Abstract
Dental trauma is a serious and highly prevalent health issue across the globe. Most of the frequent dental injuries result in the loss of teeth and affects the overall quality of life. The loss of a tooth is usually compensated by a dental implant. The common methods adopted while placing the implant tooth are platform switching and platform matching. A plethora of works has studied the qualitative performance of these methods across different situations clinically. However, a detailed comparative work studying in-depth the mechanical parameters has not been attempted yet. In this computational work, two commonly available different platform-switched and one platform-matched implant-abutment configurations were compared. A 3D model of an implant (5.5 × 9.5 mm) was designed and inserted into a human mandibular bone block using computer-aided design (CAD) and extracting the clinical imaging data. Three separate models of implant-abutment configurations such as Platform Switched (PS)-I, a 5.5 mm implant with a 3.8 mm wide abutment, Platform Switched (PS)-II, a 5.5 mm implant with a 4.5 mm wide abutment, and Platform Matched (PM), a 5.5-mm implant with a 5.5 mm wide abutment were analyzed. Clinically relevant vertical-, horizontal-, and oblique-type of occlusal loadings were applied to each model to characterize the mechanical response. Mechanical parameters such as von Mises stresses, deformations, and strain energies were obtained using finite element modeling (FEM). These parameters showed lower values for platform switching within the peri-implant bone and that may help to limit marginal bone loss. However, the same parameters were increasing more in the abutment, implant, and screw for the platform-switched implant configuration than that of platform-matched configuration. The computational framework, along with the results, are anticipated to guide the clinicians and medical practitioners in making better decisions while selecting the commonly available methods.
1. Introduction
Human body requires different types of implants for the replacement of missing organs or body parts. Out of these implantations, dental implants are being used to replace missing teeth for masticatory and aesthetic purposes. In the start of the 20th century, 5 mm to 6 mm diameter dental implants were introduced with abutments of the reduced diameter of 4.1 mm, because of the unavailability of a matched-diameter abutment. Then, such a mismatched combination of the abutment–implant was termed as “platform switching” or “platform shifting” [1]. Now, the design of most of the conventional implants are turned towards the platform-switched model because of its expansion over the prevention of crestal bone loss [2]. Vigolo and Givani, in a five-year prospective clinical trial, concluded that platform-switching implants showed significantly less crestal bone loss [3]. Canullo et al. in a clinical study reported that platform-switching implants result in better maintenance of crestal bone levels [4]. Similar conclusions were observed in several systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies performed to assess the effect of platform switching on marginal bone [5,6]. The design of implants, their diameter, material properties, and surface characteristics are the factors influencing stress in the peri-implant bone [7,8,9,10].
Platform matching is clinically more practical because switching requires larger-sized implants to be inserted if standard-sized abutments are to be used. Clinically, this is not always possible, due to compromised bone width [11]. Smaller-diameter abutments are required if implants of the normal size are inserted, which may affect the emergence profile, particularly in anterior cases [12]. Therefore, in such cases, platform matching is indicated. Baggi et al. reported on the implant diameter as the primary influencer of the stress concentration in the cortical bone around the implant neck, instead of the implant length [13]. Lazzara and Porter, in their clinical study, concluded that the long-term preservation of marginal bone was better in some patients with platform switching [14]. The mismatched diameters between the implant and crown support have been reported to decrease the overall resorption of the peri-implant bone significantly [15,16,17].
In addition to analyzing the stress distribution in peri-implant bone and natural or restored teeth, the finite element model (FEM) has been extensively utilized to assess the biomechanical behaviour of orthodontic appliances, fixed prostheses, whole dentures, and dental implants [18,19,20,21]. The implant–abutment relationship was found to be crucial for long-term clinical success in a prior study [22,23], but other investigations found that stress decreased as the implant diameter increased [24,25]. Further, a study reported a novel conical dental implant connection that produced lower maximum stress values on the implant components as well as the tissues around the implant [26]. It is proposed that the platform-switched implants can offer additional surface area for the growth and attachment of soft tissues, which could be helpful in establishing the biological width in order to achieve outstanding superficial results [27,28]. However, the vertical bone loss with the platform-switched configuration is significantly less during the first year of loading [29]. The specific design of platform switching, with the use of a lesser-diameter abutment, shifts the perimeter of the implant–abutment junction inwards and converges the edge of the implant–abutment connecting surface towards the central axis of the implant [14]. In 2009, Hsu et al., in his three-dimensional finite element analysis, found that, in reduced platform restorations, the loading forces transmitted to the bone–implant interface in the immediately loaded implant model were reduced by 10% [30].
For fracture propagation issues that are characterized by a phase-field technique, Khodadadian et al. [31] proposed a framework for parameter estimation. A Bayesian technique is used to estimate crack propagation. Here, the crucial energy release rate and uncertainty related to the solid material properties were extensively studied. THE Bayesian inversion technique was used to solve the coarse mesh and fit the parameters. For a number of mechanical issues, Noii et al. [32] used Bayesian inversion and investigated its applicability in improving model accuracy. Seven distinct boundary value issues in coupled multi-field (and multi-physics) systems were applied. A detailed modelling was performed by considering both rate-dependent and rate-independent equations. Additionally, open-source programs were presented which can be useful for upcoming advances for issues such as multi-field coupled problems.
