Abstract
This article describes preliminary research (a proof of concept test) on the potential value of formalizing Isomorphic Systems Processes (ISPs) based on systems science research using the Monterey Phoenix (MP) language, approach and tool. MP is a Navy-developed framework for behavior modeling of system, process, and software behaviors, and has a demonstrated ability to expose emergent behaviors in engineered, complex systems. In this article, we introduce the related lines of research and discuss and demonstrate use of MP in modeling ISPs. We accomplish the demonstration through a small example of the Cycles ISP and discuss several possible variations generated from an MP model of this single ISP. Among these variations, we found patterns of oscillation, lifecycle, recycling, positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, and combinations thereof, all derived from a common model of a cycle comprising six lines of MP code. Although the detection of three of these patterns (oscillations, lifecycles, and recycling) was anticipated, the involvement of the other two patterns (positive and negative reinforcement) were not anticipated in pre-model analyses and provided evidence to resolve a dispute over the application of ISPs in systems engineering. From conducting this initial experimentation at the intersection of different research domains, we found that using MP to formalize relationships within and among presently non-formally-described ISPs yielded new insights into system processes.
1. Introduction
This cross-cutting research lies at the intersection of systems science, systems engineering (SE), and software engineering. Systems Processes Theory (SPT) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] is both a candidate general systems theory and systems science. This article describes the use of the SPT as a foundation to build a formal model of cycle behavior using Monterey Phoenix (MP) [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], an approach and language implemented for systems and software behavior modeling, verification and validation. This preliminary research is a first test of concept of the potential for the application of MP software to enable SPT basic research and enhance the foundations of SE by identifying and incorporating a better understanding of complex systems from the system sciences and general systems theory.
1.1. Research Objective
There is an inherent contradiction in the term “systems science” that is not often honestly admitted to or described. To be a science is to be comprised of relations that can be and are tested. In fact, testing is of particular importance to practical engineering as well as the natural sciences. Engineering disciplines have established tools for examining their particular scale and type of system, but, in general theories of systems, one is dealing with high-level abstractions of real systems. Most of the knowledge about how processes work or do not work to establish stable systems has come from comparison of real systems that have been elucidated via experimental testing. This knowledge may have been distilled from comparing many systems, but the comparisons are still abstractions often expressed in natural language, not formalized equations. To our knowledge, none of the many general theories of systems beyond those that are purely mathematical have been tested. This research aims to answer the question, “How do you truly test abstract models of system processes?” Achieving this “testability” would be a first for systems science with many downstream applications.
The MP framework for behavior modeling [10] is used to explore this research question because of its ability to express behaviors ranging from simple to complex at a high level of abstraction, and generate many different example instances of behavior from a single specification. We aim to model and simulate one well-studied system process—a cycle—at a very high level to test MP’s potential application as a practical tool for advancing our understanding of system processes, like cycling, that manifest in many domains (Isomorphic System Processes, or ISPs) although they are often called by different domain-specific names (discipline-specific synonyms, or discinyms) [9]. Having a tool that enables the study of processes in terms of their domain-independent common properties would enable insights gained at the higher abstract level to be made available at the application level in every domain in which the process manifests. Such a capability would provide system scientists with a means to test their understanding of ISPs and further develop an ISP taxonomy with assistance from a formal reasoning tool. This article reports on the results of our experiment with cycle modeling, in which we applied MP to see if it could not only provide “mini-models”—small example instances of cycles—but also lead to significant new general knowledge about cycles using automated formal reasoning tools.
1.2. Systems Processes Theory
Circa 2010, the Systems Science Working Group (SSWG) of the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) officially started two ongoing research projects. Review of the available literature in the basic systems sciences indicated that there were many competing theories on systems but no unified or consensus theory. The SSWG recognized the importance of strengthening SE with a foundational theory of systems, but the existence of many fragmented theories, some not based on science, did not provide what was needed. Thus, the goal of the first project was to help unify that field by critiquing and expanding the SPT [1,2,3] as an integrated theory of “how systems work” for use in SE. The goal of the second project was to assemble and integrate complementary information on “how systems don’t work.” The lead for these two projects, Troncale, suggested that this second project should focus on recognizing and starting a new discipline called “Systems Pathology” [4,5,6] to identify, understand, document, and emphasize that there are common and repeating ways in which systems can fail to work. Subsequently, the INCOSE Foundation, in its first grants, provided seed funding to continue and extend both of these projects [7].
The SPT provided a strong, already developed, science-based general theory and candidate systems science to enable a jump-start for both projects. The natural system-based SPT claimed it provided the “prescriptive” part of systems approaches missing in most of the “systems thinking” and human-level approaches then popular in SE.
As a counterpoint to SPT, the existing state of awareness of systems in SE was characterized as focused solely on traditional systems thinking, which some argued was not systems science at all [29]. SE had a strong knowledge and use of systems thinking tools and system development programs, but the two projects suggested that this knowledge could and should be significantly extended by the strengths and extensive literature of the conventional sciences, just as chemical engineers study the fundamentals of chemistry as a foundation for their work or aeronautical engineers study math and physics. Furthermore, Comparative Anatomy, Comparative Physiology, Comparative Speciation, and Comparative Genomics were very successful because they compared across differences—an approach used by SPT in search of fundamental knowledge about systems that can only come from attempting to match and perceive commonalities across differences. SPT called this approach or method Comparative Systems Analysis (CSA). The SPT research of the INCOSE SSWG for the above purposes has expanded to some 20 collaborative projects [8], each involving cooperation between systems engineers and systems scientists to extend SE awareness of the results of the empirical sciences and distill them into patterns (how systems work) and pathologies (how systems don’t work), common across all natural and human systems. One team is even establishing a new professional society, the International Society for Systems Pathology (ISSP) to help several currently isolated domains learn about each other’s discoveries, share, and unify the knowledge base.
The SPT distills its insights from examination of a wide range of systems theories and natural science experiments [2]. Example experimental domains include physics, geology, astronomy, chemistry, biology, mathematics and computer science, and lately SPT has added comparisons of these natural phenomena with the engineering and human domains. Each domain contains system processes that are described in the language of its home domain. This research builds on the SPT premise that there exist isomorphic system processes (ISPs) [2] that remain constant across many domains, and that these ISPs can be expressed as domain-neutral concepts to reveal insights about how systems work in general. ISPs are termed “isomorphic” because they are found across many, if not all, mature systems and so they are iso- (same) and -morphic (form). (Note that this is quite a distinct use of the term from its use in mathematics). The term “systems” is used because ISPs are hypothesized to be the fundamental mechanisms by which the sustainability of systemness is achieved; that is, they are the minimal steps for maximal efficacy to achieve system function/purpose no matter what the scale or compositional parts of the system. ISPs are termed “processes” because they perform a similar function/purpose across all these systems by the same “process steps” or developments in an obligate sequence.
