Abstract
Feature extraction plays an important role in machine learning for signal processing, particularly for low-dimensional data visualization and predictive analytics. Data from real-world complex systems are often high-dimensional, multi-scale, and non-stationary. Extracting key features of this type of data is challenging. This work proposes a novel approach to analyze Epileptic EEG signals using both wavelet power spectra and functional principal component analysis. We focus on how the feature extraction method can help improve the separation of signals in a low-dimensional feature subspace. By transforming EEG signals into wavelet power spectra, the functionality of signals is significantly enhanced. Furthermore, the power spectra transformation makes functional principal component analysis suitable for extracting key signal features. Therefore, we refer to this approach as a double feature extraction method since both wavelet transform and functional PCA are feature extractors. To demonstrate the applicability of the proposed method, we have tested it using a set of publicly available epileptic EEGs and patient-specific, multi-channel EEG signals, for both ictal signals and pre-ictal signals. The obtained results demonstrate that combining wavelet power spectra and functional principal component analysis is promising for feature extraction of epileptic EEGs. Therefore, they can be useful in computer-based medical systems for epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection problems.
1. Introduction
In data classification, including biomedical signals classification, feature extraction is used to reduce the dimension of input data so that a classification method’s efficiency can be improved [1,2,3,4]. Many current studies of this type of research are focusing on time-frequency feature extraction. Fourier transform, wavelet transform, empirical mode decomposition and sparse representation of signals are often used to extract signal features, while principal component analysis (PCA), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), independent component analysis (ICA), as well as canonical correlation analysis (CCA), are popular techniques for dimension reduction. In [5], a method was developed to find the optimal discrete wavelet transform (DWT) settings so that classification accuracy is improved and the computational cost of seizure detection is then reduced. In [6], EEG signals are first decomposed using DWT, then extracted wavelet features were used as an input to a mixture expert network for classification. In [7], a robust feature extraction method based on PCA was designed to classify multi-class EEG signals. In [8], the DWT method was employed for pre-processing, and approximate entropy was used as features for classification using artificial neural networks. In [9], a novel patient-specific seizure detection approach using wavelet decomposition of multi-channel EEG recordings was proposed, and the features extracted from different frequency bands were used to classify the seizure and non-seizure signals. In [10], an empirical mode decomposition (EMD)-based dictionary approach was proposed for epilepsy seizure detection, and the high accuracy of the obtained results suggests that the proposed method may be promising for classifying long-term multi-channel EEG recordings. In [11], a hybrid dimension reduction model that uses ICA and PCA was developed as a feature extraction method for epileptic seizure detection. For the data they considered in [11], the results showed significant performance using the combination of ICA and PCA.
More recent research is focusing on the methods that combine both domain transformation and data dimension reduction. Wavelet PCA, multi-scale PCA, and wavelet ICA are some of the examples. In [12], a method that combines independent component analysis, and continuous wavelet transformation was used to remove EKG artifact from EEG data. The technique demonstrated that it outperformed other algorithms that used general statistical features for artifact rejection. In [13], PCA, ICA and LDA were used to reduce the dimension of input data after DWT, and the extracted features were used as the input of support vector machines. The performance of classification showed that the proposed classification process was promising. In [14], multi-scale PCA (MSPCA) was used as a de-noising method, and the study showed that MSPCA greatly improves the classification performance in epileptic seizures detection. In [15], the wavelet-based sparse functional linear model was developed to capture discriminative random components of EEG signals. The proposed method outperformed many other state-of-the-art techniques for the EEG data from the University of Bonn. EEG signals’ spectral information has been shown to be useful in epilepsy classification [16,17,18]. In [17,18], Fourier domain functional PCA was used for extracting the feature of EEG signals. The studies in [17,18] illustrated the success of combining the Fourier domain transformation and functional PCA. The rationale behind using the domain transform and dimension reduction approach is that after the data transformation, the separability of the extracted feature is greatly improved. The role of domain transform is to make data behave more discriminable.
The successful classification of the extracted low-dimensional features makes the complicated, multiple domains-based feature extraction more practical and appealing in data visualization. In medical information systems, data visualization enables a better understanding of data patterns and makes the decision more interpretable. Because of this, much of recent research focuses on data visualization problems for information systems. For instance, in [19], a medical data visualization system was developed to allow physicians to see the development of the patients at one glance. The study was done with the aim of assessing the system’s usability. To help with the processing of high-dimensional signals, enable signal visualization, and improve the performance of simple classification methods, we develop a new feature extraction approach by focusing on using wavelet transformation and low-dimensional principal component features. We propose a novel approach that extracts epileptic EEG signal features using functional principal component analysis of wavelet power spectra. The transformation of signals from the time domain to wavelet spectral-domain helps improve random signals’ functionality. Furthermore, the functional principal component analysis is applied to reduce the signal dimension. The preliminary study of this work was presented in [20], where mainly the functional mean wavelet power spectra were studied. Within this new work, we focus on an in-depth discussion of the technical aspects of the proposed methodologies. We also aim to demonstrate the proposed method’s applicability more intensively by considering additional, patient-specific, multi-channel EEG signals. Within this study, epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection problems using extracted features will be discussed.
