The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes Based on Deep Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Aims
3. Related Works
3.1. Heritage Crime
3.2. Crime Prediction
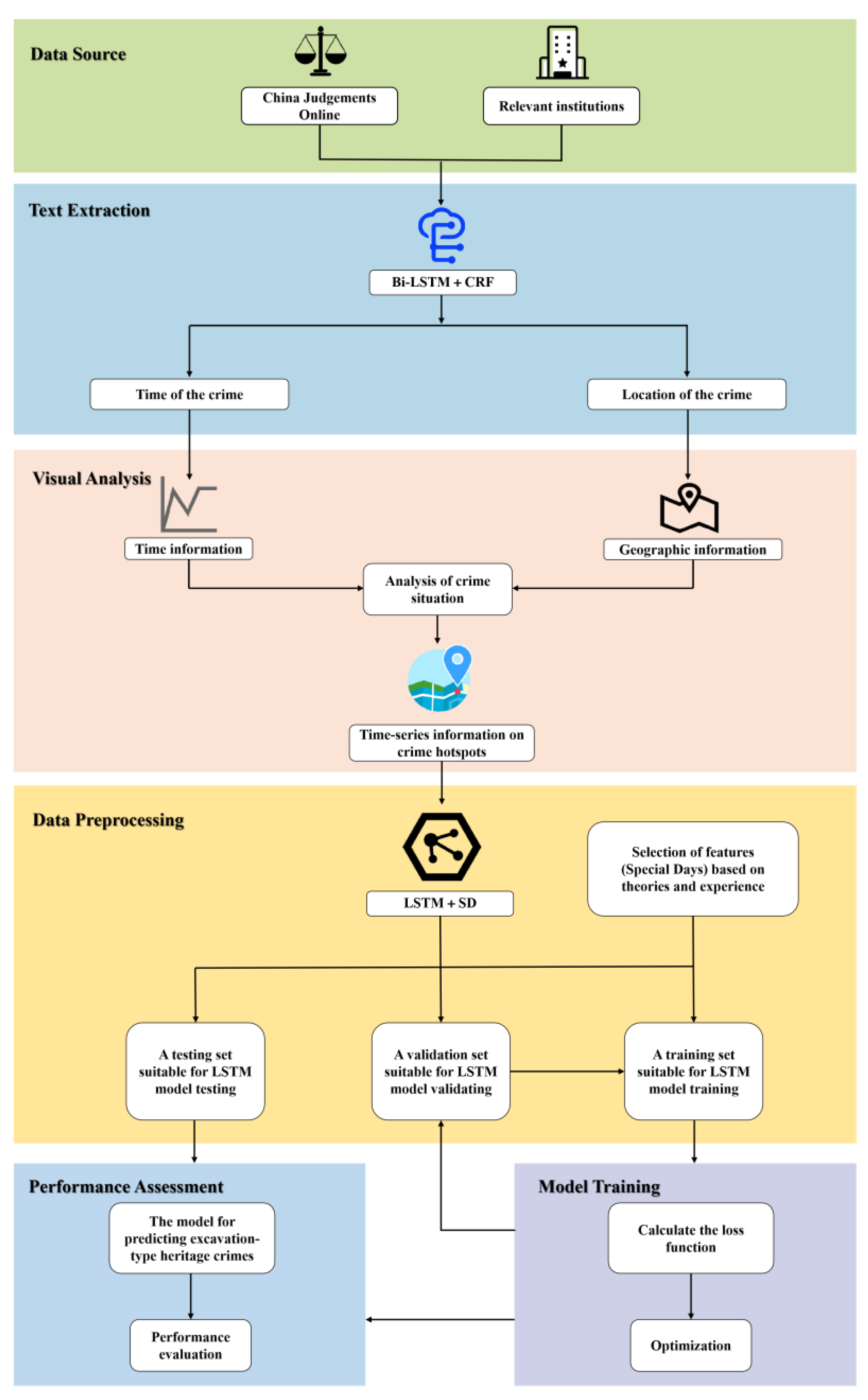
4. The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
4.1. Data
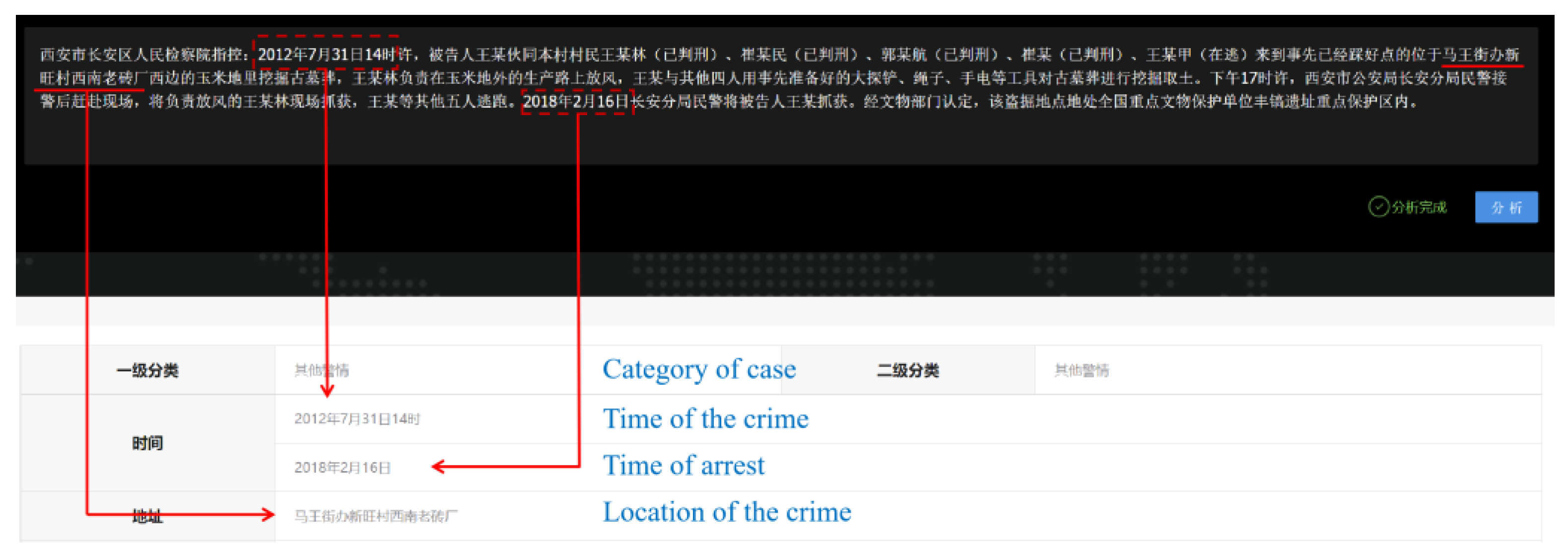
4.2. The Model of Extracting Crime Elements: Bi-LSTM + CRF Model
4.3. Analysis of Crime Elements
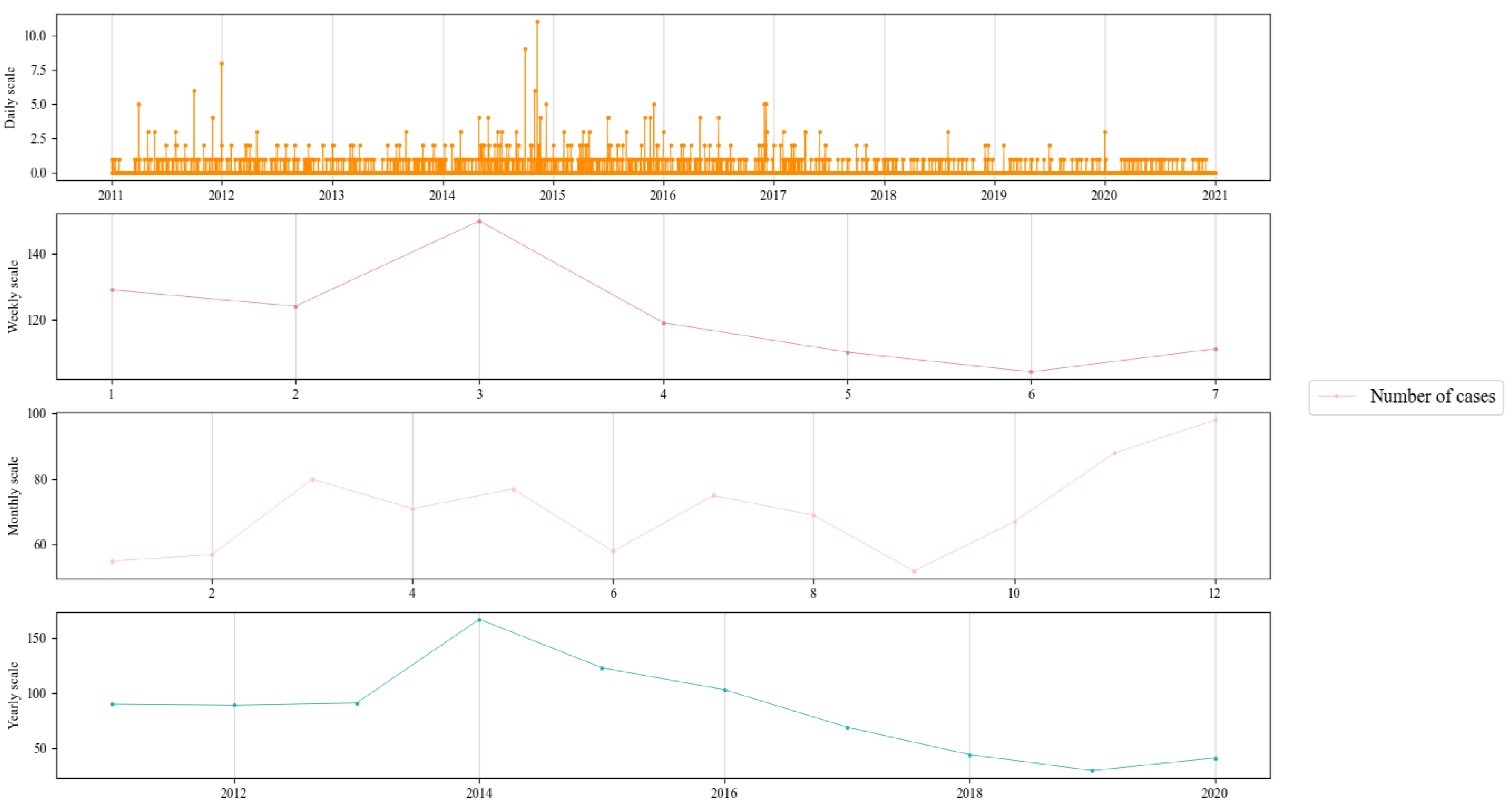
4.3.1. Temporal Characteristics of Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
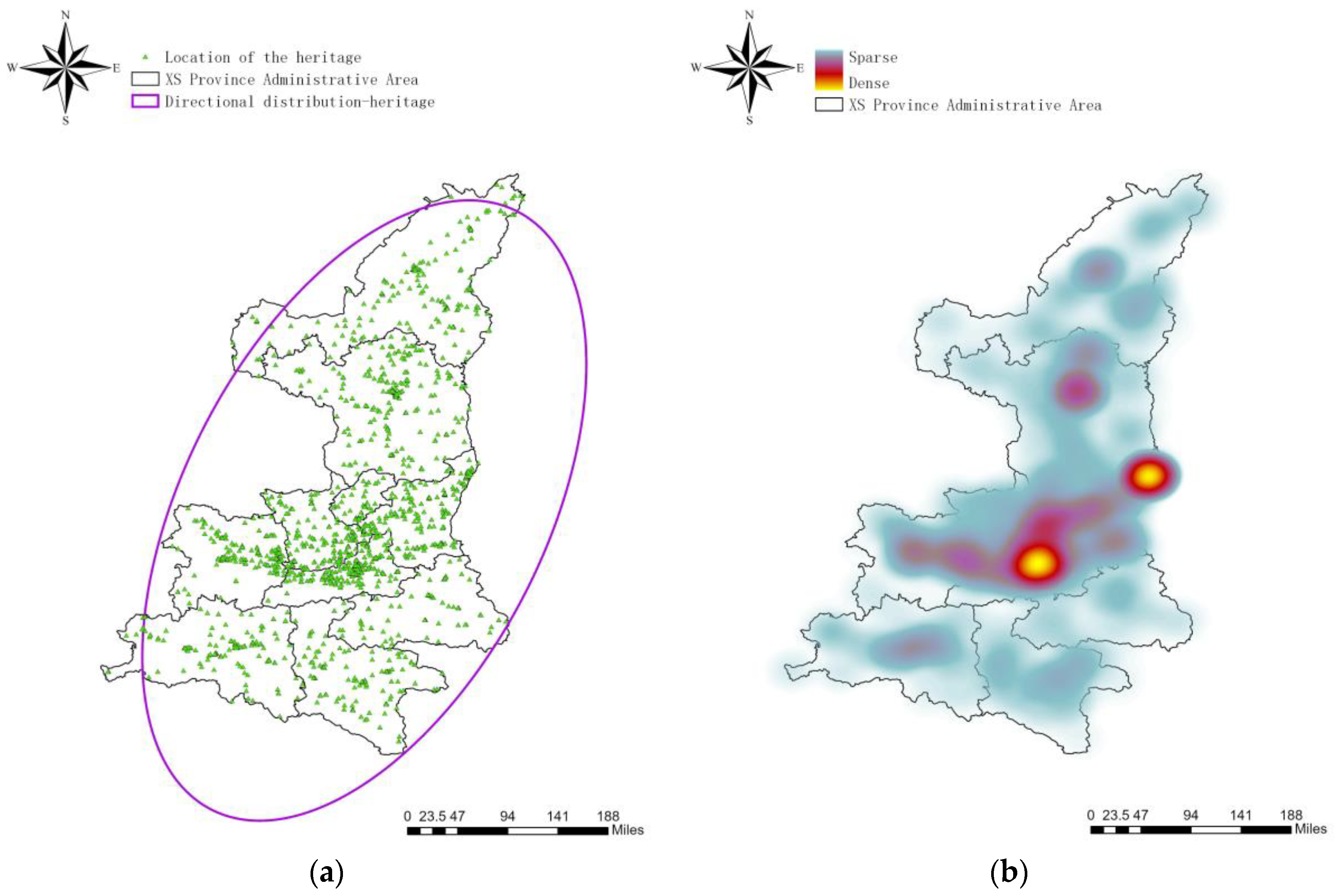
4.3.2. Spatial Characteristics of Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
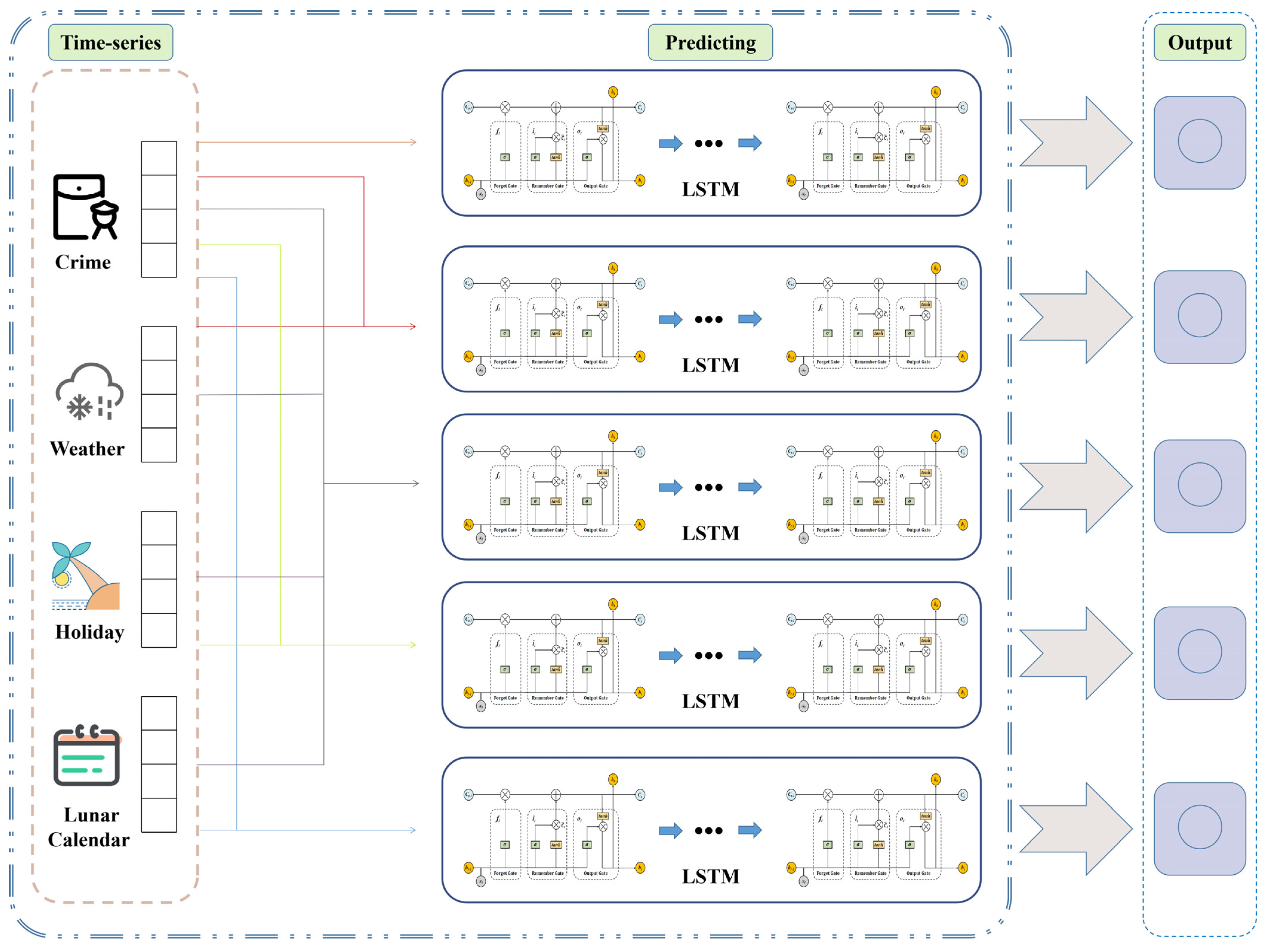
4.4. The Model of Crime Prediction: LSTM + SD (Special Day) Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, S. Understanding, Respect, and Collaboration in Cultural Heritage Preservation: A Conservator’s Developing Perspective. Libr. Trends 2007, 56, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.W.J. Heritage Crime Matters. Antiquity 2015, 89, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinsheng, M. Tomb Robbers in the Beijing Area during the Republican Period; Beijing Archives: Beijing, China, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xuebin, W. Raiders in a chaotic world: Tomb raiding and social governance in the northern areas of the republic of China (1912–1937). J. Dalian Univ. 2021, 4, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. The Current Situation of Fighting and Preventing Cultural Relic Crimes in China and the Improvement of the System. J. Chin. Acad. Crim. Police 2021, 6, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, A.; Klabjan, D. Forecasting Crime with Deep Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyser, B. Threatened Pasts: Police Officers, Heritage Practitioners, and Victims of Heritage Crime; Nottingham Trent University: Nottingham, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, T. Graph Deep Learning Model for Network-Based Predictive Hotspot Mapping of Sparse Spatio-Temporal Events. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 79, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, L. Heritocide? Defining and exploring heritage crime. Public Archaeol. 2013, 12, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.; Kent, A.; Hills, J. Project 7708 Understanding Heritage Crime in Kent and Medway—A Data Analytical Approach. 2020. Available online: https://repository.canterbury.ac.uk/item/8wx70/project-7708-understanding-heritage-crime-in-kent-and-medway-a-data-analytical-approach (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Manacorda, S.; Duncan, C. (Eds.) Crime in the Art and Antiquities World: Illegal Trafficking in Cultural Property; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, N. The criminal organization of the transnational trade in cultural objects: Two case studies. In The Palgrave Handbook on Art Crime; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2019; pp. 439–461. [Google Scholar]
- Weijun, L. The Current Situation and Countermeasures of Fighting and Preventing Crimes against Cultural Relics in China; People’s Public Security: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Balcells Magrans, M. Contemporary Archaeological Looting: A Criminological Analysis of Italian Tomb Robbers; CUNY Academic Works: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gullotta, M.A. The Protection of Cultural Heritage: The Experience of the Italian Carabinieri Command. In Contested Holy Cities; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yumeng, X. Study on the Mechanism for Detecting Crimes of Excavation of Ancient Cultural Sites, Ancient Tombs. Ph.D. Thesis, People’s Public Security University of China, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Quetelet, L.A.J. A Treatise on Man and the Development of His Faculties; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, E.G. Weather and crime. Br. J. Criminol. 1990, 30, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shu, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, D. Assessing Temporal and Weather Influences on Property Crime in Beijing, China. Crime Law Soc. Chang. 2011, 55, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruederle, A.; Jörg, P.; Gareth, R. Weather and Crime in South Africa; RWI—Leibniz-Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung: Essen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Zhai, Y. Crime prevention of bus pickpocketing in Beijing, China: Does air quality affect crime? Secur. J. 2021, 34, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merleau-Ponty, M.; Wild, J.D. The Structure of Behavior; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tan, C.-W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Management Research: A Literature Review. J. Manag. Anal. 2020, 7, 139–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.-H.; Leroy, G. A Decision Support System: Automated Crime Report Analysis and Classification for e-Government. Gov. Inf. Q. 2014, 31, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, A.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Habib, U.; Ullah, M.H.; Mazzara, M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Web News Archives for Crime Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinqiao, X.; Chundong, G.; Tian, M.; Dong, J.; Mengmeng, H.; Shuai, C. Research on the spatial and temporal distribution of internet fraud in china at the county