Abstract
With the popularization of digital technology, the problem of information pollution caused by fake news has become more common. Malicious dissemination of harmful, offensive or illegal content may lead to misleading, misunderstanding and social unrest, affecting social stability and sustainable economic development. With the continuous iteration of artificial intelligence technology, researchers have carried out automatic and intelligent news data mining and analysis based on aspects of information characteristics and realized the effective identification of fake news information. However, the current research lacks the application of multidisciplinary knowledge and research on the interpretability of related methods. This paper focuses on the existing fake news detection technology. The survey includes fake news datasets, research methods for fake news detection, general technical models and multimodal related technical methods. The innovation contribution is to discuss the research progress of fake news detection in communication, linguistics, psychology and other disciplines. At the same time, it classifies and summarizes the explainable fake news detection methods and proposes an explainable human-machine-theory triangle communication system, aiming at establishing a people-centered, sustainable human–machine interaction information dissemination system. Finally, we discuss the promising future research topics of fake news detection technology.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of big data and information dissemination technology, fake news spreads through social media, posing a destructive threat to the sustainable development of society. False information not only undermines public trust and disrupts social order but also leads to misleading decisions, social division and opposition, which hinder the normal operation and progress of society. Fake news specifically refers to news reports that are untrue or exaggerated, such as Figure 1. These reports may be deliberately created to mislead the public or promote a specific agenda. The influence of fake political news on the Internet is more obvious than that of fake news about terrorism, natural disasters, science, urban legends or financial information [1]. Compared with the truth, rumors tend to spread farther, faster and wider, which indicates fake news is more novel than real news. However, fake news often brings anxiety to people, affects the normal operation of society and threatens the sustainable development of society.
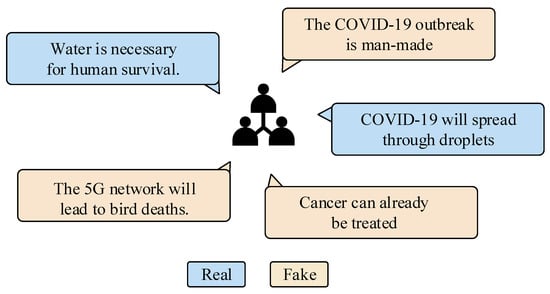
Figure 1.
News disseminated on social media.
Specifically, the dissemination of information exhibits several characteristics, including rapidity of dissemination, information overload, universality of content, indistinguishability of authenticity, harmfulness of impact, trans-regional reach, discrimination of stigma, sociability of media and so on [2,3,4,5]. A vast amount of false information is flooded on social media and major mainstream media platforms, giving rise to the phenomenon known as the information epidemic. The essence of the information epidemic is the presentation of the complex pattern of the integration of various communication mechanisms, such as mass communication, network communication and intelligent communication, against the background of new technology. Consequently, the detection of fake news technology becomes an urgent necessity in contemporary society for the identification of fake information.
In recent years, methods of fake news detection have been summarized in some studies. Zhou et al. [6] analyzed four aspects: knowledge, writing style, communication mode and source credibility. Zhang et al. [7] described the negative impact of online fake news and summarized the latest detection techniques available at that time. Hu et al. [8] summarized the fake news detection technology from three perspectives: supervised, weakly supervised and unsupervised. Athira et al. [9] conducted a systematic investigation into explainable artificial intelligence for fake news detection. These reviews lack multidisciplinary considerations, and there are still many deficiencies in the explainable, summarized fake news detection methods. Based on the analysis of the above, in order to develop a people-centered, explainable fake news detection system combined with multidisciplinary theoretical knowledge, we give a comprehensive overview of the research situation in fake news detection. The specific contributions are as follows:
- We investigate the current research status of fake news detection technology, including datasets, research methods and technical models. On this basis, it discusses the use of multimodal technology and innovatively summarizes and analyzes the research progress in communication, linguistics, psychology and other disciplines in fake news detection.
- We summarize the general fake news detection methods, which are divided into three aspects according to the development of different stages. At the same time, it analyzes explainable fake news detection and reviews the research related to explainable model structure and explainable model behavior.
- Based on the summary of the research progress on fake news detection, we propose an explainable triangular communication system consisting of humans, machines and theory that can be constructed, aiming to establish a people-centered, sustainable human–machine interaction information dissemination system. On this basis, the promising research topics of fake news detection technology in the future are discussed.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 is the overview. Section 3 provides an overview of the general models utilized for detecting fake news. Section 4 summarizes the fake news detection dataset. Section 5 evaluates the explainable fake news detection techniques. Finally, Section 6 concludes the work and suggests directions for future research.
2. Overview
2.1. Literature Search
This paper uses the Google Scholar database as a reliable source to assess recent trends in fake news detection research over the past five years. Using “fake news”, “fake news detection”, “multimodal fake news detection”, “multidisciplinary + fake news” and “explainable fake news detection” as relevant keywords, the database was queried. The search yielded a total of 18,100 references published in the fake news detection field between 2018 and 2023. The results obtained were carefully analyzed to identify the prominent research directions in the field. This review article provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research in fake news detection and highlights the most promising avenues for future investigation. With the help of deep insights into the various concerns in the field of fake news detection research, we are able to better appreciate the potential of this technique to develop more efficient and credible fake news detection techniques.
The specific research on fake news detection includes fact verification, position detection, topic detection and other tasks involving text classification, text clustering, image understanding, speech recognition and other research directions. The related research on fake news detection uses technologies such as text mining [10], machine learning [11], deep learning [12], natural language processing [13], machine vision [14] and other technologies to extract and identify key information from subjective visual perceptions of text or news pages. According to the summary and classification of a large number of references, the entire fake news detection method can be divided into three stages: (1) Machine learning stage. (2) Compared with machine learning algorithms, deep learning is not limited by manual feature extraction. It can extract text features from language texts through the self-learning ability of the network layer, which greatly improves the system performance of natural language processing tasks [12]. Deep learning networks, including convolutional neural networks [15] and recurrent neural networks [16], are applied to fake news detection tasks. They can effectively learn complex semantic features and high-level semantic representations from text and have been shown to improve the performance of fake news detection tasks. (3) However, the manual annotation of large text data is very complex, and the data used for natural language processing tasks is very limited. The application of deep learning models with strong dependency data in natural language processing is also very challenging. In order to avoid the problems of overfitting and insufficient generalization ability caused by insufficient data volume, researchers began to explore the pre-trained model for semantic representation. So far, the pre-training model based on the transformer structure [17] has been vigorously developed. The representative BERT pre-training model [18], the GPT model [19,20,21], etc., have made rapid progress in the development of natural language processing. At the same time, the relevant studies on fake news detection have also been further developed.
2.2. Fake News Classification
The categorization of fake news is multifaceted and diverse, encompassing everything from unverified hearsay circulating on social media to deceitful propaganda deliberately spread by its creators. According to references [22,23,24,25], fake news is classified into five categories, illustrated in Table 1: (1) deceptive fake news; (2) false information of rumor nature; (3) false comment information; (4) headline party-type fake news; (5) fact-based recombination of false information.

Table 1.
Classification and explanation of fake news.
2.3. Research Methods of Fake News Detection
Most of the existing research on fake news detection methods regards fake news detection as a classification task. At present, according to the main features used by the classification model, from the perspective of methods, fake news detection can be divided into three categories: content-based detection methods, social network-based detection methods and knowledge-based detection methods.
2.3.1. Content-Based Detection Method
The content-based fake news detection method aims to extract various semantic features from the news content and detect the authenticity of the news through these features. There are some linguistic differences between fake news and true news, and fake news can be detected by distinguishing the language style of true and fake news texts. Fake news is more subjective than real news. The study found that the first person and the second person are used more in fake news, and fake news contains more words that can be used for exaggeration (such as subject, transfinite words and modal adverbs), while real news often uses specific (such as numbers), objective (such as third person) and positive words. The author of fake news will be more extreme. The study analyzes the writing styles of left-wing news and right-wing news [26,27] and finds that they all have extremist tendencies, political tendencies and hatred. However, not every linguistic feature has the same weight, and the importance of different lexical features is different. Song et al. [28] extracted a complete set of content features from real and fake news, including the total number of words in the news, the length of the content, the number of capital words, special symbols, sentences at the beginning of the number, offensive words, etc. Through experiments, the importance ranking of the features is listed, and it is found that the total number of words, the length of the content and the number of capital words have a greater impact on the discrimination of real news. Abbreviations and the total number of words have a greater impact on discrimination against fake news.
