Abstract
Road transport safety is an important part of transport construction in China. China is now the world’s second-largest country for road traffic deaths. Research on the road traffic mortality rate (RTMR) in China is of great significance in promoting sustainable development in global traffic. This study analyzes the RTMR in 31 provinces in China between 2003 and 2018. Research shows that the RTMR of China demonstrated a downward trend after 2004, but it increased slightly after reaching the lowest points in 2015. The RTMR in coastal and western areas was quite high, requiring targeted management and prevention. During the study period, the RTMR in Guangdong and Tibet improved greatly, whereas the RTMR in Hubei and Guangxi deteriorated. Tobit model results show that economic development level, medical assistance level and government expenditure on health are significantly negatively correlated with RTMR, while urbanization level and motorization level significantly promote RTMR. This study provides macro policy support for improving traffic safety in China.
1. Introduction
Since the reform and opening up, the transport industry in China has made great improvements [1,2]. The overall scale of the transport industry is expanding at an amazing rate. Since 1978, the volume of road freight transport had risen by 1707.9% by 2020, and the volume of passenger transport had risen by 790.3% [3]. However, this rapid development also introduced many traffic safety problems. In China, there were 244,937 road traffic accidents in 2018: 63,194 people were killed and 227,438 people were injured [4]. Though fatalities regarding Chinese transport have declined since 2002, the situation is still far from optimistic. In the world as a whole, about 50 million people die in road traffic accidents each year; in China, the number of people who die each year from road traffic accidents accounts for about one-fifth of the world’s total, with China ranking second in the world [5]. It is estimated that passenger traffic (including car travel) and freight traffic will grow at an average annual rate of about 3.2% and 2% in China between 2021 and 2035, respectively [6]. Accordingly, road traffic safety in China is a major research focus.
Current research into the factors influencing road traffic safety in China mainly focuses on traffic participants [7,8,9,10,11,12], vehicles [9,13,14,15,16], roads [17,18,19], climate environment [20,21,22,23,24,25,26], etc., and rarely focuses on macro socio-economic factors, such as economic development, urban population scale and automobile scale. A few studies have focused on the relationship between the macro-economic factors and traffic accident casualties in China [27,28,29], but they neglect empirical analysis of the road traffic morality rate (RTMR), which is the proportion of road traffic accident deaths to the total population. The main indicators for international comparisons of road traffic safety are road deaths and/or injuries per head of population, which better reflect the total harm caused by road traffic accidents [30]. Against the background of the vigorous promotion of the construction of road transportation infrastructure and the sustainable increase in road passenger and freight transportation volumes in China, carrying out empirical research into the impact of socio-economic factors on the RTMR in China and then making policy improvements according to the relationship between the RTMR and these socio-economic factors have important theoretical significance for reducing traffic casualty rates in China.
In this paper: (1) We analyze the temporal and spatial characteristics of the RTMR in China from 2003 to 2018, which give better reference points for evaluating regional traffic safety performance. (2) Empirical analysis of the socio-economic factors influencing the RTMR in China using the Tobit model can compensate for research deficiencies and provide reference points for developing effective transport safety management policies.
This paper is divided into the following main parts: Research methodology is presented in Section 2. Section 3 analyses the overall characteristics of the RTMR in China. Section 4 conducts empirical analysis of the impact factors of the RTMR. Section 5 provides relevant policy suggestions for the improvement in traffic safety.
2. Literature Review
Traffic participants [7,8,9,10,11,12], vehicles [9,13,14,15,16], roads [17,18,19], and climate environment [20,21,22,23,24,25,26] are important factors in transport safety. Traffic participants include drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. Using descriptive statistical analysis, Zhang et al. [7] analyzed the Chinese road-fatality situation and the influencing factors, which found that the qualities and conditions of motor vehicle drivers, such as driving experience, the driver’s age, the influence of alcohol, fatigue, speeding, and the use of seat belts and headlights have obvious impacts on road safety. Zhuang and Wu [8] revealed that the inappropriate behaviors of pedestrians on roadways in China increased the casualty and fatality of accidents. Based on data from 2014, Wang et al. [9] found that speeding is the primary cause of traffic accidents. Bucsuházy et al. [10] believed that the most common factor contributing to accidents is absentminded driving according to the Czech In-depth Accident Study database. Chand et al. [11] examined that the fatigue and the distracted driving of motor vehicle drivers are two factors leading to road traffic accidents. Referring to the analysis of population-based data in Taiwan, Yu and Tsai [12] found that road safety education for motorcycle vehicle drivers has a moderate effect on reducing traffic tragedies.