scale. Geoscience 2021, 6, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.; Shen, B.; Wu, J. Risk Prediction of Theft Crimes in Urban Communities: An Integrated Model of LSTM and ST-GCN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 217222–217230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-T.; Baek, J.-G. Various Type of Wavelet Filters on Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 11th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), San Diego, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2017; pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Cai, M.; Wang, D.; Cao, L. A New Model for Predicting the Attributes of Suspects. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2020, 17, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yuan, H.; Shu, X. Forecasting Crime Using the ARIMA Model. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fifth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Jinan, China, 18–20 October 2008; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zheng, J.; Ren, J.; Hussain, A.; Li, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, Q. Big Data Analytics and Mining for Effective Visualization and Trends Forecasting of Crime Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 106111–106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoesmith, G.L. Space–Time Autoregressive Models and Forecasting National, Regional and State Crime Rates. Int. J. Forecast. 2013, 29, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, B.; Carrera, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, J.-Y. An Architecture for Emergency Event Prediction Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 97, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Yang, E.; Almagrabi, A.O.; Bashir, A.K.; Joshi, G.P. Comparative Analysis of Time Series Model and Machine Testing Systems for Crime Forecasting. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10621–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Yen, M.-F.; Yu, L.-C. Grid-Based Crime Prediction Using Geographical Features. SPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, M.; Song, G.; Xiao, L.; Chen, J. Interpretable machine learning models for crime prediction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 94, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ding, N. A Systematic Review of Multi-Scale Spatio-Temporal Crime Prediction Methods. SPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Su, Q.; Cheng, L. Spatial Variation of Multiple Air Pollutants and Their Potential Contributions to All-Cause, Respiratory, and Cardiovascular Mortality across China in 2015–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 168, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Duan, N.; Liu, S.; Shum, H.-Y. Progress in Neural NLP: Modeling, Learning, and Reasoning. Engineering 2020, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A Review of Recurrent Neural Networks: LSTM Cells and Network Architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortley, R.; Mazerolle, L. (Eds.) Willan, Environmental Criminology and Crime Analysis: Situating the Theory, Analytic Approach and Application. In Environmental Criminology and Crime Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 23–40. ISBN 978-0-203-11821-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Hou, M. Predicting time series of theft crimes based on LSTM network. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 4, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, G.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J. CSAN: A Neural Network Benchmark Model for Crime Forecasting in Spatio-Temporal Scale. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 189, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. History of Chinese Tomb Raiding; Jiuzhou press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Towers, S.; Chen, S.; Malik, A.; Ebert, D. Factors Influencing Temporal Patterns in Crime in a Large American City: A Predictive Analytics Perspective. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.; While, D.; Flynn, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Kapur, N.; Appleby, L.; Shaw, J. Do Homicide Rates Increase during Weekends and National Holidays? J. Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2019, 30, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yin, P.; Bertozzi, A.L.; Brantingham, P.J.; Osher, S.J.; Xin, J. Deep Learning for Real-Time Crime Forecasting and Its Ternarization. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 2019, 40, 949–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.E.; Felson, M. Social Change and Crime Rate Trends: A Routine Activity Approach. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1979, 44, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzgün, H.S.; Polat, E. A Spatio-Temporal Crime Prediction Model for Crime Prevention. In Counter Terrorism in Diverse Communities; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 116–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Sun, D. DuroNet: A Dual-Robust Enhanced Spatial-Temporal Learning Network for Urban Crime Prediction. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2021, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, S.D.; Miles, T.J. Economic Contributions to the Understanding of Crime. Annu. Rev. Law Soc. Sci. 2006, 2, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleson, N.; Andresen, M.A. Exploring the Impact of Ambient Population Measures on London Crime Hotspots. J. Crim. Justice 2016, 46, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Stewart, K.; Fan, J. Incorporating Space and Time into Random Forest Models for Analyzing Geospatial Patterns of Drug-Related Crime Incidents in a Major US Metropolitan Area. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 87, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|
| ARIMA | 0.544 | 0.122 |
| Random Forest | 0.516 | 0.114 |
| SVR | 0.517 | 0.166 |
| BP Neural Networks | 0.518 | 0.109 |
| LSTM | 0.515 | 0.113 |
| Feature Variables | RMSE | Improvement of RMSE | MAE | Improvement of MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 0.515 | / | 0.113 | / |
| Rain and snow | 0.482 | 6.4% | 0.06 | 46.9% |
| Holiday | 0.482 | 6.4% | 0.059 | 47.8% |
| Lunar Calendar | 0.484 | 6% | 0.064 | 43.4% |
| All | 0.482 | 6.4% | 0.062 | 45.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, H.; Ding, N.; Zhai, Y.; Du, Y.; Xie, F. The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes Based on Deep Learning Models. Systems 2023, 11, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11060289
Lv H, Ding N, Zhai Y, Du Y, Xie F. The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes Based on Deep Learning Models. Systems. 2023; 11(6):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11060289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Hongyu, Ning Ding, Yiming Zhai, Yingjie Du, and Feng Xie. 2023. "The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes Based on Deep Learning Models" Systems 11, no. 6: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11060289
APA StyleLv, H., Ding, N., Zhai, Y., Du, Y., & Xie, F. (2023). The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes Based on Deep Learning Models. Systems, 11(6), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11060289





