Abstract
Specialized, Refined, Differentiated, and Innovative (SRDI) enterprises are crucial to China’s economic development. It is important to examine how various factors’ combinations impact the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises in order to promote high-quality regional economic development. Based on the Technology–Organization–Environment (TOE) framework, this study selected SRDI enterprises as research samples, used a hierarchical clustering algorithm to divide the enterprises into groups according to the characteristics of SRDI enterprises, and employed a classification and regression tree (CART) algorithm to reveal the complex nonlinear relationships between the combinations of multiple key influencing factors and radical innovation performance from multi-source big data. The findings indicate that (1) there are significant variations in the factors affecting the radical innovation performance of different types of SRDI enterprises; (2) the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises stems from the synergistic interaction among various factors; and (3) the impact of R&D investment on radical innovation is not simply linear. This study effectively captures the complex nonlinear relationships between combinations of multiple influencing factors and radical innovation performance. It is of great practical significance for revealing SRDI enterprises’ radical innovation performance improvement pathways and enhancing their innovation capability.
1. Introduction
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are crucial for driving a country’s economic development [1]. In recent years, the Chinese government has aimed to facilitate industrial transformation and upgrading by fostering Specialized, Refined, Differentiated, and Innovative (SRDI) enterprises, also referred to as Chinese-style “Hidden Champions”. To support this initiative, various policies and subsidies have been introduced to incentivize SMEs to pursue Specialized, Refined, Differentiated, and Innovative paths. Hidden Champions is a term coined by Hermann Simon. It refers to SMEs that concentrate on a specific market segment, hold a leading position, and are regarded as the backbone of Germany’s economic development [2]. Cultivating Hidden Champions has become an important development goal for many developing countries [3]. Innovation is an essential feature of Hidden Champions and is critical for gaining a competitive advantage. As latecomers to the market, Chinese SMEs are confronted with intense competition and need assistance in adapting to rapidly changing technological requirements using progressive innovation models. It is urgent to achieve technological catch-up through the radical innovation of existing products or services [4]. Although the Chinese government has continuously strengthened the cultivation of SRDI enterprises, these enterprises still face the dilemma of high birth rates, low survival rates, and high mortality due to the lack of innovation [5]. Research on improving the innovation ability of SRDI enterprises will help with understanding how to develop them and offer valuable insights for developing countries to allocate resources effectively and create an environment that supports SMEs’ growth, thus contributing to high-quality economic development.
Radical innovation plays a significant role in driving technological progress and industry transformation [6]. Currently, numerous studies have delved into the factors that influence the innovation performance of SMEs. For instance, regarding enterprise cooperation strategy, Audretsch et al. [7] showed the varying impact of different types of partners on the innovation performance of British SMEs. Hervas-Oliver et al. [8] pointed out that an excessively high degree of enterprise agglomeration leads to being trapped in a mindset and technological lock-in, thus inhibiting radical innovation exploration. Additionally, some scholars have explored the impact of internal development strategies on radical innovation performance. For example, Lei et al. [9] examined how the cognitive structure and strategy formulation of China’s “hidden champions” affects innovation. Flor et al. [10] emphasized that the knowledge absorption capacity is the foundation for enterprises to carry out radical innovation. Some other scholars believe that an enterprise’s technological innovation is not only related to the external environment but also closely connected with the enterprise’s technological level and the socio-economic environment [11]. As a highly general and comprehensive analytical framework, the TOE framework is applicable to different research content and themes [12]. It is one of the most widely used theories by scholars when systematically identifying the internal and external factors affecting enterprises’ technological innovation. The TOE framework, which examines the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions, provides a systematic approach to analyzing the driving and hindering factors of enterprise technological innovation. Numerous scholars have utilized the TOE framework to investigate the factors influencing enterprises’ innovation performance [13]. However, most studies have been limited to exploring the linear or simple nonlinear effects of technology, organization, and environment on innovation performance. Although some research has acknowledged that the factors within the TOE framework do not operate in isolation, few studies have adopted a comprehensive perspective to delve into the complex nonlinear effects of individual factors and their combinations on enterprises’ radical innovation performance, as well as the synergistic interactions among these factors. Moreover, little attention has been paid to the heterogeneous characteristics of enterprises, and few studies have adopted a differentiated perspective to explore the varying key factors and their combinations that influence radical innovation performance under different contexts.
Therefore, in order to effectively identify the key factors affecting the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises and delve deeper into the complex mechanisms influencing radical innovation performance, this study adopts the TOE theoretical framework and employs a data-driven research approach. By integrating machine learning methods into the study of enterprise innovation management, this study aims to explore the pivotal influencing factors and diverse pathways for promoting radical innovation in Chinese SRDI enterprises based on objective data. Ultimately, this research uncovers valuable insights into the innovative growth of SMEs in China and offers practical suggestions for enterprise managers and policymakers. This study intends to answer the following questions: (1) What are the differences in the characteristics of different types of SRDI enterprises, and which types of enterprises are more likely to achieve radical innovation performance improvement? (2) How do the combined effects of multiple factors impact radical innovation performance in SRDI enterprises, and which factors are crucial in this regard? (3) Which combinations of characteristics of SRDI enterprises are more likely to result in radical innovation performance, and what are the influencing pathways?
The remainder of this study is organized as follows. Section 2 presents a literature review and summarizes past research and academic perspectives. Section 3 introduces the research framework and machine learning approaches. Following this, Section 4 outlines the variables used. Section 5 processes the related data and reports the research findings. Finally, Section 6 provides a summary of the conclusion and discussion.
2. Literature Review
To explore the influencing pathways of the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises, this study compiled the relevant research.
2.1. Radical Innovation Performance
In 1934, Schumpeter first introduced the concept of “innovation”, emphasizing its significance for economic development [14]. Innovation can be categorized into radical and incremental based on its degree of novelty. Radical innovation involves overthrowing existing technology and is seen as a breakthrough in overcoming innovation barriers. While radical innovation helps enterprises establish core competitiveness, it requires high investment and entails significant innovation risks due to its difficulty to imitate [15]. Promoting the growth of radical innovation performance is a focal issue of concern for all sectors of society. Researchers have focused on the factors influencing radical innovation performance in enterprises from internal and external perspectives.
From an internal perspective, researchers have emphasized that the primary factors influencing enterprises’ radical innovation performance reside in their organizational resources and capabilities, such as their human capital endowment, knowledge base, and strategic planning capabilities. Yang and Zheng [16] empirically examined the relationship between employees’ educational attainment and corporate innovation capabilities, and emphasized that highly educated employees are better at knowledge integration, effectively lowering the costs of knowledge acquisition and the uncertainties associated with innovation, thereby more significantly enhancing enterprises’ radical innovation performance. Genin et al. [17] systematically investigated the impact of the collective knowledge capital within employee teams on organizational innovation performance and discovered that boards with diverse experience, comprising members with different educational and industry backgrounds, as well as work experience, are more conducive to radical innovation activities. Chirico et al. [18], from an enterprise-wide perspective and grounded in organizational inertia theory, revealed that family enterprises are more likely to become conservative due to path dependency, leading them to focus on incremental innovation while reducing their exploration of radical innovation.
From an external perspective, the market environment plays a particularly significant role in driving enterprise innovation. Numerous scholars have focused on how enterprises can respond to changes in a market environment by participating in innovation networks and industrial clusters to facilitate knowledge sharing and technological exchange. For example, Pan et al. [19] suggested that collaborating with peers might slow radical innovation, while forming partnerships with research institutes and government agencies could speed it up. Chesbrough and Brunswicker [20] identified three primary measures that help large companies achieve innovation: engaging in customer co-creation, maintaining informal networks, and funding university projects. Battistella et al. [21] argued that customers, universities, and suppliers are common partners that incentivize enterprises to pursue innovation. Hervas-Oliver et al. [8] discussed how geographic agglomeration affects radical innovation, finding that a high industrial concentration causes enterprises to engage in local over-searching and leads to imitative rather than substantive radical innovation.
2.2. Technology–Organization–Environment Framework
The Technology–Organization–Environment (TOE) framework, first proposed by Tornatzky in 1990, divides the factors affecting the adoption of technological innovation by enterprises into three levels: technology, organization, and environment [22]. At the technology level, it mainly includes the technical resources and capabilities available within an enterprise, such as technology availability and innovation. The organization level mainly focuses on the internal structure, management system, and cultural atmosphere. The environment level refers to the external environment of an enterprise, including factors such as policies and regulations, industrial ecology, and market competition. Many scholars have realized that the influence of the different factors on enterprises’ innovation performance is interconnected, and these factors jointly affect enterprises’ innovation performance through various combinations.
The influence of technology on innovation in enterprises has been widely discussed by scholars. For instance, Hu et al. [23] argued that technological innovation is the core capability of technology-intensive enterprises, which are usually willing to invest heavily in research and development. Some scholars believe that substantial R&D investment may burden enterprises financially, thus hindering innovation activities. Yin et al. [24] demonstrated that R&D investment has a positive impact on enhancing the innovation performance of SMEs, with the moderating effect of external environmental factors. They believed that R&D investment had a more significant effect on improving innovation performance when the business environment was poor.
In addition, the impact of organizational factors on enterprise innovation is also a perpetual concern for scholars. According to the research of Winter [12], Schumpeter first discussed the relationship between organization size and enterprise innovation, and he believed there was a positive correlation between enterprise size and innovation, and that only large-scale enterprises could bear R&D costs and innovation risks. Since then, many scholars have tested the Schumpeter hypothesis through empirical studies. Jugend et al. [25] concluded that, contrary to Schumpeter’s study, the larger the enterprise, the less likely it is to carry out radical innovation, and vice versa. Xing et al. [26] concluded that smaller enterprises tend to be conservative in their innovation investment, and it is difficult for them to bear the risks that innovation may bring. In contrast, large-scale enterprises can enhance their innovation performance by reducing production costs and improving production efficiency. Van de Vrande et al. [27] emphasized that SMEs exhibit greater enthusiasm for engaging in innovation activities compared to large enterprises. However, they face significantly more obstacles in the processes of knowledge acquisition and commercialization.