The significance of this work is the novelty of the proposed feature extraction methodology and the achieved high separability for the data we consider, which are useful for both epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection problems. The proposed feature extraction method makes the use of simple classification methods possible. Also, the proposed methods are applicable to other types of signals, such as financial time series and long-term observational economic data for classification or pattern recognition problems. To the best of our knowledge, functional PCA in the wavelet spectral-domain is used for the first time in biomedical signal processing.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we discuss wavelet spectral analysis and functional principal component analysis. We provide a detailed mathematical description of how the proposed method is developed and how the features are extracted via functional principal component analysis. In Section 3, publicly available short-term EEG data are analyzed, and the results are analyzed, including the study of the effect of the number of components in approximating wavelet power spectra on the separability of extracted features. We also analyze a set of patient-specific multi-channel long-term epileptic EEG signals and compare the extracted features from both interictal and ictal signals. Finally, we conclude our findings and provide further remarks in Section 4.
2. Methods
In this section, we focus on the in-depth discussion of the technical aspects of our proposed method. We summarize the wavelet power spectra, including both the discrete and continuous wavelet power spectra, and principal component analysis, to ensure that the paper is self-contained. We also discuss how the functional PCA approach is combined with the wavelet power spectra to serve as a double feature extraction method. For a complete reading on the wavelet methods and functional PCA, we refer readers to [21,22].
2.1. Wavelet Power Spectra
Mathematically speaking, the power spectrum transforms a given signal from the time domain to the spectral domain. If the transformation is a wavelet function, then we have a wavelet power spectrum. There are two types of wavelet power spectrum: continuous wavelet power spectrum and discrete wavelet power spectrum. We first briefly discuss the power spectrum based on continuous wavelet transform (CWT). We then discuss the wavelet power spectrum based on the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and explain its superiority compared to CWT.
2.1.1. Continuous Wavelet Transform
The continuous wavelet transform of a continuous random signal concerning a given wavelet function is defined as
where the (*) indicate the complex conjugate and is the dilated and translated version of wavelet function with a being the dilation parameter and b being the translation parameter. In continuous wavelet transform, the most common choices of are Morlet, Mexican hat, or Paul wavelets, to name a few [22]. If the random signal is discrete and is denoted by , , the CWT of becomes
After the wavelet transforms, one can define the wavelet power spectrum as . Notice that is a two-dimensional quantity. This work further considers the global wavelet power spectrum, which is defined as the average power spectrum over all the local wavelet spectra in time. It is given as follows
for a continuous random signal. If a random signal is discrete, then the global wavelet power spectrum can be estimated by
This is referred to as the wavelet variance of a signal at the scale a.
2.1.2. Discrete Wavelet Transform
The discrete wavelet transform is done by taking discrete values of the dilation and translation factors a and b. A common approach is to take the logarithmic discretization of the dilation factor a and link it to b by making b be proportional to a. This implies that we have the following forms of discretization of the normalized wavelet function:
which is the result by taking , and , respectively, in Equation (2). Here m, n are all integers that control dilation and translation, respectively. is the fixed dilation step and is greater than one. is the location parameter that has to be greater than zero.
In practice, a common choice of and are 2 and 1, respectively. This leads to the so-called dyadic scaling of wavelet transform. The dyadic scaling wavelet function is then defined as
Based on this wavelet function, the wavelet transform of a sequence of discrete values of signal becomes
The global wavelet power spectrum is then defined as
where is the total number of translation values associated with dilation parameter m. If the signal length N is power of 2, then , and m = .
Notice that the wavelet power spectrum is different from a scaleogram for wavelets, which can be used to estimate instantaneous frequency. Instead, the wavelet power spectrum can be interpreted as a density function of instantaneous frequency. Using the wavelet power spectrum, one reduces the dimension of wavelet transform and extract the functionality of frequency values so that the application of functional principal component analysis becomes sensible.
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
In multivariate statistics, principal component analysis (PCA) of a p-variate random vector looks for a set of weight values, = , so that at the jth step, the linear combinations of variable , for j = 1,2,⋯, p, has the greatest variance [23], with being the original signal . Mathematically, the solution of weight values can be found by solving for the following maximization problem
After the first principal component is obtained, the maximization process in (9) is repeated for by replacing with the value that subtracts by the previous principal component, subject to the normalization and orthogonality constraints, which are and for , and . That is to say in Equation (9), we have
The iterative input of will lead to the solution of in the optimization problem in (9), for .
