Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services from the Perspectives of Governance and Sociotechnical Systems in Europe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Concepts of Conceptually Related Smart Cities
2.2. Smart Cities as Complex Systems
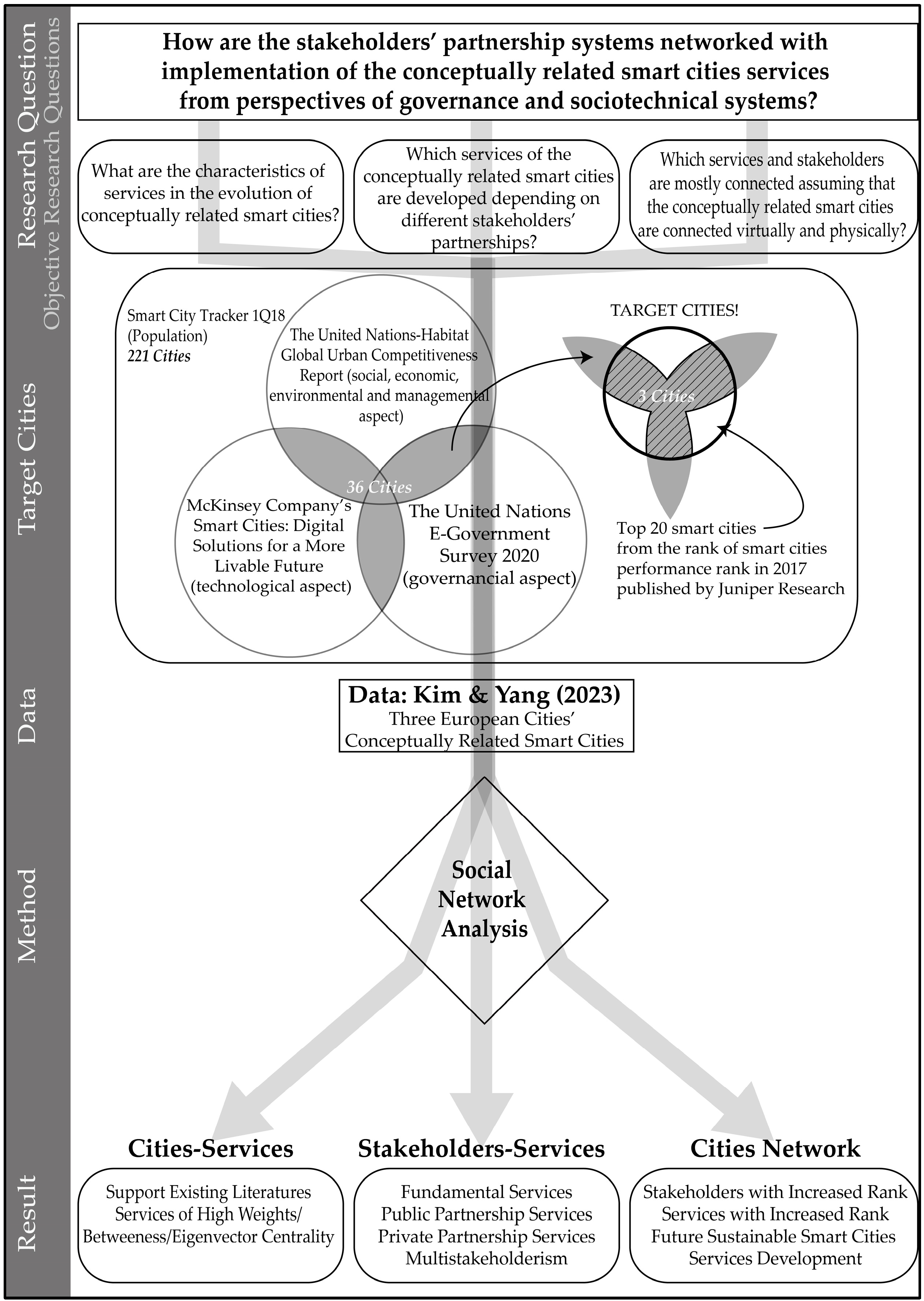
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
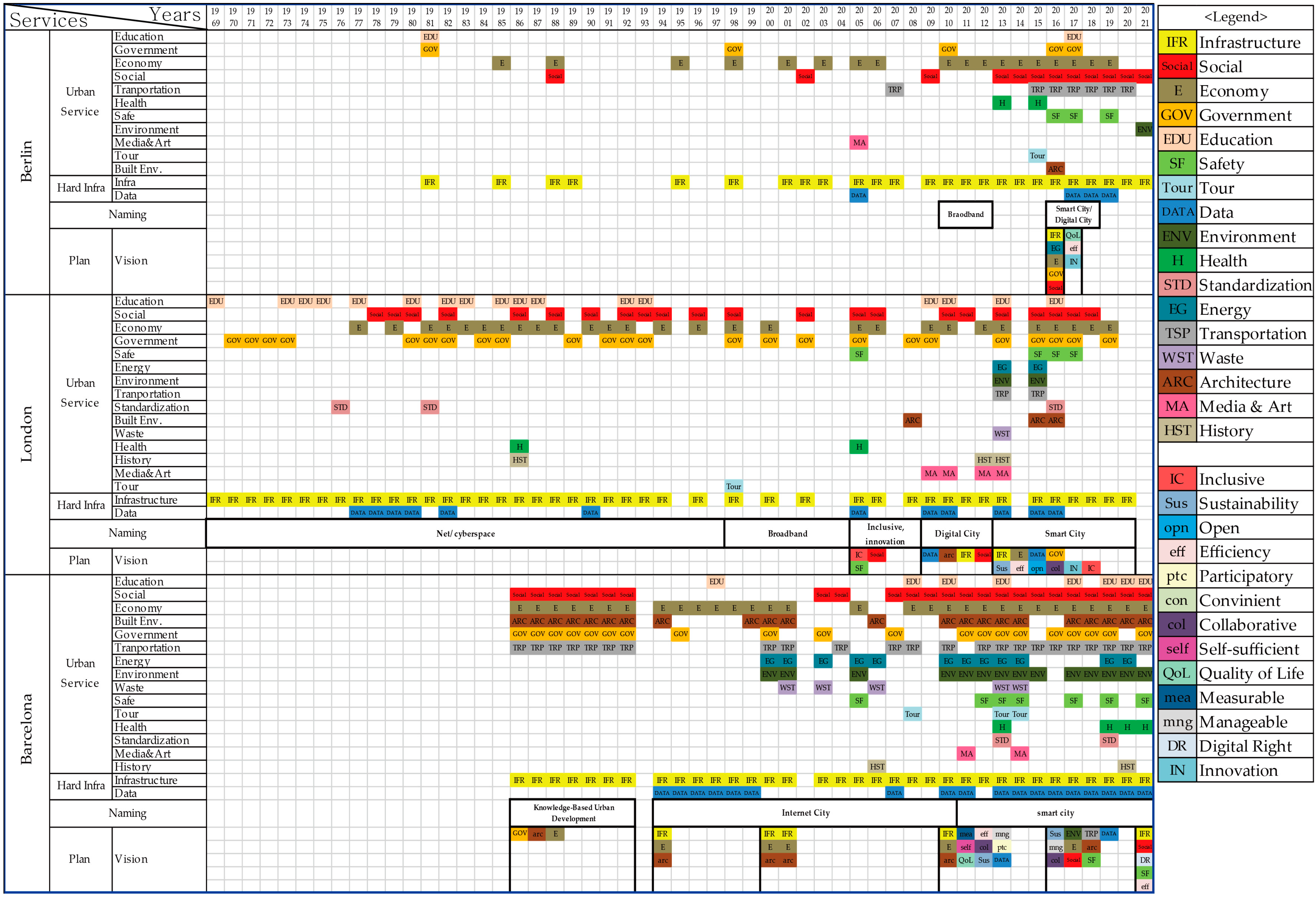
4.1. Characteristics of the Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services
4.2. Services Developments Depending on Stakeholders’ Partnerships
4.3. Networks of Conceptually Related Smart Cities
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almirall, E.; Lee, M.; Majchrzak, A. Open Innovation Requires Integrated Competition-Community Ecosystems: Lessons Learned from Civic Open Innovation. Bus. Horiz. 2014, 57, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Almirall, E.; Chesbrough, H. The City as a Lab: Open Innovation Meets the Collaborative Economy. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2016, 59, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Solés, M.; Íiguez-Rueda, L.; Subirats, J. How to Govern the Complexity? Invitation to an Hybrid and Relational Urban Governance. Athenea Digit. Rev. Pensam. E Investig. Soc. 2011, 11, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. UN E-Government Survey 2022; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme. World Cities Report 2020: The Value of Sustainable Urbanization; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UCLG Community of Practice on Digital Cities. Smart Cities Study 2019; UCLG: Bilbao, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp, P.; Kourtit, K. The “New Urban Europe”: Global Challenges and Local Responses in the Urban Century. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2013, 21, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, A. Smart City Governance: A Local Emergent Perspective. In Smarter as the New Urban Agenda: A Comprehensive View of the 21st Century City; Gil-Garcia, J.R., Pardo, T.A., Nam, T., Eds.; Public Administration and Information Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 73–85. ISBN 978-3-319-17620-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tcholtchev, N.; Schieferdecker, I. Sustainable and Reliable Information and Communication Technology for Resilient Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, E.; Cacho, N.; Lopes, F.; Batista, T.; Oquendo, F. Thinking Smart Cities as Systems-of-Systems: A Perspective Study. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Smart, Trento, Italy, 12–16 December 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, and Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, Korea, Smart Cities and Inclusive Growth; OECD: Paris, France, 2020.