For the MP modeling test of concept, therefore, the team decided to select one widespread pattern, “Cycles”, from 110 patterns available from the SPT body of work. Some patterns that appeared to be variants of cycling were part of the discussion that grouped the 110 proposed ISPs resulting in a more concise list of 55, since some of the initially considered system processes were essentially different instances of the same pattern [2]. This grouping came about by recognizing in many instances that some ISPs were actually discinyms, or discipline-specific synonyms, for the same process. Troncale argued on abstract grounds that aspects of cycling were shared by a very wide range of diverse phenomena in nature (and humans), in which different cases exhibited many of the same identifying features of cycles. These included phenomena such as oscillation, recycling, iteration/recursion, spin, solitons, waves, hypercycles, and lifecycles. However, at this stage of development of the SPT, only abstract reasoning, that is, comparisons across real natural systems from the results of their science experiments, expressed as informal linguistic-based representations informed the endless discussions and debates that ensued.
MP version 1 first became publicly available in 2015 on firebird.nps.edu, and was shortly thereafter noticed as a tool that could potentially inform these discussions in a more formal manner. Since cycles are present in literally hundreds of phenomena of the natural sciences at all scales and also found widely in human systems, any elucidation of cycles as an ISP using more formal models would significantly contribute both to engineering systems and to the theoretical knowledge of systems, so improve theory and praxis simultaneously.
Recent research by Quartuccio [28] has suggested that the presence of similar patterns and pathologies (the latter being sometimes called anti-patterns in systems and software engineering vernacular) in different domains (e.g., medical and aviation) can be identified, analyzed, and documented using MP. This work also contributed inspiration for potential practical applications of modeling SPT patterns or pathologies at a high level of abstraction in MP.
1.3. Monterey Phoenix
While these SPT research projects were evolving in the INCOSE SSWG, a new formal approach and language for system and process behavior modeling known as Monterey Phoenix (MP) was also taking shape and circulating for peer review in the software engineering community. MP is a Navy-developed behavior modeling framework composed of a formal language, a lightweight formal methods approach, and an automated tool that generates a “scope-complete” set of possible event traces from a behavior model using each of the former. For MP, “scope-complete” means exhaustive up to a maximum number of event iterations specified by the user, a defining feature of the MP approach and formalism to make an otherwise infinite model finite for simulation, and therefore practical for testing behaviors up to a given scope. MP is used to define logical or physical objects in terms of their underlying behaviors. Behavior is defined as set of events with two fundamental relations: precedence (for event sequencing) and inclusion (for event decomposition). Behavior rules can be composed from these two basic relations using event grammar that allows for concurrent, alternate, optional, and iterating events, as shown in the upcoming examples.
MP was initially conceived and developed for modeling and assessing software architectures [11,12], but it captured the interest of systems engineers when it became clear that MP provides not only a framework for software modeling, but for systems in general, including humans, organizations, hardware, software, and environment behaviors [10,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. MP provides for modeling high-level behaviors belonging to a range of system types from living to artificial and from natural to technological in nature. For example, we can model the behavior of cells, humans, animals, robotics, air and spacecraft, ground vehicles, information technology systems, environmental activity, etc., and interactions among these systems, in MP. We model systems as independent entities—defining each as a separate root event in MP—that interact through stated dependencies that are coordinated through codified natural law or design specifications. The MP event grammar provides a lightweight formal language for expressing behaviors at the level necessary to test the modeling of an ISP.
Using event grammar capable of describing anything that has behavior at a high level of abstraction, MP has been employed in thesis, dissertation, and sponsored research efforts to model behaviors for system architecture, software architecture, software-intensive systems architecture, business processes, human interactions, medical procedures, operational missions, and entertainment events [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. The precise language enables humans to describe potentially infinite combinations of system behavior in a concise and finite model, and then generate a scope-complete set of example instances of behavior from that model. Once this set of behaviors (scenario instances in the form of event traces) is generated, each instance can be tested against behavior expectations through the use of manual inspection as well as automated queries and assertion checking [10], providing a scientific basis for reasoning about system behaviors, including refutation of claims about system behavior. What sets MP apart from other behavior modeling approaches is its foundation in lightweight formal methods as a basis for these queries, assertion checking, and reasoning about behavior models. In particular, the following section further describes and illustrates what model “scope” means, how defining a scope for behavior models is different from current behavior modeling approaches, and the advantages and limitations of modeling up to a scope.
1.4. The Meaning of “Scope” in MP Behavior Modeling
Model “scope” is a key feature of the lightweight formal methods upon which MP is based. Lightweight formal methods for scenario generation [47] came into being to make an alternative available to traditional heavyweight formal methods such as model checking and theorem proving. Lightweight and heavyweight formal methods differ in scope of completeness, usability, cost, and experience required. Heavyweight methods mathematically guarantee exhaustive scenario coverage, and so are functionally attractive for mission-critical system design. Traditional formal methods are comparatively expensive and require specialized skills. Lightweight formal methods, on the other hand, trade away the 100% completeness guarantee for greater usability (lower entrance barrier to use) and faster results, while providing increased coverage over popular informal methods. MP uses lightweight formal methods and the concept of scope to denote the boundary for the included behaviors. Scope in MP is the upper limit on how many times an event should repeat, if it is on a loop. Thus, all MP models are run for a given scope, which places an upper bound on the number of event iterations to repeat. For example, running at scope 1 will execute iterating events up to one time, running at scope 2 will execute iterating events up to two times, running at scope 3 will execute iterating events up to three times, etc. This scope limit enables an otherwise infinite model to execute in a finite amount of time, trading completeness for speed and ease of use.
