Abstract
The capacity of local governments to act as frontline disaster management agencies is crucial to urban sustainability and disaster risk management systems. However, vulnerabilities in the management systems can hinder the effectiveness of disaster risk management, affecting the resilience and sustainable development of urban areas. This study examines vulnerable areas of disaster risk management from a practical perspective, based on audit findings conducted by the Board of Audit and Inspection (BAI). The stages of disaster risk management are classified as prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery. The disaster risk management activities that local governments should undertake at each stage have been identified and summarized. The vulnerabilities and associated cases related to disaster risk management were comprehensively analyzed by compiling the results of local government disaster risk management audits conducted after 2015. This study revealed vulnerabilities in areas such as disaster management funds, prevention facilities, safety inspections, forecasting and warning systems, and resident evacuation, all of which are integral to maintaining urban sustainability. To avoid the recurrence of these issues, this study suggests that local governments should develop and implement improvement measures for each vulnerable area. The findings of this study can serve as valuable guidelines for local governments on ways to enhance their disaster risk management systems.
1. Introduction
In recent years, South Korea has experienced various natural disasters, such as earthquakes, typhoons, and wildfires, as well as social disasters, such as fires, gas explosions, and maritime accidents. In the past decade (2012–2021), the average annual damage caused by natural disasters was valued at 369.1 billion KRW (277.6 million USD), with a recovery cost of 1.0326 trillion KRW (776.6 million USD) [1] (p. 16). A total of 157 social disasters, including those managed by the National Emergency Management Agency, have occurred, resulting in average annual property damage of 242.1 billion KRW (182.1 million USD) [2] (p. 53). These disasters not only impact the immediate safety of citizens but also challenge the urban sustainability of the affected areas.
National and local governments play crucial roles in preventing and preparing for disasters and accidents. Article 4 of the “Framework Act on the Management of Disasters and Safety” (hereafter, “Disaster Safety Act”) stipulates that it is a must for national and local governments to protect the lives, bodies, and property of citizens from disasters and accidents, as well as to ensure the urban sustainability of their communities. In particular, local governments are emphasized as the most important entities for the effective management of disasters and accidents [3]. This is because they are frontline disaster management agencies protecting the property and lives of residents, and they are closest to the disaster scene [4,5,6]. However, inadequate management or responses by national and local governments have been cited as the cause of many disasters and accidents.
A multitude of problems with disaster risk management at national and local government levels have been addressed in various studies, including the ambiguity of relevant laws and systems, insufficient budgets and personnel for disaster-related issues, lack of standardization and coordination in tasks, insufficient education and training, inadequate response and initial coping measures in the case of a disaster, unclear jurisdiction and responsibility avoidance, formalistic disaster safety manuals, ambiguous disaster support and compensation, and proactive analysis of vulnerabilities in disaster risk management [7]. In particular, the analysis and elimination of vulnerabilities in disaster risk management is an important activity for the comprehensive coordination capacity that national agencies or local governments should have, and is one of the important factors for enhancing disaster recovery capabilities [7]. Additionally, addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial for the sustainability of urban environments in the face of increasing disaster risks. Therefore, this study suggests that to improve disaster risk management, vulnerability analysis is necessary.
Unlike the research on legal, institutional, and operational issues related to disaster risk management, relatively few studies have been conducted on the vulnerabilities of disaster risk management. Studies that have been conducted were done separately for each field or facility of disaster risk management. In this regard, if we summarize the audit results of local governments, which constitute the most important entity in disaster risk management, we can identify the comprehensive vulnerabilities. In particular, because local governments carry out similar activities (tasks) related to disaster risk management, vulnerabilities found in one place are likely to appear in other places. Therefore, by analyzing and presenting the issues identified in previous audit results, we can increase the likelihood of preventing them before they take place.
This study analyzes the audit results of local governments’ disaster risk management by the Audit Office for the past eight years (2015–2022) to comprehensively identify vulnerable fields. Specifically, this study examined each stage of disaster risk management, namely: prevention, preparation, response, and recovery. It also reviewed the major activities at each stage.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Disaster Risk Management of Local Governments
Disasters are characterized by inherent risks and uncertainties. The magnitude and occurrence of losses caused by the risks associated with disasters are uncertain [6,8,9,10]. However, the concept of disasters has been defined differently depending on the country, era, and scholars, and has been used interchangeably with hazards or emergencies [6,11]. Lim [11] (p. 117) defined crises as small-scale incidents or imminent events that cause minor casualties and property damage, hazards as the sources of risks or extreme events that can affect people, property, and the natural environment in a certain area, and disasters as events that go beyond the scope of local government (community) management.
Under Article 3 of the Disaster Safety Act of South Korea, disasters are defined as events that could damage people’s lives, bodies, and property, as well as the nation. They are divided into natural and social categories. The specific examples of natural and societal disasters as defined by law are organized in Table 1 below. Damage caused by disasters is defined under Article 2 of the “Countermeasures against Natural Disasters Act” (hereafter, “Natural Disasters Act”). In addition, disaster management under the Disaster Safety Act is defined as “all activities to prevent, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters”. This refers to preventing, preparing for, responding to, and recovering from disasters that have the characteristics of risk and uncertainty [9,11,12,13].

Table 1.
Legal Classification of Disasters.
As mentioned in the introduction, the role of local governments is crucial for disaster management and safety. Local governments are responsible for responding to and directly handling disasters as they occur [6,14]. Together with national agencies, they have a basic obligation to prevent disasters and minimize damage in the event of a disaster (Article 2 of the Disaster Safety Act). Local governments are required to perform disaster management as responsible agencies (Article 3 of the Disaster Safety Act). This means that they must make efforts to prevent disasters and accidents, minimize damage, and establish and implement plans for prompt response and recovery in the event of damage (Article 4 of the Disaster Safety Act).