2.3.2. Detection Method Based on Social Network
The content-based approach can discover the linguistic features of true and fake news. However, sometimes fake news will mislead readers by deliberately imitating the writing techniques of real news. The content-based approach cannot distinguish the feature differences between such fake news and true news. In order to solve this problem, we can make full use of hidden information as auxiliary data, such as social background information and propagation paths in social networks. Social background information is one of the research directions. Shu et al. [29] explored the relationship between user data and fake news on social media and used the user’s social participation as auxiliary information for detection. Furthermore, Shu et al. [30] proposed a framework to simulate the triadic relationship between news publishers, news articles and users, extract effective features from the participation behavior of news publishers and readers, and then capture the interaction between them. Studies have shown that the use of social background information can not only improve the effect of fake news detection but also effectively predict it early. Another research direction detects fake news by simulating the propagation path of fake news in the network. Through experiments, Monti et al. [31] found that the mode of transmission is an important feature of fake news that exceeds other aspects such as news content, user data and social behavior. Raza et al. [32] proposed a fake news detection framework based on the Transformer architecture, which includes encoder and decoder parts. The encoder part is used to learn the representation of fake news data, and the decoder part is used to predict future behavior based on past observations. The model uses the characteristics of news content and social background to improve classification accuracy.
2.3.3. Knowledge-Based Detection Method
Knowledge-based (KB) fake news detection detects the authenticity of news by verifying fake news and facts, so this is also called fact checking. Fact checking can be divided into two categories: manual verification and automatic verification [6]. The manual method uses domain expert knowledge or the crowdsourcing method. It has high accuracy but low efficiency, which cannot meet the needs of the era of big data. The automatic verification method using natural language processing and machine learning technology has become a hot research field. Fact checking first needs to construct a knowledge base or knowledge graph from the network through knowledge extraction. Then it compares and verifies the fake news with the knowledge base or knowledge graph to judge the authenticity of the news. Pan et al. [33] used knowledge graphs to detect fake news based on news content. They solved the problem that computational fact checking is not comprehensive enough. By extracting the triples from news articles, their method’s F0 score exceeds 80.1. Hu et al. [34] developed a heterogeneous graph attention network to learn the context of news representation and encode the semantics of news content. By using an entity comparison network, they compare the context entity representation with the derived representation from the knowledge base (KB). This comparison aims to capture the consistency between the news content and the KB.
Based on the above analysis and the content fake news detection method, we try to extract effective features from text information and locate the key information about fake news. Fake news based on social networks and knowledge requires not only news information itself but also vast external resources, such as stance information, knowledge information and multi-modal feature information. In text-based fake news detection, we try to analyze the style and content characteristics of the news, capture specific features and judge the authenticity of the news. At the same time, there are also studies [35] that combine content features and environmental features as the input of the classifier. Additionally, they integrate user data, social behavior, propagation paths and other features to optimize the detection method [31]. The existing methods are all different aspects of fake news detection methods, but they also have limitations. How to combine the existing methods to improve them and effectively improve the performance of fake news detection has become an urgent problem to be solved.
2.4. Multimodal Fake News Detection
In addition to the detection method based on a single feature source, it can also combine multiple features for fake news detection. In recent years, the data used in fake news detection is no longer limited to text information, and there has been an increasing focus on visual features. Multimodal fake news detection refers to the use of multiple types (such as text, images, etc.) of data to determine whether a news report contains misleading or inaccurate content [36,37,38]. Cao et al. [39] found that visual content has become an important part of fake news. Fake news often uses unverified visual content (video, images, etc.) to mislead readers and deepen their trust in false information. Pictures, videos and other media information can also be applied to fake news detection. Figure 2 shows some examples of fake news that we collected on the network, with both textual and visual features. Fortunately, many multimodal datasets have been made available. For example, Shu et al. [23] proposed FakeNewsNet, a fake news resource library that covers news content, social environments and spatio-temporal information. It greatly enhances the capability of multi-feature fusion for detecting fake news.

Figure 2.
Fake news examples in multimodal scenarios. The source of subgraph (a) is: https://scroll.in/video/994617/watch-israelis-celebrate-near-western-wall-while-tree-burns-in-al-aqsa-mosque-compound-in-jerusalem, accessed on 5 July 2023, subgraph (b–d) are: https://www.thequint.com/news/webqoof/webqoof-quiz-25-to-30-june-pm-narendra-modi-hindu-priests-nitish-kumar-russia#read-more, accessed on 5 July 2023.
The main idea of the multimodal method is to train features from different modalities and then fuse them. Some fake news detection methods have been integrated into methods based on cross-modal comparative learning. For example, Qi et al. [40] mapped the pictures in fake news to the frequency and pixel domains and then fused the visual information in the two domains through a multi-domain visual neural network. Singhal et al. [41] obtained text features and visual features through pre-training models and fused them into new feature representations. Their simple, unified framework is shown in Figure 3 (the fake news image in Figure 3 comes from the network).
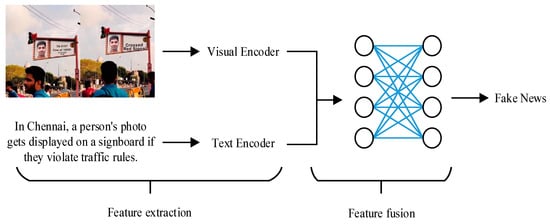
Figure 3.
Multimodal fake news monitoring flow chart.
In addition, research on multimodal fake news detection has gradually increased in recent years. Qian et al. [42] proposed a hierarchical multi-modal context attention network for fake news detection, which includes two modules: a multi-modal context attention module and a hierarchical coding module. To model the multi-modal context of news posts, the multi-modal context attention module uses pre-trained BERT [18] for text representation and pre-trained ResNet [43] for image representation, ensuring a seamless integration of both textual and visual information. It combines inter-modal and intra-modal relationships to enhance fake news detection. The hierarchical coding module captures the rich hierarchical semantics of the text to improve the representation of multimodal news.
The MCAN model proposed by Wu et al. [36] aims to learn multi-modal fusion representations by considering the dependencies between different modalities. The model includes three main steps: feature extraction, feature fusion and fake news detection. In the feature extraction step, three sub-models are used to extract features from the spatial domain, frequency domain and text. The VGG-19 [44] network is used to extract visual features from the spatial domain, and the ACNN-based sub-network is designed to extract features from the frequency domain, especially for re-compressed or tampered images. Furthermore, the BERT model is used to obtain the text features of the text content. In the feature fusion step, the deep common attention model is used to fuse multimodal features. The fusion process simulates the way that humans first see the image and then read the text. The common attention model is composed of multiple common attention layers, which capture the interdependence between different features. Finally, the fusion feature is used to detect fake news, and the output of the common attention model is used to judge the authenticity of the input news.
Wang et al. [37] proposed a cross-modal contrastive learning framework, COOLANT, for multimodal fake news detection. The framework consists of three main components: a cross-modal contrastive learning module for alignment, a cross-modal fusion module for learning cross-modal correction and a cross-modal aggregation module with an attention mechanism and guidance to improve the performance of multimodal fake news detection. The cross-modal contrast learning module aligns features by converting single-modal embedding into a shared space. It uses auxiliary cross-modal consistency learning tasks to measure the semantic similarity between images and texts and provides soft targets for the contrast learning module. The contrastive learning module uses the contrast loss to predict the actual image-text pairing in the batch.
In Table 2, we summarize several multimodal fake news detection methods, including the main techniques they use, datasets and extracted features and the corresponding accuracy performance.

Table 2.
Summary of multimodal fake news detection methods.
2.5. Multidisciplinary Research Progress
In the past few decades, there have been studies on fake news and its detection in many disciplines, including computer science, sociology, psychology, linguistics, communication and neurocognitive science [30,45,46,47]. Each field has its own research content and research methods for fake news. There are also studies [46] that combine the knowledge of these fields and use interdisciplinary methods to detect fake news. Multidisciplinary false news theory research can help the natural sciences achieve fake news detection. Figure 4 summarizes the basic problems of fake news detection in various disciplines, and we also hope that future research can combine more interdisciplinary knowledge.