The current research aims to compare and contrast the biomechanical effects of a 5.5 mm diameter implant with abutments of two different platform-switched (3.8 mm and 4.5 mm) and one platform-matched (5.5 mm) diameter. In this study, a commercially available dental implant system (XIVE Plus [Table 1]), with two platform-switched configurations and one platform-matched configuration, has been adopted. The micro-CT of the implant and prosthetic components has been performed to ensure the accuracy of the geometrical model. Three distinct implant-abutment configurations subjected to various loading conditions (magnitude and direction) were examined using modelling data, and stress, deformation, and strain energy analyses using an Ansys Standard solver (Ansys 17.2) were performed. In order to obtain more precise results, i.e., stress and deformation along with strain energy, we discretized the model (PS I, PS II, and PM) of XIVE Plus and the cortical and cancellous bone with a high number of elements and nodes. Previous literature, which primarily focuses on stress analysis in platform switching, contains very few research works on deformation analysis. In this article, the strain energy, stress, and deformation are contrasted. The results offer an in-depth comparison of numerous aspects that reflect the outcomes.

Table 1.
Specifications of the dental implant system.
2. Materials and Methods
The present study is carried out to investigate the stress distribution, deformations, and strain energy in the peri-implant bone (cortical and cancellous bone), implant, abutment, and screw due to different platform-switched and platform-matched configurations using finite element analysis (FEA). The null hypothesis of this research paper was proposed that platform-switched abutment–implant connection system would provide statistically significant reduction in peri-implant crestal bone loss as compared to that in the case of platform-matched abutment–implant connection system. The implant is made up of commercially pure titanium (Ti-55), and the abutment and screw are made of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) with higher mechanical strength with structural integrity. The analysis is carried out on the right mandibular edentulous molar region. A flow diagram for the whole analysis is shown in the Figure 1.
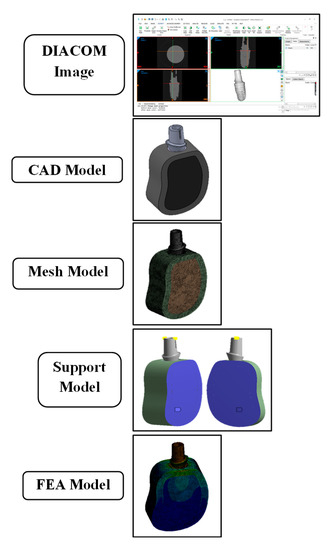
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of development of CAD model and FEA analysis: (i) Diacom image data; (ii) CAD model; (iii) mesh model; (iv) support model; and (v) FEA model.
The 3D model of mandible of a patient was obtained from an available cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The DICOM (.dcm) files of the CBCT were used to obtain the 3D model of mandible bone using Materialise Mimics Medical version 21.0 (MMM ver.-21.0) and 3-Matic Medical version 13.0 (3-MM ver.-13.0). The cross-section of the mandibular right first molar region was taken as reference for the bone model. A sectional 3D model of mandible bone was imported into Solid Works with dimensions 25 mm × 15 mm × 8 mm of height, width, and thickness, respectively. The bone block was modeled such that there is a core of cancellous bone surrounded by 2 mm of cortical bone. The surrounding gingiva and soft tissues are excluded from the study as the effect of occlusal loading was assumed as negligible on the soft tissues.
Commercially available implant and abutment per the details in Table 1 was used in the present analysis as depicted in Figure 2. The diameter and length of implant were 5.5 mm and 9.5 mm, respectively. The three aesthetic-based abutment (internal hex) having diameters of 3.8 mm, 4.5 mm, and 5.5 mm was used in this study. Using these implant and abutments, two models of platform-switched and one model of platform-matched configurations were obtained. These three model configurations were categorized as:
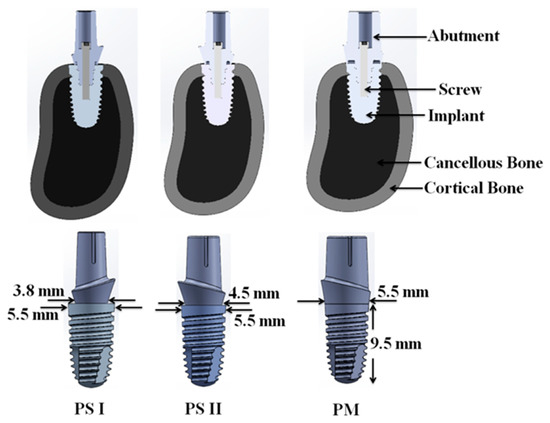
Figure 2.
CAD model of assembly (abutment, screw, implant, cancellous, and cortical bone) generated for PS I, PS II, and PM configuration.
- PS I: platform switching of 0.85 mm using 3.8 mm diameter abutment;
- PS II: platform switching of 0.5 mm using 4.5 mm diameter abutment;
- PM: no platform switching (platform matching) using 5.5 mm diameter abutment.
To obtain a detailed and precise CAD model of all three configurations, micro-CT was performed with SCANO MEDICAL micro-CT-50 setup. The DICOM files obtained were imported into MMM ver.-21 and 3-MM ver.-13.0 to obtain 3D model. These models (PS I, PS II, and PM) were imported into the Solid Works software for finalizing 3D CAD models. (Figure 2).