1.5. MP Modeling Environment and an Example Illustrating the Concept of Model Scope
An MP modeling environment called MP-Firebird is available publicly at http://firebird.nps.edu. As seen in Figure 1, the upper left pane of MP-Firebird consists of a text editor for MP code, into which the user types a model or loads an existing model previously composed. The lower left pane is a console window that logs statistics about the trace generation process as the model is run. The center pane contains a large view of the selected event trace graph generated from the model, and the right pane contains a thumbnail list of all traces for the given schema at the given scope. Run scope in MP-Firebird is controlled by using the slider bar to the right of the Run button.
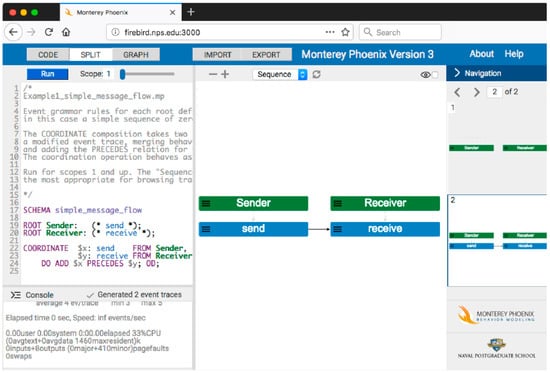
Figure 1.
The MP-Firebird modeling environment at http://firebird.nps.edu, showing the pre-loaded MP model Example01_simple_message_flow run for scope 1.
The model displayed in the figure is a pre-loaded example of a simple message flow, available from Import > Load example > Example_01_simple_message_flow. The MP code in the text editor describes two root events called Sender and Receiver, each performing its respective send or receive activity. The (*…*) parentheses surrounding each event means that the contained event iterates zero or more times. The COORDINATE statement is a separate constraint on the events in each root to enforce a precedence relation to exist between events send and receive. (Without this constraint, no dependency would exist between send and receive events and send could occur without receive, and receive could occur without send).
When the model is run up to a scope limit of 1, two event traces (scenarios) are generated consistent with the MP code. In the graphs produced, green boxes are used for root events, blue boxes are used for atomic events, dashed arrows are used to depict inclusion relations, and solid arrows are used to depict precedence relations. In trace 1, both the Sender and Receiver are idle since neither send nor receive occur (shown in Figure 1 top thumbnail on the right), and in trace 2, the Sender includes one send event that precedes one receive event in the Receiver (shown in Figure 1 center pane).
When the same model is run up to a scope limit of 2, the same scenarios that were present at scope 1 are generated plus a third trace showing the additional possibility that the coordinated send–receive events occurs two times (Figure 2a). Running the model up to a scope limit of 3 results in all scenarios from scope 2 plus a fourth trace showing the send–receive events iterating three times (Figure 2b).
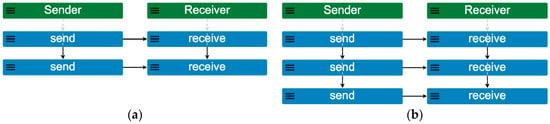
Figure 2.
Pre-loaded MP model Example01_simple_message_flow scenarios from (a) scope 2, showing the scenario containing the new maximum of two iterations of send and receive (trace 3); (b) scope 3, showing the scenario containing the new maximum of three iterations of send and receive (trace 4).
The model in Figure 1 was run for up to scope limits 1, 2, and 3 to demonstrate how scope limit works in MP models. It is conceivable to run MP models for higher scopes, but run time increases dramatically with increasing model complexity. In general, lower scope settings produce fewer scenarios in less time than higher scope settings. Shorter run times are preferable to longer ones so that the model can undergo iterative refinement many times without unreasonably long waiting periods for the event trace generator to return results. The requirement for reasonably short run times begs the sensible question: “What scope limit is high enough to include most of the behaviors of interest?” The next section addresses this question with a heuristic called the Small Scope Hypothesis [47].
1.6. Use of the Small Scope Hypothesis
Running the model at a low or small scope has advantages in speed, but are we missing important information by excluding examples from higher scopes? Our observations have been such that scenarios appearing at higher scopes are generally present in some shape at the lower scopes as well. These observations are consistent with Jackson’s Small Scope Hypothesis, which states that most errors can be exposed in small examples [47]. Browsing at scope limits of 1, 2, or 3 has often resulted in very valuable and surprising observations about our modeled system, many of which we would have missed by using traditional methods alone; but browsing at scopes 4 and above produced more traces at the expense of longer generation times and more complex graphs, but no new insights than were already gathered at scopes 1–3. Discussion of the Cycles ISP model in the sections that follow therefore provides specific examples of general patterns that can be detected at low scopes of 1–3.
2. Materials and Methods
The SPT research products are rich in details and examples of both patterns and pathologies. SPT presents a minimum of 55 classes of candidate system processes condensed from an initial list of 110 individual and distinct system processes [2]. All need further evaluation and development. A set of 30 information categories for each ISP has been created to document, extend, and enable teaching and application of SPT-ISPs [5]. To simplify this initial “test of concept”, this research examines just one of the 110 system processes using just four of the 30 information categories (Features, Functions, Processivity, and Measurables). We decided to use the MP formal behavior modeling language in order to determine if further research in this direction is warranted.
Source data for the Cycles ISP MP model came from the body of work on cycles in SPT research, in particular from [9]. From this source information, we created a simple but formal model of Cycle behavior using the MP event grammar. We conducted all experiments with this model using the publicly available MP behavior modeling tool, MP-Firebird, at http://firebird.nps.edu. MP-Firebird was used to compose, execute, and refine the Cycles ISP model to embody the identifying features of a cycle. Example outputs of this generation are illustrated and described in the sections that follow. The full set of model outputs can be reproduced by running the illustrated code on MP-Firebird.
2.1. Cycles ISP Model, Version 1
A basic MP model of the Cycles ISP was first composed as a sequence of one or more steps that move the cycle either forward or backward:
SCHEMACycle_ISP_v1
ROOTCycle: (+ ( Step_forward | Step_backward ) +).
The SCHEMA declares the name of the model (Cycle_ISP_v1). The ROOT establishes a main event, in this case, a Cycle. The Cycle event includes one or more (+…+) repetitions of Step_forward or Step_backward (the “or” operation is denoted by | ).
Note that Step_forward and Step_backward may have synonyms such as Move_up and Move_down, Move_in and Move_out, and Increase and Decrease. The SPT research has demonstrated the existence of discipline-specific synonyms, or discinyms, which also may be used to name cycle movements according to a domain taxonomy.