Alternatively, due to the fact that
the optimization problem in (9) is mathematically equivalent to the following non-linear programming problem
Furthermore, for n samples of X (with zero mean for each variate), we have a data matrix that implies , and the optimization problem becomes
which can be solved by finding the solution of the following eigen equation
where is sample variance-covariance matrix calculated based on the n samples of X, and is the eigenvalue associated with the eigenvector . There are a sequence of pairs (, ), satisfying the eigen equation. This eigen analysis leads to the solutions for both the eigenvalues and the eigenvectors. In PCA, we refer to the principal component. For feature extraction of data matrix , we then compute , for , and they are referred to as principal component scores.
2.3. Functional Principal Component Analysis
Now let us consider functional principal component analysis [24,25], which will be applied to the wavelet power spectra. We first consider the case when CWT was applied to a signal , in which the wavelet power spectra is obtained. For a set of n samples, we denote the wavelet power spectrum of the ith signal by , where = . Thus, the mean wavelet power spectrum of these n signals becomes . The functional variance-covariance at wavelet scales a and can be estimated by
Suppose that the wavelet power spectrum of a given signal can be approximated using K basis functions, and it is given as follows:
where is the functional mean of wavelet power spectra. Without the loss of generality, for the purpose of function approximation, we can take to be a constant value denoted as . Since we consider an approximation of rather than represent the function exactly using infinity number of basis functions, we may then express Equation (14) in a matrix form
where = , = , and the coefficient is matrix given as follows:
Now we consider how to obtain the functional principal components and their scores. Let us first denote the variance-covariance function by , which is defined in (13). In matrix terms the variance-covariance function is
To find the principal component weight functions, we have to solve the following eigen equation for an appropriate eigenvalue
Suppose that eigen function in the left hand side of Equation (16) has an expansion
or in matrix notation
where = . This yields
Here, = is a matrix, and it has entries , where and . The eigen equation in (16) becomes
To obtain the required principal components, we define , i.e., , Equation (18) becomes
By solving the symmetric eigenvalue problem in (19) for , and then compute to obtain the eigen function , we obtain
If are orthonormal, we have , which is an identity matrix. The eigenanalysis of functional PCA problem in (18) reduces to
This becomes a PCA problem where the variance-covariance matrix is replaced by the coefficient matrix obtained from function approximation of wavelet power spectra. However, one should realize that when orthogonal basis functions are used in functional PCA, the problem is not a standard PCA. From the discussion above, PCA conducts eigenanalysis for a covariance matrix. If we apply PCA to the signal matrix, then this p becomes the length of signal n. With function approximation using K basis function, the eigenanalysis of functional PCA is applied to a coefficient matrix, which depends on the value of K and often . From the computational complexity perspective, when using a sparse approximation, the functional PCA is more efficient.
If wavelet power spectra are obtained using DWT, then the left hand side of the equation in (14) is replaced by , which is defined as = . Let us consider the discrete wavelet transform using the dyadic scale, with m taking values from 1 to M, where M is determined by . Because of this, the value of K cannot be larger than M. The eigen equation in (16) becomes
By subsitituting the new form of eigen function , it gives the following new eigen euqation
where = is a matrix. This matrix has entries for and . The equations of (18) and (19) remain the same in the case of DWT, but one should realize that the matrices and vectors contained in the equations are corresponding to the results from DWT. Finally, the eigenfunction becomes
Feature Extraction by Functional Principal Component Analysis
After the eigen function is obtained, we can extract the jth principal component scores, denoted by , for the given power spectra by the following
Here, is a matrix, where = . We refer to the first principal component score vector of the n power spectra of signals, and is the second principal component score vector, and so on. When DWT is applied, we can simply replace and by and , respectively.
2.4. Discussion
There are other possible choices for transforming high-dimensional signals, such as Fourier transform. Additionally, different PCA variants may be considered. By comparing with our previous work in [17,18], we found that discrete wavelet domain transformation outperforms the Fourier domain transform in terms of the sparsity of functional approximation of power spectra. The Fourier power spectra tend to be less smooth, while discrete wavelet power spectra are smoother. Because of this, the separability of extracted features from power spectra is less affected by the non-smoothness for the discrete wavelet power spectra case. When CWT is used to obtain power spectra, this advantage disappears. This may imply that the sparsity on function approximation is critical for the success of feature extraction. On the other hand, to approximate the power spectra and extract the signal features, kernel PCA may be considered due to the nature of kernel methods. However, the kernel PCA is more suitable when the extension of dimension is needed rather than when dimension reduction is concerned. Functional PCA aims at approximating the function via a set of basis functions, and the sparsity of the approximation can be controlled by selecting the number of basis functions. This makes functional PCA a unique choice for feature extraction of functional data.