The 3D CAD assembly model was imported into Ansys-17.2 for FEA simulation. Majority of finite element studies makes the assumption that the abutment, screw, implant, cortical bone, and cancellous bone can be considered to be homogeneous, isotropic, and linearly elastic materials [33,34]. While there are few experimental data available, this Poisson’s ratio property seems to hold true for bone. In specimens of vertebral body cancellous bone, McElhaney et al. reported a Poisson’s ratio of 0.14 (S.D. ± 0.09) [35]. Poisson’s ratio in cortical bone is estimated to be roughly 0.38 based on data from Reilly and Burstein [36], despite the fact that this ratio is unquestionably dependent on the direction of loading due to bone anisotropy. We made the assumption that Poisson’s ratio is a linear function of apparent density and follows as in Equation (1) based on these two earlier investigations:
where apparent density (p) is expressed in g/cm3 and (v) as Poisson’s ratio [37]. Instead of “elastic modulus,” the 2-rank stiffness tensor must be taken into account for anisotropic materials but, in general, the Poisson ratios (v) are not symmetric [38]. Most of the literature have used variety of the metals with varying grades having Poisson’s ratio of mandibular bone, i.e., cortical bone (0.3) and cancellous bone (0.3), and Poisson’s ratio for different grades of titanium and titanium alloys (Grade I, Grade II, Grade III, and Grade IV) in the range of 0.31–0.37 [39,40,41,42,43,44].
v = 0.15 p + 0.13
An Ansys Standard solver was used to analyze modeling data and perform the stress, deformation, and strain energy analysis in the implant systems subjected to nine different loading conditions as shown in Figure 3. In the ANSYS Workbench, two types of displacements were pre-programed (i.e., total deformation and directional deformation). In this work, total deformation was used to model the computational framework.
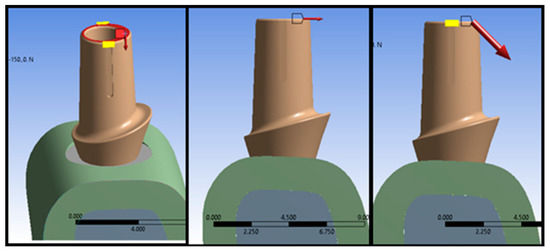
Figure 3.
Boundary conditions used in the computational framework. The red arrows show the loading di-rections considered in each simulation.
The total deformation (U) considers the fixed node(s) as the origin and computes the vectorial deformation the model has undergone [45]. Figure 4 represents the calculation of the displacement vector for a symmetric model. Equation (2) represents the method to calculate the vectorial displacement.
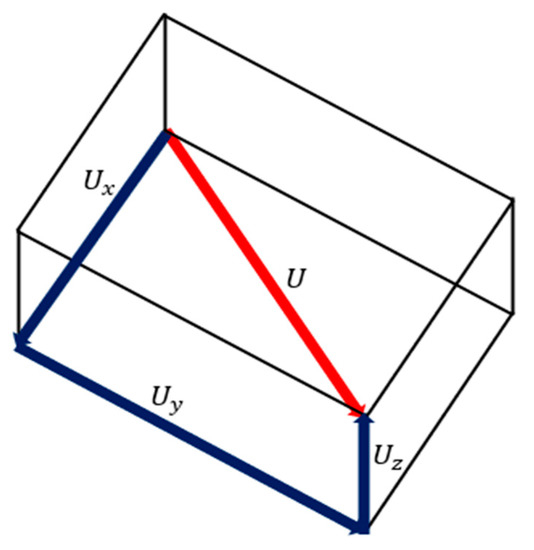
Figure 4.
Calculation of the displacement vector for a symmetric model.
As the geometries considered in this work were nonlinear (i.e., asymmetric), the displacements were modelled assuming a large strain output [46]. The applied loads acting on the models displaced it from one position to another (Figure 5). This motion can be defined by studying a position vector in the deformed {x} and undeformed {X} configuration. In the below Equation (3), [I] represents the identity matrix, and [F] represents the deformation gradient which includes the volume change, rotation, and the shape change of the deforming body.
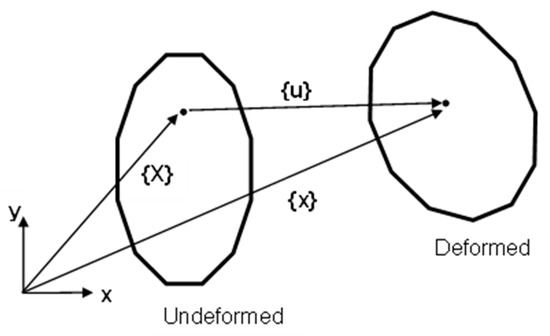
Figure 5.
Calculation of the displacement vector for a geometrically nonlinear model.
Moreover, this work considered each solid model as a linear, isotropic, and elastic material; only the Young’s modulus (E) and the material’s Poisson’s ratio (υ) were sufficient to model the material properties. It is well-known that the elasticity tensor has two independent components, i.e., shear (G) and bulk modulus (K). Hence, these moduli were automatically calculated by employing the following Equations (4) and (5):
We would also like to clarify that this work only studied the structural analysis and other analysis domains (i.e., thermal, modal, etc.) were not taken into account. Hence, a decoupled framework was considered. However, future studies, including additional and realistic boundary conditions such as thermal and modal analyses, could further increase the overall accuracy of the study. Moreover, linearization of the state-space equations was performed using the Taylor series expansion which finally leads to a continuous-time linear dynamical system.
The material properties were imported in to the Ansys software as given in Table 2. The three different loading conditions such as vertical, horizontal, and oblique loadings were applied on the occlusal surface of the abutments. Whereas, Table 3 shows the types of loading and its respective magnitude for different conditions. The models were meshed using tetrahedral elements having a 20-node SOLID186 formation as depicted in Table 4. As implemented by Gupta et al. [47,48], this particular element category has been observed to accurately account for large deformations and contact conditions. For a direct and systematic comparison, the same boundary conditions, loading conditions, and constraints were applied in each situation. We have clarified the boundary conditions in detail. The bone block was fixed in three planes on the lateral surfaces while the base was maintained as free or suspended, with loading conditions, and constraints (direct contact, which means that the contact avoids penetration, sliding, or movement between the surfaces).

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of materials [49].