The disaster management activities that the responsible agency for disaster management must perform under the law can be broadly categorized into prevention and preparation before a disaster occurs, and response and recovery after a disaster occurs, as seen in Table 2. Disaster prevention refers to the activities aimed at preventing or reducing disaster occurrence and damage in advance, such as establishing safety management plans, building safety management systems, and inspecting and managing disaster prevention facilities. Disaster preparation refers to preparing for a prompt and efficient response under the assumption that a disaster has occurred. This includes stockpiling and managing disaster management resources, developing and operating crisis management manuals, building disaster management information communication systems, and conducting disaster response training. Disaster response refers to a series of activities that deal with a disaster when it occurs, such as issuing disaster crisis warnings, taking emergency measures, and performing urgent rescue operations. Disaster recovery refers to activities aimed at restoring to a pre-disaster state after a disaster has occurred. These could include reporting and investigating disaster damage, implementing disaster recovery projects, and providing compensation for damages caused by the disaster activity [15].

Table 2.
Key DRM Tasks by Disaster Phases.
In particular, when examining the disaster risk management tasks assigned to local governments by the “Disaster Safety Act”, it is noteworthy that specific regulations for the inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities are stipulated in individual laws. These laws include the “Natural Disasters Act” and the “Act on the Preparation for Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions”, according to the type of disaster. Detailed specifications of these regulations can be found in Table A1 of Appendix A.
2.2. Audit of Local Government’s Disaster Risk Management
The International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions (INTOSAI) states that auditing during disasters can reduce the impact of the activity and enhance the effectiveness, economy, and efficiency of disaster relief [16] (p. 4). The INTOSAI states that auditing should identify the risks that must be checked during each stage of disaster management. In an audit of the prevention, preparedness, and mitigation stages of disasters, the risks related to the effectiveness of policies established by the government and various measures, compliance with legal requirements related to citizen safety, and other relevant factors should be checked. In the disaster response audit, the efficiency related to the rapid management and distribution of large-scale disaster support, risks related to inadequate or malfunctioning internal control systems, lack of pre- and post-control, and risks that operational and procedural control could be ignored due to the activation of emergency procedures for prompt processing should be checked. Finally, in the audit for recovery activities after disasters, the risks of control and the economy should be checked because a large amount of public spending is concentrated in disaster-stricken areas.
The Board of Audit and Inspection of South Korea (BAI) conducts audits in accordance with Article 97 of the Constitution of the Republic of Korea and Article 20 of the “Board of Audit and Inspection Act” to examine the settlement of national revenues and expenditures, supervising the accounting of national and legally established organizations, and inspects the duties of administrative agencies and public officials to improve administrative operations and enhance their quality. To conduct these tasks, the Board of Audit and Inspection conducts various types of audits, such as settlements and regular institutional, performance, special, and citizen proposal audits, as defined in the Board of Audit and Inspection Regulations. In particular, audits related to disaster and safety management are mainly conducted through performance audits or special audits, and are also carried out through regular institutional audits and citizen proposal audits.
Audits related to disaster safety and management can be categorized into two main types: audits related to disaster management systems, prevention, and response, and audits related to the safety management of key facilities, as seen in Table 3. One notable audit related to disaster prevention and response was the “Audit on the Status of Large-Scale Disaster Prevention and Response” conducted in 2013. Since then, audits have been conducted in more specific areas such as disaster and emergency funds, the establishment of disaster safety information systems, the sharing and dissemination of disaster information, and special subsidies for disaster risk management. In addition, safety management audits for key facilities have been conducted, covering various types of facilities such as national infrastructure, gas facilities, roads, railways, bridges, underground tunnels, reservoirs, dams, and rivers.

Table 3.
Critical Audits in Disaster Risk Management.
Between 2015 and 2022, a total of 52 criticisms were received from disaster and safety management audits, from local governments. However, in cases where audit results were notified after 2015, for example the audit on “Operation of Disaster and Hazard Funds” conducted in 2014, the results were included in the analysis. There were 24 specific-issue audits, such as the “Audit on the Management of High-Risk Slopes for Disasters” conducted in 2019, 13 performance audits such as the “Audit on the Use of Major Project Budgets for Disaster Preparedness” conducted in 2021, 14 regular audits, and one citizen-proposed audit, as seen in Table 4.

Table 4.
Status of Audit Points for Local Government Disaster Risk Management (2015–2022).
2.3. Literature Review
Kusumasari et al. [17] suggested the capacity requirements of local governments for activities before, during, and after a disaster. They stated that evaluation and monitoring, dissemination capacity for information, planning, and training were required for disaster risk mitigation. They also highlighted the importance of needs assessment, information exchange, logistical expertise, disaster support capacity for disaster response, expertise in damage assessment, debris removal, and disaster recovery. Atkinson [18] proposed an overall system that includes preparation, response, and recovery from disasters for local governments’ disaster management. For disaster preparation in particular, Atkinson [18] suggested the establishment of plans, mitigation of risks, risk reduction and management, plans for necessary personnel and cooperation, and the participation of local communities and stakeholders. Regarding disaster response, Atkinson [18] suggested the need for cooperation between local and central governments (especially the Federal Emergency Management Agency), disaster relief and support, and budget expenditures.
Recent studies have also highlighted the role of local governments in disaster risk management [19,20,21]. For instance, Busayo et al. [19] introduced ecosystem-based adaptation (EbA) in relation to flood disaster risk management in South Africa, emphasizing the critical role of local governments in managing flood risks on the ground, as well as the regulation and support provided by the central government to local authorities. Kalogiannidis et al. [20] described the importance of education in improving disaster risk management, underlining the significance of public education for local governments and local crisis management personnel, who are key actors in disaster management. Kuhlmann et al. [21] discussed the role of local governments during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany, using case studies to illustrate how local authorities, endowed with executive powers on the ground, can effectively respond to crises within a multi-level intergovernmental framework.
Several studies have been conducted on disaster risk management by local governments in South Korea. These studies can be classified into comprehensive analyses of disaster risk management systems in local governments, and research on issues and improvement measures related to each stage of disaster prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery. Park et al. [4] approached disaster management systems in local governments from the perspectives of legal and institutional, organizational and human resources, financial, and governance (cooperative). They presented problems and improvement measures for disaster risk management systems in local governments by analyzing foot-and-mouth disease response cases. As an initial response to disasters, Jung [22] suggested improvement measures to address the inadequate disaster risk management systems by local governments. In particular, Jung identified major problems such as the unclear formation of organic and cooperative relationships between central and related departments, unclear assignment of duties to relevant agencies, and insufficient provision of evacuation instructions to residents. Kim [23] proposed measures to strengthen the role of local governments in disaster management administration, such as expanding the scope of disaster management tasks, strengthening the authority to establish safety management plans, expanding the participation of residents and local communities, and building an organic cooperative system among local governments. Bae [24] examined the problems of disaster management in local governments by incident and proposed improvement measures, such as establishing a cooperative system between the national and local governments, building a primary-stage response-oriented disaster management system, and enhancing the role of local governments through decentralization.
