The Relationship between AI Adoption Intensity and Internal Control System and Accounting Information Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Approach
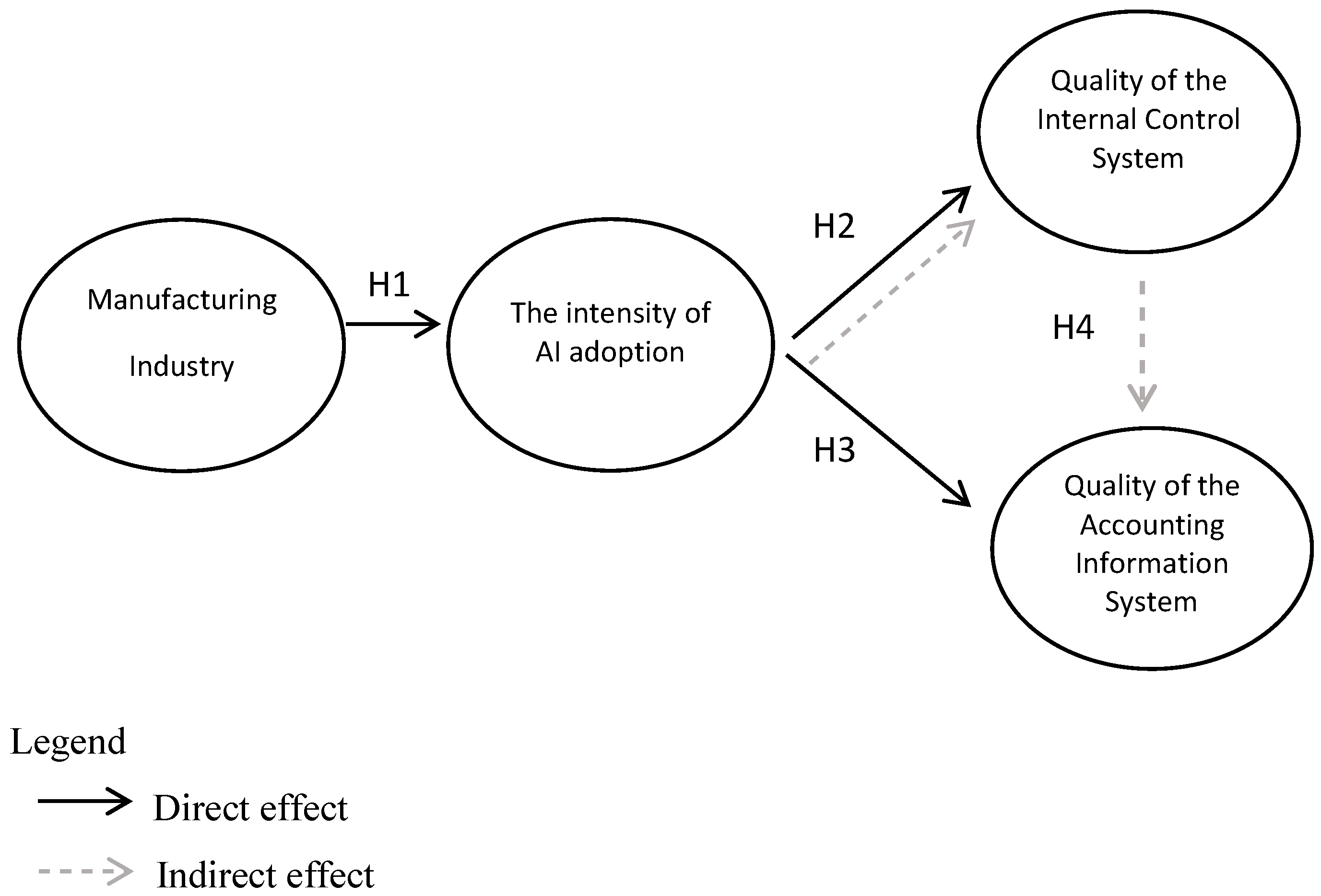
3. Research Model and Hypotheses
4. Methodology
5. Results Presentation and Discussion
5.1. Sample Characteristics
5.2. Measurement Model Evaluation
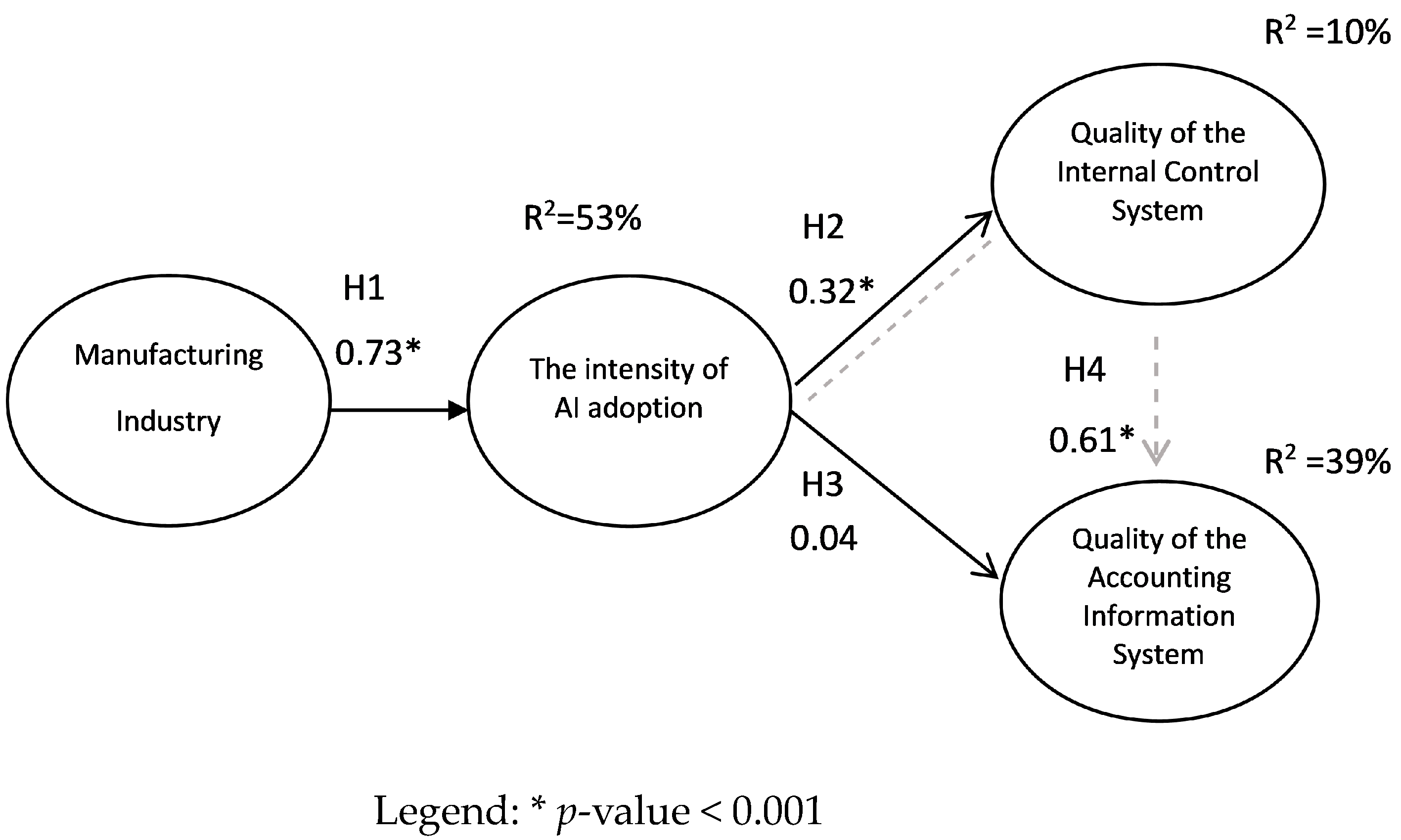
5.3. Structural model Evaluation
6. Discussion
7. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Measurement Scales—Based in Likert Scales of Five Points Where: 1—I Totally Disagree and 2—I Totally Agree
| Constructs | Measurement | References |
| AI adoption intensity | The company has implemented AI in all business processes. | Chen [10] |
| The implementation of AI had a high impact on business operations. | Chen [10] | |
| The implementation of AI, taking into account its potential for the company’s business, was an extensive process. | Chen [10] | |
| The AI implementation allowed business processes to be substantially changed. | Chen [10] | |
| Internal Control System Quality | Internal control system has improved and promoted the company’s operational efficiency and effectiveness. | Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] |
| Internal control system has allowed achieving firms’ business targets, goals and objectives. | Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] | |
| Internal control system has allowed building and creating effective operations, activity and business practices. | Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] | |
| Internal control system has allowed the company to prepare financial information with quality. | Adapted from Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] | |
| Internal control system has allowed the company to prepare non-financial information with quality. | Adapted from Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] | |
| The company complies with all required regulations, i.e., laws, rules, guidelines, standards and other related issues within internal control quality. | Phornlaphatrachakorn [67] | |
| The company’s internal control system has quality. | Pre-test | |
| Accounting Information System Quality | The automated data collection speeds up the process to generate financial statements. | Adapted from Soudani [43] |
| The current accounting information system has improved the quality of non-financial reporting. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| Accounting information system has contributed to the integrity of the financial information reporting process. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| The accounting information system has contributed to the integrity of the non-financial information reporting process. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| The data processing caused the improvement of the quality of the financial reports. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| The automated data collection speeds up the process of non-financial information preparation. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| The automated data collection speeds up the process to generate financial statements and overcome human weaknesses in data processing. | Adapted from Soudani [43] | |
| The automated data collection provides a platform with access to information, which facilitates the use of it. | Adapted from Kpurugbara et al. [66] | |
| The company’s accounting information system works efficiently and effectively. | Pre-test |
References