3. Results
3.1. Feature Extraction of Short Epileptic EEGs
To illustrate the application of the proposed method, we first use a set of epileptic EEG signals that is from the University of Bonn, Germany. (http://epileptologie-bonn.de/cms/front_content.php?idcat=193, accessed on 1 January 2018). This data set has been widely used to test machine learning algorithms for epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection. There are five different data sets, denoted as A, B, C, D and E. Signals in sets A and B are from healthy people with eyes closed and open. Signals in sets C, D and E are epileptic signals from patients who have epilepsy. Signals in set C were collected from patients’ non-epileptogenic zone, and signals in set D were from patients’ epileptogenic zone. Signals in set E were obtained when epilepsy seizure was onset. Each type of signal (i.e., A, B, C, D, E) contains 100 single-channel scalp EEG segments of 23.6 seconds, and they were sampled at 173.61 Hz (i.e., N = 4096).
In Figure 1a and Figure 2a, the extracted two-dimensional features of wavelet power spectra using CWT for signals in sets A, B, C, D, and E are presented. The maximum number of basis functions (i.e., ) is used to estimate the wavelet power spectra. The results show that the extracted features form clusters according to their signal types and are well separated by different types of signals. Even though both sets A and B are from healthy people, we do not see the same wavelet power spectra patterns. This may suggest that the brain activities (i.e., Eyes Open and Eyes Closed) can lead to different power spectra. Additionally, for epileptic signals, the wavelet power spectra depend on which zone of brains that EEG signals were collected. From Figure 2a, we observe that E set signals (i.e., seizure onset) are well separated from sets C and D (i.e., non seizure signals). This may imply that a simple classifier such as k-NN can successfully classify the signals based on the extracted two-dimensional signal features. In Figure 1b and Figure 2b, the same type of results is reported, but they are obtained using DWT with maximum number of basis functions, i.e., . Notice that the wavelet power spectra under the DWT are obtained for a dyadic scale only. They can be interpreted as the wavelet variances at the dyadic scale by summarizing the variations of the neighbouring CWT coefficients at the corresponding dyadic scale. Because of this, the wavelet power spectra under DWT capture the overall smoother pattern so that the extracted features may be less noisy and more separable in a low-dimensional feature subspace. The results shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 suggest that feature extraction by functional PCA of wavelet power spectra leads to non-linear separable features that facilitate both epileptic seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis problems.
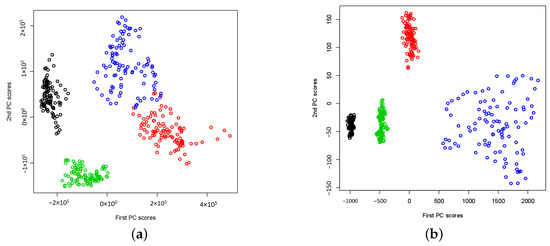
Figure 1.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional principal component scores of wavelet power spectra for data sets A (Normal: Eyes Closed, Black), B (Normal: Eyes Open, Red), C (Non-epileptogenic zone, Green) and D (Epileptogenic zone, Blue) respectively. Both and consist of wavelet power spectra from sets A, B, C and D. (a) Using CWT, (b) Using DWT.
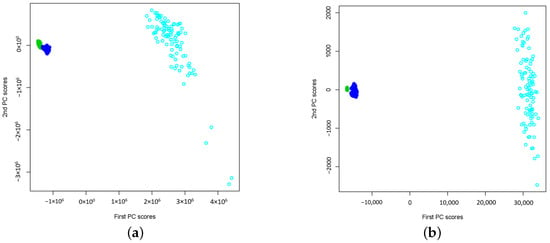
Figure 2.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional principal component scores of wavelet power spectra for data sets C (Non-epileptogenic zone, Green), D (Epileptogenic zone, Blue) and E (Seizure on set, Light Blue) respectively. Both and consist of wavelet power spectra from sets C, D and E. (a) Using CWT, (b) Using DWT.
Another interesting question is how the number of basis functions K affects the feature separability. That is, how the sparsity of the number of basis functions affects the feature separability. The influence from the choice of the value of K is much more significant when CWT is used. From the results reported in Figure 3, one can see that principal component scores are overlapped when K is smaller than 20, but the results are improved with the increase of the K value. This implies that approximation using a small number of basis functions is not enough in capturing differences among signal groups for a two-dimensional feature vector. However, when K is larger than 30, they are clearly separable for all sets, i.e., A, B, C, and D. The results are almost the same for all choices of K if . By increasing the number of basis functions, it does not give extra benefit on improving the feature separability. We conclude that the sparsity of function approximation in functional PCA affects the feature extractions. For DWT, the sparsity of functional approximation corresponds to different wavelet levels, and the level is at the dyadic scale, so the maximum level allowed in function approximation is small. This has become superior when compared to the case using CWT, which requires a much larger number of basis functions for approximating the wavelet power spectra. Our study shows that DWT is a better choice for feature extraction using functional PCA. Using the wavelet power spectra based on DWT, feature separation level is much higher than the method using CWT, for the signals we consider. The results shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4 may suggest a potential application of the proposed method to the epilepsy diagnosis problem, while the results presented in Figure 5 seem to be promising for epileptic seizure detection. Due to the significant difference in signal power spectra between seizure on-set signals (Set E) and the non-seizure signals (i.e., Sets C and D), we do not observe a significant impact from the choice of the value of K on the feature separability. One can see that the pattern of the extracted features remain the same starting from . We also notice that when , the extracted features behave differently, but it remains linearly separable in the two-dimensional feature subspace.