2.1.1. Cycles ISP Model, Version 1, Scope 1
Running this preliminary model on MP-Firebird at scope 1 illustrates two possible outcomes (as event traces) for cycle behavior: stepping forward, or stepping backward (Figure 3). Immediately, we can tell that these event traces do not fit the definition of a cycle, since there is no repetition or recurrence, as called for in the earlier presented definitions. The depicted scenarios do not contain any repetition, and so only represent a part of cycle behavior.
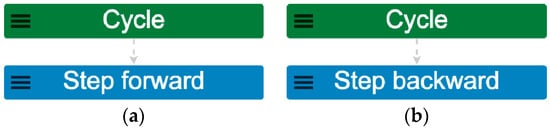
Figure 3.
Initial event trace outputs of the Cycle_ISP_v1 model, run for scope 1: (a) Cycle steps forward; (b) Cycle steps backward. Neither scenario contains any repetition and therefore only represents part of a cycle’s behavior.
To reject these event traces from the set of valid examples of a complete cycle, the following constraint is added to the model:
ENSURE #( Step_forward | Step_backward ) > 1.
Running the constrained model at scope 1 will now generate zero valid traces, having the intended effect of removing single-iteration behaviors from the Cycles ISP model.
2.1.2. Cycles ISP Model, Version 1, Scope 2
Running the constrained model at scope 2 illustrates four possible outcomes for cycle behavior (Figure 4). The cycle may step forward twice, step forward then backward, step backward then forward, or step backward twice. Each scenario contains movement, then another movement, and so each is a valid, albeit general, example of a cycle.
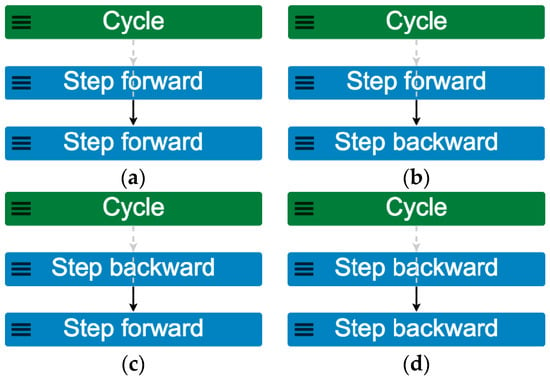
Figure 4.
Outputs from the constrained Cycle_ISP_v1 model, run for scope 2: (a) Cycle steps forward twice (trace 1); (b) Cycle steps forward then backward (trace 2); (c) Cycle steps backward then forward (trace 3); (d) Cycle steps backward twice (trace 4).
2.1.3. Cycles ISP Model, Version 1, Scope 3
Figure 5 shows four of twelve scenarios that were generated at scope 3. The output was inspected by browsing the generated event traces one at a time in the MP-Firebird tool by scrolling down the navigation pane (shown on the right side of Figure 1) and clicking on each event trace to enlarge it in the center pane. Patterns started to become visible in the scenarios: Figure 5a positive reinforcement and Figure 5b negative reinforcement are clearly present in the consecutive repeating selection of step_forward or step_backward, respectively. The scenario in Figure 5c clearly illustrates a pattern of oscillation, with step_forward followed by step_backward followed by step_forward again. The scenario in Figure 5d shows an instance where two patterns (positive reinforcement and oscillation) are present in the same scenario.
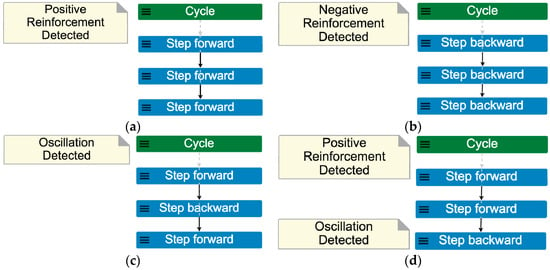
Figure 5.
Example outputs from the constrained Cycle_ISP_v1 model, run for scope 3: (a) Cycle exhibits a positive reinforcement pattern (trace 5); (b) Cycle exhibits a negative reinforcement pattern (trace 12); (c) Cycle exhibits an oscillation pattern (trace 7); (d) Cycle steps forward twice then backward once (trace 6).
Once the modeler identified the presence of a pattern in a trace, a condition was written to automatically annotate every trace containing that pattern. The graphs in Figure 5 include comment boxes that were automatically placed on the pertinent scenarios.
To automate the graph annotations, conditions are added to the model. For example, the following condition annotates all traces containing positive reinforcement:
IF EXISTS DISJ$a:Step_forward, $b:Step_forward
$aPRECEDES$bTHEN
SAY ( “Positive Reinforcement Detected” ); FI.
Likewise, graphs containing negative reinforcement are annotated using the following condition:
IF EXISTS DISJ$a:Step_backward, $b:Step_backward
$aPRECEDES$bTHEN
SAY ( “Negative Reinforcement Detected” ); FI.
Finally, the following condition annotates all traces containing oscillation:
IF EXISTS DISJ$a:Step_forward, $b:Step_backward
$aPRECEDES$bOR
$bPRECEDES$aTHEN
SAY ( “Oscillation Detected” ); FI.
These annotation rules are also formal specifications for the definition of the respective pattern. They provide the means to discuss and debate the precise meaning of each pattern.
Recall that the inspection process is based on the premise that most behaviors of interest (patterns or pathologies, in the case of this research) can be exposed on small examples, which is based on Jackson’s Small Scope Hypothesis [47]. If we run the model at a higher scope, we would see the possibilities of hundreds or even thousands of repetitions involving positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, and oscillation. These small examples demonstrate that it is not necessary to run many repetitions (high scopes) to detect these patterns; scope 3 was sufficient to produce examples of these patterns.
2.2. Cycles ISP Model, Version 2
The model is further refined to explore additional possible cycle patterns. We added an initial condition prior to the repetition steps, and an end condition after the repetition steps. The initial and final conditions may also occur one or more (+…+) times. The entire Cycle_ISP_v2 model, along with annotation conditions (lines 30–53), is depicted in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
The Cycle_ISP_v2 model.