Table 3.
Type of loading and magnitude.

Table 4.
Number of nodes and elements of all the components in PS I, PS II, and PM.
The data of mechanical parameters such as von Mises stress, deformation, and strain energy for the dental implant system were recorded for 108 simulated studies of three models (PS I, PS II, and PM), with 27 analyses of each component (abutment, implant, screw, and peri-implant bone) which includes 9 analyses each of stress, deformation and strain energy under three individual loadings on the occusal surface of abutment as mentioned in Table 3.
3. Results
3.1. Stress Analysis
The stress analysis of the dental implant system (abutment, implant, screw, and peri-implant bone) for three different model configurations, i.e., PS I, PS II, and PM, has been carried out under vertical (V), horizontal (H) and oblique (OB) static load at an angle of 45° to “V” as shown in Figure 3. Figure 6 represents the stress analysis of (a) abutment, (b) implant, (c) screw, and (d) peri-implant bone for PS I, PS II, and PM configuration under different loading conditions. Figure 6a shows the effect of loading on the stress development in the abutment. As expected, applied load increases the stress in all cases, irrespective of model configuration. However, the amount of stress generated was strictly dependent on both the model configuration and angle of the load. Another interesting result was observed in all four components, with a similar pattern in stress, where “H” leads to a maximum stress, followed by “OB”, and “V” generated the least stress.
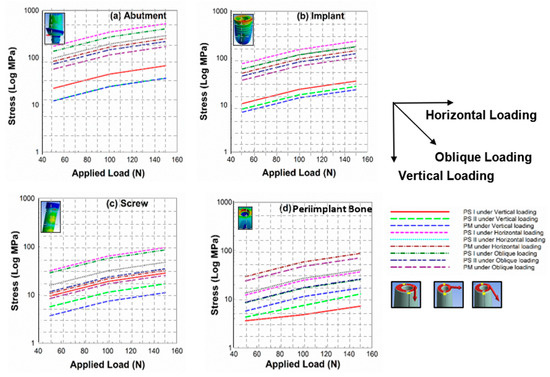
Figure 6.
Graphs representing stress analysis of (a) abutment, (b) implant, (c) screw, and (d) peri-implant bone for PS I, PS II, and PM configuration under different loading conditions.
The simulation study shows another striking similarity in all four components, that the increase in applied load by 5 times resulted in an increase in stress when “H” was applied of about 3 to 4 times, about 2 times when “OB” was applied, and about 1.3 to 1.5 times when “V” was applied. In the abutment, implant, and screw, the stress generated was higher for PS I than PS II, and lowest for the PM model. The reason may be that, as the value of platform switching (PS) increases (diameter of abutment reduces), the load is concentrated along the axis of the model configuration [25]. Therefore, the lower diameter abutment has higher stresses. Surprisingly, this stress trend was in the reverse order, i.e., maximum stress generated for PM than PS II, and least for PS I in the peri-implant bone. This may be due to the radiation of stresses towards the circumferences of the implant and abutment. Equation (6) represents the method used to calculate the stress across each component.
3.2. Deformation Analysis
The deformation analysis of the dental implant system (abutment, implant, screw, and peri-implant bone) for three different model configurations, i.e., PS I, PS II, and PM, was carried out under vertical (V), horizontal (H), and oblique (OB) static load at an angle of 45° to “V” as shown in Figure 3. The deformation analysis was employed only to compare the different platforms for the dental implant restoration process. This metric was also used to analyze the areas which experienced high deformations when the load was simulated. Due to this, analyses considering the elastic and plastic regions were not considered. Future studies including a detailed study defining the elastic and plastic zones of the considered models could further help in selecting a better platform for patient-specific requirements. The trend of the graph in Figure 7 shows that the deformation on the abutment (7a), implant (7b), screw (7c), and peri-implant bone (7d) is increasing with the increment of the vertical, horizontal, and oblique load for all three configurations. The maximum deformation was found under horizontal loading and the minimum under vertical loading with the intermediate amount under oblique-loading conditions.
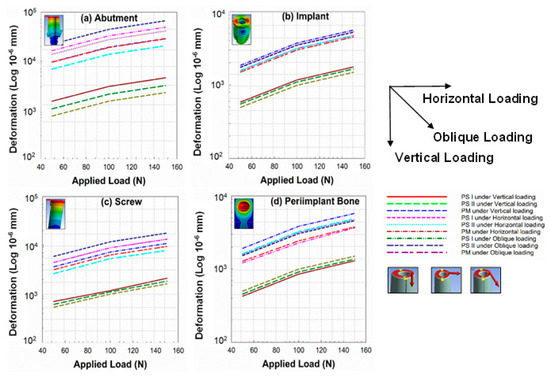
Figure 7.
Graphs representing deformation analysis of (a) abutment, (b) implant, (c) screw, and (d) peri-implant bone for PS I, PS II, and PM configuration under different loading conditions.
It was further noticed that the maximum deformation was for PS I in the case of abutment, implant, and screw, and the minimum in the case of the platform-matched (PM) configuration under all three loadings. However, a reverse order of deformation was recorded for the peri-implant bone (crestal bone level), i.e., maximum deformation for platform-matched configuration (PM) and minimum for the PS I configuration, because in the PM configuration, the loading effects are more at the crestal bone rather than the central axis of the implant system. Hence, more resorption of bone results in PM configurations.
