Griby i Mukhi: A Historical Contextualization of the Esoteric Mushroom Religion of Moscow Conceptualism: Fungal Erotic Imagery of Entheogens and Insects
Abstract
“The most beautiful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and all science. He to whom this emotion is a stranger, who can no longer pause to wonder and stand rapt in awe, is as good as dead: his eyes are closed. The insight into the mystery of life, coupled with fear, has also given rise to religion. To know what is impenetrable to us really exists, manifesting itself as the highest wisdom and the most radiant beauty, which our dull faculties can comprehend only in their most primitive forms—this knowledge, this feeling is at the center of true religiousness.”
1. Preliminary Remarks
2. Introducing the Subject: Esoteric Context and the Fungi
“I have come to the conclusion that much can be learned about music by devoting oneself to the mushroom.”.—John Cage, 1954
2.1. Mushrooms, Humans, and Religious Systems: Analytical Observations
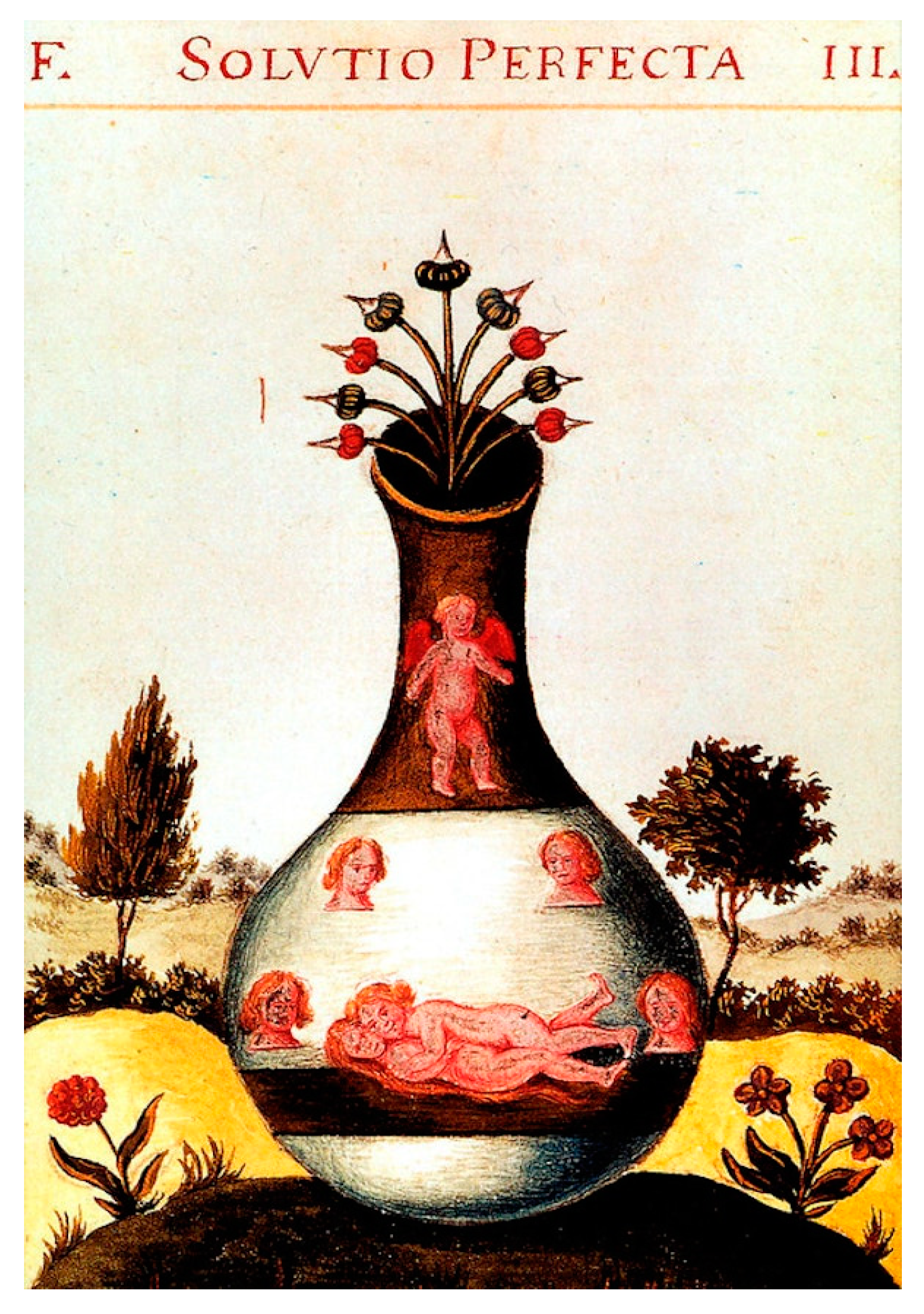
2.2. New Age Esotericism, Gnosticism, and the World of Fungi: The Problematics of Spermic Religious Imagery
Zohar Sitrei Torah 1: 147b–148b, (Jacob’s Journey)‘The secret of secrets: Out of the scorching noon of Isaac,out of the dregs of wine, a fungus emerged, a cluster,male and female together, red as a rose,expanding in many directions and paths.The male is called Sama’el,his female is always included within him.Just as it is on the side of holiness,so it is on the other side:male and female embracing one another.The female of Sama’el is called Serpent,Woman of Whoredom, End of All Flesh, End of Days.Two evil spirits joined together: the spirit of the male is subtle;the spirit of the female is diffused in many ways and pathsbut joined to the spirit of the male.’(Sitrei Torah is translated in (Zohar 1983, p. 77))
“If you force me to say something still more daring, it is his essence to be pregnant (kuein) with all things and to make them.”
“We know you, O intellectual Light, O Life of life, We know you, O Womb of every creature, We know you, O Womb pregnant by the member [physis = phallus] of the Father. We know you, O eternal permanence of the begetting/pregnant Father.”
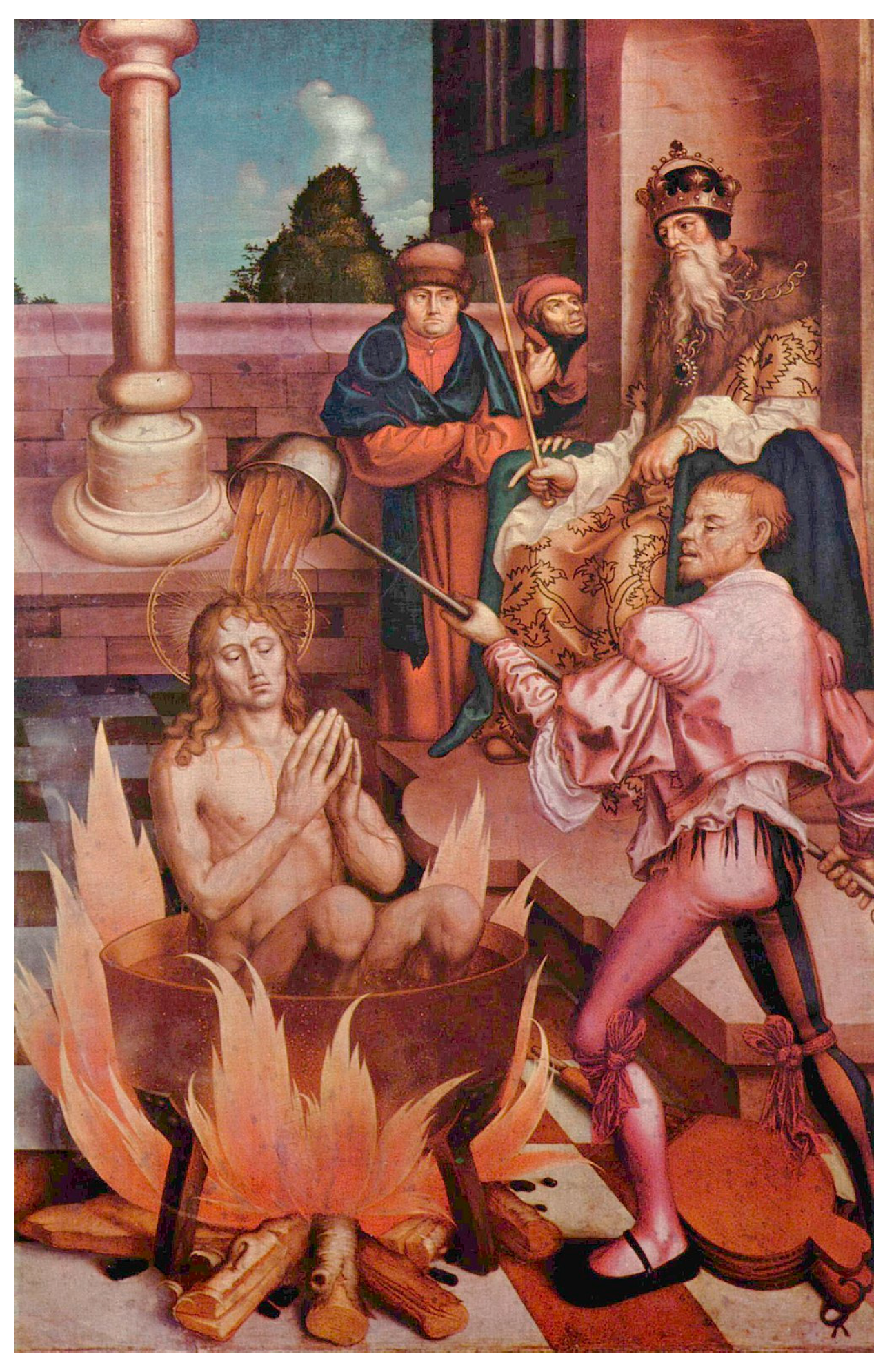
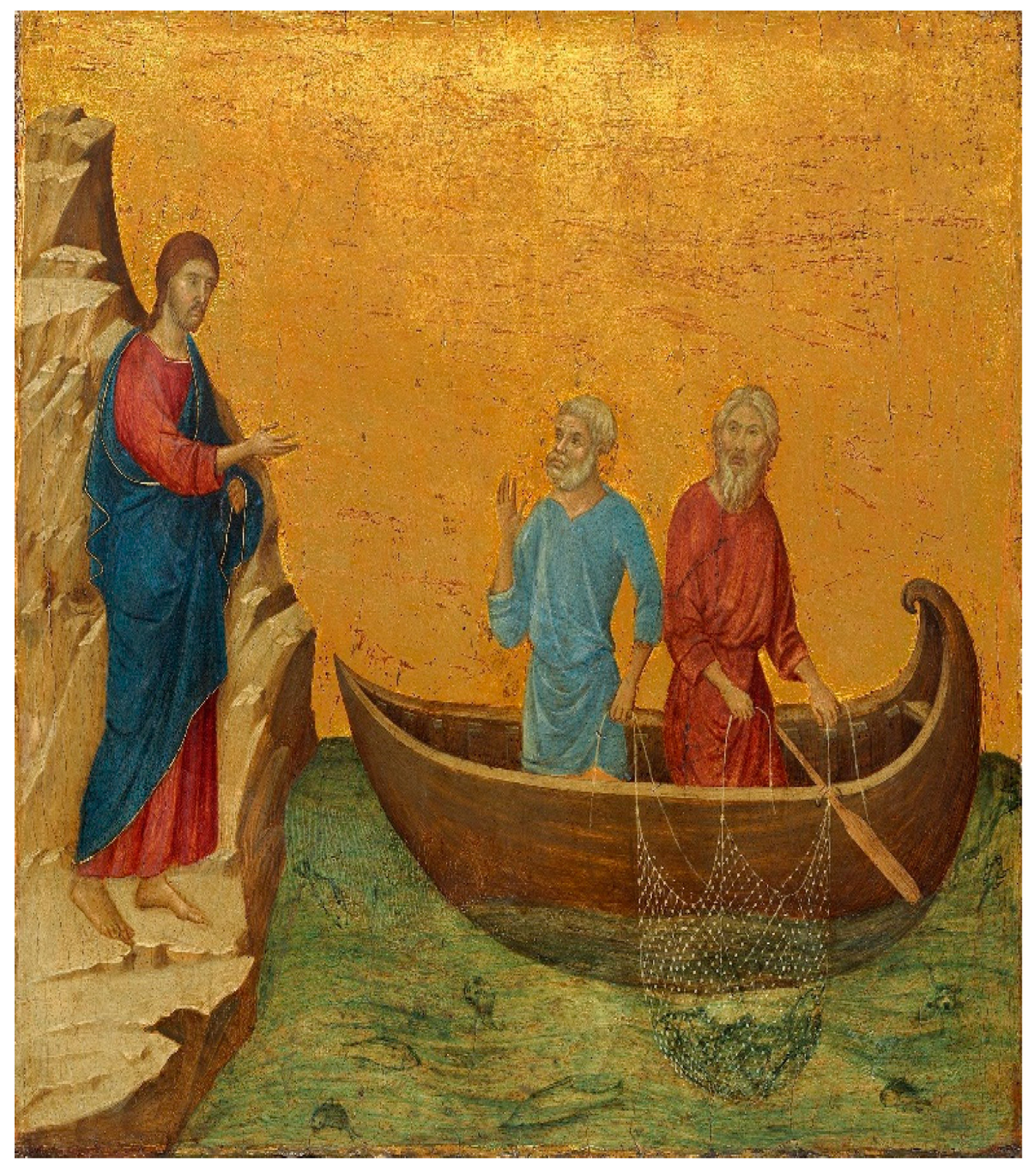
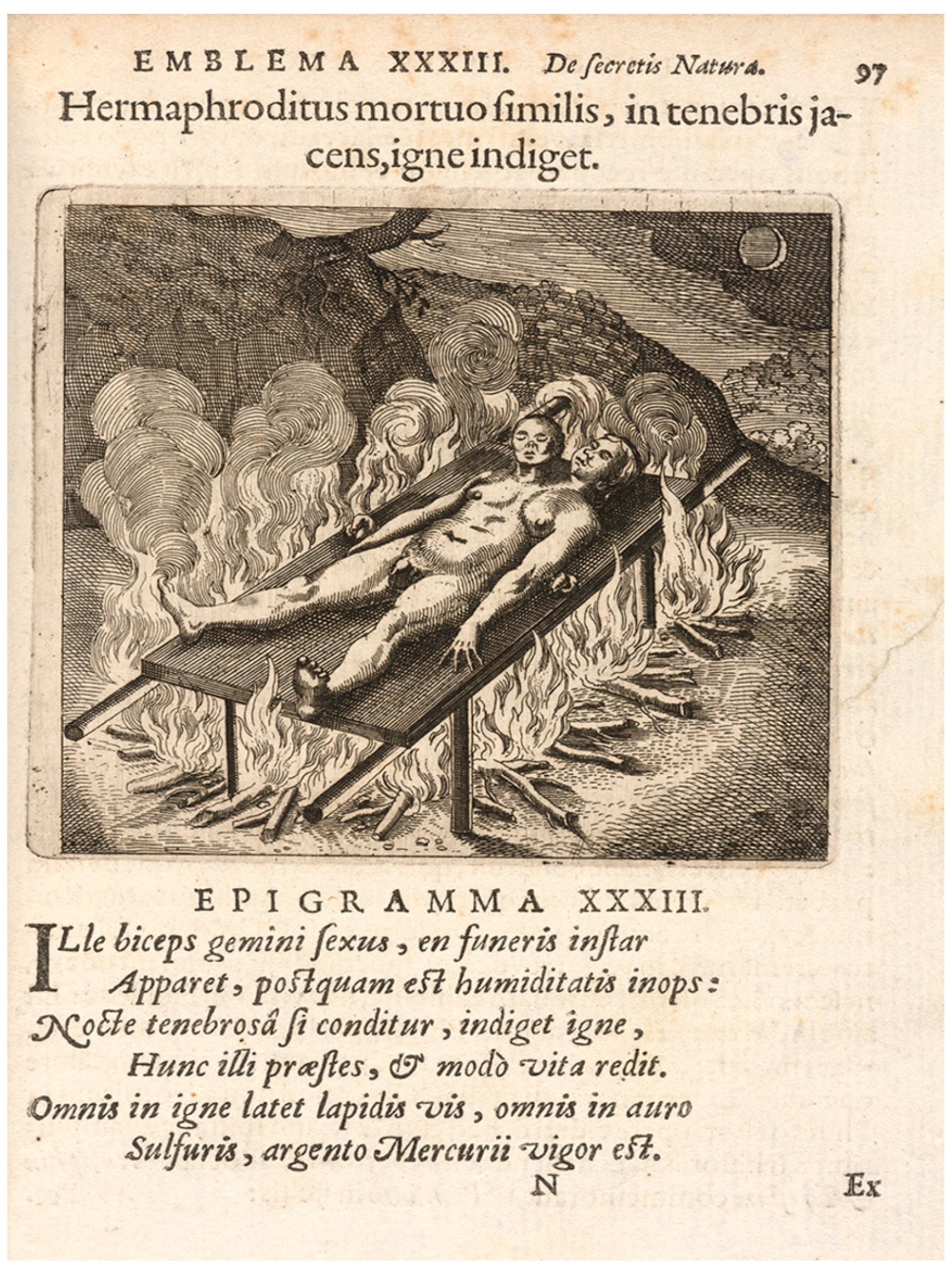
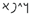 Kipa attributed by Allegro to the Semitic root which surprisingly (coincidentally) also means “mushroom”. (For various light-consuming and light-bearing representations of Peter see Figure 35). Consequently, the Church of Christ is metaphorically envisioned as growing on a colossal rock-mushroom in Allegro’s interpretation: “Saint Peter’s name is an obvious play on the Semitic word ‘pitria’ (פִּטְרִיָּה), general word for ‘mushroom’, and we have seen that his original patronymic Bar-Jonah, is really a fungus name cognate with Paeonia, the Holy Plant…. The sacred fungus was the ‘bolt’ or ‘key’ that gave access to heaven and to hell, a double reference to its shape as a knobbed bolt for opening doors, and to its ability to open the way to new and exciting mystical experiences” (Allegro 1973, p. 72). On the ‘lightning bolt and mushrooms’ see also (Wasson 1956).
