A Psychometric Analysis of Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices: Evaluating Guessing and Carelessness Using the 4PL Item Response Theory Model
Abstract
:1. Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices
2. Item Response Theory Models
3. Importance of the Present Study
4. Method
4.1. Participants and Procedures
4.2. Measures
4.3. Data Analyses
5. Results
5.1. Construct Validity between Forms A, AB, and B across 1-PL through to 4-PL IRT Models
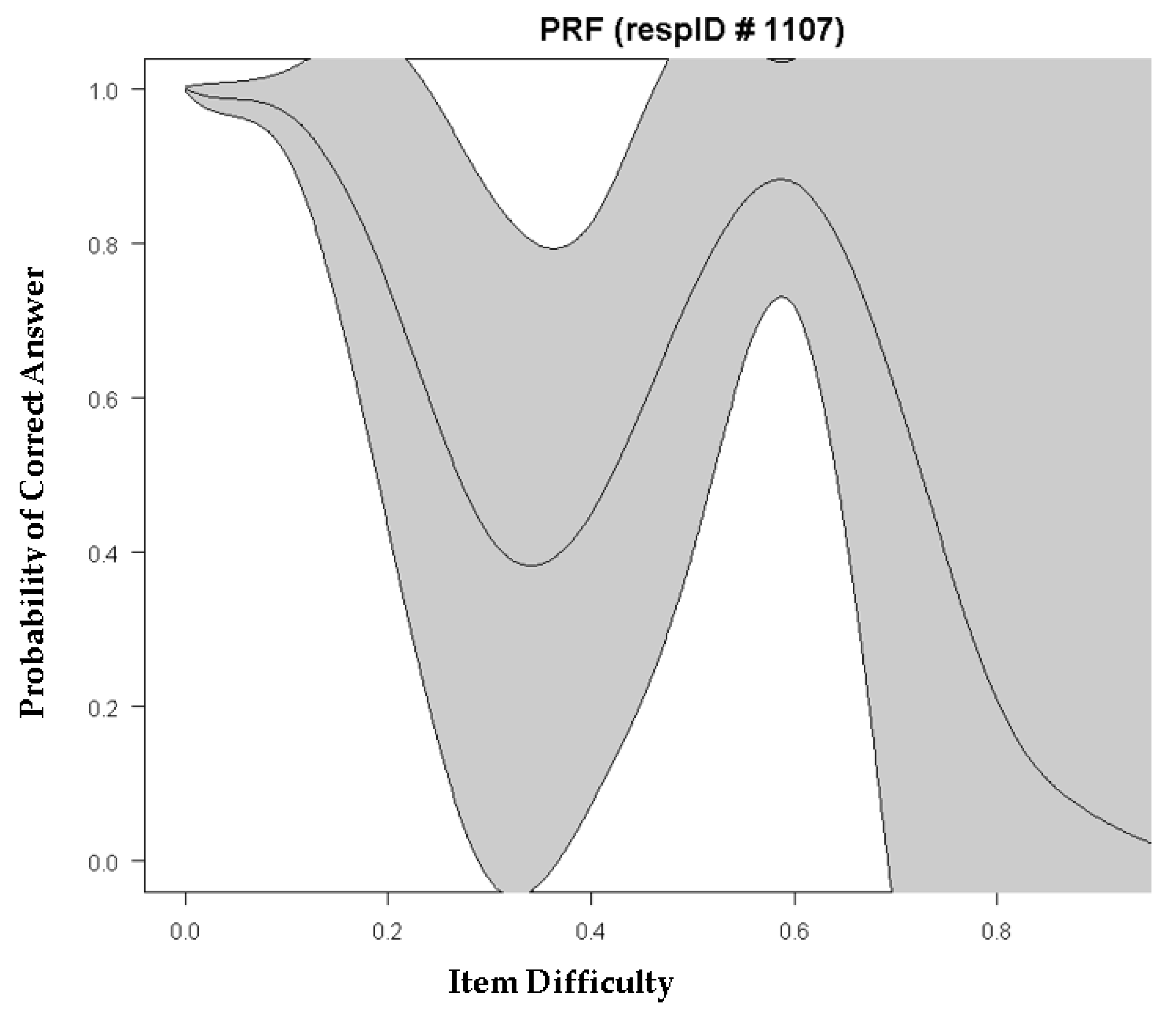
5.2. An Example of Guessing and Carelessness: Plotting Person Response Functions
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abad, Francisco, Roberto Colom, Irene Rebollo, and Sergio Escorial. 2004. Sex differential item functioning in the Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices: Evidence for bias. Personality and Individual Differences 36: 1459–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, Hirotugu. 1974. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automated Control 19: 716–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, Frank, and Seock-Ho Kim. 2004. Item Response Theory: Parameter Estimation Techniques, 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, Mark, and Frederick Lord. 1981. An Upper Asymptote for the Three-Parameter Logistic Item-Response Model. Princeton: Educational Testing Services. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, Alfred. 1968. Some latent trait models and their use in inferring an examinee’s ability. In Statistical Theories of Mental Test Scores. Edited by F. M. Lord and M. R. Novick. Reading: Addison-Wesley. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, Ryan, and Eric Anthony Day. 2006. The difference isn’t black and white: Stereotype threat and the race gap on Raven’s advanced progressive matrices. Journal of Applied Psychology 91: 979–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnham, Kenneth, and David Anderson. 2002. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference. New York: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Facon, Bruno, David Magis, Marie-Laure Nuchadee, and Paul de Boeck. 2011. Do Raven’s colored progressive matrices function in the same way in typical and clinical populations? Insights from the intellectual disability field. Intelligence 39: 281–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharpey, Hahal, David Crewther, and Sheila Crewther. 2013. Problem solving ability in children with intellectual disability as measured by the Raven’s colored progressive matrices. Research in Developmental Disabilities 34: 4366–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, Arthur. 1998. The G Factor: The Science of Mental Ability. Detroit: Praeger. [Google Scholar]
- Karabatsos, George. 2003. Comparing the aberrant response detection performance of thirty-six person-fit statistics. Applied Measurement in Education 16: 277–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, Robert, Jay Sanderson, and Keith Melton. 1966. Relation of the Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices to two measures of verbal ability in a sample of mildly retarded hospital patients. Psychological Reports 19: 731–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Siow Hoo, Siew Eng Ling, and Rasidah Mahdi. 2013. Moderating ability of item response theory through prior guessing parameter. Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 9: 277–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Wen-Wei, Rong-Guey Ho, Yung-Chin Yen, and Hsu-Chen Cheng. 2012. The four-parameter logistic item response theory model as a robust method of estimating ability despite aberrant responses. Social Behavior and Personality 40: 1679–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linacre, Mike. 2004. Item discrimination, guessing and carelessness asymptotes: Estimating IRT parameters with Rasch. Rasch Measurement Transactions 18: 959–60. [Google Scholar]