Figure 4.
Research on fake news in multidisciplinary fields.
2.5.1. Psychology
Psychological researchers mainly explore the cognitive behavior of fake news and study the psychological mechanisms of fake news dissemination [48,49]. Bordia et al. [50] found that the interactive behavior of fake news is largely based on people’s psychological needs for the truth of the facts after analyzing the content of fake news on the Internet. The psychological factors that promote the dissemination of fake news include uncertainty, anxiety, etc. Pennycook et al. [51] investigated why people believe and share fake or highly misleading news online. They believe that it is the strong causal effect of political motivation on beliefs that makes people believe fake news.
2.5.2. Neuro-Cognitive Science
The sensitivity to fake news attacks depends on whether Internet users think fake news articles/clips are real after reading them. Arisoy et al. [52] tried to understand the sensitivity of users to text-centric fake news attacks through neurocognitive methods. They studied the neural basis related to fake news and real news through electroencephalograms (EEG), designed and ran EEG experiments on human users and analyzed the neural activities related to fake news and real news detection tasks of different types of news articles. Finally, they found that human detection of fake news may be ineffective and have potentially adverse effects.
2.5.3. Linguistics
Linguistic researchers [53] use computer technology to analyze the language content of fake news in combination with relevant theoretical content and summarize the pragmatic features of fake news and the language structure that triggers the spread of fake news. Choudhary et al. [54] believed that it is promising to start from language indicators, using qualitative and quantitative data analysis as the analysis method, through the detection and comparison of 16 attributes under the three main language feature categories (vocabulary, grammar and syntactic features) manually assigned to news texts, to identify the systematic nuances between fake news and factual news.
2.5.4. Communication Science
Communication researchers mainly analyze the concept of fake news [55] and try to find out the information dissemination mechanism, prevention and governance model of fake news in the context of the continuous use of social media [56]. Jana et al. [57] proposed that the current concept of fake news is more extensive. The study believes that the essence of fake news is a two-dimensional phenomenon of public communication, which puts forward the theoretical framework of fake news research. Di et al. [58] revealed the sharing motivation related to fake news: benign online users may not share fake news in pursuit of financial or political/ideological goals but seek social recognition of the desired group by informing other members of specific related topics, which also strengthens the unity of the group.
2.6. Mitigation of the Spread of Malicious Content
Halting the distribution of malicious content online demands a blend of diverse approaches and strategies. Present studies employ deep learning architectures integrating social networks, propagation trees and other techniques to establish systems that automatically classify and screen malicious content, thereby preventing its entry into online forums or mitigating its distribution. By studying the problem of detecting geolocated content communities on Twitter, Apostol et al. [59] propose a new distributed system that offers nearly real-time information on hazard-related events and their development. Furthermore, they introduce a novel deep learning model to identify fake news, and misguided tweets will be eliminated from the display. In order to alleviate the spread of real-time fake news in social media, Truică et al. [60] proposed a real-time network awareness strategy that constructs a minimum cost-weighted directed spanning tree for the detected nodes and immunizes the nodes in the tree by using a novel ranking function to score the harmfulness of the nodes. In addition, Coban et al. [61] propose a novel COmmuNiTy-based Algorithm for network ImmuNization that uses network information to detect harmful content distributors as well as generate partitions and immunize them using subgraphs induced by each distributor.
The diffusion-based method [62,63,64] can also alleviate the spread of malicious content. By using the propagation mechanism in social networks, it can guide the propagation path of information in a targeted manner, thereby reducing the impact of malicious content. This method emphasizes active intervention and the influence of network communication structure in order to achieve the purpose of reducing the spread of malicious content.
In short, by researching how to stop the spread of malicious content, working with governments, civil society organizations and technology companies to develop relevant regulations and guidelines can be effective in combating the spread of malicious content.
3. General Technical Model of Fake News Detection
From the perspective of technical methods, the artificial intelligence technology used in fake news detection [65] involves many research fields such as natural language processing, computer vision and data mining [66]. Fake news is divided into three categories: false text news, false picture news and false video news. For false text news detection, natural language processing has gradually become an important technical means in social science and information dissemination research [6]. Its primary applications encompass sentiment analysis, which centers around text classification techniques; news summarization generation, which focuses on text summarization techniques; and opinion mining, which relies on topic modeling techniques [67]. Therefore, for the detection of false information in text data, research on the application of natural language processing technology [68] is also constantly developing. For picture news, video news, etc., in terms of false picture news detection, researchers use computer vision technology [69,70,71] to detect false pictures synthesized. In addition, the continuous development of deep synthesis technology has led to the proliferation of fake videos. Researchers use deep learning technology to detect face tampering in videos [72].
It is generally believed that false text detection has gone through three stages: the first stage, the artificial feature design stage, started in 2011, which is mainly manual feature extraction based on expert knowledge; the second stage, the data-driven stage, started in 2016, is based on the research of various methods based on deep learning. The third stage, so far, is the research and exploration of the integration of knowledge and data. This stage is based on the pre-training model. Based on the above analysis, this paper believes that the specific technical methods of fake news detection research have the following aspects:
3.1. Fake News Detection based on Machine Learning
Commonly used classification models for fake news detection based on machine learning include support vector machine [73] and naive bayes [74]. In addition, logistic regression [75] and decision trees [76], such as random forest classifiers, can also be used in fake news detection tasks [77]. The basic principle of these models is to detect text based on the manual features of expert knowledge. Specific features include: linguistic features, theme features, user features and communication features. Eldesoky et al. [78] presented a classification model with the capability to detect fake news by utilizing Doc2vec and Word2vec embeddings as feature extraction techniques. The combination of the Doc2vec model and support vector machines achieved 95.5% accuracy on a real-world dataset.
3.2. Fake News Detection based on Deep Learning
Because machine learning is based on manual feature extraction, there will be deviations, and it performs poorly in feature extraction speed. In addition, machine learning produces high-dimensional representations of language information, resulting in dimensional disasters. In contrast, deep learning has more advantages than machine learning, showing higher accuracy and precision in fake news detection. Lai et al. [79] compared several machine learning and deep learning models based on pure content features. They found that the performance of the neural network model is better than the traditional ML model, and the accuracy of the neural network model is about 6% higher than the ML model. The essence of the neural network model is to use the method of word embedding [80] to combine the language model and feature learning to detect fake news. The fake news detection model based on a neural network has achieved relevant results in the research of fake news detection in many languages by using the word embedding method. A word embedding is a numerical representation of a word that captures its semantics based on the context in a given corpus. Word embedding can help understand semantics and find contextual clues, which is helpful for false news detection. Ilie et al. [81] used three word embeddings, Word2Vec, FastText and GloVe, to preserve word context, trained multiple deep learning architectures for classification and compared their performance in detecting the authenticity of news articles, ultimately obtaining the best results using a recursive convolutional neural network-based architecture.
The most typical recurrent neural network and convolutional neural network in deep learning can be used to solve the problem of fake news detection. Ma et al. [82] first used the hidden layer of a recurrent neural network to represent fake news information and proved that the model is superior to the good performance of artificial features. Since then, a model called FNDNet (Deep CNN) [83] has been proposed to learn the discriminative features of detecting fake news using multiple hidden layers. In addition, Huang et al. [84] used a graph convolutional neural network (GCN) [85] to learn user representations from graphs created by user behavior information.
3.3. Fake News Detection Based on Pre-Training Model
Traditional word embeddings may be difficult to capture complex contextual relationships, and they regard words as independent entities without considering the entire sentence structure. Vaswani et al. [17] introduced the Transformer, a deep learning model architecture, in 2017, which yielded exceptional outcomes in natural language processing tasks. The transformer enables the model to better capture the context and semantic information in the text so as to more accurately identify malicious content. Transformer introduces position encoding to process the position information of words in the input sequence. This allows the model to distinguish words in different locations, thereby avoiding the loss of location information. Its encoder–decoder structure can understand text at different levels and provide effective detection methods for multiple types of malicious behavior. Research [32,86,87,88] and others have achieved good performance in detecting fake news using the transformer architecture. In practice, the choice of embedding depends on factors such as the size of the dataset, computing resources and the complexity of fake news detection tasks. Combining word embedding and transformer embedding may produce better results because word embedding captures the meaning of a single word while transformer embedding captures complex sentence-level semantics. Truică et al. [89] propose a new document embedding (DocEmb) constructed using word embeddings and transformers that achieves better results than more complex deep neural network models. In addition, Truică et al. [90] also proposed two bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) architectures, incorporating sentence transformers, to address two tasks: (1) a multi-class monolingual task of detecting fake news and (2) a multi-class cross-lingual task of detecting fake news. Using multiple transformer models may also achieve good performance. Truică et al. [91] proposed a new deep neural integration architecture based on transformers for false information detection (MisRoBÆRTa), which uses RoBERTa-Bart sentences to embed error information and is superior to other transformer models in false information detection tasks.