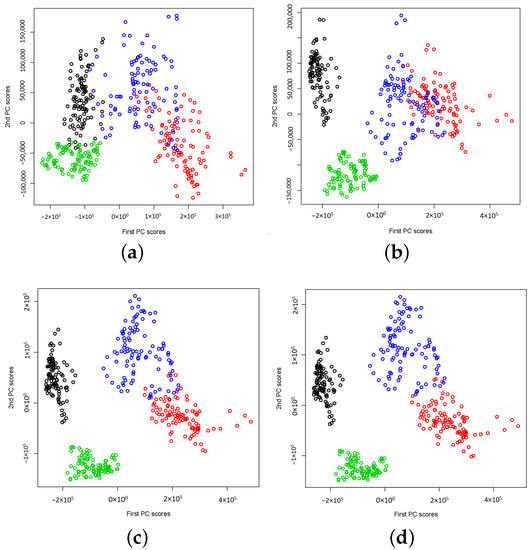
Figure 3.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional principal component scores of CWT power spectra for data sets A (Normal: Eyes Closed, Black), B (Normal: Eyes Open, Red), C (Non-epileptogenic zone, Green) and D (Epileptogenic zone, Blue) respectively, with different values of K, the number of basis functions, (a) , (b) , (c) , (d) .
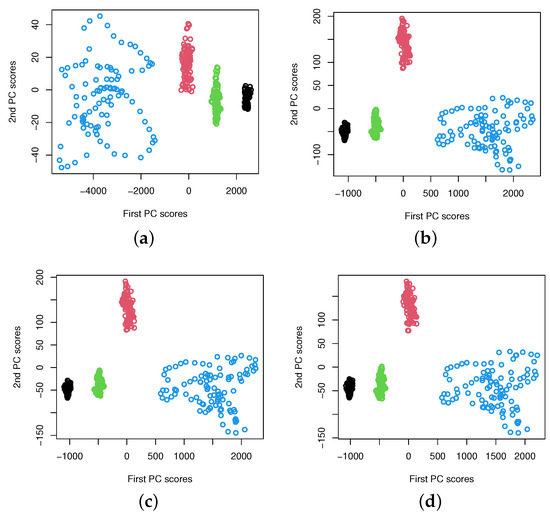
Figure 4.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional principal component scores of DWT power spectra for data sets A (Normal: Eyes Closed, Black), B (Normal: Eyes Open, Red), C (Non-epileptogenic zone, Green) and D (Epileptogenic zone, Blue) respectively, with different values of K, the number of basis functions. (a) , (b) , (c) , (d) .
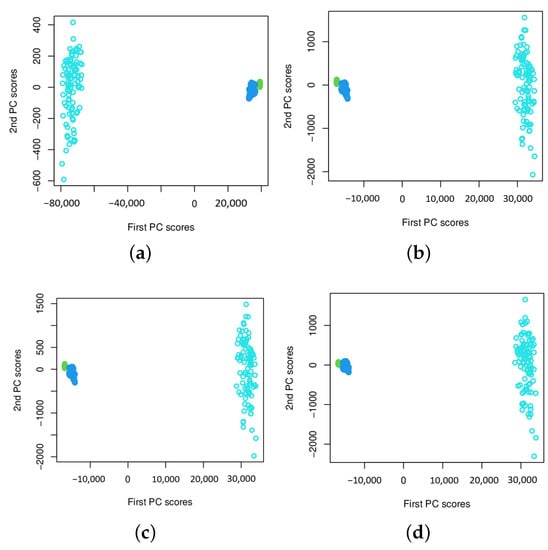
Figure 5.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional principal component scores of DWT power spectra for data sets C (Non-epileptogenic zone, Green), D (Epileptogenic zone, Blue), and E (Seizure on set, Light Blue), respectively, with different values of K, the number of basis functions. (a) , (b) , (c) , (d) .
Finally, the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the power spectra under both CWT and DWT are presented in Figure 6. The first three eigenfunctions share some commonalities in terms of their shapes of functions between CWT and DWT. For eigenvalues, the method using CWT has a higher number of significant eigenvalues than the one using DWT because CWT captures more details in the local fluctuation of the power spectra. As we have discussed, for features extracted using DWT, the signals can be separated according to their groups using only the first PC. The is reflected by the first eigenvalue shown in (c) of Figure 6.