- Loken, Eric, and Kelly Rulison. 2010. Estimation of a four-parameter item response theory model. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology 63: 509–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackintosh, Nicholas John. 1996. Sex Differences and IQ. Journal of Biosocial Science 28: 558–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magis, David. 2013. A note on the item information function of the four-parameter logistic model. Applied Psychological Measurement 37: 304–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masyn, Kathryn. 2013. Latent class analysis and finite mixture modeling. In The Oxford Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology. Edited by T. D. Little. New York: Oxford University Press, vol. 2, pp. 551–611. [Google Scholar]
- Mislevy, Robert, and Darrell Bock. 1982. Biweight estimates of latent ability. Educational and Psychological Measurement 42: 725–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osgood, D. Wayne, Barbara Morris, and Maria Potenza. 2002. Analyzing multiple-item measures of crime and deviance I: Item response theory scaling. Journal of Quantitative Criminology 18: 267–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, Vivek, Jennifer Smith, John Desmond, Gary Glover, and John Gabrieli. 1997. Neural substrates of fluid reasoning: An fMRI study of neocortical activation during performance of the Raven’s Progressive Matrices Test. Cognitive Psychology 33: 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pueyo, Roser, Carme Junque, Pere Vendrell, Ana Narberhaus, and Dolors Segarra. 2008. Raven’s coloured progressive matrices as a measure of cognitive functioning in cerebral palsy. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 52: 437–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A. E. 1995. Bayesian model selection in social research. Sociological Methodology 25: 111–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, John, John H. Court, and Jean Raven. 1998. Progressive Matrices Couleur/Colored Progressive Matrices. Paris: Les Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée. [Google Scholar]