Next, research on issues and improvement methods for each stage of a disaster can be classified according to the major areas of the local governments’ disaster risk management activities. First, research related to disaster prevention includes the establishment of safety management plans [25,26], disaster management organizations and personnel [5,6], education for disaster safety professionals [27], management and support for disaster-vulnerable groups [28,29], the accumulation and use of disaster management funds [30,31], and the collaborative relationship between social institutions and local governments [32]. These studies mainly identify obstacles and improvement methods for establishing local government safety management plans and raise issues regarding the functions and limitations of disaster management organizations and the professional competence of disaster risk management personnel. Additionally, they suggest improvements in the scope of education for disaster safety professionals, timing and duration of education, and ways to support and strengthen disaster-vulnerable groups. These studies also provide suggestions for improving the accumulation and operation of disaster management funds to ensure their effectiveness.
Second, studies related to disaster preparedness have been conducted, such as on the stockpiling and management of disaster management resources [33], the development and operation of crisis management manuals [34,35], and the establishment and operation of disaster management information communication systems [36]. These studies identified problems, suggested solutions for the management and operation of disaster management resources, reviewed the status and improvement direction of crisis management standard manuals, and proposed alternatives for establishing a unified disaster communication system centered on disaster sites.
The development direction of local government fire support systems was reviewed, and problems and improvement solutions for the operation of local government emergency rescue control teams were proposed. In addition, improvement alternatives through actual case studies of local disasters, such as earthquakes and infectious diseases like COVID-19, have been suggested.
Finally, there have been studies related to disaster recovery, such as disaster damage assessments [37,38], disaster recovery plan establishment [39,40], and disaster support [41]. These studies have examined the current issues and proposed improvement measures, including the assessment-of-damage scale in disaster damage assessment, the need for consideration in the categorization of disaster recovery and the design of recovery plans, problems with the current resident support system in disaster support, and concrete improvement measures, such as support methods and standards.
While these studies mainly focused on the problems of laws, regulations, and operational aspects of each activity in disaster risk management, this study is distinctive in that it comprehensively approaches the disaster risk management activities of local governments and examines vulnerable areas through audit results of each activity.
3. Research Methods
The research problem of this study is to analyze the vulnerabilities in local governments’ disaster risk management systems. To achieve this, we utilized audit results from the Korean National Audit Office, the Board of Audit and Inspection (BAI). The concept of vulnerability related to disaster risk management is somewhat ambiguous in theoretical terms [42]. In a practical context, the rationale related to the identification of vulnerabilities in this study is as follows: the BAI’s audits aim to identify problems within local governments and recommend improvements. Thus, the issues highlighted in the audit results indicate areas where local governments fall short in disaster risk management. Furthermore, issues that are frequently highlighted are considered to exhibit a higher degree of vulnerability.
The unit of analysis is the local government. Local governments in Korea consist of 17 macro-level and 226 primary-level entities. The macro-level entities include one special city (Seoul), six metropolitan cities (such as Busan and Incheon), and eight provinces (for example, Gyeonggi-do and Gangwon-do). The primary-level entities function within the jurisdiction of these macro-level governments, influencing local development. Notably, the 74 primary-level entities under the special and metropolitan cities are relatively more developed and have a higher level of infrastructure compared to the 152 entities within the provinces [43]. In this study, macro-level entities are referred to as metropolitan governments, and primary-level entities as local governments.
The research data include disaster risk management-related audit reports, audit lists, and lists of disposition requests from the BAI over an eight-year period, 2015–2022. The method employed to analyze the research materials is content analysis. We reviewed all 52 audit reports and organized the data, focusing on 291 audit findings and 361 audit disposition requests. The problems identified in the audits were categorized based on the disaster risk management responsibilities of local governments as stipulated in the Disaster Safety Act and related laws. The classification criteria are region, legally defined disaster risk management responsibilities, and types of disposition requests.
In this study, we present concise statistics through frequency and cross-analysis of the vulnerabilities in disaster risk management by type and describe various cases from the audit reports, focusing on their key features. The results of such analyses will significantly contribute to identifying the main vulnerabilities in the disaster risk management systems of local governments. A brief summary of the research methods and process is illustrated as follows in Figure 1.
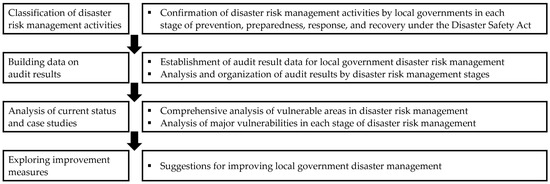
Figure 1.
Research Analysis Process.
Figure 1 illustrates the framework developed for this study. First, the stages of disaster risk management were divided into prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery, as well as the disaster risk management activities that local governments must perform as disaster management agencies. Second, audit results related to disaster risk management by local governments since 2015 were collected and analyzed, and each item was classified according to its related area of disaster risk management. Third, based on the collected data, the overall situation and major vulnerability cases of disaster risk management in local governments were analyzed. Finally, based on the analysis, improvement measures for disaster risk management by local governments were proposed.
The criteria employed in analyzing audit report data related to disaster risk management encompass the principal activities relevant to local governments, as mandated by law, summarized in Table 5. In the disaster prevention phase, there were 16 activities, such as establishing safety management plans for cities, provinces, and districts. The disaster preparedness phase had six activities which were centered around stockpiling and managing disaster management resources. The disaster response phase included seven activities with topics such as establishing and operating disaster forecasting and warning systems, while the disaster recovery phase included seven activities which were based on reporting and investigating disaster damage. However, issues related to individual laws regarding disaster safety, such as the inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities, were analyzed by matching them with the activities to which they were most similar.

Table 5.