From an environmental perspective, Schumpeter also emphasized that there is a positive correlation between the degree of industry competition and innovation, and monopolies with market power are more likely to obtain technological innovation results. The earliest response to Schumpeter’s hypothesis from an environmental perspective was put forward by Arrow, who emphasized the delaying effect of a monopoly on technological progress, and believed that a competitive market is more conducive to stimulating enterprises to carry out innovation activities than a monopoly market [12]. Since then, the discussion about the influence of market factors on innovation has intensified. Park et al. [28] believed market competition can stimulate enterprises’ awareness of crisis and promote innovation. However, excessive competition can make enterprises worry about knowledge leakage and reduce collaboration, leading to low innovation output. Nam et al. [29] argued that competition is essential for promoting technological innovation in enterprises. Due to the market uncertainty caused by competition, enterprises must always pay attention to the dynamics of their competitors to adjust their strategies, thereby reducing the risk of a competitive disadvantage through innovation. At the same time, other scholars have added other environmental factors, such as government policies and subsidies [30] and cooperative relationships [31], to the discussion.
The existing research has identified a variety of factors influencing enterprises’ radical innovation and has explored these factors from both internal and external perspectives. However, traditional studies have paid insufficient attention to the interactions between internal and external factors and their combined effects. To address this gap, some scholars have effectively integrated the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions through the TOE framework, providing a comprehensive perspective to explain the mechanisms for enhancing enterprises’ radical innovation. For example, Yin et al. [24] argued that technological and environmental factors have a combined impact on enterprise innovation performance, and demonstrated that R&D investment has a positive impact on enhancing the innovation performance of SMEs, with the moderating effect of external environmental factors. They believed that R&D investment had a more significant effect on improving innovation performance when the business environment was poor. Xing et al. [26] emphasized that digital transformation alone cannot determine the level of enterprise innovation performance, as relying solely on a single technological factor is insufficient to effectively enhance innovation performance. Instead, the improvement of innovation performance depends on the synergistic effects of multiple factors across the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions. Shang et al. [32] highlighted that organizational capabilities are a core condition for enhancing enterprise innovation, but they also require a certain level of technological foundation and support from the external environment.
Based on the literature review above, it is evident that many scholars have explored the factors influencing enterprises’ radical innovation performance. However, numerous studies have not adopted a comprehensive perspective to simultaneously analyze the impact of multi-dimensional factors on radical innovation performance. Some scholars have utilized the TOE framework to examine the influence of factors from the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions on enterprise innovation performance. Yet, most of these studies have focused solely on linear or simple nonlinear relationships between these factors and radical innovation performance, with limited research delving into the complex nonlinear interactions and combined effects of factors across the three dimensions from a holistic TOE perspective. Furthermore, the majority of the existing research has overlooked the heterogeneous characteristics of enterprises, instead adopting a generic perspective to explore the influencing factors and pathways for enhancing radical innovation performance. This approach has often failed to yield targeted conclusions or actionable managerial insights. Therefore, it is imperative to introduce machine learning methods, such as clustering and decision tree algorithms, to uncover the complex nonlinear mechanisms through which factors across the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions influence the radical innovation performance of different types of enterprises. By leveraging objective data, this approach can reveal diverse pathways for enterprises to enhance their radical innovation performance, offering new perspectives and references for enriching theoretical research in enterprise innovation management.
3. Methodology
Given the limitations of previous studies, this study aims to introduce a machine learning approach to examine the pathways for improving radical innovation performance in SRDI enterprises. The main research ideas and methods are as follows.
3.1. Research Framework
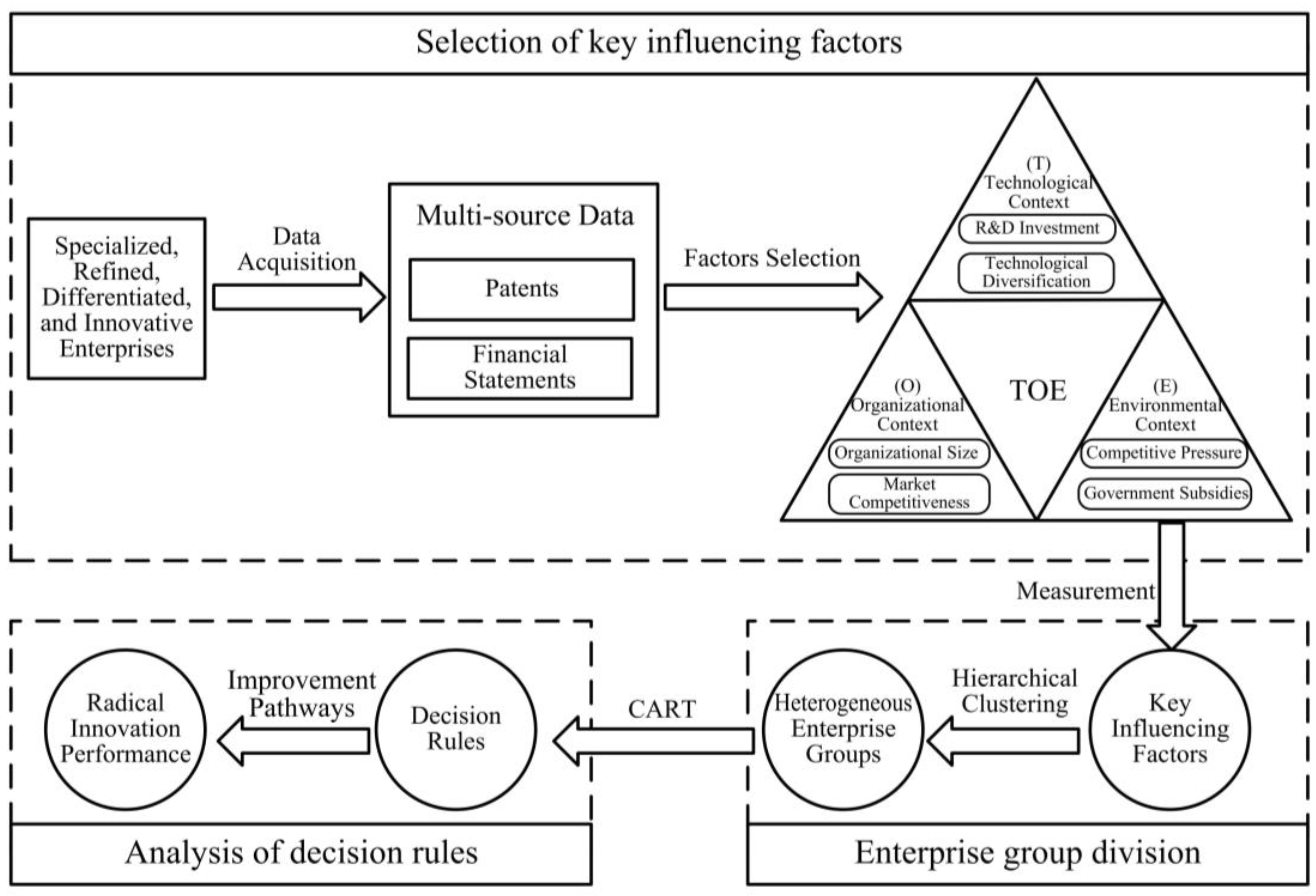
In order to specifically explore the combinations of influencing factors and promotion pathways on radical innovation performance of different types of SRDI enterprises, this study mainly consisted of three parts. Firstly, we selected key influencing factors. Key factors that affect the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises were identified using multi-source data, such as patents and financial statements, that were analyzed based on the TOE framework and existing literature. Secondly, we conducted enterprise group division. A hierarchical clustering algorithm was used to identify different types of SRDI enterprises. Meanwhile, their characteristics were further compared and analyzed. Finally, we performed an analysis of decision rules. By considering the technology, organization, and environment characteristics of different types of SRDI enterprises as conditional attributes and radical innovation performance as the decision attribute, potential rules for improving radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises were obtained using the CART algorithm. The specific research framework is shown in Figure 1.
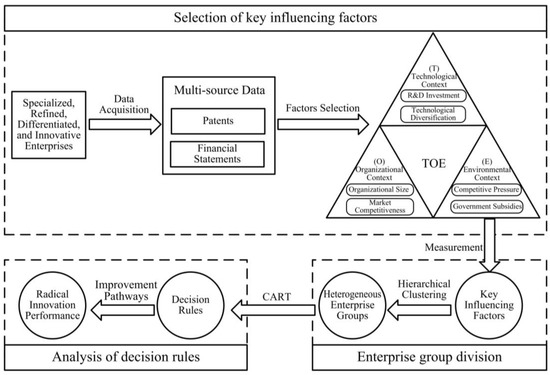
Figure 1.
Research framework.
3.2. Machine Learning Approaches
The traditional research approach involves forming hypotheses or models beforehand and then testing these with statistical analysis methods. This method can fully explain a linear or simple nonlinear relationship between variables. Still, it is challenging to explore a complex nonlinear action mechanism between variables deeply, so it is necessary to incorporate machine learning algorithms to uncover these complex relationships [33].
To understand how radical innovation performance varies across different types of enterprises while considering individual differences, this study utilizes clustering algorithms to group similar enterprises. Unsupervised clustering algorithms are machine learning methods for identifying and dividing groups of similar things into clusters without prior knowledge of the classification labels [34]. Among various clustering methods, this study selected the hierarchical clustering algorithm primarily for the following reasons: First, hierarchical clustering does not require a pre-specified number of clusters, thereby ensuring the objectivity of the clustering. This is particularly important for exploratory research where the optimal number of clusters is typically unknown, as it avoids introducing potential biases from manually setting the number of clusters. Second, hierarchical clustering can generate a dendrogram, visually representing the relationships between different data clusters, thereby providing a clearer understanding of the data structure. This study uses a cohesive hierarchical clustering algorithm based on its groupings of the distance between the data samples and follows a bottom-up approach. It starts by forming a cluster for each data sample and then iteratively merges clusters with the smallest distance between them, gradually forming larger clusters until all data samples are in one cluster or a specific termination condition is met. The aim is to use the hierarchical clustering algorithm to identify distinct and specialized SRDI enterprise groups, facilitating the subsequent comparative analysis of different enterprise characteristics.
