Effectiveness of Leadership Decision-Making in Complex Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Leadership
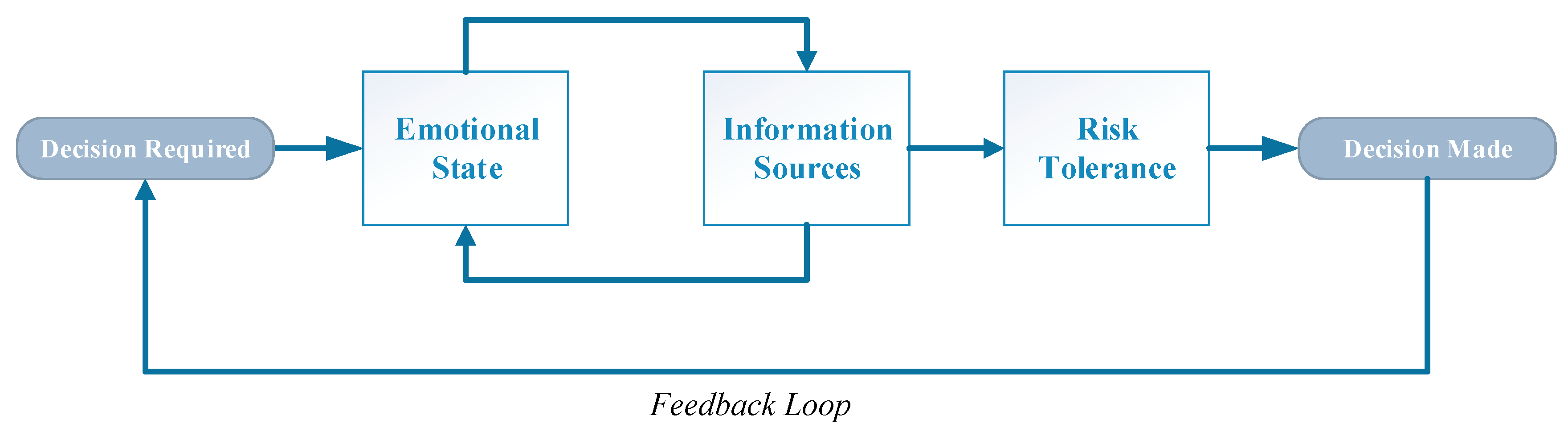
2.2. Decision-Making
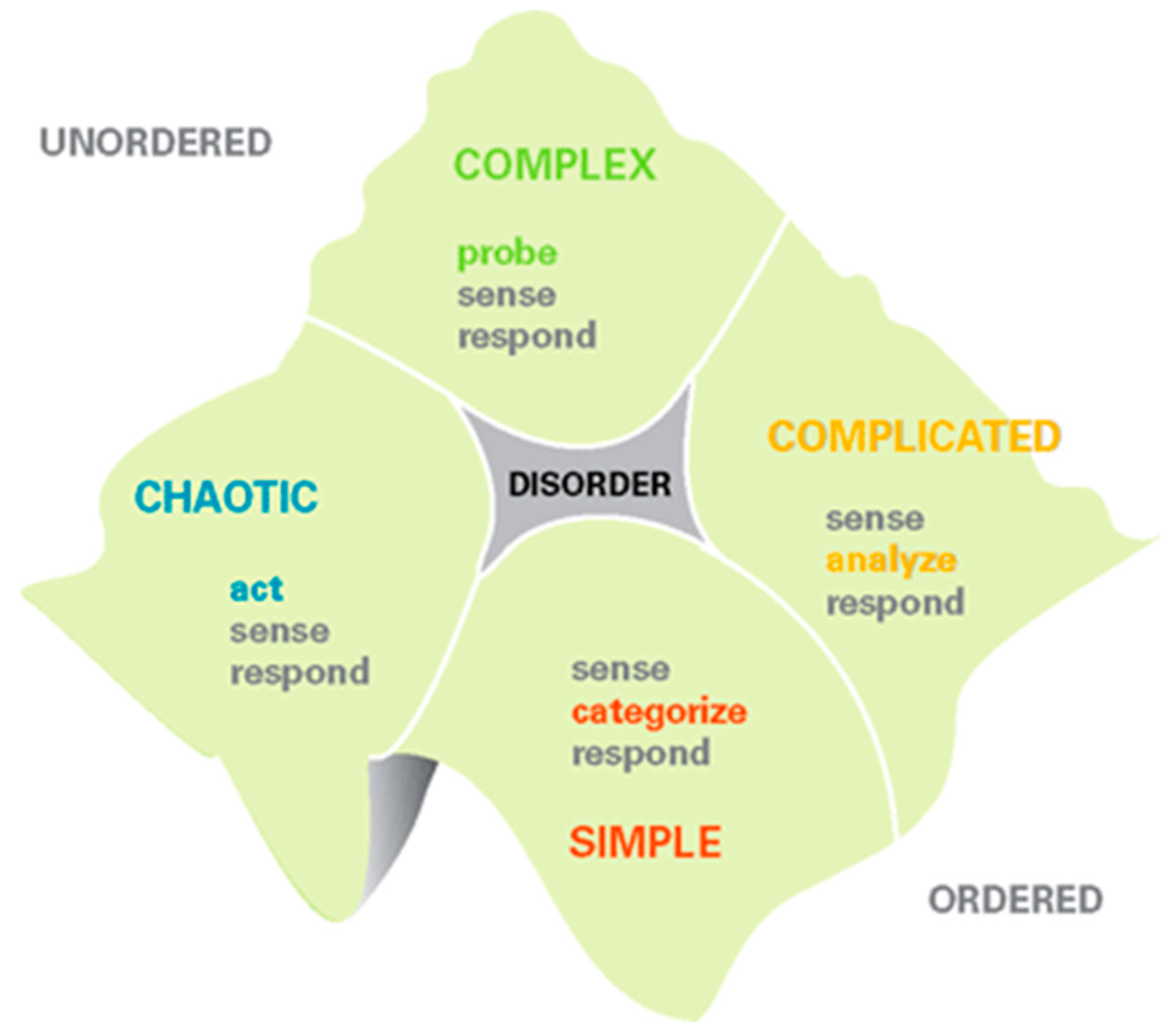
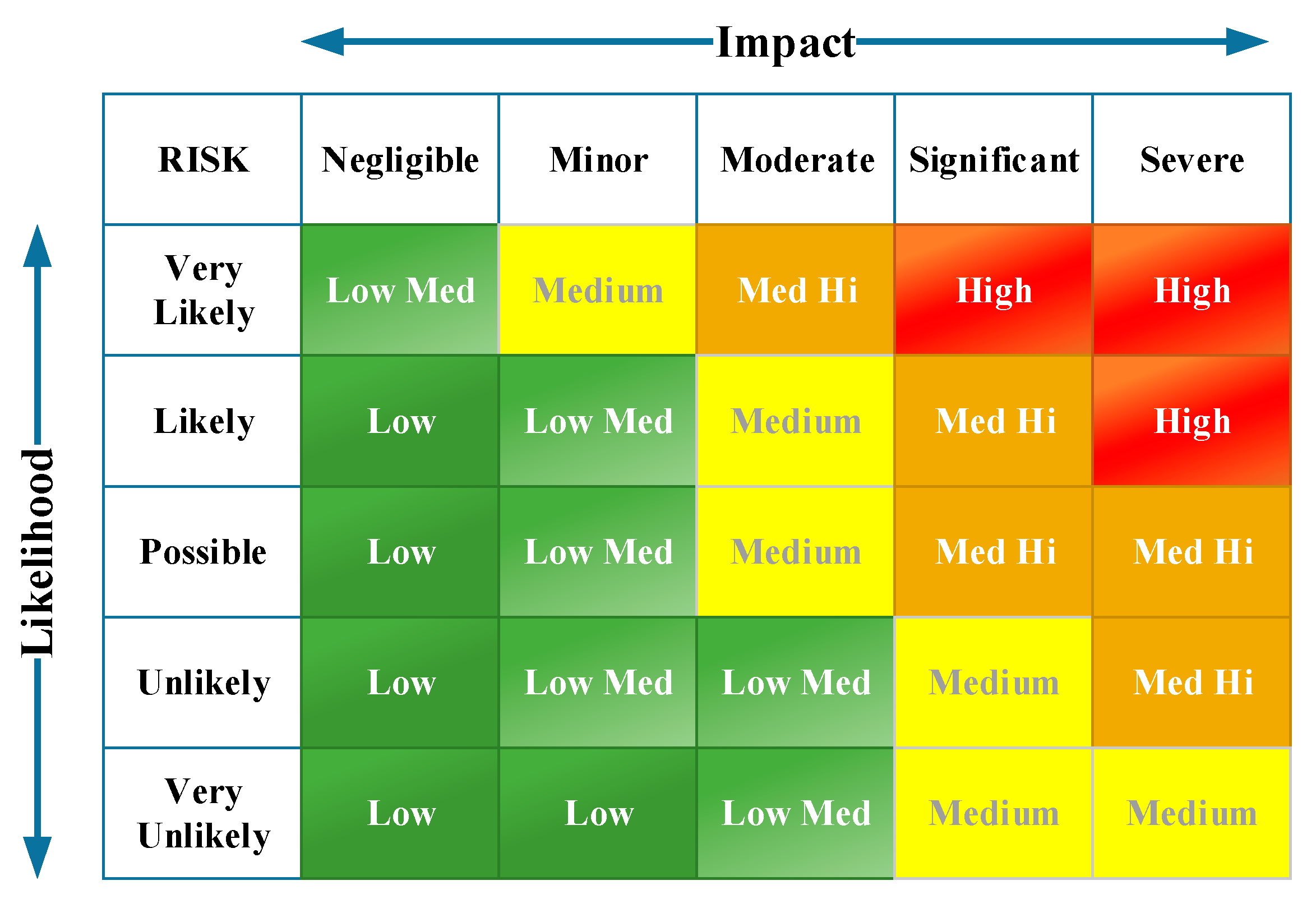
2.3. Typology of Systems in Terms of Complexity and Leadership Implications
2.4. Leadership Decision-Making Effectiveness in Complexity and Some Barriers
3. Research Method
- Define the research aims;
- Identify the population and sample;
- Decide how to collect replies;
- Design the questionnaire;
- Run a pilot survey;
- Carry out the main survey;
- Analyze the data;
- Critical evaluation.