3.3. Strain Energy Analysis
The strain energy stored in the dental implant system under different loading conditions was also analyzed under this study. Figure 8 shows that the strain energy on the abutment (8a), implant (8b), screw (8c), and peri-implant bone (8d). The variation of strain energy has a similar trend as the variation of stresses and deformations in the components. The trend shows that the strain energy is increasing with the load. PS I experiences the maximum strain energy and PM the minimum for the abutment, implant, and screw, and the reverse trend was found for the peri-implant bone (crestal bone level), i.e., minimum for PS I and maximum for PM. A surprising variation was seen for PS II under oblique loading between 70.71 N and 141.42 N. Equations (7) and (8) represents the method used to calculate the strain energy across each component in the simulated model.
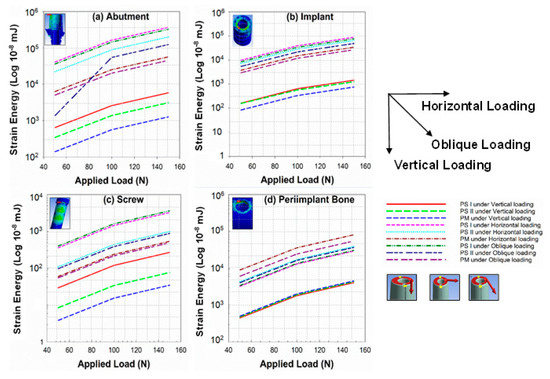
Figure 8.
Graphs representing strain energy analysis of (a) abutment, (b) implant, (c) screw, and (d) peri-implant bone for PS I, PS II, and PM configuration under different loading conditions.
4. Discussion
Implant failure can occur due to biological, mechanical, and iatrogenic issues, and improper patient education [50]. The geometry of the implant and prosthetic components play a significant role in determining the biomechanical aspects of implant therapy. The resorption of the peri-implant bone on occlusal loading can lead to implant failure due to the loss of the bone–implant contact [51]. During the first year of function, a crestal bone loss of 1.2 mm occurs in almost all cases [52]. In a multicentric clinical study, the mean vertical bone loss was less than 1.5 mm during the first year and 0.2 mm annually after the first year of function irrespective of the one-stage or two-stage technique [53]. This crestal bone loss depends on the diameter and the crest module (transosteal region) design of the implant [54]. Therefore, the implant design should be such that it distributes the stresses along the implant to the cancellous bone region and it should not exceed the mechanical limits of the prosthetic components. Overloading and excessive stresses can lead to bone resorption as well as mechanical fatigue of the implant, abutment, screw, and crown.
Underloading leads to disuse atrophy, resulting in bone loss [55,56]. The concept of platform switching was introduced to control the loss of crestal bone. PS appears to protect soft tissue and horizontal and vertical bone loss, according to a comprehensive review and meta-analysis of 1239 dental implants [57]. A review of 15 articles found that the PS approach is crucial for reducing crestal bone loss around dental implants and emphasized the need for more large-scale, randomized controlled clinical trials. However, performance was improved when abutment mismatches were greater than 0.45 mm [58]. Another one-year prospective study comparing 26 PS bone-level dental implants to 26 PM tissue-level dental implants found that both procedures resulted in uniform bone loss in the lower jaw, particularly in the area directly in front of the dental arch [59]. According to recent prospective randomized clinical research, after one year of functional loading, dental implants with PS and PM performed equally well in terms of radiographic and clinical performance [60]. Platform-switched implants appear to have less marginal bone resorption than non-platform-switched implants, according to most of the studies comparing the two types of implants.
The crestal bone loss around platform-switched and non-platform-switched implants was evaluated by Hürzeler et al. [61]. In platform-switched implants, the average crestal bone loss was 0.22 mm, compared to 2.02 mm in non-platform-switched implants. They also came to the conclusion that a 0.45 mm reduction in the abutment on each side is adequate in preventing implant-related bone loss. Another study by Cappiello et al. discovered that vertical bone loss ranged between 0.6 and 1.2 mm (mean: 0.95 ± 0.32 mm) for platform-switched individuals, while it was between 1.3 and 2.1 mm (mean: 1.67 ± 0.37 mm) for instances without PLS. Non-platform-switched implants experience an average bone loss of 1–2 mm, while platform-switched implants experience little bone loss [62]. The above-mentioned works of literature have consistently reported the effectiveness of the platform-switching configuration in limiting the crestal bone resorption.
In line with these studies, results from the current study showed that PS (i.e., both I and II) reported a maximum reduction of 26%, 58%, and 65% in stresses as compared to the PM configuration across the peri-implant bone under vertical, horizontal, and oblique loading respectively. Additionally, PS also reported a maximum reduction of 15%, 20%, and 28% in deformation as compared to the PM configuration across the peri-implant bone under vertical, horizontal, and oblique loading, respectively. Similarly, the strain energy also showed a reduction of 10%, 64%, and 44% in PS as compared to the PM configuration across the peri-implant bone under vertical, horizontal, and oblique loading, respectively. Specifically, we focused on the peri-implant bone as this location is prevalent in determining the crestal bone resorption.
The biological width (the distance between the attached gingival tissues and crest of bone around the implant) is maintained by soft tissues [63]. The main objective of platform switching is to shift the implant–abutment interface away from the crest of the alveolar bone and direct the stresses towards the center of the implant, thus away from the peri-implant bone. With the concentration of forces, and thus stress and strain generated within the implant and its components, the mechanical longevity and fatigue resistance of the implant and its prosthetic components may decrease. Fatigue in dental implants is a multi-factorial issue and, therefore, a probabilistic fatigue analysis is required for its prediction. Fatigue life is defined as the number of stress cycles required to cause the fracture of the specimen. It depends on the magnitude of stress, nature of stress, environment of fatigue, and the biomechanical properties of the material.