A CART decision tree algorithm is a machine learning algorithm used to solve classification and regression problems [35]. The advantage of a CART algorithm is its ability to handle both continuous and discrete data without making assumptions about data distribution, making it widely applicable. Additionally, a CART algorithm uses the Gini Index for node splitting, which ensures high computational efficiency and reduces bias from multi-category features [36]. Moreover, the results of a CART algorithm are highly interpretable, as it presents the decision-making process in the form of a tree diagram, which can easily be translated into clear classification rules. Therefore, this study employs a CART algorithm to help understand how different variables collectively influence the radical innovation performance of enterprises. The CART algorithm divides the data set into subsets with lower impurity according to the Gini coefficient and generates a tree structure that accurately classifies the data or makes regression predictions. In the tree structure, the leaf nodes represent the classification results, while the inner nodes represent the test conditions for property division. The path from the root node to each leaf node represents the decision rule under the combination of conditional attributes. In this study, it presents the complex relationships between variables in a visual tree structure. This study uses the CART decision tree algorithm to construct decision trees with key influencing factors for different enterprise groups as conditional attributes and radical innovation performance as decision attributes. After pruning the decision trees, decision rules are extracted to analyze the complex nonlinear relationships between the radical innovation performance of different types of SRDI enterprises and their various combinations of key factors.
4. Variable Selection and Measurement
The TOE framework has been shown to be adaptable and can systematically evaluate the allocation and development of organizational resources [12]. This study selects technological diversification, R&D investment, organizational size, market competitiveness, government subsidies, and competitive pressure as the independent variables with which to study the radical innovation performance improvement pathways of SRDI enterprises, as detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Variable description.
4.1. Dependent Variable—Radical Innovation Performance
Previous studies have suggested that radical innovation significantly deviates from the original technology path, leading to substantial innovation in existing products and services. Currently, the identification of radical innovation primarily relies on the technological advantages of innovation. Similar to the research of Zhang et al. [15], this study regards invention patents as the concentrated representation of enterprise innovation. The natural logarithm of the invention patent volume plus one is used to measure the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises.
Here, Pn represents the number of invention patents held by enterprise n.
4.2. Independent Variables
(1) Technological Context
The technological context comprises two variables—technological diversification and R&D investment—which represent enterprises’ knowledge and technology level. Technological diversification reflects the accumulation of existing knowledge and technology resources [37], while R&D investment reflects the future innovation potential of enterprises to a certain extent [38]. In an increasingly competitive technological environment, enterprises must continually acquire new knowledge and develop new technologies to address their weaknesses and build core competitiveness [39]. As technology-intensive enterprises, technology innovation is the core ability of SRDI enterprises, and technology innovation requires significant funds. Increased R&D investment strengthens enterprises’ technological innovation ability. In most cases, enterprises need to manage a large number of technologies in the process of developing and producing products and services.
① Technological diversification (TD): According to the research of Chen et al. [40], the technical field involved is measured based on the three-digit international patent classification (IPC-3) of the patent, and the specific calculation formula is as follows:
where Pi represents the proportion of patents an enterprise has that contains the IPC number i, and N represents the number of IPC numbers an enterprise has. The greater the calculated entropy is, the higher the technological diversification is.
② R&D investment (RD): based on Chen et al. [41], this study uses the average ratio of R&D investment to operating revenue to measure the RD.
(2) Organizational Context
The organizational factors, including the organizational size and market competitiveness, are vital for providing resources for innovation activities. According to the resource-based theory, an enterprise’s competitiveness is influenced by its resources and capabilities, which is evident in factors such as the market profit rate and product market share. Enterprises need to allocate significant funds and resources for innovation activities, and those with strong market competitiveness are better positioned to secure financial support and R&D resources, thereby enhancing their ability to handle innovation risks [42].
① Organizational size (OS): concerning the research of Xu et al. [42], the average value of an enterprise’s total assets is used to measure the OS.
② Market competitiveness (MC): based on the measurement indicators of innovation performance from Zhang et al. [43], this study selects the ratio of the average operating profit to the average operating income to measure the MC.
(3) Environmental Context
Government subsidies and competitive pressure are environmental factors that describe SRDI enterprises’ institutional and business environments. Radical innovation is characterized by a long cycle, large investment, high risk, and high uncertainty. When enterprises cannot benefit from the market in the short term, their enthusiasm for innovation activities is affected. Effective government subsidies can offset some of the R&D costs for enterprises, creating a favorable institutional environment for technological innovation [44]. Several scholars have explored the impact of market structure on innovation in the business environment. Some studies have indicated that a highly competitive market environment encourages enterprises to increase their innovation efforts. Enterprises aim to identify the strengths and weaknesses of their products, marketing, and processes compared to those of their competitors, hoping to gain a competitive advantage by distinguishing their products or services.
① Government subsidies (GSs): according to the research of Chen et al. [41], GSs are measured using the natural logarithm of the total amount of various types of government subsidies for the period in the notes to the financial statements of the enterprises in the China Stock Market & Accounting Research Database (CSMAR).
② Competitive pressure (CP): Based on the research design of Lou et al. [45], this study adopts one minus the Herfindahl index value to measure the CP. A greater value indicates higher competition intensity within an industry.
5. Analysis and Results
5.1. Data Collection and Processing
“Little giant” enterprises are representative of SRDI enterprises which focus on market segments and have robust innovation capabilities, a high market share, mastery of the essential core technology, excellent production quality, and productive efficiency. As a result, this study selected “little giant” enterprises as the research samples. As of August 2023, China has cultivated five batches of state-level “little giant” enterprises, totaling 12.9 thousand. Since the listed companies are subject to comprehensive information disclosure requirements, offering high data transparency and accessibility, the listed “little giant” enterprises were selected as the research sample. However, ST and *ST enterprises, typically in financial distress, were excluded to prevent their abnormal data from skewing the experimental conclusions and to enhance the model’s predictive accuracy. The data for this study were primarily sourced from the CSMAR database and the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA). The patent data, comprising 200,789 records, including 109,565 invention patents, were obtained from the CNIPA. The financial data, R&D investment, the proportion of R&D personnel, government subsidies, and other relevant information from 2013 to 2022 were extracted from the CSMAR database and matched with the patent data. The matching process utilized the enterprises’ stock codes as unique identifiers to ensure data accuracy and consistency. This study conducted rigorous quality checks to guarantee the data quality, excluding companies with missing values across all variables over time. Following these data processing steps, a sample of 531 SRDI “little giant” listed enterprises was finalized. The data processing was primarily conducted using Pycharm 2020.3.3 and RStudio 2022.02.0+443, with Python version 3.9.7 and R version 4.0.2 employed to ensure compatibility and reproducibility. During the application of the CART algorithm to generate the decision rules, the “maxdepth” parameter was used to control the growth of the decision tree, ensuring an optimal balance between model complexity and interpretability.