- Reise, Steven, and Neils Waller. 2003. How many IRT parameters does it take to model psychopathology items? Psychological Methods 8: 164–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulison, Kelly, and Eric Loken. 2009. I’ve fallen and I can’t get up: Can high ability students recover from early mistakes in computerized adaptive testing? Applied Psychological Measurement 33: 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, Andreas. 2003. Item response modeling with BILOG-MG and MULTILOG for Windows. International Journal of Testing 3: 365–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. 1975. The Construction and Interpretation of S-P Tables. Tokyo: Meiji Tosho. [Google Scholar]
- Savage-McGlynn, E. 2012. Sex differences in intelligence in younger and older participants of the Raven’s standard progressive matrices plus. Personality and Individual Differences 53: 137–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijtsma, Klaas. 1986. A coefficient of deviance of response patterns. Kwantitatieve Methoden 7: 131–45. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, Hariharan, and Janice Gifford. 1986. Bayesian estimation in the three-parameter logistic model. Psychometrika 51: 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendeiro, Jorge, Rob Meijer, and Susan Niessen. 2016. PerFit: An R package for person-fit analysis in IRT. Journal of Statistical Software 74: 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Flier, H. 1982. Deviant response patterns and comparability of test scores. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 13: 267–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herwegen, Jo, Emily Farran, and Dagmara Annaz. 2011. Item and error analysis on Raven’s coloured progressive matrices in Williams syndrome. Research in Developmental Disabilities 32: 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandekerckhove, Joachim, Dora Matzke, and Eric Wagenmakers. 