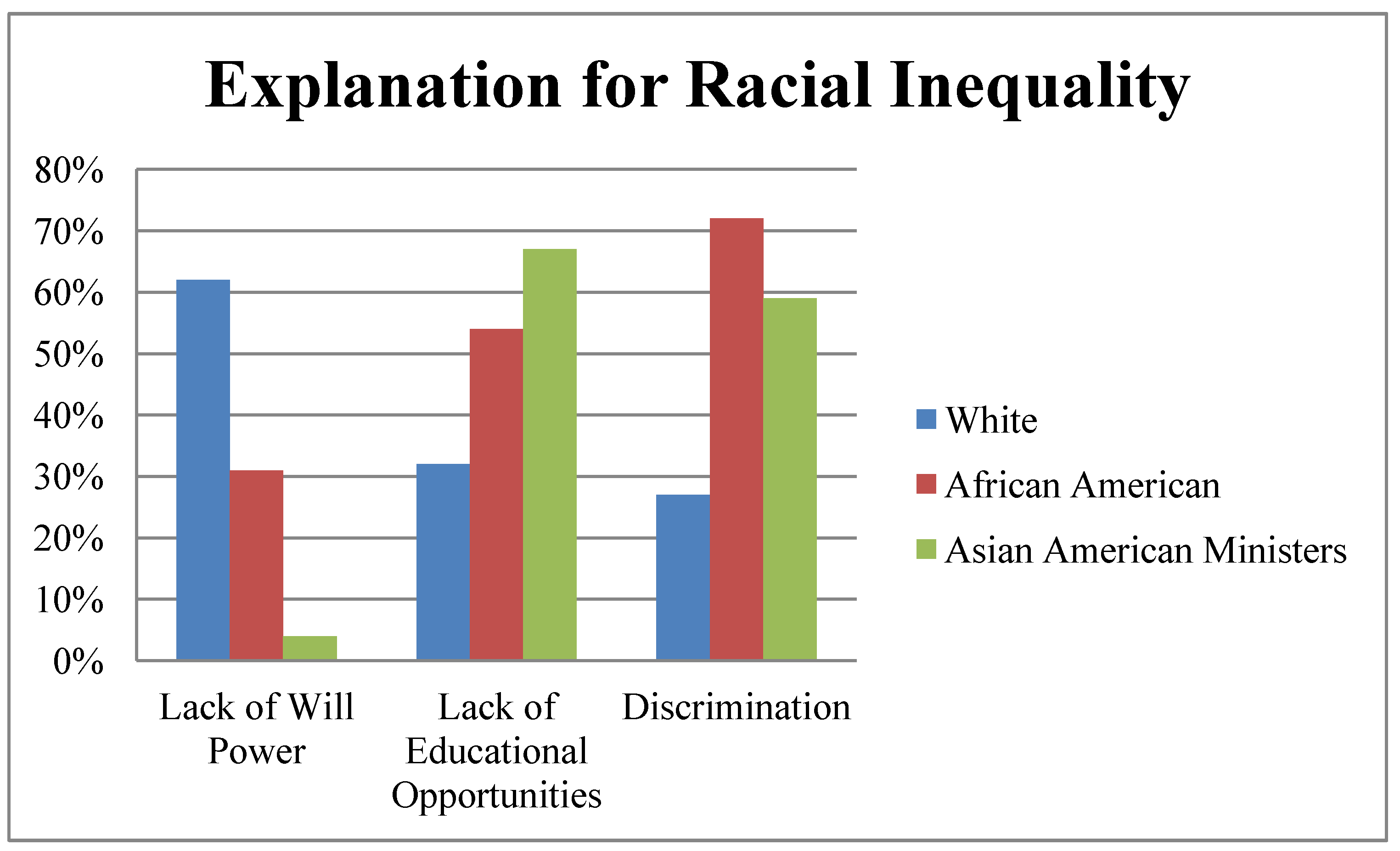1. Introduction
The United States is mythologized as a country built by immigrants and many Americans take great pride in the archetypal immigrant success story. As the story goes, groups as dissimilar as English Pilgrims and Italian Catholics have arrived on America’s shores with little more than their dreams. With hard work and perseverance, they are able to move up the economic ladder within a few generations and “make it” in America. Since the 1960s, the United States has been in the midst of another wave of immigration, larger than the European immigration at the turn of the nineteenth century, and many expect the story of successful assimilation to continue. With the help of schools and churches, the children of new immigrants from Latin America, Asia and Africa who get an education, work hard, and shed their ethnic baggage will succeed in the American workforce. One new immigrant group, the so-called “whiz kids” of Asian immigrants, has found their path up the socio-economic ladder to the racial limits of the America dream.
Imagine a young couple escaping repression in China by immigrating to Chicago in the 1970s where they find well-established ethnic institutions, such as the Chinese church, to help them get settled and maintain cultural practices. Their son, Ray Lee, is born in Chicago, attends public schools, and commits to Christ through a campus bible fellowship at the state university he attends in the 1990s. As a college-educated, Christian, middle-class professional, Ray moves with his wife and children to the Chicago suburbs seeking liberation from the parochial Chinese immigrant world of their youth. They join a suburban, non-denominational church as one of the few families of color. The White members welcome them and are encouraging when Ray later decides to enter seminary and become a minister. After graduation, Ray hopes to serve a suburban church, but the only job offers he receives are from Chinese churches looking for an “EM” or English minister to serve the American-born Chinese.
Racial barriers have not deterred Asian Americans from entering Christian ministry, but they have kept many from leadership positions within the White-dominated evangelical subculture. Following the pattern of other minority groups, Asian Americans have formed “ethnic” churches and pan-ethnic churches, but neither the ethnic nor pan-ethnic church makes sense to Ray who is deeply troubled by the persistence of ethnic divisions within the Christian church. He longs to serve a church for all nations, and with that vision Pastor Ray joins the growing cohort of evangelical Christians seeking to create multiracial churches.