When it comes to the vehicle factors, the type, performance, and condition of the vehicle are included. Rechnitzer et al. [13] hold that vehicle defects are the key factor contributing to over 6% of road traffic accidents. Goel [14] found that two-wheelers, heavy vehicles and passenger cars bear a higher risk of road fatalities in India. Wang et al. [9] noted that traffic accidents related to freight vehicles have slightly higher injuries and deaths than those related to private cars in China. Shaik and Hossain hold [15] that buses and trucks were more involved in road traffic accidents in Bangladesh. Ganji et al. [16] pointed out that the most critical part affecting vehicle safety is the braking system, followed by fuel supply and electrical systems.
The road factors mainly include the road surface conditions, road geometry, and road class. Pei [17] believed that the conditions and facilities on a road can exert influences on the behavior of traffic participants. Wang et al. [18] noted that crashes tend to occur on the segments with curves, dense access points, and a high percentage of heavy vehicles, according to the studies on 161 road segments of eight suburban arterials in Shanghai. Macioszek [19] found that motorcyclists and cyclists trajectories on small one-lane roundabouts have strongly influenced other traffic participants’ behavior.
The climate factors, such as visibility, temperature, wind speed, rainfall and moistness and others, have impacts on the likelihood and severity of vehicle collision accidents [22]. Present studies have shown that there exists a significant positive correlation between rainfall and road accidents [22]. Tu et al. [24] identified that the impacts of haze weather on driving behavior are significant. Sangkharat et al. [25] pointed out that the high rainfall levels could significantly increase road accidents in both the Southern and the Northern provinces of Thailand between 2012 to 2018. Selecting 43 main roads in Finland from 2014 to 2016 as the research object, Malin [26] examined that in poor weather and terrible road conditions, the risk of car crashes was higher on motorways than on other two-lane or multiple-lane roads.
With social and economic development, the number of vehicles in China is increasingly growing. Thus, scholars pay a lot of academic attention to the relationship between transport safety and socio-economic factors. In order to study the traffic accidents in highway tunnels, Hu et al. [27] applied Pearson correlation coefficients to analyze the influencing factors of road-traffic deaths per 100,000 people. They found strong positive correlations between road-traffic mortality and the growing economy. Sun et al. [28] used the fixed effect model to analyze the effect of various economic factors on the casualties in traffic accidents in China. They found that economic development has a positive impact on improving traffic conditions, but the new health institutions have no noticeable effect on the casualties in traffic accidents. Li and Zhang [29] applied a random effects model to analyze the impact of GDP per capita, population, and vehicle- and road-related factors on traffic accidents, injuries, and fatalities in China from 2007 to 2010. They used the Shapley value decomposition method to determine the relative contributions of these factors and their dynamic trends.
By reviewing the literature, we found that the empirical research on road traffic safety in China mainly focused on micro-specific influencing factors, while few studies involved macro socio-economic factors. Although some studies found that certain macro socio-economic factors had impacts on traffic accident casualties, there is still a lack of effective empirical analyses of influencing factors of RTMR in China from the socio-economic perspective. Compared with the number of road traffic accident casualties, the RTMR can measure the actual transport safety level [30]. Based on the panel data of 31 Chinese provinces from 2003 to 2018, we analyzed the main influence factors of the RTMR from the socio-economic view by using a Tobit pane model. The value of RTMR is limited to a certain range; hence, traditional regressions, such as ordinary least squares, could not lead to consistent estimators. On the basis of the principle of maximum likelihood estimation, the Tobit model can effectively avoid inconsistency and bias in parameter estimation, thus generating more reasonable parameter estimation results.
3. Methods
3.1. Theoretical Mechanism
In this study, we take the provincial RTMR as the dependent variable, which is the number of road fatalities per 100,000 inhabitants (Table 1). The research period is from 2003 to 2018. Considering the characteristics of the complexity of the macro socio-economic in China, the economic development level, urbanization level, vehicle density, density of medical institutions, density of health workers, and density of expenditure in medical and health care were selected as the influencing factors. A specific description of the independent variables is shown in Table 2. The data are taken from NBSC.

Table 1.
The values of RTMR for 31 provinces in China from 2003 to 2018 (per 100,000 inhabitants).
3.1.1. The Mechanism of Economic Development
In general, economic growth leads to increased traffic volume, traffic congestion, young male drivers, speeding, drunk driving, and ultimately an increase in fatal traffic accidents [31,32]. However, some authors believe that sustained economic growth enables the road users in higher-income countries to use safer transportation tools, while the users in lower-income countries would not do that [33]. Based on the previous studies of Bishai et al. [33] and Gaygisiz [34], this paper selected economic development level as a major dependent variable as a basis for carrying out empirical research; the relationship between economic development level and RTMR needs to be tested empirically.
Hypothesis 1.
Economic development level influences the RTMR in China.
3.1.2. The Mechanism of Urbanization
With the acceleration and deepening of the urbanization process, a large proportion of the rural population has poured into the city, resulting in road traffic congestion, and foot passengers and non-motorized vehicles arbitrarily passing along vehicular roads and causing a large number of traffic accidents [35]. However, some scholars hold that there are higher levels of density of health resources and road maintenance and management [36], and the higher rate of public transportation modes in urban areas means that traffic accidents tend to happen at a lower speed [37]. Based on the previous studies of Li and Zhang [29], Jadaan [38], and Atubi and Gbadamosi [39], urbanization level was selected as a major dependent variable as a basis for carrying out empirical research.