- Ammara, U.; Rasheed, K.; Mansoor, A.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Qadir, J. Smart Cities from the Perspective of Systems. Systems 2022, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, V.; Berardi, U.; Dangelico, R.M. Smart Cities: Definitions, Dimensions, Performance, and Initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, M. Four European Smart City Strategies. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Stud. 2016, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthopoulos, L.G. The Rise of the Smart City. In Understanding Smart Cities: A Tool for Smart Government or an Industrial Trick? Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 5–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chourabi, H.; Nam, T.; Walker, S.; Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Mellouli, S.; Nahon, K.; Pardo, T.A.; Scholl, H.J. Understanding Smart Cities: An Integrative Framework; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 2289–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Cisco. Cisco Visual Networking Index: Forecast and Methodology, 2011–2016; White Paper; Cisco VNI: San Jose, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Telecommunication Union. Focus Group on Smart Sustainable Cities; ITU: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Giffinger, R.; Gudrun, H. Smart Cities Ranking: An Effective Instrument for the Positioning of the Cities? ACE Archit. City Environ. 2010, 4, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebova, I.; Yasnitskaya, Y.S.; Maklakova, N. Possibilities of “Smart City” Concept Implementing: Russia’s Cities Practice. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 5, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancke, G.P.; Hancke, G.P., Jr. The Role of Advanced Sensing in Smart Cities. Sensors 2013, 13, 393–425. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC. Information Technology, Smart Cities, Preliminary Report 2014; ISO/IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaroiu, G.C.; Roscia, M. Definition Methodology for the Smart Cities Model. Energy 2012, 47, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, J.H.; Leem, Y.T.; Yigitcanlar, T. Towards Ubiquitous City: Concept, Planning, and Experiences in the Republic of Korea. In Knowledge-Based Urban Development: Planning and Applications in the Information Era; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 148–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, P.; Giordano, S.; Farouh, H.; Yousef, W. Modelling the Smart City Performance. Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2012, 25, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naphade, M.; Banavar, G.; Harrison, C.; Paraszczak, J.; Morris, R. Smarter Cities and Their Innovation Challenges. Computer 2011, 44, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neirotti, P.; De Marco, A.; Cagliano, A.C.; Mangano, G.; Scorrano, F. Current Trends in Smart City Initiatives: Some Stylised Facts. Cities 2014, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Oktaria, D.; Kurniawan, N.B. Smart City Services: A Systematic Literature Review; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Yesner, R. Fatma Ozdemir Understanding Smart City Transformation with Best Practices; IDC: Framingham, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yovanof, G.S.; Hazapis, G.N. An Architectural Framework and Enabling Wireless Technologies for Digital Cities & Intelligent Urban Environments. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2009, 49, 445–463. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Yang, S. Characteristics of Conceptually Related Smart Cities (CRSCs) Services from the Perspective of Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Bolívar, M.P. (Ed.) Transforming City Governments for Successful Smart Cities, 2015th ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-03166-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhlandt, R.W.S. The Governance of Smart Cities: A Systematic Literature Review. Cities 2018, 81, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Yang, S. Sociotechnical Characteristics of Conceptually Related Smart Cities’ Services from an International Perspective. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 196–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lom, M.; Pribyl, O. Smart City Model Based on Systems Theory. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgazzar, R.F.; El-Gazzar, R. Smart Cities, Sustainable Cities, or Both. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2017), Porto, Portugal, 22–24 April 2017; pp. 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Höjer, M.; Wangel, J. Smart Sustainable Cities: Definition and Challenges. In ICT innovations for sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 333–349. [Google Scholar]
- WeGO. The Statue for the World Smart Sustainable Cities Organization; WeGO: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. Available online: http://we-gov.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/%E2%98%85WeGO-STATUTE-adopted-at-4th-GA_2017_Final.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- Al-Nasrawi, S.; Adams, C.; El-Zaart, A. A Conceptual Multidimensional Model For Assessing Smart Sustainable Cities. JISTEM J. Inf. Syst. Technol. Manag. 2015, 12, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. Smart Sustainable Cities of the Future: An Extensive Interdisciplinary Literature Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzguenda, I.; Alalouch, C.; Fava, N. Towards Smart Sustainable Cities: A Review of the Role Digital Citizen Participation Could Play in Advancing Social Sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.L.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; Da Costa, E.M.; Selig, P.M.; Yigitcanlar, T. Knowledge-Based, Smart and Sustainable Cities: A Provocation for a Conceptual Framework. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development-Our Common Future; A/42/251 82e Environment; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Keeble, B.R. The Brundtland Report: ‘Our Common Future. Med. War 1988, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, D.; Sindhu, U.; Balaouras, S.; Dines, R.A.; Hayes, N.; Nelson, L.E. Helping CIOs Understand “Smart City” Initiatives. Growth 2009, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.-M.; Huang, Z.-L.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Guo, X.-R.; Nkeli, M.J. Bibliometric Analysis on Smart Cities Research. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3606. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; El-Zaart, A.; Adams, C. Smart Sustainable Cities Roadmap: Readiness for Transformation towards Urban Sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; Deakin, M. Untangling Smart Cities: From Utopian Dreams to Innovation Systems for a Technology-Enabled Urban Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. On the Social Shaping Dimensions of Smart Sustainable Cities: A Study in Science, Technology, and Society. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarstad, H. Constructing the Sustainable City: Examining the Role of Sustainability in the ‘Smart City’Discourse. J. Environ. Policy Plann. 2017, 19, 423–437. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, J.T.; de Francisco, A.C.; Piekarski, C.M.; Prado, G.F. do Data Mining and Machine Learning to Promote Smart Cities: A Systematic Review from 2000 to 2018. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Ren, Y.; Ochoa, J.J.; Guo, Z.; Yan, H.; Wu, Z. A Lessons Mining System for Searching References to Support Decision Making towards Sustainable Urbanization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Martino, L. International Politics in the Digital Age. In Proceedings of the XXVIth SISP Conference, Florence, Italy, 12–14 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tampouridou, A.; Pozoukidou, G. Smart Cities and Urban Sustainability: Two Complementary and Inter-Related Concepts. RELAND Int. J. Real Estate Land Plan. 2018, 1, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Buuse, D.; van Winden, W.; Schrama, W. Balancing Exploration and Exploitation in Sustainable Urban Innovation: An Ambidexterity Perspective toward Smart Cities. J. Urban Technol. 2021, 28, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winden, W.V.; Buuse, D.V.D. Smart City Pilot Projects: Exploring the Dimensions and Conditions of Scaling Up. J. Urban Technol. 2017, 24, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Panori, A.; Tsarchopoulos, P. Smart City Planning from an Evolutionary Perspective. J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W. Technological Transitions as Evolutionary Reconfiguration Processes: A Multi-Level Perspective and a Case-Study. Res. Policy 2002, 31, 1257–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, I. The Techno-Politics of Data and Smart Devolution in City-Regions: Comparing Glasgow, Bristol, Barcelona, and Bilbao. Systems 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, E. IT CookBook, Introduction to Information and Communication in the Era of the 4th Industrial Revolution; Hanbit Academy: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020; ISBN 979-11-5664-476-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Kim, K.; Heo, Y. Introduction to Information and Communication; Ohsung Media: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2002; ISBN 978-89-89464-25-9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.-C.; Bae, C.; Sin, J. Introduction to Information and Communication (Revised); Ungbo Publishing House: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2006; ISBN 978-89-8462-198-5. [Google Scholar]
- D’Aniello, G.; Gaeta, M.; Orciuoli, F.; Sansonetti, G.; Sorgente, F. Knowledge-Based Smart City Service System. Electronics 2020, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, A.; Tregua, M.; Vallejo-Martos, M.C. Modern Conceptions of Cities as Smart and Sustainable and Their Commonalities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, M.; Ishida, T.; Aurigi, A. The Advancement of World Digital Cities. In Handbook of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 939–958. [Google Scholar]
- Deakin, M.; Al Waer, H. From Intelligent to Smart Cities. Intell. Build. Int. 2011, 3, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchia, A. Smart and Digital City: A Systematic Literature Review. In Smart City; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 13–43. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, T.; Pardo, T.A. Conceptualizing Smart City with Dimensions of Technology, People, and Institutions; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, V.B. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications; George Braziller Inc.: Mahattan, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, B.J.L. Cities as Systems within Systems of Cities. Pap. Reg. Sci. Assoc. 1964, 13, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Cities in Disequilibrium. In Non-Equilibrium Social Science and Policy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 81–96. ISBN 978-3-319-42422-4. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M. Building a Science of Cities. Cities 2012, 29, S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Urban Dynamics; M.I.T. Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Bettencourt, L.; West, G. A Unified Theory of Urban Living. Nature 2010, 467, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Lobo, J.; Helbing, D.; Kühnert, C.; West, G.B. Growth, Innovation, Scaling, and the Pace of Life in Cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7301–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hendy, M.; Atalla, S.; Miniaoui, S.; Daradkeh, M.; Mansoor, W.; Bin Hashim, K.F. Hybrid Approach for Developing Strategic ICT Framework for Smart Cities—A Case Study of Dubai’s Toll Gates (Salik). Smart Cities 2022, 5, 1554–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Park, S.C. Service-Oriented Technology Roadmap (SoTRM) Using Patent Map for R&D Strategy of Service Industry. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 6754–6772. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Phaal, R.; Lee, S.-H. An Integrated Service-Device-Technology Roadmap for Smart City Development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, T.; Suhardi; Kurniawan, N.B. Smart City Service System Engineering Based on Microservices Architecture: Case Study: Government of Tangerang City. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on ICT For Smart Society (ICISS), Tangerang, Indonesia, 18–19 September 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Polese, F.; Botti, A.; Monda, A.; Grimaldi, M. Smart City as a Service System: A Framework to Improve Smart Service Management. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 2018, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, S.J.; McKee, D.W.; Xu, J. Service-Oriented Reference Architecture for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Service-Oriented System Engineering (SOSE), South San Francisco, California, CA, USA, 6–9 April 2017; pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, C.; Eckman, B.; Hamilton, R.; Hartswick, P.; Kalagnanam, J.; Paraszczak, J.; Williams, P. Foundations for Smarter Cities. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2010, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Arias, P.; Poveda-Villalón, M.; García-Castro, R.; Corcho, O. Ontological Representation of Smart City Data: From Devices to Cities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. UN E-Government Survey 2020; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, S.G.; Nelson, R.R. An Evolutionary Theory of Economic Change; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dosi, G. Technological Paradigms and Technological Trajectories: A Suggested Interpretation of the Determinants and Directions of Technical Change. Res. Policy 1982, 11, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, F. Sectoral Systems of Innovation: A Framework for Linking Innovation to the Knowledge Base, Structure and Dynamics of Sectors. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2005, 14, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B.; Stankiewicz, R. On the Nature, Function and Composition of Technological Systems. J. Evol. Econ. 1991, 1, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijker, W.E.; Hughes, T.P.; Pinch, T. The Social Construction of Technological Systems, Anniversary Edition: New Directions in the Sociology and History of Technology; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-262-30087-2. [Google Scholar]
- OECD The Path to Becoming a Data-Driven Public Sector; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2019.