5.2. Correlation Analysis
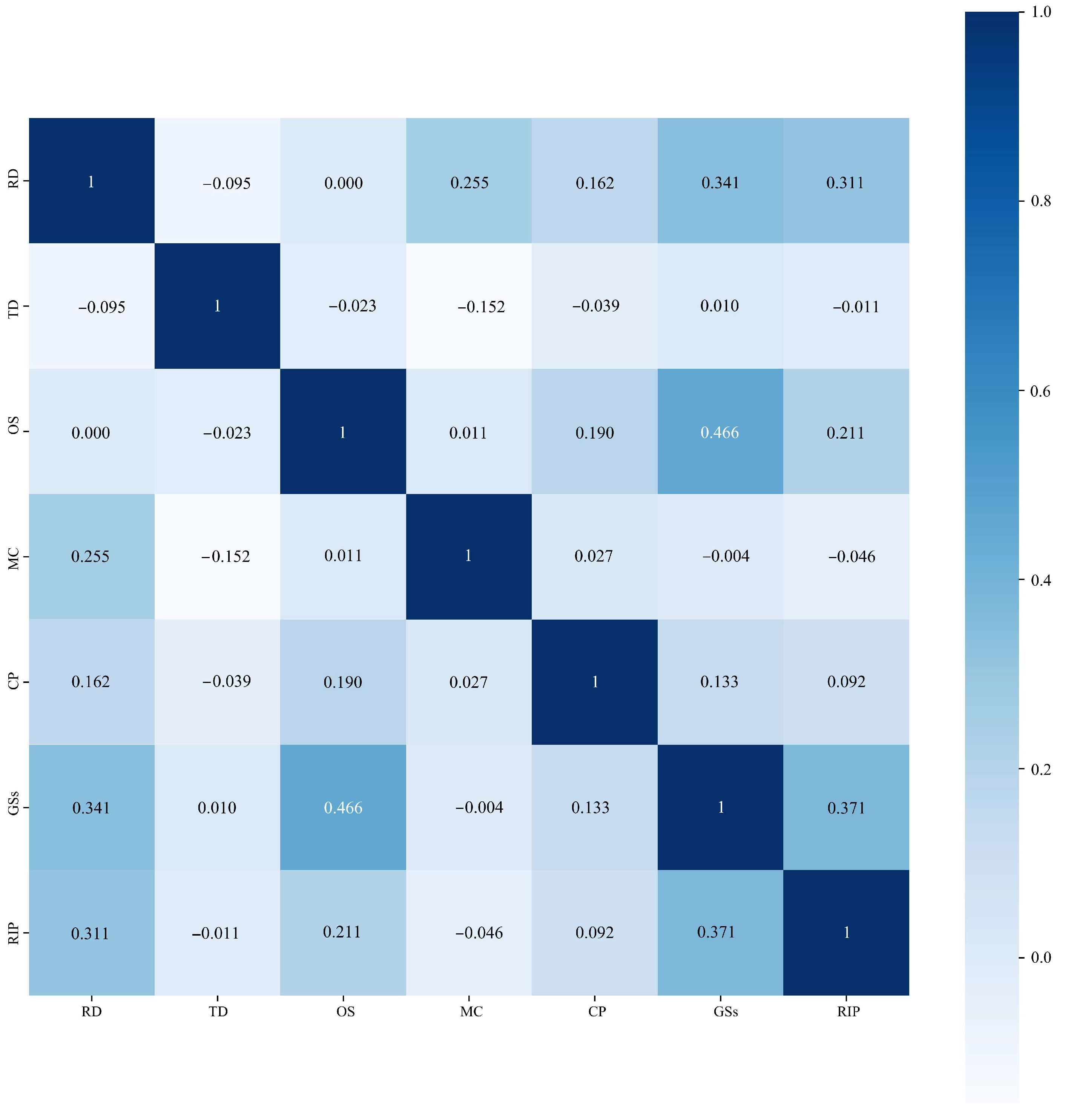
Due to the complexity of radical innovation activities, there may be an interaction between the variables. When an independent variable is a linear combination of one or more other independent variables, it can cause multicollinearity, which may impact the accuracy of the research results. Therefore, conducting a thorough correlation analysis of the variables is important before proceeding with further data analysis. Figure 2 displays the correlation coefficients between the technological diversification, R&D investment, organizational size, market competitiveness, government subsidies, competitive pressure, and radical innovation performance. As illustrated in Figure 2, some of the seven variables in this study (including both the independent and dependent variables) exhibit positive correlations. For instance, the Pearson correlation coefficient between R&D investment (RD) and radical innovation performance (RIP) is 0.311, indicating a moderate positive relationship between the two. Similarly, the correlation coefficient between government subsidies (GSs) and radical innovation performance is 0.371, suggesting that government subsidies may positively influence enterprises’ radical innovation performance. However, some variables demonstrate negative correlations. For example, the correlation coefficient between technological diversification (TD) and radical innovation performance (RIP) is −0.011, indicating a slight negative relationship. Additionally, the correlation coefficient between technological diversification (TD) and market competitiveness (MC) is −0.152, implying that as the degree of technological diversification (TD) increases, the market competitiveness (MC) may decline. The results indicate that there is no strong correlation among the key influencing factors. Similarly, there is no high correlation between radical innovation performance and the key influencing factors, suggesting that the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises is not determined by a single factor but rather by multiple factors. This study will utilize hierarchical clustering and CART algorithms to investigate the complex relationships between the key influencing factors and the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises.
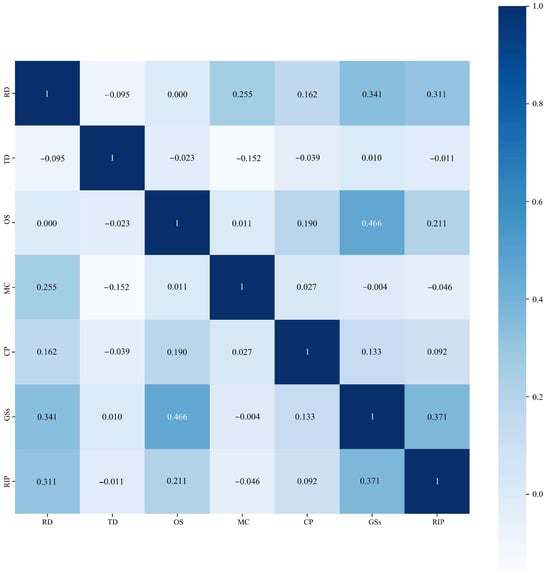
Figure 2.
Correlation analysis of independent variables and radical innovation performance.
5.3. Group Division
The technological, organizational, and environmental aspects of SRDI enterprises significantly differ, leading to varying development strategies and business objectives. Most current studies overlook these differences and treat all enterprises as equal when exploring the impact of radical innovation performance, which yields research conclusions that are lacking in relevance. Therefore, it is essential to accurately categorize enterprises based on their technological, organizational, and environmental traits to understand their development status and strengths and weaknesses. A hierarchical clustering algorithm, which does not require a predetermined number of clusters and provides objective results, is utilized in this study to group the focal enterprises based on “similarity within groups and differences between groups”. The characteristics of each enterprise group are presented in Table 2, where the level of radical innovation performance is based on the median, and performance exceeding the median is considered to be high.

Table 2.
The specific characteristics of each cluster.
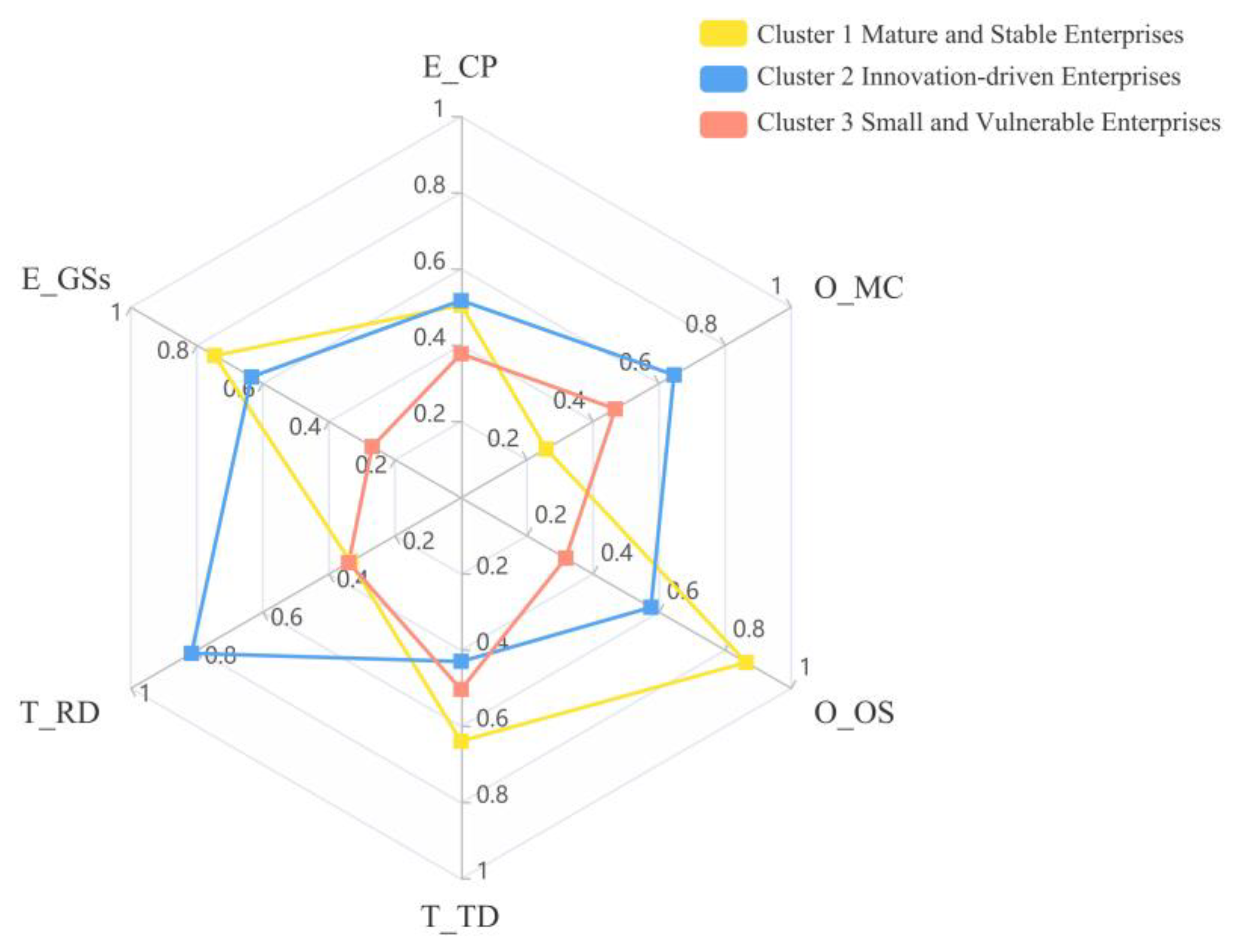
As shown in Figure 3, this study classifies enterprises into three clusters based on their technological, organizational, and environmental characteristics: mature and stable (cluster 1), innovation driven (cluster 2), and small and vulnerable (cluster 3).
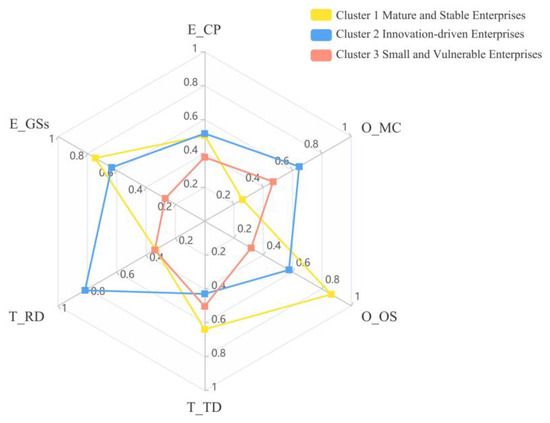
Figure 3.
Radar map of RD, TD, MC, OS, GSs, and CP.
Mature and stable enterprises have a high level of technological diversification, indicating a broad knowledge base and solid technical flexibility. Despite having a large organizational size, they have weak market competitiveness and face intense industry competition, leading to survival pressure. From an environmental perspective, these enterprises receive the highest government subsidies and are favored by the government. Moreover, they excel in innovation, with up to 60.20% achieving high radical innovation performance, showcasing significant innovation advantages.