Hypothesis 2.
Urbanization level influences the RTMR in China.
3.1.3. The Mechanism of Motorization
Motorization level refers to the number of motor vehicles per unit of population in a certain period. The increase in the number of vehicles and road lengths has enabled closer and more frequent regional communication, brought increased convenience to people’s lives, and made great contributions to the economic development of all regions. Furthermore, it has led to the rapid expansion of road users and drivers, especially novice drivers [40]. In 1949, when Smeed studied the relationship between traffic accidents and economic growth, he used the number of motor vehicles per thousand people as an explanatory variable. Based on previous studies by Li and Zhang [29], Ali et al. [41] and He et al. [42], the motorization level was added to the regression model in this research.
Hypothesis 3.
Raising the motorization level improves the RTMR in China.
3.1.4. The Mechanism of Medical Assistance
Research has indicated that road traffic accident fatality rates may be reduced by first aid, specialist transport and emergency treatment of the victims [33,43]. An effective medical emergency system based on a rescue chain makes it easier for aid agencies to save victims of road accidents. Based on the study by Ali et al. [41] and La Torre et al. [44], medical assistance level was selected as a major dependent variable as a basis for carrying out empirical research, and the number of medical personnel in health care institutions per 10,000 inhabitants as a proxy variable of medical assistance level.
Hypothesis 4.
Raising the medical assistance level inhibits the RTMR in China.
3.1.5. The Mechanism of Government Regulation
“Traffic accident” has now been listed as the world’s fourth-largest killer threatening people’s lives and property [5]. Government expenditure on health, such as improving the healthcare services system, transferring payments to less advanced areas in medical and health services, and providing assistance to victims in road traffic accidents, would help to reduce traffic deaths. Therefore, this paper selects government expenditure on health as an important variable for regression analysis.
Hypothesis 5.
Government expenditure on health inhibits the RTMR in China.

Table 2.
Influencing factors of RTMR.
Table 2.
Influencing factors of RTMR.
| Explanatory Variables | Definitions of Variables | Key References | Pre-Judgment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development level (DEL) | Per capita GDP (Dollar 10,000) | Li and Zhang [29]; Song and Zhang [32]; Bishai et al. [33]; Lu et al. [34]; | Unknown |
| Urbanization level (TIL) | Proportion of city population in total inhabitants (%) | Li and Zhang [29]; Jadaan [38]; Atubi and Gbadamosi [39]; Ali et al. [41]; | Unknown |
| Motorization level (ML) | Motor vehicles per 100,000 inhabitants (persons) | Li and Zhang [29]; Ali et al. [41]; He et al. [42]; | Positive |
| Medical assistance level (MAL) | Medical personnel in health care institutions per 100,000 inhabitants (persons) | Bishai et al. [33]; Ali et al. [41]; Mock et al. [43]; La Torre et al. [44]; | Negative |
| Government regulation (GR) | Government expenditure on health (RMB 100,000) | Li and Zhang [29]; Ali et al. [41]; Castillo-Manzano et al. [45]; | Negative |
3.2. Tobit Regression Model
The value of the provincial RTMR in China from 2003 to 2018 is between 1.63 and 22.83, which are limited dependent variables; when using the traditional ordinary least squares (OLS) to test the factors influencing the RTMR, the estimated results will be biased and inconsistent [38,39]. The Tobit regression model proposed by Tobin [40], which is known as the truncated regression model, can effectively handle this type of data with the Maximum Likelihood Estimation [41,42,43,46,47,48,49,50,51]. Therefore, we applied the Tobit model to estimate the unknown parameters. The econometric model can be defined as Equation (1):
where i and t stands for the ith province in time t. Y refers to the dependent variables, X indicates the explanatory variable, β stands for the correlation coefficient, and ε is the random error with the distribution of n(0, σ2).
4. Characteristics Analysis of RTMR
4.1. The Temporal Characteristics of RTMR
Considering in terms of their spatial characteristics, most of the provinces with higher RTMRs are located in the developed coastal areas and the underdeveloped northwest regions, while most of the provinces with lower RTMRs are located in the central region (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The factors leading to regional difference are manifold. The developed coastal areas have higher urbanization rates and higher per capita car ownership, resulting in more frequent traffic accidents. Although underdeveloped western areas have lower urbanization rates and lower higher per capita car ownership, the medical and health conditions in the areas are poor [29], resulting in higher RTMRs. Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjiang are the three provinces with the highest RTMRs in China. These are vast territories with small populations and adverse natural conditions. When accidents occur on wild highways, it takes a long time for medical rescue teams to reach the accident scenes. In these provinces, the economic development and education levels are generally low, and the proportion of high-grade highways is relatively small [52]. Significantly, Zhejiang and Fujian are the two provinces with the highest RTMRs in the eastern region. These two provinces are characterized by a high population density and a rugged mountainous terrain, which pose a barrier to the improvement in the road transportation system and generate more road traffic accidents.