Analysis Criteria.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Description of Vulnerable Areas in Local Disaster Risk Management
From 2015 to 2022, 52 problematic audit items, which included comments from local governments, were identified through disaster risk management audits. The results in Table 6 showed 361 cases in total, of which 47.9% (173 cases) were warnings, and the rest were notifications (37.7%, 136 cases), disciplinary actions (7.8%, 28 cases), and corrections (6.6%, 24 cases). No compensation decisions, recommendations, requests for investigation, or reports were made. The types of institutions subjected to warnings and other measures were 52.9% (191 cases) local governments and 44.9% (162 cases) metropolitan governments. Additionally, although 2.2% (eight cases) were requested by national agencies such as the Ministry of Public Administration and Security or the Korea Forest Service, the actual problems occurred in local governments.

Table 6.
Audit Results on Disaster Risk Management of Local Government.
According to the audit results, there may be cases in which there is only one audit measure for a single incident, but there are also cases in which two or more audit measures are issued for a single incident, depending on the circumstances. For example, in the case of improper handling of duties by a government official, both disciplinary and corrective action regarding improper work procedures or systems may be required simultaneously [44].
Therefore, to examine the vulnerable areas of disaster risk management in local governments, it is necessary to look at the issues raised on a case-by-case basis rather than the number of audit measures issued. When the 361 audit measures were reorganized by issue, the number was 291, as shown in Table 7. When examining these issues at each stage of disaster risk management, prevention-related issues accounted for the majority (75.9%, 221 cases), followed by recovery-stage issues (10.0%, 29 cases), response-stage issues (5.8%, 17 cases), and preparedness-stage issues (4.8%, 14 cases).

Table 7.
Audit Results of Vulnerable Areas in Local Governments’ Disaster Risk Management Activities.
Specifically, during the prevention phase, the most common type of feedback (83 cases, 28.5%) was related to disaster management fund savings and operations. Other common issues were the inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities (81 cases, 27.8%), safety checks and measures for disaster prevention (22 cases, 7.6%), the operation of safety management consulting teams and safety responsibility managers (17 cases, 5.8%), and the designation and management of specific management target areas (8 cases, 2.7%).
During the preparedness phase, feedback included the creation and operation of crisis management manuals (10 cases, 3.4%), construction and operation of disaster management information and communication systems (2 cases, 0.7%), and establishment and implementation of disaster preparedness training plans (2 cases, 0.7%).
In the response phase, feedback included the construction and operation of disaster forecast and warning systems (12 cases, 4.1%), emergency response measures such as crisis notification and management in disaster areas (2 cases, 0.7%), and the mobilization of resources, issuance of evacuation orders, designation of danger zones, and implementation of emergency rescue and on-site command operations (1 case, 0.3% each).
Finally, during the recovery phase, feedback included the establishment and implementation of disaster recovery plans and business management (16 cases, 5.5%), execution of disaster management funds (6 cases, 2.1%), national disaster relief for disaster areas (5 cases, 1.7%), and investigation of the causes of the disaster (2 cases, 0.7%).
Upon reorganizing the data presented in Table 7 through a cross-analysis categorized by region type and disaster management stages, the findings are delineated in Table 8. For metropolitan governments, 108 cases (78.3%) were identified as vulnerabilities in the prevention phase. Among these, 52 cases are related to the “inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities”, as per the analysis criteria in Table 5, and 22 cases are related to “accumulation and operation of disaster management funds”. For local governments as well, 113 cases (77.4%) were pointed out as DRM vulnerabilities in the prevention stage. To elaborate, 61 cases were related to “accumulation and operation of disaster management funds”, and 29 cases were associated with “inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities”. In summary, both metropolitan and local governments exhibited the highest proportion of DRM vulnerabilities related to the prevention stage. However, for the metropolitan governments, the majority of issues were related to the “inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities”, while for local governments, the highest proportion of issues was related to “accumulation and operation of disaster management funds”.

Table 8.
Audit Results of Vulnerabilities in Disaster Management by Type of Region.
Following the analysis of the second-highest proportion of issues within the disaster management phases, it was discovered that for metropolitan governments, the preparedness stage accounted for 7.25%, while for local governments, the recovery stage was at 13.0%. This difference can be interpreted as a result of the distinct roles in DRM between metropolitan and local governments. In the event of an actual disaster, local governments are responsible for on-site response and recovery operations according to the recovery manuals, which could explain why DRM vulnerabilities related to these aspects are revealed in audit results.
4.2. Results of Vulnerability Analysis by Disaster Risk Management Phases
4.2.1. Prevention Phase
While examining major disaster prevention cases, issues related to the gathering and management of disaster management funds were identified. Local governments are required to accumulate a certain amount of funds for disaster management under Article 67 of the Disaster Safety Act and for disaster relief under Article 15 of the Disaster Relief Act. However, it has been pointed out that many local governments have failed to raise these funds. For example, at the time of the audit, it was found that 23 local governments, including ▲▲1 Metropolitan City, had accumulated significantly less than the legally required amount of disaster management funds (based on cumulative standards) and were neglecting their obligation to accumulate funds for disaster and relief management.
The second major case in the disaster prevention phase is vulnerability, which is related to the inspection and management of disaster-prevention facilities. As the responsible disaster management agencies, local governments are required to inspect and manage disaster prevention assets such as rivers, sewage systems, agricultural production infrastructure, buildings, dams, sightseeing boats, roads, and ports under Article 29 of the Disaster Safety Act and Article 37 of the same Act’s enforcement decree. This applies to many disaster-prevention projects and measures implemented by local governments. When the 81 identified issues related to inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities were categorized by facility type, more than 95% were related to road facilities. Among these, common safety issues related to shock-absorbing facilities, and other road-related issues accounted for 49.4% (40 cases), followed by bridges at 22.2% (18 cases), tunnels at 14.8% (12 cases), and underground passages at 6.2% (5 cases).
Looking at the representative case of road facilities, it has been pointed out that inadequate safety measures were taken in the design and construction of median barriers requiring shock-absorbing facilities in the event of vehicle accidents in regions such as ▲▲ Province. Moreover, despite inspection results showing that the reflectivity performance of road markings (lanes, characters, symbols) were unsuitable, some regions such as ▲▲ Metropolitan City and ▲▲ County proceeded with the installation and completion of road marking construction anyway. Furthermore, although guardrails should be installed on local roads to reduce traffic accident damage caused by vehicle departure and falls, certain regions such as ▲▲ Province were criticized for installing guardrails that did not meet performance standards, among other safety problems. Regarding bridges, it was pointed out that certain regions such as ▲▲ City have not taken necessary measures such as repair or reinforcement for discovered defects through precision inspections. Concerning tunnels, various problems such as insufficient installation of essential safety equipment, lack of automatic fire detection equipment, insufficient length of fire hoses in indoor fire hydrants, expired durability of fire extinguishers, inadequate installation intervals and damage of emergency broadcasting equipment, and absence of smoke exhaust and smoke control equipment were identified in certain regions such as ▲▲ Province. In relation to underground passages, it was pointed out that certain regions such as ▲▲ City have been poorly constructed, with continuous flooding due to the failure to establish fundamental flood prevention measures.