Liu et al. performed a non-linear finite element analysis on platform switching [49]. They concluded that, with platform switching, there is reduction of the stress concentration on the cortical bone around the implant but the risk of implant failure due to fracture is increased as compared to the conventional platform matching design. Paul et al. evaluated the strain in the bone by platform-switched (abutment–implant diameter difference of 1 mm) and non-platform-switched implants [64]. They found that micro strains of 50–3000 is exhibited by the platform-switching configuration, which are the ideal bone-remodeling values of micro strain. The aim of this study was to compare the stress distribution, deformation, and strain energy among two platform-switched and one platform-matched model (PS I, PS II, and PM). A linear, static, 3 D finite element analysis was performed. FEA has become an excessively useful tool for the evaluation of mechanical parameters which is not possible in vivo. The maximum stress-generated area of the stress concentration and the fatigue probability of different components can be predicted with FEA. In earlier studies, simplified models were used. In this study, to obtain more relatable CAD models for the actual implant and bone and accurate results, methods to replicate the bone and implant and its components were used. For the CAD model of the bone block, the CBCT of the patient was used.
For the implant models, PS I, and PS II, instead of medical CT, the micro-CT machine was used so that the finite element model is the same replica of the implant-abutment size, geometry, design, thread number, pitch of the threads, depth of the threads, crevice, aesthetic base, and horizontal screw hole. In the analysis, the bone, implant, and abutments were considered to be linear, elastic, homogeneous, and isotropic. The bite forces are different in magnitude and location throughout the arch in different individuals. In edentulous patients, the vertical component of bite forces ranges from 100 to 2400 N. The average value of the bite force by patients treated with implants is reported to be 50 N and the maximum value to be 150 N [65]. The highest magnitude of occlusal forces is experienced at the mandibular molar regions, about four times that in anterior teeth [66]. The cross-section of the mandibular right molar region was taken for the model of the bone block. The models were subjected to 50, 100, and 150 N of single, static, vertical load, and 50 and 100 N of single, static, horizontal load for the analysis. In a recent study by Carossa et al. [63], the clinical results of a full-arch loading rehabilitation using implants, with and without using implant-abutment units, was described. Patients were observed over a period of two years. The peri-implant soft tissues were found to be stable at all implant sites and no major differences were observed between implants with or without abutments. However, further investigations, to confirm these outcomes, were recommended.
Stress, deformation, and strain energy increases on increasing the magnitude of load. The maximum stress values for implant, abutment, and screw are found in the case of PS I and the minimum in PM, and vice versa for the peri-implant bone. The deformation on the abutment and screw increases with the increment of the load for all three configurations. Under vertical loading, deformation increases with the load. Under horizontal loading, it reduces from PM to PS I. Under oblique loading, deformation is the maximum for PS I and the minimum for PS II. The maximum deformation occurs at the crestal bone in the case of PM and the minimum in PS I under all loading conditions. Hence, this explains the greater crestal bone loss in the platform-matched configuration as compared to the platform-switched. The value of strain energy increased with the increase in load. The values of strain energy decreased from PS I to PM, and the result is the opposite for the crestal bone around the implant.
Some limitations should be acknowledged. In this study, a linear finite element analysis is performed by considering the isotropic properties of all biological parts, while in the actual conditions, the biological structures are of the anisotropic type and a nonlinear finite element analysis provide better results. This study is carried out under the consideration of static loading, while, in actual conditions, a varying amount of dynamic loads acts. A loading angle of 45 degrees was considered in our work. This particular loading metric was found to be prevalent in a previous study by Chang et al., and SU et al. etc. [34,67]. Different researchers opted for a different oblique loading in the magnitude and also in the directions from 15 degree to 45 degree [34,39,40,67,68]. However, future studies including different angles and loading conditions could further help in increasing the overall accuracy and precision of the computational framework.
5. Conclusions
The magnitude of the compressive and tensile stresses, deformation, and strain energy increases within the implant-abutment assembly on increasing the platform switch. The stress concentration is reduced at the crest of the peri-implant bone and is shifted in the cancellous bone region, more apically. The implant and abutment are subjected to the maximum stress concentration in almost all loading conditions; thus, failure can occur early at the implant and abutment. Therefore, per the graph trends in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 obtained from the simulation study, it can be concluded that platform switching does provide a statistically significant mechanical advantage to the peri-implant bone by decreasing the stress concentration. PS reported a maximum reduction of 65%, 28%, and 64% in stress, deformation, and strain energy, respectively, as compared to the PM configuration across the peri-implant bone. Hence, PS could be the better choice for dental surgeons or medical practitioners. However, it also compromises the mechanical integrity of the narrower-diameter abutment which can lead to implant failure due to abutment fracture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., A.T., A.C. and S.A.; methodology, M.A., A.T. and A.C.; software, M.A. and A.T.; validation, M.A., S.G., A.T., S.A. and A.C.; formal analysis, M.A., S.G., A.T., S.A. and A.C.; investigation, M.A., S.G., A.T., S.A. and A.C.; data curation, M.A., A.T., S.A. and A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A., A.T., S.A. and A.C.; supervision, A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during this current study are not publicly available due to the fact that they are large datasets, but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jemt, T.; Lekholm, U.; Gröndahl, K. 3-year followup study of early single implant restorations ad modum Brånemark. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1990, 10, 340–349. [Google Scholar]