In 2018, with the emergence and development of pre-training models, natural language processing tasks entered the era of pre-training models. Fine-tuning based on the BERT model [18] has significantly improved the performance of many natural language tasks. For fake news detection in natural language processing tasks of text data, the BERT pre-training model and related improved models gradually replace the original language model, which has become the basis of current research. Jwa et al. [87] combined news data in the pre-training phase to improve fake news recognition skills; Kaliyar et al. [92] proposed a BERT-based deep convolution method (fakeBERT) to detect fake news. The advantage of the pre-trained model is that the BERT method is unique in identifying and capturing contextual meanings in sentences or texts. In the model learning process, it does not need to go deep into the details of fake news to achieve good detection performance.
After several years of development, the BERT pre-training model based on transformer structure has gradually produced many related models [93,94,95] after structural adjustment, performance optimization and retraining. These models are collectively referred to as BERTology series models and have achieved good performance in various tasks. In summary, the fake news detection method based on the pre-trained model is already a research trend in this field. However, despite the complex characteristics of fake news, fake news detection based on pre-trained models still cannot achieve good performance in practical applications, like other practical tasks. How to extract features from more complex semantic information about fake news and establish a more effective fake news detection model for the ‘pre-training + fine-tuning’ paradigm of the pre-training model [96] is still an urgent problem to be solved.
4. Dataset
In the detection of fake news, the dataset used can be divided into single-modal and multi-modal data, as shown in Figure 5. We gathered prevalent fake news datasets from the past five years based on citations. Multimodal data has a more diverse form, typically comprising a combination of images or video text, as demonstrated in Table 3. Abbreviations for technical terms are defined upon first use. In contrast, unimodal datasets exclusively comprise text, providing a more extensive characterization. According to the dataset-construction method, data characteristics and adaptation tasks, it can be divided into three categories:
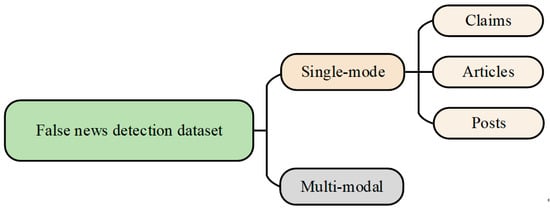
Figure 5.
Dataset division of fake news detection.

Table 3.
The dataset of Multimode.
- (1)
- Claims/Statements
A statement is one or more sentences that contain information that needs to be verified for authenticity. As shown in Table 4, this type of data includes claims and statements collected from debates, campaigns, Facebook, Twitter, interviews, advertisements, etc., as well as entries in the Weki encyclopedia. Such datasets are often related to fact checking, and sometimes clear evidence is introduced to determine whether a particular claim is correct.

Table 4.
The dataset of Single-mode claims.
- (2)
- Posts
Social media posts are also composed of one or more sentences with a more focused theme, such as in Table 5. But more importantly, it introduces user information, network information and other information on social media, which helps to build a high-quality fake news detection model.

Table 5.
The dataset of Single-mode posts.
- (3)
- Articles
A text is a whole text composed of many interrelated sentences. As shown in Table 6, the salient feature of the chapter is that the structure is often title + text, and there is a contextual relationship between sentences. The corresponding problems are often not clearly given evidence, and it is necessary to analyze the evidence from the writing style of the text itself and so on.

Table 6.
The dataset of Single-mode articles.
5. Explainable Fake News Detection
With the rapid development and application of machine learning and artificial intelligence technology in various fields, it is very important to explain the results of the algorithm’s output to the user. The interpretability of artificial intelligence means that people can understand the choices made by artificial intelligence models in their decision-making process, including the reasons, methods and content of decision making [138]. Simply put, interpretability is the ability to turn artificial intelligence from a black box into a white box. At present, explainable artificial intelligence methods are applied to different fields in different industries, including biomedical, financial applications, video payment, and media industries. The core of explainable artificial intelligence is to obtain human trust. From this, we can see that there are two important concepts that can explain artificial intelligence: trust and interpretation. For explainable artificial intelligence, the connotation of interpretation is that agents must communicate, exchange and run into different people repeatedly before they can gain human trust. Therefore, for the agent, when explaining, it is necessary to consider the different educational backgrounds, knowledge levels and other factors of the audience and then design the content and form of the explained information.
Figure 6 shows an interactive, explainable AI framework for human–machine communication. The main participants in the system are interpreters and interpretive audiences. Interpreters refer to artificial intelligence agents with many explainable AI methods that can make decisions based on specified tasks; the audience listens to the explanations given by the interpreters, who are generally the affected people involved in a task as well as decision makers and developers. The interpreter provides different forms of interpretation results to the interpretation audience according to different task scenarios; the interpreter, in turn, asks the interpreter questions so that the interpreter can make adjustments and optimizations. In this way, the interpreter will be more intelligent and put forward more convincing interpretation results.
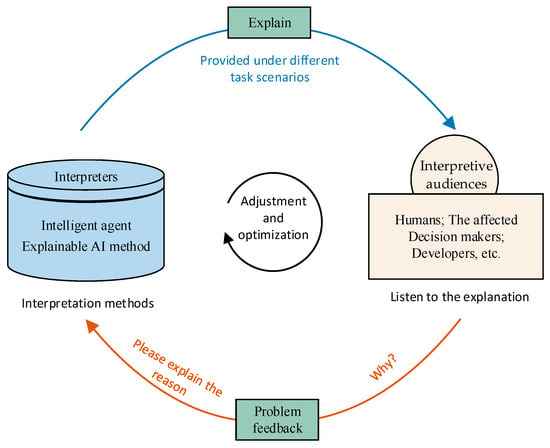
Figure 6.
Explainable AI framework diagram for human–machine communication interaction.
In order to reduce the risk of fake news dissemination compared with the pure data-driven method, in addition to the interpretability analysis of the model structure through machine learning, it is also necessary to interpret the model behavior of fake news detection through multidisciplinary, comprehensive research in the framework of human–machine communication and interaction, hence continuously optimizing the fake news detection system. In the face of the research problem of explainable fake news detection, how to explain the results of fake news detection and develop an intelligent fake news detection system that enables effective human–machine collaboration, comprehension, interpretability and sustainability has become a crucial research topic. The artificial intelligence research methods are divided into two kinds: one is derived from the interpretability of the model structure to make humans understand the working principle of the model; the other focuses on the behavioral explanation of the model, that is, letting the model give the score or reason for the prediction result rather than only a cold label. Based on the above two, we first summarize and review them in Section 5.1 and Section 5.2, respectively. In Section 5.3, we propose a human-machine-theory triangle communication system for fake news detection based on the interactive explainable AI framework of human–machine communication, which may help us better realize explainable fake news detection.
5.1. Explainable Model Structure
The explainable model structure is to analyze and understand the internal structure of the model through explainable technology and to understand the working principle and working mechanism of the model. Structural analysis involves comprehending the operating mechanism and fundamental principles of the model structure. Only by fully understanding the working mechanism and working principle of the model structure can researchers and developers determine what problems exist in the model and when it is difficult to continue improving its performance. Only then, on the premise of understanding the characteristics of the model structure, can they point out the next optimization direction of the model. This enables them to improve the performance of the model in a better and faster way. Most of these explainable models use deep learning methods such as knowledge graphs and attention mechanisms.