2015. Model comparison and the principle of parsimony. In The Oxford Handbook of Computational and Mathematical Psychology. Edited by Jerome Busemeyer, Zheng Wang, James Townsend and Ami Eidels. Oxford: Oxford Library of Psychology, pp. 300–19. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, Neils, and Leah Feuerstahler. 2017. Bayesian modal estimation of the four-parameter item response model in real, realistic, and idealized data sets. Multivariate Behavioral Research 52: 350–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, Neils, and Steven Reise. 2009. Measuring psychopathology with non-standard IRT models: Fitting the four-parameter model to the MMPI. In New Directions in Psychological Measurement with Model-Based Approaches. Edited by Susan Embretson and John Roberts. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. [Google Scholar]
- Zumbo, Bruno. 2007. Three generations of DIF analyses: Considering where it has been, where it is now, and where it is going. Language Assessment Quarterly 4: 223–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
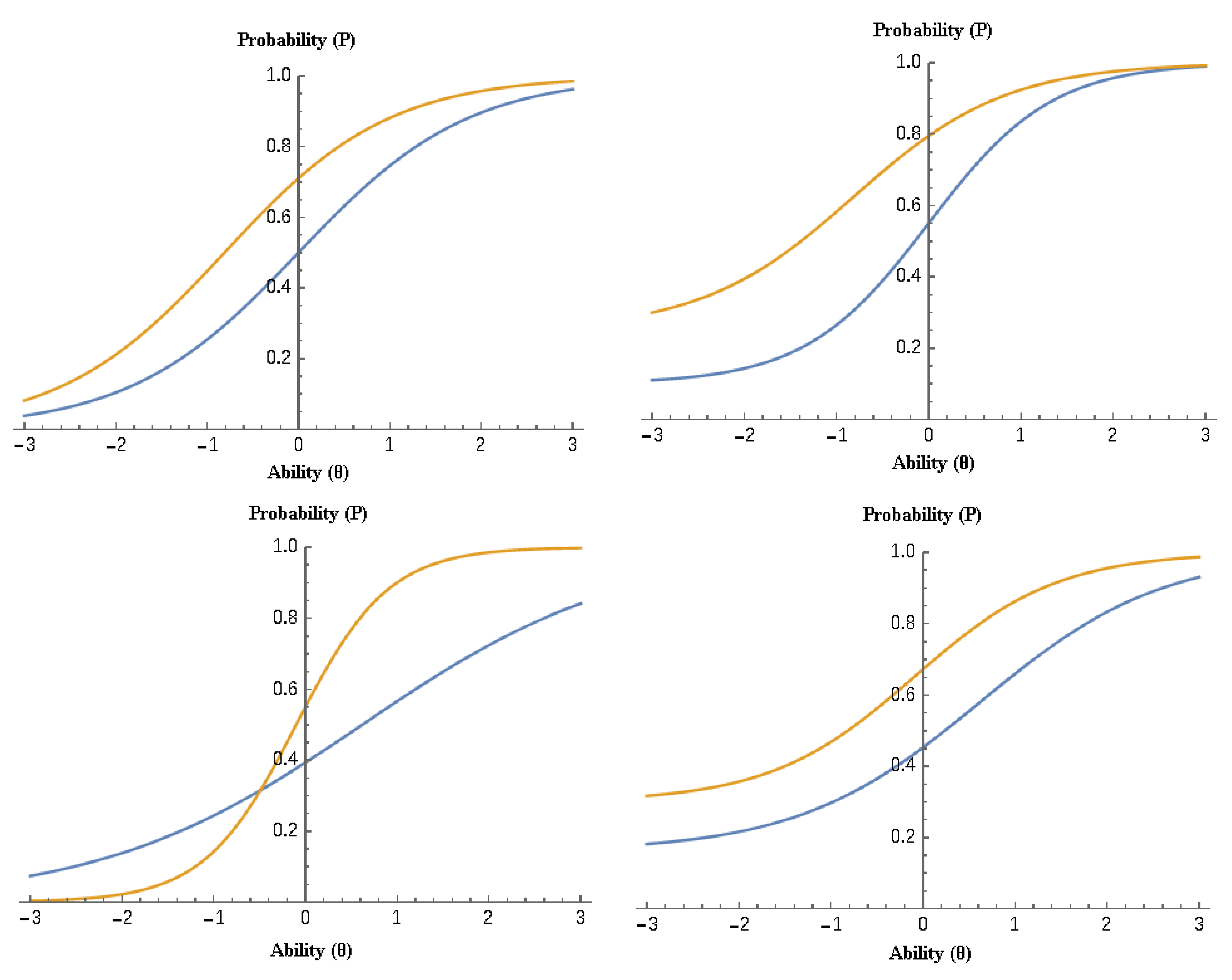

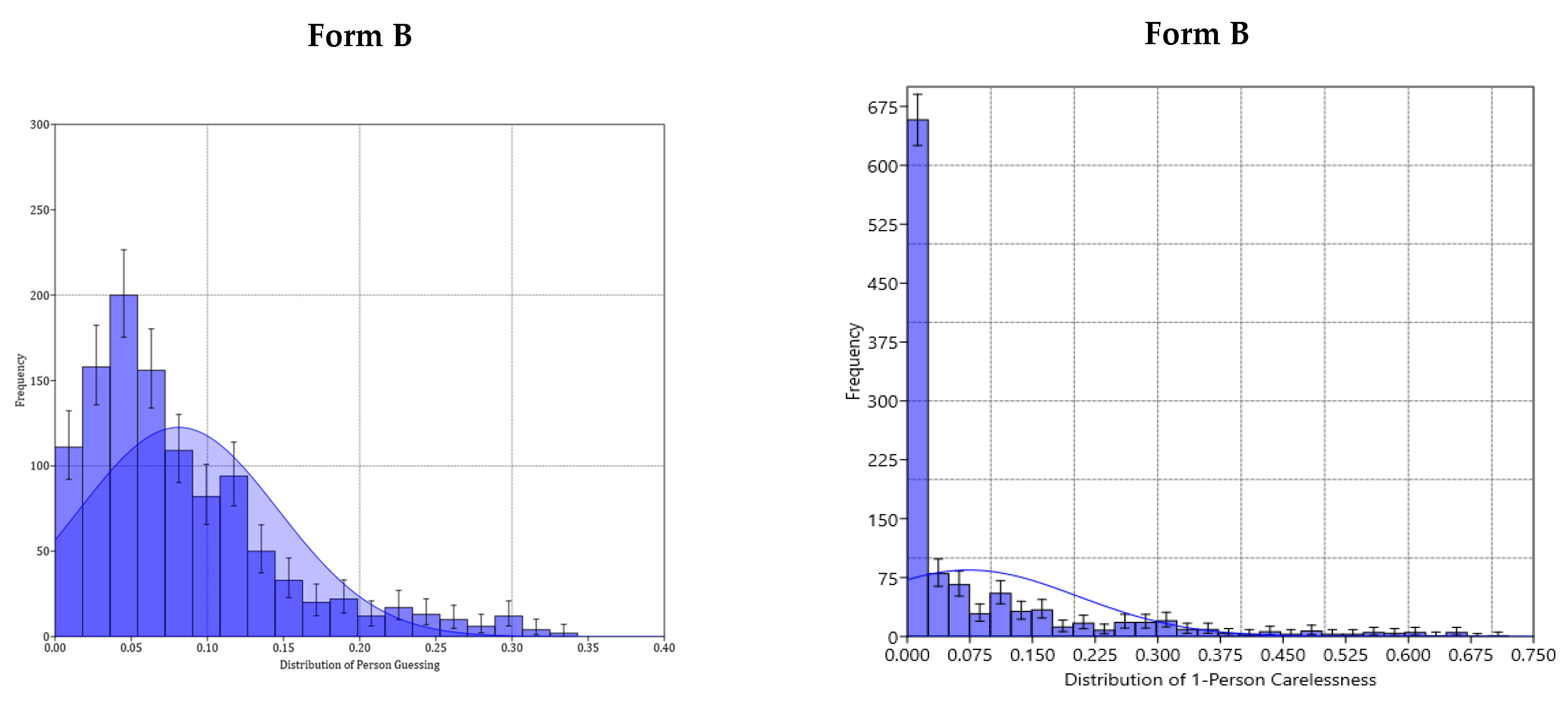
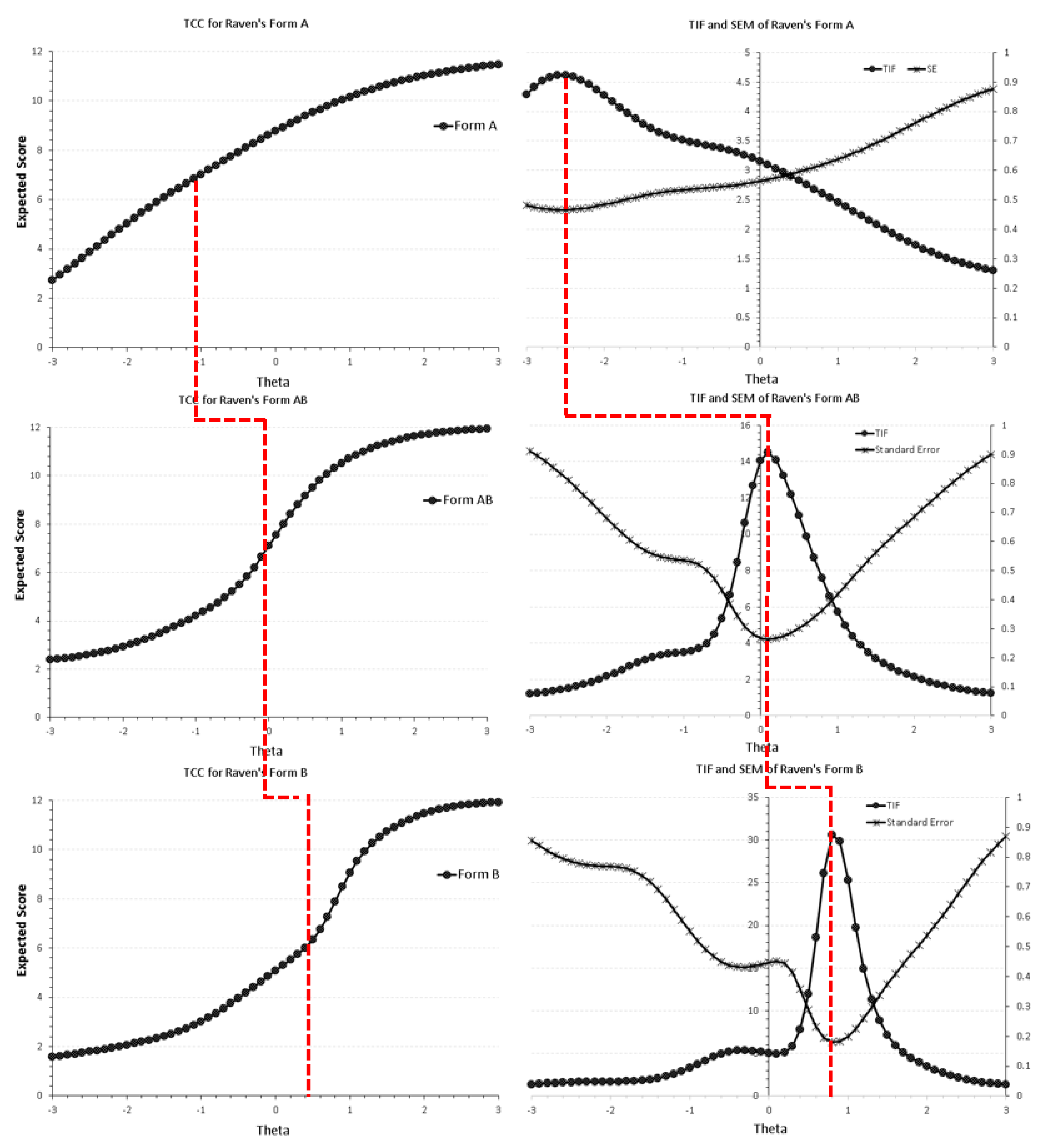
| Models Tested | LL | Npar | scf | Model Comparison | LRTS | Dtsc/d.d.f. | Chi-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form A | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | −5067.533 | 12 | 0.981 | - | - | - | - |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | −5019.974 | 24 | 1.118 | M1 vs. M2 | 95.118 | 1.255/12 | 75.791 *** |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | −4985.443 | 36 | 1.146 | M2 vs. M3 | 69.062 | 1.202/12 | 57.456 *** |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | −4970.947 | 48 | 1.044 | M3 vs. M4 | 28.992 | 0.738/12 | 39.285 *** |