- Baqain, Z.H.; Moqbel, W.Y.; Sawair, F.A. Early dental implant failure: Risk factors. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 50, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigolo, P.; Givani, A. Platform-switched restorations on wide-diameter implants: A 5-year clinical prospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Canullo, L.; Rossi-Fedele, G.; Iannello, G.; Jepsen, S. Platform switching and marginal bone-level alterations: The results of a randomized-controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nsour, M.M.; Chan, H.-L.; Wang, H.-L. Effect of the platform-switching technique on preservation of peri-implant marginal bone: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Strietzel, F.P.; Neumann, K.; Hertel, M. Impact of platform switching on marginal peri-implant bone-level changes. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, S.; Linke, J.; Graef, F.; Foitzik, C.; Wichmann, M.; Weber, H.-P. Stress and inflammation as a detrimental combination for peri-implant bone loss. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraisat, A.; Abu-Hammad, O.; Al-Kayed, A.M.; Dar-Odeh, N. Stability of the Implant/Abutment Joint in a Single-Tooth External-Hexagon Implant System: Clinical and Mechanical Review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2004, 6, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.Y.-J.; Huang, H.-L.; Hsu, J.-T.; Chee, W. Biomechanical effects of the implant material and implant–abutment interface in immediately loaded small-diameter implants. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.Y.-J.; Hsu, J.-T.; Huang, H.-L. An In Vitro Biomechanical Evaluation of a New Commercial Titanium-Zirconium Alloy Dental Implant. Implant. Dent. 2014, 23, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, C.; Prasad, K.D.; Shetty, M.; Bansal, N. Platform switching: An answer to crestal bone loss. J. Dent. Implant. 2011, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunder, U.; Gracis, S.; Capelli, M. Influence of the 3-D bone-to-implant relationship on esthetics. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Baggi, L.; Cappelloni, I.; Di Girolamo, M.; Maceri, F.; Vairo, G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, R.J.; Porter, S.S. Platform switching: A new concept in implant dentistry for controlling postrestorative crestal bone levels. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2006, 26, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vela-Nebot, X.M.; Rodríguez-Ciurana, X.; Rodado-Alonso, C.; Segalà-Torres, M.M. Benefits of an Implant Platform Modification Technique to Reduce Crestal Bone Resorption. Implant. Dent. 2006, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchetto, R.; Traini, T.; Caddeo, F.; Celletti, R. Evaluation of hard tissue response around wider platform-switched im-plants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2010, 30, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Enkling, N.; Jöhren, P.; Klimberg, V.; Bayer, S.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Jepsen, S. Effect of platform switching on peri-implant bone levels: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, L.; Gandini, L.G., Jr.; Shintcovsk, R.L.; Gandini, M.R.E.A.S. Scientific use of the finite element method in Orthodontics. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2015, 20, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Nakano, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ono, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sato, T.; Yatani, H. Effects of Implant–Abutment Connection Type and Inter-Implant Distance on Inter-Implant Bone Stress and Microgap: Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2021, 14, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Sundram, R.; Abdemagyd, H.A.E. Application of finite element model in implant dentistry: A systematic review. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2019, 11, S85–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanyk, D.L.; Vafaeian, B.; Addison, O.; Adeeb, S. The use of finite element analysis in dentistry and orthodontics: Critical points for model development and interpreting results. Semin. Orthod. 2020, 26, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandgar, V.; Kharsan, V.; Mirza, A.; Jagtiani, K.; Dhariwal, N.; Kore, R. Comparative evaluation of three abutment–implant interfaces on stress distribution in and around different implant systems: A finite element analysis. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournasrollah, A.; Negahdari, R.; Gharekhani, V.; Torab, A.; Ataei, S.J. Investigating the effect of abutment–implant connection type on abutment screw loosening in a dental implant system using finite element method. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2019, 13, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Huh, Y.-H.; Park, C.-J.; Cho, L.-R. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of the Stress Distribution at the Internal Implant-Abutment Connection. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, e49–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; de Ibarra, N.L.S.; Martín, I.M.; Rotaeche, L.S. Influence of Dental Implant Diameter and Bone Quality on the Biomechanics of Single-Crown Restoration. A Finite Element Analysis. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, L.; Cicciù, M.; D’Amico, C.; Mauceri, R.; Oteri, G.; Cervino, G. Finite Element Method and Von Mises Investigation on Bone Response to Dynamic Stress with a Novel Conical Dental Implant Connection. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2976067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumbo, C.; Marigo, L.; Somma, F.; La Torre, G.; Minciacchi, I.; D’Addona, A. Implant platform switching concept: A liter-ature review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, J.P.; Pereira, J.; Vahey, B.R.; Henriques, B.; Benfatti, C.A.M.; Magini, R.S.; López-López, J.; Souza, J.C.M. Morse taper dental implants and platform switching: The new paradigm in oral implantology. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-Montesinos, A.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Solá-Ruiz, M.F.; Marco-Pitarch, R.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; Fons-Badal, C. Comparative Study by Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Peri-Implant Effect of Two Types of Platforms: Platform-Switching versus Conventional Platforms. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.-T.; Fuh, L.-J.; Lin, D.-J.; Shen, Y.-W.; Huang, H.-L. Bone Strain and Interfacial Sliding Analyses of Platform Switching and Implant Diameter on an Immediately Loaded Implant: Experimental and Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analyses. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadian, A.; Noii, N.; Parvizi, M.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Wick, T.; Heitzinger, C. A Bayesian estimation method for variational phase-field fracture problems. Comput. Mech. 2020, 66, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noii, N.; Khodadadian, A.; Ulloa, J.; Aldakheel, F.; Wick, T.; François, S.; Wriggers, P. Bayesian Inversion with Open-Source Codes for Various One-Dimensional Model Problems in Computational Mechanics. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 4285–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, J.; Pereira, J.; Faria, J.; Pereira, C.; Alves, J.; Henriques, B.; Souza, J.; López-López, J. Finite element analysis of stress extent at peri-implant bone surrounding external hexagon or Morse taper implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 71, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-N.; Chang, C.