2.2.1. Cycles ISP Model, Version 2, Scope 2
As in version 1 of the model, version 2 has zero traces at scope 1 due to the ENSURE constraint (line 26 in Figure 6). Executing the model at scope 2 produces 40 possible scenarios, two of which are illustrated in Figure 7. Scenario (a) shows an example of a positive reinforcement pattern in the first lifecycle, and an oscillation pattern in the second lifecycle. Scenario (b) shows an example of a negative reinforcement pattern in the first lifecycle, and a positive reinforcement in the second lifecycle. Both scenarios are examples of recycling, in which one lifecycle concludes (first End_condition) and another begins afterwards (second Initial_condition). Both scenarios also contain patterns nested within other patterns. Thus, we see how a small, minimal MP model of a cycle can lead to potentially thousands of process combinations, before constraints are added to shape, govern, or otherwise bring order to a system’s behavior.
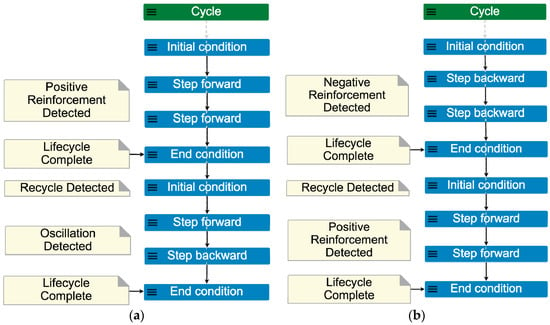
Figure 7.
Example event trace outputs of the Cycle_ISP_v2 model, run for scope 2: (a) Lifecycle 1 contains positive reinforcement and Lifecycle 2 contains an oscillation pattern (trace 20); (b) Lifecycle 1 contains negative reinforcement and Lifecycle 2 contains positive reinforcement (trace 37). Both scenarios contain the recycling pattern.
2.2.2. Cycles ISP Model, Version 2, Scope 3
There are 2952 cycle instances generated at scope 3, revealing many more possible combinations of the identified patterns. Running the model at scope 3 increases the number of cycle movements within the patterns exposed at scope 2. As the number of scenarios increase into the thousands, manual inspection becomes impractical. MP has assertion checking and querying tools to check these large data sets for properties of interest, but the Small Scope Hypothesis affords us the convenience of exposing many patterns and pattern combinations on a small number of examples that are also present among the large number of examples.
2.3. Example Applications of Cycles across Different Domains
The main criterion for identifying a process as an ISP is testing for its isomorphic nature. This requires looking at many types of systems and scales of systems; otherwise, it would not fulfill the criteria for a general theory of how systems work. For SPT, this means examining the experimental results of many sciences and abstracting out similar, common, identical, alike structures, relationships, and patterns from the particulars of each discipline to more general descriptions (abstractions) of the steps in the process that are true of all of the specific systems. Abstraction followed by comparison is the key. Are the generalized steps the same even though the particulars going through the steps are not?
In his 90-min online InfoLab© lectures on 14 of the ISPs (for a graduate course, Intro to Systems Science for Systems Engineers, SE 510) for the purpose of providing more details on SPT, Troncale cites and describes numerous case studies from the conventional sciences for each ISP. Each case study is from a phenomenon experimentally elucidated by one of the sciences. These included case studies of real, proven phenomena from Astronomy, Cosmology, Physics, Chemistry, Geology, Biology, Mathematics, and Computer Science as reported in the reductionist science literature. Recently, these have been expanded by additional case studies from the various Human Sciences, Engineering, and a category entitled, “interdisciplinary”.
Specifically for the ISP Cycles, the aforementioned SE 510 lecture cited 87 case studies of cycling occurring in the above named sciences. To test the application of the Cycles ISP MP model in different domains, we selected four case studies from [9] and substituted discipline-specific event names from the case studies for domain-independent event names in the Cycles ISP MP model (Table 1). The four case studies selected were cell division, human diurnal activity, geological activity, and a beating heart.

Table 1.
Event discinyms for four example domain-specific types of cycles.
After making the event name substitutions shown in Table 1, we ran the domain-specific MP models and obtained the cycle model scenarios for each domain. Figure 8 shows four examples of oscillation from different domains, each of which map onto the same Cycle model.
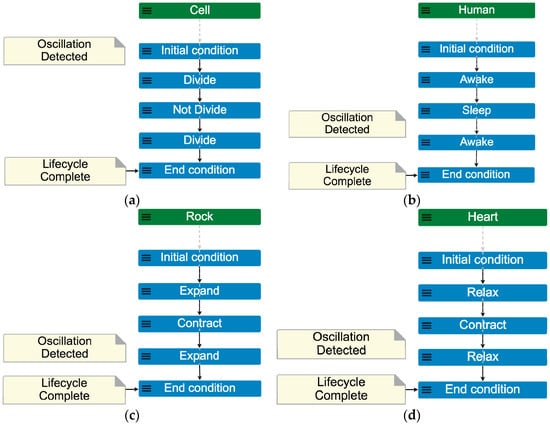
Figure 8.
Example outputs from the constrained Cycle_ISP_v2 model (trace 7 in each case), with discinyms substituted for Move_forward and Move_backward, and run for scope 3: (a) process of cell division; (b) process of diurnal activity in humans; (c) process of geological activity; (d) process of a beating heart.
Note once more the effect of limiting the scope, to 3 in this case: only three iterations occur in each example, but it is enough for the oscillation pattern to be quite visible. Additional types of cycles and variants are left for exploration in future work.
3. Results
A simple formal model of the Cycles ISP starting with just two lines of MP code (version 1) exposed patterns of oscillation, positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, and combinations thereof. Revisions to this model (version 2) contained six lines of code and exposed these same patterns plus additional patterns of lifecycle, recycling, and all combinations thereof. Table 2 provides the run statistics for the number of cycle examples produced at each scope and the scenario generation times on MP-Firebird.

Table 2.
Cycles ISP MP model run statistics.
The number of possible combinations of unique cycle patterns is visible in the exponential growth in the number of scenarios as scope increases. From a small model of six lines of code, we see that thousands of cycle scenarios are possible. These numbers represent the exhaustive set of cycle model scenarios, providing full coverage of possible outcomes up to the indicated scope [10].
An objective of this research was to see if any MP behavior scenarios presented mini-models of previously discussed variants for the Cycle ISP. We indeed found patterns for oscillation, recycling, and lifecycles in the MP model of the Cycle ISP. We did not isolate patterns for waves, solitons, iteration/recursion, spin, and hypercycles during this initial effort, but these may become evident after further inspection or refinement of the model and consideration of different discinyms for event names. The act of modeling may raise significant new questions about these currently considered variants on cycling that challenge the SPT community’s initial hypotheses of their being the same pattern as cycling. Constraining the list of variants on cycling would be an important advance in SPT and to applications of cycling to SE.