4. Research Findings and Discussion
4.1. Research Findings
- Participants reported that the human aspects of decision-making are the most challenging for them;
- Managers tend to seek assistance from those around them, particularly in getting advice from their friends and family members;
- Feeling tired or tense are emotions which respondents say have the most impact on their decision-making efficiency;
- There were some significant differences between genders in self-rated effectiveness in the technical, financial and human aspects of complex situations.
4.2. Research Discussion
5. Research Implications
6. Research Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Research Questionnaire
- (1)
- What is your gender?
- Male
- Female
- (2)
- What is your age?
- Under 30 years old
- 30–39 years old
- 40–49 years old
- Over 50 years old
- (3)
- How many years have you been working in the industry as a senior manager where you are responsible for the work of other people?
- Less than 5 years
- 5–10 years
- 10–20 years
- More than 20 years
- (4)
- How would you describe your personality? Please choose the option which is most like you.
- friendly
- logical
- optimistic
- decisive
- (5)
- In what aspect of your work is it difficult for you to make important decisions?
- Technical aspect
- Financial aspect
- Human aspect
- Other
- (6)
- When you suffer difficulties in making decisions, what source do you use most to help you with problem-solving?
- Friends and colleagues
- Family and relatives
- Internet and social networks
- Experts
- (7)
- Which of the below emotional states do you think would affect your leadership decisions most?
- Happy
- Sad
- Tense
- Tired
- (8)
- Do you often make decisions based on your subjective opinion?
- Always (>80%)
- Often (50–80%)
- Sometimes (<50%)
- Never (0%)
- (9)
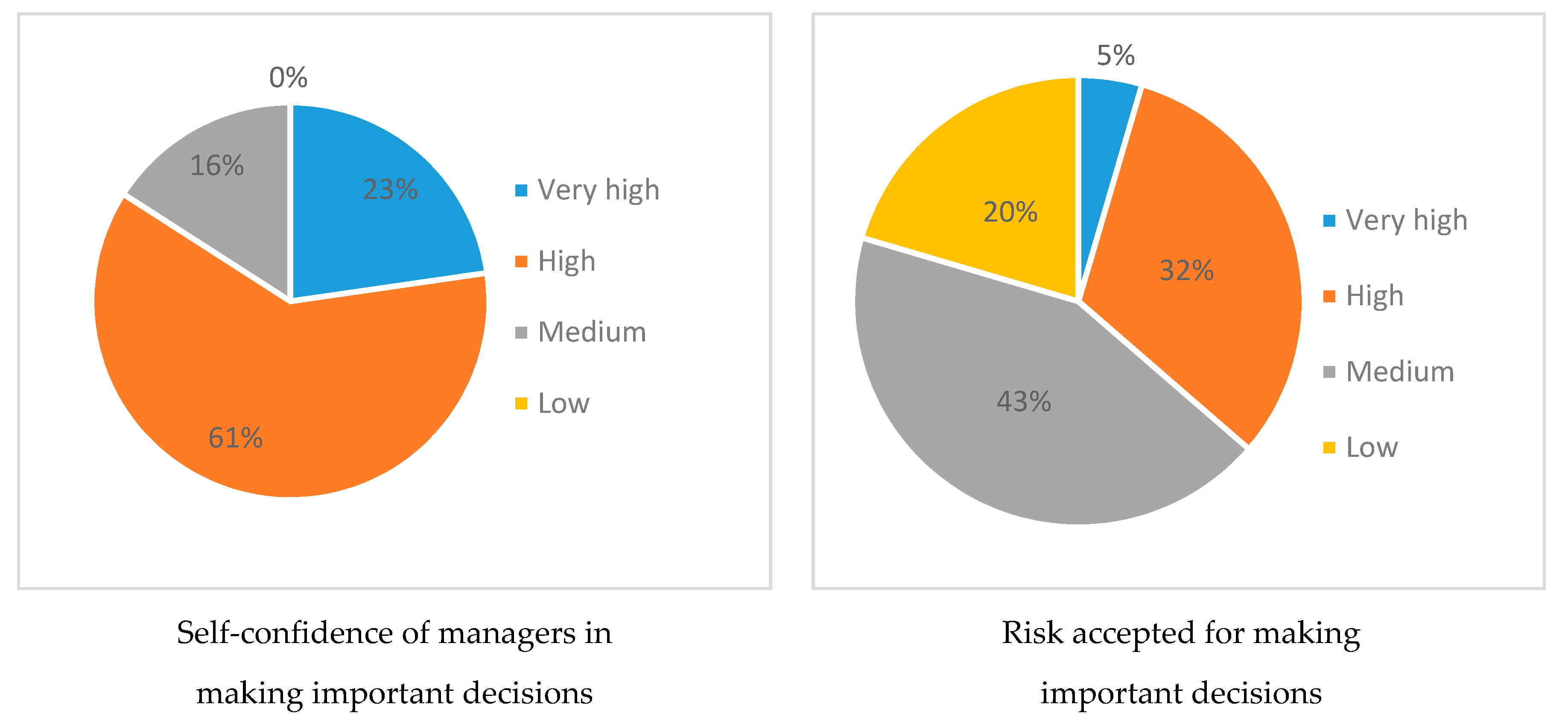
- How confident are you with yourself when making important decisions?