- van Waart, P.; Mulder, I.; de Bont, C. A Participatory Approach for Envisioning a Smart City. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2016, 34, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, A.; Bolívar, M.P.R. Governing the Smart City: A Review of the Literature on Smart Urban Governance. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2016, 82, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. A Conceptualization of Smart City and Strategies of Services Development; University of Seoul: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuval Noah Harari on Big Data, Google and the End of Free Will. Financial Times, 2016. Available online: https://www.ft.com/content/50bb4830-6a4c-11e6-ae5b-a7cc5dd5a28c (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Babbie, E.R. The Practice of Social Research; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.; Woods, E. Smart City Tracker 1q18: Global Smart City Projects by World Region, Market Segment, Technology, and Application; Navigant Consulting, Incorporated: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, M.; Ni, P.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Ma, H.; Xu, H.; Gauntner, L.P.; Allou, S.; Aldon, L.; Eguino, H.; et al. Global Urban Competitiveness Report (2019–2020); UN HABITAT: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McKinsey Global Institute; Woetzel, J.; Remes, J.; Boland, B.; Katrina, D.C.; Sinha, S.; Strube, G.; Means, J.; Law, J.; Cadena, A.; et al. Smart Cities: Digital Solutions For A More Livable Future; McKinsey Global Institute: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. UN E-Government Survey 2010; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.; Carrington, P.J. The SAGE Handbook of Social Network Analysis; SAGE: Singapore, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4462-5011-2. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J. Social Network Analysis: Developments, Advances, and Prospects. SOCNET 2011, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweezy, P.M. Interest Groups in the American Economy; The Present as History; Monthly Review Press: New York, NY, USA, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, J. The Sphere of Influence; American Sociological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Volume 37, pp. 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, W.L.; Lunt, P.S. The Social Life of a Modern Community; The Social Life of a Modern Community; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1941; p. xviii-460. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H. The Dynamics of China’s Collaborative Innovation Network in Agricultural Biotechnology: A Spatial-Topological Perspective. Systems 2023, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, C.M.; Slava, S.; Rădulescu, A.T.; Toader, R.; Toader, D.-C.; Boca, G.D. A Pattern of Collaborative Networking for Enhancing Sustainability of Smart Cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scornavacca, E.; Paolone, F.; Za, S.; Martiniello, L. Investigating the Entrepreneurial Perspective in Smart City Studies. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2020, 16, 1197–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Yi, M.S. A Study on the Connectivity between the Smart City Comprehensive Plan and Smart City Planning Using the Social Network Analysis—Focusing on Gwangmyeong and Chuncheon Smart City Services. J. Korean Soc. Surv. Geod. Photogramm. Cartogr. 2018, 36, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajahat, A.; Nazir, A.; Akhtar, F.; Qureshi, S.; ullah, F.; Razaque, F.; Shakeel, A. Interactively Visualize and Analyze Social Network Gephi. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Sukkur, Pakistan, 29–30 January 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Betweeness-Centrality of Grid Networks. Available online: https://ieeexplore-ieee-org-ssl.openlib.uos.ac.kr/document/5359703/ (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-674-02909-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bulkley, N.; Van Alstyne, M. Information, Communications & Output: Does E-Mail Make White-Collar Workers More Productive? In Proceedings of the North American Association for Computational Social and Organization Science (NAACSOS), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 June 2008; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kuyper, T. Smart City Strategy & Upscaling: Comparing Barcelona and Amsterdam. Master’s Thesis; University Pompeu Fabra: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Shukla; Skea, J.; Reisinger, A. Climate Change 2022 Mitigation of Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- UN-HABITAT. Urban Planning for City Leaders|UN-Habitat; UN-HABITAT: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012; ISBN 978-92-1-132505-8. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, A. Urban Economics, 9th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-07-802178-7. [Google Scholar]