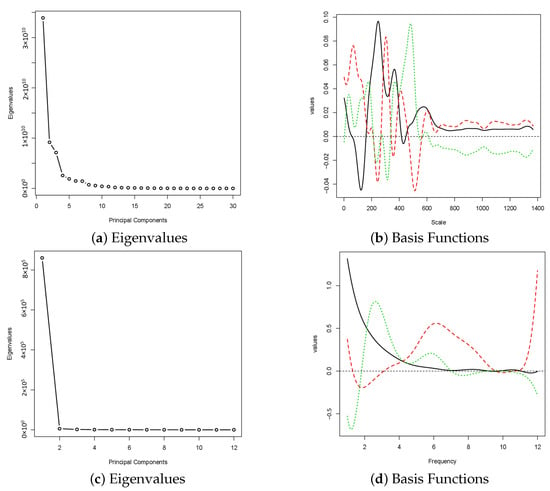
Figure 6.
The eigenvalues and the first three eigenfunctions under the maximum number of basis functions for functional principal components of power spectra. The signals from Sets A, B, C and D are used. The first eigenfunction is in black, the second eigenfunction is in red and the third eigenfunction is in green. The results shown in (a,b) are corresponding to power spectra using CWT, while (c,d) are the results using DWT.
3.2. Feature Extraction of Long Term Multi-Channel Patient Specific Epileptic EEGs
To further demonstrate the applicability of the proposed method in the epileptic seizure detection problem, we analyze EEG signals at interictal and ictal stages from four epileptic patients. These EEG signals were collected from six channels. Figure 7 displays the DWT power spectra of each channel’s signals of interictal patients. We observe that all wavelet power spectra contain some commonalities: the overall decaying pattern is the same, but some power spectra of selected channels appear to have heavy tails. The feature extraction from these power spectra would then become separable due to the different tail patterns of wavelet power spectra. This can be seen from the results displayed in Figure 8. The results clearly show the separability of the extracted features according to each channel of signals. The principal component score values are high when the tail of wavelet power spectra is heavy. For instance, features of channel 2 signals (in red) of patient 1 have the largest values of principal component scores, and they are well separated. Channel 4 of patient 3, channels 5 and 6 of patient 4, and channel 2 of patient 6 lead to linearly separable feature patterns that may be associated with the epileptic zone. This indicates that signals from the epileptic zone have higher values of wavelet power for the higher wavelet decomposition level. To study the variability of the extracted features, which are the principal component scores, we report the 95% confidence intervals for both first and second PCs, by patients and by channels. The results are displayed in Table 1. The comparison by channels between different patients is shown in Figure 9. The obtained results demonstrated that extracted features behave completely differently for a different channel between patients. For example, using the signals from channel 2 or 3, the first principal component scores can be used to differentiate EEG signals. It seems that channel 6 shares more commonalities than other channels due to the similar extracted features. This may suggest that the analysis of interictal epileptic EEGs should be done on a patient-specific basis. If combining signals from different patients, then an effort to select a specific channel less affected by the patients may be needed.
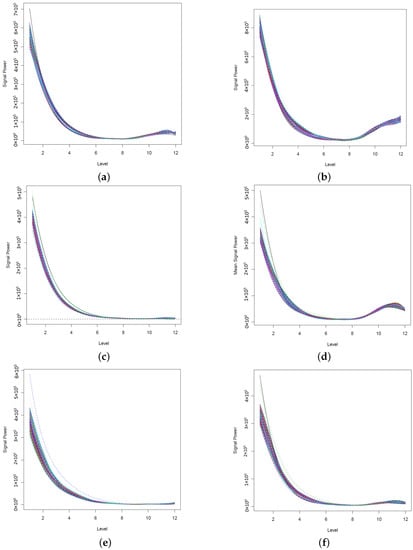
Figure 7.
The plots of functional wavelet power spectra for six channels long term interictal signal of patient 1. The maximum number of B-splines basis functions are used to smooth the sample wavelet power spectra, i.e., . (a) Channel 1, (b) Channel 2, (c) Channel 3, (d) Channel 4, (e) Channel 5, (f) Channel 6.
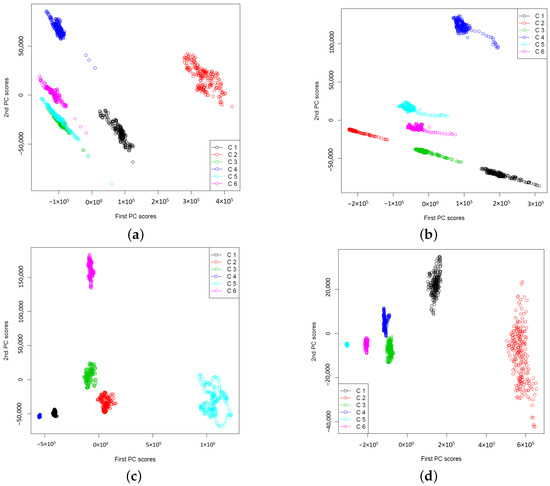
Figure 8.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional features of DWT wavelet power spectra of patient specific interictal EEG signals. The maximum number of B-splines basis functions are used to smooth the sample wavelet power spectra, i.e., . (a) Patient 1, (b) Patient 3, (c) Patient 4, (d) Patient 6.