Ray Lee’s experience of rejection by White evangelicals is all too common, but it is not the only path Asian Americans take to multiracial ministry. In this article, we explore why Asian American evangelicals choose to lead multiracial congregations and how their ethnic identity and racial attitudes shape their approach multiracial ministry. Asian Americans are the fastest growing racial group in the United States, and a growing, vibrant demographic within American Christianity [
1]. According to Michael Emerson, about two-thirds of U.S-born Asian Protestants currently attend churches where at least 20 percent of attendees are of another race. He writes, “Should the pattern continue, it also suggests that multiracial congregations will become more common, their growth driven by immigrants and especially by their children and future generations” [
2]. As they join, create and lead multiracial churches Asian Americans are helping shape not only the future of evangelicalism but also the changing patterns of race relations in the United States.
2. Asian American Evangelicals
Though they make up only two percent of the American evangelical population, Asian Americans have a noticeable presence within evangelicalism [
3]. Given that they are the highest- income and best-educated racial group in the United States, this should come as no surprise [
1]. Scholars and the popular media have noticed the vitality of Asian American evangelicals calling them “God’s Whiz Kids” and the model minority of Christianity [
4]. Asian American ministers have planted almost one hundred congregations in California alone since 1996 [
5]. Asian American evangelicals have been particularly noticed on college campus where they are re-energizing the Christian student movement [
6]. In this article, we focus on a subject that has not been studied to our knowledge: the efforts of Asian American evangelicals to form and lead multiracial churches (hereafter MRCs).
Before collaborating on this chapter, the authors independently found evidence of Asian American leadership of MRCs. Russell Jeung began studying the formation of pan-Asian churches in the San Francisco Bay Area in 1989 [
7]. In the last decade, many pan-Asian churches have broadened their membership and identity beyond Asian Americans creating Asian American-majority multiracial churches. Many of the pastors interviewed for this article are helping to transition their congregations from pan-Asian to multiracial identity. Kathleen Garces-Foley began studying the evangelical movement to create MRCs in 2002 and found Asian Americans at the forefront of racial reconciliation efforts in churches and college bible fellowships in Los Angeles [
8]. To better understand the reasons why Asian American evangelicals are leading MRCs, and how their approach to MRC-ministry reflects their experience as racial minorities, the authors conducted telephone interviews with twenty-seven Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs across the United States. We also wanted to examine their racial attitudes and how they talk about racial problems in the United States in order to compare their responses with those of previously studied White evangelicals, who account for 81 percent of American evangelicals [
3]. As discussed in the literature review below, most White evangelicals reject social explanations of racial inequality preferring to blame inequality on individuals [
8]. Our interview data indicates that Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs do not share the racial views of White evangelicals. Instead, they are conscious of the reality of social structures that limit the opportunities for racial minorities in the United States and this is reflected their approach to MRC-ministry.
3. Review of Scholarship
The most important scholarly work on the racial attitudes of American evangelicals is Michael Emerson and Christian Smith’s
Divided by Faith: Evangelical Religion and the Problem of Race in America (2000) [
9]. Using national survey data and in-depth interviews, they seek to explain the stark difference between the way White and Black conservative Protestants understand the causes of Black poverty, as well as the solutions they propose to overcome the “problem of race.”
1 Nearly two-thirds of White conservative Protestants say that Blacks are poor because they lack sufficient motivation, and 10 percent say that Blacks are poor because they have less inborn ability to learn. On the opposite side of the racial divide, Black conservative Protestants hold a very different perspective; they explain racial inequality through structural patterns: 72 percent identify discrimination as the cause and 54 percent point to lack of educational opportunities. Emerson and Smith explain the racial attitudes of White evangelicals in terms of their theological commitment to individualism, relationalism and anti-structuralism. Viewing the world through this cultural “toolkit,” White evangelicals utilize a colorblind racial discourse that rejects the reality of racialization—that is, the ways in which racial categories afford benefits to some while limiting the opportunities of others [
10].
Because Whites and Blacks view the American “race problem” differently, they employ different solutions. Since the 1990s, White evangelicals have actively engaged in anti-racism efforts that focus on “changing hearts” of individuals rather than changing institutional structures. Emerson and Smith describe how White evangelicals took up the cause of racial reconciliation by advocating repentance, cross-racial friendships and church partnerships across racial lines. Emerson and Smith, conclude that because of their ignorance of an ineffectual response to structural racism, White evangelicals perpetuate racialization. In the follow-up book,
United by Faith, DeYoung
et al. argue passionately that Christians should create multiracial churches because these churches play an important role in reducing racial division and inequality [
11]. Evangelical efforts to form MRCs have grown considerably since these publications and scholars have taken notice.
The first in-depth study of a multiracial church is sociologist Gerardo Marti’s
A Mosaic of Believers: Diversity and Innovation in a Multiethnic Church [
12]. Through interviews with members, Marti examines Mosaic—a thriving, youthful, evangelical church in Los Angeles with a very racially diverse membership. Surprisingly, Mosaic does not highlight or promote its racial diversity. Instead it purposely obscures effaces ethnic identity through a process Marti calls “ethnic transcendence.” Marti suggests that we think of Mosaic as multiethnic and monocultural; though demographically diverse, Mosaic embraces the popular culture of middle-class White America. Mosaic’s approach to MRC-ministry has clear resonances with the colorblind approach to race prevalent among White Evangelicals. Given the racial attitudes of Black conservative Protestants, it’s not surprising that few African Americans attend Mosaic. While Mosaic is very successful at attracting a diverse membership, the lack of attention to racial issues at Mosaic undermines the ability of this MRC to work for racial equality in society at large.
Though Emerson and colleagues are optimistic that MRCs will make a positive contribution to the problem of race in America, sociologist Korey Edwards book
The Elusive Dream: the Power of Race in Interracial Churches argues that MRCs perpetuate white hegemony [
13]. Edwards profiles Crosstown Community Church, a White, Midwestern evangelical church that intentionally reached out to African Americans when its membership dwindled and hired a Black minister to lead the newly diverse congregation. Even with a Black-majority membership, Edwards found that Crosstown continued to reinforce white cultural norms and avoid confronting racial issues because it was the only way to keep the remaining White members from leaving. Based on this case study and extensive analysis of national survey data, Edwards concludes that even when White members are in the minority, MRCs perpetuate white privilege. Though the studies published by Edwards and Marti point to the “colorblind” limitations of evangelical MRCs, other studies have identified MRCs that actively address racial issues and encourage awareness of the racialization.