Chien et al. [139] proposed the Explainable AI (XAI) framework XFlag, used LSTM [140] to carry out the fake news detection model and used the Layered Relevance Propagation (LRP) [141] algorithm to explain the model. Wu et al. [142] used knowledge graphs to enhance the embedded representation learning framework to detect fake news while providing interpretations of relationships. In this study, an external dataset was used to extract a knowledge graph, and a graph neural network was utilized to pre-train structured features for entities and relationships. The pre-trained features and semantic features were then combined to integrate explainable structured knowledge for recognizing fake news. Chen et al. [143] designed an explainable modular structure for automatically detecting rumors on social media. They utilized a two-level attention mechanism to capture the relative importance both between features and between feature classes. Furthermore, they highlighted the most significant features in the news to explain the algorithmic results. In addition, based on multidisciplinary explainable fake news detection, Qiao et al. [144] used multidisciplinary language synthesis methods to train features that are understandable to humans and then used these features to train a deep learning classifier with a bidirectional recurrent neural network (BRNN) structure [145], so that the classifier can obtain more explainable detection results in news data.
Silva et al. [146] proposed a novel fake news early detection technology called Propagation2Vec, as shown in Figure 7. The technology assigns different levels of importance to nodes and cascades in the propagation network and reconstructs knowledge of the complete propagation network based on their partial propagation network during the early detection phase. The study further presents a comprehensive explanation of the underlying logic of Propagation2Vec according to the attention weights assigned to different nodes and cascades. This enhances the applicability of the method and stimulates future research in the domain of fake news detection utilizing propagation networks.
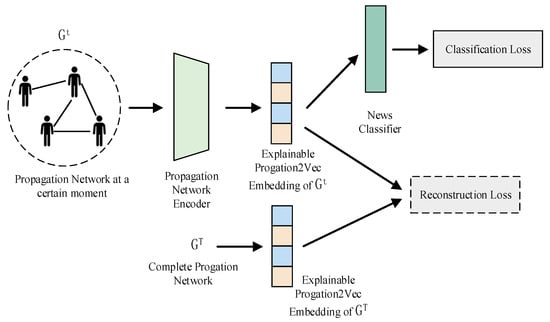
Figure 7.
Overview of Propagation2Vec.
We summarize the explainable model structure methods in Table 7, including the main techniques they use, datasets and accuracy performance.

Table 7.
Structural analysis of explainable fake news detection model.
5.2. Explainable Model Behavior
Explainable model behavior, that is, explainable analysis of the results of model prediction behavior, provides the basis for prediction results. Behavioral analysis typically involves comprehending the foundation of a model’s anticipated behavior. Since deep learning algorithms consist of nonlinear structures, these successful models are commonly obscure and have difficulty revealing the rationale of their forecasts in a format that humans can grasp. The absence of transparency and intelligibility regarding a model’s forecasts can lead to grave consequences.
Shu et al. [55] used the sentence-comment joint attention sub-network to improve the performance of fake news detection, aiming to capture the inherent interpretability of news phrases and user comments. The dEFEND algorithm module facilitates search functionalities for searching news dissemination networks, trending news, top statements and related news. Moreover, it presents test results and explanations. In a similar vein, Lu et al. [151] utilized the graph-aware common attention network (GCAN) to assess the authenticity of source tweets on social media while providing explanations for the results. GCAN uses the attention mechanism to capture three aspects of the algorithm results: highlighting key words in source tweets, identifying characteristics of retweet propagation paths and understanding the behavior of retweeters. Chi et al. [152] proposed an automated explainable decision-making system (QA-AXDS) based on quantitative argumentation. This system can detect fake news and explain the results to users. It automatically captures human-level knowledge, constructs an interpretation model based on a dialogue tree and employs natural language to help users understand the reasoning process within the system. Notably, QA-AXDS is fully automated and does not require expert experience as pre-input, which enhances the robustness of the system. Ni et al. [153] studied the use of a multi-view attention mechanism network (MVAN) [154] to detect fake news in social networks and provide explanations for the results. MVAN incorporates a dual attention mechanism, encompassing text semantic attention and propagation structure attention, to capture clues in source tweets and propagation structures. It identifies crucial keywords and generates explainable detection results. Raha et al. [155] proposed a neural model for factual inconsistency classification with explanations. By training four neural models, they can predict the inconsistency type and provide explanations for a given sentence. However, Bhattarai et al. [156] introduced an explainable fake news detection framework based on the Tsetlin Machine (TM) [157]. By capturing lexical and semantic features of true and fake news texts, this framework achieves accurate detection of fake news and the credibility score is used to provide interpretability.
Fu et al. [158] introduced a comprehensive and explainable false information detection framework called DISCO, as depicted in Figure 8. This framework addresses the challenge of detecting false information by leveraging the heterogeneity of false information and offering explanations for the detection results. Their approach demonstrates commendable accuracy and interpretability in a real-world fake news detection task.
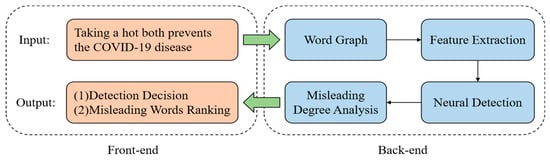
Figure 8.
System architecture of DISCO.
We summarize the explainable model behavior analysis methods in Table 8, including the main techniques they use, datasets and accuracy performance.

Table 8.
Behavior analysis of explainable fake news detection model.
5.3. Human-Machine-Theory Triangle Communication System
Based on the interactive, explainable AI framework for human–machine communication presented in Figure 6, we have augmented the system by incorporating multidisciplinary theoretical knowledge. We introduce a triangular communication system that humans, machines and theory can form. As depicted in Figure 9, this represents a potentially more comprehensive solution for achieving explainable fake news detection. In this system, the machine leverages a multidisciplinary theoretical training model, which can be a general technical model or an explainable AI model, to provide prediction results to humans. The human, equipped with theoretical knowledge, assesses the prediction results and provides feedback to the machine. Through this iterative process, the explainable fake news detection system can be continuously adjusted and improved, thereby enhancing human trust in the system.
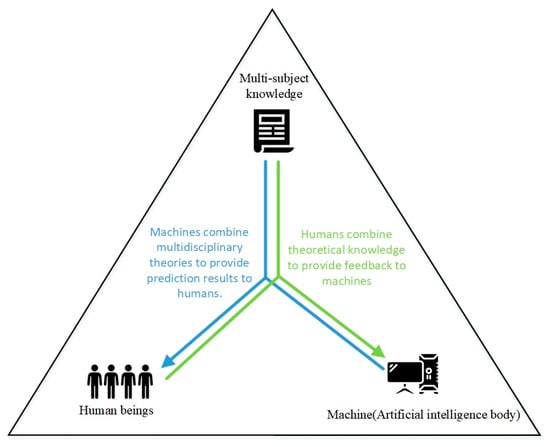
Figure 9.
Human-machine-theory explainable triangular communication framework diagram for fake news detection.
Unlike the interactive, explainable AI framework shown in Figure 6, this framework emphasizes the crucial role of these three components. The machine encompasses various fake news detection methods, including machine learning, deep learning, pre-training and multimodality. The human is responsible for reviewing and evaluating the prediction results generated by the machine and providing feedback. The theory refers to the multidisciplinary knowledge involved in fake news detection. This paper has introduced the relevant multidisciplinary research progress in Section 2.5. In terms of operation, to achieve improved detection results, the machine combines multi-disciplinary theory to facilitate the detection of fake news. The prediction results can be in the form of labels or explanatory content. Once the human receives these prediction results, they may question or doubt them, prompting verification by referring to the theory. The verification results are then fed back to the machine, forming a cycle of communication. With each iteration, the performance of the machine gradually improves, leading to an increase in human trust in the machine. Based on the above principles, the triangular communication system involves humans, machines and theory, integrates multidisciplinary knowledge, and employs artificial intelligence algorithms for information detection. Simultaneously, in collaboration with human feedback, the accuracy of fake news detection can be continuously enhanced and the fake news detection system can be promoted to become an agent that can be trusted by human beings.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
The accuracy and reliability of information dissemination are of great help to the sustainable development of society and the economy. To embrace digital transformation, green information technology and responsible information production and consumption, we can reduce resource consumption and improve efficiency. These measures can achieve the long-term benefits of information dissemination.