Table 1.
The 95% confidence intervals for the mean value of extracted features by different patients and different channels for both interictal and ictal signals. The features are the principal component scores of DWT power spectra at the thousand scale.
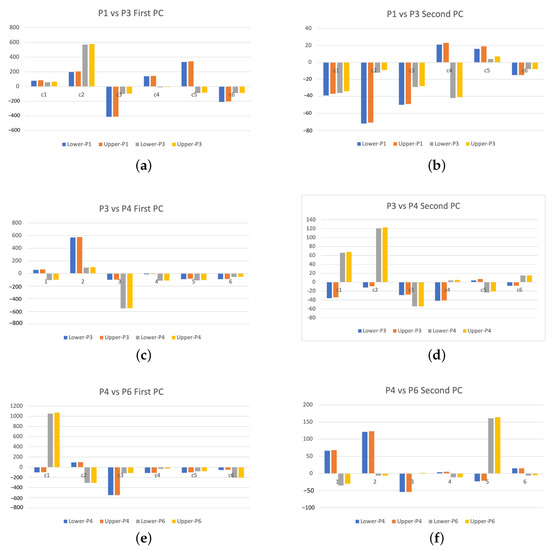
Figure 9.
The pairwise comparisons of lower and upper 95% confidence limits of extracted first and second principal component scores of DWT power spectra for all channels (i.e., c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, and c6) for patients at the interitcal stage. (a) Patient 1 vs. Patient 3, 1st PC, (b) Patient 1 vs. Patient 3, 2nd PC, (c) Patient 3 vs. Patient 4, 1st PC, (d) Patient 3 vs. Patient 4, 2nd PC, (e) Patient 4 vs. Patient 6, 1st PC, (f) Patient 4 vs. Patient 6, 2nd PC.
The results obtained from the ictal signals are presented in Figure 10. We can observe that the extracted features are formed into clusters by different channels and by different patients. Channels 1 and 2 are significantly overlapped for patients 1, 3 and 4, while they are well separated for patient 6. channels 3 and 4 and channels 5 and 6 are also overlapped for patients 1, 3 and 4. Although for patient 6, the extracted features are well separated by different channels, we still can see that they make into three groups, similar to those for patients 1, 3 and 4. This may imply that there are commonalities of the extracted features for the ictal signals from epileptic patients, and they may be useful in computer-aided epileptic seizure detection. To further verify this, we compare the variability by constructing the 95% confidence intervals for the first two PC of extracted features for both interictal and ictal. The results are shown in Table 2. We observe that the 95% confidence intervals do not overlap for interictal signals and ictal signals. In Figure 11, we observe some big differences in the first PC of wavelet power spectra between interictal and ictal types for channels 1 and 2, channels 3 and 4, and channels 5 and 6, for different patients. The large values of the PC scores are due to the stage of seizure onset. Due to this clear separation of extracted features and their low variability, feature extraction of DWT power spectra via functional PCA becomes useful for classifying the interictal and ictal signals. Additionally, the high degree of separation of these two types of signals through the proposed feature extraction methods implies the usability of simple classification method methods such as the K-NN classifier. This makes computer-aided medical diagnosis easily developed due to the simplicity of the classification method.
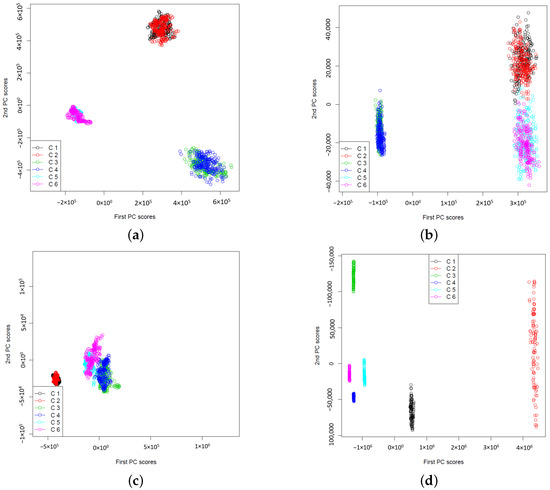
Figure 10.
The plots of extracted two-dimensional features of DWT wavelet power spectra of patient specific ictal EEG signals. The maximum number of B-splines basis functions are used to smooth the sample wavelet power spectra, i.e., . (a) Patient 1, (b) Patient 3, (c) Patient 4, (d) Patient 6.

Table 2.
The 95% confidence intervals for the mean value of extracted features by different patients and different groups of channels for both interictal and ictal signals. The features are the principal component scores of DWT power spectra at the thousand scale.