- Very high confidence (>75%)
- High confidence (60–75%)
- Medium confidence (40–60%)
- Low confidence (<40%)
- (10)
- How risky are you prepared to be when you make important decisions which will have an impact on other people?
- Very High (>75%)
- High (60–75%)
- Medium (40–60%)
- Low (<40%)
- (11)
- Overall, how would you rate the effectiveness of your decision-making on the technical aspect in complex situations?
- Very High (>75%)
- High (60–75%)
- Medium (40–60%)
- Low (<40%)
- (12)
- Overall, how would you rate the effectiveness of your decision-making on the financial aspect in complex situations?
- Very High (>75%)
- High (60–75%)
- Medium (40–60%)
- Low (<40%)
- (13)
- Overall, how would you rate the effectiveness of your decision-making on the human aspect in complex situations?
- Very High (>75%)
- High (60–75%)
- Medium (40–60%)
- Low (<40%)
References
- Mack, O.; Khare, A.; Krämer, A.; Burgartz, T. Managing in a VUCA World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Maak, T.; Pless, N.M. Responsible leadership in a stakeholder society—A relational perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 66, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Scholar. Leardership. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.au/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&inst=10766572768758193013&q=Leadership&btnG= (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Tal, D.; Gordon, A. Leadership of the present, current theories of multiple involvements: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 107, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C. Leadership Research and Theory. In Leadership Theory and Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, F.; Stone, S. The emergence of leadership styles: A clarified categorization. Rev. Manag. Comp. Int. 2017, 18, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Western, S. Leadership: A Critical Text; SAGE Publications Limited: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M. Going beyond heroic leaders in development. Public Adm. Dev. 2016, 36, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuser, J.D.; Gardner, W.L.; Dinh, J.E.; Hu, J.; Liden, R.C.; Lord, R.G. A network analysis of leadership theory: The infancy of integration. J. Manag. 2016, 42, 1374–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBrin, A.J. Leadership: Research Findings, Practice, and Skills; Nelson Education: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Northouse, P.G. Leadership: Theory and Practice; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.L.; Robert, C.G.; Gordon, J.C. Contingency theories of leadership. In Leading Organizations: Perspectives for a New Era; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, D.; Zhang, N. An argumentation interface for expert opinion evidence. Ratio Juris 2016, 29, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, G.C.; McCauley, K.D.; Gardner, W.L.; Guler, C.E. A meta-analytic review of authentic and transformational leadership: A test for redundancy. Leadersh. Q. 2016, 27, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, J.E.; Lord, R.G.; Gardner, W.L.; Meuser, J.D.; Liden, R.C.; Hu, J. Leadership theory and research in the new millennium: Current theoretical trends and changing perspectives. Leadersh. Q. 2014, 25, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Risku, M.; Collin, K. A meta-analysis of distributed leadership from 2002 to 2013: Theory development, empirical evidence and future research focus. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 2016, 44, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, M.; Runhaar, P.; Wesselink, R.; Mulder, M. Towards distributed leadership in vocational education and training schools: The interplay between formal leaders and team members. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 2019, 47, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, D.S.; Hayes, R.E. Power to the Edge: Command... Control... in the Information Age; Office of the Secretary of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Piersol, B. Employee engagement and power to the edge. Perform. Improv. 2007, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, T.A.; Ilies, R.; Bono, J.E.; Gerhardt, M.W. Personality and leadership: A qualitative and quantitative review. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, T.A.; Bono, J.E.; Judge, T.A.; Bono, J.E. Five-factor model of personality and transformational leadership. J. Appl. Psychol. 