This paper focuses on investigating existing fake news detection technology and providing an overview of the research status of fake news detection methods. We collected almost all commonly used datasets, classified them from the perspectives of single-mode and multi-mode and summarized the research methods for fake news detection. This includes content-based detection methods, social network-based detection methods and knowledge-based detection methods. Considering the popularity of multimodal technology, we have also sorted out multimodal fake news detection methods. Additionally, this paper also discusses the research progress of fake news in multidisciplinary fields.
Furthermore, we discuss the general fake news detection technology along with the explainable fake news detection method. Specifically, we propose a human-machine-theory explainable triangular communication framework. It is characterized by being people-centered, incorporating multidisciplinary knowledge and aiming to establish the sustainable development of a human–machine interaction information dissemination system.
Finally, based on the review of fake news detection presented above, several topics deserve further investigation in the future: (1) With the emergence of large models like ChatGPT, a wave of large models has been set off. These large models are far better than previous models in terms of language ability. There is potential for utilizing the knowledge and language abilities of these models to achieve improved performance in false information detection. However, research on fake news detection using large models is currently lacking. (2) In the era of AI-generated content, deep forgery technology is becoming more prevalent in various fields such as film and television, games and privacy protection. However, the malicious use of deep forgery technology poses threats to personal reputation, social stability and political security. Therefore, future research should focus on developing deep forgery generation and defense methods to address these challenges. (3) From the perspective of explainable fake news detection, there is a need to develop comprehensive and explainable solutions. Currently, both in terms of model structure analysis and model behavior analysis, explainable artificial intelligence methods for fake news detection are not yet fully established. Designing an explainable fake news detection system has become crucial in the current complex information dissemination environment. (4) Brain science, neuropsychology, psychology and other multidisciplinary content are relatively cutting-edge fields of knowledge. At present, research on the neural mechanism of fake news is very limited. We believe that the special means in this field can contribute to the identification, defense and deeper understanding of fake news.
We hope that more efficient fake news detection methods can be developed in the future, thus promoting the sustainable development of information dissemination.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by L.Y. The first draft of the manuscript was written by L.Y. and H.J. Software, H.S.; Data curation, H.J.; Writing—review and editing, N.C. and L.S. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. CUC23GY005) and the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Trusted Software (No. KX202315).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vosoughi, S.; Roy, D.; Aral, S. The spread of true and false news online. Science 2018, 359, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apuke, O.D.; Omar, B. Fake news and COVID-19: Modelling the predictors of fake news sharing among social media users. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 56, 101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Linden, S.; Roozenbeek, J.; Compton, J. Inoculating against fake news about COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2020, 2020, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, Y.M.; de Moura, G.A.; Desidério, G.A.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Lourenço, F.D.; de Figueiredo Nicolete, L.D. The impact of fake news on social media and its influence on health during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. J. Public Health 2021, 31, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscadelli, A.; Albora, G.; Biamonte, M.A.; Giorgetti, D.; Innocenzio, M.; Paoli, S.; Lorini, C.; Bonanni, P.; Bonaccorsi, G. Fake news and Covid-19 in Italy: Results of a quantitative observational study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R. A survey of fake news: Fundamental theories, detection methods, and opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2020, 53, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ghorbani, A.A. An overview of online fake news: Characterization, detection, and discussion. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, B. Deep learning for fake news detection: A comprehensive survey. AI Open 2022, 3, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, A.B.; Kumar, S.M.; Chacko, A.M. A systematic survey on explainable AI applied to fake news detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106087. [Google Scholar]
- Hotho, A.; Nürnberger, A.; Paaß, G. A brief survey of text mining. J. Lang. Technol. Comput. Linguist. 2005, 20, 19–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-H. Machine Learning; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, K.; Chowdhary, K.R. Natural language processing. In Fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 603–649. [Google Scholar]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep learning for computer vision: A brief review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training. OpenAI Blog 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, N.; Dredze, M. Named Entity Recognition for Chinese Social Media with Jointly Trained Embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; pp. 548–554. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Mahudeswaran, D.; Wang, S.; Lee, D.; Liu, H. Fakenewsnet: A data repository with news content, social context, and spatiotemporal information for studying fake news on social media. Big Data 2020, 8, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y. “Liar, Liar Pants on Fire”: A New Benchmark Dataset for Fake News Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.00648. [Google Scholar]
- Zellers, R.; Holtzman, A.; Rashkin, H.; Bisk, Y.; Farhadi, A.; Roesner, F.; Choi, Y. Defending Against Neural Fake News. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1905.12616. [Google Scholar]
- Potthast, M.; Kiesel, J.; Reinartz, K.; Bevendorff, J.; Stein, B. A stylometric inquiry into hyperpartisan and fake news. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.05638. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkin, H.; Choi, E.; Jang, J.Y.; Volkova, S.; Choi, Y. Truth of varying shades: Analyzing language in fake news and political fact-checking. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017; pp. 2931–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikhi, S. An effective fake news detection method using WOA-xgbTree algorithm and content-based features. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 109, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Understanding user profiles on social media for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), IEEE, Miami, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Beyond news contents: The role of social context for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 11–15 February 2019; pp. 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, F.; Frasca, F.; Eynard, D.; Mannion, D.; Bronstein, M.M. Fake news detection on social media using geometric deep learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06673. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Ding, C. Fake news detection based on news content and social contexts: A transformer-based approach. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2022, 13, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.Z.; Pavlova, S.; Li, C.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Content based fake news detection using knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the Semantic Web–ISWC 2018: 17th International Semantic Web Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 8–12 October 2018; Proceedings, Part I 17. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 669–683. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, W.; Tang, D.; Shi, C.; Duan, N.; Zhou, M. Compare to the knowledge: Graph neural fake news detection with external knowledge. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Virtual Event, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 754–763. [Google Scholar]
- Bauskar, S.; Badole, V.; Jain, P.; Chawla, M. Natural language processing based hybrid model for detecting fake news using content-based features and social features. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z. Multimodal fusion with co-attention networks for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, Online Event, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 2560–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, S. Cross-modal Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Fake News Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14057. [Google Scholar]
- Amri, S.; Sallami, D.; Aïmeur, E. Exmulf: An explainable multimodal content-based fake news detection system. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Foundations and Practice of Security, Paris, France, 7–10 December 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Qi, P.; Sheng, Q.; Yang, T.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Exploring the role of visual content in fake news detection. In Disinformation, Misinformation, and Fake News in Social Media: Emerging Research Challenges and Opportunities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Cao, J.; Yang, T.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Exploiting multi-domain visual information for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), IEEE, Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; pp. 518–527. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, S.; Shah, R.R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P.; Satoh, S. Spotfake: A multi-modal framework for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), IEEE, Singapore, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Fang, Q.; Xu, C. Hierarchical multi-modal contextual attention network for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, 11–15 July 2021; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R.; Shu, K.; Liu, H. Fake news: Fundamental theories, detection strategies and challenges. In Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 11–15 February 2019; pp. 836–837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Jain, A.; Phoha, V.V.; Zafarani, R. Fake news early detection: An interdisciplinary study. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.11679. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, K.; Yu, Z. The mass, fake news, and cognition security. Front. Comput. Sci. 2021, 15, 153806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifeneder, R.; Jaffe, M.; Newman, E.; Schwarz, N. The Psychology of Fake News: Accepting, Sharing, and Correcting Misinformation; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Hanne, T.; Castillo, O.; Gandhi, N.; Rios, T.N.; Hong, T.-P. Hybrid Intelligent Systems: 20th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems (HIS 2020), 14–16 December 2020; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, Online, 2021; Volume 1375. [Google Scholar]
