Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling for Ex Vivo Data Analysis: Insights into Liver Transplantation and Pathobiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Liver Pathophysiology: Challenges and Opportunities Related to Liver Transplantation
2.1. Liver Metabolism/Biochemistry
2.2. Liver Transplantation
2.3. Liver/Transplant Immunology and Inflammation
2.3.1. Preoperative
2.3.2. Intraoperative
2.3.3. Postoperative
3. Organ Perfusion: Generating Ex Vivo Data
3.1. Data Types in Perfusion Experiments
3.2. Data Analysis in Perfusion Experiments
4. Computational Modeling: A Systems Biology Tool for Gaining Insights into Liver Disease and Transplantation
4.1. Data Types in the Context of Liver Disease and Transplantation
4.2. What Is a Model?
4.3. Goals of Computational Modeling
4.4. Modeling Approaches: Data-Driven vs. Mechanistic Modeling
4.5. Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling Methods
4.5.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4.5.2. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLS)
4.5.3. Dynamic Network Analysis (DyNA)
4.5.4. Dynamic Bayesian Network Inference (DyBN)
5. Case Studies of Computational Methods in the Setting of Liver Pathology and Preservation
5.1. #1: Using Networks as Biomarkers [60]
5.1.1. Background
5.1.2. The Problem
5.1.3. The Solution
5.2. #2: Making Sense of Metabolomics [21]
5.2.1. Background
5.2.2. The Problem
5.2.3. The Solution
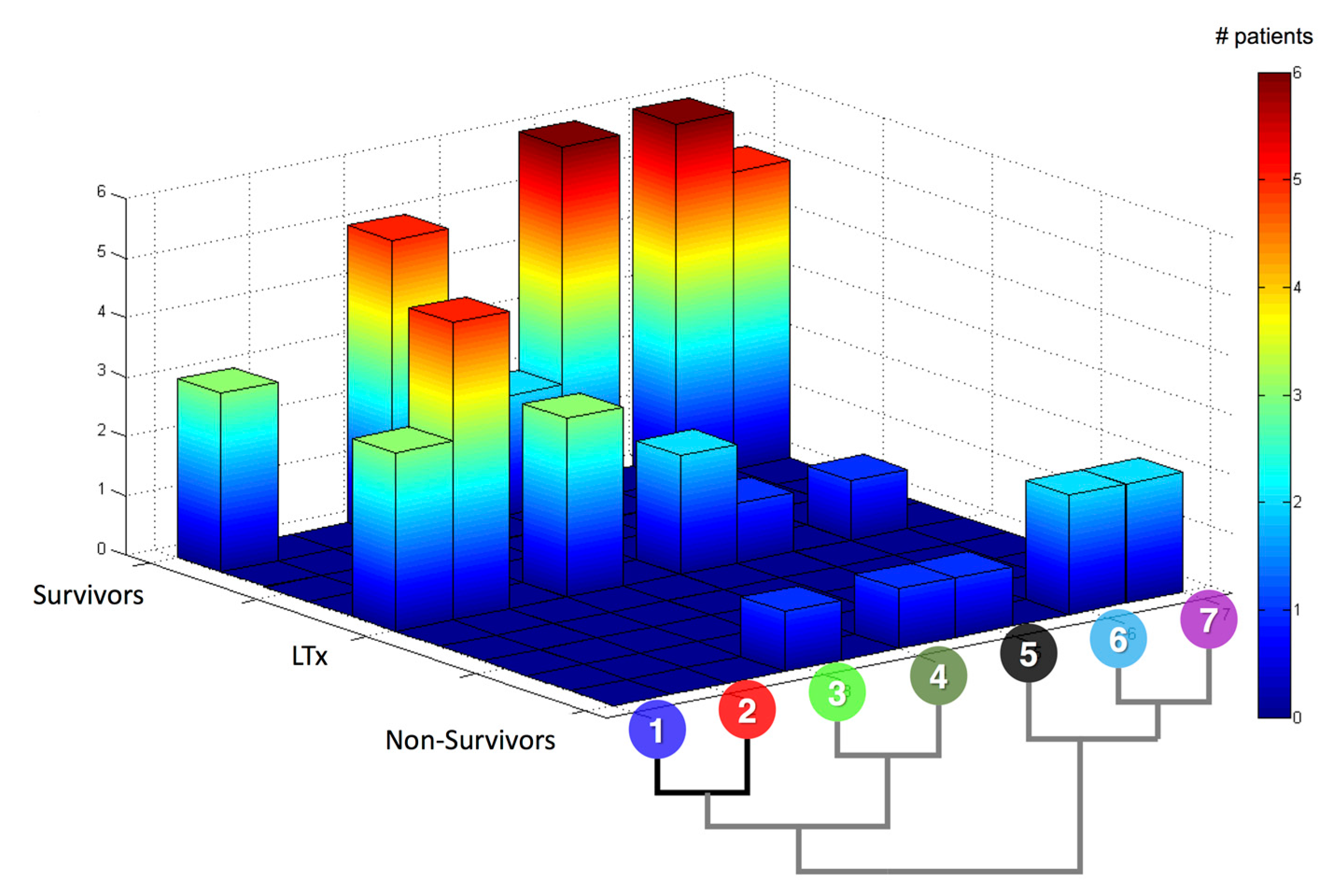
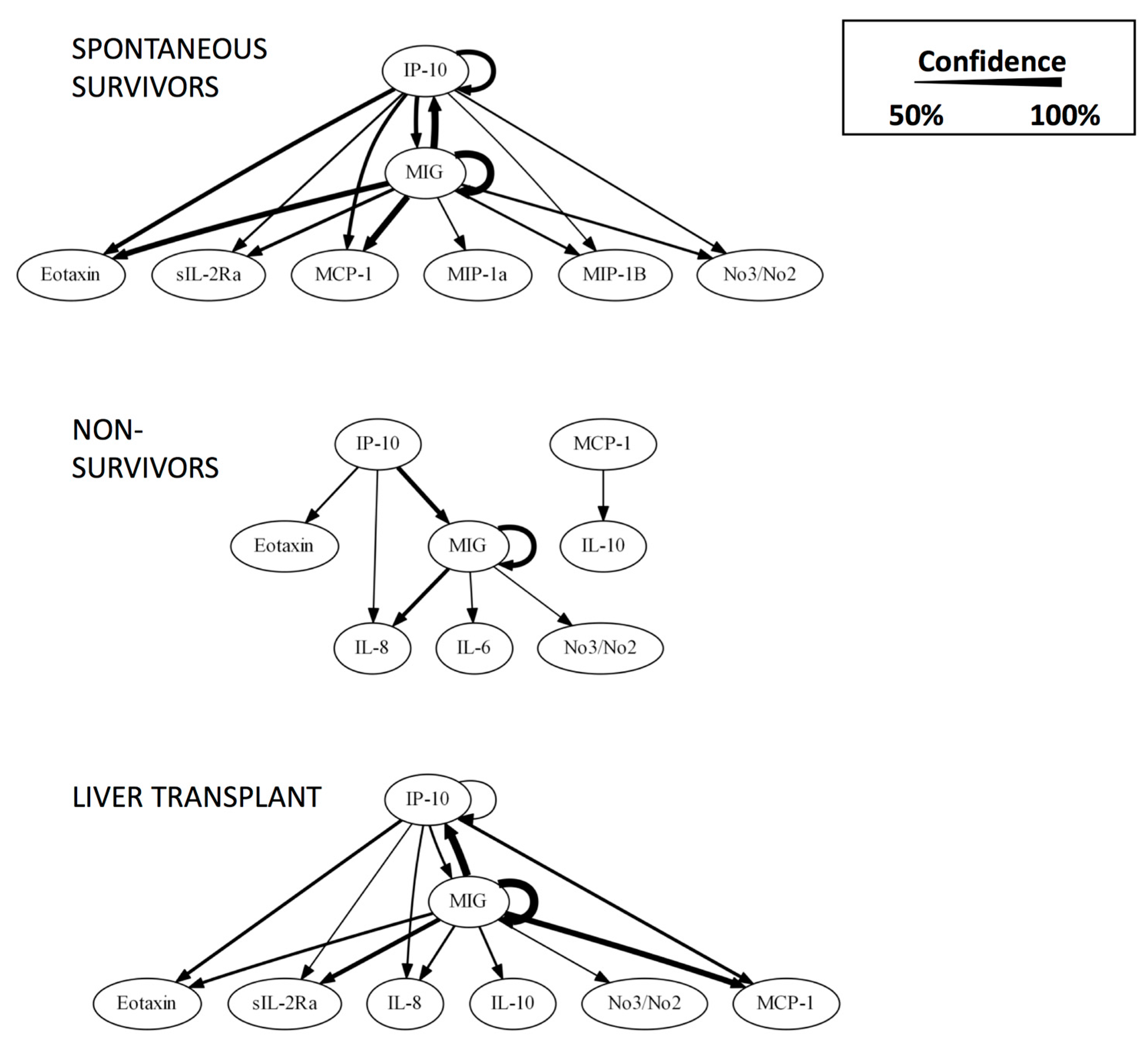
5.3. #3: A Second Look at Inflammation [22]
5.3.1. Background
5.3.2. The Problem
5.3.3. The Solution
6. Implications and Future Directions
6.1. Implications for Basic Science
6.2. Implications for Translational Science
6.3. Implications for Clinical Science
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rui, L. Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L.; Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz, E.; Kuntz, H. Biochemistry and Functions of the Liver; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 35–76. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, J.L. Bile formation and secretion. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1035–1078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liver Transplantation. Available online: http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/liver-disease/liver-transplant/Pages/facts.aspx (accessed on 18 July 2015).
- Setiawan, V.W.; Stram, D.O.; Porcel, J.; Lu, S.C.; Le Marchand, L.; Noureddin, M. Prevalence of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis by underlying cause in understudied ethnic groups: The multiethnic cohort. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrinpar, A.; Busuttil, R.W. Liver transplantation: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.K.; Guturu, P.; Hmoud, B.; Kuo, Y.F.; Salameh, H.; Wiesner, R.H. Evolving frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation based on etiology of liver disease. Transplantation 2013, 95, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transplants in the U.S. By State. Available online: http://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/converge/latestData/rptData.asp (accessed on 18 July 2015).