In his 2006 book,
People of the Dream: Multiracial Congregations in the United States Michael Emerson highlights the story of Wilcrest Baptist Church [
2]. Like Crosstown Community Church that Edwards studied, Wilcrest was a White church that reached out to people of color when it hit hard times. Wilcrest hired an Asian American pastor, Rodney Woo, to promote multiracial ministry. Also similar to Crosstown, many of the White members at Wilcrest had a difficult time giving up white cultural norms. However, Emerson shows how under Woo’s leadership Wilcrest has continued to raise consciousness of racial power and privilege. Another interesting example is Evergreen Baptist Church, where Garces-Foley found that racial issues were openly discussed, and members were encouraged to explore and acknowledge their ethnic cultures [
8]. Garces-Foley calls Evergreen’s approach to diversity “colorconscious” in contrast to a colorblind approach that ignores or avoids racial issues. In the colorconscious approach “race talk” is allowed, encouraged, and modeled by the church leadership. Racial issues are addressed regularly through sermons, worship music, religious education, social events and service activities, and are often explicitly promoted in the church mission statement. Political scientist Nancy Wadsworth found in interviews with evangelicals attending a conference on MRC building, that their efforts are “considerably more nuanced than a reiteration of white privilege or neoconservatism” ([
14], p. 260). Indeed, several evangelical ministers have written books advocating a colorconscious approach to MRC-ministry [
15,
16,
17,
18].
We find it useful to think of colorblind and colorconscious approaches to diversity within a MRC as contrasting ideal types of MRC-ministry. In real MRCs, one can find subtle variations of these ideal types and often multiple, conflicting racial attitudes are apparent within a single congregation. Following Emerson and Smith’s analysis, we expect that colorconscious MRCs will have a more positive impact on race relations in the United States [
9]. With limited data on MRCs currently available, we do not know if evangelical MRCs are more likely to be colorblind or colorconscious in their ministry approach. However, among well-known evangelical leaders and organizations promoting MRCs, the colorconscious approach is clearly preferred [
15,
16,
17,
18].
2 Nor do we know if the racial identity of the minister is correlated with one type of MRC-ministry more than another. In our research, we set out to learn if Asian American ministers of MRCs tend toward a colorblind or colorconscious approach to MRC-ministry. Given the stark divide Emerson and Smith found between the racial attitudes of Whites and Blacks, we wondered where Asian Americans fit in this framework and how that translated into their leadership of MRCs.
In the American racial landscape, Asian Americans occupy an ambiguous status as model minorities and perpetual foreigners [
1]. Many studies have established the importance of the Asian American ethnic church in the processes of ethnic maintenance and reproduction for the next generation [
19,
20,
21]. We do not have national data on the racial attitudes of Asian American evangelicals, but ethnographic studies show little evidence that Asian American evangelicals are advocates for systematic anti-racism policies. In his ethnographic study of two Asian American churches—primarily Korean American in membership—Antony Alumkal found these churches espoused a superficial commitment to racial reconciliation without any institutional implementation of this goal [
22]. Alumkal argues that Asian American evangelicals experience normative pressure to conform to the goals of White evangelicals.
In college Christian fellowships, Asian American evangelicals also find themselves under strong pressure to assimilate to White evangelical norms. According to Rudy Busto, conforming to White evangelical norms leads to the “curious disappearance of Asianness” from bible studies specifically designed by and for Asian groups [
6]. Busto suggests that on the college campus evangelical identity serves as an alternative to ethnic identity for those Asian Americans seeking to escape racial antagonism and the pressures to succeed academically. Other studies have shown that in some Asian American evangelical churches, ethnic identity is actively demonized. Jeung writes in his study of pan-Asian churches,
By categorizing ethnic traditions and values as, at worst, ‘satanically inspired’ and, at best, ‘unhealthy patterns,’ Asian American pan-ethnic congregations discard cultural resources and experiences that might make them distinct from other evangelical Christians.
In contrast, Garces-Foley’s research reveals an Asian American-majority MRC in which members are expected to assert ethnic identity and develop racial consciousness in this multiracial setting [
8]. In a more recent study of three Asian American-majority multiracial churches in Los Angeles, Karen Yonemoto found they “actively create a politicized racial identity and address issues of race and racism through the pulpit” [
23].
Current scholarship reveals a variety of ways in which Asian American evangelicals relate their ethnic identity to their Christian identity and engage in racial discourse, but there is still much we do not know. The purpose of this study is to learn from Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs how they have addressed issues of ethnic identity and racialization in their congregations.
4. Interview Sample
This article is based on telephone interviews with Asian American evangelical ministers leading multiracial churches.
3 According to the Multiracial Congregations Survey, a multiracial congregation is defined as having no more than 80 percent of members of a single racial group [
11]. This is the standard definition of a MRC used by most scholars; however, we chose not to begin with this definition and instead looked for Asian American ministers who identify their own churches as multiracial or broadly multiethnic.
4]Using a less-stringent definition of MRC and enabled us to find enough ministers to interview for our study. More importantly, we utilized an “emic” rather than “etic” definition because our focus is on the ministers’ approach to MRC-ministry, not the racial dynamics of the congregations they lead.
We first located potential interview subjects, with the help of D.J. Chuang, the executive director of the L2 Foundation, which develops Asian American leadership. From the initial list, Chuang provided we increased our sample size by non-probability sampling, which means we asked each minister if he (rarely she) knew of other Asian American evangelicals leading multiracial MRCs. In all we collected almost 40 names of ministers who fit these criteria and were able to persuade twenty-seven of them to participate in the study. The interviewees were predominantly English-speaking, 1.5 or second generation Americans and, in all but one case, male. In telephone interviews, which lasted on average 45 minutes to one hour, we asked the ministers to tell us about their vision for multiracial ministry, as well as their views on political issues and racial inequality. Of those we interviewed, 17 (63 percent) of their congregations meet the demographic definition of multiracial, while the other eleven congregations would be considered pan-Asian using this definition.