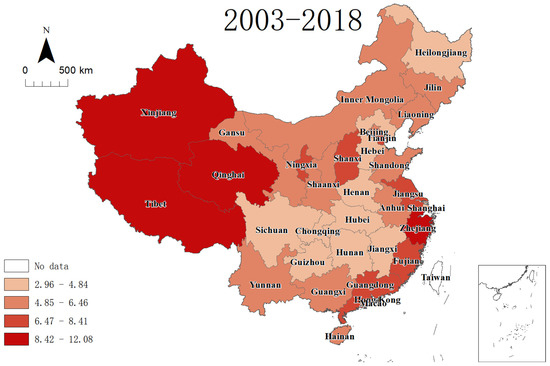
Figure 1.
RTMR (per 100,000 inhabitants) intervals in 31 provinces from 2003 to 2018.
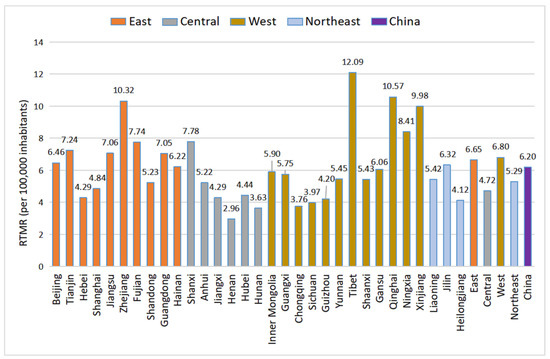
Figure 2.
The mean values of RTMR in China’s major economic zones from 2003 to 2018.
4.2. The Temporal Characteristics of RTMR
From temporal change features, the RTMR tended to change in line with road transport accidents and casualties, and obviously decreased after 2003, rebounding since 2016 (Figure 3). On the one hand, as many transport safety policies were implemented by China’s government, traffic accidents decreased year by year, and the RTRM also decreased at the same time. From another perspective, the traffic accident rescue system has improved greatly, and China has improved its financial expenditure on medical services, especially in the transportation sector, both of which factors are conducive to the sharp decline in the RTMR. The standard deviation of provincial RTMR also shows a downward trend after 2003, but a rebound since 2017, which means the regional difference in the RTMR shows a convergence trend from 2003 to 2016. In 2016–2018, the RTMRs in many provinces showed a marked deterioration compared with the previous year, which affects the national RTMR.
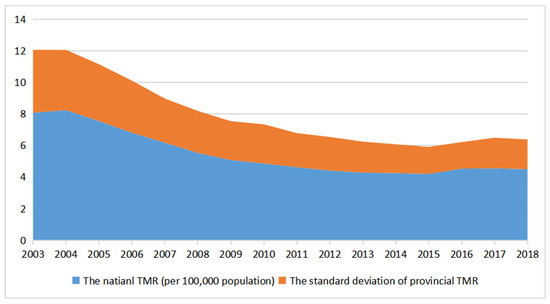
Figure 3.
The evolutionary trend of the national RTMR from 2003 to 2018.
4.3. The Temporal-Spatial Changes of the RTMR
With the application of arcgis 10.2 software, the spatial distribution maps of the RTMR of China in 2003, 2010 and 2018 were made. The RTMR classifications are based on the Jenks Natural Breaks Classification Method [53]. The RTMR is divided into four grades (from high to low).
By observing Figure 4, it can be found that in 2003, the first class only included Tibet, the second class included Ningxia, Zhejiang, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Guangdong, Fujian, Beijing, Tianjin and Shanxi, and the third class included Shandong, Jiangsu, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Gansu, Jilin, Shanghai, Guangxi, Yunnan and Hebei. The remaining 11 provinces were in the fourth class.

Figure 4.
RTMR (per 100,000 inhabitants) intervals in 31 provinces in 2003.
In 2010 (Figure 5), Tibet was still in the first class, while the second class had changed greatly. The number of provinces the second class had decreased from nine in 2003 to five. Zhejiang, Qinghai and Xinjiang entered the first class. The numbers in the first class increased from one in 2003 to four in 2010. Both Beijing and Shangdong dropped from the second class to the third class. Shanxi, Fujian, Tianjin and Ningxia remained in the second class. The members of the third class also changed greatly. Jiangsu rose from the third to the second class, while Yunnan and Hebei fell from the third to the fourth class. Shangdong, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Gansu, Jilin, Shanghai and Guangxi remained unchanged and were still in the third class. As for the fourth class, Hainan, Shaanxi and Anhui were upgraded from the fourth class in 2003 to the third class in 2010, and the remaining members of the fourth class remained unchanged. In addition, Yunnan and Hebei dropped from the third to the fourth class. The fourth class had 10 members in 2010.