Third, disaster management authorities should conduct joint and focused safety inspections of vulnerable cases related to disaster prevention, safety inspection, and measures. However, it has been pointed out that in the case of ▲▲ district, during the period of focused safety inspections, the district reported having conducted safety inspections on a total of 67 apartments and other facilities without actually visiting the site for 10 days. There have also been many cases of safety inspections and supervisor-related issues, mainly regarding large retaining walls and other facilities. Maintenance companies have falsely reported conducting safety inspections without actually doing so, management entities have not properly verified these, and local governments have been negligent in managing and supervising such cases.
The fourth issue identified in terms of disaster prevention is related to safety responsibilities and management, particularly regarding the appointment of elevator safety managers. Many elevators in the country operate without appointed safety managers, despite the obligation under Article 29 of the Elevator Safety Management Act to appoint such managers.
Fifth, vulnerabilities were identified in the designation and management of specific management target areas, as stipulated by Article 27 of the Disaster Safety Act, under which local governments and other related organizations are required to designate and manage areas or facilities that are at high risk of disasters or require management for disaster prevention. It has been pointed out that proper designation and management of such areas have not been carried out, resulting in weak safety management of these specific management target areas. For example, at the time of the audit in a certain city, it was found that a total of 170 facilities were omitted from the list of specific management target areas.
Finally, a major issue identified during the disaster prevention phase was the inadequate establishment of safety management systems. Disaster management agencies are responsible for developing safety management systems and regulations in high-risk, disaster-prone areas. However, it was pointed out that organizations such as ▲▲ Hospital selected several hospitals without having specialist medical personnel for infectious diseases at regional infectious disease control centers when establishing a hospital network for infectious disease preparedness and response, indicating a lack of proper safety management systems for infectious diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a comprehensive safety management system to address these risks.
4.2.2. Preparedness Phase
In terms of disaster preparedness stages, major cases include issues related to the development and operation of crisis management manuals. During an inspection of operating manuals for fire suppression equipment in multiple privately owned cities, including ▲▲ city, it was pointed out that incorrect operational conditions had been set, or no operational conditions had been set, for the fire suppression equipment in the event of a fire.
Second, there are problems related to the establishment and operation of disaster-management information and communication systems. Although the current national disaster management information system is designed for the joint use of disaster information by other institutions, it was pointed out that there have been cases of interruption in disaster information linkage or changes made to the structure and storage location of the database without consultation with relevant agencies, leading to linkage interruption. In addition, it was pointed out that some relevant information was missing from the databases of local disaster safety information systems established in industrial parks and other areas.
Third, there are issues related to the establishment and implementation of disaster preparedness training plans. Subway operating agencies are required to establish and implement emergency response training plans for fires, terrorism, and other railway emergencies, considering the history of subway stations. However, during an audit of seven subway operating agencies nationwide, including ▲▲ city subway, it was pointed out that three agencies did not have established training standards, and training was not conducted for about 40% of the total of 287 subway stations over the course of a year.
4.2.3. Response Phase
The main cases in the disaster response stage are as follows. First, in the case of problems related to disaster warnings, local governments should review and reflect on whether there is duplication or coordination with other projects in the comprehensive plan for establishing an alarm system, which is formulated every five years. However, there was no review of whether there was duplication or coordination with other projects in 17 cities and provinces nationwide. In particular, it was pointed out that as a result, 17 out of 100 disaster warning and civil defense warning devices were duplicated in ▲▲ Province. Although disaster warning devices are mainly installed and operated in rural areas, civil defense warning devices are also installed and operated in urban areas. However, it was pointed out that in urban areas such as ▲▲ Metropolitan City (especially in areas without disaster warning devices), civil defense warning devices are not being utilized for disaster warnings.
Second, in the case of problems related to crisis alert notifications and emergency measures in disaster areas, the Korea Forest Service and local governments have established evacuation systems for residents in landslide-prone areas to disseminate information on the risk of landslides and issue evacuation orders; however, they have failed to provide disaster information to residents outside of landslide-prone areas and external visitors. According to an audit conducted by the Board of Audit and Inspection in 2018 of the 178 landslide warnings and alerts issued by local governments in 2016–2017, only 20 urgent disaster text messages were sent. Furthermore, local governments are required to disinfect areas contaminated by infectious pathogens to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. However, it was pointed out that the ▲▲ Health Center was negligent in preventing additional cases of MERS, as it failed to properly inspect and manage the isolation and treatment of confirmed patients at ▲▲ Hospital and the disinfection of potentially contaminated areas.
Third, in cases related to mobilization and evacuation orders, it was pointed out that necessary measures, such as the evacuation of residents, should be taken when the level of crisis alert is raised to the caution stage in the case of potential flash floods in the vicinity of dams, but such measures were not properly taken. In other words, in 2017, when there was a possibility of flash floods in ▲▲ Dam, a caution stage was declared, but ▲▲ County failed to take measures to evacuate residents and only sent an urgent disaster text message.
Fourth, in cases related to the setting of risk areas and restrictions on passages, citizens’ passages should be restricted in the case of some ventilation systems, such as diagonal ventilation systems that do not meet safety conditions, as they can cause accidents. However, it was pointed out that such measures were not properly taken in ▲▲ City.
4.2.4. Recovery Phase
In terms of disaster recovery stages, major issues related to the formulation and implementation of the disaster recovery plan were noted. In particular, many flood damage restoration projects in rivers, steep slopes, mountainous areas, and roads have been improperly designed owing to heavy rainfall. There is a concern that disasters may recur because of inadequate safety verification or inaccurate estimation of river width. For instance, in the design phase of flood restoration work for the ▲▲ embankment in ▲▲ county, the stability assessment for embankment leakage and slope activities was not performed, and the supervising engineer failed to confirm it properly, leading to a risk of leakage in the completed embankment.