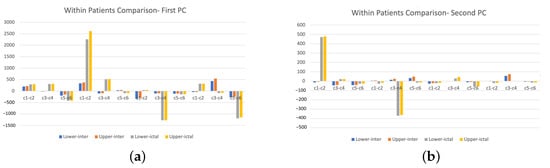
Figure 11.
The plots of lower and upper 95% confidence limits of extracted first and second principal component scores of DWT power spectra for combined channels (i.e., c1–c2, c3–c4, and c5–c6) at both interitcal and ictal stages. (a) Interictal vs. Ictal, 1st PC, (b) Interictal vs. Ictal, 2nd PC.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we proposed an approach that first transforms signals to the wavelet power spectra. Then Functional PCA is used to extract features of wavelet power spectra to facilitate epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection problems. Transforming EEG signals to wavelet power spectra enhances the functionality of input signals so that functional PCA becomes useful in feature extraction. We applied the proposed method to both short EEGs and long-term, multi-channel EEGs. Using the proposed method, different types of epileptic EEG signal becomes linear or non-linear separable in the low-dimensional feature subspace. The extracted features are formed into clusters by channels for multi-channel signals and behave differently and non-linear separable for different patients. The degree of feature separation depends on selecting the number of basis functions used to approximate the power spectra in functional PCA. These may indicate the natural complexity of epileptic signals, and the analysis needs to be done on patient-specific. Fortunately, we can produce linear or non-linear separable features to classify the interictal and ictal signals. The obtained results demonstrated that the proposed method is promising for epilepsy diagnosis and seizure detection problems. The proposed method can also be applied to other types of random signals, such as financial or economic time series, for similar purposes. Our future work will be investigating how different ways of achieving sparsity of functional approximation of power spectra affect the separability of extracted low-dimensional features.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ceylan, R. The effect of feature extraction based on dictionary learning on ecg signal classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2018, 6, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Athavale, Y. Trends in biomedical signal feature extraction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 43, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Lawniczak, A.T.; Song, Y.; Liò, P. Feature extraction via dynamic pca for epilepsy diagnosis and epileptic seizure detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Kittila, Finland, 29 August–1 September 2010; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Krishnan, S. Model based sparse feature extraction for biomedical signal classification. Int. J. Stat. Med. Res. 2017, 6, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wan, S.; Xiang, J.; Bao, F.S. A high-performance seizure detection algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform (dwt) and eeg. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subasi, A. Eeg signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and a mixture of expert model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2007, 32, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuly, S.; Li, Y. Designing a robust feature extraction method based on optimum allocation and principal component analysis for epileptic eeg signal classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 119, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, O.; Acharya, U.R.; Adeli, H.; Adeli, A. Wavelet-based eeg processing for computer-aided seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2017, 7, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaleem, M.; Guergachi, A.; Krishnan, S. Patient-specific seizure detection in long-term eeg using wavelet decomposition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 46, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleem, M.; Gurve, D.; Guergachi, A.; Krishnan, S. Patient-specific seizure detection in long-term eeg using signal-derived empirical mode decomposition (emd)-based dictionary approach. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matin, A.; Bhuiyan, R.A.; Shafi, S.R.; Kundu, A.K.; Islam, M.U. A hybrid scheme using pca and ica based statistical feature for epileptic seizure recognition from eeg signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint 8th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2019 3rd International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), Cheney, WA, USA, 26–29 April 2019; pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaneh, M.B.; Chitravas, N.; Kaiboriboon, K.; Lhatoo, S.D.; Loparo, K.A. Automated removal of ekg artifact from eeg data using independent component analysis and continuous wavelet transformation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasi, A.; Gursoy, M.I. Eeg signal classification using pca, ica, lda and support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 8659–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. The effect of multiscale pca de-noising in epileptic seizure detection. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Krishnan, S. Wavelet-based sparse functional linear model with applications to eegs seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsipouras, M.G. Spectral information of eeg signals with respect to epilepsy classification. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2019, 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Lawniczak, A. Feature extraction of epileptic eeg in spectral domain via functional data analysis. In Proceedings of the ICPRAM, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–21 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Lawniczak, A.T. Fourier spectral domain functional principal component analysis of eeg signals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–21 February 2019; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, M.; Wiltner, S.; Rind, A.; Aigner, W.; Miksch, S.; Turic, T.; Drexler, F. Patient development at a glance: An evaluation of a medical data visualization. In Proceedings of the IFIP Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Lisbon, Portugal, 5–9 September 2011; pp. 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Krishnan, S. Feature extraction of epileptic eeg using wavelet power spectra and functional pca. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2551–2554. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, J.O. Functional data analysis. In Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolliffe, I. Principal component analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1094–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, J. Functional data analysis. In Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Chiou, J.M.; Müller, H.G. Functional data analysis. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2016, 3, 257–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).