Kipa attributed by Allegro to the Semitic root which surprisingly (coincidentally) also means “mushroom”. (For various light-consuming and light-bearing representations of Peter see Figure 35). Consequently, the Church of Christ is metaphorically envisioned as growing on a colossal rock-mushroom in Allegro’s interpretation: “Saint Peter’s name is an obvious play on the Semitic word ‘pitria’ (פִּטְרִיָּה), general word for ‘mushroom’, and we have seen that his original patronymic Bar-Jonah, is really a fungus name cognate with Paeonia, the Holy Plant…. The sacred fungus was the ‘bolt’ or ‘key’ that gave access to heaven and to hell, a double reference to its shape as a knobbed bolt for opening doors, and to its ability to open the way to new and exciting mystical experiences” (Allegro 1973, p. 72). On the ‘lightning bolt and mushrooms’ see also (Wasson 1956).2.3. Fungal Eros: Phallic Occult Esotericism and Russian Cultural Links
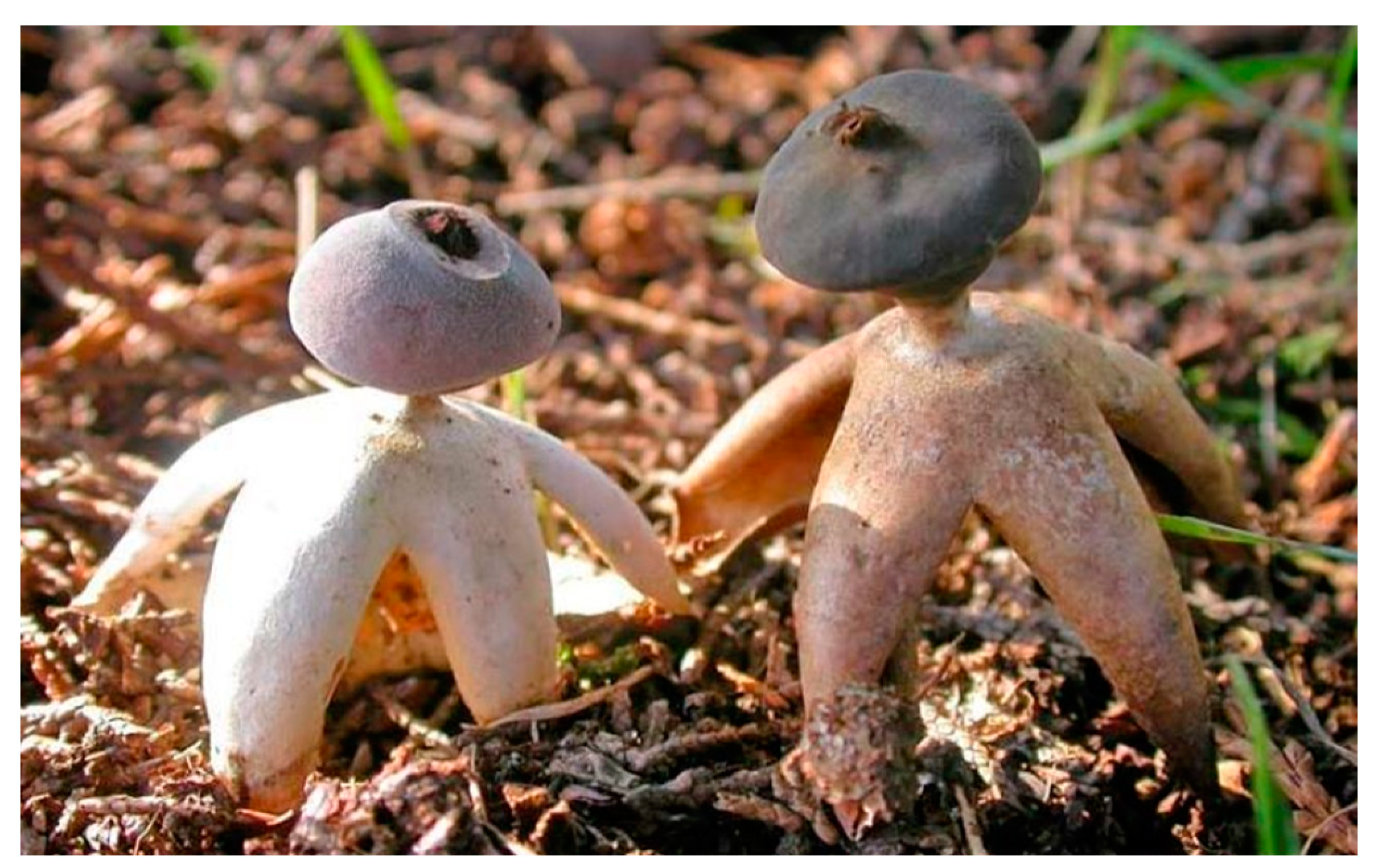
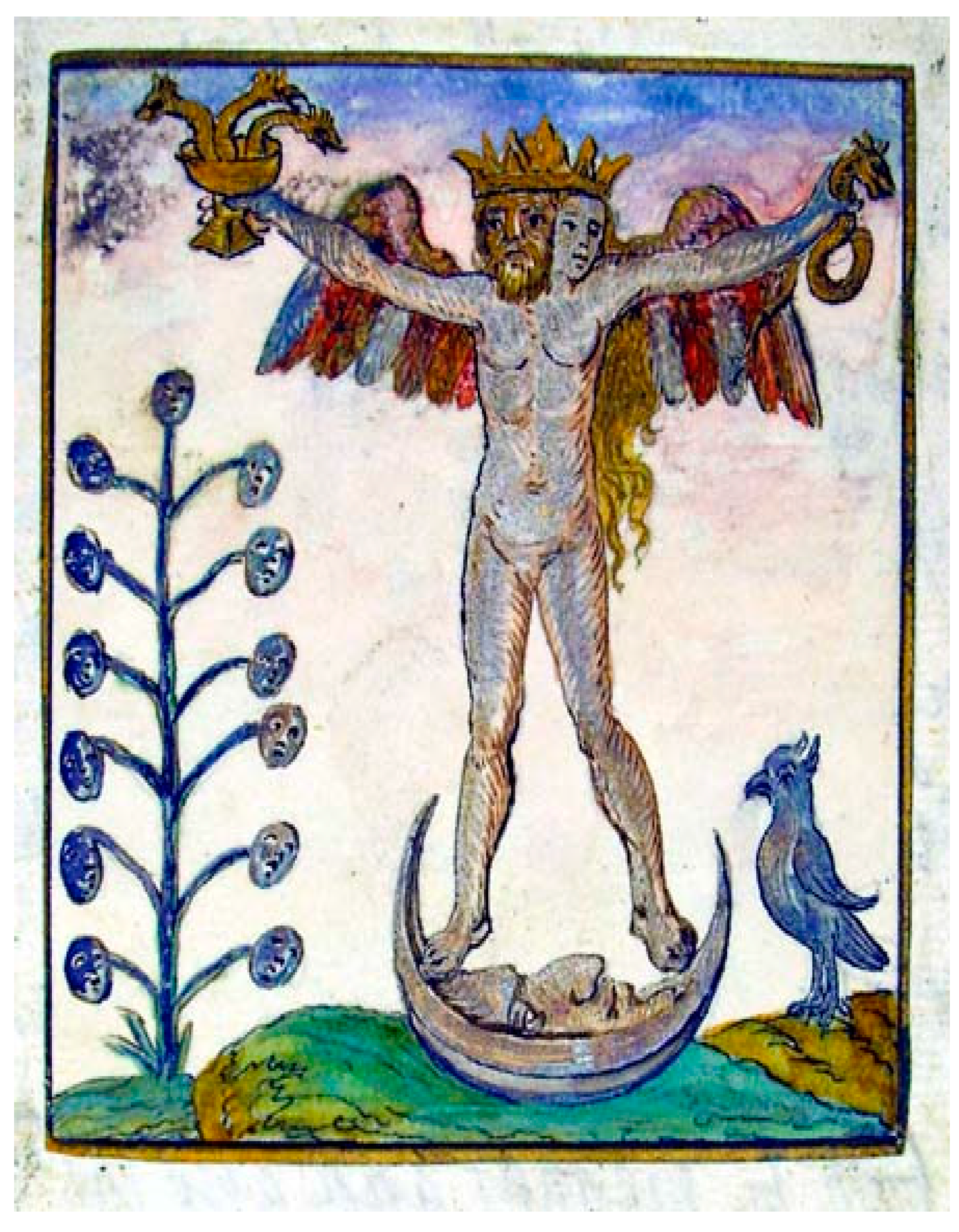
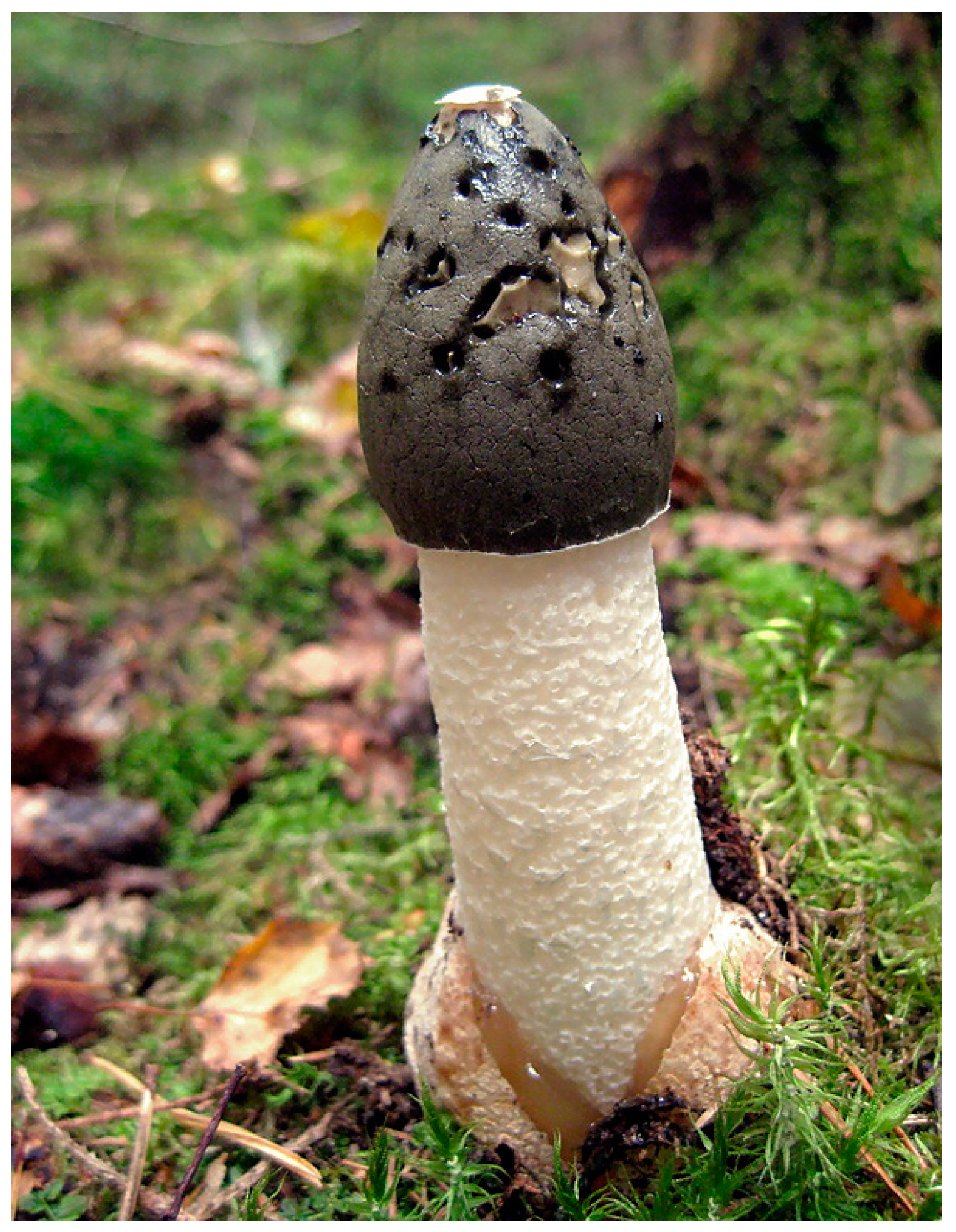
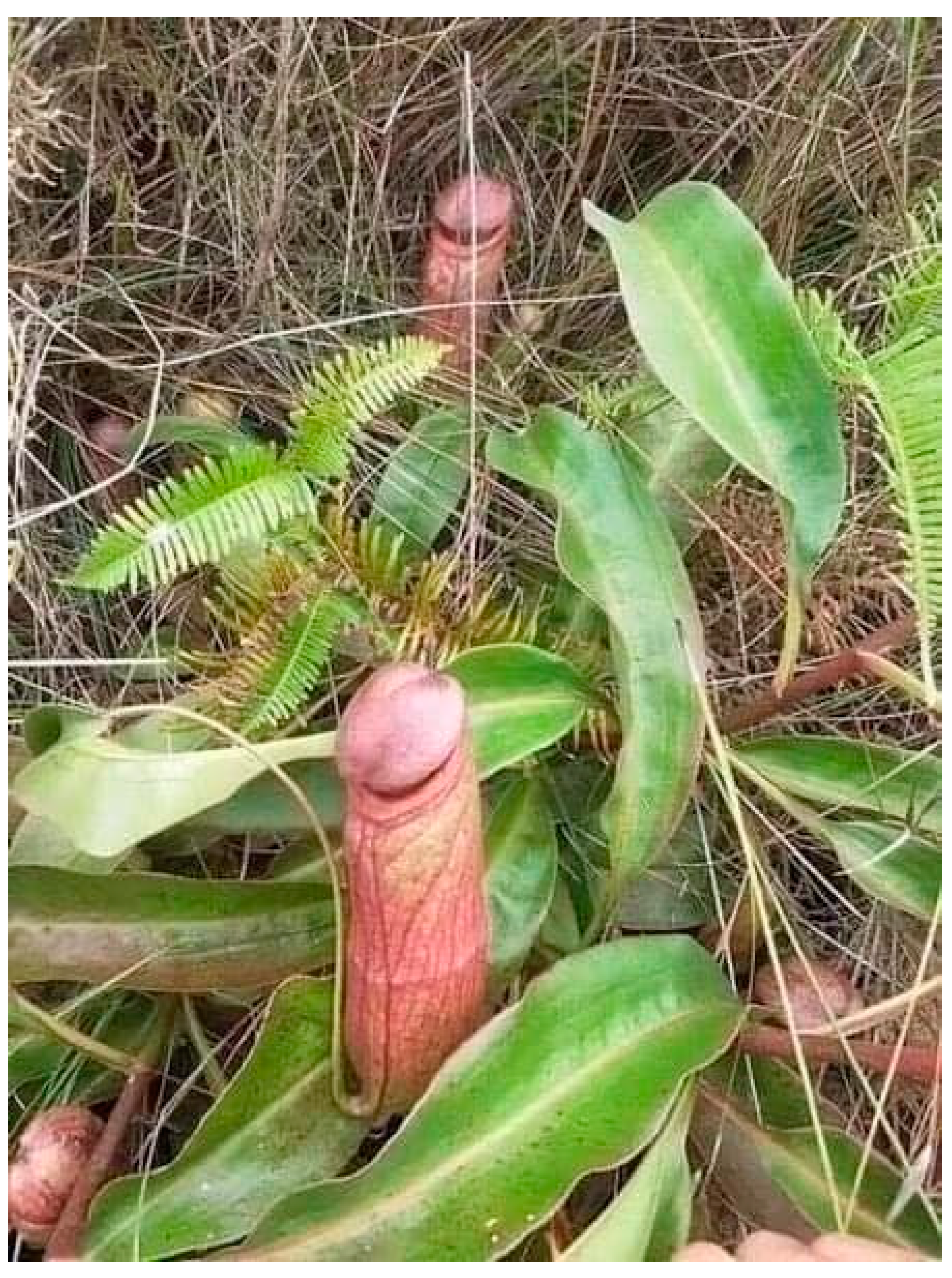
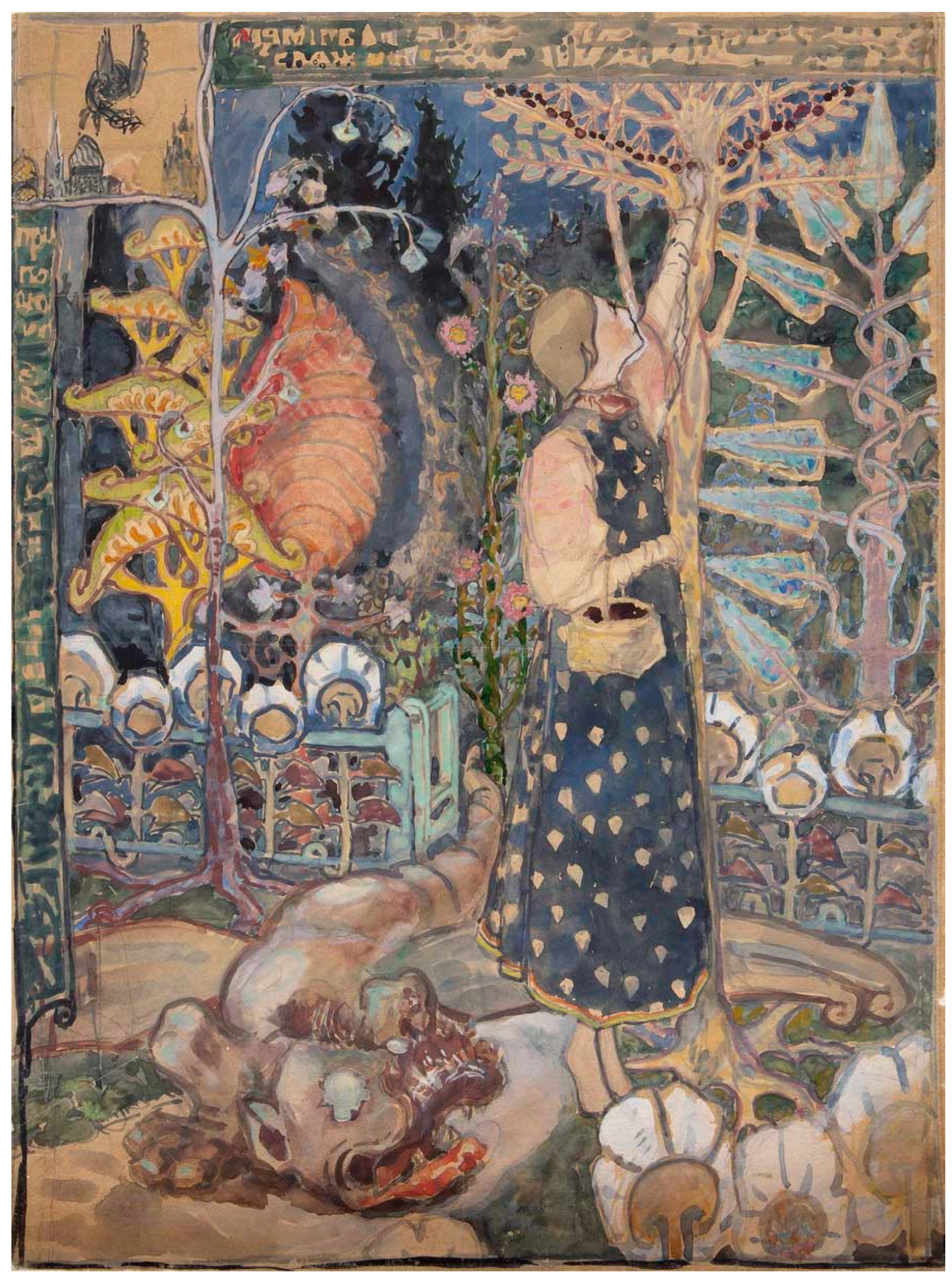
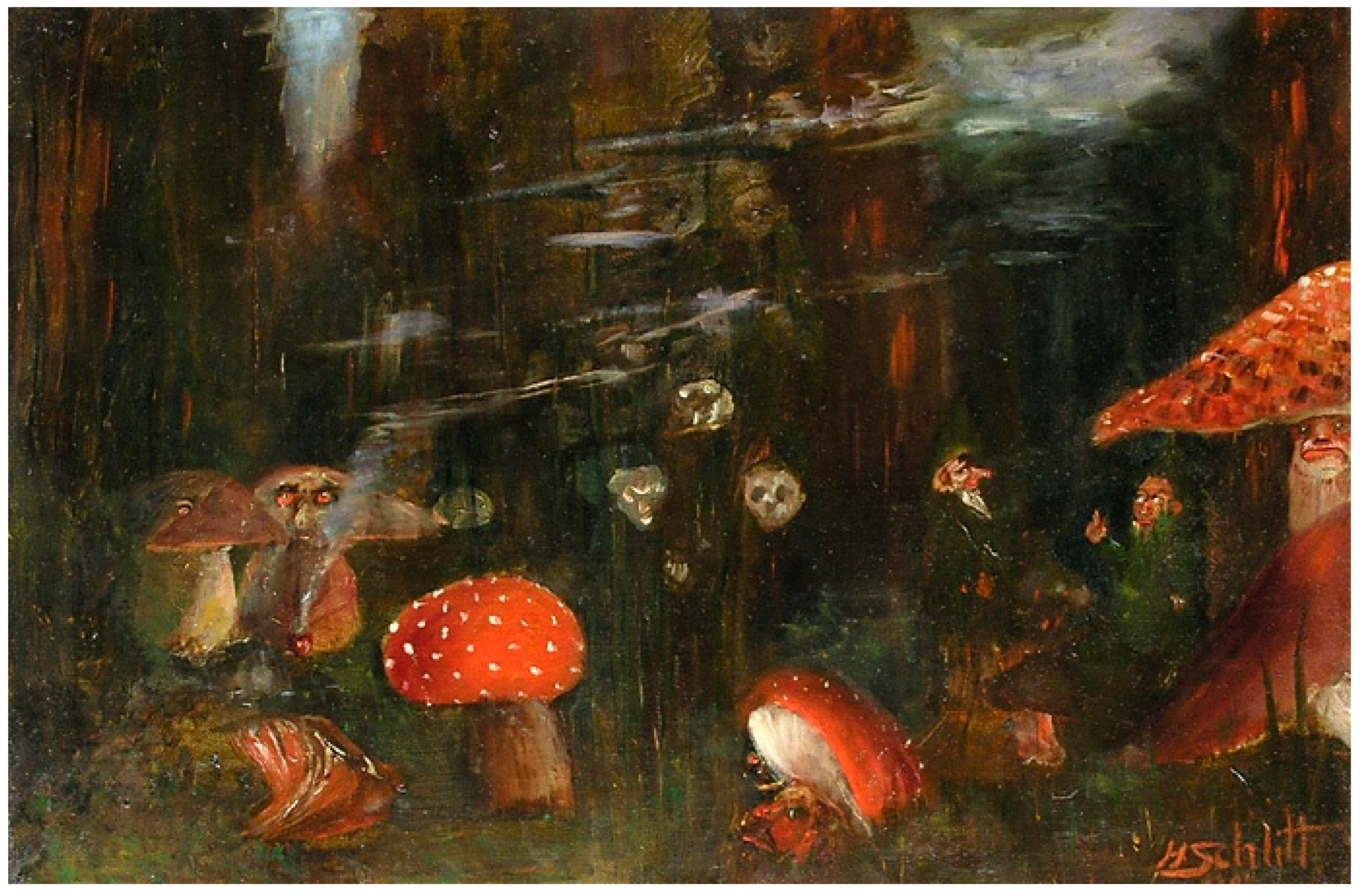
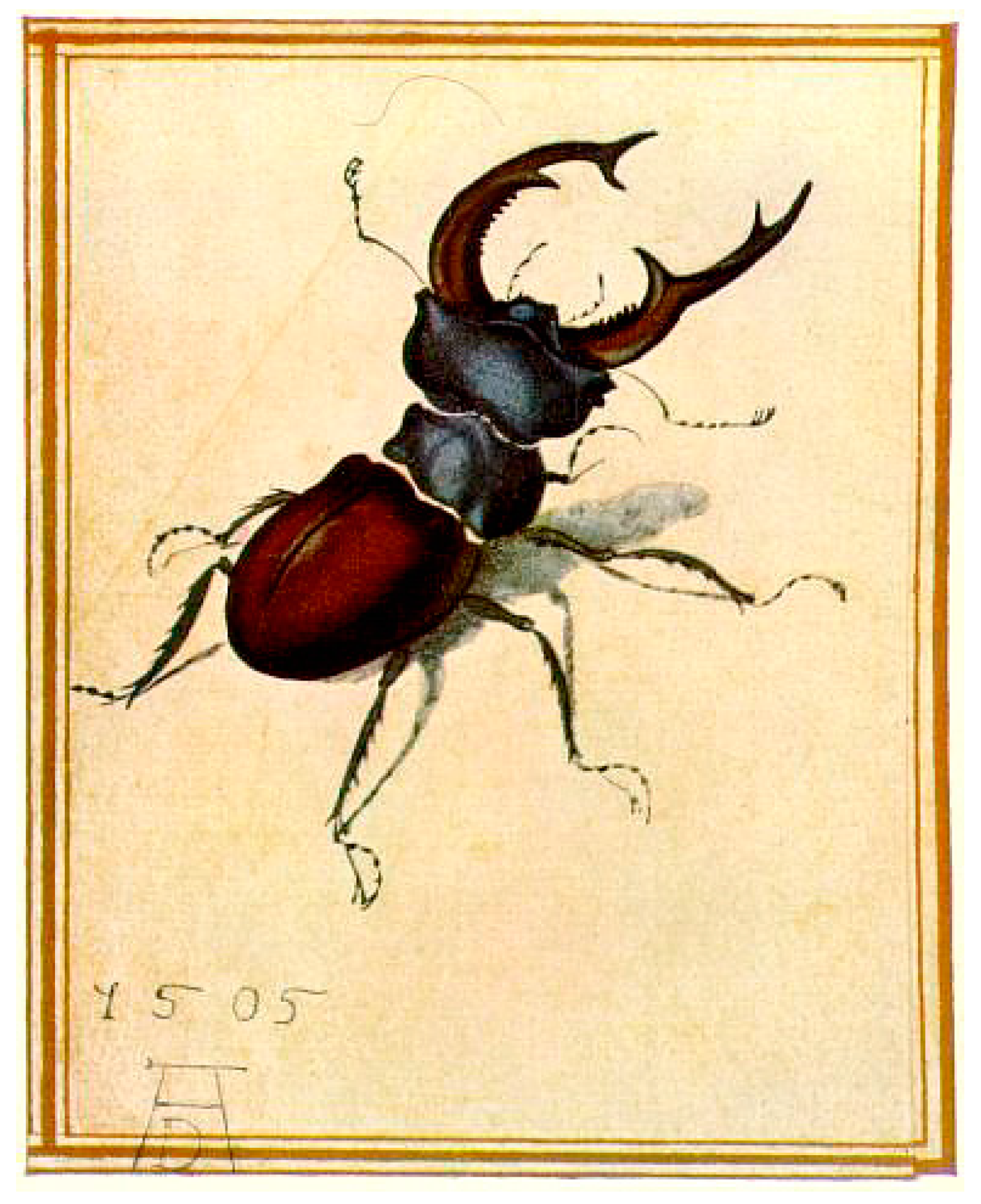
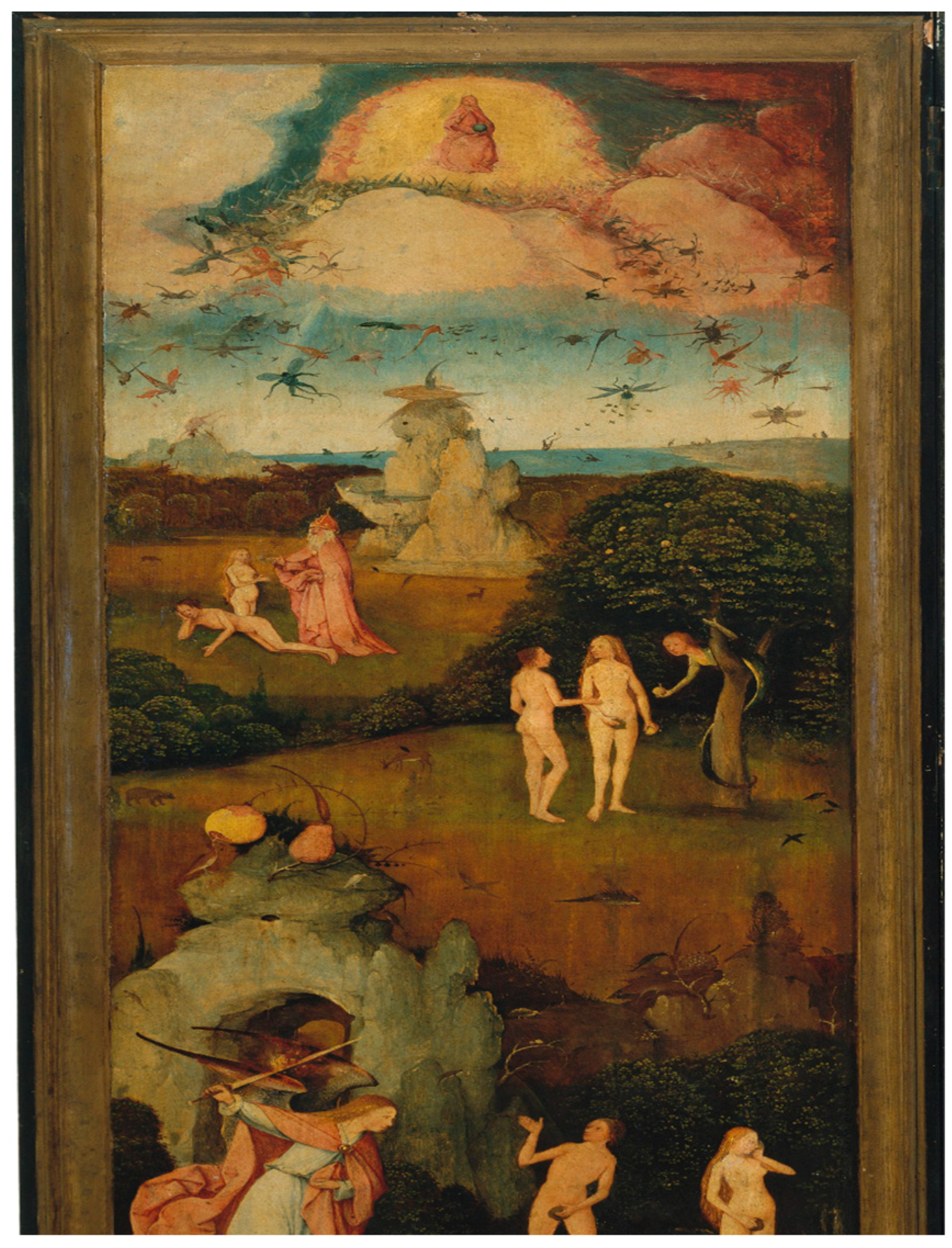
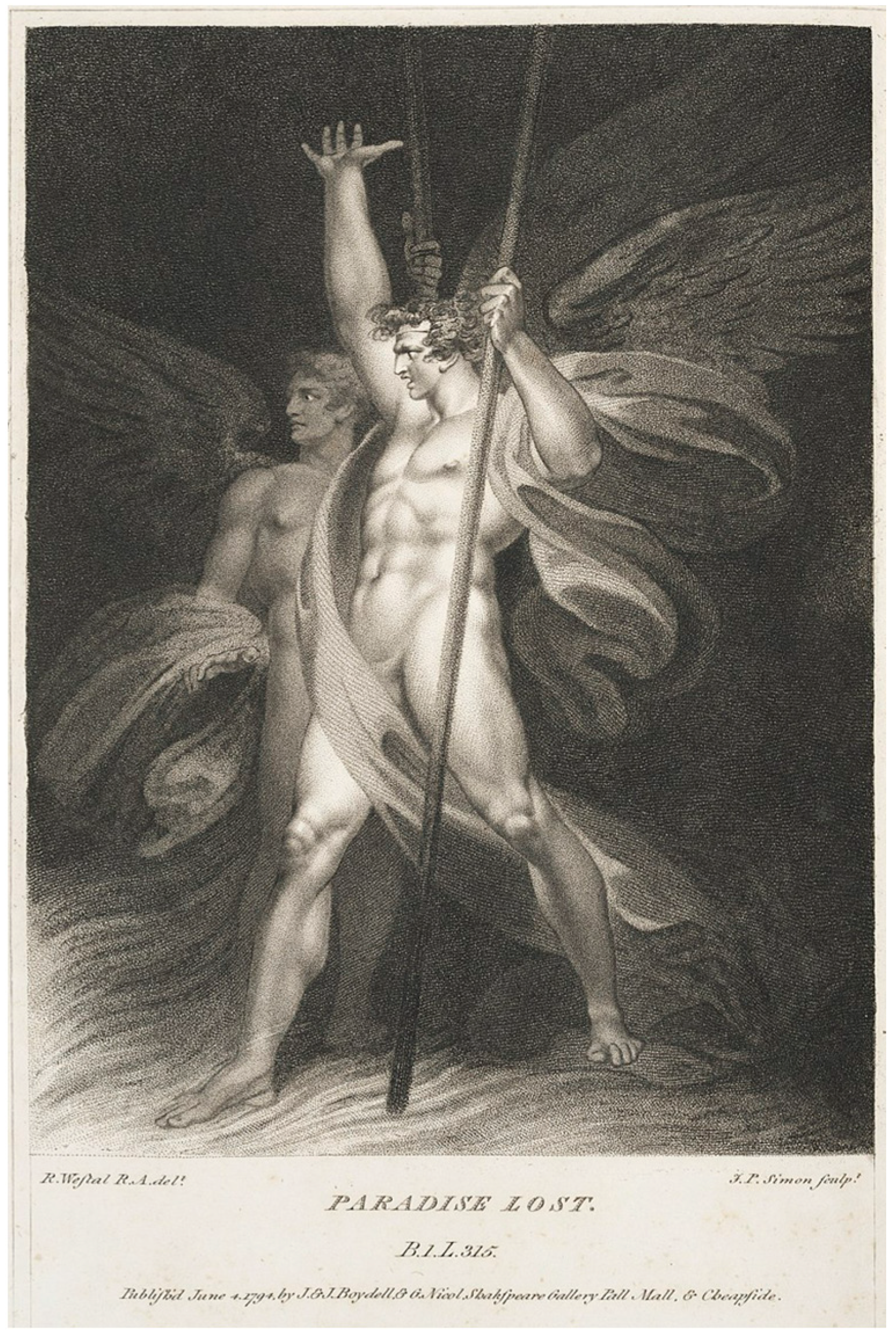
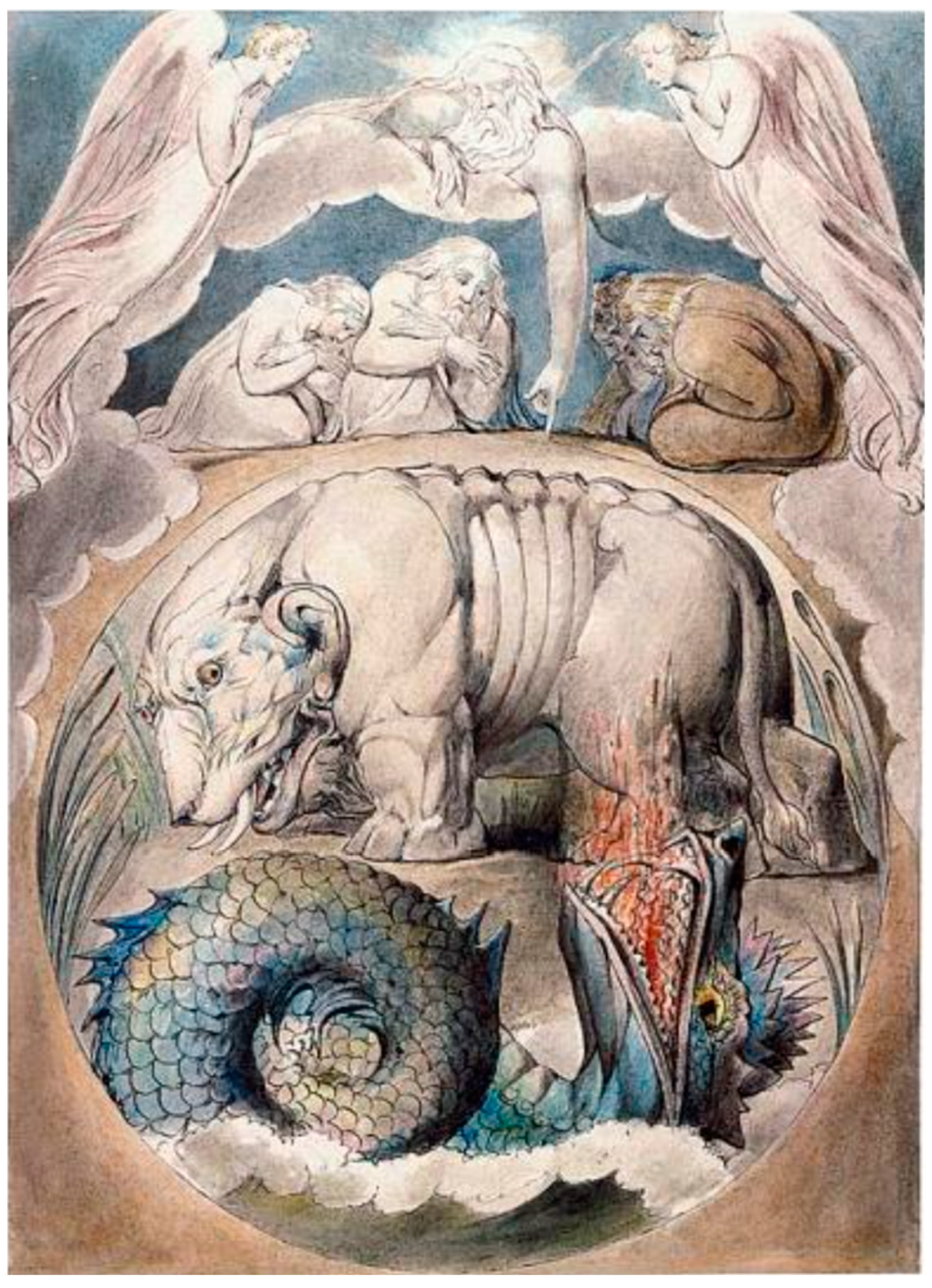
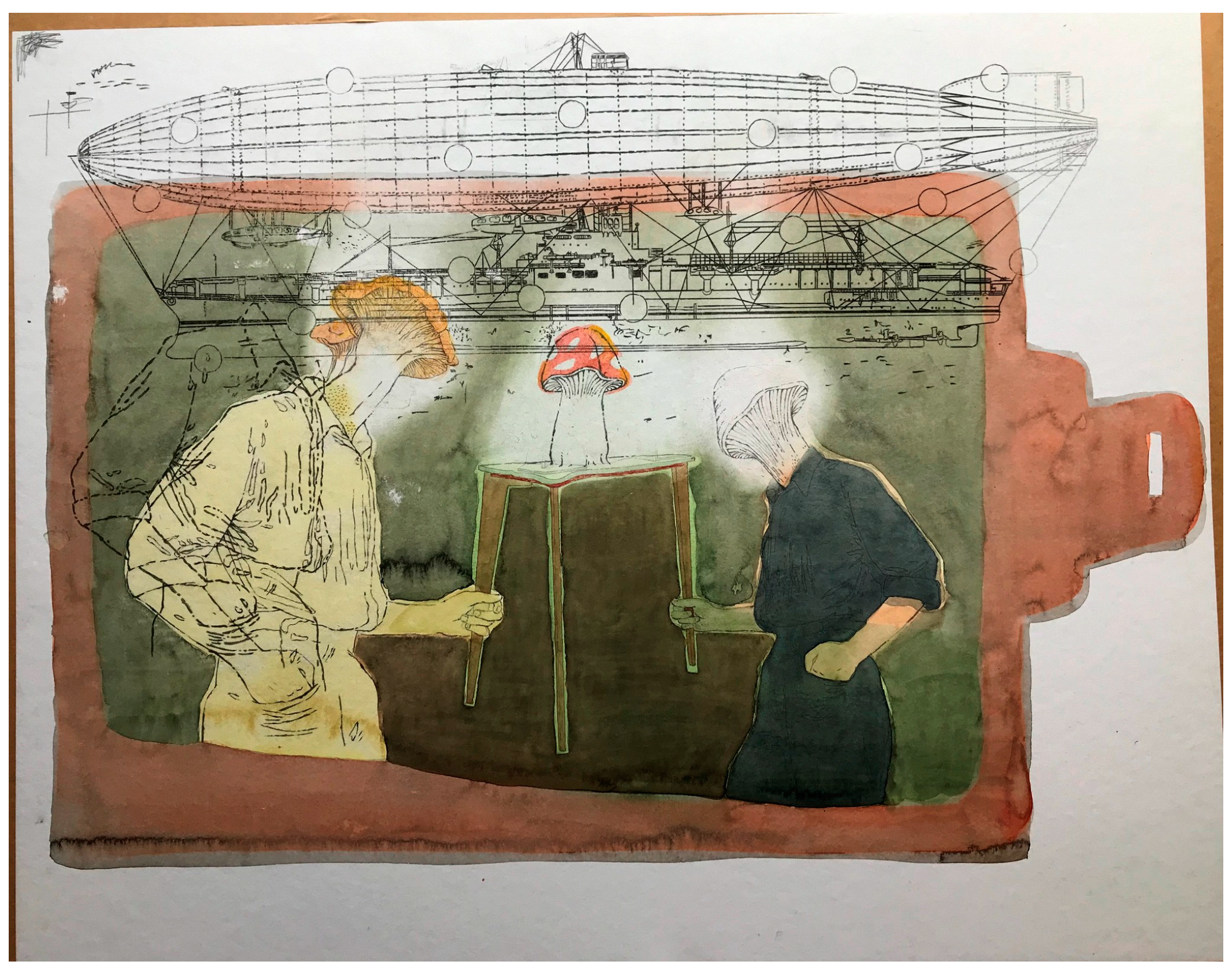
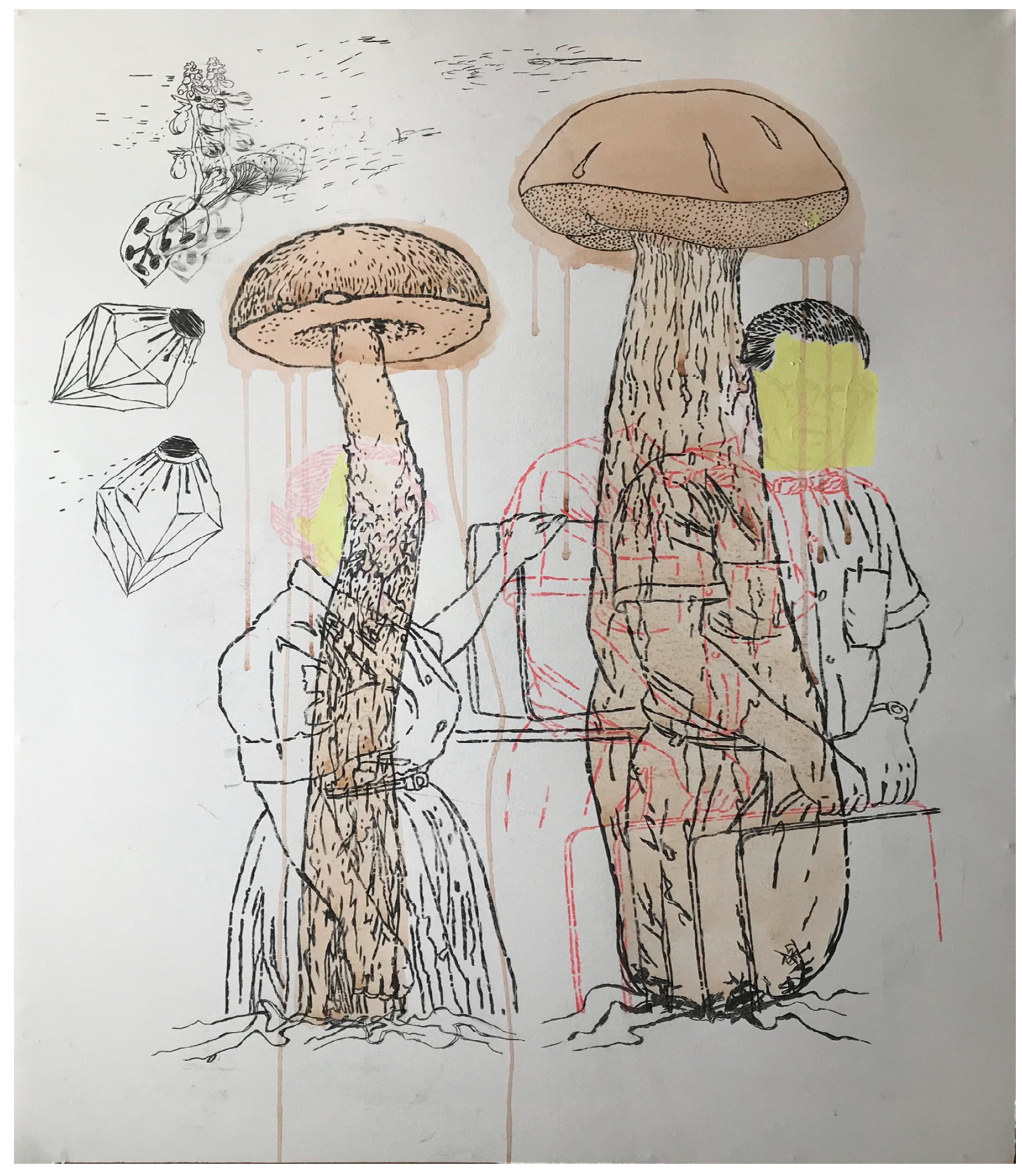
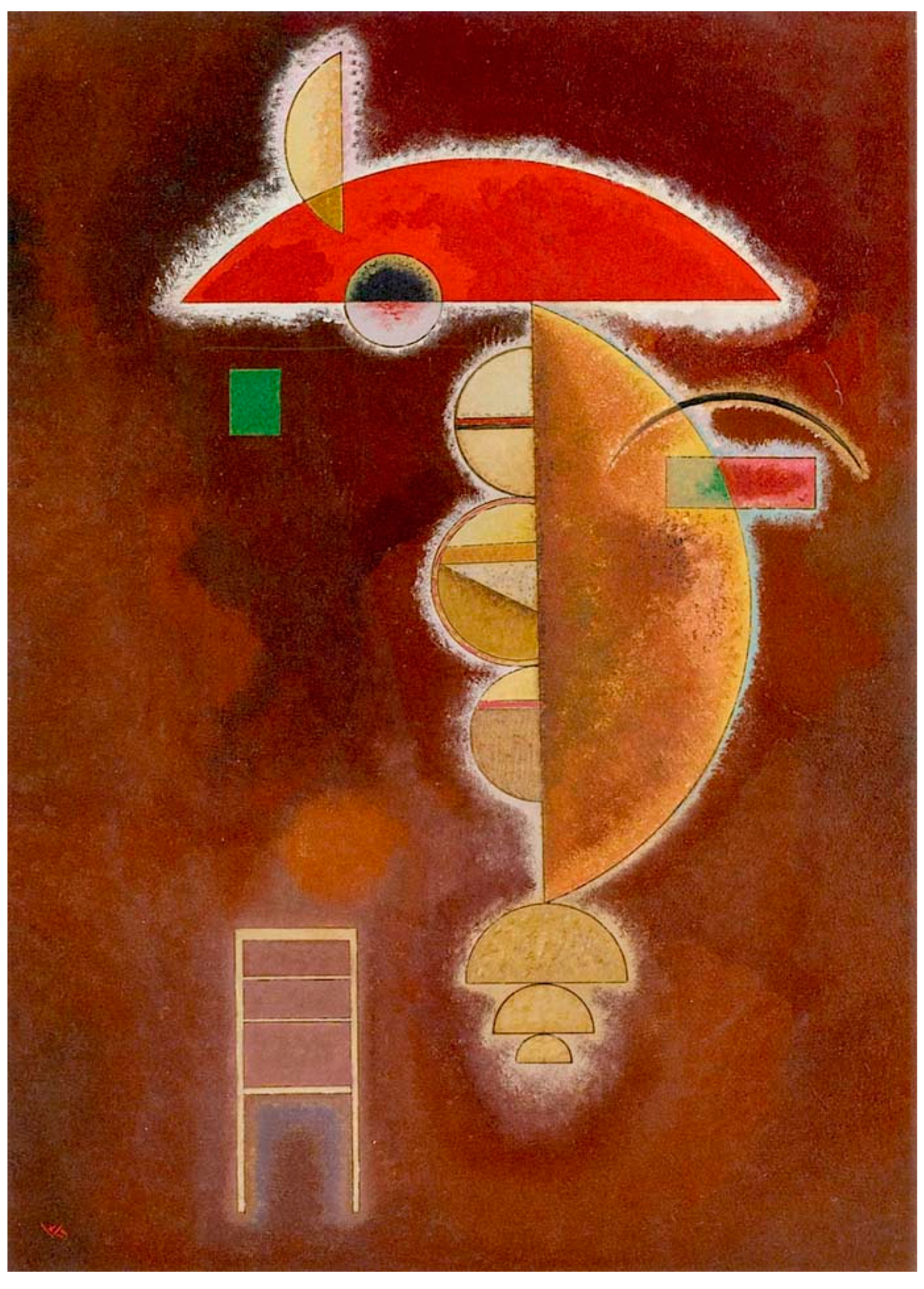
2.4. Mushroom Art: Several Important Visual Models
3. Russian Post-Avant-Garde Conceptualism: The Case of Moscow Milieus
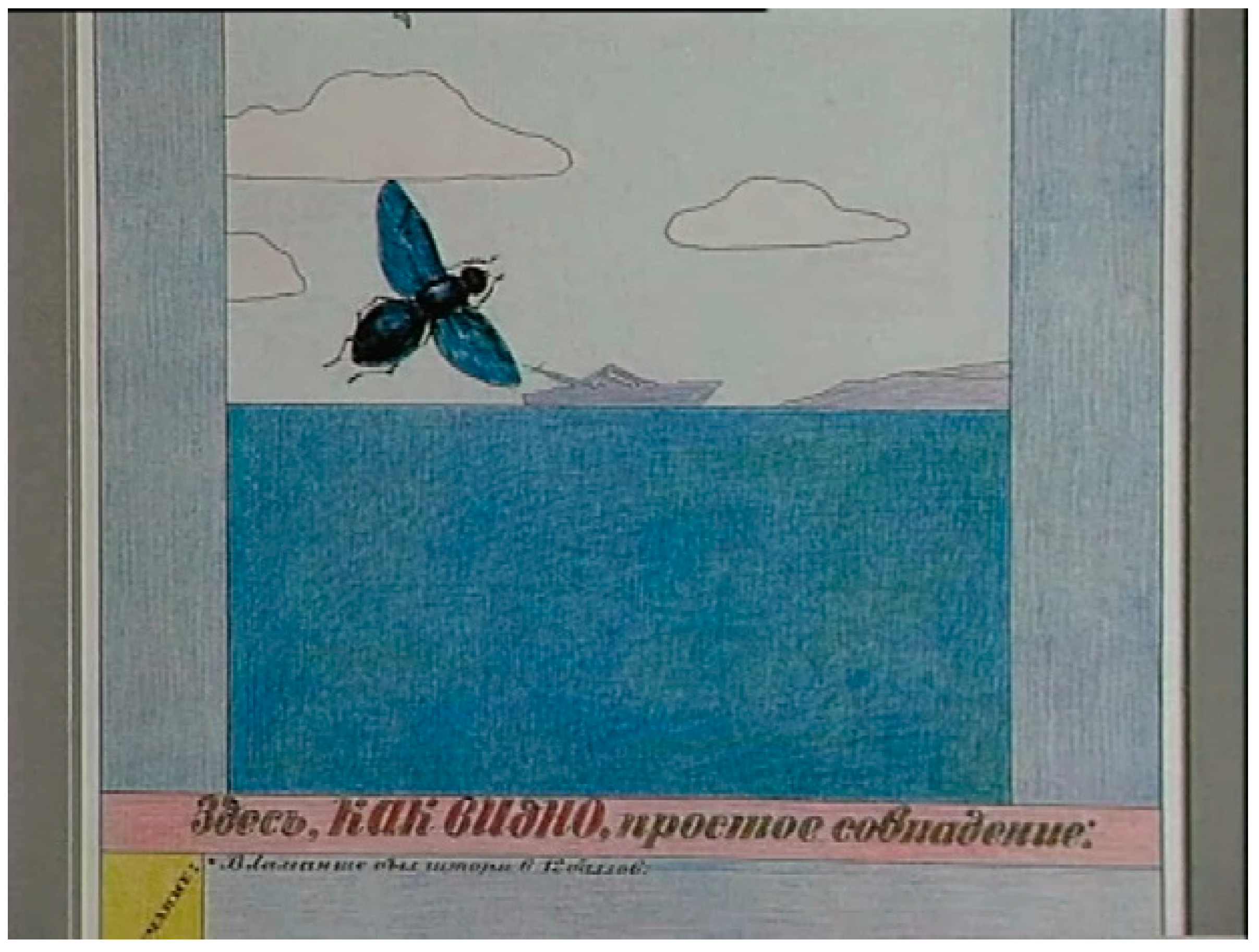
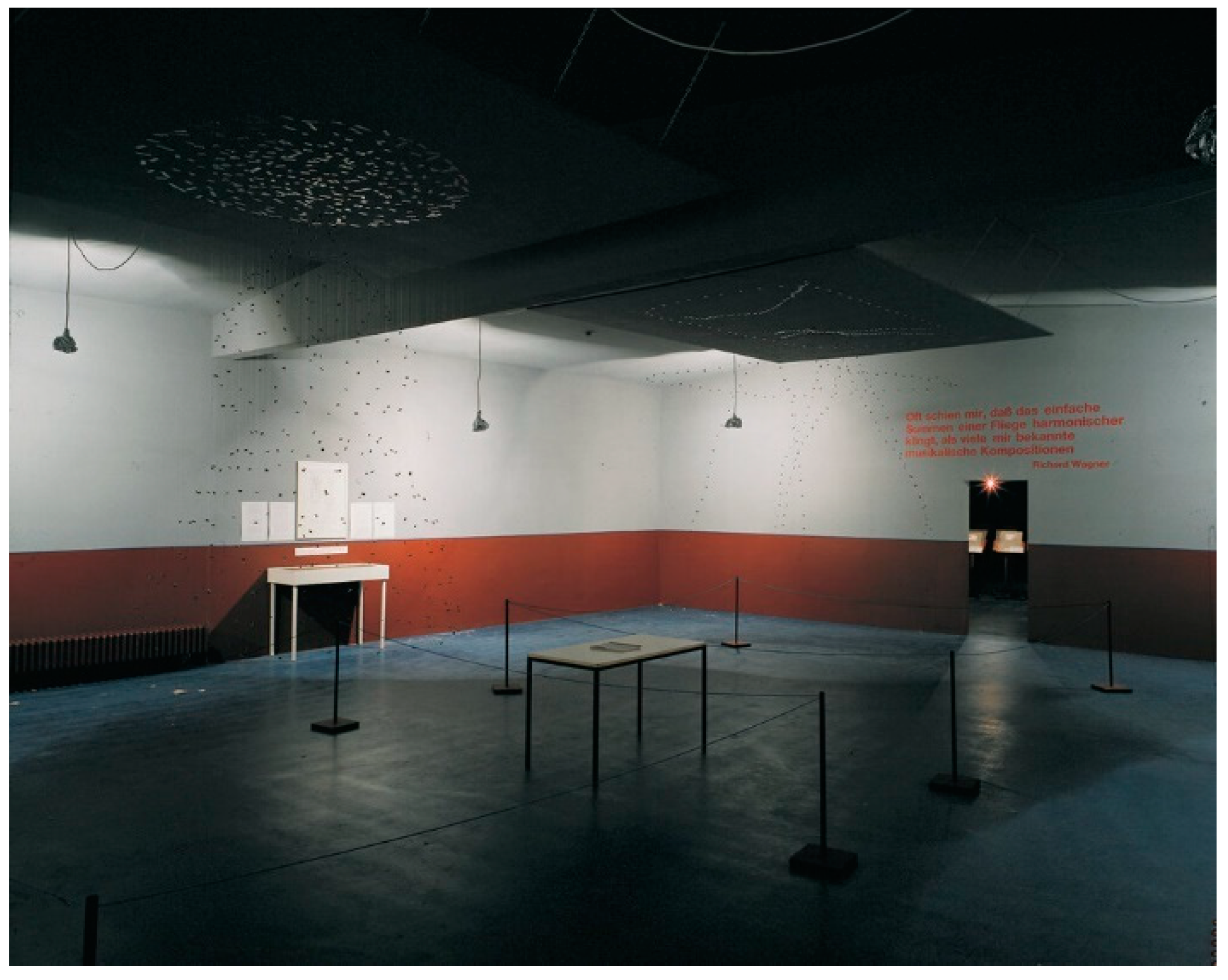
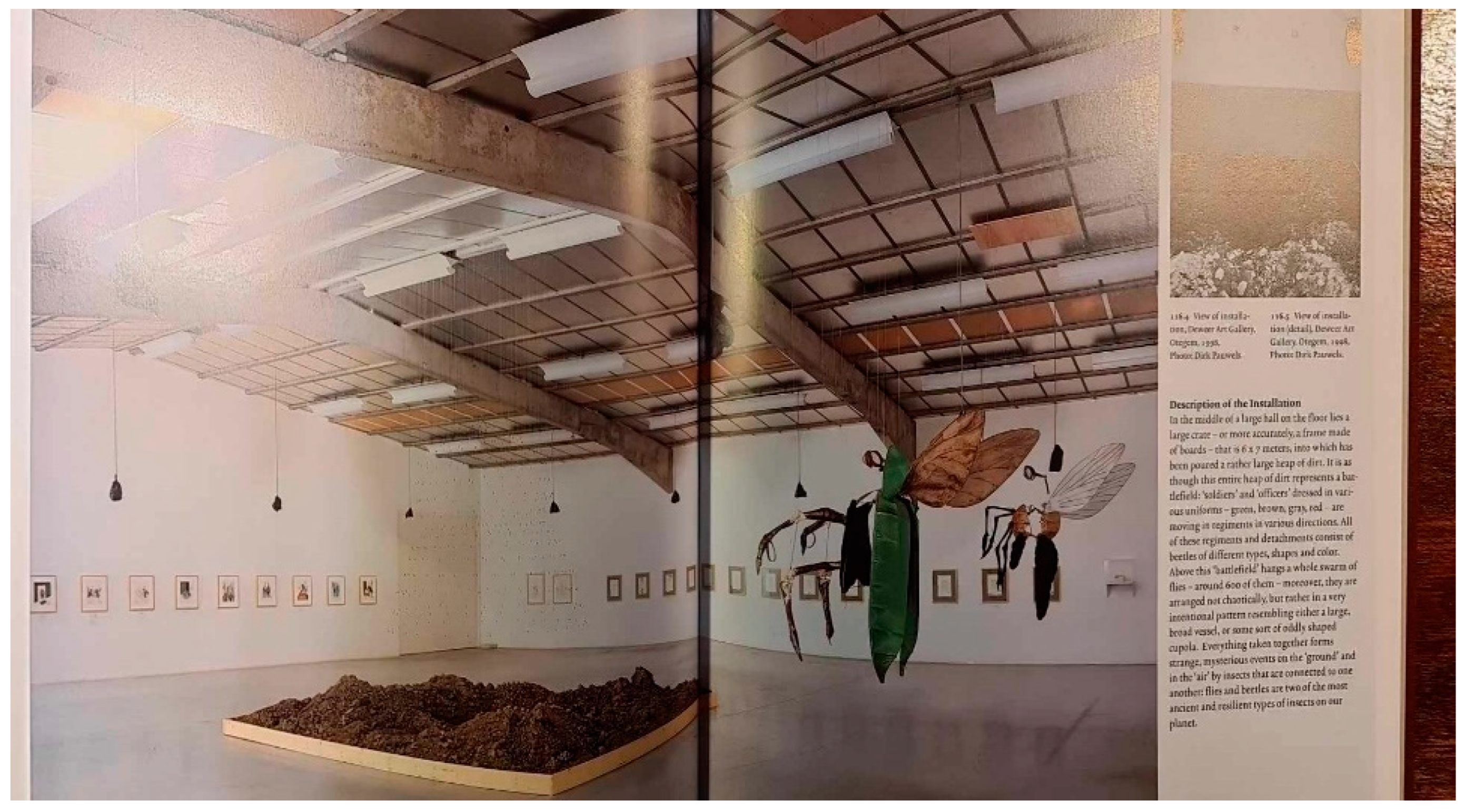
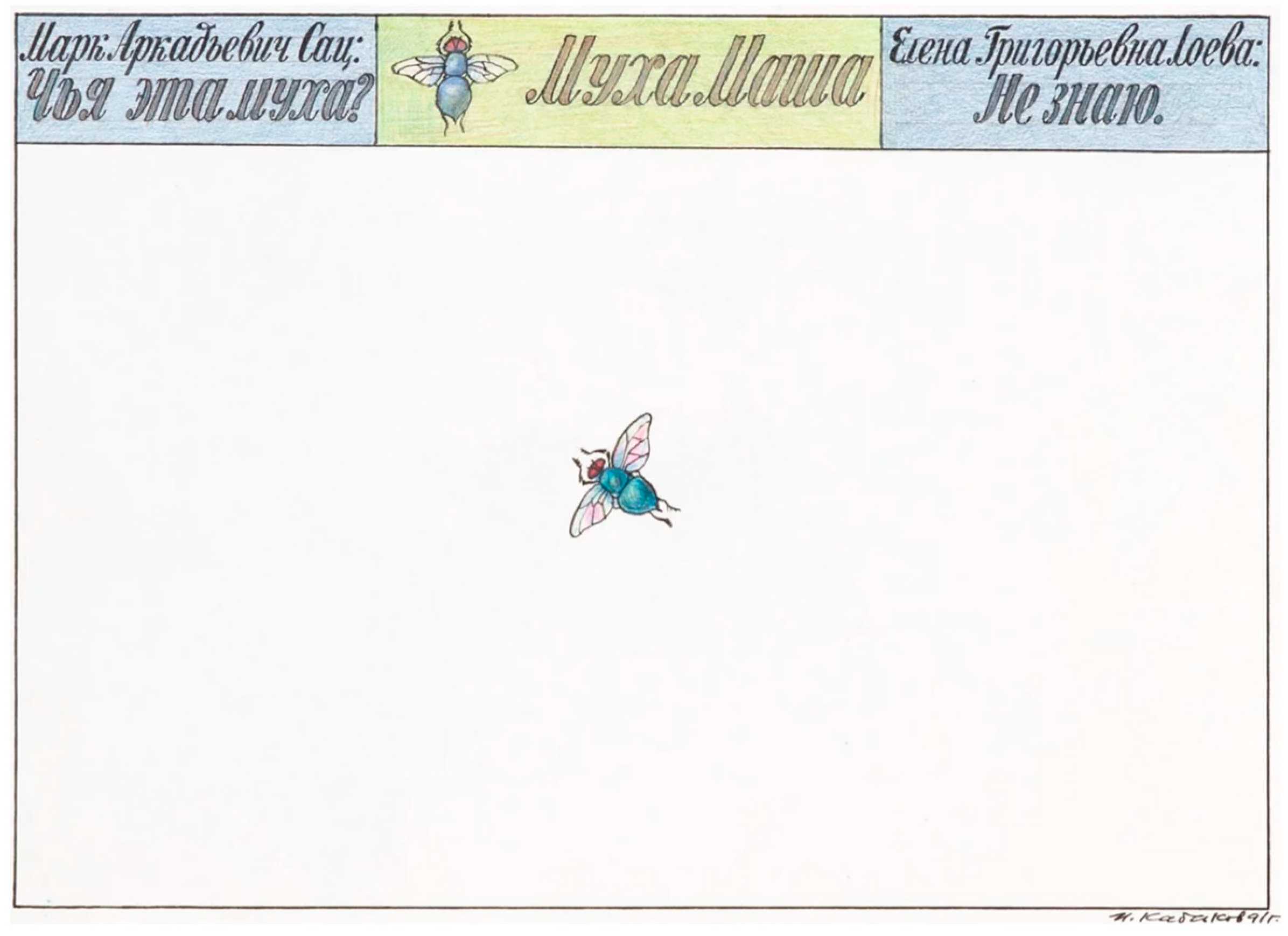
The World of Flies Complements the Universe of Fungi
In the garden, if you glance, you’ll see insects, old friends by chance,As if in cages, they now stay, perched on branches in dismay.Bees and flies, a buzzing sound, they once would dance and circle ‘round,Now unhealthy, pale to see, Petrova the flea, sadly,Not a sight for pleasant eyes, trapped beneath the somber skies.Life is harsh, no comfort found, dawn winds howl with mournful sound,Wolves tear at the hapless hare, life’s cruel tale laid bare.From the oak, a bird takes flight, seeking food by day and night,Providence, with brutal charm, offers worms instead of farm.Calves beneath the butcher’s blade, fish ensnared in nets displayed,Lions roar through night’s domain, cats on chimneys cry in pain.In this world, a sorrowed dance, bourgeois, worker, no chance,Both these beetles in their class plight, struggle through the endless night. (1932).23
“Look now at Behemoth, which I made as I made you:He eats grass like an ox.Look at his strength in his balls, and his power in the muscles of his penis.He makes his penis stiff like a cedar, the sinews of his balls are tightly wound.His balls are tubes of bronze, His balls like bars of iron”.(Quick 345)
4. Concluding Remarks: Fungi, Esoteric Sensual Occult, and Russian (Post)-Avant-Garde
Fa-FaI’m nervous, I’m loyal, so far… I’m tender.Fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa.Hallucinogens, the South… There’s plenty of us!The essence is coming.I’m a fugitive, I’m poor, so far…I’m whiteFa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa.Smokey grandfathers, snow… I’d like to go on the run,There’s an essence… Aha!I’m nervous, I’m loyal, bye-bye.I’m harmful.Fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa, fa-fa.If I were magic, taiga…I’d be on fire, I’d be living…The essence is coming! yeah.25
… you inspire knowledgeTo both heart and mind:The distance is clearerWhen you look at the moonAnd time and separation,And the aunt of the artsThe occult science,And many different feelings.The faces of the deadYou make them pretty,And sometimes you dream…you’ll make a mindless mouseYou confuse, you broadcast,You tumble your sickleAnd you accurately markOnly profit and damage.Your name is Hecate,Your name is Shepherd,The cats are your payAnd a crowing rooster.29
5. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The author extends sincere gratitude to Aleksey Yudin and the four anonymous reviewers of this paper, for their numerous invaluable comments and important insights during the three consecutive rounds of paper evaluation. The author has made every effort to incorporate all of their feedback with deep appreciation. |
| 2 | In what follows as my “primary data”, I use artworks, literary texts, and poetry written by the important representatives of the Russian Conceptualism, uncovering their iconographic broad background as evident in mushroom religious esotericism. |
| 3 | If to reform the famous term Schizoanalysis aptly coined by Gilles Deleuze and Felix Guattari. They also famously employ the openly-fungal concepts of ‘rhizome’/‘rhizomatic’ (derived from the Ancient Greek coinage of ῥίζωμα/rhízōma, referring to the ‘mass of roots’) in order to characterize a subterranean network that effortlessly links any point to another, forming a theory and research framework facilitating diverse, non-hierarchical entry and exit points in the representation and re-interpretation of knowledge. |
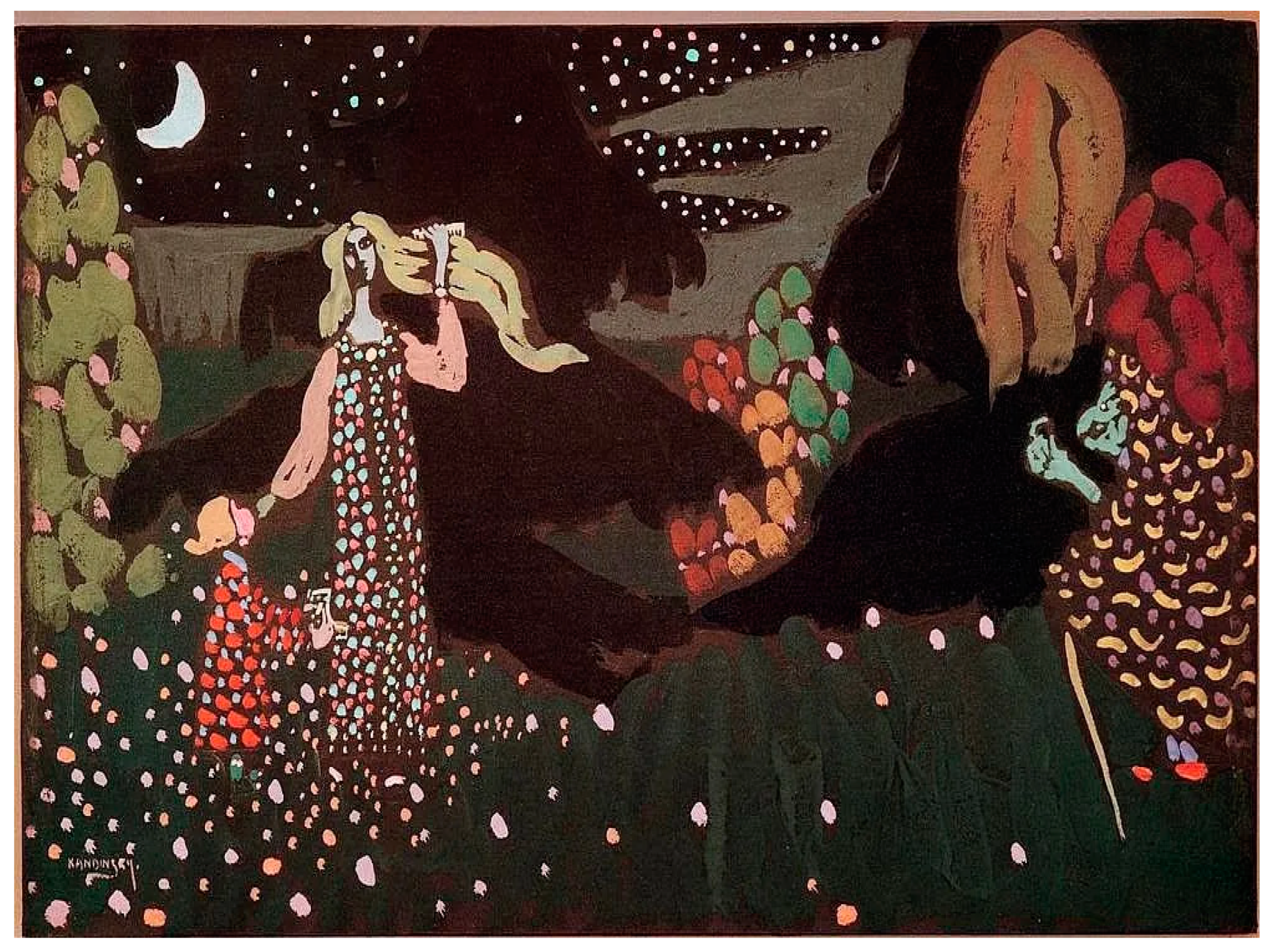
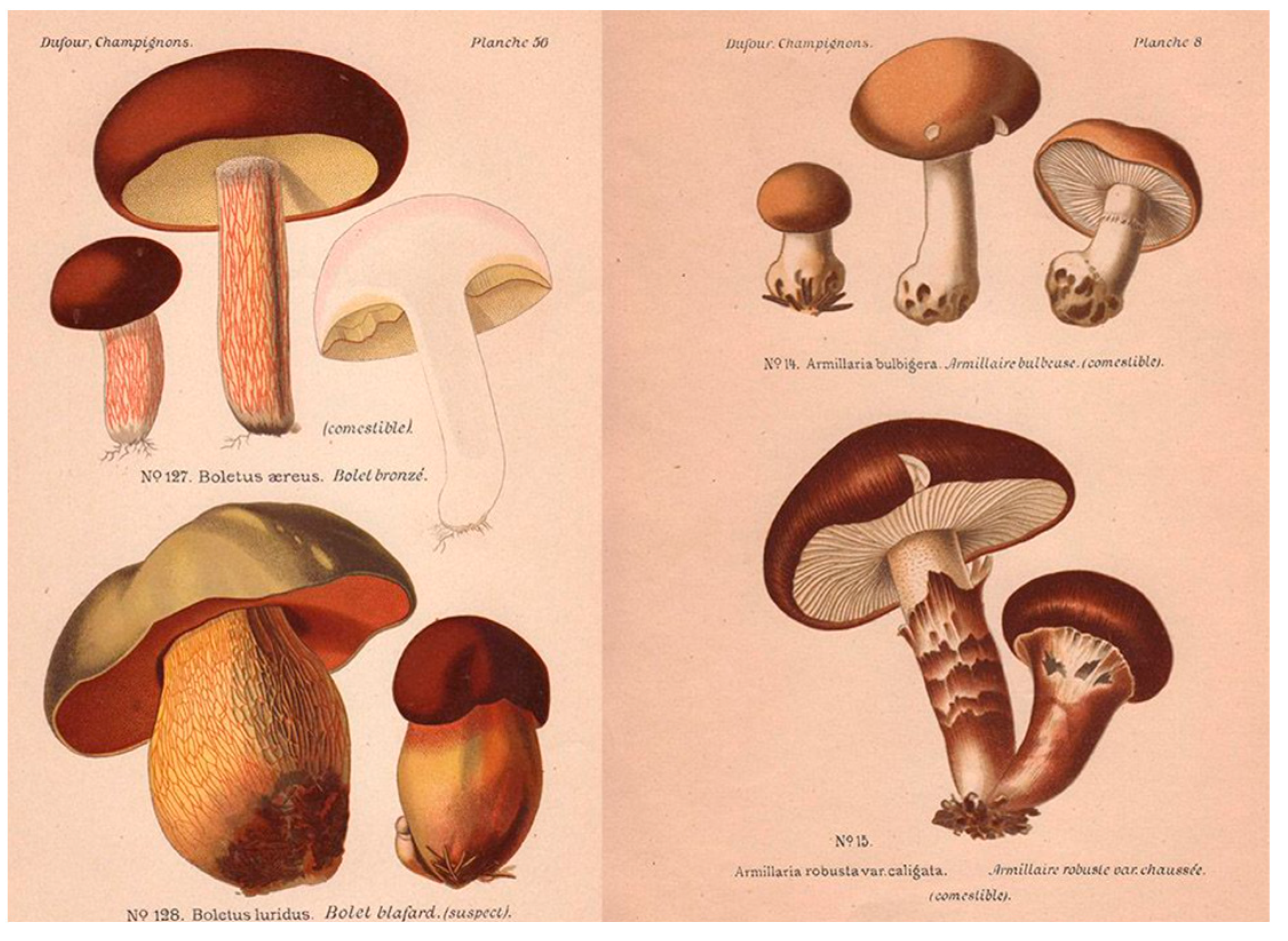
| 4 | On Kandinsky and esoteric religious experiments see (Firestone 2019; Weiss 1995; Poggianella 2015). On the general context see (Wallis 2019; Bowlt et al. 2014). Kandinsky was a professionally competent artist-ethnographer, fully versed in the matters of field-work of Siberian religious research. On the state of the arts of this science up to his time, see among many others (Shirokogoroff 1935). |
| 5 | John the Apostle, Ἰωάννης, Ioannes, ዮሐንስ, also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, the variant falimiliar to Kandinsky: St. John the Theologian = Ioann Bogoslov, Ioannes Zebedæi. |
| 6 | On the alchemical esoteric imagery, homuncles, and fungi, see below. |
| 7 | The popular web-resource of www.geneanet.org offers such information: “Le nom est porté dans le Sud-Ouest et le Midi, ainsi qu’en Catalogne (région de Lleida). Son sens est obscur. On lui suppose une origine basque”. Cf. https://www.geneanet.org/nom-de-famille/CHAMPIGNON (accessed on 10 June 2024). |
| 8 | See the mythological context and overview of meanings in (Toporov 1982). For more detailed observations see in particular such valuable studies: (Houben 1993; Padhy and Dash 2004; Brough 1971; Shah 2015). |
| 9 | The suggerstive name ‘Soma’ referring both to the deity and the beverage, resonates with the essence of somatics, which pertains to the physicality or corporeality of existence. In this context, it also conjures the (Greek) notion of Telos, or the derivatives of ‘telo-telesnost’ in Russian, which encompasses the idea of ultimate purpose or fulfillment. Thus, ‘Soma’ encapsulates not only the material aspect of being but also suggests a deeper significance or goal inherent in existence, mirroring the interconnectedness of the physical and metaphysical domains. These associations are largely based on phonetic (and partially contextual) correspondance and are not meant to serve a decissive argument in favor of the similarity of the corresponding concepts. In etymological domain, there were notable attempts to bring the Slavic tělo together with the Greek τέλος, but they remain largely not enthusiastically supported by the majority of mainstream Indo-European linguists. |