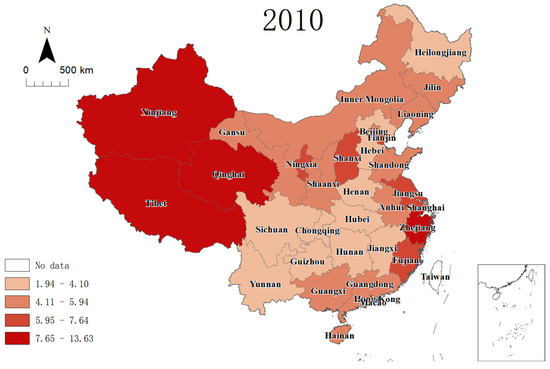
Figure 5.
RTMR (per 100,000 inhabitants) intervals in 31 provinces in 2010.
In 2018 (Figure 6), there were great changes for all four classes. Qinghai, Xinjiang and Zhejiang were still in the first class, while Hubei was upgraded from the third to the first class. The number of provinces in the first class was still four. In the second class, there were eight provinces: Guizhou, Zhejiang, Beijing, Ningxia, Xinjiang, Yunnan, Shanxi and Jiangsu. It is worth noting that both Zhejiang and Tibet came down to the second class from the first class, while Guizhou and Yunnan rose to the second class from the fourth class, and the other provinces remained unchanged. The number of provinces in the third class had decreased a little, from 12 in 2010 to 11 in 2018. The third class included Gansu, Tianjin, Fujian, Jilin, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Liaoning, Anhui, Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi and Tibet. More specifically, Tibet dropped from the first to the third class, and Tianjin and Fujian dropped from the second to the third class, and Jiangxi rose from the fourth to the third class. Shandong, Heilongjiang, Hebei, Chongqing, Sichuan, Henan, Shanghai and Hunan all belonged to the fourth class. Shandong and Shanghai went down from the third to the fourth class, and the improvement in traffic safety in Shandong and Shanghai was obvious, while the other nine provinces in the fourth class remained unchanged.
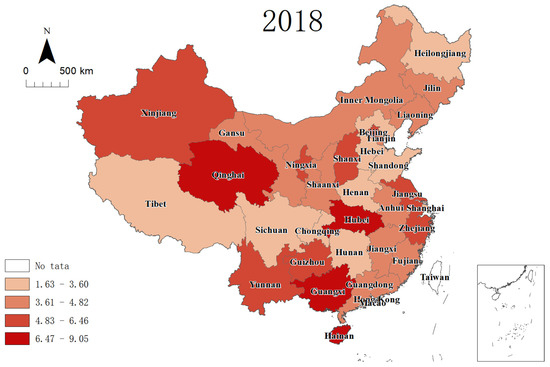
Figure 6.
RTMR (per 100,000 inhabitants) intervals in 31 provinces in 2018.
In general, although there are significant temporal-spatial changes in the RTMR in some provinces from 2003 to 2018, for instance, the RTMR in Guangdong and Tibet decreased greatly, and the RTMR in Hubei and Guangxi improved, there was little temporal-spatial change in the country as a whole. The overall RTMRs in the eastern and western regions are higher, while in the middle it was lower. This means that the eastern region urgently needs to strengthen the traffic administration, as well as the promotion of traffic safety among citizens, while the western region is in dire need of improving the road traffic environment and enforcing the emergency medical service system.
5. Empirical Analysis
5.1. The Unit Root and VIF Tests
The panel data on the economic development level, urbanization level, motorization level, medical assistance level, government expenditure on health, and road traffic morality rate from 2003 to 2018 for the 31 provinces in China are used for our analysis. Before using the Tobit model, it was necessary to confirm the stationary data to avoid spurious regression. This paper applies Levin, Lin and Chu (LLC), Im, Pesaran and Shin (IPS), ADF-Fisher, and PP-Fisher tests to examine the stationary properties of the four variables. The test results are displayed in Table 3, which indicate that all the variables are second-order difference stationary. So, it is appropriate to use these variables for the co-integration test. We then applied the Kao panel co-integration test. The test result (t-Statistic = −2.500028 ***) rejected the original hypothesis at a significant level of 5%, which suggests that there exists a long-term equilibrium relationship among all the variables. In general, although there are significant temporal-spatial changes in the RTMR in some provinces from 2003 to 2018; for instance, the RTMR in Guangdong and Tibet improved greatly, and the RTMR in Hubei and Guangxi deteriorated, there was little temporal-spatial change in the country as a whole. The overall RTMR in the west and east was higher, while in the middle it was lower.

Table 3.
The panel unit root test results.
In order to avoid multicollinearity among all the independent variables, the variance inflation factor (VIF) test was conducted. Table 4 gives the VIF test results. It can be seen that the VIF values of all independent variables are less than 10, implying that the multicollinearity problem is not present in the regression analysis.