Second, regarding issues related to disaster support (mainly national subsidies), there was much criticism regarding the application and use of special disaster management grants. Local governments should thoroughly review the necessity of each project, including its similarities and overlaps with other projects, before applying for special disaster management grants. However, it was pointed out that ▲▲ county applied for grants for projects that were already being funded or underway or that duplicated the projects in progress. If the usage was intended for a different purpose than that initially designated or approved, it was requested and approved by the Ministry of Administration and Safety in advance. However, it was pointed out that ▲▲ county and others had used the received special disaster management grants for other purposes without applying for a change in purpose, or used them for other purposes before receiving approval for the change.
Third, regarding the dispensation of disaster management funds, many local governments were found to have used them inappropriately for purposes other than emergency recovery or urgent measures. Specifically, many local governments use funds for purposes unrelated to emergency recovery and disaster prevention, such as rural road paving, parking lot installation, and promotional electronic displays. For example, during the implementation of the ▲▲ project in ▲▲ county, rural road paving work, which was not part of the initial plan, was added to the project and executed using disaster management funds due to demands from village residents.
Finally, regarding issues related to disaster-cause investigations, the Ministry of Administration and Safety and the Disaster Management Agency are required to conduct disaster-cause investigations when a disaster occurs. However, many local governments have pursued disaster recovery projects without investigating the causes of the disasters. For example, ▲▲ county proceeded with a road repair project without conducting a cause investigation of a landslide which was identified as the cause of the disaster.
4.3. Discussions for Improvement of Disaster Management
Looking at the problems with disaster risk management by local governments at each stage identified from the study described above, the following improvement measures can be considered:
First, in the disaster prevention stage, it is necessary to ensure that each local government complies with the legal obligation to reserve and operate disaster management funds, including disaster relief funds, without violating their prescribed minimum reserve amounts. In addition, to inspect and manage disaster prevention facilities, safety facilities must be installed in accordance with the manuals or regulations for each facility, and effective safety inspections and measures must be conducted. Specifically, maintenance companies for each facility must conduct regular safety inspections (self-inspections) and report the results through the relevant information systems. The management entity must verify these results, and local governments must ensure thorough management and supervision. Furthermore, measures to eliminate the risk of disaster occurrence must be continuously implemented for the designation and management of specific target areas.
Second, during the disaster preparedness phase, field action manuals or facility-specific operation manuals suitable for each type of disaster should be prepared to create and operate crisis management manuals. In other words, the measures and specific conditions for each stage of disaster response should be systematically reflected in a situation-specific manner, and practical disaster response activities or measures should be promptly implemented according to the manual. In the establishment and operation of disaster management information and communication systems, relevant information should be reflected as comprehensively as possible when constructing the system. During the system operation process, issues such as system errors, malfunctions that may occur during the joint use of disaster information, and coordination problems for the joint use of information should be continuously monitored and managed. Furthermore, disaster preparedness training should be effectively conducted according to the type of disaster or facility.
Third, during the disaster response phase, periodic checks should be conducted on the installation and operation status of disaster warnings, alert equipment, and civil defense alert equipment to prevent duplication of equipment that can be jointly used. Depending on the characteristics of an area, such as whether it is rural or urban, disaster warning and alert equipment and civil defense alert equipment should be installed and utilized in a mutually compatible manner to ensure effective disaster warnings and alerts. When providing crisis alerts, checks should be conducted to prevent blind spots in notifications based on the type of disaster or regional characteristics. Emergency measures in disaster areas should also be re-evaluated according to the type of disaster, region, and facility to ensure that they can be properly implemented in the event of a disaster. Regarding mobilization and evacuation orders, residents should be evacuated according to the evacuation facilities and methods specified in the field action manual, and safety measures such as traffic restrictions should be checked and managed without fail for danger zones.
Finally, regarding the disaster recovery phase, it is important to ensure safety in the initial facility design, which serves as the basis for disaster recovery planning, to prevent similar disasters from recurring after recovery work is completed. In addition, regarding disaster support, a strict verification of whether there are any similar or overlapping designs with other projects should be conducted during the local government’s application process for a special grant for disaster risk management. Disaster management funds should also be managed so that they are not used for purposes unrelated to emergency recovery or disaster prevention. Meanwhile, in the event of a disaster, the cause and process of the accident should be investigated, and appropriate measures should be taken to prevent similar disasters from occurring again based on the management issues identified during the investigation [45] (p. 33).
5. Conclusions
Disaster risk management requires the participation and cooperation of various actors, but the role of government agencies remains one of the most important. In particular, the disaster response capabilities of local governments as frontline disaster management agencies have been emphasized. Additionally, these capabilities are integral to maintaining urban sustainability in the face of various disasters. To effectively strengthen local governments’ disaster risk management systems, a proactive examination of current deficiencies within these systems is essential. Practical approaches are necessary to examine the weaknesses of disaster risk management activities carried out by local governments, in addition to identifying problems in laws, regulations, and operations. Therefore, this study examined the weaknesses of disaster and safety management activities in a practical dimension by analyzing audit results from the national audit office, which can effectively assist in identifying vulnerabilities.
The analysis results showed that, first, in the disaster prevention stage, problems were identified, such as noncompliance with the obligation to accumulate disaster management funds; inadequate installation, inspection, and management of disaster prevention facilities; insufficient safety inspections and measures, and poor management and supervision. Second, in the disaster preparedness stage, there were problems with inadequate manual preparation and operation that did not adequately reflect situational conditions, a lack of connectivity and comprehensiveness within the disaster management information and communication system, and insufficient planning and execution of disaster preparedness training at the facilities. Third, in the disaster response stage, problems were identified, such as inadequate joint use of duplicate emergency warning systems and equipment, the occurrence of blind spots in crisis warnings by disaster type, inadequate emergency measures in disaster areas, and failure to implement safety measures, such as resident evacuation and traffic restrictions. Fourth, in the disaster recovery stage, inappropriate implementation design and restoration work, duplication of special disaster management grants, misuse of disaster management funds for purposes other than their intended use, and failure to investigate the causes of disasters and accidents were identified. Therefore, to prevent the recurrence of these vulnerabilities, it is essential to establish improvement measures for each vulnerable area presented in this study and implement them in local governments. These measures are not only crucial for disaster management but also for enhancing the urban sustainability of the affected communities.