- Liou, I.W.; Larson, A.M. Role of Liver Transplantation in Acute Liver Failure. Available online: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/584467_4 (accessed on 20 July 2015).
- Starzl, T.E. History of clinical transplantation. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 759–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Santos, V.; Nacif, L.S.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Ducatti, L.; Andraus, W.; D’Alburquerque, L.C. Simplified technique for auxiliary orthotopic liver transplantation using a whole graft. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva ABCD (Braz. Arch. Dig. Surg.) 2015, 28, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starzl, T.E. The saga of liver replacement, with particular reference to the reciprocal influence of liver and kidney transplantation (1955–1967). J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2002, 195, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Rega, F.; Devos, T.; Pirenne, J. Machine perfusion in organ transplantation: A tool for ex-vivo graft conditioning with mesenchymal stem cells? Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2013, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnel, A.R.; Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. Immune dysfunction and infections in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Ke, Q.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Donation after cardiac death liver transplantation: Graft quality evaluation based on pretransplant liver biopsy. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halldorson, J.B.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Montenovo, M.; Dick, A.; Rayhill, S.; Perkins, J.; Reyes, J. Differential rates of ischemic cholangiopathy and graft survival associated with induction therapy in dcd liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molmenti, E.P.; Netto, G.J.; Murray, N.G.; Smith, D.M.; Molmenti, H.; Crippin, J.S.; Hoover, T.C.; Jung, G.; Marubashi, S.; Sanchez, E.Q.; et al. Incidence and recurrence of autoimmune/alloimmune hepatitis in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant. 2002, 8, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchana, N.; Peck, J.R.; Whitson, B.A.; Henry, M.L.; Elkhammas, E.A.; Black, S.M. Preservation solutions used during abdominal transplantation: Current status and outcomes. World J. Transplant. 2015, 5, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Petrowsky, H.; Hong, J.C.; Busuttil, R.W.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.W. Ischaemia-reperfusion injury in liver transplantation—From bench to bedside. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, P.; Lopez, R.; van der Plaats, A.; Vodovotz, Y.; Minervini, M.; Scott, V.; Soltys, K.; Shiva, S.; Paranjpe, S.; Sadowsky, D.; et al. Liver preservation with machine perfusion and a newly developed cell-free oxygen carrier solution under subnormothermic conditions. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowsky, D.; Zamora, R.; Barclay, D.; Yin, J.; Fontes, P.; Vodovotz, Y. Machine perfusion of porcine livers with oxygen-carrying solution results in reprogramming of dynamic inflammation networks. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, M.; Hauser, L.; Jun, S.R.; Nookaew, I.; Leuze, M.R.; Ahn, T.H.; Karpinets, T.; Lund, O.; Kora, G.; Wassenaar, T.; et al. Insights from 20 years of bacterial genome sequencing. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van El, C.G.; Cornel, M.C.; Borry, P.; Hastings, R.J.; Fellmann, F.; Hodgson, S.V.; Howard, H.C.; Cambon-Thomsen, A.; Knoppers, B.M.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing in health care: Recommendations of the european society of human genetics. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. Overview of mrna expression profiling using DNA microarrays. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; Ausubel, F.M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalarski, C.E.; Kirkpatrick, D.S. A biologist’s field guide to multiplexed quantitative proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, R.P.; Kenny, L.C. ‘Omic’ technologies: Genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Obs. Gynaecol. 2011, 13, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, N.H.W.; Peterson, J.; Garges, S.; Giovanni, M.; McInnes, P.; Wang, L.; Schloss, J.A.; Bonazzi, V.; McEwen, J.E.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; et al. The nih human microbiome project. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Miquel, S.; Langella, P.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G. The role of metagenomics in understanding the human microbiome in health and disease. Virulence 2014, 5, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, K.M.; Weinstock, G.M.; Storch, G.A. Emerging view of the human virome. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2012, 160, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardini, C.; Dent, J.; Tieri, P. Editorial: Multi-omic data integration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksenov, S.V.; Church, B.; Dhiman, A.; Georgieva, A.; Sarangapani, R.; Helmlinger, G.; Khalil, I.G. An integrated approach for inference and mechanistic modeling for advancing drug development. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellner, S.P.; Guckenheimer, J. Dynamic Models in Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- An, G.; Nieman, G.; Vodovotz, Y. Computational and systems biology in trauma and sepsis: Current state and future perspectives. Int. J. Burns Trauma 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vodovotz, Y.; Billiar, T.R. In silico modeling: Methods and applications to trauma and sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodovotz, Y.; An, G. Systems biology and inflammation. In Systems Biology in Drug Discovery and Development: Methods and Protocols; Yan, Q., Totowa, N., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 181–201. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, J.M.; Haddad, W.M.; An, G.; Vodovotz, Y. From data patterns to mechanistic models in acute critical illness. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namas, R.A.; Mi, Q.; Namas, R.; Almahmoud, K.; Zaaqoq, A.M.; Abdul-Malak, O.; Azhar, N.; Day, J.; Abboud, A.; Zamora, R.; et al. Insights into the role of chemokines, damage-associated molecular patterns, and lymphocyte-derived mediators from computational models of trauma-induced inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 1370–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodovotz, Y. Translational System Biology; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vodovotz, Y.; An, G. Complex Systems and Computational Biology Approaches to Acute Inflammation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Janes, K.A.; Yaffe, M.B. Data-driven modelling of signal-transduction networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowsky, D.; Nieman, G.; Barclay, D.; Mi, Q.; Zamora, R.; Constantine, G.; Golub, L.; Lee, H.M.; Roy, S.; Gatto, L.A.; et al. Impact of chemically-modified tetracycline 3 on intertwined physiological, biochemical, and inflammatory networks in porcine sepsis/ards. Int. J. Burns Trauma 2015, 5, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folkerts, U.; Nagel, D.; Vogt, W. The use of cluster analysis in clinical chemical diagnosis of liver diseases. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. Z. Klinische Chem. Klinische Biochem. 1990, 28, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelson, W.; Hoare, M.; Unitt, E.; Palmer, C.; Gibbs, P.; Coleman, N.; Davies, S.; Alexander, G.J. Heterogeneous inflammatory changes in liver graft recipients with normal biochemistry. Transplantation 2010, 89, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.Y.; Guo, Z.Z.; Guan, Y.; Du, J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Liu, P.; Huang, S.; Su, S.B. Serum levels of micrornas can specifically predict liver injury of chronic hepatitis b. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5188–5196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, V.; Gabbert, C.; Raina, A.; Bell, L.N.; Cooper, S.; Malik, S.; Behari, J. Serum metabolomic profiling in acute alcoholic hepatitis identifies multiple dysregulated pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Predictive model for inflammation grades of chronic hepatitis b: Large-scale analysis of clinical parameters and gene expressions. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H. Partial least squares regression (pls-regression). In Encyclopedia for Research Methods for the Social Sciences; Lewis-Beck, M., Bryman, A., Futing, T., Eds.; Sage: Thousand Oak, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 792–795. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.Y.; Shin, S.K.; Heo, H.