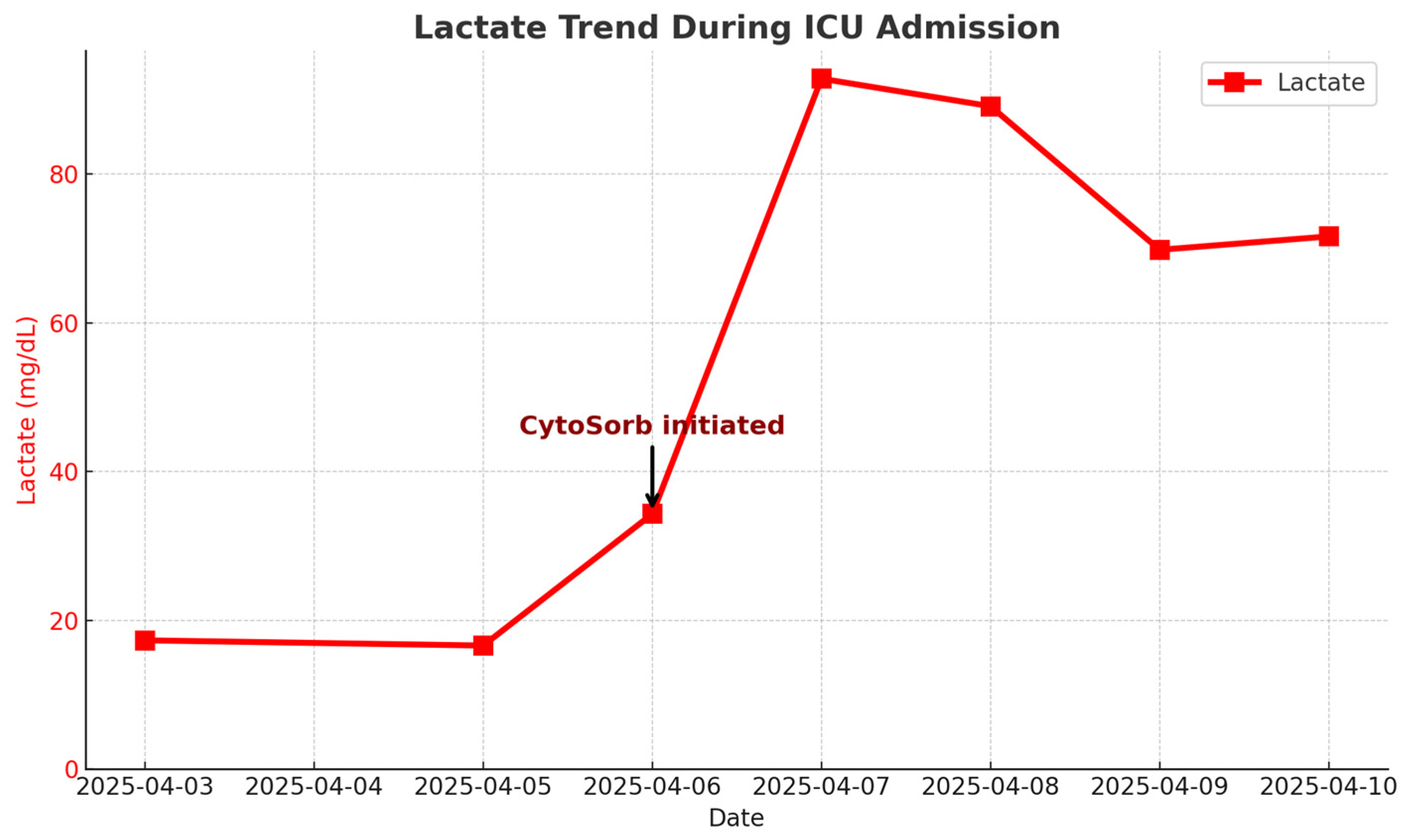
2.5. Supportive Care and Clinical Course
2.6. Outcome
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Course
Microbiological Outcomes
3.2. Hematologic and Organ Support
3.3. Outcome
4. Discussion
- (1)
- persistent culture positivity despite early aggressive therapy underscores the limited efficacy of current antibiotics;
- (2)
- (3)
4.1. CRPA Sepsis and Current Treatment Paradigm
4.2. Rationale and Evidence for CytoSorb™ Hemoadsorption
4.3. Study Limitations and Gaps
4.4. Why Certain Measures Were Not Done
4.5. Clinical and Research Implications
4.6. Attribution and Confounding
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Saldaña-Gastulo, J.J.C.; Llamas-Barbarán, M.R.; Coronel-Chucos, L.G.; Hurtado-Roca, Y. Cytokine hemoadsorption with CytoSorb® in patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Sci. 2023, 35, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, M.; Schorer, R.; Putzu, A. Mortality and adverse events of hemoadsorption with CytoSorb® in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2022, 66, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Huang, X.; Tan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Hemoadsorption in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients requiring venovenous ECMO: A systematic review. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schädler, D.; Pausch, C.; Heise, D.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Brederlau, J.; Weiler, N.; Spies, C.; Putensen, C.; Gründling, M.; Petros, S. The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawchar, F.; László, I.; Öveges, N.; Trásy, D.; Tánczos, K.; Mikor, A.; Szakmány, T.; Lovas, A.; Osztrosits, N.; Kocsi, S. Extracorporeal cytokine adsorption in septic shock: A proof of concept randomized, controlled pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2019, 49, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, P.; Schwier, E.; Eickmeyer, C.; Dieterich, M.; Drolshagen, N.; Henzler, D.; Busch, H.J.; Vieten, C.; Jansen, M.; Wiesner, O. High-dose CytoSorb hemoadsorption is associated with improved survival in patients with septic shock: A retrospective cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2021, 64, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelmann, K.; Jarczak, D.; Scheller, M.; Drüner, M. Hemoadsorption by CytoSorb in septic patients: A case series. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugg, C.; Klose, R.; Bachler, M.; Koegerl, M.; Schmid, A.; Staudinger, T.; Boesing, N.; Lahmer, T.; Huber, W.; Schmid, B. Advanced extracorporeal cytokine removal may improve survival of patients with septic shock: A propensity score analysis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, M.; Schalk, E.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.; Beutel, G.; Buchheidt, D.; Christopeit, M.; Hentrich, M.; Maschmeyer, G.; Penack, O.; Pohlmann, C. Management of sepsis in neutropenic cancer patients: 2018 guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) and Intensive Care Working Party (iCHOP) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Maertens, J.; Lemiale, V.; Mourvillier, B.; Darmon, M.; Van de Louw, A.; Barrett, N.A.; Chabannon, C.; Malfuson, J.V.; Mokart, D. How I manage acute respiratory failure in patients with hematological malignancies. Blood 2024, 143, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.K. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome during neutropenia recovery in patients with hematologic malignancies. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippel, C.; Kim, Y.; Wallau, A.; Blaschke, S.; Siegert, S.; Abou-El-Ardat, K.; Lenz, G.; Hiddemann, W.; Subklewe, M.; Fiegl, M. AML versus ICU: Outcome of septic AML patients in an intensive care setting. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secreto, C.; Chean, D.; van de Louw, A.; Demoule, A.; Azoulay, E.; Lemiale, V.; Moreau, A.S.; Bergeron, A.; Mokart, D.; Schnell, D. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with acute myeloid leukemia admitted to ICU with acute respiratory failure: A post-hoc analysis of a prospective multicenter study. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Galfo, V.; Tiseo, G.; Leonildi, A.; Menichetti, F.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Bussini, L.; Perrella, A.; Luzzati, R.; Luciani, D.; et al. Not all carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains are alike: Tailoring antibiotic therapy based on resistance mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 37, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Cortés, P.; Campos-Fernández, S.; Cuenca-Fito, E.; Perez-Panero, E.; Cores, M.; Lage, E.; Hernández, M.; Giráldez, A.; Del Castillo, S.; Rodríguez-López, M.; et al. Difficult-to-Treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in critically ill patients: A comprehensive review and treatment proposal. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J.; Vinnard, C.; Wong, J.; Servoss, J.C.; Simner, P.J.; et al. IDSA 2022 Guidance on the treatment of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with difficult-to-treat resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.; Del Sorbo, L.; Goligher, E.C.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; Walkey, A.J.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Amato, M.B.P.; Bartlett, R.H.; Bellani, G.; et al. An Official ATS/ESICM/SCCM Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical ventilation in adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazian, L.; Aubron, C.; Brochard, L.; Chiche, J.D.; Combes, A.; Dreyfuss, D.; Forel, J.M.; Guérin, C.; Jaber, S.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; et al. Formal guidelines: Management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.; Hajage, D.; Capellier, G.; Demoule, A.; Lavoué, S.; Guérin, C.; Da Silva, D.; Zafrani, L.; Tirot, P.; Veber, B.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (EOLIA Trial). N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Alkherb, Z.; Ghonem, L.; Albekairy, A.; Alshehri, S.; Alghamdi, S.; Alshahrani, M.; Alqahtani, S.; Alsulaiman, T.; Alarfaj, A.; et al. Ceftazidime-avibactam versus colistin for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A multicenter cohort study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczak, D.; Kluge, S.; Nierhaus, A. Sepsis—Pathophysiology and therapeutic concepts. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 628302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supady, A.; Brodie, D.; Wengenmayer, T. Extracorporeal haemoadsorption: Does the evidence support its routine use in critical care? Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, C.; Reignier, J.; Richard, J.C.; Beuret, P.; Gacouin, A.; Boulain, T.; Mercier, E.; Badet, M.; Mercat, A.; Baudin, O.; et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A.; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute ARDS Clinical Trials Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freifeld, A.G.; Bow, E.J.; Sepkowitz, K.A.; Boeckh, M.J.; Ito, J.I.; Mullen, C.A.; Raad, I.I.; Rolston, K.V.; Young, J.A.; Wingard, J.R.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the IDSA. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e56–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houschyar, K.S.; Pyles, M.N.; Rein, S.; Nietzschmann, I.; Siemers, F.; Stillaert, F.; Harhaus, L.; Chelliah, M.P.; de Buys Roessingh, A.; Sahin, H.; et al. Continuous hemoadsorption with a cytokine adsorber (CytoSorb®) in a septic shock patient: A case report and review of the literature. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 40, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Antonelli, M.; Foster, D.; Klein, D.J.; Marshall, J.C.; Mehta, N.M.; Palevsky, P.M.; Payen, D.; Phua, J.; et al. Effect of targeted polymyxin B hemoperfusion on 28-day mortality in endotoxemic septic shock (EUPHRATES Trial). J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 320, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zusman, O.; Altunin, S.; Koppel, F.; Dishon Benattar, Y.; Gedik, H.; Paul, M.; Leibovici, L.; Friberg, L.E.; Eliakim-Raz, N. Polymyxin monotherapy or in combination against carbapenem-resistant bacteria: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, B.; Finfer, S.; Cohen, J.; Rajbhandari, D.; Arabi, Y.; Bellomo, R.; Billot, L.; Correa, M.; Glass, P.; Harward, M.; et al. Adjunctive glucocorticoid therapy in patients with septic shock (ADRENAL Trial). N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annane, D.; Renault, A.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Megarbane, B.; Quenot, J.P.; Siami, S.; Cariou, A.; Forceville, X.; Schwebel, C.; Martin, C.; et al. Hydrocortisone plus fludrocortisone for adults with septic shock (APROCCHSS Trial). N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Singer, M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Machado, F.R.; Marshall, J.C.; Finfer, S.; Pelosi, P.; Brazzi, L.; Aditianingsih, D.; et al. Prevalence and outcomes of infection among patients in intensive care units in 2017 (EPIC III). JAMA 2020, 323, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Niederman, M.S.; Chastre, J.; Ewig, S.; Fernandez-Vandellos, P.; Hanberger, H.; Kollef, M.; Li Bassi, G.; Luna, C.M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlot, G.; Carocci, P.; Votrico, V.; Iacoviello, B.; Taverna, N.; Gerini, U.; di Maso, V.; Tomasini, A. Real-World Outcomes of Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb® in Patients with Septic Shock: Insights from a Single-Center Study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2025, 40, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.S.; Narwal, M. CytoSorb® in Combination with CRRT in a Patient Suffering from Septic Shock, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): A Case Report. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2023, 13, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Date | Sample | Pathogen/Method | Result | Sensitivity/MIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 April | Blood | CRPA, Staph. spp. | Positive | Colistin S (MIC 0.5), others R |
| 4 April | CVC tip | MR-CNS | Positive | |
| 5 April | BAL | CRPA | Positive | Same as above |
| 6 April–9 April | Sputum | CRPA | Positive | |
| 7 April | BAL | Culture, FilmArray: CRPA | Positive | |
| 6 April | Fungus, CVC | Negative | Negative | |
| 6 April | Virus, Blood | Not Detected | Negative | |
| 7 April | BAL | Gram-stain, AFB, TB, Fungus | Negative | |
| 8 April | Sputum | CRPA | Positive | |
| 8 April | Sputum | TB, Fungus | Negative | |
| 8 April | Blood | CRPA | Positive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.-H.; Hu, T.-Y.; Kuo, L.-K. Early CytoSorb Hemoadsorption in a Neutropenic Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Septic Shock and ARDS. Diseases 2025, 13, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120382
Chang W-H, Hu T-Y, Kuo L-K. Early CytoSorb Hemoadsorption in a Neutropenic Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Septic Shock and ARDS. Diseases. 2025; 13(12):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120382
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Wei-Hung, Ting-Yu Hu, and Li-Kuo Kuo. 2025. "Early CytoSorb Hemoadsorption in a Neutropenic Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Septic Shock and ARDS" Diseases 13, no. 12: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120382
APA StyleChang, W.-H., Hu, T.-Y., & Kuo, L.-K. (2025). Early CytoSorb Hemoadsorption in a Neutropenic Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Septic Shock and ARDS. Diseases, 13(12), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120382