- Bordia, P.; DiFonzo, N. 10 Rumors during organizational change: A motivational analysis. In The Psychology of Organizational Change: Viewing Change from the Employee’s Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- Pennycook, G.; Rand, D.G. The psychology of fake news. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2021, 25, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisoy, C.; Mandal, A.; Saxena, N. Human Brains Can’t Detect Fake News: A Neuro-Cognitive Study of Textual Disinformation Susceptibility. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th Annual International Conference on Privacy, Security & Trust (PST), IEEE, Fredericton, NB, Canada, 22–24 August 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Giachanou, A.; Ríssola, E.A.; Ghanem, B.; Crestani, F.; Rosso, P. The role of personality and linguistic patterns in discriminating between fake news spreaders and fact checkers. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Information Systems: 25th International Conference on Applications of Natural Language to Information Systems, NLDB 2020, Saarbrücken, Germany, 24–26 June 2020; Proceedings 25. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, A.; Arora, A. Linguistic feature based learning model for fake news detection and classification. Expert Syst. Appl. May 2021, 169, 114171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Cui, L.; Wang, S.; Lee, D.; Liu, H. defend: Explainable fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, V.L. Disinformation and misinformation triangle: A conceptual model for “fake news” epidemic, causal factors and interventions. J. Doc. 2019, 75, 1013–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egelhofer, J.L.; Lecheler, S. Fake news as a two-dimensional phenomenon: A framework and research agenda. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 2019, 43, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, G.; Sit, J.; Ishizaka, A.; Nunan, D. Fake news, social media and marketing: A systematic review. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostol, E.-S.; Truică, C.-O.; Paschke, A. ContCommRTD: A Distributed Content-based Misinformation-aware Community Detection System for Real-Time Disaster Reporting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12984. [Google Scholar]
- Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S.; Nicolescu, R.-C.; Karras, P. MCWDST: A Minimum-Cost Weighted Directed Spanning Tree Algorithm for Real-Time Fake News Mitigation in Social Media. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.12190. [Google Scholar]
- Coban, Ö.; Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S. CONTAIN: A Community-based Algorithm for Network Immunization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.01934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tong, H.; Prakash, B.A.; Tsourakakis, C.E.; Eliassi-Rad, T.; Faloutsos, C.; Chau, D.H. Node Immunization on Large Graphs: Theory and Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2016, 28, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, A.; Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.S.; Karras, P. Sparse Shield: Social Network Immunization vs. Harmful Speech. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, New York, NY, USA, 1–5 November 2021; p. 1436. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Prakash, B.A. Data-Aware Vaccine Allocation Over Large Networks. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2015, 10, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshikawa, R.; Qian, J.; Wang, W.Y. A survey on natural language processing for fake news detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00770. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake news detection on social media: A data mining perspective. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.C.; Correia, A.; Murai, F.; Veloso, A.; Benevenuto, F. Supervised learning for fake news detection. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.A.; Vilares, D.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C.; Vilares, J. Sentiment analysis for fake news detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.I.; Ahmed, K.; Li, D.; Zheng, Z.; Alkahtani, H.K.; Mostafa, S.M.; Mamyrbayev, O.; Abdel Hameed, H. EFND: A semantic, visual, and socially augmented deep framework for extreme fake news detection. Sustainability 2022, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldani, M.H.; Momtazi, S.; Safabakhsh, R. Detecting fake news with capsule neural networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, M.; Liu, A.; Owens, A.; Efros, A.A. Fighting fake news: Image splice detection via learned self-consistency. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.; Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Learning rich features for image manipulation detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1053–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E. Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973; Volume 3, Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:12946615 (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Hosmer Jr, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 398. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, E.B.; Marin, J.; Stone, P.J. Experiments in Induction; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Antony Vijay, J.; Anwar Basha, H.; Arun Nehru, J. A dynamic approach for detecting the fake news using random forest classifier and NLP. In Computational Methods and Data Engineering: Proceedings of ICMDE 2020, Volume 2; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesoky, I.; Moussa, F. Fake news detection based on word and document embedding using machine learning classifiers. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2021, 99, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.-M.; Chen, M.-H.; Kristiani, E.; Verma, V.K.; Yang, C.-T. Fake News Classification Based on Content Level Features. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Ilie, V.-I.; Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S.; Paschke, A. Context-Aware Misinformation Detection: A Benchmark of Deep Learning Architectures Using Word Embeddings. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 162122–162146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Mitra, P.; Kwon, S.; Jansen, B.J.; Wong, K.-F.; Cha, M. Detecting rumors from microblogs with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliyar, R.K.; Goswami, A.; Narang, P.; Sinha, S. FNDNet–a deep convolutional neural network for fake news detection. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2020, 61, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, B. Deep structure learning for rumor detection on twitter. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), IEEE, Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Tarlow, D.; Brockschmidt, M.; Zemel, R. Gated graph sequence neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05493. [Google Scholar]
- Low, J.F.; Fung, B.C.M.; Iqbal, F.; Huang, S.-C. Distinguishing between fake news and satire with transformers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 115824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwa, H.; Oh, D.; Park, K.; Kang, J.M.; Lim, H. exbake: Automatic fake news detection model based on bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (bert). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundapu, S.; Mamidi, R. Transformer based Automatic COVID-19 Fake News Detection System. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.00180. [Google Scholar]
- Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S. It’s All in the Embedding! Fake News Detection Using Document Embeddings. Mathematics 2023, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S.; Paschke, A. Awakened at CheckThat! 2022: Fake News Detection using BiLSTM and Sentence Transformer. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2022: Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Bologna, Italy, 5–8 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Truică, C.-O.; Apostol, E.-S. MisRoBÆRTa: Transformers versus Misinformation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyar, R.K.; Goswami, A.; Narang, P. FakeBERT: Fake news detection in social media with a BERT-based deep learning approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 11765–11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Gunel, B.; Du, J.; Conneau, A.; Stoyanov, V. Supervised contrastive learning for pre-trained language model fine-tuning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.01403. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Levy, S.; Wang, W.Y. r/Fakeddit: A New Multimodal Benchmark Dataset for Fine-grained Fake News Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.03854. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D. FauxWard: A Graph Neural Network Approach to Fauxtography Detection Using Social Media Comments. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2020, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boididou, C.; Papadopoulos, S.; Zampoglou, M.; Apostolidis, L.; Papadopoulou, O.; Kompatsiaris, Y. Detection and visualization of misleading content on Twitter. Int. J. Multimed. Info. Retr. 2018, 7, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, S.; Rossetto, L.; Schuldt, H. The PS-Battles Dataset—An Image Collection for Image Manipulation Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04866. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A.; Christodoulopoulos, C.; Mittal, A. FEVER: A large-scale dataset for Fact Extraction and VERification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.05355. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, W.; Vlachos, A. Emergent: A Novel Data-Set for Stance Classification[EB/OL]; ACL: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://aclweb.org/anthology/N/N16/N16-1138.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Popat, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Strötgen, J.; Weikum, G. Credibility Assessment of Textual Claims on the Web. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international on conference on information and knowledge management, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 24–28 October 2016; p. 2178. [Google Scholar]
- Popat, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Yates, A.; Weikum, G. DeClarE: Debunking Fake News and False Claims using Evidence-Aware Deep Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.06416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanselowski, A.; Stab, C.; Schulz, C.; Li, Z.; Gurevych, I. A Richly Annotated Corpus for Different Tasks in Automated Fact-Checking. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.01214. [Google Scholar]
- Augenstein, I.; Lioma, C.; Wang, D.; Lima, L.C.; Hansen, C.; Hansen, C.; Simonsen, J.G. MultiFC: A Real-World Multi-Domain Dataset for Evidence-Based Fact Checking of Claims. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.03242. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A.; Cocarascu, O.; Christodoulopoulos, C.; Mittal, A. The FEVER2.0 Shared Task. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Fact Extraction and VERification (FEVER), Hong Kong, China, 3 November 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Hong Kong, China, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, R.; Guo, Z.; Schlichtkrull, M.; Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A.; Christodoulopoulos, C.; Cocarascu, O.; Mittal, A. FEVEROUS: Fact Extraction and VERification Over Unstructured and Structured information. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.05707. [Google Scholar]