Innovation-driven enterprises are known for their high R&D investment and strong market competitiveness. Although their technological diversification is lower than that of mature and stable enterprises, these enterprises direct significant R&D funds toward specific areas to gain a leading edge through technological innovation. Moreover, innovation-driven enterprises exhibit the highest market competitiveness and receive lavish government subsidies, underscoring their positive reception from both the market and the government. A total of 63.10% of innovation-driven enterprises achieved high radical innovation performance, ranking first among the three enterprise clusters.
Small and vulnerable enterprises have limited organizational size, R&D investment, and government subsidies, which may lead to weak anti-risk ability and resource shortages. These enterprises also face low industrial competitive pressure. Due to their technological, organizational, and environmental limitations, only 35.90% achieved high radical innovation performance, which is the lowest among the three enterprise clusters.
5.4. Decision Rule Analysis
The radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises is not determined by a single factor but by the combination of multiple factors. Therefore, it is necessary to further explore the complex influence mechanism of the combination of key factors on radical innovation performance to reveal a potential improvement pathway for the radical innovation performance of different SRDI enterprises. In this study, a CART algorithm is employed, with the independent variables serving as the conditional attributes and radical innovation performance as the decision attribute, based on the partitioning results of the enterprise clusters. The decision rules derived from this analysis are presented in Table 3. The support degree refers to the proportion of the sample size corresponding to a specific decision rule relative to the total sample size. A higher support degree indicates that the decision rule explains a larger portion of the sample. The confidence degree refers to the proportion of the sample size that supports the final classification of the decision rule relative to the total sample size. A higher confidence degree suggests that the decision rule is more reliable. Taking the first decision rule for small and vulnerable enterprises as an example, 21.1% indicates the proportion of enterprises supporting this rule relative to all the small and vulnerable enterprises, while 87.2% signifies that there is an 87.2% probability that enterprises conforming to this decision rule will achieve low radical innovation performance. The classification of performance levels in the decision results is based on the median radical innovation performance of the 531 focal enterprises. Performance above the median is categorized as high radical innovation performance, whereas performance below the median is classified as low radical innovation performance.

Table 3.
Decision rules for RIP.
The decision rules presented in Table 3 indicate the following results: First, from the perspective of the influence of the variables related to the technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions, the radical innovation performance of enterprises is subject to the interactive effects of the factors from across these three dimensions. Among them, technological diversification, R&D investment, organizational size, market competitiveness, and government subsidies affect the radical innovation performance of different types of SRDI enterprises in a combined manner. However, competitive pressure does not appear in the decision rules for the three clusters, suggesting that it is not a critical factor influencing the radical innovation performance of enterprises. Second, regarding the combination of influencing factors, the key factors affecting radical innovation performance vary across the different clusters of SRDI enterprises. This indicates that it is necessary to categorize the SRDI enterprises into groups before conducting a decision rule analysis to a certain extent. It also implies that enterprises of different types should fully consider their unique characteristics when engaging in radical innovation activities, adopting tailored optimal innovation strategies and models to avoid inefficiencies and resource wastage resulting from inappropriate innovation strategies. Furthermore, the decision rules derived from the CART algorithm exhibit an average confidence level of 84.8%, indicating high interpretability. This also demonstrates that these decision rules hold significant guiding value for promoting the enhancement of enterprises’ radical innovation.
By employing the CART algorithm to uncover the rules governing enterprises’ radical innovation performance, this approach not only circumvents the limitations of traditional regression methods, which often impose strict requirements on the sample data distribution, but also provides deeper insights into the combined effects of multiple characteristic factors and the complex relationships among the variables that influence radical innovation performance. Below, an in-depth analysis of the decision rules pertaining to radical innovation performance across the distinct clusters of enterprises is presented.
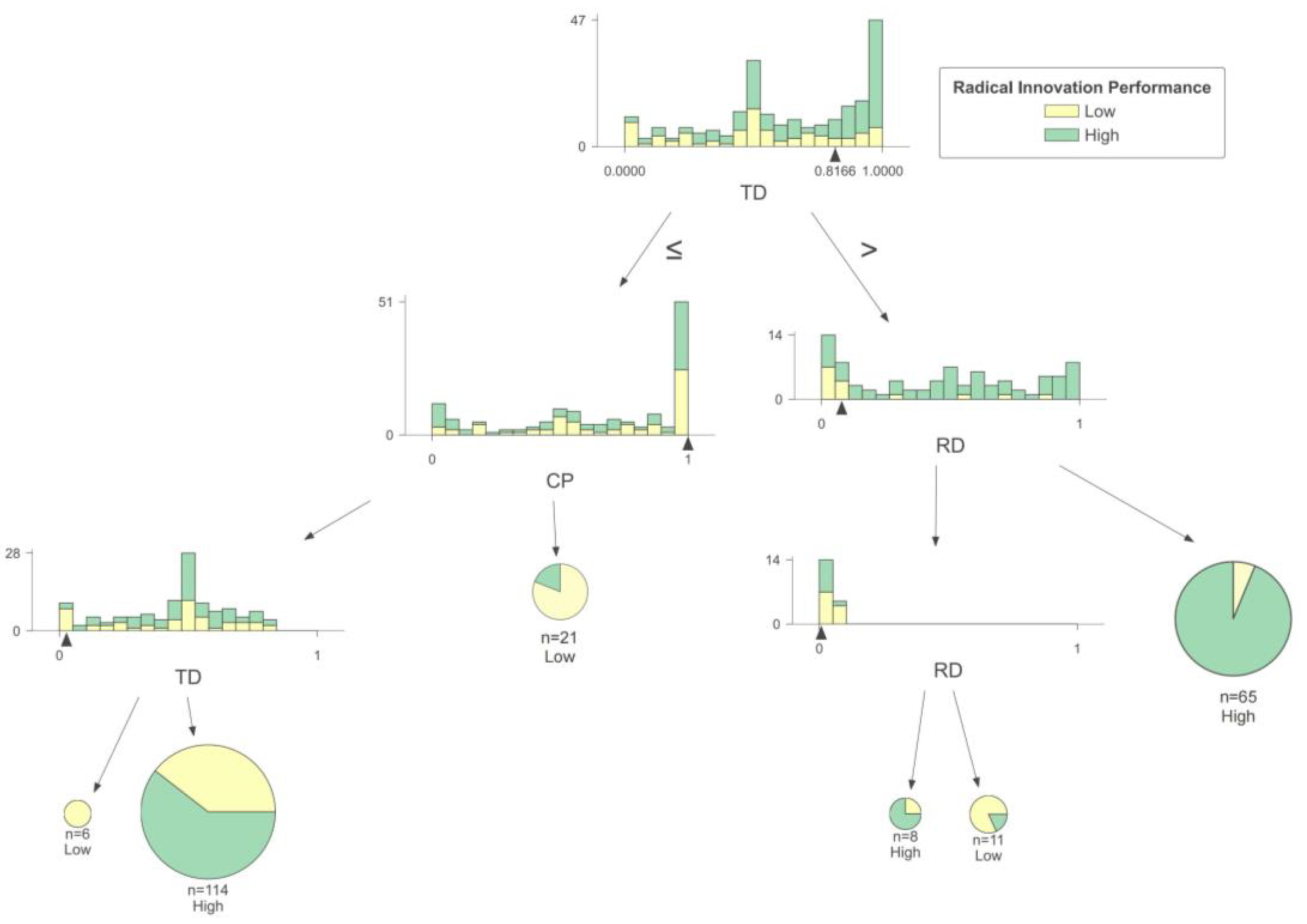
(1) Mature and stable enterprises
As shown in Figure 4, organizational size, R&D investment, and market competitiveness have complex effects on the radical innovation performance of mature and stable enterprises. When the organizational size is low, radical innovation performance tends to be low. This could be due to the organization’s smaller size, resulting in a lower risk tolerance, which is necessary for radical innovation. As a result, the enterprise may opt for a more conservative innovation strategy to ensure its long-term operation. When the organizational size is high, most enterprises can achieve high levels of radical innovation even with low R&D investment. This is because larger enterprises have more knowledge about market dynamics and customer demand, allowing them to develop innovations that align closely with market needs [12]. As a result, they can maintain high R&D efficiency even with modest investment. This efficient use of knowledge and technology contributes to enhance radical innovation performance.
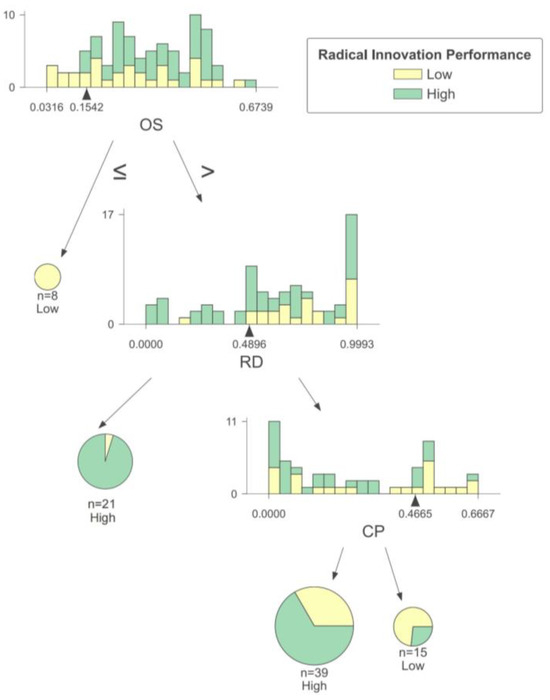
Figure 4.
Decision rules for mature and stable enterprises.