As mentioned in the introduction, one of the recurring causes of similar disasters and accidents is inadequate management and response by national and local government agencies. If the errors and mistakes made by local government agencies are corrected and eliminated in relation to the types of disasters and accidents occurring in different facilities, the occurrence of disasters and safety accidents caused by administrative problems within the control range can be minimized. Furthermore, appropriate responses and measures can be taken quickly even after disasters and accidents occur. Therefore, continuous vulnerability analysis, dissemination, and removal efforts are needed for the disaster risk management activities (tasks) of national and local government agencies. This is essential not only for effective disaster management but also for maintaining and improving urban sustainability in the long term.
Lastly, we identify the study’s limitations and suggest directions for future research. While this study focused on examining the audit results of the Board of Audit and Inspection (BAI), incorporating the findings from internal audits conducted by each local government might reveal additional vulnerabilities. Furthermore, our comprehensive approach to assessing local government disaster risk management could result in a lack of specific and detailed measures for addressing these vulnerabilities. Additionally, we employed content analysis of audit reports to evaluate the disaster risk management systems of local governments, yet the study did not quantitatively assess the degree of vulnerability. Future research that develops and applies a quantitative analysis method stands to produce more refined research outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C.; methodology, H.C.; software, H.C.; validation, H.C. and N.C.; formal analysis, H.C.; investigation, H.C. and N.C.; resources, H.C.; data curation, H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.; writing—review and editing, N.C.; visualization, N.C.; supervision, N.C.; project administration, N.C.; funding acquisition, N.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Gachon University research fund of 2023 (GCU-202304980001).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
In this appendix, specific details regarding disaster risk management tasks of local governments, as stipulated by the provisions of the Disaster Safety Act, are presented in a tabular format.

Table A1.
DRM activities of local governments.
Table A1.
DRM activities of local governments.
| Category | Disaster Risk Management Tasks | Disaster Safety Act |
|---|---|---|
| Prevention | Development of disaster safety plans at the city, district, and county levels. | Article 24, Article 25, etc. |
| Establishment and improvement of disaster response organizations. | Article 25-2 | |
| Establishment of a system for disaster prediction and utilizing information. | Article 25-2 | |
| Promotion of disaster preparedness education and prevention measures. | Article 25-2 | |
| Establishment and improvement of safety management systems, regulations, and preparations. | Article 25-2 | |
| Designation and management of special control areas, including disaster risk improvement zones. | Article 25-2, Article 27, etc. | |
| Inspection and management of disaster prevention facilities. | Article 25-2, Article 29, etc. | |
| Implementation of education for disaster safety workers. | Article 29-2 | |
| Conducting safety inspections, measures, management, and supervision for disaster prevention. | Article 30, Article 31, Article 32, Article 32-3, etc. | |
| Supporting a safe environment for vulnerable groups. | Article 31-2 | |
| Disclosure of disaster management situations. | Article 33-3, etc. | |
| Promotion of safety culture policies. | Article 66-4 | |
| Safety management measures for local festivals. | Article 66-11 | |
| Accumulation and operation of disaster management funds, development and distribution of disaster insurance. | Article 67, Article 68, Article 76, etc. | |
| Operation of safety advisory groups and safety responsibility officials. | Article 75, Article 75-2 | |
| Preparedness | Reserve and management of disaster management resources. | Article 25-2, Article 34, etc. |
| Establishment of emergency communication means at disaster sites. | Article 34-2 | |
| Development and utilization of disaster response plans. | Article 34-4 | |
| Development and operation of crisis management manuals. | Article 34-5, Article 34-6 | |
| Construction and operation of disaster management information and communication systems. | Article 34-8, Article 74, Article 74-2, etc. | |
| Development and implementation of disaster preparedness training plans. | Article 25-2, Article 34-9, Article 35 | |
| Response | Establishment and operation of disaster forecasting and alert systems. | Article 38-2 |
| Emergency measures such as warning and evacuation orders, restricted areas and passages, and emergency support. | Article 36, Article 37, Article 38, Article 46, Article 47, etc. | |
| Issuance of mobilization and evacuation orders. | Article 39, Article 40, Article 42 | |
| Setting-up of danger zones and restrictions on movement. | Article 41, Article 43 | |
| Providing support and emergency relief. | Article 44, Article 45 | |
| Emergency rescue and site command, information provision, and requests. | Article 49-52, Article 56, Article 57, Article 74-3, etc. | |
| Enhancement of disaster preparedness capabilities. | Article 55 | |
| Recovery | Reporting and investigation of disaster damages. | Article 58 |
| Establishment and implementation of disaster recovery plans, project management. | Article 59, Article 59-2 | |
| Suggestions and support for the declaration of special disaster areas. | Article 60, Article 61 | |
| Compensation for emergency support (loss/treatment) and disaster support. | Article 62-65-2 | |
| Disaster support including national financial aid for disaster areas. | Article 66-66-3, Article 66-13 | |
| Execution of disaster management funds. | Article 68 | |
| Investigation of disaster causes and management of disaster situation records. | Article 69, Article 70 |
Source: Referenced from the “Disaster Safety Act”.