- Langmann, R. Automatisierungssysteme Mit Web-Technologien. Atp Ed.-Autom. Prax. 2014, 56, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, T. Neo-Liberal Urban Planning Policies: A Literature Survey 1990–2010. Prog. Plan. 2011, 76, 147–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, J.; Walravens, N.; Ballon, P. Beyond Defining the Smart City. Meeting Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches in the Middle. TeMA J. Land Use Mobil. Environ. 2014, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, S. Connectography: Mapping the Global Network Revolution. By Parag Khanna. Int. Aff. 2016, 92, 1533–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.; Parycek, P.; Falco, E.; Kleinhans, R. Smart Governance in the Context of Smart Cities: A Literature Review. Inf. Polity 2018, 23, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. New Urban Agenda; United Nations: Quito, Ecuador, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, C.K. Emerging Dimensions of Decentralisation Debate in the Age of Globalisation. Indian J. Fed. Stuties 2009, 1, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, S.P. Cities in Evolution: An Introduction to the Town Planning Movement and to the Study of Civics; Williams: London, UK, 1915. [Google Scholar]
| Study Population | First Screening Result | Second Screening Result | European Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore, Tokyo, New York, London, San Francisco (Oakland), Paris, Hong Kong, Osaka, Los Angeles-Long, Beach-Santa Ana, Chicago, Barcelona, Moscow, Stockholm, Seoul, Munich, Stuttgart, Boston, Madrid, Shenzhen, Frankfurt am Main, Philadelphia, Toronto, Taipei, Houston, Miami, Berlin, Melbourne, Rome, Shanghai, Seattle, Manchester, Atlanta, San Jose, Cleveland, Sydney, Hiroshima, Birmingham, Beijing, Milan, Montreal, Dallas-Fort Worth, Buenos Aires, Vienna, Tel Aviv-Yafo, Denver-Aurora, Hamburg, Zurich, Nagoya, Baltimore, Kitakyushu-Fukuoka, Copenhagen, Hannover, Salt Lake City, San Diego, Perth, Washington D.C., Incheon, Suzhou, Raleigh, Kuala Lumpur, Vancouver, Amsterdam, Astana, Geneva, Brussels, Detroit, Guangzhou, Austin, Orlando, West Yorkshire, Cologne, Helsinki, Daejeon, Istanbul, Ulsan, Richmond, Valencia, Jerusalem, Columbus, Sao Paulo, Bridgeport Stamford, Phoenix-Mesa, Nanjing, Doha, Haifa, Antwerp, Hartford, Riyadh, Sapporo, Gwangju, Busan, Naples, Xiamen, Milwaukee, Glasgow, Adelaide, Dubai, Daegu, Santiago de Chile, Malaga, Athens, Wuxi, Dortmund, Louisville, Pretoria, Essen, Tianjin, Foshan, Taichung, Brisbane, Auckland, Dresden, Saint Petersburg, Virginia Beach, Calgary, Las Vegas, Bogota, Medina, Dongguan, Wuhan, Lima, Kaohsiung, Dusseldorf, Tampa-St., Petersburg, Belfast, Jedda, Worcester, Hangzhou, Lyon, New Haven, Leipzig, Dublin, Hamilton, Hague, Buffalo, Charlette, Liege, Zaragoza, Torino, Colorado Springs, Chengdu, Qingdao, Nashville-Davidson, Macao, Rio de Janeiro, San Antonio, Zhongshan, Minneapolis-Saint Paul, Sendai, Lisbon, Silo, Ningbo, Lille, Liverpool, Provo-Orem, Changzhou, Zhengzhou, Amman, Venice, Dammam, Rotterdam, Tainan, Changsha, Leicester, Tehran, San Juan, Providence, Shizuoka-Hamamatsu M.M.A., Verona, Johannesburg, Baton Rouge, Bangkok, New Orleans, Gold Coast, Ottawa-Gatineau, Bologna, Leon, Solfa, Indianapolis, Shenyang, Pittsburgh, Ogden, Florence, Kansas City, Budapest, Montevideo, Zhuhai, Honolulu, Barcelona-Puerto La Cruz, Oklahoma City, Dallin, Minsk, Porto, Mecca, Xi’an, Ahvaz, Hefei, Marseille-Aix-en Provence, San Francisco, Tallinn, Roma, São Paulo, Mexico City, Warsaw, Prague, Almaty | Singapore, New York, Stockholm, Seoul, Shanghai, Amsterdam, Helsinki, San Francisco, Chicago, Copenhagen, Barcelona, Melbourne, London, Tokyo, Paris, Moscow, Madrid, Toronto, Berlin, Bogota, Buenos Aires, Istanbul, Brussels, Dubai, Mexico City, Sydney, Johannesburg, Lisbon, Athens, Kuala Lumpur, Seattle, Austin, Vienna, Beijing, Shenzhen | Singapore, New York, San Francisco, Chicago, Barcelona, Melbourne, London, Tokyo, Berlin, Dubai, Mexico City, Seoul | Barcelona, London, Berlin |
| 207 cities | 36 cities | 12 cities | 3 cities |
| Barcelona | London | Berlin | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | BC | Rank of BC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | BC | Rank of BC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | BC | Rank of BC | ||
| Stakeholders | Public | 53.641 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 90.719 | 1 | 23.69 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 142.3 | 1 | 9.5833 | 3 | 0.9588 | 2 | 78.75 | 1 |
| Private | 8.5936 | 4 | 0.9167 | 2 | 40.88 | 2 | 13.09 | 3 | 0.4862 | 6 | 24.538 | 2 | 13.468 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 56.75 | 2 | |
| People | 3.8318 | 10 | 0.7833 | 3 | 18.945 | 3 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.3211 | 11 | 1.4929 | 11 | 2.1151 | 6 | 0.6365 | 5 | 1.25 | 9 | |