In terms of their ethnic identity, 16 of the ministers we interviewed were Korean American and eleven were Chinese American, numbers that generally reflect English-speaking Asian American leadership today. Approximately 4,000 Korean American congregations and 900 Chinese American churches have been established in the United States [
2]. Despite having four times the number of churches, most Korean Americans are foreign-born with a second generation more recently emerging. By contrast, the smaller Chinese American Christian community, with a longer historic presence in the United States, has a larger pool of second, third and fourth generation ministers capable of starting English-speaking multiracial churches. Surprisingly, even though Japanese American ministers have been at the forefront of the pan-Asian American Christian movement none of the ministers identified in our sampling are Japanese American.
The great majority (89 percent) of the ministers we surveyed lead MRCs that are affiliated with an American evangelical denomination, from which they receive financial support, training, and encouragement to develop. What is surprising about these denominational ties is that Chinese American churches have tended to be independent and half of all Korean American churches are affiliated with the Presbyterian Church, USA, rather than affiliated with the Presbyterian Church of America [
24]. One common pattern we found is to affiliate with denominations that are small but aggressively planting new churches, such as the Evangelical Covenant Church (n = 5), the Presbyterian Church of America (n = 4), and the Evangelical Free Church (n = 3). Denominational networks do influence the way MRC ministers approach racial issues. In the case of the Evangelical Covenant Church, which has actively promoted racial reconciliation and community transformation among its member churches, ministers are colorconscious. Asian American ministers belonging to the Presbyterian Church of America, whose leadership has not promoted MRC, look to the successful model of Redeemer Presbyterian Church in New York, which is “seeking to renew the city socially, spiritually, and culturally.” Redeemer’s emphasis on the renewal of cities necessarily includes an embrace of multiraciality and the diverse populations found in our urban cores. Four of the ministers lead MRCs affiliated with the mainline denomination Presbyterian Church, USA, which has actively encouraged multiracial church plants in recent years [
25]. The remaining churches identify as follows: Southern Baptist Convention (n = 3), American Baptist (n = 1), Evangelical Free Church (n = 3), Chinese for Christ (n = 1), Christian and Missionary Alliance (n = 1), Independent or unknown (n = 5).
The geographic location of the ministers and their congregations generally reflect the dispersion of Asian Americans across the United States. Just as 51 percent of Asian Americans live in the West, 59 percent of our respondents came from there [
26]. They included 30 percent from the Los Angeles area, 19 percent from the San Francisco Bay Area, and 7 percent from the Northwest. The predominance of Asian American-led, multiracial congregations on the West Coast can be explained by their larger and longer historical presence in this region of the country, as well as the greater acceptance of ethnic diversity fostered there. In contrast, Midwestern pastors make up only 11 percent of our respondents, just as Midwesterners compose 12 percent of the Asian American population. The South, with 19 percent of the Asian American population, is underrepresented in our sample. We interviewed only one Southern minister in Texas. While disappointing, this result was not entirely surprising since the South has higher numbers of recent immigrants, especially from South Asia, who are more tied to ethnic churches than American-born Asians of East Asian descent.
5. Asian American-Led Multiracial Congregations
Each of the ministers we spoke with had a different story to tell about why and how his church became more diverse. A few of their churches were started as multiracial, but most transition from monoracial to multiracial. We asked those in the latter group why their church moved in this direction. Two patterns were evident. Nineteen (70 percent) of the churches made a clear decision to become multiracial, while the others found themselves moving in this direction unintentionally or reluctantly as they were forced to respond to changes in their membership and their neighborhoods.
5.1. Reasons for Becoming a MRC
In many cases ministers reported that their movement toward racial diversity has been a gradual and natural progression. For example, a minister from Oregon explained that though his church began ten years ago with a Japanese-American membership, intermarriage has naturally moved the church toward greater diversity.
Multicultural marriages have had a lot to do with our church becoming multiethnic. While this progression from a pan-Asian church commenced naturally, the church is now in process of intentionally merging with another church which is predominantly Caucasian. This merger is occurring because there have been so many Asian American-Caucasian intermarriages over the past five years.
As the internal demographics changed, members gradually became more interested in diversity issues and began to think intentionally about becoming a multiracial church. While intermarriage was noted as a causal factor by several ministers, in other cases it was the changing neighborhood demographics that pushed the church to broaden its focus. One Midwestern pastor shared that his church’s transformation began when a non-Asian visitor walked into the Korean American church because it was the closest church to his house. This recent immigrant from Africa enjoyed the preaching and fellowship and soon brought his large extended family. A few years later, the church supports an African choir and has begun reaching out to other new immigrant groups. Other churches decided to become more intentional about diversity when it became clear that their Asian focus was too exclusive. One minister described the process of change as “reluctant submission.” He explained, “Being in a Hispanic and African American community, it didn’t seem right to segregate ourselves and keep putting up walls and fences.” He believes the church’s reluctance to change continues to impede their progress in reaching those in the surrounding community.
For those churches that were intentional about becoming more diverse, ministers provided both theological and social rationales. Thirty-three percent stated that they wanted the church to reflect the diversity of the early Christian church or the future gathering of all the tribes and nations after the Second Coming. Almost the same number (30 percent) stressed the importance of reflecting the diversity of the local community or the United States as a whole. As one pastor in the Northeast explained, “In order for the church to be a safe place for different people to come to; it would have to be diverse. We didn’t feel we had a choice in the matter.” In almost every case, the catalyst for change was the pastor who felt called to challenge his congregants to move beyond their ethnic enclave, but in one case, the pastor noted it was the young adults of the church that first began to question the theological validity of the ethnic church.
5.2. Overcoming Barriers to Diversity
Research has shown that it is much easier to start a MRC from scratch than to transition a monoracial church to a multiracial church. We were very interested to learn about the challenges Asian American evangelical ministers face when leading a congregation through this process. In
Against All Odds: The Struggle of Racial Integration in Religious Organizations, Brad Christerson, Korie Edwards and Michael Emerson identify several factors that contribute strongly to the instability of multiracial congregations [
27]. These include (1) internal organizational dynamics, such as the “niche edge effect” in which minority members are more likely to feel marginalized and, thus, more likely to leave; (2) external socioeconomic structures, including the greater sense of entitlement that Whites holds; and (3) internal religious dynamics, whereby members may be less tolerant of other cultural styles because of their religious ethnocentrism. These destabilizing factors are present in the Asian American-led MRCs we learned about through our interviews, but their effects are minimized by strong homogeneity in age and socioeconomic status as well as the shared cultural values of Whites and Asians who make up the majority of these congregations.