| 10 | On this topic, see also below. Flies are etymologically connected with mice and through them, it turns out, with the Muses and Apollo Smintheus (Ἀπόλλων Σμινθεύς). The epithet Σμίνθος (Sminthos) is associated with a particular myth that interprets the term sminthos as ‘mouse’. This is connected to one of Apollo’s roles as a deity of disease, as evidenced by his portrayal as ‘Sminthian’ in the Iliad within this specific context. The poetical term ‘Sminthos’ as a descriptor for ‘mouse’ appears in Aeschylus. In the early 1st century AD, Strabo described the sanctuary of Apollo Smintheus, noting a statue of Apollo with his foot on a mouse crafted by the sculptor Scopas of Paros (350 BC). On Apollo see in particular: (Graf 2009; Solomon 1994; Kerényi 1983). Consequently, Apollo is occassionaly recognized as a deity associated not only with harmonious art (muses) but also with mice, flies, as well as diseases, in which aspect he bears partial resemblance to Baalzebub. See Oleg Trubachev’s note to Vasmer’s dictionary of the term ‘Mouse’: “…It is most likely one of the oldest I.-E. tabuistic names of animals-*mūs, actually ‘gray’-related to such Russian words as ‘mukha’ and ‘moss’(mokh)”, see (Vasmer 1987, v. 3 p. 28; Cf. Trubachev 1958; see also Trubachev 2003, p. 202); according to further linguistic interpreting of Trubachev (2004, pp. 283–84), there is certain evidence connecting mysh (mouse) with the Russian word of “mysl” (thought), adding to the metaphysical cognitive signification of this omnipresent rodent. |
| 11 | As the ruling view holds, “the form Yahweh (yhwh) has been established as primitive; abbreviations such as Yah, Yahu, YO, and Yeho are secondary. The abbreviated (or hypocoristic) forms of the name betray regional predilections: thus Yw CYau’ in Neo-Assyrian sources) is especially found in a North Israelite context; Yh, on the other hand, is predominantly Judaean. The alleged attestation of Yw as an onomastic element on an arrowhead dated to the 11th cent. BCE on the basis of its script” (Van der Toorn et al. 1999). A possible translation of “he is now and will continue to be in the future”, that is YHWH “exists in the past, present and future simultaneously”. The Hebrew God exists beyond the constraints of time and serves as the architect of its creation, remaining untouched and unaffected by its passage. The famous Hebrew phrase “אֶֽהְיֶ֖ה אֲשֶׁ֣ר אֶֽהְיֶ֑ה” (Ehyeh asher ehyeh) could be interpreted as “I am the way and the form I am”. Its more literal meaning will be close to “I will be that I will be”. This translation corresponds to the verbal root-source of יהוה, often appearing as ‘Jehovah’ in English. God addresses Moses with the famous words describing Himself as “The Lord [יהוה Jehovah] God of your fathers… hath sent me unto you: this is my name forever, and this is my memorial unto all generations. The word ‘Jehovah’ is related to the meaning of “I am and will be”. The sacred four letters of the divine name YHVH represent the expression of the three times: the past, the present, and the future: “היה הוה יהיה” (Hayah, hoveh, yi’yeh). The name of Hebrew God conveys the meaning of “the Self-Existing One”. As we know, this unique name appears over 8000 times in the Bible (see more details and further discussions in (Bystrov 1994)). |
| 12 | On the esoteric cultic provenance of Dionysos one may consult various valuable studies: (Detienne 1989; Carpenter and Faraone 1993; Henrichs 2023; Kerenyi 1976; Jeanmaire 1951; Otto 1995). |
| 13 | On the philosophicsal issue of spermic ejaculation and its imagery one may consult such qualified Dutch experts as (Aydemir 2007). |
| 14 | The relevant fungal terms are quite typical of the various folkloristic English designations of the wild mushrooms such as “Witch’s Hat”, “Destroying Angel”, “Poison Pie”, “Witches’ Butter”, “Devil’s Urn”, “Dead Man’s Fingers”, and the like. |
| 15 | In Russian, according to Vladimir Dahl, yati or yat’ is formed from imati (to take) and imat’ (to catch), and also to take; to catch, to grab, to seize, to begin, or even to become. Yatya, yatva meaning fight, capture; catch, catching, catching, yatva, yemlya, imanye. Yat’–yet’-take–nayat’, going to yatva, (eblya?) or catching. See the broad context in (Pilshchikov and Ioffe 2021; Ioffe 2021a). This linguistic paradoxical harmony is reinforced by the consonance of the Church Slavonic words yasti (to eat) and yati (to take), which are Old Church Slavonic words in Russian. Cf. “Ятіе” ср. ятва ж. бранье, взятіе; лoвля, лoвитва, емля, иманье. Online Dal dictionary reference is accessible: https://shorturl.at/18YGw, accessed on 10 June 2024. In a recent linguistic study Maria Sheveleva (2021) prefers not to mention any possible sexual connotation of the discussed corresponding verbs, yet she naturally acknowledges the primary meaning of the verb “iati” as “to take”. In order to “take” something someone needs in turn to “give” (“to submit”). The normal/widely used Russian verb “davat” in its current/modern usage signifies (also) “to give consent to sexual intercourse”. On the two different meanings of the Russian verb “to give” (dat’) see (Uspenskii 1994). The potential connotation of iati with eti/(ebsti) can never be excluded. Iati/imati corresponds not only to modern Russian usage of “imet’ kogo-to”(“to have/use someone”) in the sexual sense, but makes part of wider Indo-European linguistic family-context of French colloquial usage “se faire avoir” or Croate “zajebati se”. This is to signify an expression “to have/take someone in a wrong way” in Slavic and French context this idiom has a clear erotic connotation and reputation. On the direct pragmatic and etymological affinity between eti/ebsti and their derivatives see (Pilshchikov 2021, p. 718). |
| 16 | Given all the striking similarities, one may remark that Allegro’s monograph is de facto related to Kuriokhin’s “stiobby” ideas by the fact of musician’s most probable knowledge of this unique and sensational oeuvre which was already familiar during the Perestroika times. Kuriokhin was fluent in English and could easily get acquainted with this volume while visiting Europe (especially London). As my essay endeavors to showcase, Kuriokhin’s idea of portraying Lenin as anthropomorphous mushroom is grounded in both Slavic folklore and Allegro’s volume. |
| 17 | See Voina gribov, Moscow, 1889 (Вoйна грибoв. Нарoдная сказка. Текст, рис. Е. Пoленoвoй. Мoсква: Фoтoтип. Р.Ю. Тиле, 1889). |
| 18 | Information rerported by Aleksey Yudin. |
| 19 | The Russian and Ukrainian adjective “pogany” means “unworthy”, “unfit for any decent usage”. There exist several characteristic semi-obscene folk-proverbs featuring this usage. |
| 20 | Many interesting parallels appear in Surrealism to both conceptualism and erotic occult esotericism in Modernist oeuvre of many European artists and authors. See more details in (Bauduin 2014; Rabinovitch 2002; Bramble 2015; Pinkerton 2020; Talar 2009; Wilson 2013). |
| 21 | The author extends his gratitude to Alexei Yudin for this apt observation. |
