Anomalous Solute Transport Using Adsorption Effects and the Degradation of Solute
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
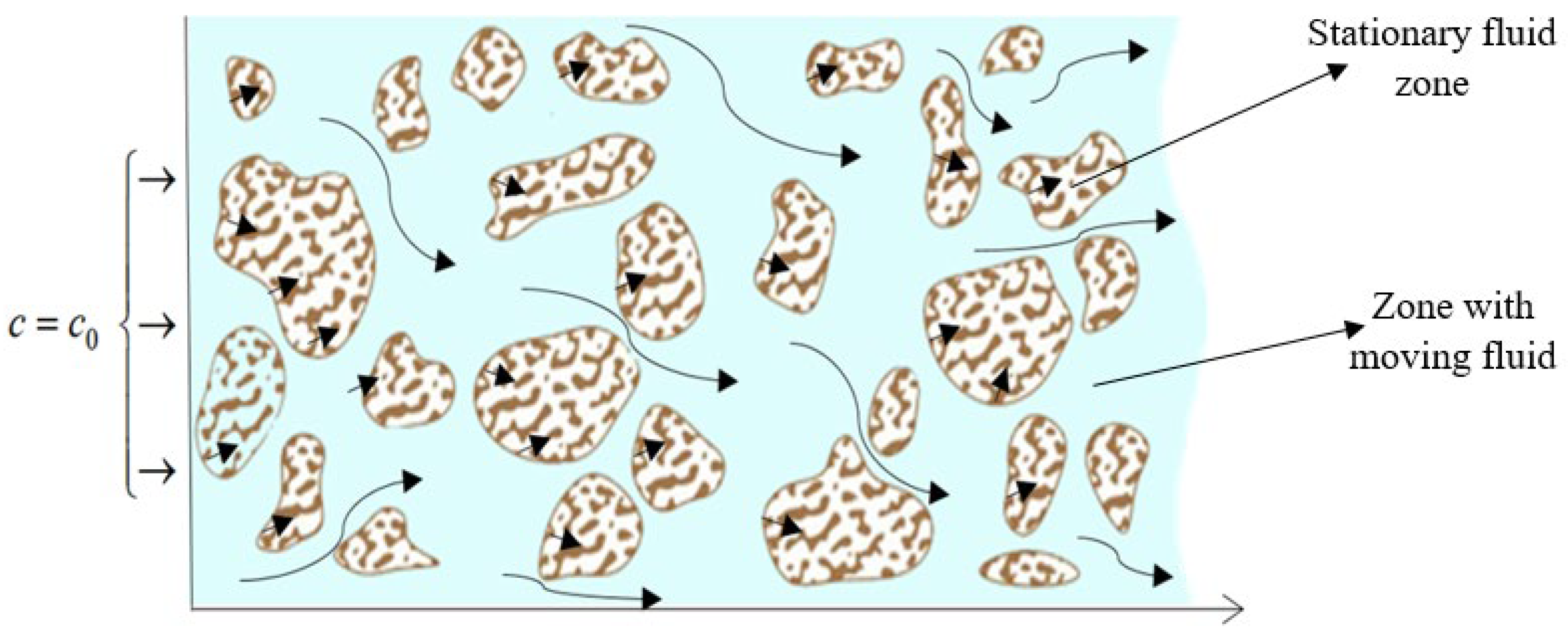
2.1. Formulation of the Problem
2.2. Solution Procedure
- Constant case
- 2.
- Linear case
- 3.
- Exponential case
3. Results and Discussion
- Constant case
- 2.
- Linear case
- 3.
- Exponential case
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| constant in exponential distance-dependent dispersivity () | |
| constant in exponential distance-dependent dispersivity () | |
| solute concentration in mobile region | |
| solute concentration in immobile region | |
| constant source concentration | |
| dispersion coefficient in mobile region () | |
| molecular diffusion coefficient () | |
| fraction of adsorption sites equilibrating instantaneously with mobile liquid region | |
| constant in linear distance-dependent dispersivity | |
| distribution coefficient for linear sorption | |
| time (s) | |
| mobile pore-water velocity | |
| Distance | |
| water content in mobile region | |
| water content in immobile region | |
| dispersivity () | |
| mass transfer coefficient () | |
| bulk density of porous medium | |
| first-order degradation coefficient in mobile adsorbed solid phase () | |
| first-order degradation coefficient in immobile liquid region () | |
| first-order degradation coefficient in mobile adsorbed solid phase () | |
| first-order degradation coefficient in immobile adsorbed solid phase () |
References
- Dagan, G. Flow and Transport in Porous Formations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gelhar, L.W. Stochastic Subsurface Hydrology; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gelhar, L.W.; Welty, W.; Rehfeldt, K.R. A critical review of data on field-scale dispersion in aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1955–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Selim, H.M. Scale-dependent dispersion in soils: An overview. Adv. Agron. 2003, 80, 223–263. [Google Scholar]
- Pickens, J.F.; Grisak, G.E. Scale-dependent dispersion in a stratified granular aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1191–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Jury, W.A. A laboratory study of the dispersion scale effect in column outflow experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1990, 5, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Toride, N.; van Genuchten, M.T. Experimental investigation of solute transport in large, homogeneous and heterogeneous, saturated soil columns. Transp. Porous Media 1995, 18, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Makuch, D. Longitudinal dispersivity data and implications for scaling behavior. Ground Water 2005, 43, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderborght, J.; Vereecken, H. Review of dispersivities for transport modeling in soils. Vadose Zone J. 2007, 6, 29–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cai, S.; Huang, G.; Ye, Z. Stochastic Theory for Solute Transport in Porous Media; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcraft, S.W.; Tyler, S.W. An explanation of scaledependent dispersivity in heterogeneous aquifers using concepts of fractal geometry. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.R.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Biggar, J.W. Water flow and solute transport processes in unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 89S–108S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Wierenga, P.J. Mass transfer studies in sorbing porous media: II. Experimental evaluation with tritium (3H2O). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, J.W.; Barry, D.A.; Parlange, J.Y. Interpretation of two-region model parameters. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, I.Y.; Jim Yeh, T.C.; Conklin, M.H. The effect of water content on solute transport in unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3303–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Close, M.E. Field-scale physical non-equilibrium transport in an alluvial gravel aquifer. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1999, 38, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toride, N.; Inoue, M.; Leij, F. Hydrodynamic dispersion in an unsaturated dune sand. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Feng, S.; Zhan, H.; Huang, G.; Mao, X. Evaluation of anomalous solute transport in a large heterogeneous soil column with mobile-immobile model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhan, H.; Feng Sh Huang, G.; Mao, X. Comparison of alternative models for simulating anomalous solute transport in a large heterogeneous soil column. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.; Gorelick, S.M. Rate-limited mass transfer or macrodispersion: Which dominates plume evolution at the Macrodispersion Experiment (MADE) site? Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, R.; Harvey, C.F.; von Schwerin, C.F.; Meigs, L.C. What controls the apparent timescale of solute mass transfer in aquifers and soils? A comparison of experimental results. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W01510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehley, C.E.; CM Zheng Molz, F.J. A dual-domain mass transfer approach for modeling solute transport in heterogeneous aquifers: Application to the Macrodispersion Experiment (MADE) site. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2501–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valocchi, A.J. Validity of the local equilibrium assumption for modeling sorbing solute transport through homogeneous soils. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, R.; Gorelick, S.M. Multiple-rate mass transfer for modeling diffusion and surface reactions in media with pore-scale heterogeneity. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2383–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Bromly, M.; Hinz, C. Non-Fickian transport in homogeneous unsaturated repacked sand. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W07402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Meerschaert, M.M. A simple and efficient random walk solution of multi-rate mobile/immobile mass transport equations. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, R.; Mckenna, S.A.; Meigs, L.C. On the late-time behavior of tracer test breakthrough curves. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Wagenet, R.J. Two-site/two-region models for pesticide transport and degradation: Theoretical development and analytical solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, A.; Swami, D. Solute Transport Through Saturated Soil Column with Time-Dependent Dispersion. Hydrol. J. 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Zhan, H.; Feng, S.; Fu, B.; Ma, Y.; Huang, G. A new mobile-immobile model for reactive solute transport with scale-dependent dispersion. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W08533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuzhayorov, B.; Usmonov, A.; Kholliev, F. Numerical Solution of Anomalous Solute Transport in a Two-Zone Fractal Porous Medium. In APAMCS 2022: Current Problems in Applied Mathematics and Computer Science and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 702, pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Pickens, J.F.; Grisak, G.E. Modeling of scale-dependent dispersion in hydrogeologic systems. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarskiy, A.A. Theory of Difference Schemes; Science: Moscow, Russia, 1989; p. 616. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L. Numerical solution of time-space fractional advection-dispersion equations. Int. Conf. Comput. Exp. Eng. Sci. 2009, 9, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Khuzhayorov, B.; Usmonov, A.; Nik Long, N.M.A.; Fayziev, B. Anomalous solute transport in a cylindrical two-zone medium with fractal structure. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.S.; Sun, C.L.; Jia, X.Z.; Du, D.H. Numerical solution to the multi-term time fractional diffusion equation in a finite domain. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 2016, 9, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 , Linear:
, Linear:  , Exponential:
, Exponential:  .
.
 , Linear:
, Linear:  , Exponential:
, Exponential:  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.
 , :
, :  , :
, :  .
.

 , Linear:
, Linear:  , Exponential:
, Exponential:  .
.
 , Linear:
, Linear:  , Exponential:
, Exponential:  .
.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khuzhayorov, B.K.; Viswanathan, K.K.; Kholliev, F.B.; Usmonov, A.I. Anomalous Solute Transport Using Adsorption Effects and the Degradation of Solute. Computation 2023, 11, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110229
Khuzhayorov BK, Viswanathan KK, Kholliev FB, Usmonov AI. Anomalous Solute Transport Using Adsorption Effects and the Degradation of Solute. Computation. 2023; 11(11):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110229
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhuzhayorov, B. Kh., K. K. Viswanathan, F. B. Kholliev, and A. I. Usmonov. 2023. "Anomalous Solute Transport Using Adsorption Effects and the Degradation of Solute" Computation 11, no. 11: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110229
APA StyleKhuzhayorov, B. K., Viswanathan, K. K., Kholliev, F. B., & Usmonov, A. I. (2023). Anomalous Solute Transport Using Adsorption Effects and the Degradation of Solute. Computation, 11(11), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110229