With a few exceptions, the congregations we learned about through our interviews are relatively new churches with only one or two generations represented in the congregation. Because their members come primarily from Generation X and Y and thus grew up in a post-Civil Rights era, they are more likely to value multiraciality and espouse non-prejudicial attitudes [
8,
12]. For these younger Americans, segregated churches are a relic from the ugly history of race relations in the United States. Voicing the value for diversity so characteristic of this generation, a pastor from New Jersey asserts that the postmodern church is necessarily multiracial:
As a member myself of Generation X, I think the construction of the American church in the postmodern world should strive for diversity. A church that does not cross this barrier is misplaced in our contemporary world.
Targeting young adults has been key to growing diversely, according to a Texan minister we spoke with, whose church membership is on average 22 years old. To reach this generation, his church targeted young adults at a nearby college by emphasizing their common life experiences.
A lot of people we reach, we call them “irreligious spirituals.” People who are spiritual but disinterested or angry at the church. That specific group, and the culture and language that comes with it, transcends the differences of race. And because we were reaching out to that specific segment, people of different ethnicities and races were able to identify with something that transcended their own cultural background.
Because many Asian American-led MRCs are monogenerational or bigenerational, they are able to avoid the common generational conflicts over worship style and draw on a shared appreciation of contemporary music and multimedia in worship.
In addition to age and socioeconomic homogeneity, the Asian American-led multiracial congregations we learned about are predominantly composed of Asians and Whites, with Latinos, Blacks and persons of mixed-ethnic heritage making up much smaller percentages of the whole. Marriage between Whites and Asian is a major reason why Whites attended predominantly Asian American congregations, but some also join because of prior mission experience in Asia or a strong commitment to racial reconciliation. Another reason for the prevalence of Asian-White multiracial congregations is that when Asian Americans join White-dominant congregations they find this setting familiar since they are already accustomed to negotiating within mainstream White culture. It was also noted that since the way Asian Americans live, speak, and worship has a great deal in common with White Americans, Whites and Asians have more readily formed mixed congregations than other racial groups.
Most of the ministers we interviewed led MRCs made up of White and Asian members. They had few Latinos or African Americans members in their churches. When asked why they had difficulty attracting Latinos and African Americans, pastors identified residential segregation, language, and worship style as barriers to reaching Latinos and Blacks. In regard to the last barrier of worship style, it was noted repeatedly that the distance between American-Born Asian and White worship style was much easier to bridge than that between Asians, African Americans and Latinos [
28]. One minister also claimed that being accepted as “honorary Whites” puts Asian American pastors at a disadvantage when trying to attract Latinos and especially African Americans to their congregations.
Asian American-led MRCS are also strongly homogeneous in terms of socioeconomic class. As stated earlier, many of the churches we learned about are recent start-ups targeting either university students or urban professionals. None of the congregations has been very successful at drawing in neighbors who are low-income, even though some of the churches support ministry programs serving their low-income neighbors. Because Asian Americans and Whites in these congregations come from similar neighborhoods, schools, workplaces, and social networks, they have thus far been able to overcome the destabilizing factors identified by Christerson
et al. in
Against All Odds. Though cultural familiarity and commonalities are clearly a stabilizing factor in Asian-White churches, tensions between Whites and Asians continue to exist in these churches and there was no suggestion from the pastors we interviewed that Asians and Whites shared completely a common culture or that Asians had “become White.”
5 5.3. Colorblind versus Colorconscious
As noted in the literature review, scholars have sought to understand how MRCs approach race in order to gauge their potential to contribute to racial equality in the United States. We identified colorblind and colorconscious as ideal types of MRCs and asked ministers which of these types best characterizes how their church approaches diversity. Though we were prepared to explain what we meant by these terms (
i.e., a colorblind approach to diversity ignores racial and ethnic differences and a colorconscious approach recognizes racial and ethnic) none of the interviewees asked for an explanation. For some this question was easy to answer like the Northeast minister who quickly replied, “This church most certainly follows a colorconscious, inclusive approach. A colorblind approach would be inappropriate.” Many ministers found this question more difficult to answer because they could point to ways in which their church took both approaches. Here’s an example from a Western pastor whose church is roughly 80 percent Asian American and 20 percent Caucasian:
I’d say we’d probably be following more closely the colorblind approach. When I talk, I do not make any shared references about Asian culture. For example, I don’t say, ‘I value this, I have strict parents, blah, blah, blah.’ I’ll usually assume I’m speaking to Euro-Americans…. The only place where we are more colorconscious is we almost practice reverse discrimination in terms of getting people up front. I think people who do announcements we definitely prefer females to do it, and possibly we have Caucasian females do it. And also in terms of the band members we’ve got Caucasian folks in there. We’d like as much as possible if the whole band isn’t Asian up there. Right now we’re in the process of selecting an elder board. I wouldn’t call this a reverse affirmative action, but we’re definitely conscious of wanting our elder board members, our leadership board, to kind of lead the way and make a statement in regards to our approach towards ethnicity.
Though many churches utilize both colorblind and colorconscious approaches at various times, all the ministers were able to identify one type as the primary approach: 19 churches (70 percent) as colorconscious and the remaining eight as colorblind. It is important to note that of the eight colorblind-type churches, three have a White-majority membership, while all of the colorconscious-type churches have an Asian American-majority membership. Given the findings of Emerson and Smith and Edwards, we were not surprised that these White-majority MRCs, even when led by as Asian American minister, utilize a colorblind approach to racial diversity [
9,
13].
What does the colorconscious approach look like in practice? Most often ministers noted their efforts to hire a racially-diverse staff and present diverse faces during worship. At a minimum, being colorconscious means recognizing that there are ethnic and racial differences among members. All of the colorconscious congregations affirm publicly that these differences are real and Christians need to be aware of how they matter in the lives of church members and in American society. Here are a few examples pastors offered for how their churches do this:
All the people that I put up in front, all of the people who were presiding, leading music, ushering, they were all non-Asian…. We have a mixed staff, mixed leadership. That’s very important. If you’re not intentional, you’re ultimately going to be a church that reflects one particular culture.