Table 4.
The VIF test.
5.2. Discussion of Regression Result
After confirming that there are no problems of spurious regression and multicollinearity, this paper evaluated the impact of the above factors influencing the RTMR in China by the Tobit regression model, which is as follows
where β0, β1, β2,……, β6 stands for the coefficient of the independent variables and uit is a random disturbance term. The parameters were estimated by Stata12.0 software. Additionally, after that, the Tobit regression analysis was carried out with the adoption of software STATA 12.0. The panel Tobit results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Tobit regression results.
The rconomic development level has obviously negatively impacted the RTMR. With the strengthening of the comprehensive economic power of China, the rate of spending on transport safety management, medical health, and road maintenance is increasing, which would offset the increase in the number of deaths caused by the rapid development of urbanization and motorization. For example, the Chinese government has formulated a national reform of health care and implemented a series of policies benefitting people since 2009 [54]. Motorists and pedestrians in economically developed regions have a stronger awareness of traffic safety, and the traffic laws are forcefully implemented; the use of seatbelts and helmets are also more self-conscious, which make road traffic injuries less likely [29].
The urbanization level has a significantly positive impact on the RTRM. China is experiencing one of the largest urbanization processes, which has lasting and deep effects on local and national public health [55]. The unplanned mode of urbanization development in some cities in China makes the problem of “urban disease” more and more outstanding. The increase in population density and the imperfection of traffic facilities mean that traffic congestion is very serious, the load capacity of urban roads seriously exceeds the norm, and traffic accidents occur frequently.
Motorization level has a significantly positive impact on the RTRM. Since the 2000s, civilian vehicle ownership in China has grown at a rapid rate: from 23.83 million vehicles in 2003 to 232.31 million in 2018. This has brought a greater heavy traffic burden and further increased the risk of traffic accidents. Although a string of transport safety policies implemented in China from the late 1990s may have resulted in lower speeds and more traffic congestion [27], the rapid growth of automobile possession increases the risk of exposure to road transport accidents and the expanded size of the urban population might result in an increase in the scale of road transport mortality [45,56].
The regression coefficients of medical assistance levels are significantly negative. Providing better geographical coverage of health care for road accidents helps reduce the likelihood of traffic-related deaths [57]. At present, there are obvious differences between urban and rural areas and between different regions in the allocation of public medical resources in China [58]. The level of medical and health development lags behind in some western areas and in many remote villages, which requires the government’s adjustment policy to allocate medical resources rationally.
The regression coefficient of government expenditure on health is significantly negative, which is in line with expectations. Although the proportion of fiscal expenditure on medical care in GDP increased from 4% to 7.1% from 2003 to 2018, it is still lower than the average level in OECD countries. According to WHO data, in 2018, the proportion of government expenditure on health care to GDP in the UK was 19%, in the USA it was 22%, and in Japan it was 24%, respectively [59], which was much higher than that of China in the same period. In order to curb the RTMR, the Chinese government needs to increase fiscal expenditure on health.
6. Conclusions
Road safety has always been and will remain a top priority of the road transport industry [60]. As one of the fastest-growing economies, China has made great progress in traffic safety, and the RTMR has dropped significantly since 2004 [3]. China plays an extremely important role in the realization of the target for the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011–2020. However, the RTMR has deteriorated since 2016 [3]. To achieve the goal set out in the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021–2030, China needs to intensify its efforts to improve safety in transport.
Our research aims to fill a research gap by building the Tobit model to analyze the factors influencing the RTMR from socio-economic factors. The results show that economic development levels, medical assistance levels and government expenditure on health are significantly negatively correlated with the RTMR, while urbanization levels and motorization levels significantly promote the RTMR. In order to improve transport safety in China, according to the research results, we offer the following policy suggestions:
Firstly, vigorously promote traffic safety knowledge. In line with economic development, ownership and mobility of vehicles are growing rapidly in China, and many novice drivers and pedestrians show a lack of traffic safety awareness. It is therefore necessary to implement the following measures: (1) TV, newspapers, the Internet, and other media should honor the legal obligations to (freely) promote traffic safety knowledge (without charge); (2) Promote traffic safety education in schools; and (3) Adopt various approaches to popularize traffic safety knowledge in rural areas.
Secondly, speed up the informatization and intellectualization of traffic safety facilities management. The transport sector should use computer and information technology to promote the management of traffic safety facilities. For example, it can develop the information management system software of traffic safety facilities so that the electronic traffic map can display the current status of traffic safety facilities in real time, and so that we can obtain updates, the maintenance status, performance attributes and other information about traffic safety facilities.
Thirdly, strengthen the supervision of the manufacturing and use of motor vehicles and improve the safety performance of motor vehicles to further perfect the national system of vehicle safety and encourage and guide the development of vehicles with higher safety performance standards. In particular, three-wheeled vehicles, low-speed trucks, minibuses, and so on, all need to be improved in terms of product quality and safety performance.