2000, 85, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderhjelm, T.M.; Larsson, G.; Sandahl, C.; Björklund, C.; Palm, K. The importance of confidence in leadership role: A qualitative study of the process following two Swedish leadership programmes. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2018, 39, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eragula, R. Confidence in Leadership. Adv. Econ. Bus. Manag. 2015, 2, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yammarino, F.J. Procrastination in Organizations: Role of Trait-State Anxiety and Leadership. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Briarcliff Manor, NY, USA, 2017; p. 11794. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, A.D.; Lanza, S.T.; Bernthal, P. Personality profiles of effective leadership performance in assessment centers. Hum. Perform. 2016, 29, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, R.J.; Hanges, P.J.; Javidan, M.; Dorfman, P.W.; Gupta, V. Culture, Leadership, and Organizations: The GLOBE Study of 62 Societies; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenbach, J.D.; Beenackers, M.A.; Noordzij, J.M.; Oude Groeniger, J.; Lakerveld, J.; van Lenthe, F.J. The moderating role of self-control and financial strain in the relation between exposure to the food environment and obesity: The GLOBE study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Quast, L.N.; Jang, S.; Wohkittel, J.; Center, B.; Edwards, K.; Bovornusvakool, W. GLOBE Study culture clusters: Can they be found in Importance ratings of managerial competencies? Eur. J. Train. Dev. 2016, 40, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G.A. Leadership in Organizations; Pearson Education: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pyc, L.S.; Meltzer, D.P.; Liu, C. Ineffective leadership and employees’ negative outcomes: The mediating effect of anxiety and depression. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2017, 24, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.I.; Giessner, S.R. The thin line between empowering and laissez-faire leadership: An expectancy-match perspective. J. Manag. 2018, 44, 757–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, L.; O Connell, A. A brief history of decision making. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Google Scholar. Decision-Making. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.au/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&inst=10766572768758193013&q=Decision-making&btnG (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Appelt, K.C.; Milch, K.F.; Handgraaf, M.J.J.; Weber, E.U. The Decision Making Individual Differences Inventory and guidelines for the study of individual differences in judgment and decision-making research. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2011, 6, 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Halperin, E.; Porat, R.; Tamir, M.; Gross, J.J. Can emotion regulation change political attitudes in intractable conflicts? From the laboratory to the field. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G. Naturalistic decision making. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D. Thinking, Fast and Slow; Pearson Education Inc: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schutten, D.; Stokes, K.A.; Arnell, K.M. I want to media multitask and I want to do it now: Individual differences in media multitasking predict delay of gratification and system-1 thinking. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2017, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Klein, G. Conditions for intuitive expertise: A failure to disagree. Am. Psychol. 2009, 64, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigerenzer, G.; Kurzenhaeuser, S.S. Fast and Frugal Heuristics in Medical Decision Making. In Science and Medicine in Dialogue: Thinking Through Particulars and Universals; Praeger: Westport, CT, USA, 2005; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, H. Rational choice and the structure of the environment. Psychol. Rev. 1956, 63, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. Rational decision making in business organizations. Am. Econ. Rev. 1979, 69, 493–513. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, H. Administrative Behaviour: A Study of Decision-Making Processes in Administrative Organisations, 4th ed.; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dane, E.; Pratt, M.G. Exploring intuition and its role in managerial decision making. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.A.; van den Pligt, J.; Kleef, G.A. Deliberation versus intuition: Decomposing the role of expertise in judgment and decision making. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2013, 26, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.M. When to believe instinct. Havard. Bus. Rev. 2001, 2, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Remmers, C.; Zander, T. Why you don’t see the forest for the trees when you are anxious: Anxiety impairs intuitive decision making. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 6, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; George-Curran, R.; Smith, M.L. The Role of Emotional Intelligence in the Career Commitment and Decision-Making Process. J. Career Assess. 2003, 11, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.; Västfjäll, D.; Gärling, T.; Slovic, P. Affect and decision making: A “hot” topic. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2006, 19, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, J.S.; Li, Y.; Weber, E.U. The financial costs of sadness. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, J.S.; Li, Y.; Valdesolo, P.; Kassam, K.S. Emotion and decision making. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 799–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. Making management decisions: The role of intuition and emotion. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 1987, 1, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, G.; Gemser, G.; Wijnberg, N.M. The interplay between intuition and rationality in strategic decision making: A paradox perspective. Organ. Stud. 2017, 38, 365–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydman, C.; Camerer, C.F. The Psychology and Neuroscience of Financial Decision Making. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2016, 20, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, W.L. Financial Illiteracy in America: A Perfect Storm, a Perfect Opportunity. J. Financ. Serv. Prof. 2004, 58, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax, L.M. The Securities Law Implications of Financial Illiteracy. Va. Law Rev. 2018, 104, 1065. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, W.B. Why do things become more complex. Sci. Am. 1993, 268, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalanffy, L. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications; G. Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.C.; Keys, P.H. Towards a system of systems methodologies. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1984, 35, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorod, A.; Gandhi, S.J.; Sauser, B.; Boardman, J. Flexibility of System of Systems. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2008, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, D.J.; Boone, M.E. A Leader’s Framework for Decision Making. (cover story). Harv. Bus. Rev. 2007, 85, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gray, B. The Cynefin framework: Applying an understanding of complexity to medicine. J. Prim. Health Care 2017, 9, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G. Cynefin as reference framework to facilitate insight and decision-making in complex contexts of biomedical research. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykstra, J.A.; Orr, S.R. Acting in the unknown: The cynefin Framework for Managing Cybersecurity Risk in Dynamic Decision Making. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Cyber Conflict (CyCon US), Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shalbafan, S.; Leigh, E.; Pollack, J.; Sankaran, S. Decision-making in project portfolio management: Using the Cynefin framework to understand the impact of complexity. Int. Res. Netw. Organ. Proj. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, M.J.; Birkinshaw, J. The sources of management innovation: When firms introduce new management practices. J. Bus. Res. 2009, 62, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.E.; Schoemaker, P.J.; Russo, E.J. Decision Traps: Ten Barriers to Brilliant Decision-Making and How to Overcome Them; Doubleday/Currency: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, J.S.; Keeney, R.L.; Raiffa, H. The hidden traps in decision making. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Speed and strategic choice: How managers accelerate decision making. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1990, 32, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkus, V.O.; Mannor, M.J.; Campbell, J.T.; Crossland, C. Fast and Rigorous: Configurational Determinants of Strategic Decision-Making Balance. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Briarcliff Manor, NY, USA, 2018; p. 10243. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.; Reb, J.; Gigerenzer, G. Ecological rationality: Fast-and-frugal heuristics for managerial decision making under uncertainty. Acad. Manag. J. 2019, 62, 1735–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigerenzer, G. Towards a Rational Theory of Heuristics. In Minds, Models and Milieux; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 34–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bakonyi, Z. Why do firms centralise their strategic decision-making during crisis? A qualitative study. J. Organ. Chang. Manag. 2018, 31, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Seetharaman, P.; Samarah, I.; Mykytyn, P. Understanding Conflict in Virtual Teams: An Experimental Investigation Using Content Analysis. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2005; p. 44a. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Making fast strategic decisions in high-velocity environments. Acad. Manag. J. 1989, 32, 543–576. [Google Scholar]
- Robert Baum, J.; Wally, S. Strategic decision speed and firm performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 1107–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenleaf, R.K. Servant Leadership: A Journey into the Nature of Legitimate Power and Greatness; Paulist Press: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, I.; Gorod, A.; Hallo, L.; Nguyen, T. Developing a System of Systems Management Framework for the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster Recovery. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 21–23 July 2017; pp. 563–568. [Google Scholar]
- Gorod, A.; Hallo, L.; Nguyen, T. A Systemic Approach to Complex Project Management: Integration of Command-and-Control and Network Governance. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2018, 35, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, H.; Lichtenstein, B.M.B. Relationality in organizational research: Exploring the space between. Organ. Sci. 2000, 11, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl-Bien, M.; Marion, R.; McKelvey, B. Complexity Leadership Theory: Shifting leadership from the industrial age to the knowledge era. Leadersh. Q. 2007, 18, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl-Bien, M.; Marion, R. Complexity leadership in bureaucratic forms of organizing: A meso model. Leadersh. Q. 2009, 20, 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.E.; Lichtenstein, B.B.; Milosevic, I.; Poelmans, S.; Sipahi-Dantas, A. Leadership for Organizational Adaptability: Enabling the Adaptive Process. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Briarcliff Manor, NY, USA, 2018; p. 11322. [Google Scholar]
- Regmi, P.R.; Waithaka, E.; Paudyal, A.; Simkhada, P.; Van Teijlingen, E. Guide to the design and application of online questionnaire surveys. Nepal J. Epidemil. 2016, 6, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.F. A General Introduction to the Design of Questionnaires for Survey Research; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hallo, L.; Gunawan, I.; Nguyen, T. System Complexity Leadership: The Relationship between Emotion and Decision-Making. In Proceedings of the 2018 Annual IEEE International Systems Conference (SysCon), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 23–26 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lundin, R.W. Alfred Adler’s Basic Concepts and Implications; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.A.; Watson, D. Temperament: A new paradigm for trait psychology. Handb. Personal. Theory Res. 1999, 2, 399–423. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.A.; Watson, D. An Organizing Paradigm for Trait Psychology. In Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 265–286. [Google Scholar]
- Dörner, D.; Funke, J. Complex Problem Solving: What It Is and What It Is Not. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.A.; Crozier, K. How do informal information sources influence women’s decision-making for birth? A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, L.; Bender, J.; Hueniken, K.; Kassirian, S.; Yang, D.; Mitchell, L.; Paulo, C.B.; Magony, A.; Smith, E.C.; Liang, M.; et al. 1748PCancer care-related social media (SM) and internet usage differences between adolescents and young adults (AYA), adults and elderly patients with cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezar, A.; Maxey, D. The Delphi technique: An untapped approach of participatory research. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2016, 19, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, M.J. Delphi: A technique to harness expert opinion for critical decision-making tasks in education. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 17, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, K.G.; Hertwig, R. Emotions and decisions: Beyond conceptual vagueness and the rationality muddle. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowicz, D. Why does subjectivity make us nervous? Making the tacit explicit. J. Intellect. Cap. 2001, 2, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, S. A Decision-Making Model of Disaster Resilience and Recovery. In Proceedings of the SECED 2015 Conference: Earthquake Risk and Engineering towards a Resilient World, Cambridge, UK, 9–10 July 2015; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Lee, L.; Danescu-Niculescu-Mizil, C. When Confidence and Competence Collide: Effects on Online Decision-Making Discussions. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 1381–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Van Raaij, W.F. Understanding Consumer Financial Behavior: Money Management in an Age of Financial Illiteracy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lusardi, A. Financial literacy: Do people know the ABCs of finance? Public Underst. Sci. 2015, 24, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Mendis, B. Male vs female leaders: Analysis of transformational, transactional & laissez-faire women leadership styles. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 2017, 9, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wuwong, N.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Information Security Risk Management Framework for the Cloud Computing Environments. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Bradford, UK, 29 June–1 July 2010; pp. 1328–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Purdy, G. ISO 31000: 2009—Setting a new standard for risk management. Risk Anal. Int. J. 2010, 30, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, A.; Bortolotti, L.; Kuzmanovic, B. What is unrealistic optimism? Conscious. Cogn. 2017, 50, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.E.; Brown, J.D. Positive illusions and well-being revisited: Separating fact from fiction. Psychol. Bull. 1994, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.A.; Kleitman, S.; Howie, P.; Stankov, L. Cognitive abilities, monitoring confidence, and control thresholds explain individual differences in heuristics and biases. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, L.; Antrobus, M. Costs and benefits of realism and optimism. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2015, 28, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



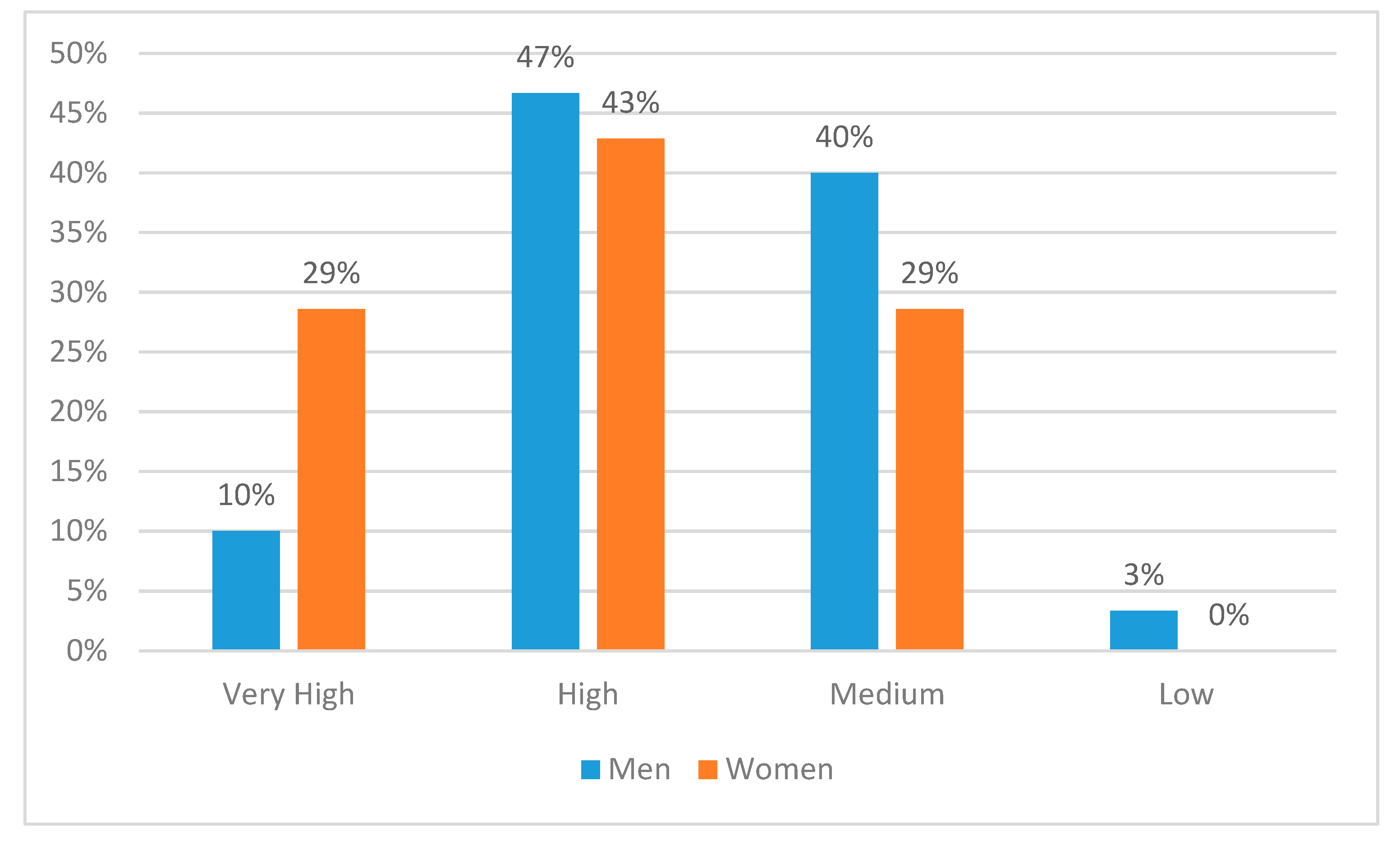
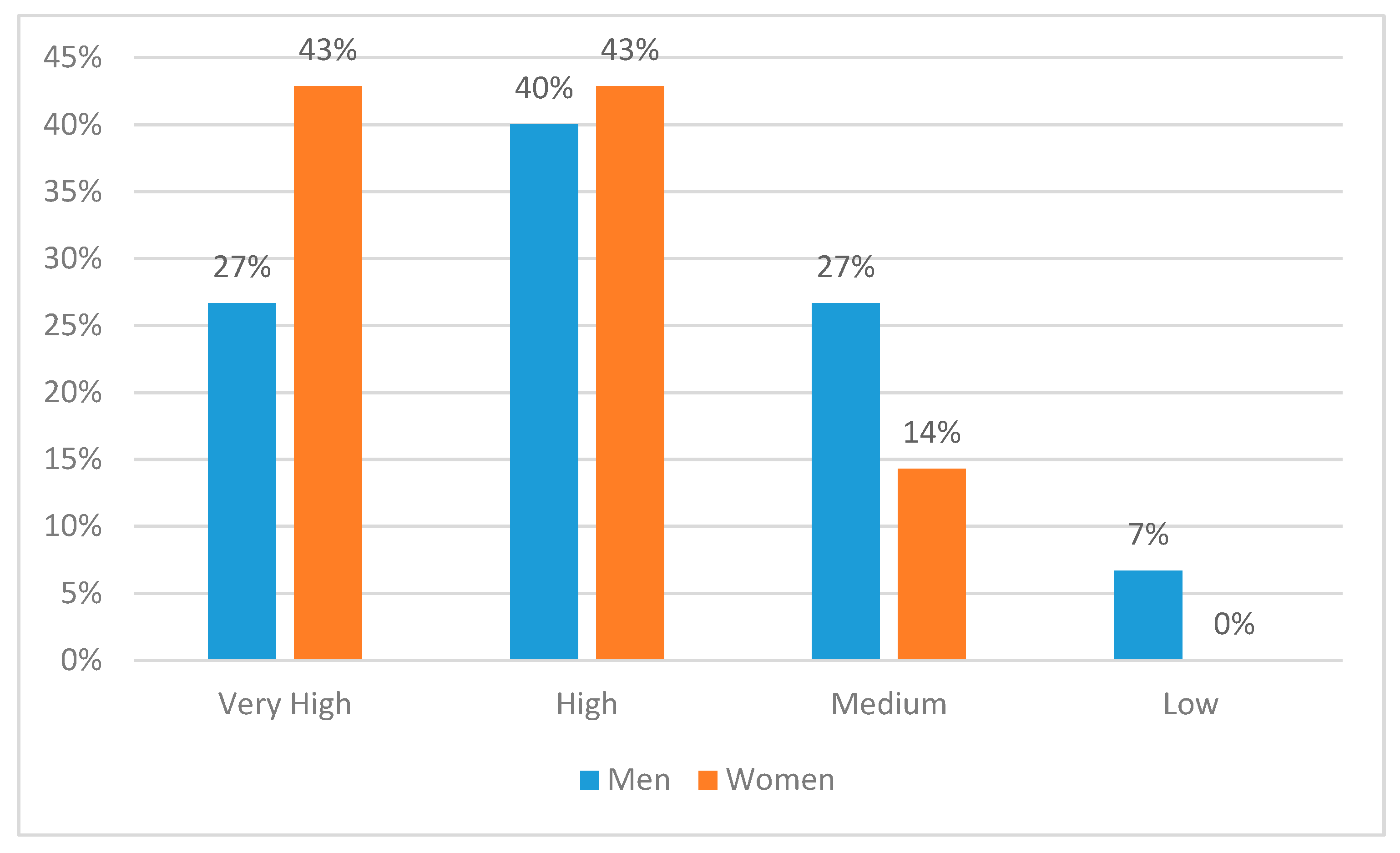
| Gender | Age Range | Complex Management Experience | Personality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 68% of 44 participants are male | 48% of participants are older than 50 years | 36% of participants have less than 5 years of experience | 45% of participants describe themselves as “friendly” |
| 20% of participants are 40–49 years old | 27% of participants have from 5 to 10 years of experience | 34% of participants describe themselves as “logical” | |
| 32% of 44 participants are female | 16% of participants are 30–39 years old | 27% of participants have from 10 to 20 years of experience | 14% of participants describe themselves as “optimistic” |
| 16% of participants are under 30 years | 25% of participants have more than 20 years of experience | 7% of participants describe themselves as “decisive” |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hallo, L.; Nguyen, T.; Gorod, A.; Tran, P. Effectiveness of Leadership Decision-Making in Complex Systems. Systems 2020, 8, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems8010005
Hallo L, Nguyen T, Gorod A, Tran P. Effectiveness of Leadership Decision-Making in Complex Systems. Systems. 2020; 8(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems8010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleHallo, Leonie, Tiep Nguyen, Alex Gorod, and Phu Tran. 2020. "Effectiveness of Leadership Decision-Making in Complex Systems" Systems 8, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems8010005
APA StyleHallo, L., Nguyen, T., Gorod, A., & Tran, P. (2020). Effectiveness of Leadership Decision-Making in Complex Systems. Systems, 8(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems8010005