(Northeast region)
Intentionally diverse staff with Asian, Black, White, Very intentionally making lay leadership reflecting of congregation, but these leaders also must be prepared and spiritually mature and trained.
(Midwestern region)
We’re having a missions weekend so we’re having foods from different continents. We name our classrooms after the different cities of the continents.
(Mid-Atlantic region)
We’ve made a real strong effort to diversify both our leadership, our staff.
(Northeast region)
Each week, a member of the church from a different country offers a Christian prayer, stated in his or her native tongue, to the entire congregation.
(Northeast region)
Our church has an internal “Diversity Team,” which is a group of people comprising the various races represented within the church. The team works together and teaches regular courses on multiculturalism to church members…. There is an open dialogue within the church regarding issues of race and multiethnicity. The leadership within the church is also very multiethnic. Church leaders also go through three months of “diversity training” at the church. During this training, the Bible is studied and leaders are educated on what God has to say about multiculturalism.”
(Midwest region)
I preach on the theme regularly. “We have an “arrangement” in America: minorities are co-opted into the white middle class euroamerican system. The reverse happens when whites come to Korean church. But our vision is to change that. We’re not going to treat them like they have treated Koreans.”
(Midwest region)
In a variety of ways, these MRCs seek to educate and inspire members to live out the biblical mandate to “break down the walls of hostility.” Several pastors told us this message is applied beyond interpersonal relations to racial inequality in the United States. A pastor from the Northeast shared that for his congregants, “It’s not the PC thing for them; it’s not kind of a superficial sort of thing, they really are concerned about not just being an ethnically-diverse church but concerned about socioeconomic diversity, concerned about racial justice issues.” One Midwestern pastor who regularly preaches on race issues, could not imagine ignoring racism because it is the “mega-idolatry and meta-narrative of American history.” He shared proudly that his church is not afraid to deal with these difficult issues: “We are prophetic, naming names, naming the powers and principalities.” These two pastors were not the only ones who talked about working toward racial justice, but it is important to recognize that the colorconscious approach does not necessarily imply working for racial justice. We asked each minister a series of questions to gauge their attitudes on racial issues in America and turn now to their responses.
5.4. Racial Attitudes of Asian American Ministers of MRCs
Earlier we described the stark divide between the racial attitudes of White and Black evangelicals, which Michael Emerson and Christian Smith analyze in
Divided by Faith [
9]. To learn how our sample of Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs compares to White and Black evangelicals, we asked the same four questions on race from the General Social Survey that Emerson and Smith use in their analysis ([
8], pp. 94–98). When asked, “Do you think our country has a race problem?” all 27 ministers answered yes. Next we asked how they explain the fact that Blacks on average have worse jobs, income, and housing than Whites giving them two options that point toward individual deficiencies and two options that point to social-structural deficiencies. None of the interviewees attributed these inequalities to Black’s inborn abilities, but one minister attributed them to a lack of willpower. Table 1 compares the responses of our interviewees with those of White and Black evangelicals in general. While 62 percent of White evangelicals and 31 percent of Black evangelicals pointed to individual deficiencies of Blacks, the Asian American MRC ministers we interviewed pointed to structural explanations for the gap in jobs, income and housing. Sixty-seven percent of the ministers agreed that a lack of educational opportunities is to blame and 59 percent agreed that economic disparity is “mainly due to discrimination.” Their responses are much closer to the explanations given by conservative Black Protestants than those given by conservative White Protestants (
Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Evangelical Explanations of Racial Inequality.
Figure 1.
Evangelical Explanations of Racial Inequality.
When it comes to explaining the economic marginalization of Black Americans, our sample of Asian American ministers of MRCs clearly favored structural explanations. We were curious if they would use structural explanations for the economic success of Asian Americans in the United States. We asked respondents to agree or disagree with four explanations for Asian American success, two of which were clearly individualistic and two structural kinds of explanations. The results are listed in
Figure 2. None of the ministers agreed that Asian American success is due to their inborn abilities and only one attributed this success to motivation and willpower. Instead, the vast majority gave structural explanations: 63 percent pointed to the fact that Asians immigrate with better educational training and middle class backgrounds, and 52 percent agreed that Asians have greater opportunities through their social networks. Whether thinking about economic status of Black Americans or Asian Americans, our sample of Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs, did not rely on individualistic explanations for economic disparity as White evangelicals do.
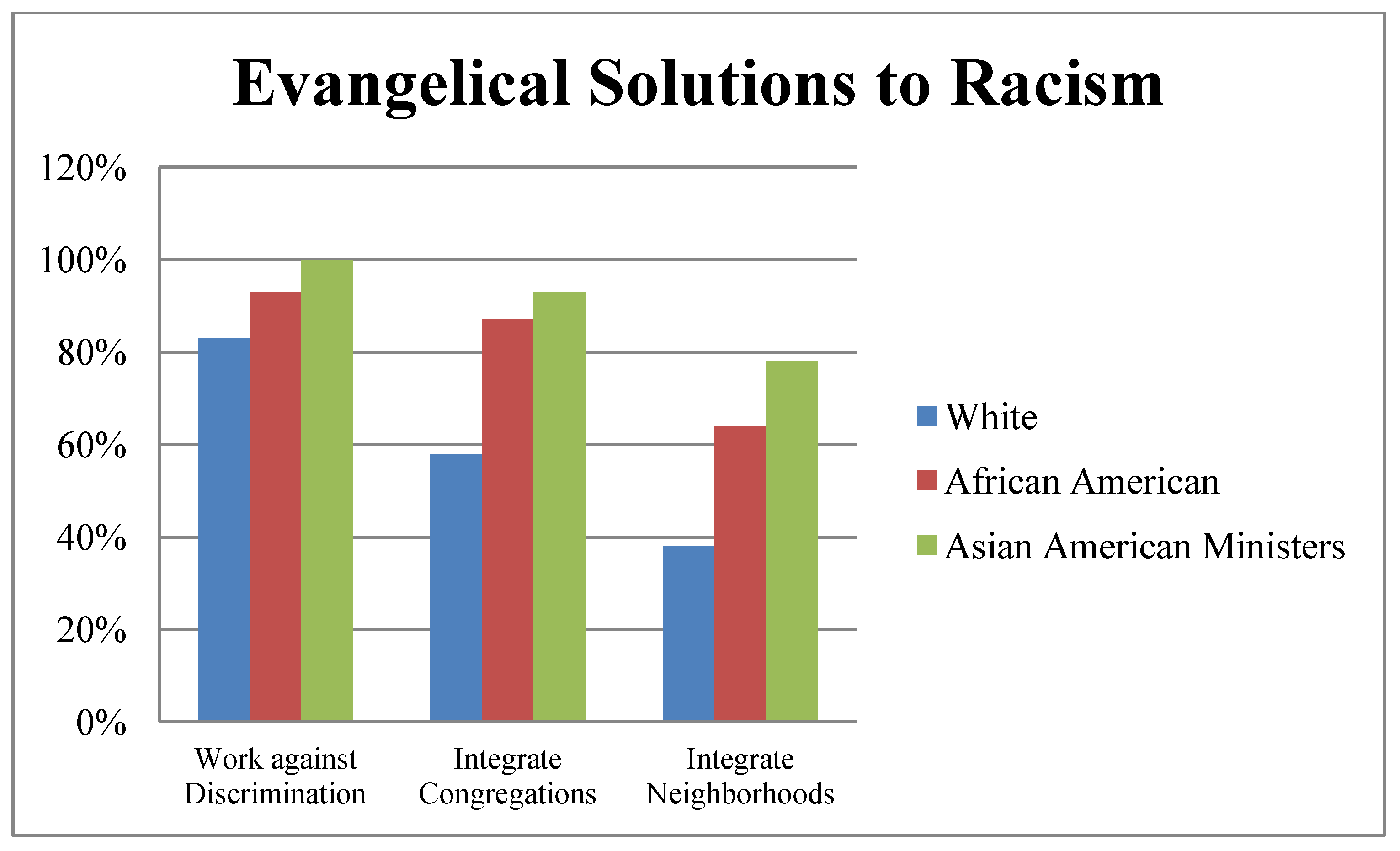