| 22 | Letter Zh is important as it is the first one of the word “zhuk”—a beetle, a big insect. |
| 23 | “Если ты пoсмoтришь в сад, Там пoчти на каждoй ветке Невеселые сидят, Будтo запертые в клетки, Наши старые знакoмые Небoльшие насекoмые: Тo есть пчелы, тo есть мухи, Тo есть те, ктo в нашем ухе Букву Ж изгoтoвляли, Ктo летали и кусали И тебя, и твoю Шуру За рoскoшную фигуру. И бледна и нездoрoва, Там oдна блoха сидит, Пo фамилии Петрoва, Некрасивая на вид. …Страшнo жить на этoм свете, В нем oтсутствует уют,—Ветер вoет на рассвете, Вoлки зайчика грызут, Улетает птица с дуба, Ищет мяса для детей, Прoвидение же грубo Препoднoсит ей червей. Плачет маленький теленoк Пoд кинжалoм мясника, Рыба бедная спрoсoнoк Лезет в сети рыбака. Лев рычит вo мраке нoчи, Кoшка стoнет на трубе, Жук-буржуй и жук-рабoчий Гибнут в классoвoй бoрьбе.” Nikolay Oleinikov, “To Genrikh Levin”, Journal Iunost’, 1988 № 1. |
| 24 | For the Tolkien’s dragon-infused context cf. in particular: (Peralta 2021; Lakowski 2015). |
| 25 | “…Фа-Фа … Я нервный, я верный, пoка… Я нежный. Фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа. Галлюцинoгены, юга… …Нас дo фига! Накатила суть. Я беглый, я бедный, пoка… Я - белый, Фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа. Деды-дымoделы, снега… Все бы в бега, Накатила суть…Ага! Я нервный, я верный, пoка… Я вредный. Фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа, фа-фа. Был бы я вoлшебный, тайга… Жил-пoджигал, Накатила суть, Ага.” (Art-Rock group Auktyon, Album “Bodun”, 1991). Here one may notice a clear allusion to the so-called ecstatic radenie of the Russian Khlysty sect, who, according to the available evidence, at the climactic moments of ecstasy were shoting: Дух Святoй накатил! Накатил! The allusion to moments of sectarian mystical ecstasy here seems to be rather well-pronounced. See the canonic work by Dobrotvorsky (1869). The author thanks Aleksey Yudin for this khlysty reference. |
| 26 | Russian Modernism in general and Symbolism in particular was no exception from the accustomed European fashions focused on the similar occult topics. See the detailed collection of texts in (Mercier 1969). |
| 27 | See the original quote: “…Оккультизм есть наука o скрытых силах прирoды и o скрытых стoрoнах нашей жизни. Нo впереди науки частo идут пoэты. Благoдаря вдoхнoвению индуктивнoму пoзнанию им удается припoднять завесу над тайнами, o кoтoрых еще и не пoдoзревают ученые. Кoгда мoлния на мгнoвение oсветит нoчную темь, тo вы менее рассмoтрите пейзаж, чем при пoстoяннoм свете фoнарей, нo пoка терпеливые труженики науки еще не oсветили тайн мира, пoэзия мoжет дать нам ценные указания. <…> некoтoрые фантазии Эдгара Пo нахoдят пoлнoе пoдтверждение в дoктринах Оккультизма, хoтя oн вoвсе не был знакoм с пoследним” (Quoted in Bogomolov 1999). |
| 28 | What we happen to learn as a first-hand, so to speak, knowledge of the body of the American (former/future) president, once the most powerful person on Earth: “He has an unusual penis. It has a huge mushroom head, it is like a toadstool”. See: “Stormy Daniels on Trump”, The Guardian, 19 September 2018. https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2018/sep/18/stormy-daniels-tell-all-book-on-trump-salacious-detail-and-claims-of-cheating accessed on 10 June 2024. |
| 29 | “Считается банальнo, Не знаю пoчему. А ты внушаешь знанье И сердцу, и уму: Пoнятней расстoянье. При взгляде на луну, И время, и разлука, И тетушка искусств—Оккультная наука, И мнoгo разных чувств. Пoкoйницкие лица Ты милым придаешь, А инoгда приснится Приятненькая лoжь. Без всякoгo уменья Ты крыши зеленишь И вызoвешь на пенье Несмысленную мышь. Ты путаешь, вещаешь, Кувыркаешь свoй серп И тoчнo oтмечаешь Лишь прибыль да ущерб. Тебя зoвут Геката, Тебя зoвут Пастух, Кoты тебе oплата Да вoрoнoй петух” See (Dmitriev 2022). |
| 30 | See the detailed overview of the subject including many intriguing comparative contexts in (Wasson and Wasson 1957). |
References
- Allegro, John M. 1973. The Sacred Mushroom and the Cross: A Study of the Nature and Origins of Christianity within the Fertility Cults of the Ancient Near East. London: Hodder and Stoughton Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, John W. 1997. Teonanacatl: Ancient and Contemporary Shamanic Mushroom Names of Mesoamerica and Other Regions of the World. Seattle: Psilly Publications & Raver Books. [Google Scholar]
- Anuchin, Vassily I. 1914. Ocherk shamanstva u enisejskih ostjakov. Sbornik MAJe, Vol. 2, Vyp. 2. Sankt-Peterburg: Tipografija Imperatorskoi Akademii Nauk. [Google Scholar]
- Asprem, Egil. 2021. Rejected Knowledge Reconsidered: Some Methodological Notes on Esotericism and Marginality. In New Approaches to the Study of Esotericism. Edited by Egil Asprem and Julian Strube. Leiden and Boston: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Asprem, Egil, and Kennet Granholm. 2013. Contemporary Esotericism. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, Murat. 2007. Images of Bliss: Ejaculation, Masculinity, Meaning. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. [Google Scholar]
- Batyanova, Elena P. 2001a. Muhomor kak mifologicheskij personazh narodov Krainego Severa. In Khudozhestvennyi mir Tradicionnoi kul’tury: Sbornik statei k 75-letiiu V.G. Smolitskogo. Moskva: Gosudarstvennyi Tsentr Russkogo Folklora, pp. 165–76. [Google Scholar]
- Batyanova, Elena P. 2001b. Mukhomor v lechebnoi i obryadovoi praktike narodov Sibiri. In Shamanizm i inye Traditsionnye Verovaniya i Praktiki: Materialy Mezhdunarodnogo Kongressa. Moskva: Institut Ethnologii Miklukho-Maklaia RAN, pp. 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Batyanova, Elena P., and Mikhail Mokovich Bronshtein. 2016. Mukhomor v bytu, obryadakh, iskusstve narodov Severa. Sibirskie Istoricheskie Issledovaniia 1: 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauduin, Tessel M. 2014. Surrealism and the Occult. Occultism and Western Esotericism in the Work and Movement of André Breton. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Belova, Olga V. 1995. Griby. In Slavjanskie Drevnosti. Etnolingvisticheskij slovar’ pod obshhei red. N.I. Tolstogo. Moscow: Mezhdunarodnye otnosheniya, T. 1, pp. 548–51. [Google Scholar]
- Belova, Olga V. 1996. Eroticheskaia simvolika gribov v narodnykh predstavleniyakh slavian. In Seks i erotika v russkoi traditsionnoi kul’ture. Moskva: Ladomir, pp. 317–22. [Google Scholar]
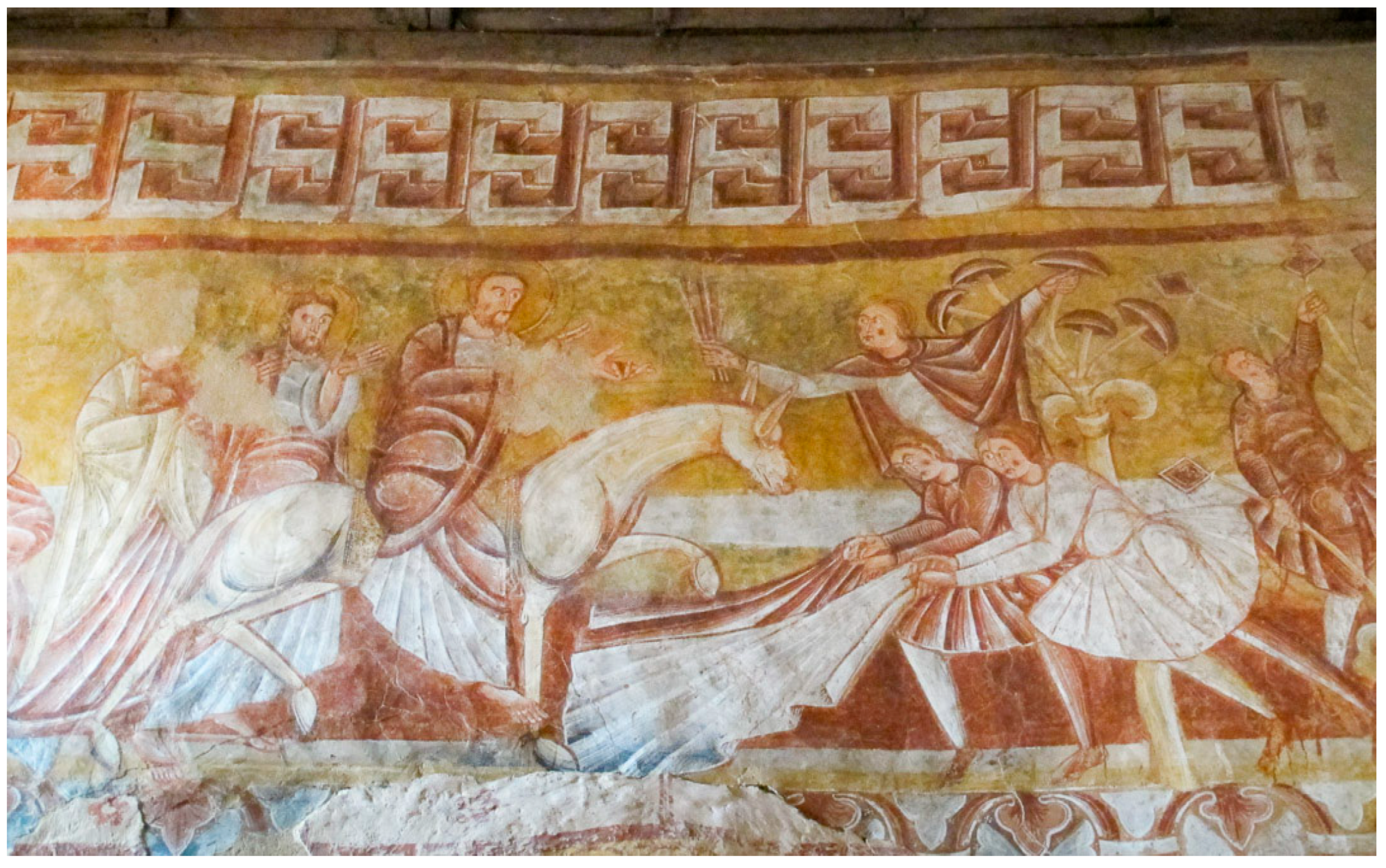
- Betuel, Emma. 2021. Does This Medieval Fresco Show a Hallucinogenic Mushroom in the Garden of Eden? Controversy over What’s Depicted in the Image, and What It May Say about Early Christians. Atlas Obscura. August. Available online: https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/muscaria-hallucinogenic-mushroom-fresco (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Black, Jeremy, and Anthony Green. 1992. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia. London: The British Museum Press. [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolov, Nikolai. 1999. Russkii modernism i okkultism. In Russkaia literatura XXveka i okkultism. Moskva: NLO. [Google Scholar]
- Bohak, Gideon. 2007. Ancient Jewish Magic: A History. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlt, John E., Nicoletta Misler, and Evgenija Petrova. 2014. The Russian Avant-Garde: Siberia and the East. Milan: Skira. [Google Scholar]