| Form AB | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | −6856.604 | 12 | 0.958 | - | - | - | - |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | −6646.828 | 24 | 1.043 | M1 vs. M2 | 419.552 | 1.128/12 | 371.943 *** |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | −6547.913 | 36 | 1.055 | M2 vs. M3 | 197.830 | 1.079/12 | 183.346 *** |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | −6540.517 | 48 | 20.585 | M3 vs. M4 | 14.792 | 79.175/12 | 0.187 |
| Form B | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | −6336.923 | 12 | 0.941 | - | - | - | - |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | −6108.592 | 24 | 1.079 | M1 vs. M2 | 456.662 | 1.217/12 | 375.236 *** |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | −5971.200 | 36 | 1.001 | M2 vs. M3 | 274.784 | 0.845/12 | 325.188 *** |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | −5957.052 | 48 | 1 | M3 vs. M4 | 28.296 | 0.997/12 | 28.381 ** |
| Model Tested | AIC | BIC | SABIC | CAIC | AWE | AICc | HQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form A | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | 10,159.066 | 10,219.394 | 10,181.278 | 10,231.394 | 10,339.722 | 10,159.35 | 10,181.86 |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | 10,087.948 | 10,208.604 | 10,132.373 | 10,232.604 | 10,449.259 | 10,089.04 | 10,133.54 |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | 10,042.886 | 10,223.869 | 10,109.523 | 10,259.869 | 10,584.853 | 10,045.33 | 10,111.27 |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | 10,037.894 | 10,279.205 | 10,126.744 | 10,327.205 | 10,760.516 | 10,042.26 | 10,129.08 |
| Form AB | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | 13,737.208 | 13,797.536 | 13,759.420 | 13,809.536 | 13,917.864 | 13,737.49 | 13,760.00 |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | 13,341.656 | 13,462.312 | 13,386.081 | 13,486.312 | 13,702.967 | 13,342.74 | 13,387.25 |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | 13,167.826 | 13,348.809 | 13,234.463 | 13,384.809 | 13,709.793 | 13,170.27 | 13,236.21 |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | 13,177.034 | 13,418.345 | 13,265.884 | 13,466.345 | 13,899.656 | 13,181.40 | 13,268.22 |