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kwon, E.Y.; Park, J.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, E.J.; et al. Time-dependent network analysis reveals molecular targets underlying the development of diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Genes Nutr. 2013, 8, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Q.; Constantine, G.; Ziraldo, C.; Solovyev, A.; Torres, A.; Namas, R.; Bentley, T.; Billiar, T.R.; Zamora, R.; Puyana, J.C.; et al. A dynamic view of trauma/hemorrhage-induced inflammation in mice: Principal drivers and networks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziraldo, C.; Vodovotz, Y.; Namas, R.A.; Almahmoud, K.; Tapias, V.; Mi, Q.; Barclay, D.; Jefferson, B.S.; Chen, G.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. Central role for mcp-1/ccl2 in injury-induced inflammation revealed by in vitro, in silico, and clinical studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namas, R.A.; Vodovotz, Y.; Almahmoud, K.; Abdul-Malak, O.; Zaaqoq, A.; Namas, R.; Mi, Q.; Barclay, D.; Zuckerbraun, B.; Peitzman, A.B.; et al. Temporal patterns of circulating inflammation biomarker networks differentiate susceptibility to nosocomial infection following blunt trauma in humans. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, A.; Namas, R.A.; Ramadan, M.; Mi, Q.; Almahmoud, K.; Abdul-Malak, O.; Azhar, N.; Zaaqoq, A.; Namas, R.; Barclay, D.A.; et al. Computational analysis supports an early, type 17 cell-associated divergence of blunt trauma survival and mortality. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e1074–e1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, R.; Ravuri, S.K.; Plock, J.A.; Vodovotz, Y.; Gorantla, V.S. Differential inflammatory networks distinguish responses to bone marrow-derived versus adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapies in vascularized composite allotransplantation. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 83, S50–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Malak, O.; Vodovotz, Y.; Zaaqoq, A.; Almahmoud, K.; Peitzman, A.; Sperry, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Namas, R.A. Elevated admission base deficit is associated with a distinct and more complex network of systemic inflammation in blunt trauma patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y.; Mi, Q.; Barclay, D.; Yin, J.; Horslen, S.; Rudnick, D.; Loomes, K.; Squires, R.H. Data-driven modeling for precision medicine in pediatric acute liver failure. Mol. Med. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramirez, F.; Schelhorn, S.E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing topological parameters of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzegorczyk, M.; Husmeier, D. Improvements in the reconstruction of time-varying gene regulatory networks: Dynamic programming and regularization by information sharing among genes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, N.; Ziraldo, C.; Barclay, D.; Rudnick, D.A.; Squires, R.H.; Vodovotz, Y.; Pediatric Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Analysis of serum inflammatory mediators identifies unique dynamic networks associated with death and spontaneous survival in pediatric acute liver failure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucuvalas, J.; Filipovich, L.; Yazigi, N.; Narkewicz, M.R.; Ng, V.; Belle, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Squires, R.H. Immunophenotype predicts outcome in pediatric acute liver failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.M. Acute liver failure. New Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.E.; Tisdale, J.; Barrett, A.J.; Dunbar, C.E.; Young, N.S. Hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolando, N.; Harvey, F.; Brahm, J.; Philpott-Howard, J.; Alexander, G.; Gimson, A.; Casewell, M.; Fagan, E.; Williams, R. Prospective study of bacterial infection in acute liver failure: An analysis of fifty patients. Hepatology 1990, 11, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Morra, R.; Ingiliz, P.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Thabut, D.; Messous, D.; Munteanu, M.; Massard, J.; Benhamou, Y.; Ratziu, V. Biomarkers of liver fibrosis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2008, 46, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammerich, L.; Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Role of il-17 and th17 cells in liver diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 345803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N. Biomarkers for diabetes prediction, pathogenesis or pharmacotherapy guidance? Past, present and future possibilities. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2012, 29, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, C.; Ladner, D.; Wang, E.; Lyuksemburg, V.; Kang, R.; Chang, Y.; Feinglass, J.; Holl, J.L.; Abecassis, M.; Skaro, A.I. A comprehensive risk assessment of mortality following donation after cardiac death liver transplant—An analysis of the national registry. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.K.; Wen, H.; Ting, J.P. The inflammasome nlrs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti-Andreoni, C.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Mortellaro, A. The inflammasomes in health and disease: From genetics to molecular mechanisms of autoinflammation and beyond. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Szabo, G. Interleukin-1 and inflammasomes in ald/aah and nafld/nash. Hepatology 2016, 64, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menu, P.; Vince, J.E. The nlrp3 inflammasome in health and disease: The good, the bad and the ugly. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyr, A.R.; Domann, F.E. The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: From mechanisms to functional consequences. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 551–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintu, L.; Yong, J.; Antebi, Y.E.; McCue, K.; Kazuki, Y.; Uno, N.; Oshimura, M.; Elowitz, M.B. Dynamics of epigenetic regulation at the single-cell level. Science 2016, 351, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J. Chip-seq: Advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, G.; Bartels, J.; Vodovotz, Y. In silico augmentation of the drug development pipeline: Examples from the study of acute inflammation. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
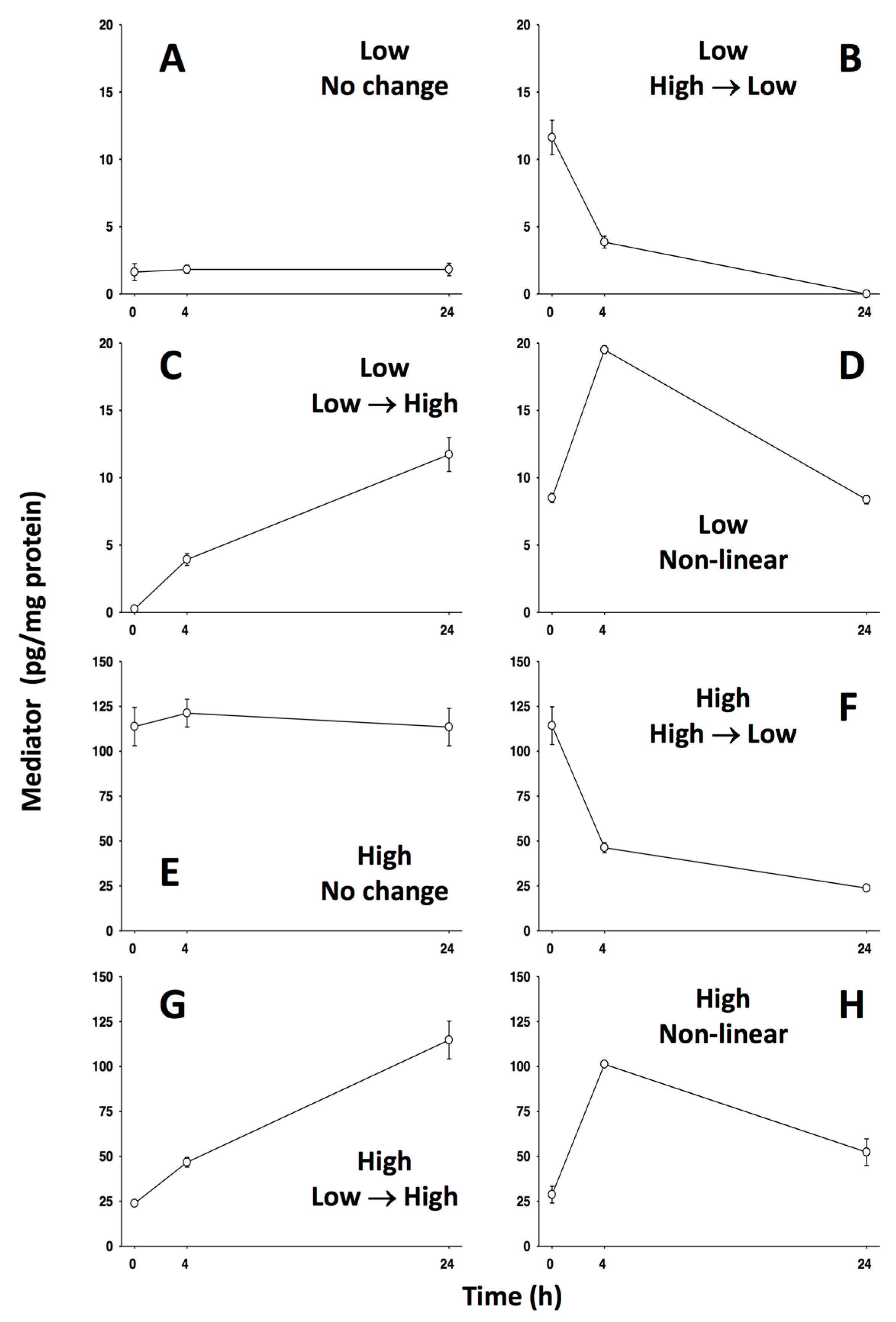
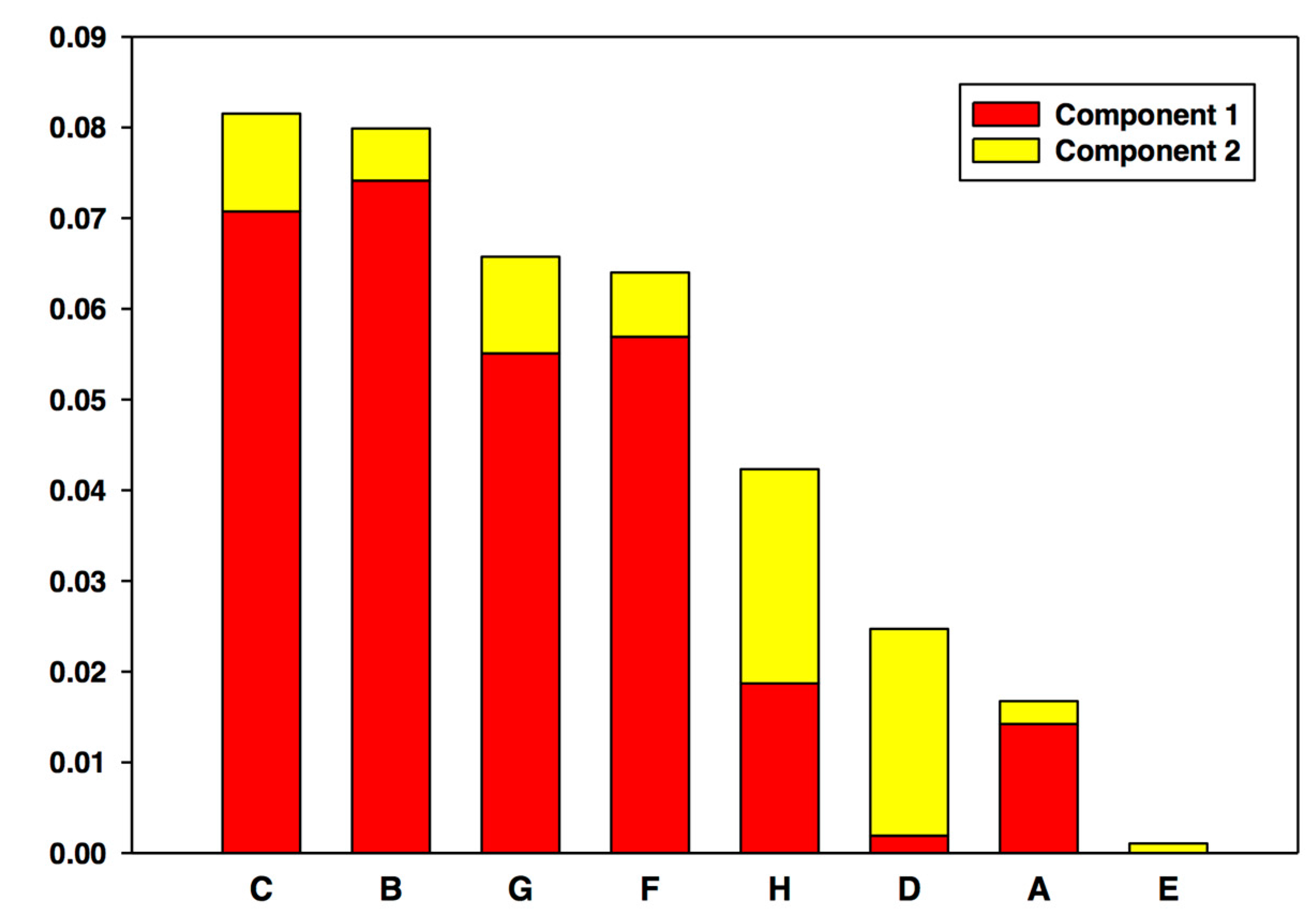
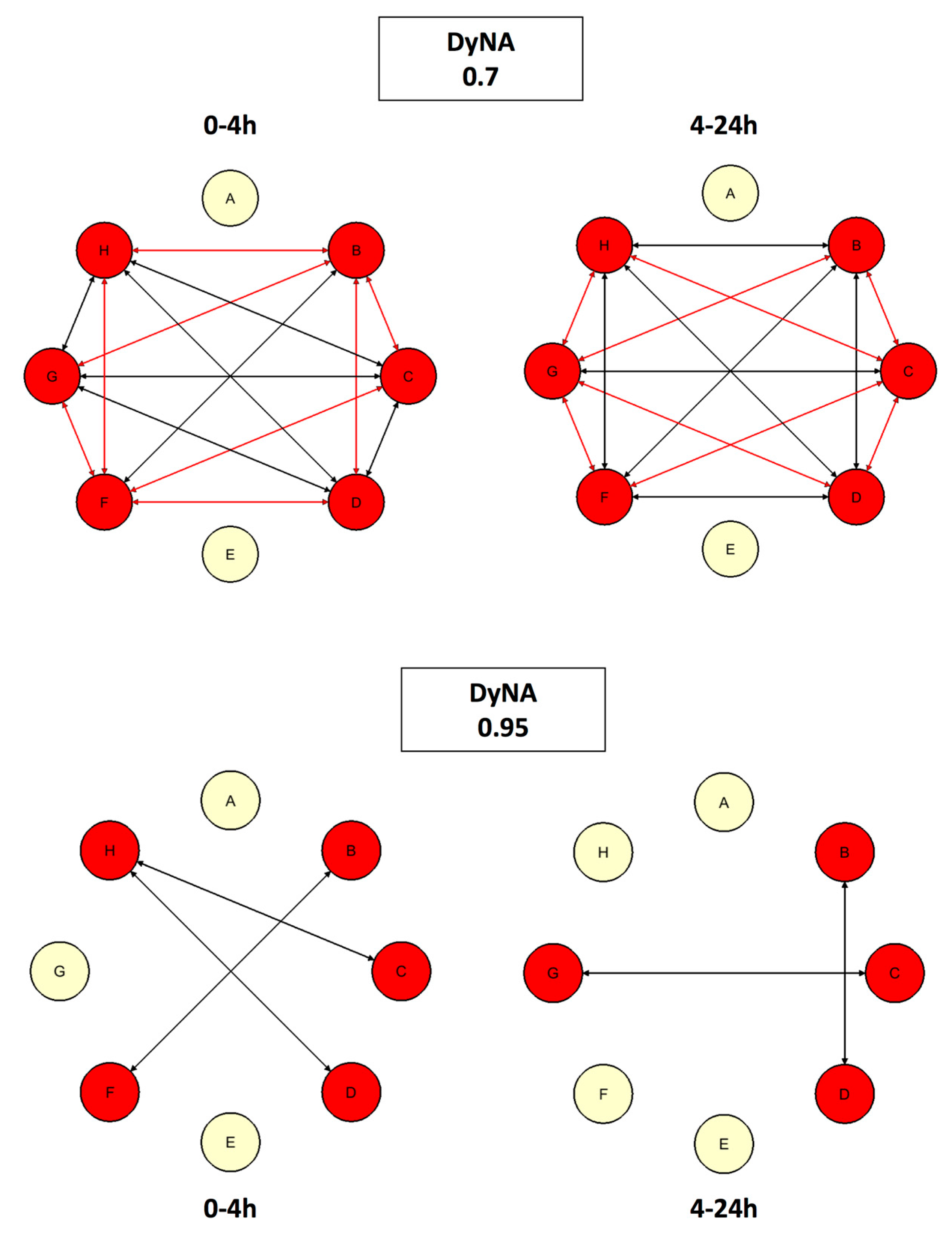
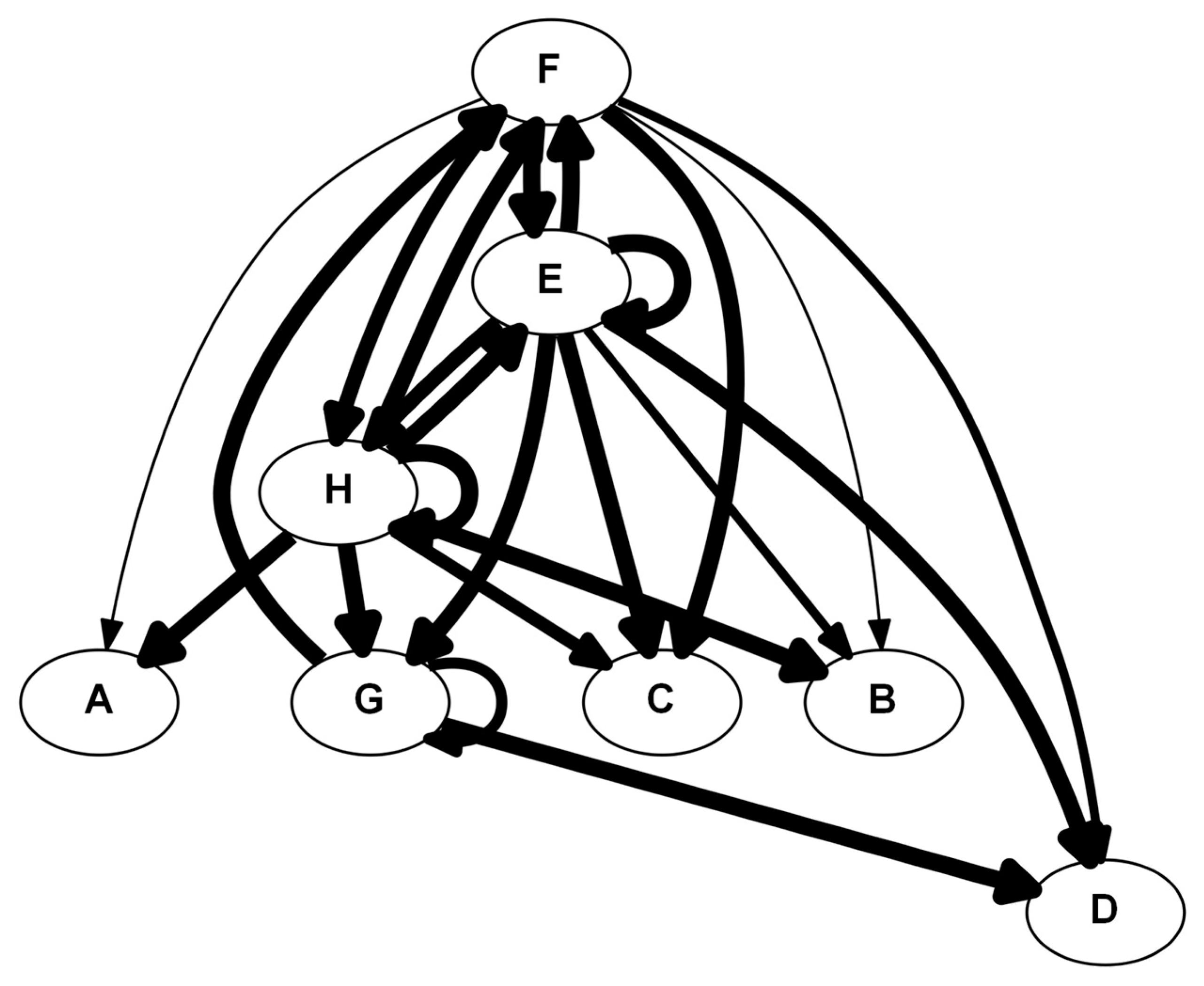
| Rank | CSP | MP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ethanolamine | Ribulose |
| 2 | Isoleucine | Ribose |
| 3 | Glycerol-3-Phosphate | GSSG |
| 4 | Cysteine | Glycolate (OH-acetate) |
| 5 | Lactate | Xylonate |
| Mediator | Significant? (p Value) |
|---|---|
| IFN-α | 0.001 |
| TNF-α | 0.032 |
| IFN-γ | 0.022 |
| IL-4 | 0.021 |
| IL-1β | <0.001 |
| IL-12/IL-23 (p40) | <0.001 |
| IL-10 | No |
| IL-6 | No |
| IL-8 | No |
| GM-CSF | No |
| IL-1α | No |
| IL-1RA | No |
| IL-2 | No |
| IL-18 | No |
| Sample Type | Cytokine | Protocol | Mean ± SEM, pg/mL | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perfusate | IL-18 | CSP | 738 ± 111 | 0.299 |
| MP | 932 ± 155 | |||
| IL-1RA | CSP | 230 ± 34 | 0.005 | |
| MP | 7317 ± 1953 | |||
| Tissue | IL-18 | CSP | 1600 ± 153 | 0.839 |
| MP | 1544 ± 243 | |||
| IL-1RA | CSP | 2478 ± 270 | 0.539 | |
| MP | 2733 ± 324 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadowsky, D.; Abboud, A.; Cyr, A.; Vodovotz, L.; Fontes, P.; Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y. Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling for Ex Vivo Data Analysis: Insights into Liver Transplantation and Pathobiology. Computation 2017, 5, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5040046
Sadowsky D, Abboud A, Cyr A, Vodovotz L, Fontes P, Zamora R, Vodovotz Y. Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling for Ex Vivo Data Analysis: Insights into Liver Transplantation and Pathobiology. Computation. 2017; 5(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadowsky, David, Andrew Abboud, Anthony Cyr, Lena Vodovotz, Paulo Fontes, Ruben Zamora, and Yoram Vodovotz. 2017. "Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling for Ex Vivo Data Analysis: Insights into Liver Transplantation and Pathobiology" Computation 5, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5040046
APA StyleSadowsky, D., Abboud, A., Cyr, A., Vodovotz, L., Fontes, P., Zamora, R., & Vodovotz, Y. (2017). Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling for Ex Vivo Data Analysis: Insights into Liver Transplantation and Pathobiology. Computation, 5(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5040046