- Nakov, P.; Barrón-Cedeño, A.; Elsayed, T.; Suwaileh, R.; Màrquez, L.; Zaghouani, W.; Atanasova, P.; Kyuchukov, S.; Martino, G. Overview of the CLEF-2018 CheckThat! Lab on Automatic Identification and Verification of Political Claims. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference of the CLEF Association, CLEF 2018, Avignon, France, 10–14 September 2018; pp. 372–387, ISBN 978-3-319-98931-0. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, T.; Nakov, P.; Barrón-Cedeño, A.; Hasanain, M.; Suwaileh, R.; Martino, G.D.S.; Atanasova, P. Overview of the CLEF-2019 CheckThat!: Automatic Identification and Verification of Claims. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.15118. [Google Scholar]
- Barron-Cedeno, A.; Elsayed, T.; Nakov, P.; Martino, G.D.S.; Hasanain, M.; Suwaileh, R.; Haouari, F.; Babulkov, N.; Hamdan, B.; Nikolov, A.; et al. Overview of CheckThat! 2020: Automatic Identification and Verification of Claims in Social Media 2020. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference of the CLEF Association, CLEF 2020, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baly, R.; Mohtarami, M.; Glass, J.; Marquez, L.; Moschitti, A.; Nakov, P. Integrating Stance Detection and Fact Checking in a Unified Corpus. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.08012. [Google Scholar]
- Khouja, J. Stance Prediction and Claim Verification: An Arabic Perspective. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.10410. [Google Scholar]
- Nørregaard, J.; Derczynski, L. DanFEVER: Claim verification dataset for Danish. In Proceedings of the 23rd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics (NoDaLiDa), Reykjavik, Iceland (Online), 31 May–2 June 2021; Linköping University Electronic Press: Linköping, Sweden, 2021; pp. 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Kotonya, N.; Toni, F. Explainable Automated Fact-Checking for Public Health Claims. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.09926. [Google Scholar]
- Wadden, D.; Lin, S.; Lo, K.; Wang, L.L.; van Zuylen, M.; Cohan, A.; Hajishirzi, H. Fact or Fiction: Verifying Scientific Claims. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.14974. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Bang, Y.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Misinformation Has High Perplexity. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04666. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, T.; Logan Iv, R.L.; Ugarte, A.; Matsubara, Y.; Young, S.; Singh, S. COVIDLies: Detecting COVID-19 Misinformation on Social Media. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for COVID-19 (Part 2) at EMNLP 2020, Online, 20 November 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Bordia, S.; Zhong, Z.; Dognin, C.; Singh, M.; Bansal, M. HoVer: A Dataset for Many-Hop Fact Extraction And Claim Verification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.03088. [Google Scholar]
- Patwa, P.; Sharma, S.; Pykl, S.; Guptha, V.; Kumari, G.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ekbal, A.; Das, A.; Chakraborty, T. Fighting an Infodemic: COVID-19 Fake News Dataset. In Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages during Emergency Situation; Chakraborty, T., Shu, K., Bernard, H.R., Liu, H., Akhtar, M.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1402, pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, T.; Gilbert, E. CREDBANK: A Large-Scale Social Media Corpus With Associated Credibility Annotations. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2015, 9, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.; Hoi, G.W.S.; Tolmie, P. Analysing How People Orient to and Spread Rumours in Social Media by Looking at Conversational Threads. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santia, G.; Williams, J. BuzzFace: A News Veracity Dataset with Facebook User Commentary and Egos. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2018, 12, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer-Vine, C.S.; Strapagiel, L.; Shaban, H.; Hall, E. Jeremy Hyperpartisan Facebook Pages Are Publishing False and Misleading Information at an Alarming Rate[EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/craigsilverman/partisan-fb-pages-analysis (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Shu, K.; Liu, H. MM-COVID: A Multilingual and Multimodal Data Repository for Combating COVID-19 Disinformation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04088. [Google Scholar]
- Hanselowski, A.; PVS, A.; Schiller, B.; Caspelherr, F.; Chaudhuri, D.; Meyer, C.M.; Gurevych, I. A Retrospective Analysis of the Fake News Challenge Stance Detection Task. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.05180. [Google Scholar]
- Szpakowski, M. Fake News Corpus[CP/OL]. Available online: https://github.com/several27/FakeNewsCorpus (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Gruppi, M.; Horne, B.D.; Adalı, S. NELA-GT-2020: A Large Multi-Labelled News Dataset for The Study of Misinformation in News Articles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04567. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, A.; Riedel, S. Fact Checking: Task definition and dataset construction. In Proceedings of the ACL 2014 Workshop on Language Technologies and Computational Social Science, Baltimore, MD, USA, 26 June 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2014; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Horne, B.; Adali, S. This Just In: Fake News Packs A Lot In Title, Uses Simpler, Repetitive Content in Text Body, More Similar To Satire Than Real News. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2017, 11, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Srihari, R. BREAKING! Presenting Fake News Corpus for Automated Fact Checking. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Student Research Workshop, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019; pp. 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.; Traore, I.; Saad, S. Detection of Online Fake News Using N-Gram Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques. In Intelligent, Secure, and Dependable Systems in Distributed and Cloud Environments; Traore, I., Woungang, I., Awad, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10618, pp. 127–138. ISBN 978-3-319-69154-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Kleinberg, B.; Lefevre, A.; Mihalcea, R. Automatic Detection of Fake News. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.07104. [Google Scholar]
- Torabi Asr, F.; Taboada, M. Big Data and quality data for fake news and misinformation detection. Big Data Soc. 2019, 6, 2053951719843310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Salem, F.K.; Al Feel, R.; Elbassuoni, S.; Jaber, M.; Farah, M. FA-KES: A Fake News Dataset around the Syrian War. ICWSM 2019, 13, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas Durán, J.; Gomez Adorno, H.; Sidorov, G.; Moreno, J. Detection of fake news in a new corpus for the Spanish language. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, G.K.; Nandini, D. FakeCovid—A Multilingual Cross-domain Fact Check News Dataset for COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11343. [Google Scholar]
- Confalonieri, R.; Coba, L.; Wagner, B.; Besold, T.R. A historical perspective of explainable Artificial Intelligence. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, 11, e1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-J.; Yu, F. XFlag: Explainable fake news detection model on social media. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2022, 38, 1808–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Wong, W.-K.; Woo, W. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, A.; Bach, S.; Montavon, G.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. Layer-wise relevance propagation for deep neural network architectures. In Proceedings of the Information Science and Applications (ICISA) 2016; Springer: Singapore; pp. 913–922.
- Wu, K.; Yuan, X.; Ning, Y. Incorporating relational knowledge in explainable fake news detection. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Virtual Event, 11–14 May 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 403–415. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wang, N.; Subbalakshmi, K.P. Explainable rumor detection using inter and intra-feature attention networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.11057. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Wiechmann, D.; Kerz, E. A language-based approach to fake news detection through interpretable features and BRNN. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Rumours and Deception in Social Media (RDSM), Online, 13 December 2020; pp. 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Han, Y.; Luo, L.; Karunasekera, S.; Leckie, C. Propagation2Vec: Embedding partial propagation networks for explainable fake news early detection. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pentyala, S.K.; Mohseni, S.; Du, M.; Yuan, H.; Linder, R.; Ragan, E.D.; Ji, S.; Hu, X. Xfake: Explainable fake news detector with visualizations. In Proceedings of the The World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 3600–3604. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Liao, H.; Xie, X. Towards Fine-Grained Reasoning for Fake News Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasinski, L.; Mihailescu, R.-C. Towards machine learning explainability in text classification for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), IEEE, Miami, FL, USA, 14–17 December 2020; pp. 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, H.; Luo, Z.; Chang, Y. A Coarse-to-fine Cascaded Evidence-Distillation Neural Network for Explainable Fake News Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.14642. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Li, C.-T. GCAN: Graph-aware co-attention networks for explainable fake news detection on social media. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11648. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.; Liao, B. A quantitative argumentation-based Automated eXplainable Decision System for fake news detection on social media. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 242, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Li, J.; Kao, H.-Y. MVAN: Multi-view attention networks for fake news detection on social media. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 106907–106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, S.; Wu, R.; Fan, C.; Cui, P. Mvan: Multi-view attention networks for real money trading detection in online games. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2536–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Raha, T.; Choudhary, M.; Menon, A.; Gupta, H.; Srivatsa, K.V.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. Neural models for Factual Inconsistency Classification with Explanations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.08872. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, B.; Granmo, O.-C.; Jiao, L. Explainable tsetlin machine framework for fake news detection with credibility score assessment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.09114. [Google Scholar]
- Granmo, O.-C. The Tsetlin Machine–A Game Theoretic Bandit Driven Approach to Optimal Pattern Recognition with Propositional Logic. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.01508. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.; Ban, Y.; Tong, H.; Maciejewski, R.; He, J. DISCO: Comprehensive and explainable disinformation detection. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 4848–4852. [Google Scholar]
- De Magistris, G.; Russo, S.; Roma, P.; Starczewski, J.T.; Napoli, C. An explainable fake news detector based on named entity recognition and stance classification applied to COVID-19. Information 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).