Note
| 1 | In the audit result reports, the names of the cities that received audit dispositions are anonymized. In this paper, the names of these cities have also been anonymized by inserting triangle symbols. |
References
- Ministry of Interior and Safety. Yearbook of Disaster: Natural Disaster 2021; Ministry of Interior and Safety: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- Ministry of Interior and Safety. Yearbook of Disaster: Social Disaster 2021; Ministry of Interior and Safety: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- van Niekerk, D. Local government disaster risk management. In Municipal Management: Serving the People; Ven der Waldt, G., Ed.; Juta and Company Ltd.: Cape Town, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.K.; Yang, G.G.; Ryu, S.I. The Strengthening efficiency measures for disaster management system. Korean Local Gov. Rev. 2012, 13, 131–154. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.G.; Cha, J.Y. Study on Improving the Competency of Emergency Management Personnel in Local Government; Korea Institute of Public Administration: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, E.J.; Eom, Y.H. What is to Determine the Local Government’s disaster Management? Korean J. Local Gov. Stud. 2017, 20, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K. Necessary capacity and direction of change for disaster risk management of Local Government. Admin. Focus 2022, 160, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- French, S.P. The technical feasibility of risk analysis. In Sharing Environmental Risks: How to Control Governments’ Losses in Natural Disasters; Raymond, J.B., Ed.; Westview Press, Inc.: Boulder, CO, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E. An Issue Analysis of the Disaster Management System Reshuffling and Its Future directions. Korean J. Public Admin. 2004, 42, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.G. A case study on organizational learning in disaster management: Focusing on the collapse of the World Trade Center and the Daegu subway fire. Korean Public Admin. Rev. 2004, 38, 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.J. International comparison of the disaster management evaluation system and its implication to South Korea: Focusing on local governments in the US, UK and Australia. J. Local Gov. Stud. 2020, 32, 115–144. [Google Scholar]
- Picket, J.H.; Block, B.A. Day-to-day management. In Emergency Management: Principles and Practice for Local Government; Thomas, E.D., Hoetmer, G.J., Eds.; International City Management Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lindell, M.K.; Prater, C.; Perry, R.W. Introduction to Emergency Management; John Wiley & Sons: Danvers, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, I.B. A study on the development of local disaster management system in Korea: Focusing on benchmarking in major developed countries. J. Soc. Sci. 2002, 9, 193–223. [Google Scholar]
- The Board of Audit and Inspection. Audit Report on the Large-Scale Disaster Prevention and Response Status 2013. Available online: https://www.bai.go.kr/bai/result/branch/detail?srno=1512 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- INTOSAI Professional Standards Committee. Introduction to the 5500 Series of ISSAIs and INTOSAI GOV 9250 (ISSAI 5500). 2019. Available online: https://www.issai.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/issai-5500-e.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Kusumasari, B.; Alam, Q.; Siddiqui, K. Resource capability for local government in managing disaster. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2010, 19, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.L. Local Government emergency management. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busayo, E.T.; Kalumba, A.M.; Afuye, G.A.; Olusola, A.O.; Ololade, O.O.; Orimoloye, I.R. Rediscovering South Africa: Flood disaster risk management through ecosystem-based adaptation. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 14, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiannidis, S.; Toska, E.; Chatzitheodoridis, F.; Kalfas, D. Using School Systems as a Hub for Risk and Disaster Management: A Case Study of Greece. Risks 2022, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, S.; Franzke, J. Multi-level responses to COVID-19: Crisis coordination in Germany from an intergovernmental perspective. Local Gov. Stud. 2022, 48, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.U. A Study on Improvement Methods of Disaster Risk Management System and Legislation by Municipalities; Korea Legislation Research Institute: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.C. A legal status of the local governments as the administrative subject of the disaster management: To strengthening the role of the local governments in the disaster and safety management act. Local Gov. Law J. 2014, 14, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.H. Problems of disaster management due to the corruption of local bureaucrats and how to improve legal system. Anti-Corrupt. Law 2019, 2, 63–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W. An investigation of reestablishment of municipal government’s safety and disaster management plans. Policy Sci. 2015, 24, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, C.J.; Rheem, S.K.; Choi, W.J. A study on the improvement of Local Government safety management plan: Focusing on comparison of emergency operations plan by USA. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2016, 16, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Yeo, E.T. Legal advice for improving the education system for persons engaging in the field of disaster and safety. J. Law. 2020, 28, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.W. A study on the prevention and management policy for the disaster vulnerable class in the event of a disaster. J. Soc. Converg. Stud. 2020, 4, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Direction of Safety Management Policy for the Safety Vulnerable. Admin Focus 2020, 147, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, Y.M. Review of Local Government ordinances related to disaster management funds. Soc. Welf. Law J. 2018, 9, 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, I.W.; Kim, S.J.; Han, D.Y.; Kim, J.W. A Study on Improving Utilization and Stable Operation of Disaster Management Funds; Ministry of Public Safety and Security: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2016.
- Cho, K.W.; Park, D. Emergency Management Policy Issues during and after COVID-19: Focusing on South Korea. J. Contemp. East. Asia 2023, 22, 49–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Jung, J.W. A study on the management improvement of disaster recovery Resources of municipality with field survey. J. Korean Soc. Disaster 2020, 16, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.G.; Park, K.J.; Kim, H.W. Study on earthquake hazard response process by “Pohang earthquake” case analysis. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2021, 21, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.I.; Jang, C.R.; Jang, M.Y. A Study on Improvement of the Local Government “Manual for Actions at Scene” to Increase Field Applicability. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2019, 19, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.Y. Study on the Establishment of an Efficient Disaster Emergency Communication System Focused on the Site. J. Korean Soc. Disaster. Inf. 2014, 10, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.E.; Yoo, S.S.; Kim, I.H. A study on the improvement of legal system for the investigation of natural disaster damage. In Proceedings of the Korea Society of Hazard Mitigation Academic Conference, Republic of Korea, 27–28 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Seo, Y.J.; Park, K.Y. Analyzing damage investigation method for storm and flood damage prediction: Focus on increasing accuracy. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2019, 19, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E. What’s the disaster recovery? Types and preimpact plan of recovery. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2011, 11, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, H.Y. Long-term disaster recovery plan in Japan and US: Policy implications of natural disaster recovery plan in Korea. Crisis Emerg. Manag. 2017, 13, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Hwang, H.U. A Study on the Current Status and Improvement of the Support System for the Victims of Social Disaster in Goyang City; Goyang Research Institute: Goyang, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Orru, K.; Hansson, S.; Gabel, F.; Tammpuu, P.; Krüger, M.; Savadori, L.; Meyer, S.F.; Torpan, S.; Jukarainen, P.; Schieffelers, A.; et al. Approaches to ‘vulnerability’ in eight European disaster management systems. Disasters 2022, 46, 742–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, N. Analyzing Local Government Capacity and Performance: Implications for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S. An analysis of type and characteristics of corruption in the procedure of authorization and permission of local governments: Focusing on audit results of the Board of Audit and Inspection. Korea Local Admin. Rev. 2021, 35, 43–74. [Google Scholar]
- The Board of Audit and Inspection. Audit Report on the Agricultural Reservoir Safety Management Status 2021. Available online: https://www.bai.go.kr/bai/result/branch/detail?srno=2634 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).