When enterprises have large R&D investments and strong market competitiveness, it may not necessarily lead to enhanced radical innovation performance. This could be because large-size enterprises with high R&D investment often have well-established business models, and introducing radical innovations may disrupt existing product and service models. As a result, highly competitive enterprises may be more cautious about pursuing radical innovation [24]. Conversely, enterprises with low market competitiveness face pressure to innovate radically in order to compete effectively in the market and overcome their inferior position.
Comparing horizontally, it is evident that organizational factors play a leading role in mature and stable enterprises. An enterprise’s radical innovation performance is low when its organizational size is low. When the organizational size is large, obtaining high radical innovation performance is difficult only when the R&D investment and market competitiveness are high. Therefore, these enterprises should prioritize optimizing their organizational structure and unleashing their innovative potential.
(2) Innovation-driven enterprises
As depicted in Figure 5, the interplay of technological diversification, market competitiveness, and R&D investment has a multifaceted impact on the radical innovation performance of innovation-driven enterprises. When an enterprise has low technological diversification, high market competitiveness does not necessarily lead to high radical innovation performance. This could be because low technological diversification implies that an enterprise focuses its resources and energy on a specific area. In this scenario, if an enterprise gains a significant competitive advantage in that area, it may prefer a more conservative innovation strategy to avoid risking its existing business with radical innovation [46].
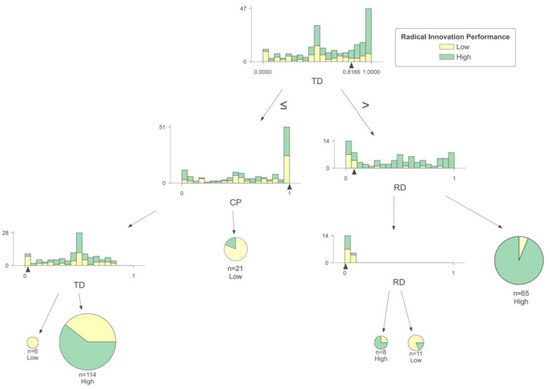
Figure 5.
Decision rules for innovation-driven enterprises.
On the other hand, enterprises with low market competitiveness may urgently need radical innovation to quickly enhance their technological capabilities or product performance in order to catch up with industry leaders [47]. In this case, these enterprises are more willing to engage in radical innovation activities. However, the level of radical innovation performance they achieve is also influenced by their own technological diversification. Radical innovation requires integrating a substantial amount of knowledge, so achieving better innovation results is challenging even for enterprises with a strong willingness to pursue radical innovation when their technological diversification is low. Furthermore, when enterprises are compelled to pursue radical innovation to survive, maintaining a certain level of technological diversification can be beneficial. This can help enterprises achieve technological breakthroughs by reorganizing their existing knowledge to enhance their radical innovation performance.
Under high technological diversification, the relationship between R&D investment and radical innovation performance follows a U-shaped curve. When R&D investment is low, enterprises are more likely to focus on radical innovation projects with high returns due to their limited resources and innovation capabilities. When R&D investment is at a medium level, it becomes challenging to fully apply existing knowledge and technology to innovation due to the limited capital and energy. Enterprises at this level need to invest significant effort into identifying helpful information and incur high maintenance costs, which can hinder radical innovation activities [48]. However, when R&D investment is high, enterprises have more resources for knowledge reorganization, leading to enhanced radical innovation performance.
Based on the above analysis, it can be found that the technological and organizational dimensions of innovation-driven enterprises have complex and nonlinear interactive effects on the improvement of radical innovation performance, in which technological diversification plays a leading role.
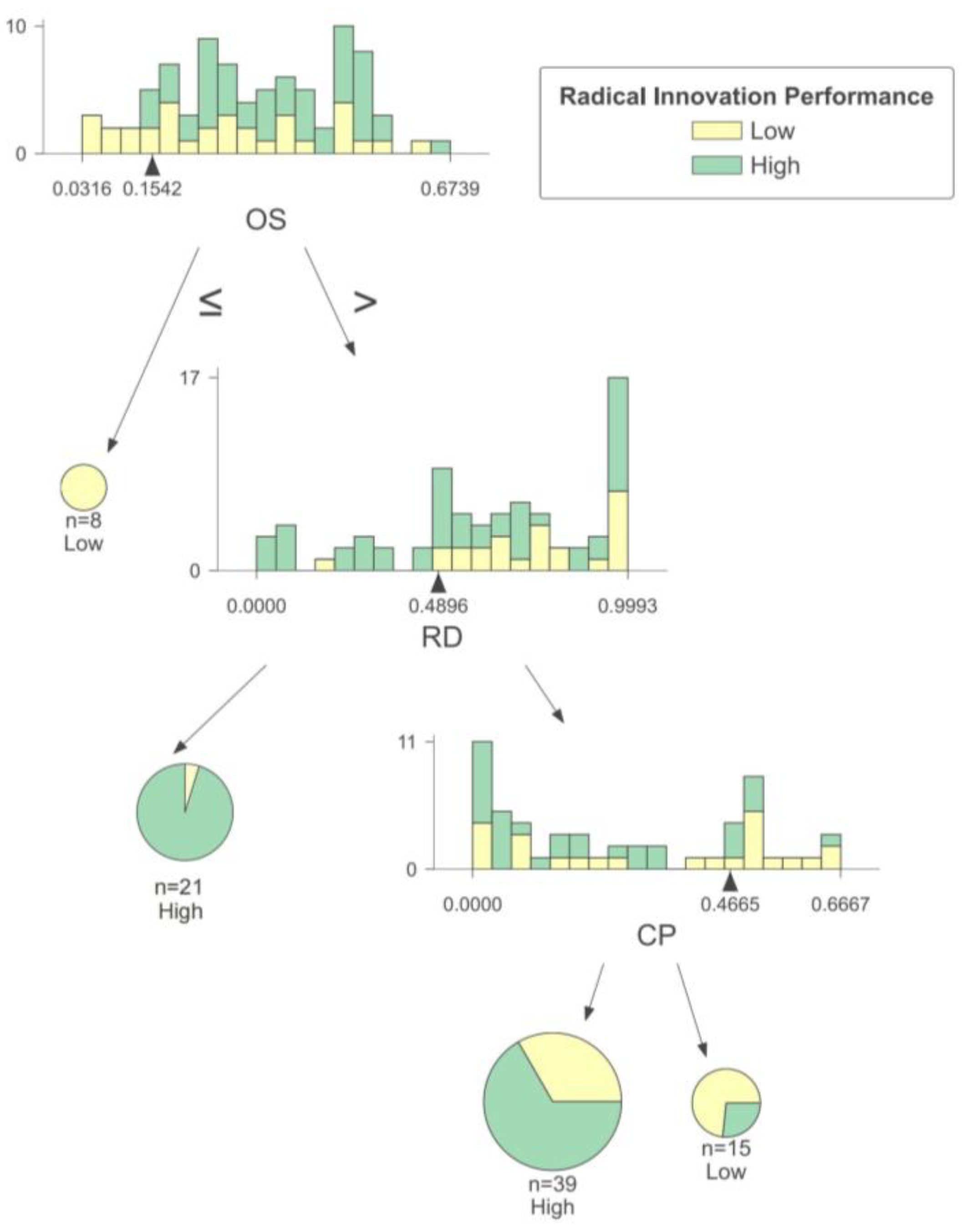
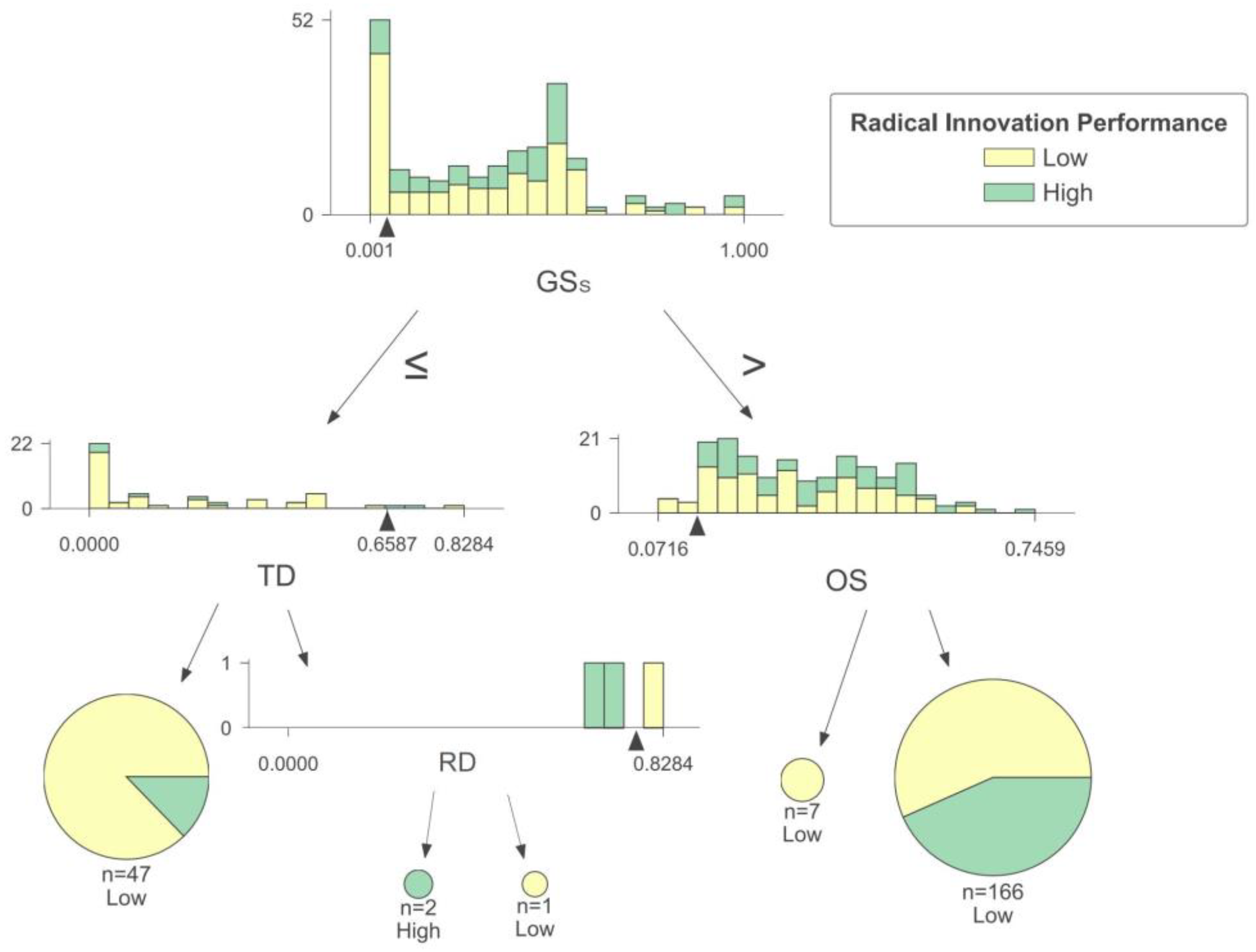
(3) Small and vulnerable enterprises
As illustrated in Figure 6, the interplay of government subsidies, technological diversification, R&D investment, and organizational size has an intricate impact on the radical innovation performance of small and vulnerable enterprises. When the government subsidies received by enterprises are low, those with limited technological diversification face more significant challenges in achieving high radical innovation performance. This may be due to the absence of external incentive policies, these enterprises’ relatively weak technology reserves, and the lack of conducive conditions for carrying out innovation activities, all of which significantly diminish the motivation for innovation. As a result, these enterprises are more likely to pursue low-risk innovation [49]. However, when enterprises receive minimal government subsidies and have high technological diversification, the level of radical innovation performance is also influenced by the R&D investment. A high technological diversification means enterprises have accumulated knowledge in multiple technological fields. Enterprises with high R&D investment can undertake extensive R&D activities and fully leverage their potential for restructuring knowledge, making the achievement of high radical innovation performance easier [23]. Conversely, enterprises with low R&D investment lack the resources to translate their extensive knowledge into market-demanded products, thus facing challenges in improving their radical innovation performance.