One surprising result from this research was the presence of both positive and negative reinforcements in the cycle examples. These were not anticipated or identified as directly associated with the Cycles ISP in previous SPT research. Cycles and Feedbacks are actually separate systems processes in the current consensus on SPT, if we consider positive and negative reinforcements as positive and negative feedbacks. SPT has linkage propositions that connect + and − feedback with oscillations, but this has been challenged by SE members of INCOSE in past International Workshop discussions. It appears models of real biological systems incorporate feedback to get oscillating behavior but that this is less known in the physical sciences. To have independently found them in MP event traces of cycling brings new information to the SE debate.
There is precedent for this development, from an MP modeling perspective. MP has delivered surprising scenarios before by containing unanticipated behavior examples in models by different users, of different systems, in different domains [33,37,39,41,44]. This research adds to the body of work showing MP’s ability to illuminate unexpected emergent behaviors, and potential to be put to use for the SPT research.
4. Discussion
The results summarized in the previous section are discussed in more detail in the subsections that follow.
4.1. Complex Cycle Examples Arose from a Simple Model of a Cycle
The first significant finding from formally modeling a cycle in MP was that such a simple model of a cycle (on the order of six lines of code) could produce such an impressively large and diverse number of “cycle instances” (nearly 3000 unique instances of cycle behavior when the model is run at scope 3). A very simple model of a cycle gave rise to a large number of behaviors whose complexity increased with run scope. This supports the notion that simple rules exist at the foundation of complex behaviors, and suggests that if we can distill and formalize these simple system and process behavior rules, we can (to some extent) reproduce more complex system behaviors in simulation for study and comparison with actual systems. MP also provides a capability to check for the presence or absence of model properties of interest in large sets of simulation instances. In practical terms, this means that, if we know or suspect a particular cycle instance could occur, we can query the data set to see if there are any examples of it. MP modeling therefore provides the SPT community with a means for formally testing, verifying and validating ideas that have to date only been informally discussed, debated, and refuted without automated tools to support the discourse.
4.2. Cycle ISP Patterns Previously Discussed and Described Informally Were Inherently Present among the MP-Generated Examples
Upon inspection of these automatically generated instances, it became apparent that some of the instances inherently contained similar patterns. The patterns that emerged, in fact, matched many of the identifying features for cycles that had been informally discussed and debated as part of the ongoing SPT research, including oscillation, recycling, and lifecycles. These results provide an affirmation that the earlier SPT discussions on cycling pertaining to the recognition of oscillations, recycling, and lifecycles as related ISPs was warranted and supported by results of the MP runs. There is a significant extension of this result. Just as MP generates many versions of the original ISP process in computer “space”, so also does nature in real systems generate many variants on cycling in real, dimensional space (e.g., through evolution). This MP feature could lead to the examination of the potential for generation of “artificial systems” de novo in computer space.
Furthermore, MP generated both singular and compound examples of patterns, i.e., examples that contained each pattern by itself, and patterns combined with or nested within other patterns. Moreover, because MP is exhaustive in its scenario generation, we can guarantee the set of examples generated contains every possible pattern combination expressible by the model up to the scope limit [10]. As discussed earlier, scope limit is a lightweight formal methods concept that places an upper bound on the number of event iterations in the model in order to limit the simulation run time. The Small Scope Hypothesis [47] is used as a heuristic to enable us to find most of what we are interested in knowing about cycles at a small run scope (typically scopes 1, 2, or 3). Cycle patterns that present at scopes 4 and 5 are also expected to present in some shape at scope 3. Prior experiments with run scopes [48] lend some confidence to this heuristic, but these current assumptions for MP can also be tested for the Cycles ISP model as part of follow on work.
By implication, the recognition of some known patterns in the generated example set suggests that several other possible variants on cycling should also be explored. Waves, solitons, iteration/recursion, spin, and hypercycles [9] are some of the other recognized variants of the Cycle ISP that were not observed in scenarios arising from the current Cycles ISP MP model, but the as-is MP model of a cycle provides a canvas for exploring how these variants could also possibly emerge from this model or from a revised model containing refinements informed by reasoning with MP tools. The Cycles ISP MP model lays the groundwork for follow on research to determine whether the aforementioned variants should be considered as the same thing as the Cycling ISP or as completely independent ISPs. Such experiments should support the development of a repeatable methodology for using MP modeling to inform SPT research on this question and across all the 110 candidate ISPs.
4.3. Positive and Negative Reinforcements Emerged in the Cycle Examples
Although the previously discussed patterns had been recognized and debated in SPT research, we did not even discover, recognize or debate the involvement of two additional behaviors until the MP modeling exposed them: namely, “reinforcements”. Among the Cycles ISP MP model examples were completely unforeseen influences and essential participation of both positive and negative reinforcements as part of the process. Reinforcements have commonly known relationships with cycles, but we did not foresee them emerging in examples from the Cycles ISP MP model. Positive and negative feedback had been argued by one SPT cohort as necessary for oscillation to occur; however, other cohorts disagreed. The presence of these patterns could provide a basis for reasoning about how positive and negative reinforcements influence cycling, as well as what “reinforcement” actually means in models of real phenomena. This discovery opens the door to a further line of questioning: How can emergent patterns and behaviors like this inform the aforementioned debates? How were these cycling, and how likely was each instance? Should they each be explored as individual isomorphs, or be considered variations on each other? How many additional behaviors could MP discover for SPT for the other 54 or 110 ISPs?
4.4. Implications for Systems Science Research
Modeling SPTs using MP provides a promising virtual “systems laboratory” to examine billions of years of optimization or improvement or evolution of natural systems. The basic tenet of SPT is that the reason we now can see and empirically or experimentally prove the existence of common patterns (ISPs) is that all of these systems, composed of entirely different parts, originating at different times, at totally different scales, across many types of systems, solve their myriad challenges by “falling into” these common isomorphic dynamics or solutions. By definition, SPT models are prescriptive and not just descriptive. This is their distinction from other System Dynamics (SD), or Soft Systems Methodology (SSM), or Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) models. They do not compete with those; they should be added to those as the possibly prescriptive component.