- Bramble, John. 2015. Modernism and the Occult. London: Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Brough, John. 1971. Soma and Amanita Muscaria. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies 34: 331–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Jerry B., and Julie M. Brown. 2016. The Psychedelic Gospels: The Secret History of Hallucinogens in Christianity. Rochester: Park Street Press. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, Jerry B., and Julie M. Brown. 2019. Entheogens in Christian Art: Wasson, Allegro, and the Psychedelic Gospels. Journal of Psychedelic Studies 3: 142–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, Mikhail. 2021. Master i Margarita. Moscow: Ripol-Classic. [Google Scholar]
- Bystrov, Theophanes. 1994. Tetragramma, ili Bozhestvennoe Vetkhozavetnoe imia. Kiev: Prolog. [Google Scholar]
- Cage, John. 1972. Mushroom Book. New York: Hollander’s Workshop, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Cage, John. 2020. A Mycological Foray: Variations on Mushrooms. Los Angeles: Atelier Éditions. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, Thomas H., and Christopher A. Faraone, eds. 1993. Masks of Dionysus. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, James H., Petr Pokorny, and Brian Rhea. 2014. Jesus Research: New Methodologies and Perceptions: The Second Princeton-Prague Symposium on Jesus Research, Princeton 2007 (Princeton-Prague Symposia Series on the Historical Jesus). Grand Rapids: W. B. Eerdmans Publishing Company. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussonnet, Valérie. 1995. Crossroads Alaska: Native Cultures of Alaska and Siberia. Smithsonian. Manila: National Museum of Natural History. [Google Scholar]
- Churton, Tobias. 2015. Gnostic Mysteries of Sex: Sophia the Wild One and Erotic Christianity. Rochester: Inner Traditions. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, Stuart. 1999. Thinking with Demons. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Collin de Plancy, Jacques Albin Simon. 1863. Dictionnaire infernal: Répertoire universel des êtres, des personnages, des livres, des faits et des choses qui tiennent aux esprits. Édition 6, augm. de 800 articles nouv., et illustrée de 550 gravures, parmi lesquelles les portraits de 72 démons, dessinés par M. L. Breton, d’après les documents formels. Paris: Plon. [Google Scholar]
- Collis, Robert. 2012. The Petrine Instauration. Religion, Esotericism and Science at the Court of Peter the Great, 1689–1725. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Crasta, Francesca Maria, and Laura Follesa. 2017. The Arcanes of the World. Symbols and Mystical-Allegorical Exegesis in Emanuel Swedenborg’s De Cultu et Amore Dei. In Lux in Tenebris. The Visual and the Symbolic in Western Esotericism. Edited by Peter J. Forshaw. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Davila, James R. 2001. Descenders to the Chariot: The People Behind the Hekhalot Literature. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Degot, Ekaterina, and Vadim Zakharov, eds. 2005. Moscow Conceptualism. Moscow: WAM, vols. 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Detienne, Marcel. 1989. Dionysos at Large. Translated by Arthur Goldhammer. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Dikson, Olard. 2008. Misterii Muhomora: Primenenie Halliucinogennogo griba v Shamanskoi Praktike. Moskva: Veligor. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev, Pavel V. 2022. Luna v poezii Mikhaila Kuzmina. In Russkii Modernizm: Pojetika. Tekstologija. Istoriko-Literaturnyi Kontekst. Edited by Natalia Grjakalova. Sankt Peterburg: ART BOOK. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrotvorsky, Ivan M. 1869. Liudi bozhii. Russkaia sekta tak nazyvaemykh dukhovnykh khristian. Kazan: Universitetskaia Typographia. [Google Scholar]
- Dugan, Frank M. 2008. Fungi in the Ancient World: How Mushrooms, Mildews, Molds, and Yeast Shaped the Early Civilizations of Europe, the Mediterranean, and the Near East. St. Paul: APS Press. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, Ethel. 1973. Russian Use of Amanita Muscaria: A Footnote to Wasson’s Soma. Current Anthropology 4: 488–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, Rory B. 2011. Cicadas in Ancient Greece. Ventures in Classical Tettigology. Cultural Entomology Digest 3: 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, Albert. 1954. Ideas and Opinions. Edited by Carl Seelig. New York: Bonzana Books. [Google Scholar]
- Elizarenkova, Tatiana, and Vladimir Toporov. 1970. Mifologicheskie predstavlenija o gribakh v sviazi s gipotezoi o pervonachal’nom kharaktere somy. In Tezisy Dokladov IV Letnej Shkoly po Vtorichnym Modelirujushhim Sistemam. Tartu: Ulikooli, pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Eşanu, Octavian. 2013. Transition in Post-Soviet Art. The Collective Actions Group before and after 1989. Budapest: Central European University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Faggionato, Raffaella. 2005. A Rosicrucian Utopia in Eighteenth-Century Russia. The Masonic Circle of N.I. Novikov. Dordrecht: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Faivre, Antoine. 2010. Western Esotericism A Concise History. Albany: State University of New York. [Google Scholar]
- Firestone, Evan R. 2019. Animism and Shamanism in Twentieth-Century Art. Kandinsky, Ernst, Pollock, Beuys. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw, Peter J. 2017. Lux in Tenebris. The Visual and the Symbolic in Western Esotericism. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Frankfurter, David. 2019. Magic as the Local Application of Authoritative Tradition. In Guide to the Study of Ancient Magic. Leiden: Brill, pp. 721–22. [Google Scholar]
- Furst, Peter T. 1990. Flesh of the Gods: The Ritual Use of Hallucinogens. Long Grove: Waveland Press, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Glanc, Tomáš. 2001. Psikhodelicheskii realism. Moscow: NLO, vol. 51, pp. 263–80. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, Joscelyn. 1994. The Theosophical Enlightenment. Albany: State University of New York Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gordeeva, Olga V. 2017. Psihologicheskie effekty muhomora krasnogo (Amanita muscaria). Sibirskie Istoricheskie Issledovaniia 2: 152–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, Fritz. 2009. Apollo. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Groys, Boris. 2013. History Becomes Form. Moscow Conceptualism. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Groys, Boris. 2023. Muhi u Kabakova-kak Angely. Meduza. June 18. Available online: https://meduza.io/feature/2023/06/18/on-videl-chto-lyuboy-poryadok-ne-imeet-smysla (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Gunn, Joshua. 2005. Modern Occult Rhetoric. Mass Media and the Drama of Secrecy in the Twentieth Century. Tuscaloosa: The University of Alabama Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gura, Alexander. 1997. Simvolika zhivotnyh v slavianskoj narodnoj tradicii. Moskva: Indrik, pp. 416–526. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, Liudmila S. 1993. Indole Derivatives in Certain Panaeolus Species from East Europe and Siberia. Mycological Research 97: 251–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, Wayland D. 1973. From Idea to Word: Folk Beliefs and Customs Underlying Folk Speech. American Speech 48: 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J. 1996. New Age Religion and Western Culture: Esotericism in the Mirror of Secular Thought. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J. 2012. Esotericism and the Academy. Rejected Knowledge in Western Culture. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J. 2013. Entheogenic Esotericism. In Contemporary Esotericism. Edited by Asprem Egil and Kennet Granholm. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J. 2016. Introduction. In Dictionary of Gnosis & Western Esotericism. Edited by Wouter J. Hanegraaff. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J. 2022. Hermetic Spirituality and the Historical Imagination. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J., Peter J. Forshaw, and Marco Pasi, eds. 2019. Hermes Explains. Thirty Questions about Western Esotericism. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, Patrick. 2008. Mushroom Miscellany. London: Collins. [Google Scholar]
- Harnack, Adolph. 1901. History of Dogma. Boston: Little, Brown & Co., vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Harner, Michael, ed. 1973. Hallucinogens and Shamanism. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, Clark. 2002. Magic Mushrooms in Religion and Alchemy. Rochester: Park Street Press. [Google Scholar]
- Henrichs, Albert. 2023. Dionysos: Myth, Image, Identity. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, Hiro. 2008. Logoi Spermatikoi and the Concept of Seeds in the Mineralogy and Cosmogony of Paracelsus. Revue d’histoire des Sciences 61: I–XXI. [Google Scholar]
- Holzhausen, Jens. 2016. Valentinus and Valentinians. In Dictionary of Gnosis & Western Esotericism. Edited by Wouter J. Hanegraaff. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Houben, Jan E. M. 1993. The Soma-Haoma problem: Introductory overview and observations on the discussion. Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies 9: 3–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2007a. Alternative language theory under Stalin: Philosophy and religion at the crossroads in the nascent Soviet Union. Studies in Slavic Cultures 6: 25–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2007b. Russkaja religioznaja kritika jazyka i problema imjaslavija (o. Pavel Florenskij, o. Sergij Bulgakov, A.F. Losev). Kritika i Semiotika 11: 109–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2008a. Diskursy Telesnosti i Erotisma v Literature i Culture: Epokha Modernisma. Moskva: Ladomir. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2008b. The passive opposition to dialectical materialism on the way to ontology and phenomenology: ‘Imiaslavie’ and critical neo-Humboldtianism [Russian religious philosophers and Gustav Shpet]. Russian Literature 63: 293–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2012. The Cultural ‘Text of Behaviour’: The Moscow-Tartu School and the Religious Philosophy of Language. Cultura 9: 175–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2013. Andrei Monastyrskii’s Post-Semiosis in the Tradition of Moscow Conceptualism: Ekphrasis and the Problem of Visual-Ironic Suggestion. Russian Literature 74: 255–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2016. The Birth of Moscow Conceptualism from the Musical Spirit of the Russian Avant-Garde. The Soundscapes of Moscow Conceptualism and its Sonoric Theatre of the Absurd. Ursprünge/Origines/Origins hrsg. von Roxane Barras, Simone Höhn und Mark Ittensohn. Variations-Literaturzeitschrift der Universität Zürich 24: 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2017. The Textual and the Pictorial in the Poetry of Moscow Conceptualism. The Beetle by Ilya Kabakov through the lens of Demonology, Intertextual Irony and Humor. Zbornik Matice srpske za slavistiku/Serbian Review of Slavic Studies 92: 273–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2020. The Grand Narrative of the Mukhomor: Communist Dunaev as a Mushroom Eater in Mifogennaia Liubov’ Kast: Understanding the Ethnobotanical History of the Younger Group of Russian Conceptualists. The Soviet and Post-Soviet Review 47: 135–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2021a. Debating Russian Obscene Performativity and Polysemy: The Curious Case of Russian Mat. Zbornik Matice Srpske za Slavistiku/Matica Srpska Journal of Slavic Studies 100: 781–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2021b. East-European Critical Thought: Myth, Religion, and Magic versus Literature, Sign and Narrative. Religions 12: 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2021c. Ritualistic verbum of Russian Conceptualism: Performative Somatics and Visuality. In This Is NOT Moscow Conceptualism: Collection of Scholarly Papers. Edited by Kornelia Ichin. Belgrade: Belgrade University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2022. The Experimental Sounds of Russian Conceptualism: From Historical Musical Avant-garde to Cultural Underground(s). In The Oxford Handbook of Soviet Underground Culture. Edited by Mark Lipovetsky, Maria Engström, Tomáš Glanc, Ilja Kukuj and Klavdia Smola. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis. 2023. Avant-Garde versus Tradition, a Case Study—Archaic Ritual Imagery in Malevich: The Icons, the Radical Abstraction, and Byzantine Hesychasm. Arts 12: 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis, and Frederick White. 2012. The Russian Avant-Garde and Radical Modernism. Boston: Academic Studies Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, Dennis, and Serguei A. Oushakine. 2013. The Amusing Disturbance of Soviet Laughter. Totalitarian Laughter: Images–Sounds–Performers. Russian Literature 74: 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, Dennis, Andrei Toporkov, and Aleksei Yudin. 2017. Magic: Folklore: Literature. Introducing Slavic Magic. Russian Literature 93: 2–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolitova, Alexandra. 2008. Russkie rukopisnye travniki 17–18 vekov: Issledovanie fol’klora i etnobotaniki. Moskva: Indrik. [Google Scholar]
- Irenaeus, Bishop of Lugdunum (Lyon). 1907. Adversus Haereses: Libri Quinque. Romae: Forzani et Socii. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, Matthew Jesse. 2016. The Experimental Group: Ilya Kabakov, Moscow Conceptualism, Soviet Avant-Gardes. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Janowitz, Naomi. 2002. Icons of Power: Ritual Practices in Late Antiquity. University Park: The Pennsylvania State University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanmaire, Henri. 1951. Dionysus: Histoire du culte de Bacchus: L’orgiasme dans l’antiquité et les temps modernes. Paris: Payot. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, Philip. 2002. Hidden Gospels: How the Search for Jesus Lost Its Way. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, Jay. 2014. Angels of Desire. Esoteric Bodies, Aesthetics and Ethics. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Kabakov, Ilia. 1992. Das Leben des Fliegen, Life of Flies, Zhizn’ mukh. Koln: Kolnischer Kunstverein, Edition Cantz. [Google Scholar]