Since the corresponding practical operation remains inaccessible, the research can be improved by further studies. First, as the paper only focused on the RTMR levels of administrative spaces, future work should focus on the RTMR levels of specific vehicle types, such as cars, buses, trucks, motorcycles and so on. Moreover, the ultimate goal of RTMR research, reducing road traffic accidents and improving traffic safety levels, should be kept in mind. Therefore, further research should dive into the application and practice of an intelligent traffic safety system, which can assess the status of road traffic safety, forecast the trend of road traffic safety, and provide useful suggestions for policymakers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, H.L.; supervision, X.L.; methodology, software, validation, H.H.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, C.L.; investigation, X.Y.; data curation, D.G.; writing—original draft preparation, K.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data were obtained from National Bureau of Statistics of China.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, P.; Lyu, D.; Hu, H.; Cao, Y.; Xie, J.; Pang, L.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, D. Population-development oriented compre-hensive modern transport system in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 2699–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, P.; Hu, H.; Zeng, L.; Wu, K.S.; Lv, D. Transport infrastructure and urban-rural income disparity: A municipal-level analysis in China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 99, 103292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). Annual Data of the Province in China. 2022. Available online: http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=E0103 (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Yearbook of China Transportation & Communications. Yearbook House of China Transportation & Communications, Beijing. Available online: https://data.cnki.net/yearbook/Single/N2021040178 (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://www.who.int/roadsafety/events/2015/Appendix_14.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. Yearbook House of China, the State Council of the People’s Republic of China. 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-02/24/content_5588654.htm (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Zhang, W.; Tsimhoni, O.; Sivak, M.; Flannagan, M.J. Road safety in China: Analysis of current challenges. J. Saf. Res. 2010, 41, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Wu, C. Pedestrians’ crossing behaviors and safety at unmarked roadway in China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2011, 43, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, H. Road traffic accident severity analysis: A census-based study in China. J. Saf. Res. 2019, 70, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucsuházy, K.; Matuchová, E.; Zůvala, R.; Moravcová, P.; Kostíková, M.; Mikulec, R. Human factors contributing to the road traffic accident occurrence. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 45, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, A.; Jayesh, S.; Bhasi, A. Road traffic accidents: An overview of data sources, analysis techniques and contributing factors. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 5135–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tsai, W.-D. The effects of road safety education on the occurrence of motorcycle violations and accidents for novice riders: An analysis of population-based data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 163, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechnitzer, G.; Haworth, N.; Kowadlo, N. The Effect of Vehicle Roadworthiness on Crash Incidence and Severity; Report No. 164; Monash University Accident Research Centre: Clayton, Australia, 2000; Available online: http://www.monash.edu/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/216710/muarc164.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Goel, R. Modelling of road traffic fatalities in India. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 112, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, E.; Hossain, Q.S. Application of Statistical Models: Parameters Estimation of Road Accident in Bangladesh. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, S.R.; Rassafi, A.A.; Kordani, A.A. Vehicle Safety Analysis based on a Hybrid Approach Integrating DEMATEL, ANP and ER. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4580–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.L.; Ma, J. Research on countermeasures for road condition causes of traffic accidents. China J. Highw. Transp. 2003, 16, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, R.; Schultz, G.G. Safety modeling of urban arterials in Shanghai, China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 83, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macioszek, E. The Influence of Motorcycling and Cycling on Small One-Lane Roundabouts Capacity. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Mikulski, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelias, P.; Papadimitriou, F.; Papandreou, K.; Prevedouros, P. Urban Freeway Crash Analysis: Geometric, Operational, and Weather Effects on Crash Number and Severity. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 2015, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eboli, L.; Forciniti, C.; Mazzulla, G. Factors influencing accident severity: An analysis by road accident type. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 47, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergel-Hayat, R.; Debbarh, M.; Antoniou, C.; Yannis, G. Explaining the road accident risk: Weather effects. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 60, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, F.; Wets, G.; Brijs, T. A Regression Model with ARMA Errors to Investigate the Frequency and Severity of Road Traffic Accidents. Steunpunt Verkeersveiligheid; Steunpunt Verkeersveiligheid: Diepenbeek, Belgium, 2008; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265674721 (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Tu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, L. Driving Simulator Fidelity and Emergency Driving Behavior. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2518, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkharat, K.; Thornes, J.E.; Wachiradilok, P.; Pope, F.D. Determination of the impact of rainfall on road accidents in Thailand. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, F.; Norros, I.; Innamaa, S. Accident risk of road and weather conditions on different road types. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 122, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wen, M.; Baker, T.D.; Baker, S.P. Road-traffic deaths in China, 1985–2005: Threat and opportunity. Inj. Prev. 2008, 14, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-L.; Liu, D.; Chen, T.; He, M.