| Academia | 1.9229 | 13 | 0.7448 | 4 | 12.6 | 4 | 5.39 | 6 | 0.4702 | 7 | 4.5381 | 10 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 11 | |
| NGO | 0.1538 | 21 | 0.2849 | 16 | 1.8554 | 16 | 2.18 | 9 | 0.5417 | 2 | 17.127 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 0.2859 | 10 | 0.25 | 10 | |
| Services | Infrastructure | 17.353 | 2 | 0.5432 | 5 | 6.8139 | 5 | 18.09 | 2 | 0.4883 | 3 | 12.234 | 4 | 12.147 | 2 | 0.6431 | 3 | 13.5 | 3 |
| Social | 7.9701 | 5 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 4.9 | 7 | 0.4883 | 3 | 12.234 | 4 | 3.5754 | 5 | 0.6431 | 3 | 13.5 | 3 | |
| Economy | 9.877 | 3 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 6.43 | 4 | 0.3947 | 10 | 8.7301 | 7 | 5.8459 | 4 | 0.4389 | 7 | 4 | 6 | |
| Data | 4.9591 | 8 | 0.5432 | 5 | 6.8139 | 5 | 2.04 | 10 | 0.4325 | 8 | 7.7126 | 8 | 1.0635 | 7 | 0.5789 | 6 | 6 | 5 | |
| Government | 5.6171 | 7 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 6.4 | 5 | 0.4325 | 8 | 7.7126 | 8 | 0.8155 | 10 | 0.2165 | 14 | 0 | 11 | |
| Education | 0.9575 | 15 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 3.85 | 8 | 0.4883 | 3 | 12.234 | 4 | 0.375 | 12 | 0.2165 | 14 | 0 | 11 | |
| Environment | 3.045 | 12 | 0.5432 | 5 | 6.8139 | 5 | 0.24 | 16 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0.25 | 13 | 0.2165 | 14 | 0 | 11 | |
| Health | 0.619 | 18 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 0.17 | 17 | 0.2675 | 12 | 1.0476 | 12 | 0.1111 | 15 | 0.2224 | 11 | 0 | 11 | |
| Architecture | 4.6015 | 9 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 0.58 | 11 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0.0238 | 18 | 0.2165 | 14 | 0 | 11 | |
| Transport | 6.0872 | 6 | 0.5007 | 8 | 2.0264 | 9 | 0.07 | 18 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0.8624 | 9 | 0.4389 | 7 | 4 | 6 | |
| Safety | 0.8163 | 16 | 0.2798 | 17 | 0.256 | 18 | 0.44 | 12 | 0.2675 | 12 | 1.0476 | 12 | 0.1012 | 16 | 0.4389 | 7 | 4 | 6 | |
| Tourism | 0.4192 | 19 | 0.2798 | 17 | 0.256 | 18 | 0.07 | 18 | 0.0843 | 22 | 0 | 15 | 0.037 | 17 | 0.2224 | 11 | 0 | 11 | |
| Standardization | 0.0379 | 22 | 0.1465 | 21 | 0 | 21 | 0.04 | 20 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0.5 | 11 | 0.2165 | 14 | 0 | 11 | |
| Energy | 3.1438 | 11 | 0.3223 | 15 | 3.1488 | 8 | 0.04 | 20 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 11 | |
| Waste | 1.7134 | 14 | 0.2798 | 17 | 0.256 | 18 | 0.02 | 22 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 11 | |
| Media and art | 0.2301 | 20 | 0.2599 | 20 | 0.4573 | 17 | 0.27 | 15 | 0.1739 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0.125 | 14 | 0.2224 | 11 | 0 | 11 | |
| History | 0.6952 | 17 | 0.1465 | 21 | 0 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.2675 | 12 | 1.0476 | 12 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 11 | |
| Barcelona | London | Berlin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Degree |  |  |  |
| Eigenvector Centrality | 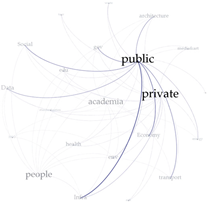 | 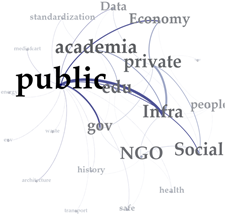 |  |
| Betweenness Centrality |  |  | 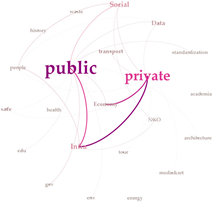 |
| Label | Private–People | Public–People | Public–Academic–NGO | Private–Academic–NGO | Public–Private | Public–Private–People–Academic-NGO | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | WD | Rank of WD | EC | Rank of EC | |
| Barcelona | 6.2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 29 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 28 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 34 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| London | 13 | 3 | 0.5 | 3 | 23 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 31 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 21 | 1 | 0.8 | 2 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 44 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Berlin | 15 | 2 | 0.7 | 2 | 11 | 8 | 0.7 | 16 | 9.6 | 4 | 0.7 | 3 | 14 | 3 | 0.7 | 3 | 22 | 4 | 0.9 | 3 | 25 | 4 | 0.9 | 3 |
| Infrastructure | 16 | 1 | 0.4 | 4 | 72 | 1 | 0.9 | 3 | 23 | 3 | 0.4 | 4 | 18 | 2 | 0.4 | 4 | 32 | 2 | 0.4 | 4 | 39 | 2 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Economy | 9.2 | 4 | 0.4 | 4 | 28 | 4 | 0.9 | 3 | 8.6 | 5 | 0.4 | 4 | 9.2 | 4 | 0.4 | 4 | 17 | 5 | 0.4 | 4 | 4.6 | 8 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Social | 4.6 | 6 | 0.4 | 4 | 27 | 5 | 0.9 | 3 | 7.2 | 7 | 0.4 | 4 | 4.6 | 6 | 0.4 | 4 | 8.8 | 7 | 0.4 | 4 | 12 | 6 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Data | 1.4 | 7 | 0.4 | 4 | 14 | 7 | 0.9 | 3 | 3.2 | 10 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.5 | 8 | 0.4 | 4 | 4.3 | 9 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.6 | 19 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Government | 1 | 8 | 0.3 | 13 | 35 | 2 | 0.9 | 3 | 8.6 | 6 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.4 | 9 | 0.3 | 11 | 9.1 | 6 | 0.4 | 4 | 18 | 5 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Education | 0.5 | 10 | 0.3 | 13 | 9.3 | 9 | 0.9 | 3 | 3.9 | 8 | 0.4 | 4 | 2.3 | 7 | 0.3 | 11 | 2.3 | 11 | 0.4 | 4 | 9.6 | 7 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Safety | 0.3 | 13 | 0.3 | 9 | 6.1 | 13 | 0.9 | 3 | 0.7 | 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.4 | 11 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.8 | 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 4.5 | 9 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Environment | 0.3 | 11 | 0.2 | 15 | 7.1 | 12 | 0.9 | 3 | 1.6 | 12 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.3 | 13 | 0.2 | 16 | 1.8 | 12 | 0.4 | 4 | 1 | 15 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Transport | 0.7 | 9 | 0.3 | 9 | 8.6 | 11 | 0.9 | 3 | 3.7 | 9 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.7 | 10 | 0.3 | 14 | 4.4 | 8 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Architecture | 0.2 | 17 | 0.2 | 15 | 9.3 | 10 | 0.9 | 3 | 2.9 | 11 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 16 | 3 | 10 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.9 | 12 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Standardization | 0 | 19 | 0.2 | 15 | 2.7 | 17 | 0.6 | 17 | 1.1 | 14 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.3 | 11 | 0.9 | 15 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.1 | 14 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Health | 0.3 | 14 | 0.3 | 9 | 3.2 | 16 | 0.8 | 13 | 0.3 | 19 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.3 | 12 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.4 | 19 | 0.4 | 4 | 4.4 | 10 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Tourism | 0.2 | 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.7 | 20 | 0.4 | 20 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.2 | 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.6 | 13 | 0.3 | 18 |
| Media and art | 0.3 | 15 | 0.3 | 9 | 5.4 | 14 | 0.8 | 13 | 0.4 | 18 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.1 | 17 | 0.3 | 14 | 0.6 | 17 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.9 | 16 | 0.3 | 18 |
| Energy | 0.3 | 12 | 0.2 | 15 | 4.4 | 15 | 0.7 | 15 | 1.3 | 13 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.3 | 14 | 0.2 | 16 | 1.6 | 13 | 0.3 | 18 | 3 | 11 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Waste | 0.1 | 18 | 0.2 | 15 | 1.3 | 18 | 0.5 | 18 | 0.8 | 15 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.2 | 16 | 0.9 | 14 | 0.3 | 18 | 0.7 | 17 | 0.4 | 4 |
| History | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 0.8 | 19 | 0.5 | 19 | 0.7 | 17 | 0.3 | 15 | 0.1 | 19 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.6 | 18 | 0.3 | 18 | 0.7 | 18 | 0.3 | 18 |
| Weighted Degree | Rank of WD | Eigencentrality | Rank of EC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private | 30.756 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Public | 58.546 | 1 | 0.92 | 2 |
| People | 4.3643 | 11 | 0.8262 | 3 |
| Academia | 6.2567 | 7 | 0.6943 | 4 |
| NGO | 3.2436 | 12 | 0.5887 | 5 |
| Infrastructure | 38.396 | 2 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Data | 4.6273 | 8 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Social | 11.805 | 5 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Government | 9.5752 | 6 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Education | 4.4658 | 9 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Environment | 1.9131 | 14 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Health | 0.5849 | 21 | 0.524 | 6 |
| Economy | 17.793 | 4 | 0.4469 | 13 |
| Transport | 4.4252 | 10 | 0.4469 | 13 |
| Architecture | 3.0277 | 13 | 0.4469 | 13 |
| Media and art | 0.696 | 19 | 0.3569 | 16 |
| Standardization | 1.1053 | 16 | 0.3402 | 17 |
| Safety | 0.9881 | 17 | 0.3273 | 18 |
| Energy | 1.5842 | 15 | 0.3273 | 18 |
| Tourism | 0.3064 | 22 | 0.2502 | 20 |
| Waste | 0.8745 | 18 | 0.2502 | 20 |
| History | 0.6655 | 20 | 0.1974 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Yang, S. Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services from the Perspectives of Governance and Sociotechnical Systems in Europe. Systems 2023, 11, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11040166
Kim N, Yang S. Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services from the Perspectives of Governance and Sociotechnical Systems in Europe. Systems. 2023; 11(4):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11040166
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nammi, and Seungwoo Yang. 2023. "Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services from the Perspectives of Governance and Sociotechnical Systems in Europe" Systems 11, no. 4: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11040166
APA StyleKim, N., & Yang, S. (2023). Conceptually Related Smart Cities Services from the Perspectives of Governance and Sociotechnical Systems in Europe. Systems, 11(4), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11040166