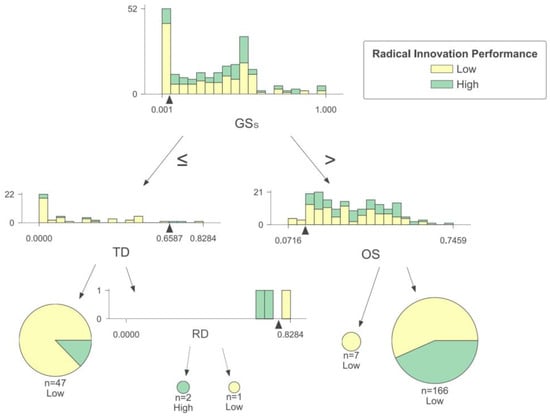
Figure 6.
Decision rules for small and vulnerable enterprises.
When enterprises receive higher government subsidies, most tend to have a lower radical innovation performance. Some studies have suggested that public innovation subsidies might hinder or replace private R&D capital investment. If enterprises receive substantial government financial support, their R&D budget may decrease, ultimately impacting their innovation capability [28]. Large enterprises are more likely to achieve high radical innovation performance than small-size enterprises. Some studies have proposed that this phenomenon is a result of the information asymmetry between government and enterprises. It is challenging for a government to effectively identify and supervise the innovation quality of enterprises, which may compel small-size enterprises to engage in simple incremental innovation activities to obtain subsidies, and they may have limited willingness to pursue radical innovation due to the high R&D difficulty and extended R&D cycles [50]. In contrast, large enterprises possess more robust innovation capabilities and a greater willingness to undertake radical, innovative research to maintain market dominance [51].
Based on the above analysis, the radical innovation performance of small and vulnerable enterprises is greatly affected by government subsidies. Therefore, it is crucial for the government to enhance the identification process for the innovation accomplishments of small-size enterprises and offer specific financial subsidies for enterprises that achieve radical innovation. Enterprises must promptly adapt their technological development in response to external environmental factors to align with government policy changes.
6. Conclusions and Discussions
6.1. Conclusions
This study acquired patent data, basic information, financial statement notes, and other data from 531 SRDI enterprises from the CNIPA and the CSMAR database. Then, it identified the influencing factors within the three areas of technology, organization, and environment, based on the TOE framework. A hierarchical clustering algorithm was employed to classify the focal enterprises into three clusters: mature and stable, innovation-driven, and small and vulnerable enterprises. A CART algorithm was used to deeply explore the complex combined influence of multiple key factors on the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises. The following conclusions were obtained:
(1) Radical innovation performance is the result of a synergistic interaction among various antecedents, which aligns with the perspectives of Xing et al. [26] and Luo et al. [45]. Specifically, it supports their view that achieving high levels of innovation performance is not solely determined by a single factor but is driven by the synergistic mechanisms of multiple factors. This study explored the multiple pathways to enhance radical innovation performance in different types of enterprises, and found that high levels of radical innovation performance are not solely dependent on R&D investment, technological diversification, market competitiveness, organizational size, or government subsidies. From the configuration perspective, radical innovation performance improvement is primarily influenced by organizational size, technological diversification, and government subsidies. Additionally, R&D investment and market competitiveness play a supporting role in this improvement.
(2) Technological factors have a significant positive effect on radical innovation performance, while high market competitiveness may somewhat inhibit the improvement of radical innovation performance. A combination of high technological diversification and R&D investment is a typical pathway to enhance radical innovation performance, and increasing the technological investment has a significant effect on radical innovation performance. This suggests a complementary effect between technological diversification and R&D investment. Although expanding the organizational size increases the probability of obtaining high radical innovation performance, excessively high market competitiveness may hinder radical innovation performance. This finding partially supports Schumpeter’s perspective [12]. Sun et al. [52] explained the reasons behind this phenomenon, suggesting that larger enterprises can leverage their brand advantages to mitigate the cost pressures and market risks associated with innovation activities, thereby promoting innovation performance. However, beyond this, the research results also reveal that simply enhancing organizational factors will not necessarily have a favorable impact on radical innovation performance.
(3) R&D investment is a common factor for significantly improving the performance of various SRDI enterprises, which aligns with traditional perspectives [53]. This is because radical innovation involves significant transformations to existing products, processes, or business models, thereby requiring substantial R&D investment as a critical enabler [54]. The impact of R&D investment on radical innovation is not simply linear, but exhibits diverse nonlinear effects within different enterprises’ different internal and external factors’ configurations. When the organizational size and market competitiveness are high, excessive R&D investment may not lead to enhanced radical innovation performance. Additionally, when there is high technological diversification, the relationship between R&D investment and radical innovation performance follows a U-shaped pattern.
6.2. Theoretical Contributions and Managerial Implications
This study makes significant theoretical contributions in the following aspects. First of all, exploring the complex nonlinear effects of multiple factor combinations within the TOE framework on enterprises’ radical innovation performance confirms the synergistic interactions among the factors within the TOE framework. This enhances the framework’s explanatory power within complex management contexts and further expands the theoretical boundaries of TOE framework research. Second, adopting a differentiated research perspective, this study investigates diverse pathways for enterprises to enhance their innovation performance under varying management scenarios, yielding targeted conclusions and differentiated management strategies. This addresses the limitations of previous research, which often overlooked the heterogeneous characteristics of different enterprises and relied solely on a generic perspective, thereby providing new insights for future theoretical research on enterprise innovation management. Finally, grounded in enterprise innovation management theory and a data-driven research approach, this study uncovers the complex nonlinear relationships between the influencing factors and enterprise innovation performance from objective data. It explores and extracts the hidden variable relationships and valuable knowledge rules embedded within the data, offering significant findings for advancing innovation management theory research.
The research findings also have managerial implications for both SRDI enterprises and governmental agencies. From the perspective of SRDI enterprises, they should prioritize establishing connections between different elements, maintaining a suitable level of R&D investment, and improving their enterprises’ capacities to absorb knowledge. They should also focus on accelerating the assimilation, integration, and application of new knowledge to enhance their radical innovation performance significantly. Simultaneously, they should make reasonable adjustments to their organizational structure. This involves enhancing their ability to manage risks to address the uncertainties associated with radical innovation effectively and avoiding a haphazard expansion that could lead to the dispersion of resources and negatively impact their overall innovation capability. Furthermore, SMEs with limited market competitiveness should concentrate their resources on specific market segments to enhance their visibility and influence in the industry, broaden their access to information channels, and establish a solid market foundation and information support for radical innovation.
For governments, first, it is essential to recognize the critical role of the technological factors in enhancing enterprises’ radical innovation performance. Governments should actively establish platforms for inter-enterprise communication and collaboration, facilitating the flow and absorption of diverse technological elements among enterprises. This includes promoting the integration of more SMEs into the supply chains of key industries dominated by large enterprises, enabling SMEs to absorb advanced technological elements from industry leaders and gain competitive market advantages. Second, governments should emphasize the synergistic effects of multiple factors on enterprises’ radical innovation performance. This could be achieved by implementing proactive fiscal policies to facilitate financing for SMEs; providing financial support to enterprises at critical stages of development, such as R&D, production, and market entry; and helping SMEs to overcome financing challenges to grow into exemplary firms within their industries. Additionally, the government should initially pay attention to the differences among enterprises and create tailored incentive policies based on the individual nature of each enterprise. This could include various innovation incentives, like tax breaks and financial aid, to provide specific support to key enterprises with significant potential for groundbreaking innovation.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
The main innovations of this study are as follows: Firstly, it integrates machine learning algorithms into innovation management research to explore the key factors influencing the radical innovation performance of SRDI enterprises based on extensive and objective data. The research conclusions obtained are both objective and accurate, thereby broadening the scope of relevant research methodologies. Secondly, the complex nonlinear relationships between the combinations of multiple key influencing factors and radical innovation performance are revealed, breaking through the limitations of previous studies that could only explore the linear or simple nonlinear relationships between variables. It also provides a configuration perspective for enterprise innovation performance research. Finally, enterprise groups are divided according to the characteristics of SRDI enterprises, and the heterogeneity of the enterprise groups is innovatively incorporated into the path analysis of radical innovation performance improvement, giving full consideration to the diversity of enterprise types and the complexity of innovation behaviors, providing a new idea for innovation management research.