Next, we asked questions regarding how Christians should work against racism. Again their responses looked much more like those of Black evangelicals than those of White evangelicals. All the ministers said it is very important for Christians to get to know people of another race and to work against discrimination in the job market and legal system. Ninety-three percent agreed that Christians should work to racially integrate congregations, and 78 percent agreed that Christians should work to integrate residential neighborhoods compared with 58 percent and 38 percent of White evangelicals respectively. It is interesting to note that our sample of Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs had more interest in integrating congregations and neighborhoods than Black evangelicals who support these goals 87 percent and 64 percent of the time (
Figure 2) ([
9], pp. 94–98).
Because of the small-size and sampling methods used for our study, we cannot assume these results are representative of Asian American evangelical ministers of MRCs generally, or of Asian American evangelicals more broadly. Given their experience as racial minorities in the United States, however, it is not surprising that the ministers we interviewed are more attuned than White evangelicals to the reality of racialization. For most of those we interviewed, this awareness was directly related to their preference for a colorconscious approach to MRC-ministry. As one pastor, who identified his approach as colorconscious, explained:
I don’t embrace multiculturalism, but I do believe in ultimate truth…. If the gospel is all about, as Paul says in Cor. 2:5, reconciliation, then how can we talk about reconciliation, about the peace that we call shalom, about unity in diversity, without demonstrating that in the church? We need to talk about racial issues, social action and mercy issues, which most English-speaking Asian American churches rarely address.
Figure 2.
Evangelical Solutions to Racism.
Figure 2.
Evangelical Solutions to Racism.
6. Asian Americans as Bridge Builders
Seventeen of the twenty-seven churches we learned about through interviews have no more than eighty percent of one racial group thus meeting the sociological definition of a MRC. Given the rarity of multiracial Protestant churches across the country, we found this number impressive and asked the ministers to share their thoughts on this success, as well as what advantages and disadvantages Asian American ministers face in leading MRCs compared to ministers from other racial groups. While they all acknowledged that being Asian American had its disadvantages in leading multiracial churches, such as being seen as too White, they were not discouraged in their attempts at racial integration and noted many more advantages. Interestingly, most of the advantages they identified are not based on the cultural assets of being Asian or on their educational training. Instead, their ability to lead MRCS depends upon the unique position of Asian Americans in the racialized context of the United States.
When asked, “Do you think Asian Americans will be more successful in creating multiracial churches than other ethnic groups?” 17 answered yes and, of these, 13 attributed this to their racial minority status and experience of racial prejudice, which help them relate sympathetically with other minorities. As discussed in
Section 5.4 on racial attitudes, all of the ministers interviewed acknowledge that the United States has a race problem, and almost all identified structural causes of this problem. Not surprisingly, they related discrimination against Blacks to that experienced by Asian Americans. For example, a pastor from the Western region related the stereotypes of African Americans to those directed at Asian Americans:
There are false beliefs about Blacks propagated by media sources. This same problem about the public perception of Asian Americans is constructed through the media. I see Asians on television presented as effeminate, but I know Korean culture is highly masculine.
As minorities in the United States, Asian American ministers are sensitive to the experience of being a minority. This transfers into paying attention to the racial minorities within their own churches. One minister from the Midwest explained that he does not want non-Asian members to feel co-opted by the Asian majority the way Asians have been co-opted by the middle-class Euro-American system: “We’re not going to treat them like they have treated Koreans.” They are especially attuned to the need to diversify their staff and leadership in order to make minorities within the congregation feel more comfortable and acknowledged. A Southern Californian minister summarized the advantage of Asian American leadership this way:
We are familiar with struggle, and understand minorities struggling to succeed in this country. I feel Asian American ministers will be highly sensitive to the needs of minority groups.
Besides understanding the marginalization experienced by people of color, the ministers we interviewed believe that their experience in negotiating different social contexts also serves as an advantage in multiracial ministry. As racial minorities, Asian Americans must learn to be adaptable and culturally flexible in this country. These skills, which their White counterparts have not needed to develop as the dominant majority, are a valuable asset in bringing diverse groups together. A pastor from the Northeast explains about the minority experience of adapting to dominant society:
I think minority leadership would be more successful [at creating multiracial congregations] than majority leadership. We know by experience what it means to be adaptable to the system, especially living in America.