5. Conclusions
The various teams working on SPT have been exploring SPT research as a candidate for a General Systems Theory (GST) and for systems science, both of which need a means for testing abstract models. This research answered the question, “How do you test abstract models of systems?” By modeling the Cycles ISP using MP, we were able to test and reason about cycles in a new and formal way, using automated tools to unravel and expose the inherent patterns within cycles occurring both alone and in groups. This paper thus established productive applicability of MP software to the SPT problem space, in which MP event traces could comprise a library of mini-models envisioned for each ISP.
Earlier discussions about cycles and other ISPs were based on natural language descriptions and informal models at best. None of the discussions were supported with formal models of behavior like the cycle model contained herein. MP was tried as a tool for generating mini-models of systems mechanisms that are general and discipline-independent. Cycle behavior was described as a set of step-by-step procedures—an algorithm—that was executable in computer space to see many possible instances and variants of cycles. These mini-models of cycle instances did generate additional information about cycles that had not been obtained to date by comparison of the real systems counterparts to the modeled mechanism (specifically, illustrating the connection of positive and negative reinforcements to cycles). It also demonstrated that many of the known cycle variants arise from a single compact formal specification of cycle behavior. The MP model of just one ISP was a source of new knowledge about the mechanism for that individual ISP, showing that MP is a productive framework for describing the Cycles ISP as a formal and executable model, in terms of a simple and straightforward event grammar.
The abstract Cycles ISP MP model shown in Figure 6 was tested in four different domains by adapting the event name language as shown in Table 1. The MP simulation results of each model “unraveled” specific instances of cycles that fit the patterns previously considered distinct ISPs. In Figure 5, we have evidence from the MP simulation runs that some ISPs previously considered as separate from cycles are in fact special cases of cycles. Figure 8 shows the oscillation pattern emerging from each of the four domain-specific cycle models tested, demonstrating the isomorphic nature of the Cycles ISP. MP provides automation to facilitate the study of how ISPs are related, and opens the door to future work in this area.
6. Future Work
Since the use of MP achieved both extension of our knowledge base of cycles and cycling and at the same time provided the means to test that knowledge base, we consider it a promising potential source of significant advancements in both general theories and specific applications. Future work will apply instances of the Cycles ISP in several different domains to generate more concrete examples of where these patterns occur, and which deviations might result in system dysfunctions or pathologies. MP will be used as an experimental framework for collecting synthetic data about modeled ISPs for comparison to empirical data collected from real world systems, opening a new avenue for hypothesis testing for SPT. Knowledge gained through the use of automated modeling tools like MP might contribute to knowledge of why deviations from expectation occur at the fundamental general systems level, what exact impacts they have, and how they might be corrected, especially when modeled in the context of interactions with other systems. Producing more models of many ISPs would allow placing the abstracted model in computer space for artificial systems research [7]. Additional steps would then be taken to integrate other proposed ISPs into an overall SPT-MP meta-model, creating more exploratory executions of ISP behaviors and eventually of ISP interactions, and cataloging the formal MP models of ISPs. The ultimate goal would be to interconnect a sufficient number of the ISPs to yield a very general model of sustainable systems dynamics at all scales and for many types or classes of systems as well as models of dysfunction that are often encountered in engineering and natural systems.
Another fascinating challenge would be to encode the SPT Linkage Propositions (LPs) that describe behavioral influences of one ISP on any other or between many ISPs [49]. This activity would be expected to challenge and yield strong benefits or expansions of understanding of both SPT and MP. For example, how could one encode LPs (perhaps the most creative and original contribution of SPT) in MP models, given that it itself explores behavioral alternatives? How would MP handle hundreds of LPs? Would such MP SPT systems models then more adequately approach or explore such conundrums as “complexity” and “emergence” which are of great interest to both systems engineers and systems scientists?
Beyond the LP extension of individual ISP MP models, future work could include using MP to explore another line of research spun off from SPT, namely, Systems Pathology. MP has already demonstrated its ability to expose the negative aspects of a process, i.e., how systems don’t work or dysfunction [27,39]. Once the alternative behaviors of an ISP are modeled, MP could be used to eliminate some of the behaviors, constraints, or LPs and assess how this changed or caused dysfunction in the normal operation of an ISP in various and changing environments and contexts.
MP provides a virtual systems laboratory for reasoning about the behaviors of systems based on a series of events that unfold given the presence or absence of linkages or dependencies. MP may be used in the future to support or refute various claims made about cycles and other ISPs, leveraging the formality it brings to the description of ISPs and their various manifestations.
Author Contributions
K.G. wrote the MP models, performed the experiments, and contributed the descriptions of the MP framework to the paper. L.T. provided the source data for the models, contributed the descriptions of the SPT, and documented the implications. Both K.G. and L.T. wrote the Introduction, Conclusions, and Future Work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. No sponsor had a role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Troncale, L. Linkage Propositions Between Systems Isomorphies. In A General Survey of Systems Methodology; Troncale, L., Ed.; Intersystems Publ.: Seaside, CA, USA, 1982; Volume I, pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Friendshuh, L.; Troncale, L. SoSPT I: Identifying Fundamental Systems Processes for a General Theory of Systems (GTS). In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Conference, International Society for the Systems Sciences (ISSS), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–20 July 2012; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, C.; Troncale, L. SoSPT II: How to Find & Map Linkage Propositions for a General Theory of Systems from the Natural Sciences Literature. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Conference, International Society for the Systems Sciences (ISSS), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–20 July 2012; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Troncale, L. SPT V: Proving Isomorphy by 52 Case Studies: Testing for Cycles and Cycling Across Disciplines, Domains, and Scales. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Conference, Int’l Society for the Systems Sciences (ISSS), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–20 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Troncale, L. SysInformatics and Systems Mimicry: New Fields Emerging from a ‘Science’ of Systems Process Engineering. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Systems Engineering Research, Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 21–22 March 2014; Elsevier: New York City, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Troncale, L. Pre-requisites, Discinyms, Discriminations & Mutuality in the SPT (a poster showing 26 discinyms for 6 SPs). In Proceedings of the 51st Annual ISSS Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 5–10 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Troncale, L. Would A Rigorous Knowledge Base in Systems Pathology Add Significantly to the SE Portfolio. In Proceedings of the CSER’11 Proceedings, Conference on Systems Engineering Research, Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 14–16 April 2011; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- INCOSE Systems Science Working Group. SSWG Wiki Site. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/syssciwg/ (accessed on 26 May 2018).