-H.; Wang, C.-H. Mechanical analysis of a dental implant system under 3 contact conditions and with 2 mechanical factors. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhaney, J.; Alem, N.; Roberts, V. A Porous Block Model for Cancellous Bones. Available online: https://wbldb.lievers.net/10037028.html (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Reilly, D.T.; Burstein, A.H. The elastic and ultimate properties of compact bone tissue. J. Biomech. 1975, 8, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, R.; Carter, D.; Harris, W. Stress distributions in the acetabular region—I. Before and after total joint replacement. J. Biomech. 1982, 15, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasik, M.; Lambert, F.; Bacevic, M. Biomechanical Properties of Bone and Mucosa for Design and Application of Dental Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Velasco, A.B.; Ríos-Santos, J.-V.; Lasheras, F.S.; Lemos, B.F.; Gil, F.J.; Carvalho, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. Effect of Different Implant Designs on Strain and Stress Distribution under Non-Axial Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menacho-Mendoza, E.; Cedamanos-Cuenca, R.; Díaz-Suyo, A. Stress analysis and factor of safety in three dental implant systems by finite element analysis. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-T.; Cheng, K.-J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.-F.; Ding, Y.-D.; Yang, F. Effect of the prosthetic index on stress distribution in Morse taper connection implant system and pe-riimplant bone: A 3D finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, M.I.; El-Zawahry, M.M. A three dimensional finite element study on dental implant design. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2011, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Miura, J.; Taki, I.; Sogo, M. Biomechanical analysis on platform switching: Is there any biomechanical rationale? Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli-Ghahroudi, A.A.; Geramy, A.; Yaghobee, S.; Khorsand, A.; Yousefifakhr, H.; Rokn, A.; Soolari, A. Evaluation of Platform Switching on Crestal Bone Stress in Tapered and Cylindrical Implants: A Finite Element Analysis. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2015, 17, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaki, H.M.; Salih, S.A.; Gorgis, I.N. IRJET- Analysis of deformation of RC beam with addition of fly ash: A Finite element based modeling. IRJET 2020, 25, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanical APDL Theory Reference. Available online: https://www.mm.bme.hu/~gyebro/files/ans_help_v182/ans_thry/ans_thry.html (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Biomechanical modeling of novel high expansion auxetic skin grafts. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, e3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, G.; Chanda, A. Prediction of diabetic foot ulcer progression: A computational study. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2021, 7, 065020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, C.; Yu, J.; Dai, W.; Bao, Y.; Hu, D. The effect of platform switching on stress distribution in implants and periimplant bone studied by nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Hirsch, J.-M.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants, (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 527–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, S.; Coulthard, P. Implant Failure: Etiology and Complications. 2011. Volume 16, pp. e42–e44. Available online: https://roderic.uv.es/handle/10550/60196 (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Delucchi, F.; Ambrogio, G.; Canepa, C.; Carossa, M.; Pera, F. One-stage versus two-stage technique using two splinted extra-short implants: A multicentric split-mouth study with a one-year follow-up. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.-J.; Yoon, J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.-L. The Causes of Early Implant Bone Loss: Myth or Science? J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, W.C.; Piazza, S.; Zysset, P. Biomechanics of fracture risk prediction of the hip and spine by quantitative computed tomography. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 1991, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Deporter, D.A.; Watson, P.A.; Valiquette, N. Dental implant design-effect on bone remodeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieh, M.A.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Atieh, A.H. Platform Switching for Marginal Bone Preservation Around Dental Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1350–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Girolamo, M.; Calcaterra, R.; Di Gianfilippo, R.; Arcuri, C.; Baggi, L. Bone level changes around platform switching and platform matching implants: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oral Implant. 2016, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bilhan, H.; Erdogan, O.; Geçkili, O.; Bilgin, T. Comparison of Marginal Bone Levels Around Tissue-Level Implants with Platform-Matched and Bone-Level Implants with Platform-Switching Connections: 1-Year Results of a Prospective Cohort Study with a Split-Mouth Design. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraz, A.; Isler, S.C.; Cula, S.; Tunc, S.; Yalim, M.; Cetiner, D. Platform-switched implants vs platform-matched implants placed in different implant-abutment interface positions: A prospective randomized clinical and microbiological study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 22, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürzeler, M.; Fickl, S.; Zuhr, O.; Wachtel, H.C. Peri-Implant Bone Level Around Implants With Platform-Switched Abutments: Preliminary Data From a Prospective Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappiello, M.; Luongo, R.; Di Iorio, D.; Bugea, C.; Cocchetto, R.; Celletti, R. Evaluation of peri-implant bone loss around platform-switched implants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2008, 28, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T.; Swarup, S.; Paul, S. Comparison of strain generated in bone by “platform-switched” and “non-platform-switched” implants with straight and angulated abutments under vertical and angulated load: A finite element analysis study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, A.; Postaire, M.; Lipinski, P. Biomechanical study of mandible bone supporting a four-implant retained bridge: Finite element analysis of the influence of bone anisotropy and foodstuff position. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, M. Bite Force and Occlusion. Semin. Orthod. 2006, 12, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Chuang, S.-F.; Ng, E.Y.K. Biomechanical Evaluation of Endodontic Post-Restored Teeth—Finite Element Analysis. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2013, 13, 1350012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrotenboer, J.; Tsao, Y.-P.; Kinariwala, V.; Wang, H.-L. Effect of Platform Switching on Implant Crest Bone Stress: A Finite Element Analysis. Implant. Dent. 2009, 18, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).