| Form B | |||||||
| M1. Rasch Model | 12,697.846 | 12,758.174 | 12,720.058 | 12,770.174 | 12,878.502 | 12,698.13 | 12,720.64 |
| M2. 2-PL IRT Model | 12,265.184 | 12,385.840 | 12,309.609 | 12,409.840 | 12,626.495 | 12,266.27 | 12,310.77 |
| M3. 3-PL IRT Model | 12,014.400 | 12,195.383 | 12,081.037 | 12,231.383 | 12,556.367 | 12,016.84 | 12,082.79 |
| M4. 4-PL IRT Model | 12,010.104 | 12,251.415 | 12,098.954 | 12,299.415 | 12,732.726 | 12,014.47 | 12,101.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoniou, F.; Alkhadim, G.; Mouzaki, A.; Simos, P. A Psychometric Analysis of Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices: Evaluating Guessing and Carelessness Using the 4PL Item Response Theory Model. J. Intell. 2022, 10, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence10010006
Antoniou F, Alkhadim G, Mouzaki A, Simos P. A Psychometric Analysis of Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices: Evaluating Guessing and Carelessness Using the 4PL Item Response Theory Model. Journal of Intelligence. 2022; 10(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence10010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoniou, Faye, Ghadah Alkhadim, Angeliki Mouzaki, and Panagiotis Simos. 2022. "A Psychometric Analysis of Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices: Evaluating Guessing and Carelessness Using the 4PL Item Response Theory Model" Journal of Intelligence 10, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence10010006
APA StyleAntoniou, F., Alkhadim, G., Mouzaki, A., & Simos, P. (2022). A Psychometric Analysis of Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices: Evaluating Guessing and Carelessness Using the 4PL Item Response Theory Model. Journal of Intelligence, 10(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence10010006