- Troncale, L. Intro to Cycles, Lifecycles & More as an Isomorphic Systems Process; SE 510 Lab 5 Course Lecture Notes, Masters Program in Systems Engineering; California State Polytechnic University: Pomona, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M. System and Software Architecture and Workflow Modeling Language Manual (Version 3). 2018. Available online: https://wiki.nps.edu/display/MP/ (accessed on 26 May 2018).
- Auguston, M. Software Architecture Built from Behavior Models. ACM SIGSOFT Softw. Eng. Notes 2009, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguston, M. Monterey Phoenix, or How to Make Software Architecture Executable. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN conference companion on Object oriented programming systems languages and applications (OOPSLA’09), Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 October 2009; pp. 1031–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M.; Whitcomb, W. System Architecture Specification Based on Behavior Models. In Proceedings of the 15th ICCRTS Conference (International Command and Control Research and Technology Symposium), Santa Monica, CA, USA, 22–24 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M.; Whitcomb, C.; Giammarco, K. A New Approach to System and Software Architecture Specification Based on Behavior Models. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Model-Based Systems Engineering (IC-MBSE 2010), Fairfax, VA, USA, 27–28 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.; Auguston, M.; Finkbine, R. Applying Architecture Modeling Methodology to the Naval Gunship Software Safety Domain. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Systems & Software Technology Conference (SSTC 2011), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 16–19 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M.; Whitcomb, C. Behavior Models and Composition for Software and Systems Architecture. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Software & Systems Engineering and their Applications (ICSSEA 2012), Paris, France, 23–25 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Auguston, M.; Sun, J.; Song Dong, J. Using Monterey Phoenix to Formalize and Verify System Architectures. In Proceedings of the 19th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC 2012), Hong Kong, China, 4–7 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K.; Auguston, M. Well, You didn’t Say not to! A Formal Systems Engineering Approach to Teaching an Unruly Architecture Good Behavior. In Proceedings of the Complex Adaptive Systems Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 13–15 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Farah-Stapleton, M.; Auguston, M. Behavioral Modeling of Software Intensive System Architectures. In Proceedings of the Complex Adaptive Systems Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 13–15 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K.; Auguston, M.; Baldwin, W.C.; Crump, J.; Farah-Stapleton, M. Controlling Design Complexity with the Monterey Phoenix Approach. In Proceedings of the Complex Adaptive Systems Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 3–5 November 2014; pp. 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M. Behavior Models for Software Architecture; NPS Technical Report NPS-CS-14-003; Naval Postgraduate School: Monterey, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb, C.A.; Auguston, M.; Giammarco, K. Composition of Behavior Models for Systems Architecture. In Modeling and Simulation Support for System of Systems Engineering Applications; Rainey, L.B., Tolk, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 361–391. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Auguston, M.; Sun, J.; Song Dong, J.; Chen, T. Formalizing and verifying stochastic system architectures using Monterey Phoenix (SoSyM abstract). In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM/IEEE 18th International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems (MODELS), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 30 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Auguston, M.; Giammarco, K.; Baldwin, W.C.; Crump, J.; Farah-Stapleton, M. Modeling and Verifying Business Processes with Monterey Phoenix. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 44, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Auguston, M.; Sun, J.; Dong, J.S.; Chen, T. Formalizing and verifying stochastic system architectures using Monterey Phoenix. Softw. Syst. Model. 2016, 15, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah-Stapleton, M.; Auguston, M.; Giammarco, K. Executable Behavioral Modeling of System and Software Architecture Specifications to Inform Resourcing Decisions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 95, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammarco, K.; Auguston, M. Behavior modeling approach for the early verification and validation of system of systems emergent behaviors. In Engineering Emergence: A Modeling and Simulation Approach; Rainey, L.B., Jamshidi, M., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, in press.
- Quartuccio, J.; Giammarco, K. A model-based approach to investigate emergent behaviors in systems of systems. In Engineering Emergence: A Modeling and Simulation Approach; Rainey, L.B., Jamshidi, M., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, in press.
- Warfield, J.N. An Introduction to Systems; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J. Software System Architecture Modeling Methodology for Naval Gun Weapon Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, T.L. Generating GraphML XML Files for Graph Visualization of Architectures and Event Traces for the Monterey Phoenix Program. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, S.S. Model Based Systems Engineering in the Execution of Search and Rescue Operations. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher, J.D. Generation of Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DODAF) Models Using the Monterey Phoenix Behavior Modeling Approach. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Steward, V. Functional Flow and Event-Driven Methods for Predicting System Performance. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J. Un-Building Blocks: A model of Reverse Engineering and Applicable Heuristics. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel, S. System Behavior Models: A Survey of Approaches. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Revill, M.B. UAV Swarm Behavior Modeling for Early Exposure of Failure Modes. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farah-Stapleton, M. Executable Behavioral Modeling of System and Software Architecture Specifications to Inform Resourcing Decisions. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K.; Giles, K. Verification and validation of behavior models using lightweight formal methods. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference on Systems Engineering Research, Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 23–25 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K. Practical Modeling Concepts for Engineering Emergence in Systems of Systems. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 18–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K.; Giles, K.; Whitcomb, C.A. Comprehensive use case scenario generation: An approach and template for modeling system of systems behaviors. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 18–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Quartuccio, J.; Giammarco, K.; Auguston, M. Identifying Decision Patterns Using Monterey Phoenix. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 18–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Quartuccio, J.; Giammarco, K.; Auguston, M. Deriving Stochastic Properties from Behavior Models Defined by Monterey Phoenix. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 18–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K. Verification and Validation (V&V) of System Behavior Specifications; Interim Technical Report; Systems Engineering Research Center: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K.; Allen, B. Methodologies and Patterns for Model Centric Systems Engineering; NPS-SE-18-002, Naval Research Program; Naval Postgraduate School: Monterey, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, K. Mission-Based Architecture for Swarm Composability. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D. Software Abstractions: Logic, Language, and Analysis; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giammarco, K. Architecture Model Based Interoperability Assessment. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Troncale, L. Linkage Propositions between Fifty Principal Systems Concepts. In Applied General Systems Research: Recent Developments and Trends: N.A.T.O. Conference Series II. Systems Science; Klir, G.J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).