- Vaaler, P.M.; McNamara, G. Are technology-intensive industries more dynamically competitive? No and yes. Organ. Sci. 2010, 21, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudud-Ul-Huq, S. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Development of Accounting Systems: A Review. IUP J. Account. Res. Audit. Pract. 2014, 13, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lasi, H.; Fettke, P.; Kemper, H.G.; Feld, T.; Hoffmann, M. Industrie 4.0. Wirtschaftsinformatik 2014, 56, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniuk, S.; Grabowska, S.; Straka, M. Identification of Social and Economic Expectations: Contextual Reasons for the Transformation Process of Industry 4.0 into the industry 5.0 Concept. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breque, M.; De Nul, L.; Petridis, A. Industry 5.0. Towards a Sustainable, Human-Centric and Resilient European Industry. 2021. Available online: https://op.Europe.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/468a892a-5097-11eb-b59f-01aa75ed71a1/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Bhimani, A. Digital data and management accounting: Why we need to rethink research methods. J. Manag. Control. 2020, 31, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, T.C. Data Driven: Profiting from Your Most Important Business Asset; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, A.; Rasool, A. Time Series Missing Value Prediction: Algorithms and Applications. In Information, Communication and Computing Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- CGMA. CGMA Competency Framework. 2019, pp. 1–78. Available online: https://www.cgma.org/content/dam/cgma/resources/tools/downloadabledocuments/cgma-competency-framework-2019-edition.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Chen, J. The Augmenting Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Marketing Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX, USA, 1 January 2019. Available online: https://scholarworks.utep.edu/open_etd/1976 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Niu, Y.; Ying, L.; Yang, J.; Bao, M.; Sivaparthipan, C.B. Organizational business intelligence and decision making using big data analytics. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autenrieth, P.; Lörcher, C.; Pfeiffer, C.; Winkens, T.; Martin, L. Current Significance of IT-Infrastructure Enabling Industry 4.0 in Large Companies. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), Stuttgart, Germany, 17–20 June 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.A.; Brown, C.E.; Trinkle, B.S. Opportunities for artificial intelligence development in the accounting domain: The auditing case. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. Int. J. 2006, 14, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.G.; Holt, M.; Arnold, V. “The reports of my death are greatly exaggerated”—Artificial intelligence research in accounting. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2016, 22, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, A.I. A contingency model of perceived effectiveness in accounting information systems: Organizational coordination and control effects. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2000, 1, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Haohao, S.; Ming, F. Research on the impact of artificial intelligence technology on accounting. In Proceedings of the 4th International Seminar on Computer Technology, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering (ISCME 2019), Chengdu, China, 13–15 December 2019; Volume 1486, p. 032042. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaey, M.; Jamshidi, M.B.; Hojatpour, Y. Applications of artificial neural networks in information system of management accounting. Int. J. Mechatron. Electr. Comput. Technol. 2017, 7, 3523–3530. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, A.; Cepêda, C. Accounting information systems: Scientific production and trends in research. Systems 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinez, J.F.; Chang, Q.; Gao, R.X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J. Artificial intelligence in advanced manufacturing: Current status and future outlook. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 110804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevner, A.R.; March, S.T.; Park, J.; Ram, S. Design science in information systems research. MIS Q. 2004, 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, J.E. Management research based on the paradigm of the design sciences: The quest for field-tested and grounded technological rules. J. Manag. Stud. 2004, 41, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H. The Sciences of the Artificial, 3rd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hjørland, B.; Albrechtsen, H. Toward a new horizon in information science: Domain-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1995, 46, 400–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzes, J.M.; Mico, P.R. Domain Theory: An Introduction to Oganizational Behavior in Human Service Organizations. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 1979, 15, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezatti, F. The “economic paradigm” in management accounting: Return on equity and the use of various management accounting artifacts in a Brazilian context. Manag. Audit. J. 2007, 22, 514–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Rocha, D.; Duarte, J.C. Simulating human behaviour in games using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Games and Digital Entertainment (SBGames), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–31 October 2019; pp. 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Intelligence Artificielle: Avec Plus de 500 Exercices; Pearson Education: France, Paris, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, S. Artificial intelligence. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, R.J. A inteligência artificial no contexto da ciência da informação: Uma análise de domínio. Mestrado em Ciência da Informação. Master’s Thesis, FEUP, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, K.; Mijwil, M.M.; Al-Mistarehi, A.H.; Alomari, S.; Gök, M.; Alaabdin, A.M.Z.; Abdulrhman, S.H. Has the Future Started? The Current Growth of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Iraqi J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2022, 3, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, A.T.; Haleem, A.; Bahl, S.; Javaid, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) and its applications in Indian manufacturing: A review. In Current Advances in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- NetBase Quid. AI Index Report. 2022. Available online: https://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/2022-AI-Index-Report_Master.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Telles, E.S.; Barone, D.A.C.; da Silva, A.M. Inteligência Artificial no Contexto da Indústria 4.0. In Anais do I Workshop Sobre as Implicações da Computação na Sociedade; SBC: Porto Alegre, Brasil, 2020; pp. 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Dremel, C.; Herterich, M.M.; Wulf, J.; Waizmann, J.-C.; Brenner, W. How AUDI AG established big data analytics in its digital transformation. MIS Q. Exec. 2017, 16, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, M.; Madan, R.; Joha, A.; Sivarajah, U. Ethical framework for Artificial Intelligence and Digital technologies. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 62, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. The Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI 2022). 2022. Available online: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/digital-economy-and-society-index-desi-2022 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Zharfan, M.; Hendra, H. Changing role of millennial accountants in the information revolution era (Industry 4.0) and challenges in the society generation scope (Society 5.0). Enrich. J. Manag. 2023, 13, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.C.; Azevedo, G.; Marques, R.P.; Bastos, M.A. Challenges of education in the accounting profession in the Era 5.0: A systematic review. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2023, 10, 2220198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.S. Ethical Decision-Making Theory: An Integrated Approach. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 139, 755–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sori, Z.M. Accounting information systems (AIS) and knowledge management: A case study. Am. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, A.H. Determinants of Accounting Information Systems Quality: Empirical Evidence from Vietnam. Accounting 2020, 6, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.P.; Vale, J.; Leite, E.; Lis, M.; Kurowska-Pysz, J. The impact of information systems and non-financial information on company success. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2022, 45, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudani, S.N. The usefulness of an accounting information system for effective organizational performance. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2012, 4, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnenko, V.I.; Tkach, I.M.; Potetiuieva, M.V.; Mechetenko, M.Y.; Tkach, M.Y.; Holota, O. Analysis of approaches to assessing effectiveness of the system of internal control of the military organization as the element of public internal financial control of Ukraine. Espacios 2020, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hla, D.; Susan, P.T. Efficiency of Accounting Information System and Performance Measures-Literature’ ‘Review’. Int. J. Multidiscip. Curr. Res. 2015, 3, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzolan, S.; Antti, M. The Quality of Mandatory Non-Financial (Risk) Disclosures: The Moderating Role of Audit Firm and Partner Characteristics. SSRN Electron. J. 2019, 56, 2150008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Green IoT and edge AI as key technological enablers for a sustainable digital transition towards a smart circular economy: An industry 5.0 use case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gärtner, B.; Hiebl, M.R. Issues with big data. In The Routledge Companion to Accounting Information Systems; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, C.B.; Osborne, M.A. The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 114, 254–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. The Future of Jobs Report. Retrieved from Geneva. 2020. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/publications/the-future-of-jobs-report-2023 (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Yuksel, A.S.; Tan, F.G. DeepCens: A deep learning-based system for real-time image and video censorship. Expert Syst. 2023, e13436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richins, G.; Stapleton, A.; Stratopoulos, T.C.; Wong, C. Big data analytics: Opportunity or threat for the accounting profession? J. Inf. Syst. 2017, 31, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, J.; Yigitbasioglu, O. The role of internet-related technologies in shaping the work of accountants: New directions for accounting research. Br. Account. Rev. 2019, 51, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damerji, H.; Salimi, A. Mediating effect of use perceptions on technology readiness and adoption of artificial intelligence in accounting. Account. Educ. 2021, 30, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosteanu, N.R.; Faccia, A. Digital systems and new challenges of financial management–FinTech, XBRL, blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Qual. Access Success J. 2020, 21, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, T.; Selos, E.; Laine, T.; Suomala, P. Exploring the programmability of management accounting work for increasing automation: An interventionist case study. Account. Audit. Account. J. 2020, 34, 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B. Inside Terrorism; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, Y.D.; Sahoo, A. Towards understanding of artificial intelligence in accounting profession. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. Res. 2021, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, M.; Vitolla, F. Internal control over financial reporting: Opportunities using the COBIT framework. Manag. Audit. J. 2014, 29, 736–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, H.; Toraj, D. How Influence the Accounting Information Systems Quality of Internal Control on Financial Reporting Quality. J. Mod. Dev. Manag. Account. 2019, 2, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.M.; Darren, H.; Daniel, P.L. Supplier Internal Control Quality and the Duration of Customer-Supplier Relationships. Account. Rev. 2018, 93, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, K.; Hay, D.; Khlif, H. Internal control in accounting research: A review. J. Account. Lit. 2019, 42, 80–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.; Myllymäki, E.R. Real earnings management before and after reporting SOX 404 material weaknesses. Account. Horiz. 2016, 30, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, M.J.; Petruska, K.A.; Alam, P.; Yu, B. Internal control weaknesses and evidence of real activities manipulation. Adv. Account. 2016, 33, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, S.B.; Pinello, A.S.; Skaife, H.A. The implications of ineffective internal control and SOX 404 reporting for financial analysts. J. Account. Public Policy 2014, 33, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpurugbara, N.; Akpos, Y.E.; Nwiduuduu, V.; Tams-Wariboko, I. Impact of accounting information system on organizational effectiveness-a study of selected small and medium scale enterprises in Woji, Portharcourt. Int. J. Res. Bus. Manag. Account. 2016, 2, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Phornlaphatrachakorn, K. Internal control quality, accounting information usefulness, regulation compliance and decision-making success: Evidence from canned and processed foods businesses in Thailand. Int. J. Bus. 2019, 4, 198–215. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, A.P.; Vale, J.; Silva, A.; Pereira, C. Impact of the internal control and accounting systems on the financial information usefulness: The role of the financial information quality. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, T.M.; Rodrigues, L.L. Determinants of the attitudes of Portuguese accounting students and professionals towards earnings management. J. Acad. Ethics 2020, 18, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainur, A.K.; Sayang, M.D.; Jannoo, Z.; Yap, B.W. Sample Size and Non-Normality Effects on Goodness of Fit Measures in Structural Equation Models. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, B. Structural Equation Modeling with LISREL, PRELIS and SIMPLIS: Basic Concepts, Applications and Programming; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Marôco, J. Análise de Equações Estruturais—Fundamentos Teóricos, Software e Aplicações, 3rd ed.; ReportNumber, Ld.: Pêro Pinheiro, Portugal, 2013; Volume XI (432), p. 24. ISBN 978-989-96763-6. [Google Scholar]
- Siguaw, J.A.; Diamantopoulos, A. Introducing Lisrel: A Guide for the Uninitiated; Introducing LISREL Sage Publications Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2013/34/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of June 26, 2013, Regarding the Annual Financial Statements, Consolidated Financial Statements and Related Reports of Certain Types of Enterprises, amending Directive 2006/43/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Council Directives 78/660/EEC and 83/349/EEC, Brussels. 2013. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/RO/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32013L0034 (accessed on 4 February 2019).