In addition, it was pointed out that Asian Americans are perceived in the wider culture as un-threatening and a “friendly race.” One minister gave us this example of how a church member has been identified in his international corporation as a cultural bridge-builder:
One of the guys at my church, in the tech business, is flying all over the world working on problems between countries. He’s Japanese and they hired him to do this because he’s more willing to massage a situation than come straight on like the ugly American. Most Asian Americans are like that—we are in the position to do reconciliation.
The fact that Asian Americans stand outside of the historical division between Whites and Blacks in the United States, is another important advantage that was noted by several ministers. Because of the United States’ history of slavery, the deeply ingrained antagonism between Whites and Blacks, and their sharply different worship styles, it is not hard to understand why Sunday morning continues to be the most segregated hour in America. Yet, Asian Americans, as well as Latinos, are outside of this Black/White divide and are more likely to be accepted as leaders by members of both of these groups.
Interviewees also suggested that because of their ambiguous racial status Asian Americans may be sought after to serve as reconcilers and pastors or MRCs. One minister suggested people of color might be more attracted to an Asian American-led multiracial church, as “a break from traditional Whiteness attached to American Christian churches.” In addition, for those Whites wanting to join a multiracial church, an Asian American leader may be perceived as less threatening than a Black minister. Not everyone we interviewed agreed that being perceived as unthreatening is an advantage. A pastor in the West argued that Whites may associate unthreatening with a lack of leadership skills:
In the general public you’re more likely to see Asians following a Caucasian than a Caucasian following an Asian. There are racial stereotypes that the general cultural will trust an Asian for science or technical expertise. But to be a strong moral leader that they’re looking for, they don’t think of Asians. It’s more of an uphill battle for an Asian to go through that [stereotype] that a Caucasian doesn’t have to.
Most of those we interviewed saw the unique placement of Asian Americans within the American racial hierarchy as an advantage positioning them to be more likely bridge-builders than Black or White pastors, and yet, this
potential for leadership is also limited by several important factors.
The pastors we interviewed had strong criticisms of Asian American churches and Asian American ministers that severely dampen their optimism about Asian Americans establishing multiracial congregations. The primary reason why pastors felt other Asian Americans would not lead the Christian multiracial movement is that they believe many Asians are too “exclusive” and “clannish.” A Midwestern minister explains that many Asian Americans, especially immigrants, are self-segregated in their own communities:
Asian Americans are largely enclosed within their own communities and the majority live in this bubble. To be effective in the task [of building multiracial churches], Asian Americans need to gain wider experiences than those in the bubble have.
In fact, none of the ministers even foresaw that we would be able to identify 17 Asian American ministers leading multiracial congregations. Instead, their perception was that most Asian American attempts at multiracial churches were unable to move beyond a pan-Asian membership. A Minnesotan minister complains,
Many Asian Americans are still very ethnocentric. Understanding the scripture as a tool to see the big picture, or thinking outside of an ethnocentric box is something that we really need work on.
This ethnocentrism narrows their visions for their local congregations and even shapes their theology. One different minister called this preference for one’s own group an “innate tribalism,” and shared with all those we interviewed the view that ethnic pride and ethnocentrism result from our sinful nature. This is how they explain why they have a difficult time convincing Asian Americans to look beyond the needs of the ethnic church.
A second substantial challenge interviewees voiced is that Asian American churches have not developed their leaders well. Because most Asian American churches are immigrant congregations, the English-speaking ministers tend to be relegated to youth ministries. They lack opportunities to be creative when their staffing, resources, and salaries are restricted, and they have little power to shape the overall mission of the church. Ministers who do feel called to multiracial ministry often have to form a new church in order break out of the ethnocentric mold. As we have seen from this study, there are many young Asian American ministers doing just that and finding they can inspire others to join them.
7. Asian American Evangelical Leadership
The challenges Asian American evangelical ministers face in developing MRCs also limit their ability to shape the concerns and values of American evangelicalism more broadly. With growing diversity among evangelicals, the need for leaders able to build cultural and racial bridges is greater than ever before if churches are to move beyond self-segregation and model true reconciliation for the larger society. Many Asian Americans clearly have the awareness and skills to rise to this leadership role and across the country, there are Asian American ministers already doing so. Several of the pastors we interviewed have been invited to speak at predominantly White evangelical conferences or to serve on boards of mainstream evangelical organizations. To make a significant impact, however, more leaders are needed who can speak to both Asian Americans and a wider evangelical audience.
The most insightful comments we heard in this regard addressed the need to develop and articulate an Asian American Christian voice. A minister from the Northeast offered this analysis:
Asian Americans have kind of operated as honorary White people in American culture, which has given us no internal authority and we cannot legitimize who we are. We garner a certain amount of acceptance, but we’re being accepted for being Whites rather than being accepted for being Asians. So there has to be a clearer voice as the Asian American community that is not just mimicking White American evangelicalism.
This minister’s comment resonates clearly with the strategies of conforming to White evangelical norms that Antony Alumkal found common in pan-Asian churches [
22]. It does not accurately describe the experience of most of the Asian American ministers we interviewed, however. In our interview sample of 27 ministers, 16 are leading congregations with a colorconscious approach rather than the colorblind approach preferred by White evangelicals. In this way they are not mimicking the norms of White American evangelicalism, but developing a distinctly Asian American evangelical approach to MRC-ministry.
Our interviews suggest that Asian American evangelical MRC-ministry is shaped by three primary assumptions: (1) the United States is a racialized society with a clear race problem that MRCs should work to solve; (2) the United States has a racial hierarchy, divided most clearly between Whites and African Americans with Asian Americans racially-situated in a position to bridge these racial groups; and (3) ethnic and racial difference should be acknowledged and celebrated. We call this combination of sensitivity to racialization and appreciation of diversity “racialized multiculturalism.” Distinct from the colorblind approach that typifies most White churches, and the political activism of many Black churches, racialized multiculturalism enables Asian American ministers to bring together the mission of evangelism to all the nations, with an affirmation of cultural diversity, and a commitment to racial justice. Asian American evangelicals are developing this approach through strong informal networking among Asian American leaders of MRCs across the country. While their impact on the broader evangelical culture will depend in large part on whether White evangelicals are willing to listen to their voices, Asian American leaders are already changing the racial dynamics of American evangelicalism one church at a time.