However, this study still has the following limitations that need to be addressed in the future. Firstly, the TOE framework does not cover the internal key factors, such as corporate culture, senior management capability, and the innovation climate within enterprises. Future studies could explore the interaction mechanisms of the more internal and external factors on innovation performance to broaden the research perspective. Secondly, future research should consider including incremental innovation within the scope of their studies, based on the theory of dual innovation to more accurately reflect enterprise innovation management strategy. Additionally, although selecting the data from the SRDI-listed enterprises for this research demonstrated a high degree of rationality and rigor, it somewhat overlooked the unique characteristics of the non-listed enterprises, in terms of their innovation strategies and governance approaches. This limitation affects the applicability of the research findings to SRDI SMEs. Therefore, future research could expand the sample scope by including non-listed enterprises as research subjects, thereby enhancing the diversity of the enterprise sample and improving the generalizability of the research conclusions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and X.W.; methodology, H.Q. and H.L.; validation L.Z.; data curation, H.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Q. and J.C.; writing—review and editing, L.Z. and X.W.; visualization, H.L.; supervision, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Social Science Foundation Project of Fujian Province of China (FJ2024BF039) and Huaqiao University’s Academic Project Supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2024HQYJ15).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhu, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, B. The Rise of Specialized and Innovative Little Giant Enterprises under China’s ‘Dual Circulation’ Development Pattern: An Analysis of Spatial Patterns and Determinants. Land 2023, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, T.; Chang, P.; Mardani, A. The impact of digital leadership on hidden champions’ competitive advantage: A moderated mediation model of ambidextrous innovation and value co-creation. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 182, 114819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, A.; Khalik, M.; Godinez, J. The internationalization of hidden champions from Germany and the UK: An extension to the Born-Again Global path. J. Int. Manag. 2024, 30, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Song, M. Mechanism of latecomer enterprises’ technological catch-up in technical standards alliances–An ambidextrous innovation perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 154, 113321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Z.; Liu, X. The determinants of hidden champion enterprises: Evidence from China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, L.; Miroshnychenko, I.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; De Massis, A. Family CEO and radical innovation: A stewardship perspective. Res. Policy 2025, 54, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Belitski, M.; Caiazza, R.; Phan, P. Collaboration strategies and SME innovation performance. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 164, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas-Oliver, J.; Sempere-Ripoll, F.; Moll, C.B. Zooming into firms’ location, capabilities and innovation performance: Does agglomeration foster incremental or radical innovation? Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2022, 28, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wu, X.; Tan, Z. The growth of hidden champions in China: A cognitive explanation from integrated view. Chin. Manag. Stud. 2020, 14, 613–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, M.L.; Sarah, Y.C.; María, J.O. External knowledge search, absorptive capacity and radical innovation in high-technology firms. Eur. Manag. J. 2018, 36, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, X.; Yang, X.; Li, L. How Does Digital Transformation Impact Green Supply Chain Development? An Empirical Analysis Based on the TOE Theoretical Framework. Systems 2023, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- wael AL-khatib, A. Drivers of generative artificial intelligence to fostering exploitative and exploratory innovation: A TOE framework. Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shankar, A. Building a sustainable future with enterprise metaverse in a data-driven era: A technology-organization-environment (TOE) perspective. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 81, 103986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.G. The logic of appropriability: From Schumpeter to Arrow to Teece. Res. Policy 2006, 35, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, Z.; Gong, F. Examining the Mechanism of Political Knowledge on Radical Innovation Performance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 60, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, X. Examining the interaction effect of digitalization and highly educated employees on ambidextrous innovation in Chinese publicly listed SMEs: A knowledge-based view. Technol. Soc. 2024, 78, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genin, A.; Ma, W.; Bhagwat, V.; Bernile, G. Board experiential diversity and corporate radical innovation. Strateg. Manag. J. 2023, 44, 2634–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.F.; Ireland, D.; Pittino, D.; Sanchez-Famoso, V. Radical innovation in (multi)family owned firms. J. Bus. Ventur. 2022, 37, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, W. Antecedents of radical innovation speed from a knowledge network perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 271, 109219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, H.; Brunswicker, S. A fad or a phenomenon? The adoption of open innovation practices in large firms. Res. Technol. Manag. 2014, 57, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Battistella, C.; De Toni, A.F.; Pessot, E. Practicing open innovation: A reference framework. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2017, 23, 1311–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Y.; Ngayo, G.; Hong, S.P. Applying Blockchain, Causal Loop Diagrams, and the Analytical Hierarchy Process to Enhance Fifth-Generation Ceramic Antenna Manufacturing: A Technology–Organization–Environment Framework Approach. Systems 2024, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Hong, G. Management equity incentives, R&D investment on corporate green innovation. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104533. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Qi, L.; Ji, J.; Zhou, J. How does innovation spirit affect R&D investment and innovation performance? The moderating role of business environment. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100398. [Google Scholar]
- Jugend, D.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Scaliza, J.A.A.; Rocha, R.S.; Junior, J.A.G.; Latan, H.; Salgado, M.H. Relationships among open innovation, innovative performance, government support and firm size: Comparing Brazilian firms embracing different levels of radicalism in innovation. Technovation 2018, 74–75, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, T. Digital transformation and innovation performance of China’s manufacturers? A configurational approach. Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vrande, V.; De Jong, J.P.J.; Vanhaverbeke, W.; De Rochemont, M. Open innovation in SMEs: Trends, motives and management challenges. Technovation 2009, 29, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Srivastava, M.K.; Gnyawali, D.R. Walking the tight rope of coopetition: Impact of competition and cooperation intensities and balance on firm innovation performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, H. Business analytics adoption process: An innovation diffusion perspective. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Shen, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Xia, X.; Luo, K. Can government subsidies improve innovation performance? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Econ. Model. 2023, 120, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Can public R&D subsidy facilitate firms’ exploratory innovation? The heterogeneous effects between central and local subsidy programs. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104221. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, M.; Jia, C.; Zhong, L.; Cao, J. What determines the performance of digital transformation in manufacturing enterprises? A study on the linkage effects based on fs/QCA method. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, K.; Hauptman, A.; Rosenboim, R.L. Prediction of corporate credit ratings with machine learning: Simple interpretative models. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taweesan, A.; Kanabkaew, T.; Surinkul, N.; Polprasert, C. Integrating clustering algorithms and machine learning to optimize regional snapshot municipal solid waste management for achieving sustainable development goals. Environ. Adv. 2025, 19, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westreich, D.; Lessler, J.; Funk, M.J. Propensity score estimation: Neural networks, support vector machines, decision trees (CART), and meta-classifiers as alternatives to logistic regression. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2010, 63, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, G.B.M.; Lee, L.C.; Samsudin, A.S.B.; Sino, H. Evaluation of ensemble data preprocessing strategy on forensic gasoline classification using untargeted GC–MS data and classification and regression tree (CART) algorithm. Microchem. J. 2022, 182, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Yao, J.; Xie, J.; Hu, C. Innovation performance feedback and inter-organization knowledge search in high-tech firms: The moderating role of technical knowledge complexity. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 182, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, K.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhuang, R. Can Green Credit Improve the Innovation of Enterprise Green Technology: Evidence from 271 Cities in China. Systems 2024, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pel, B.; Haxeltine, A.; Avelino, F.; Dumitru, A.; Kemp, R.; Bauler, T.; Kunze, I.; Dorland, J.; Wittmayer, J.; Jørgensen, M.S. Towards a theory of transformative social innovation: A relational framework and 12 propositions. Res. Policy 2020, 49, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Lin, F. Does technological diversification matter to firm performance? The moderating role of organizational slack. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 1970–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Driving forces of digital transformation in Chinese enterprises based on machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2014, 14, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ye, P.; Zhao, F.; Jahanger, A. Technology spillover and market competitiveness in green credit induced corporate green innovation: An evolutionary game theory and empirical study. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 207, 123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Study on the Improvement Path of Innovation Performance of “SRDI” Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2024, 42, 873–884+896. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H. Corporate financial fragility, R&D investment, and corporate green innovation: Evidence from China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105190. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, S.; Yao, C.; Zhang, D. How to promote green innovation of high-pollution firms? A fuzzy-set QCA approach based on the TOE framework. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, I.; Bengtsson, L. Unravelling appropriability mechanisms and openness depth effects on firm performance across stages in the innovation process. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 120, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, G.M.J.; Fernández, L.S.; Rodeiro, P.D. Foreign knowledge sources and innovation: Differences across large and small and medium-size multinational enterprises (MNEs). Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 92, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Jin, J. Impact of different patent cooperation network models on innovation performance of technology-based SMEs. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2020, 32, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Feng, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. Do government grants promote innovation efficiency in China’s high-tech industries? Technovation 2016, 57–58, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Cheng, Y. More is better or in waste? A resource allocation measure of government grants for facilitating firm innovations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 197, 122918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, J. Investment deregulation and innovation performance of Chinese private firms. J. Financ. Stab. 2024, 70, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Cai, C.; Tan, H.; Ji, H.; Tian, G.L. Corporate ESG Performance and Competitive Strategies from the Perspective of Financial Markets: Strategic Significance of Firm Size. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 77, 107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Yu, Z.; Tian, G.; Wang, D.; Wen, Y. Market Competition, Environmental, Social and Corporate Governance Investment, and Enterprise Green Innovation Performance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 77, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, S. R&D investment management and ambidextrous technological innovation: Evidence from Chinese listed firms. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 88, 843–860. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).