- Decree-Law No. 98/2015. Alteracões ao Sistema de Normalizacão Contabilístico (Amendments to SNC). Diário República 2015, 8, 106. Available online: http://www.cnc.min-financas.pt/snc2016.html (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Garver, M.S.; Mentzer, J.T. Logistics research methods: Employing structural equation modeling to test for construct validity. J. Bus. Logist. 1999, 20, 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D. Evaluating structural equation models with unobserved variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of the structural equation model. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S. The forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolution: Its impact on society and firms. Futures 2017, 90, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Characteristics | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal form | Public companies | 197 | 52 |
| Private collective companies | 121 | 32 | |
| Individual companies | 17 | 4 | |
| Other | 46 | 12 | |
| Industry | Services | 160 | 42 |
| Industry | 126 | 33 | |
| Commercial | 53 | 14 | |
| Other | 42 | 11 | |
| Size * | Small-sized companies | 64 | 16.8 |
| Large-sized companies | 317 | 83.2 |
| Construct | Sc |
|---|---|
| AI Adoption Intensity (CR = 0.97, AVE = 0.83) | |
| The company has implemented AI in all business processes. | 0.745 * |
| The AI implementation had a high impact on business operations. | 0.950 * |
| The AI implementation, considering its potential for the company’s business, was an extensive process. | 0.945 * |
| The AI implementation on allowed business processes to be substantially changed. | 0.947 * |
| Accounting Information System Quality (CR = 0.917, AVE = 0.610) | |
| The data processing causes an improvement in the financial report’s quality. | 0.864 * |
| Automated data collection speed up the process to generate financial statements. | 0.758 * |
| Automated data collection speed up the process to generate financial statements and overcome human weaknesses in the data processing. | 0.744 * |
| Automated data collection provides a platform with access to information, which facilitates its use of it. | 0.752 * |
| Internal Control System Quality (CR = 0.97, AVE = 0.83) | |
| The internal control system has improved and promoted the company’s operational efficiency and effectiveness. | 0.904 * |
| The internal control system has allowed the building and creation of effective operations, activities and business practices. | 0.834 * |
| The internal control systems have allowed the company to prepare financial information with quality. | 0.824 * |
| The company complies with all required regulations, i.e., laws, guidelines, standards and other issues related to internal control. | 0.667 * |
| Hypothesis | Β | p-Value | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 0.73 | <0.001 | ✓ |
| H2 | 0.32 | <0.001 | ✓ |
| H3 | 0.004 | >0.05 | X |
| H4 | 0.61 | <0.001 | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro, A.; Cepêda, C.; Da Silva, A.C.F.; Vale, J. The Relationship between AI Adoption Intensity and Internal Control System and Accounting Information Quality. Systems 2023, 11, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11110536
Monteiro A, Cepêda C, Da Silva ACF, Vale J. The Relationship between AI Adoption Intensity and Internal Control System and Accounting Information Quality. Systems. 2023; 11(11):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11110536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro, Albertina, Catarina Cepêda, Amélia Cristina Ferreira Da Silva, and Joana Vale. 2023. "The Relationship between AI Adoption Intensity and Internal Control System and Accounting Information Quality" Systems 11, no. 11: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11110536
APA StyleMonteiro, A., Cepêda, C., Da Silva, A. C. F., & Vale, J. (2023). The Relationship between AI Adoption Intensity and Internal Control System and Accounting Information Quality. Systems, 11(11), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11110536