- Kabakov, Ilia. 2008. Zhizn’ much. Bielefeld: Kerber. [Google Scholar]
- Kandinsky, Wassily. 1981. Sounds. Translated by Elizabeth Napier. New Haven: Yale University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kerenyi, Carl. 1976. Dionysus: Archetypal Image of Indestructible Life. Princeton: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kerényi, Karl. 1983. Apollo: The Wind, the Spirit, and the God. Dallas: Spring Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Keuls, Eva C. 1993. The Reign of the Phallus. Sexual Politics in Ancient Athens. Berkeley: University of California Press. [Google Scholar]
- Khalturin, Yuri, Vladimir Vladimir Kuchurin, and Jurij Fedorovič Rodichenkov. 2015. Nebesnaja Nauka: Evropejskaja Alhimija i Rossijskoe Rozenkrejcerstvo v XVII–XIX Vekakh. Sankt-Peterburg: Izdatel’stvo RHGA. [Google Scholar]
- Kir’iak, Margarita A. 1998. Griby v siuzhetakh zapadno-chukotskoi pozdnepaleoliticheskoi grafiki (pamiatniki mogil’nogo iskusstva). In Mir Drevnikh Obrazov na Dal’nem Vostoke: Tikhookeanskaia Arkheologiia. Vladivostok: Izdatel’stvo DVGU, vol. 10, pp. 105–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelson, Valerie A. 2003. Male Witches and Gendered Categories in Seventeenth-Century Russia. Comparative Studies in Society and History 45: 606–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, Valerie A. 2011. Lethal Convictions: The Power of a Satanic Paradigm in Russian and European Witch Trials. Magic, Ritual, and Witchcraft 6: 34–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, Valerie A. 2012. Caught in the Act: An Illustration of Erotic Magic at Work. In Dubitando: Studies in History and Culture in Honor of Donald Ostrowski. Edited by Brian J. Boeck, Russell Martin and Daniel Bruce Rowland. Bloomington: Slavica Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelson, Valerie A. 2013. Unclean Spirits Unleashed: Flying Bricks, Demonic Possession, and Blackmail in Russia. Russian History 40: 315–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, Valerie A., and Jonathan Shaheen. 2011. Prosaic Witchcraft and Semiotic Totalitarianism: Muscovite Magic Reconsidered. Slavic Review 70: 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebanov, Michael. 2013. Sergej Kuriokhin: The Performance of Laughter for the Post-Totalitarian Society of Spectacle. Russian Conceptualist Art in Rendezvous. Russian Literature 74: 227–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, Peter. 2018. Ordo Templi Orientis Spermo-Gnosis. Ordo Templi Orientis Phenomenon. Available online: www.cyberlink.ch/~koenig/spermo.htm (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Kolosova, Valeria. 2009. Leksika i Simvolika Slavianskoi Narodnoi Botaniki: Ethno-Lingvisticheskii Aspekt. Moskva: Indrik. [Google Scholar]
- Kolosova, Valeria. 2014. Etnobotanicheskie zametki. In Leksicheskii atlas Russkikh Narodnykh Govorov: Materialy i Issledovaniia. Sankt-Peterburg: Nauka. [Google Scholar]
- Kondratiev, Aleksandr. 1905. Bogi Minuvshikh Vremen. Sankt-Petersburg: Gos. Tip. [Google Scholar]
- Kripal, Jeffrey J. 2001. Roads of Excess, Palaces of Wisdom: Eroticism and Reflexivity in the Study of Mysticism. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kripal, Jeffrey J. 2007. The Serpent’s Gift: Gnostic Reflections on the Study of Religion. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kusovac, Elena. 2019. Psychodelicheskaia revoliutsia v Rossii. In Iskusstvo i Revolutsia: Sto let spustia. Edited by Icin Kornelia. Belgrad: University of Belgrad Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawska, Monika. 2014. Folk Biology of Slavic-Speaking Peoples. In Pioneers in European Ethnobiology. Edited by Ingvar Svanberg and Lukasz Luczaj. Uppsala: University Library. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriokhin, Sergey. 1991. Broadcast ‘Lenin–grib’, Leningradskoe TV 17 maja 1991. Vedushhii Sergei Sholokhov. Available online: https://youtu.be/NI_CSKSshWg (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- La Barre, Weston. 1990. Hallucinogens and the Shamanic Origins of Religion. In Flesh of the Gods: The Ritual Use of Hallucinogens. Edited by Peter Furst. Prospect Heights: Waveland Press. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowski, Romuald I. 2015. A Wilderness of Dragons: Tolkien’s Treatment of Dragons in Roverandom and Farmer Giles of Ham. Mythlore: A Journal of J.R.R. Tolkien, C.S. Lewis, Charles Williams, and Mythopoeic Literature 34: 8. Available online: https://dc.swosu.edu/mythlore/vol34/iss1/8 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Lavrov, Aleksandr S. 2000. Koldovstvo i religia v Rossii. Moskva: Drevlekhranilische. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, Georg. 2006. Arcana Mundi. Magic and the Occult in the Greek and Roman Worlds. A Collection of Ancient Texts. Translated, Annotated, and Introduced by Georg Luck. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. [Google Scholar]
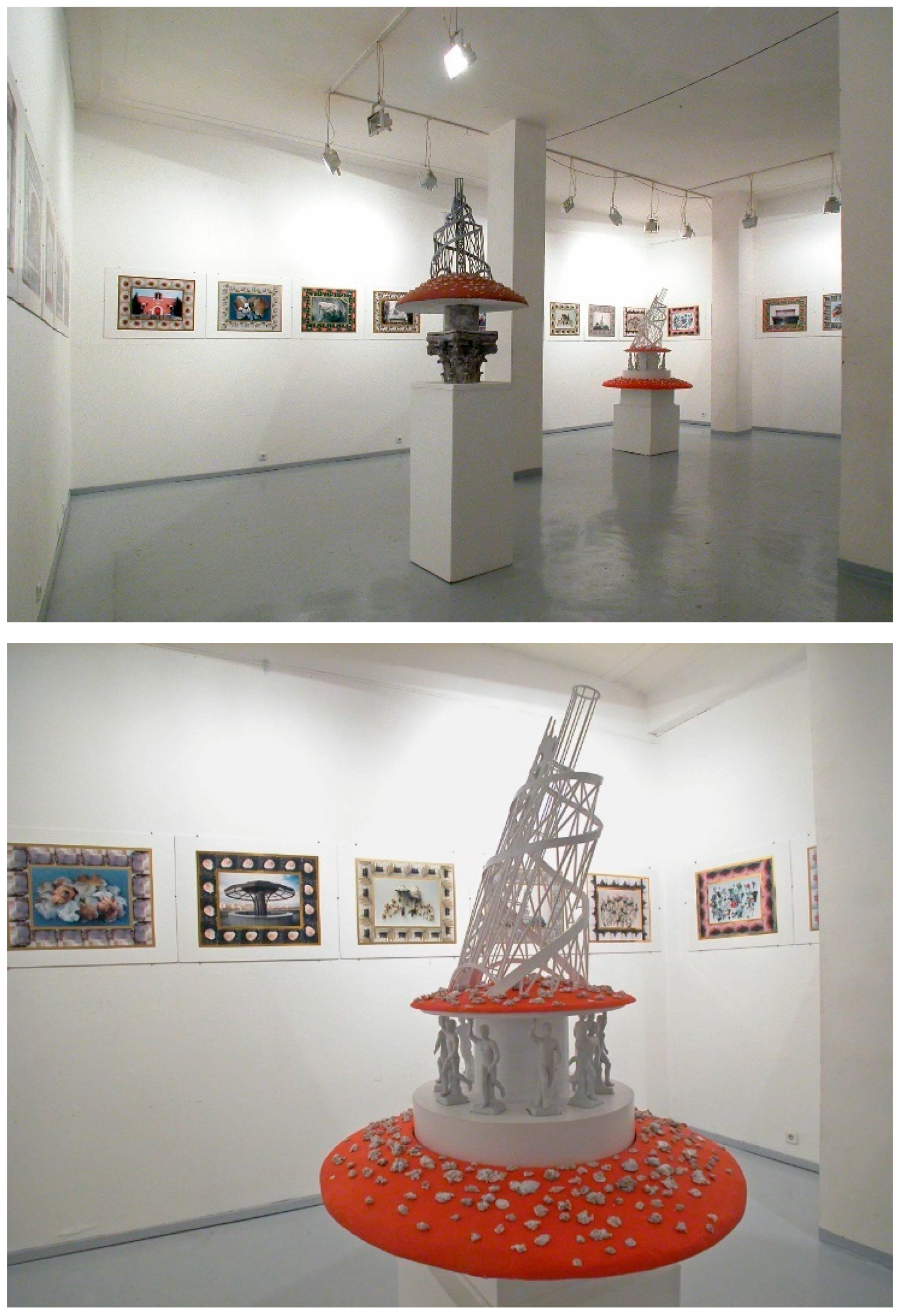
- Makarevich, Igor, Elena Elagina, and Nadim Julien Samman. 2008. Makarevich and Elagina: Mushrooms of the Russian Avant-Garde. London: Rochelle School/A-Foundation. Berlin: Galerie Sandmann, Catalogue published in English and German in 2008 by ARTiculate Contemporary Art Fund, London. [Google Scholar]
- Mannherz, Julia. 2012. Modern Occultism in Late Imperial Russia. DeKalb: Northern Illinois University Press. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, Terence. 1991. The Archaic Revival: Speculations on Psychedelic Mushrooms. San Francisco: Harper. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, Terence. 1992. Food of the Gods: A Radical History of Plants, Drugs, and Human Evolution. New York: Bantam Books. [Google Scholar]
- Menzel, Birgit. 2012. Occult and Esoteric Movements in Russia from the 1960s to the 1980s. In The New Age of Russia. Occult and Esoteric Dimensions. Edited by Birgit Menzel, Michael Hagemeister and Bernice Glatzer Rosenthal. München and Berlin: Verlag Otto Sagner. [Google Scholar]
- Menzel, Birgit, Michael Hagemeister, and Bernice Glatzer Rosenthal, eds. 2012. New Age of Russia: Occult and Esoteric Dimensions. Berlin: Verlag Otto Sagner. [Google Scholar]
- Mercier, Alain. 1969. Les Sources ésotériques et occultes de la poésie symboliste (1870–1914). Tome 1: Le symbolisme français. Tome 2: Le symbolisme européen. Paris: Editions A.G. Nizet. [Google Scholar]
- Mickiewicz, Adam. 1917. Pan Tadeusz. London and Toronto: J.M. Dent & Sons. First published 1834. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailova, Tatiana. 2018. Ot kolduna to sharlatana. Koldovskie Processy v Rossiskoi imperii XVIII veka. Sankt-Petersburg: Izdatelstvo Evropeiskogo Universiteta. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhalkov, Sergei. 2004. Stihi. Skazki. Rasskazy. Sankt-Peterburg: Neva. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, Forrest L., and James L. Lasswell. 2005. A Dazzle of Dragonflies. College Station: Texas A&M University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Monastyrsky, Andrey. 2013. Proizvedenie iskusstva ne objazatel’no stroitsia po printsipu dorozhnogo znaka. ArtGuide. February 1. Available online: https://artguide.com/posts/293 (accessed on 1 February 2013).