-T. Analysis on the accident casualties influenced by several economic factors based on the traffic-related data in China from 2004 to 2016. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2019, 22, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Road traffic safety and differences in regional economic development: Evidence from random effects model and shapley value decomposition. In Road Safety in China; Zhang, G., Zhong, Q., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, J.; Sivak, M. Why is road safety in the U.S. not on par with Sweden, the U.K., and the Netherlands? Lessons to be learned. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2014, 6, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, S.; Yahya, F.; Mir, Z.; Zafar, R. Provincial analysis of traffic accidents in Pakistan. Soc. Sci. Hum. 2012, 3, 365–374. Available online: https://www.oalib.com/paper/2072288 (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Song, L.; Zhang, S.S. VAR model study on the impact of scale and speed of economic growth on traffic safety risk. China Public Saf. 2016, 3, 83–85. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgggaq-xsb201603019 (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Bishai, D.; Quresh, A.; James, P.; Ghaffar, A. National road casualties and economic development. Health Econ. 2006, 15, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, P.; Dong, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, L. Accessibility of high-speed rail stations and spatial disparity of urban-rural income gaps. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 41, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Harsha, V.; Subramanian, G.H. Evolution of Urban Transportation Policies in India: A Review and Analysis. Transp. Dev. Econ. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. A study of differences in the incidence rate of traffic accidents (First report) Factors affecting incidence of traffic accidents in the prefectures of Japan. Jpn. J. Health Hum. Ecol. 1984, 50, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okui, T.; Park, J. Analysis of the regional distribution of road traffic mortality and associated factors in Japan. Inj. Epidemiol. 2021, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaan, K.S. Traffic accidents in Kuwait: An economic dimension. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1990, 22, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atubi, A.O.; Gbadamosi, K.T. Global positioning and socio-economic impact of road traffic accidents in Nigeria: Matters arising. Am. Int. J. Contemp. Res. 2015, 5, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, Q. Economic development and road traffic safety in China: A status Quo analysis. In Road Safety in China; Zhang, G., Zhong, Q., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Yaseen, M.R.; Khan, M.T.I. Road traffic fatalities and its determinants in high-income countries: A continent-wise comparison. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19915–19929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Paichadze, N.; Hyder, A.A.; Bishai, D. Economic development and road traffic fatalities in Russia: Analysis of federal regions 2004–2011. Inj. Epidemiol. 2015, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, C.N.; Jurkovich, G.J.; Arreola-Risa, C.; Maier, R.V. Trauma mortality patterns in three nations at different economic levels: Implications for global trauma system development. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1998, 44, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, G.; Van Beeck, E.; Quaranta, G.; Mannocci, A.; Ricciardi, W. Determinants of within-country variation in traffic accident mortality in Italy: A geographical analysis. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2007, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Manzano, J.I.; Castro-Nuño, M.; Fageda, X. Can health public expenditure reduce the tragic consequences of road traffic accidents? The EU-27 experience. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2014, 15, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.C.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, L.E. Research on China’s Carbon Dioxide Emissions Efficiency from 2007 to 2016: Based on Two Stage Super Efficiency SBM Model and Tobit Model. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2021, 57, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.-J.; Zeng, L.-E.; Lu, H.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H.-Y.; Wei, X.-Y. Green economic efficiency and its influencing factors in China from 2008 to 2017: Based on the super-SBM model with undesirable outputs and spatial Dubin model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J. Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 1958, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H. Analysis of Regional Differences and Influencing Factors on China’s Carbon Emission Efficiency in 2005–2015. Energies 2019, 12, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L. China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zeng, L.; Li, P.; Lu, H.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Zheng, M.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, D.; et al. China’s transportation sector carbon dioxide emissions efficiency and its influencing factors based on the EBM DEA model with undesirable outputs and spatial Durbin model. Energy 2022, 238, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Duan, J.; Zhang, H. The assessment of traffic accident risk based on grey relational analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Rao, K.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q. Health Care in China: Improvement, Challenges, and Reform. Chest 2013, 143, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Song, J.; Lin, T.; Dixon, J.; Zhang, G.; Ye, H. Urbanization and health in China, thinking at the national, local and individual levels. Environ. Health 2016, 15, S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Chan, C.L.W. Estimated trends and patterns of road traffic fatalities in China, 2002–2012. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchmueller, T.C.; Jacobson, M.; Wold, C. How far to the hospital? The effect of hospital closures on access to care. J. Health Econ. 2006, 25, 740–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.L.; Wang, Z. Regional inequality in China’s health care expenditures. Health Econ. 2009, 18, S137–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Health Expenditure Database. 2021. Available online: https://apps.who.int/nha/database/Select/Indicators/en (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- World Road Transport Organisation. The Industry’s Commitment. Available online: https://www.iru.org/what-we-do/being-trusted-voice-mobility-and-logistics/people/road-safety (accessed on 10 July 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).