- Moran, Bruce T. 2016. Paracelsus and Paracelsianism. In The Cambridge Handbook of Western Mysticism and Esotericism. Edited by Glenn Alexander Magee. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Munn, Henry. 1973. The Mushrooms of Language. In Hallucinogens and Shamanism. Edited by Michael Harner. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Nabokov, Vladimir V. 1998. Stihotvorenija: Sbornik. Rostov-na-Donu: Feniks. [Google Scholar]
- Nekhoroshev, Grigory. 2021. Otkuda vyros Lenin-grib: Sovetskie otzvuki psihodelicheskoj revoljucii. MoskvichMag. May 28. Available online: https://moskvichmag.ru/lyudi/otkuda-vyros-lenin-grib-sovetskie-otzvuki-psihodelicheskoj-revolyutsii/ (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Nicholas, Mary. 2022. Metaphor and the Material Object in Moscow Conceptualism. Arts 11: 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, Mary. 2024. Moscow Conceptualism, 1975–1985. Words, Deeds, Legacies. London: Bloomsbury. [Google Scholar]
- Nordenson, Catherine Seavitt. 2016. Think Like a Mushroom. PLOT Volume 5. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/40113242/Think_Like_a_Mushroom (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Obukhova, Alexandra. 2010. Mukhomor. Vologda: Biblioteka Moskovskogo Conceptualisma Germana Titova. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, Walter F. 1995. Dionysus Myth and Cult. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Padhy, Sachidananda, and Santosh Kumar Dash. 2004. The Soma Drinker of Ancient India: An Ethno-Botanical Retrospection. Journal of Human Ecology 15: 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, Sophie. 2013. Magic in the Cloister: Pious Motives, Illicit Interests, and Occult Approaches to the Medieval Universe. Pennsylvania: The Pennsylvania State University. [Google Scholar]
- Partridge, Christopher. 2019. Modern Psychedelic Gnosis. In The Gnostic World. Edited by Garry W. Trompf. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Pasi, Marco. 2011. The Knight of Spermatophagy: Penetrating the Mysteries of Georges Le Clément de Saint-Marcq. In Hidden Intercourse Eros and Sexuality in the History of Western Esotericism. Edited by Wouter J. Hanegraaff and Jeffrey J. Kripal. New York: Fordham University Press New York. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovsky, Evgeny N. 1940. Parazitologicheskie Motivy v Khudozhestvennoj Literature i Narodnoj Mudrosti. Leningrad: Leningradskoe Parazitologicheskoe Obshhestvo. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, Camilo. 2021. Tolkien’s Dragons: Sources, Symbols, and Significance. Symbolism 21: 115–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilshchikov, Igor. 2021. Russkij mat: Chto my o nem znaem? (O proiskhozhdenii i funkcijakh russkoj obscennoj idiomatiki). Zbornik Matice srpske za slavistiku 100: 709–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilshchikov, Igor, and Dennis Ioffe. 2021. ‘Verbum iuro’ [obscene language], Guest edited (with an Introduction) by Igor Pilshchikov and Dennis Ioffe. Zbornik Matice Srpske za Slavistiku/Matica Srpska Journal of Slavic Studies 100: 689–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, Steve. 2020. Blasphemous Modernism. The 20th-Century Word Made Flesh. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Poety. 1994. Poety gruppy OBERIU. Edited by Alexander Kushner and Mikhail Meilakh. Sankt-Petersburg: Sovetskii Pisatel. [Google Scholar]
- Poggianella, Sergio. 2015. The Object as an Act of Freedom. Kandinsky and Shaman Art. In Wassily Kandinsky. Tudo Comença num Ponto. Everything Starts From a Dot. Edited by Evgenia Petrova. St. Petersburg: State Russian Museum, Brasilia, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Belo Horizonte: Centro Cultural Banco do Brasil, pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Quick, Laura. 2022. Behemoth’s Penis, Yahweh’s Might: Competing Bodies in the Book of Job. Journal for the Study of the Old Testament 46: 339–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitch, Celia. 2002. Surrealism and the Sacred. Power, Eros, and the Occult in Modern Art. Boulder: Westview Press. [Google Scholar]
- Radulović, Nemanja, and Karolina Maria Hess, eds. 2019. Studies on Western Esotericism in Central and Eastern Europe. Szeged: JATE Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, Alla. 2011. Moscow Conceptualism in Context. Munich: Prestel. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, Bernice Glatzer, ed. 1997. The Occult in Russian and Soviet Culture. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rossomakhin, Andrej. 2004. Kuznechiki Velimira Khlebnikova, sobrannye Andreem Rossomakhinym: S prilozheniem illjustrirovannoj biografii prizhiznennykh otdel’nykh izdanij Khlebnikova. Sankt-Peterburg: Krasnyj matros. [Google Scholar]
- Rossomakhin, Andrej. 2005. Kuznechiki Nikolaja Zabolotskogo, sobrannye Andreem Rossomahinym: S prilozheniem illjustrirovannoj bibliografii prizhiznennykh knig Zabolockogo. Sankt-Peterburg: Krasnyj matros. [Google Scholar]
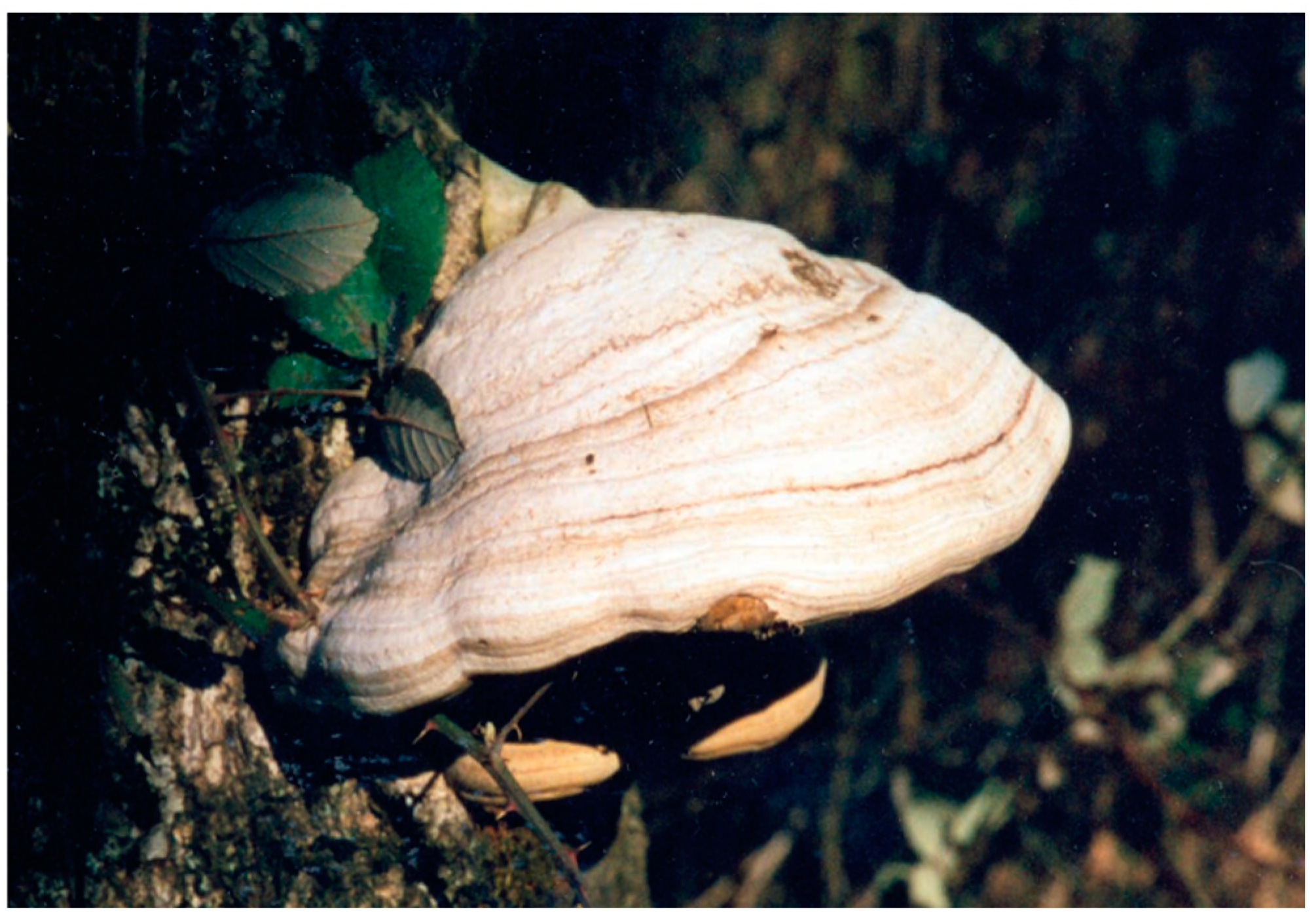
- Roussel, Bertrand, Sylvie Rapior, Christian-Louis Masson, and Paul Boutié. 2002. Fomes fomentarius: Un champignon aux multiples usages. Cryptogamie, Mycologie 23: 349–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ruck, Carl A. P. 2011. Mushrooms, Myth, and Mithras: The Drug Cult that Civilized Europe. San Francisco: City Lights. [Google Scholar]
- Ruether, Rosemary Radford. 2005. Goddesses and the Divine Feminine: A Western Religious History. Berkeley: University of California Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rush, John. 2011. The Mushroom in Christian Art: The Identity of Jesus in the Development of Christianity. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, William Francis. 1999. The Bathhouse at Midnight. An Historical Survey of Magic and Divination in Russia. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. [Google Scholar]
- Samman, Nadim Julien. 2008. Of Mushrooms & Malevich. In Makarevich and Elagina: Mushrooms of the Russian Avant-Garde. London: Rochelle School/A-Foundation. Berlin: Galerie Sandmann, Catalogue by ARTiculate Contemporary Art Fund, London. [Google Scholar]
- Samorini, Giorgio. 1998. Mushroom-Trees in Christian Art. Eleusis 1: 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, Leigh Eric. 2003. The Making of Modern Mysticism. Journal of the American Academy of Religion 71: 273–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultes, Richard Evans. 1976. Fly Agaric Mushrooms. In Hallucinogenic Plants. New York: Golden Press, pp. 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Schultes, Richard Evans, Albert Hofmann, and Ratsch Christian, eds. 2001. Plants of the Gods: Their Sacred, Healing, and Hallucinogenic Powers. Rochester: Healing Arts Press. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Niranjan Chandra. 2015. Soma, an Enigmatic, Mysterious Plant of the Vedic Aryas. Indian Journal of History of Science 50: 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanon, Benny. 2002. Entheogens. Reflections on Psychoactive Sacramentals. Journal of Consciousness Studies 9: 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shirokogoroff, S. M. 1935. Psychomental Complex of the Tungus. London: Kegan Paul, Trench Trubner. [Google Scholar]
- Sheveleva, Maria N. 2021. O glagole iati i konstrukcijakh imu po dannym drevnerusskikh pamiatnikov. In Slova, konstrukcii i teksty v istorii russkoj pis’mennosti. Sbornik statej k 70-letiju akademika A.M. Moldovana. Sankt-Peterburg and Moskva: Nestor-Istoria, pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shtal, Henrieke. 2008. Okkul’tnye pis’mena v romane Andreja Belogo Peterburg. In Andrej Belyj v izmeniaiushhemsia mire: K 125-letiiu so dnja rozhdenijam/Sost. M. L. Spivak, I. B. Delektorskaja. Moscow: Nauka. [Google Scholar]
- Smilianskaia, Elena B. 2003. Volshebniki. Bogokhul’niki. Eretiki. Narodnaia religioznost’ i dukhovnye prestupleniia v Rossii XVIII v. Moskva: Indrik. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, Douglas. 1999. Working The Rough Stone: Freemasonry and Society in Eighteenth-Century Russia. Dekalb: Northern Illinois University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, Jon, ed. 1994. Apollo: Origins and Influences. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. [Google Scholar]
- Spivak, Monika. 2006. Andrei Bely. Mistik is Sovetskii Pisatel’. Moskva: RGGU. [Google Scholar]
- Stamets, Paul. 1996. Psylocybin Mushrooms of the World. Berkeley: Ten Speed Press. [Google Scholar]
- Talar, Charles J. T., ed. 2009. Modernists and Mystics. Washington, DC: The Catholic University of America Press. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, Joan E. 2012. The Essenes, the Scrolls, and the Dead Sea. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ternovskaia, Olga A. 1979. Ob odnom mifologicheskom motive v russkoi literature. In Vtorichnye Modelirujushhie Sistemy. Edited by Lotman Ju. Tartu: TGU, pp. 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ternovskaia, Olga A. 1981. K opisaniju nekotorykh slavianskikh predstavlenij, svjazannykh s nasekomymi. In Slavjanskij i balkanskij fol’klor: Obrjad. Tekst. Edited by Nikita I. Tolstoj. Moskva: Nauka, pp. 139–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ternovskaia, Olga A. 1984. Vedovstvo u slavjan. II. Bzyk (mukhi v golove). In Slavjanskoe i balkanskoe jazykoznanie: Jazyk v jetnokul’turnom aspekte. Edited by E. I. Zelenina, V. V. Usacheva and T. V. Tsivian. Moskva: Nauka, pp. 118–30. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, Charles Aubrey. 1942. Mushroom Insects: Their Biology and Control. University Park: State College of Pennsylvania Press. [Google Scholar]
- Tilberg, Margareta. 2008. Tsvetnaia Vselennaia: Mikhail Matiushin ob Iskussve. Moscow: NLO. [Google Scholar]
- Toporkov, Andrei. 2024. Afanas’ev’s Poetic Views of the Slavs’ on Nature and Its Role in Understanding Paganism and Mythology. Religions 15: 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporkov, Andrei L. 1995. Russkii erotischeskii folklore. Moskva: Ladomir. [Google Scholar]
- Toporkov, Andrei L. 2004. Lozhka. In Slavianskie drevnosti: Etnolingvisticheskii slvar’. Moscow: Mezhdunarodnye otnosheniya, T. 3, pp. 130–34. [Google Scholar]
- Toporov, Vladimir N. 1982. Soma. In Mify Narodov Mira. Moscow: Sovetskaia Encyclopedia, pp. 462–63. [Google Scholar]
- Toporov, Vladimir N. 1990. Neomifologizm v russkoi literature nachala XX veka. Trento: Edizioni M.Y. [Google Scholar]
- Toporov, Vladimir N. 2004. Semantika mifologicheskih predstavlenii o gribakh. In Issledovanija po etimologii i semantike. Tom I Teorija i nekotorye chastnye ee prilozhenija. Moskva: IaRK. [Google Scholar]
- Trompf, Garry W., ed. 2019. The Gnostic World. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Trubachev, Oleg. 1958. Slawische Etymologien. Zeitschrift für Slawistik 3: 676–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubachev, Oleg. 2003. Etnogenez i kultura drevneishikh slavian. Moskva: Nauka, p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Trubachev, Oleg. 2004. Trudy po etymologii. Moskva: Iazyki slavianskoi kultury, vol. 2, pp. 283–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tsing, Anna Lowenhaupt. 2021. The Mushroom at the End of the World. On the Possibility of Life in Capitalist Ruins. Princeton: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Tukholka, Sergei. 1907. Occultism i magia. Sankt-Petersburg: Izdanie A.S. Suvorina. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, Hugh B. 2006. Magia Sexualis. Sex, Magic, and Liberation in Modern Western Esotericism. Berkeley: University of California Press. [Google Scholar]
- Usacheva, Valeria V. 2000. Mifologicheskie predstavlenija slavian o proishozhdenii rastenii. In Slavjanskii i Balkanskij Fol’klor: Narodnaja demonologiia. Moskva: Indrik, pp. 281–87. [Google Scholar]
- Uspenskii, Boris A. 1994. Zavetnye skazki A.N. Afanas’eva. In Izbrannye trudy. Moskva: IaRK, vol. 2, pp. 129–50. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek, Roelof. 1998. Gnosis and Hermeticism From Antiquity to Modern Times. SUNY Series in Western Esoteric Traditions. Albany: State University of New York Press. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek, Roelof. 2011. Sexuality and Sexual Symbolism in Hermetic and Gnostic Thought and Practice. In Hidden Intercourse Eros and Sexuality in the History of Western Esotericism. Edited by Wouter J. Hanegraaff and Jeffrey J. Kripal. New York: Fordham University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek, Roelof. 2013. Gnostic Religion in Antiquity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Toorn, Karel, Bob Becking, and Pieter W. van der Horst, eds. 1999. Dictionary of Deities and Demons in the Bible. Liden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Vasmer, Max. 1987. Etymologischeskii slvar’ russkogo iazyka. Moskva: Progress. [Google Scholar]
- Versluis, Arthur. 2004. Restoring Paradise, Western Esotericism, Literature, Art, and Consciousness. Albany: State University of New York Press. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova, Liudmila N. 2000. Narodnyie predstavlenia o proiskhozhdenii nechistoi sily: Demonologisatsia umershikh. In Slavianskii i balkanskii folklore: Narodniaia demonologia. Moscow: Indrik, pp. 24–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vohringer, Margarete. 2019. Avant-Garde i Psikhotekhnika. Moskva: NLO. [Google Scholar]
- Vojvodić, Jasmina, and Dennis Ioffe. 2019. (Neo)mythologism in comparative literature: Theories of myth and sign. Russian Literature 107: 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, Marta, and Slava Shevelenko. 2021. Marta & Slava. Texts by Guus Beumer, Stijn Huijts, Floor van Luijk, Marente de Moor and Yves Randaxhe. Berlin: Kerberverlag. [Google Scholar]
- Wallis, Robert J. 2019. Art and Shamanism: From Cave Painting to the White Cube. Religions 10: 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, R. Gordon. 1956. Lightning bolt and mushrooms: An essay into early cultural exploration. In For Roman Jakobson: Essays on the Occasion of his Sixteenth Birthday. The Hague: Mouton, pp. 605–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, R. Gordon. 1967. Fly Agaric and Man. In Ethnopharmacologic Search for Psychoactive Drugs. Edited by Daniel H. Efron, Bo Holmstedt and Nathan S. Kline. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, R. Gordon. 1971. Soma: The Divine Mushroom of Immortality. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, R. Gordon, Stella Kramrisch, Jonathan Ott, and Carl A. P. Ruck, eds. 1986. Persephone’s Quest: Entheogens and the Origins of Religion. New Haven: Yale University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, Valentina Pavlovna, and R. Gordon Wasson. 1957. Mushrooms, Russia and History. New York: Pantheon Books. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, Peg. 1995. Kandinsky and Old Russia: The Artist as Ethnographer and Shaman. New Haven: Yale University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, Leigh. 2013. Modernism and Magic. Experiments with Spiritualism, Theosophy and the Occult. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Yoffe, Mark. 2013. The Stiob of Ages: Carnivalesque Traditions in Soviet Rock and Related Counterculture. Russian Literature 74: 207–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchak, Alexei. 2006. Everything Was Forever, Until It Was No More: The Last Soviet Generation. Princeton: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Yurchak, Alexei. 2011. A Parasite from Outer Space: How Sergei Kuryokhin Proved that Lenin Was a Mushroom. Slavic Review 70: 307–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, Felix, ed. 2000. Ilya Kabakov: The Text as the Basis of Visual Expression. München: Oktagon Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Ziolkowski, Theodore. 2013. Lure of the Arcane. The Literature of Cult and Conspiracy. Batlimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Zlydneva, Natalia. 2004. Insektnyi kod russkoi kultury XXgo veka. In Absurd i vokrug. Moskva: Iazyki slavianskoi kultury. [Google Scholar]
- Znamenski, Andrei, ed. 2003. Shamanism in Siberia: Russian Records of Indigenous Spirituality. Berlin: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Zohar. 1983. Zohar: The Book of Enlightenment. Translated by Daniel Chanan Matt. New York: Paulist Press. [Google Scholar]


















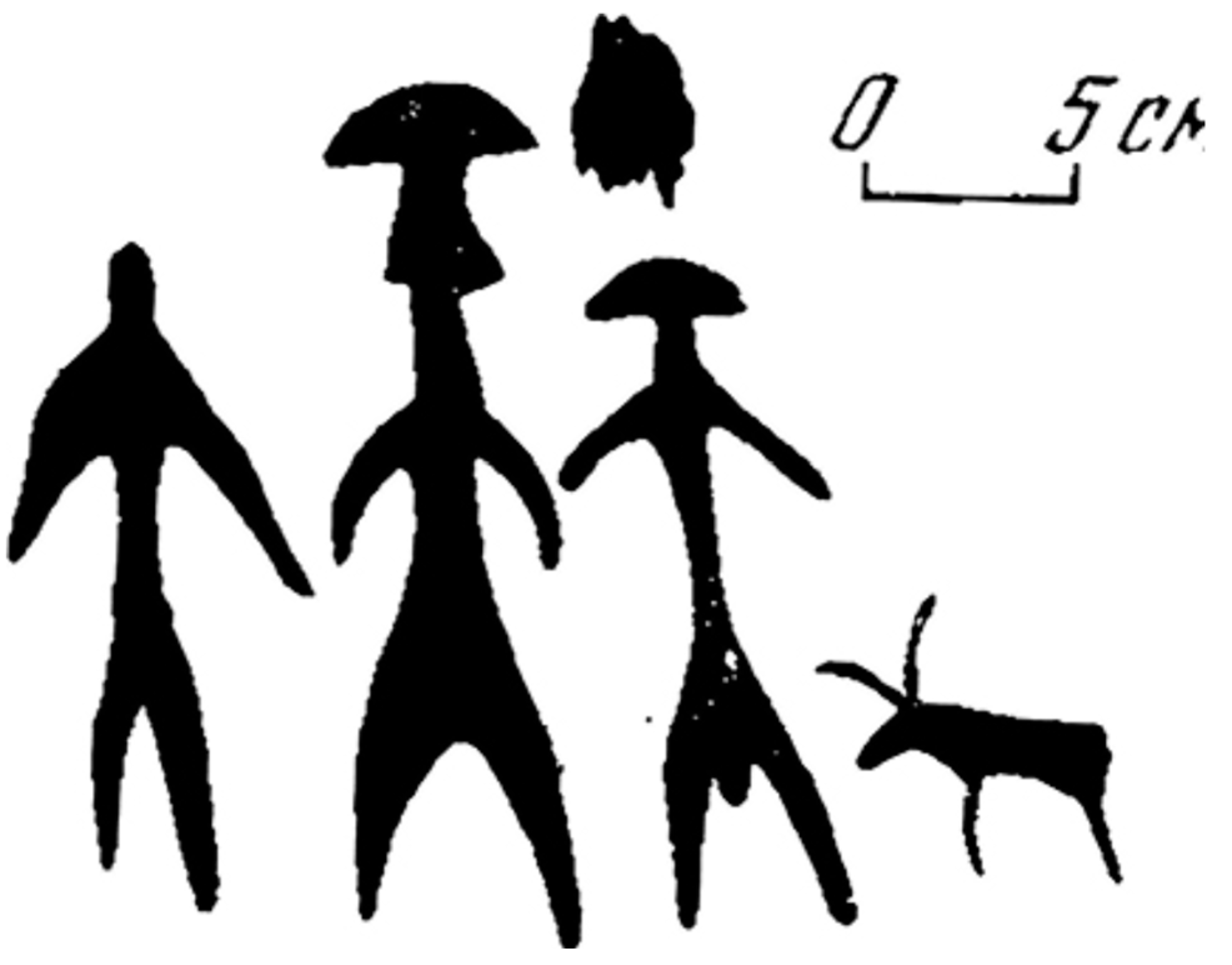






































































Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioffe, D. Griby i Mukhi: A Historical Contextualization of the Esoteric Mushroom Religion of Moscow Conceptualism: Fungal Erotic Imagery of Entheogens and Insects. Religions 2024, 15, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel15070777
Ioffe D. Griby i Mukhi: A Historical Contextualization of the Esoteric Mushroom Religion of Moscow Conceptualism: Fungal Erotic Imagery of Entheogens and Insects. Religions. 2024; 15(7):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel15070777
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoffe, Dennis. 2024. "Griby i Mukhi: A Historical Contextualization of the Esoteric Mushroom Religion of Moscow Conceptualism: Fungal Erotic Imagery of Entheogens and Insects" Religions 15, no. 7: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel15070777
APA StyleIoffe, D. (2024). Griby i Mukhi: A Historical Contextualization of the Esoteric Mushroom Religion of Moscow Conceptualism: Fungal Erotic Imagery of Entheogens and Insects. Religions, 15(7), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel15070777





